Keep calm: Understanding Canada’s Hazardous Material Transport rules
Transporting hazardous materials in Canada might sound daunting, but with the right knowledge, it can be a smooth and safe process. Let us give you the tools and confidence needed to navigate the complexities of hazardous material transport and guide you through the essential regulations to ensure compliance and safety. Transporting hazardous materials in Canada is a critical task that requires strict adherence to the Transportation of Dangerous Goods (TDG) Act, 1992 and the accompanying TDG Regulations. These regulations are designed to ensure public safety and security during the transportation of dangerous goods.
Classification of Dangerous Goods
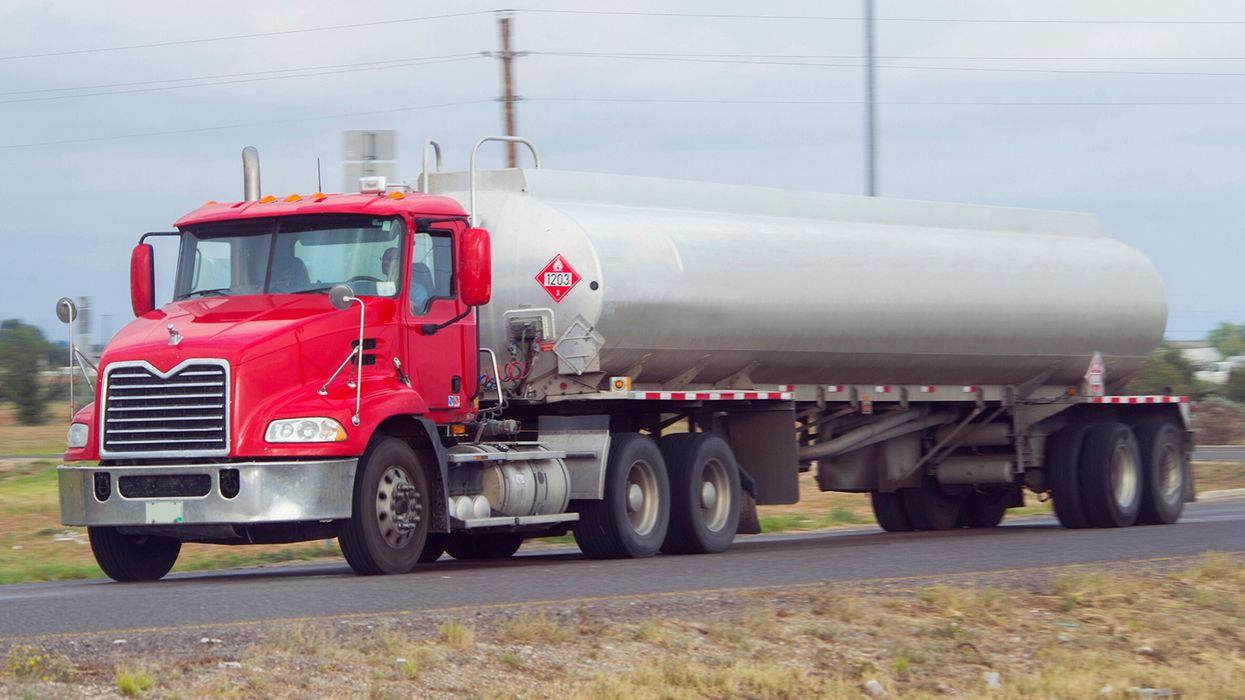
The first step is understanding the classification system. Dangerous goods are classified into different classes based on their properties and risks. Proper classification is crucial for determining the appropriate handling and transportation methods. The TDG Regulations outline nine classes of dangerous goods, ranging from explosives to radioactive materials. Each class has specific requirements for packaging, labeling, and documentation.
Documentation requirements
Having accurate and complete documentation is key when it comes to the TDG Regulations. This includes shipping documents, safety marks, and emergency response assistance plans (ERAPs). Shipping documents must include detailed information about the dangerous goods being transported, such as the proper shipping name, classification, and quantity. Safety marks, such as labels and placards, must be displayed on the packaging and transport units to indicate the presence of dangerous goods. ERAPs are required for certain high-risk dangerous goods and provide detailed instructions for emergency response in case of an incident.
Packaging standards
Packaging is another key aspect that you need to understand. Dangerous goods must be packaged according to specific standards to prevent leaks, spills, and other hazards during transportation. The regulations identify the types of packaging that can be used for different classes of dangerous goods, as well as the requirements for these packages to ensure safety during the transport process.
Training and certification
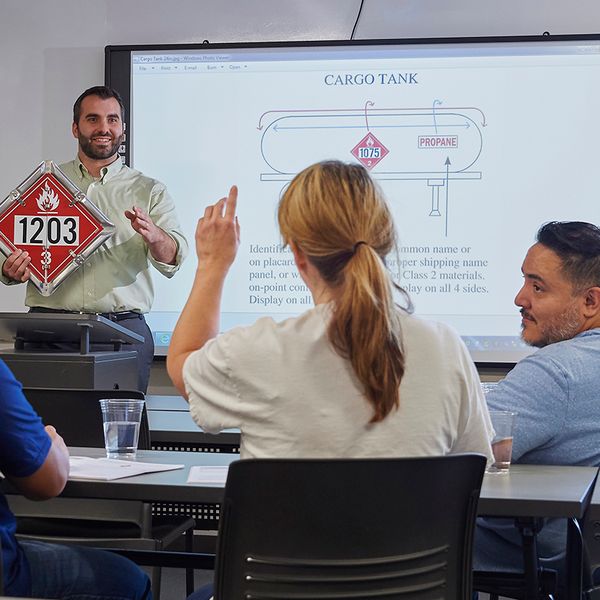
Training is a key component of the TDG Regulations. Anyone involved in the transportation of dangerous goods must receive proper training to understand the regulations and how to manage these materials safely. This includes your shipper/receiver, your drivers, and basically anyone who handles, loads, or transports dangerous goods. Your training programs must cover the specific requirements of the TDG Regulations that apply to your operations.
Emergency response
The TDG Regulations also mandate that you, the carrier must have an emergency response plan in place and ready to be implemented, if necessary. CANUTEC, the Canadian Transport Emergency Centre, provides a 24-hour emergency telephone service to assist with incidents involving dangerous goods. This service offers expert advice and guidance to first responders and transporters to help mitigate the impact of an incident.
What is CID
The Client Identification Database (CID) is a new registration platform introduced by Transport Canada for entities involved in dangerous goods (DG) activities. It collects information about who is importing, offering for transport, handling, or transporting dangerous goods in Canada. If you transport dangerous goods you must register with the CID by October 25, 2024. This database gathers details about dangerous goods activities, including types of dangerous goods, transportation modes, and involved sites. This information helps Transport Canada assess risks, enhance safety measures, and prioritize inspections. Compliance with CID registration is mandatory, and failure to comply can result in penalties.
Essential for safety
Hazmat (hazardous materials) and dangerous goods refer to substances that pose risks to health, safety, or the environment. Both terms are used interchangeably to describe items requiring special handling, packaging, and transportation to prevent accidents and ensure safety, so essentially, they mean the same thing. By understanding the classification system, adhering to documentation requirements, following packaging standards, ensuring proper training, and being prepared for emergency response, you can comply with the TDG Regulations and contribute to public safety.
Key to remember: Ensuring compliance with these regulations, you ensure the safe and lawful transportation of hazardous materials, thereby protecting public safety and the environment.