Bite-Proof? Protecting outdoor workers from insect hazards
Outdoor workers are at risk of encountering various stinging and biting insects, which can transmit diseases and lead to serious hazards. As the summer season arrives, many workers are tasked with outdoor jobs that expose them to these dangerous bugs, including landscapers, groundskeepers, and other outdoor workers. Employers must prioritize their safety by addressing the risks associated with insect bites and stings and their related hazards.
Stinging insects
Stinging insects like bees, wasps, and hornets can indeed cause workers to experience allergic reactions. These reactions can range from mild discomfort to life-threatening anaphylactic shock.
It’s important to seek immediate medical attention if you experience symptoms such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, dizziness, or a rapid heartbeat after being stung.
Here are some tips for workers to prevent allergic reactions to stinging insects:
- Wear protective clothing: When working in areas where stinging insects are present, it's important to wear long pants, socks, and long-sleeved shirts to provide protection from stings. Make sure to seal clothing at the wrists and ankles to prevent insects from entering under clothing.
- Avoid scented products: Stinging insects are attracted to scents, so it's best to avoid using products such as colognes, perfumes, scented soaps, shampoos, and deodorants.
- Remain calm and still: If a single stinging insect is flying around, remain calm and still. Swatting at an insect can lead to stings and may attract additional insects. If you are attacked by several stinging insects at once, leave the area as quickly as possible.
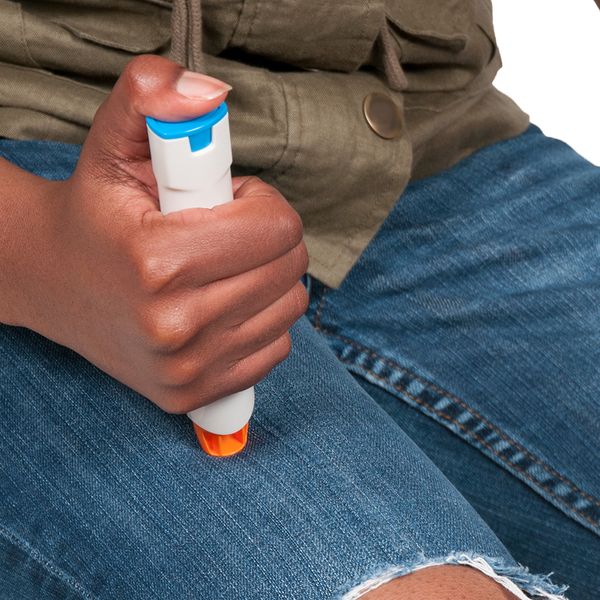
- Carry an epinephrine auto-injector: If you are allergic to certain insects, it's important to carry an epinephrine auto-injector at all times. As a best practice, make your fellow workers and employer aware of your allergy just in case.
Biting insects
Vector-borne transmission refers to the transfer of disease-causing agents, like parasites, bacteria, or viruses, through bites from mosquitoes or ticks.
Ticks are most commonly known for causing Lyme disease, which is characterized by symptoms like a circular rash, fever, joint and muscle pains, headache, fatigue, and swollen lymph nodes.
Mosquitoes can carry diseases like the Zika virus and the West Nile virus. Symptoms of mosquito-borne diseases can include body and muscle aches, fever, headaches, fatigue, joint pain, rash, stiff neck, and in severe cases, paralysis.
Here are some tips for workers to prevent the effects of vector-borne diseases from biting insects:
- Wear protective clothing: Similar to stinging insects, when working in areas where mosquitoes and ticks are present, wear protective clothing that covers your skin. Opt for neutral-colored attire to reduce the attraction.
- Treat clothing and gear: CDC recommends using products containing 0.5 percent Permethrin, which is effective in killing ticks upon contact. It’s important to note that Permethrin should not be applied directly to the skin, but can be used to treat shoes, clothing, and gear. Alternatively, consider using pre-treated clothing that already contains Permethrin.
- Use a repellent: Look for a repellent that contains 20 to 30 percent DEET or 20 percent Picaridin and apply it to exposed skin. Be sure to follow the manufacturer's instructions for reapplication.
- Minimize stagnant water sources: Stagnant water sources serve as breeding grounds for these types of insects. By eliminating these sources, you can help reduce the presence of biting insects and minimize the potential for exposure.
What can employers do to protect their workers?
- Training and education: Provide workers with comprehensive training on the risks associated with insect stings and bites, including information on common insects in the area, their behavior, and the diseases they may transmit. Educate workers on proper use of protective clothing, repellents, and first aid measures.
- Personal protective equipment (PPE): Ensure that workers have access to appropriate PPE, such as long-sleeved shirts, pants, hats, and gloves, to minimize exposed skin. Additionally, provide workers with insect repellents approved for use in outdoor settings.
- Regular inspections and maintenance: Regularly inspect outdoor work areas for potential insect breeding grounds, such as standing water or overgrown vegetation. Implement measures to eliminate or minimize these breeding grounds to reduce the presence of insects.
- Communication and reporting: Encourage workers to report any insect-related incidents or sightings promptly. Establish a clear communication channel for workers to report concerns or seek assistance.
Key to remember: By implementing proper safety precautions, providing training, and ensuring access to appropriate protective measures, employers can protect their workers from the hazards associated with insects.