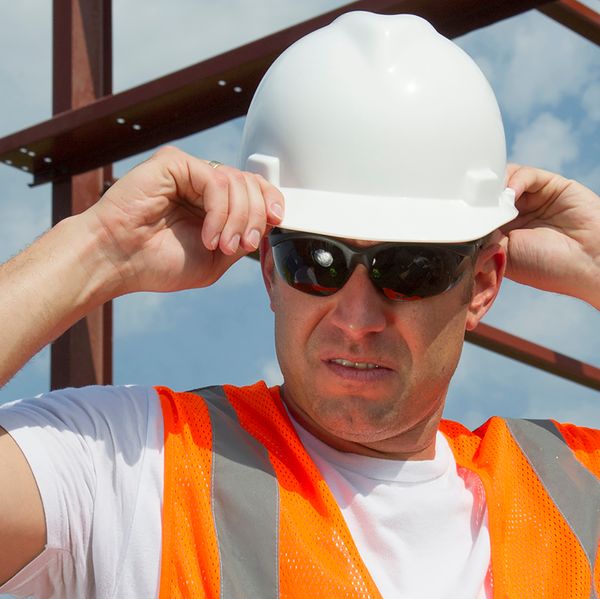
Does OSHA suddenly require “helmets” now instead of hard hats?
Ever since OSHA published its Trade Release on December 11, 2023, people have been scratching their heads about the “new” PPE requirement.
But here’s the thing. There isn’t a new requirement for “helmets” instead of hard hats.
So where’s the confusion? And what is actually required?
OSHA’s announcement on helmets vs. hard hats
OSHA released a Safety and Health Bulletin (SHIB 11-22-2023) on November 22, 2023, detailing the key differences and benefits of using modern safety helmets over traditional hard hats.
And just a few weeks later, in the December 11, 2023 Trade Release, the Agency announced it would now require its inspectors to wear Type II head protection, which is also commonly referred to as safety helmets.
The two main benefits of Type II safety helmets
The November 22, 2023 SHIB discussed two main benefits of choosing modern safety helmets over traditional hard hats -- the construction of materials and the use of chinstraps.
| Construction of Materials: | The SHIB first explained that one of the benefits of safety helmets lies in their construction materials. While hard hats are made from hard plastics, safety helmets incorporate a combination of materials, including lightweight composites, fiberglass, and advanced thermoplastics. Such materials can help enhance the impact resistance of the helmets but also include the added benefit of reducing the overall weight of the helmet. This reduces neck strain and improves comfort during extended use. |
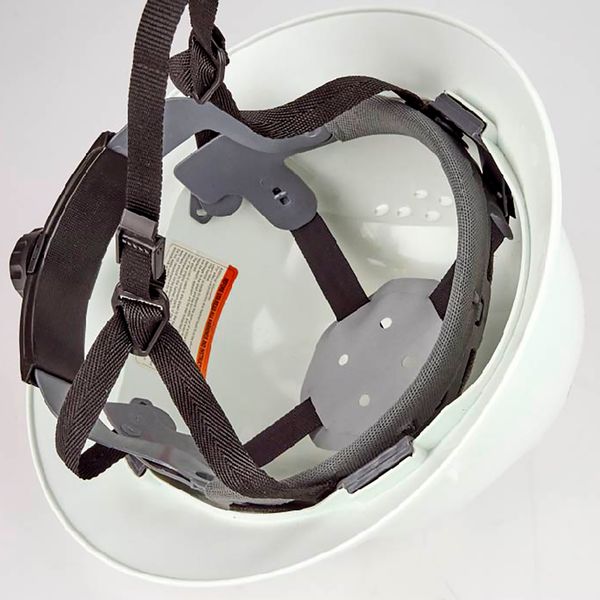
| Use of Chinstraps: | The SHIB also discussed the potential benefits of chinstraps used in conjunction with Type II safety helmets. The general idea here is that chinstraps can be helpful in maintaining the position of the safety helmet and protecting the worker’s head in the event of a slip, trip, or fall. According to data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics, head injuries accounted for nearly 6% of non-fatal occupational injuries involving days away from work. About 20% of those were caused by slips, trips, and falls. |
And while OSHA has recognized the benefits of Type II safety helmets, and is actively taking steps to protect its own employees, it’s important to understand that there is not a new requirement for employers to make the switch to safety helmets.
That being said, a growing number of employers have recognized the benefits of added head protection and are choosing to use Type II helmets for their workers. In addition, some clients are starting to contractually require their construction contractors to make the switch as well.
Understanding the different types of head protection
Hard hats will have a Type I or Type II rating on the manufacturer’s sticker. These markings are based on ANSI Z89.1’s impact ratings.
Type I hard hats protect from objects or impacts from the top center area of the hard hat and are often used in work areas with no lateral head impact hazards.
Type II hard hats, on the other hand, offers protection from both top and lateral impacts and objects and is often found on construction job sites or complex general industry settings where workers face multiple head contact exposures.
Hard hats are classified based on their level of voltage protection. See the chart below.
| Class G – (General) low voltage protection. Class E – (Electrical) high voltage protection. Class C – (Conductive) no voltage protection. |
Choosing the right head protection for your employees
Employers should conduct a job hazard analysis and/or a PPE assessment to determine which style hard hat is best for their workers. In general, OSHA recommends the use of Type II safety helmets at the following locations:
1. Construction Sites: For construction sites, especially those with high risks of falling objects and debris, impacts from equipment, or slips, trips, and falls, safety helmets have enhanced impact resistance and additional features that offer superior protection compared to the components and construction of traditional hard hats.
2. Oil and Gas Industry: In these sectors where workers face multiple hazards, including potential exposure to chemicals and severe impacts, safety helmets with additional features can provide comprehensive protection.
3. Working from Heights: For tasks or jobs that involve working from heights, safety helmets offer protection of the entire head and include features that prevent the safety helmet from falling off.
4. Electrical Work: For tasks involving electrical work or proximity to electrical hazards, safety helmets with non-conductive materials (Class G and Class E) provide protection to prevent electrical shocks. However, some traditional hard hats also offer electrical protection.
5. High-Temperature Environments: In high temperatures or where there is exposure to molten materials, safety helmets with advanced heat-resistant properties can provide additional protection to workers.
Key to remember: While there isn’t a new requirement for safety helmets, employers should review their workplace hazards to determine which style of hard hat will best protect their employees.