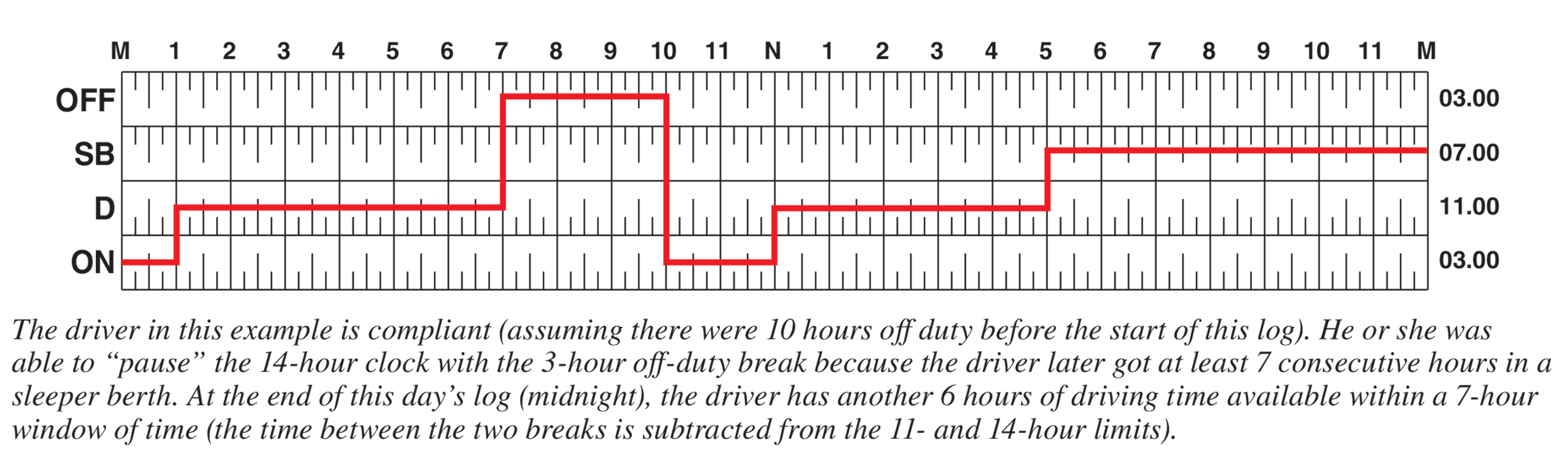
Prevent fires with proper hand-powered tool inspections
OSHA requires employees authorized to use, maintain, or service powered hand tools to be trained to recognize applicable hazards related to each tool. Don’t assume every employee knows what to look for or underestimate the chance of fire from defective tools. Instead, walk them through a proper inspection.
An example of a proper inspection
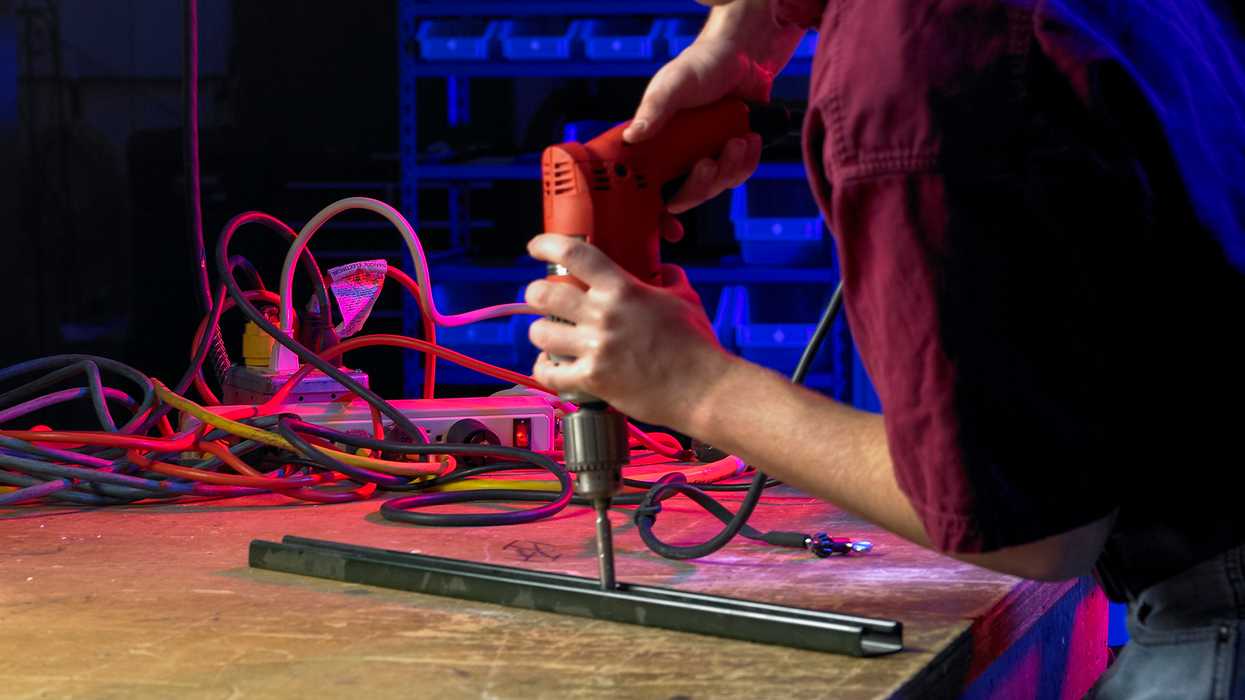
Powered hand tools with defective cords are especially prone to electrical fires, which are quite challenging to extinguish. Because of this challenge, fires can spread quickly to other areas creating devastating consequences for the workplace.
Here’s one example of a hand-powered tool inspection for a drill. Supervisors can use it as a template to walk through other hand tools to ensure all components are inspected before use.
A thorough pre-use hand-powered drill inspection ensures:
- The drill, cord, and drill bits are approved for the type of task being performed.
- A removal from service of any drill that’s defective, has frayed or damaged cords or plugs, is missing grounds or guards, has bent bits or chucks, etc.
- The chuck and bits are securely tightened before drilling.
- Protective devices, such as clamps or vices, are utilized to control material movement.
- Drill cords are plugged into direct power whenever possible, aren’t in the line of drilling action, and aren’t daisy chained.
- Work areas are kept clean and organized to avoid buildup of combustibles and flammables.
- Proper procedures are followed for drill use and shortcuts aren’t being taken.
- Drills are disconnected from any power source when adjustments are made or when bits are changed.
- Hand-powered drills aren’t used in damp or muddy locations.
- Proper personal protective equipment (PPE) is donned to avoid burns, flying sparks, and fire hazards. IMPORTANT: Gloves aren’t typically recommended when there’s a danger of entanglement.
Keys to remember
Employers should never assume employees know the hazards associated with defective hand-powered tools, including major fires. Pre-use inspections should be performed on all parts of each hand tool for defects, deformities, improper fit, and faulty electrical components.