Train workers to avoid bringing lead contamination home
Employees who work with lead can carry it home on their skin, hair, clothes, shoes, and personal items. This can contaminate their vehicles and homes, putting them and their family members at risk.
Keeping lead out of their homes and cars is easier than cleaning it up. Employees should know how to minimize the risk of taking lead home by planning before going to work, following safety protocols at work, and applying extra precautions at home after work.
For more information, see our article Updates on OSHA updating its lead standards.
Going to work
Remind workers that anything they bring to work could get lead on it. Minimizing personal items helps reduce the number of objects that might get contaminated.
If workers pack their own meals and snacks, explain that bringing food and drinks in disposable containers further reduces the number of items they’ll take back home.
At work
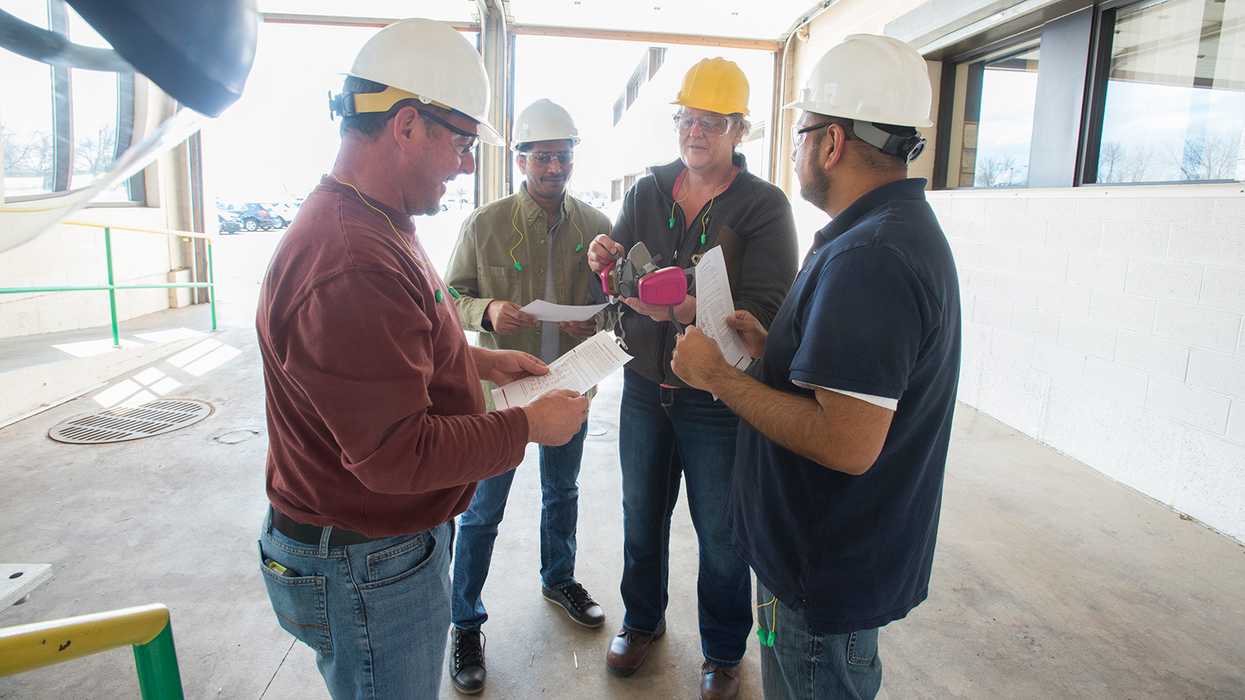
If possible, employees should change into clothes and shoes that stay at the workplace. Even if exposure levels are low enough that OSHA doesn’t require showers, employers should consider offering changing rooms where employees can store clean clothes, shoes, and personal items in a dedicated clean locker or a closed container.
Safety practices when working with lead include:
- Always wear required personal protective equipment (PPE) correctly.
- Avoid touching your face and mouth.
- Clean your work area throughout the day.
- Use a high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) vacuum or wet methods to clean surfaces with lead exposure.
- Never dry sweep or use compressed air to clean up dust.
- After working with lead or cleaning a work area, wash hands as soon as possible with soap designed to remove lead and using proper handwashing techniques.
- Do not remove PPE while in a lead work area. When removing PPE, follow the manufacturer’s instructions to avoid cross-contamination.
Breaks and lunch
Employees working with lead should wash their hands with soap designed to remove lead before they eat, drink, touch their faces, or smoke. The employer should have an approved location for eating and drinking away from lead dust or other contamination.
Employees should not enter a break or meal area before removing protective outer garments and washing their faces, hands, and arms.
Leaving work
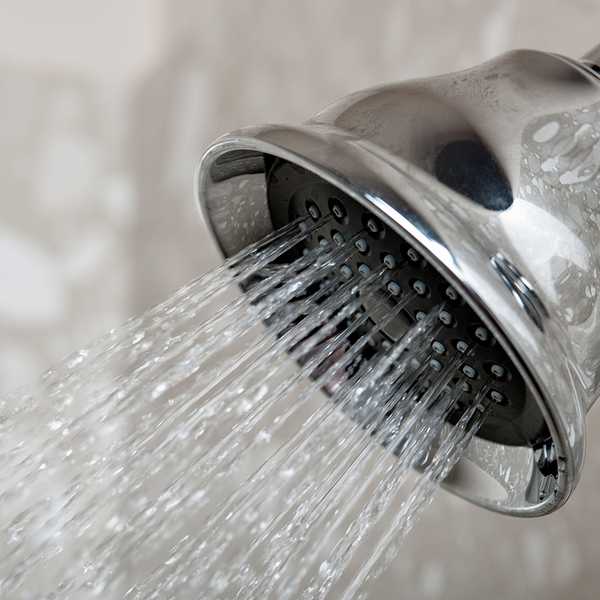
Whenever possible, employees should shower and wash their hair before leaving work. If showers aren’t available, they should wash as much of their skin as possible with soap designed to remove lead.
Employees should also change clothes and shoes before going home, leaving dirty clothes and shoes at work for cleaning. If the employer doesn’t offer a cleaning service, store work clothes in a closed plastic bag away from all other clothes. At home, wash and dry work clothes alone and not with any other clothes.
At home after work
Never wear work shoes into the house. Take them off outside and store them in a closed plastic bag.
If employees don’t shower at work, they should shower as soon as they get home. Avoid touching family members or handling household items until after showering.
Clean the car and the home often. For hard floors and furniture, use wet cleaning methods. For carpets and fabrics, use a vacuum cleaner with a HEPA filter. Segregate cleaning supplies for lead and do not use them in the rest of the home. This will help minimize the risk of spreading lead throughout the home.
Key to remember: Reducing the risk of lead exposure requires planning before work, following safety steps at work, and minimizing contamination that could enter the home after work.