Are my drivers exempt from Canada’s ELD regulations?
This question is probably one of the most frequently asked questions we get — and for good reason. Exemptions from the regulations can be confusing especially when you consider provincial rules. How do you know if you are required to comply with Canada’s electronic logging device (ELD) rule? Let’s have a look at that question and see if we can clear it up.
Is my fleet exempt?
It may seem like a simple question, but it is actually complex. You need to know more about the nature of your operation and the province(s) in which you operate before you can determine if you’re exempt. First off, is your transportation company under provincial or federal jurisdiction? In Canada, a motor carrier involved in extra-provincial transportation falls under federal jurisdiction. Most provinces will apply the federal rule for fleets under federal jurisdiction. However, if a company operates within a single province, it is under provincial jurisdiction.
Second, if you’re under provincial jurisdiction, you should be aware that some provinces have rules that differ from the federal rules for their intra-provincial fleets and may not even require the use of an ELD for those fleets operating solely within the province. For most provinces, the use of ELDs will be required for intra-provincial operations. Currently, however, Alberta, Saskatchewan, Prince Edward Island, and Nunavut do not intend to make ELDs mandatory. However, know that the situation may change. To determine if your provincially regulated fleet is exempt from using ELDs, you must determine if the province in question will make ELDs mandatory for intra-provincial operations.
Are the trucks your drivers drive exempt under the federal rule?
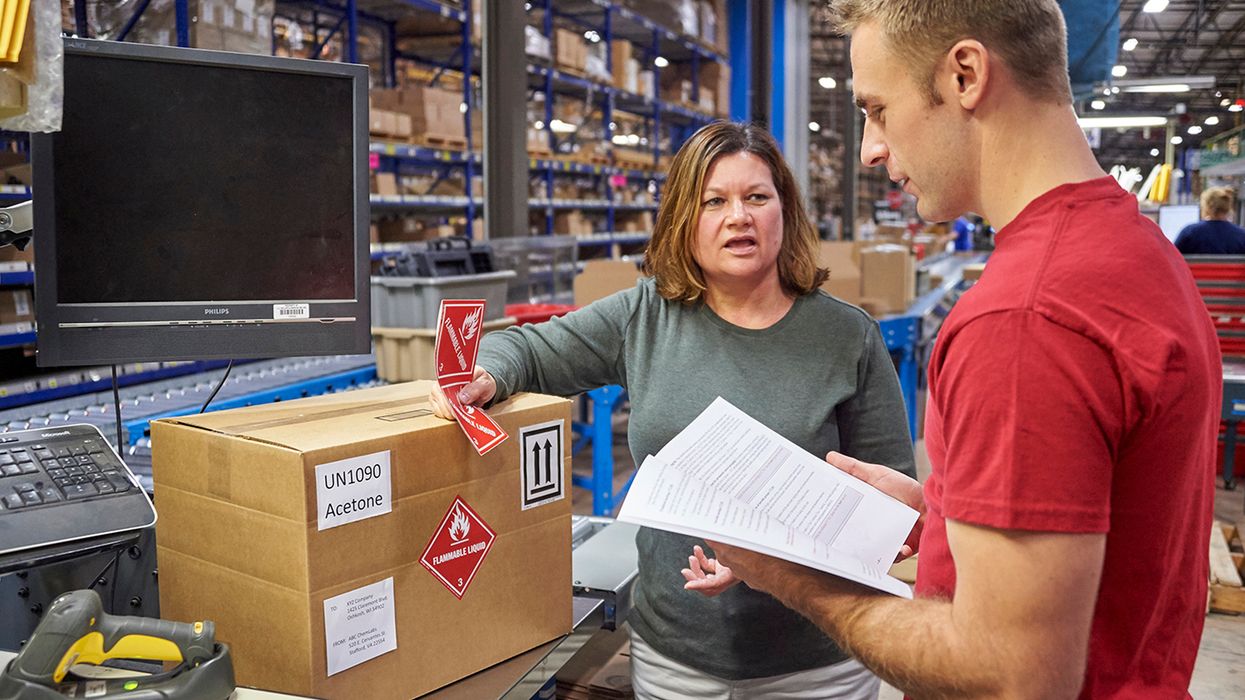
According to the definition outlined in the hours-of-service regulations, a commercial vehicle is a truck, tractor, trailer or any combination of them that has a registered gross vehicle weight in excess of 4,500 kilograms, or a bus that has a seating capacity of more than 10 persons, including the driver.
If your transportation company is federally regulated and your trucks are commercial vehicles, unfortunately, you’re not exempt. But if your drivers are operating any of the following vehicles, then you are exempt from Canada’s ELD regulations:
- Vehicles operated by a motor carrier under a permit;
- Vehicles operated by a motor carrier to which an exemption has been issued under the Act;
- Vehicles that is the subject of a rental agreement of no longer than 30 days that is not an extended or renewed rental of the same vehicle;
- Vehicle manufactured before the model year 2000.
Canadian ELD exemptions
Exemptions to the ELD rule are sometimes confusing. Canada’s ELD regulations are designed to replace paper logbooks with an electronic method of recording and do not change any of the hours of service regulations or requirements. In most cases, a driver who is exempt from keeping a daily log will also be exempt from the requirement to use an ELD. To be exempt from using an ELD, drivers must:
- Operate within a 160-kilometer radius of their home terminal;
- Return to their home terminal each day to take at least 8 consecutive hours of off-duty time; and
- Not be covered by a permit for exemption from the hours of driving and off-duty time.
If drivers operate outside of the 160-kilometer radius or no longer meet the conditions of the exemption, they would be subject to using an ELD.
Final thoughts
Remember that the Canadian ELD rule does not change the hours of service rules, only how the hours are recorded and tracked. The main exemptions are relatively straightforward, but if your operation is not typical, be sure to ask the appropriate authorities to verify compliance. You’ll need to know your operation and the types of vehicles your drivers operate. If you are a carrier under provincial jurisdiction, know that different rules might apply and finally remember, enforcement of the federal ELD mandate starts on January 1, 2023.
Key to remember: The Canadian ELD rule applies to federally regulated carriers, but provinces may also impose it on provincially regulated carriers. Exemptions may apply, but be sure you fully understand them before declaring your fleet or your drivers exempt from the rules.