86 FR 61402 COVID-19 Vaccination and Testing; Emergency Temporary Standard
DEPARTMENT OF LABOR
Occupational Safety and Health Administration
29 CFR Parts 1910, 1915, 1917, 1918, 1926, and 1928
[Docket No. OSHA-2021-0007]
RIN 1218-AD42
COVID-19 Vaccination and Testing; Emergency Temporary Standard
AGENCY: Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), Department of Labor.
ACTION: Interim final rule; request for comments.
SUMMARY: The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) is issuing an emergency temporary standard (ETS) to protect unvaccinated employees of large employers (100 or more employees) from the risk of contracting COVID-19 by strongly encouraging vaccination. Covered employers must develop, implement, and enforce a mandatory COVID-19 vaccination policy, with an exception for employers that instead adopt a policy requiring employees to either get vaccinated or elect to undergo regular COVID-19 testing and wear a face covering at work in lieu of vaccination.
DATES: The rule is effective November 5, 2021. The incorporation by reference of certain publications listed in the rule is approved by the Director of the Federal Register as of November 5, 2021.
Compliance dates: Compliance dates for specific provisions are in 29 CFR 1910.501(m).
Comments: Written comments, including comments on any aspect of this ETS and whether this ETS should become a final rule, must be submitted by December 6, 2021 in Docket No. OSHA-2021-0007. Comments on the information collection determination described in Additional Requirements (Section V.K. of this preamble) (OMB review under the Paperwork Reduction Act of 1995) may be submitted by January 4, 2022 in Docket No. OSHA-2021-0008.
ADDRESSES: In accordance with 28 U.S.C. 2112(a), the Agency designates Edmund C. Baird, the Associate Solicitor for Occupational Safety and Health, Office of the Solicitor, U.S. Department of Labor, to receive petitions for review of the ETS. Service can be accomplished by email to zzSOL-Covid19-ETS@dol.gov.
Written comments. You may submit comments and attachments, identified by Docket No. OSHA-2021-0007, electronically at www.regulations.gov, which is the Federal e-Rulemaking Portal. Follow the online instructions for making electronic submissions.
Instructions: All submissions must include the agency's name and the docket number for this rulemaking (Docket No. OSHA-2021-0007). All comments, including any personal information you provide, are placed in the public docket without change and may be made available online at www.regulations.gov. Therefore, OSHA cautions commenters about submitting information they do not want made available to the public, or submitting materials that contain personal information (either about themselves or others), such as Social Security Numbers and birthdates.
Docket: To read or download comments or other material in the docket, go to Docket No. OSHA-2021-0007 at www.regulations.gov. All comments and submissions are listed in the www.regulations.gov index; however, some information ( e.g., copyrighted material) is not publicly available to read or download through that website. All comments and submissions, including copyrighted material, are available for inspection through the OSHA Docket Office. Documents submitted to the docket by OSHA or stakeholders are assigned document identification numbers (Document ID) for easy identification and retrieval. The full Document ID is the docket number plus a unique four-digit code. OSHA is identifying supporting information in this ETS by author name and publication year, when appropriate. This information can be used to search for a supporting document in the docket at http://www.regulations.gov. Contact the OSHA Docket Office at 202-693-2350 (TTY number: 877-889-5627) for assistance in locating docket submissions.
FOR FURTHER INFORMATION CONTACT:
General information and press inquiries: Contact Frank Meilinger, OSHA Office of Communications, U.S. Department of Labor; telephone (202) 693-1999; email OSHAComms@dol.gov.
For technical inquiries: Contact Andrew Levinson, OSHA Directorate of Standards and Guidance, U.S. Department of Labor; telephone (202) 693-1950; email ETS@dol.gov.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION:
The preamble to the ETS on COVID-19 vaccination and testing follows this outline:
Table of Contents
I. Executive Summary and Request for Comment
A. Executive Summary
B. Request for Comment
II. Pertinent Legal Authority
III. Rationale for the ETS
A. Grave Danger
B. Need for the ETS
IV. Feasibility
A. Technological Feasibility
B. Economic Analysis
V. Additional Requirements
VI. Summary and Explanation
A. Purpose
B. Scope and Application
C. Definitions
D. Employer Policy on Vaccination
E. Determination of Employee Vaccination Status
F. Employer Support for Employee Vaccination
G. COVID-19 Testing for Employees Who Are Not Fully Vaccinated
H. Employee Notification to Employer of a Positive COVID-19 Test and Removal
I. Face Coverings
J. Information Provided to Employees
K. Reporting COVID-19 Fatalities and Hospitalizations to OSHA
L. Availability of Records
M. Dates
N. Severability
O. Incorporation by Reference
VII. Authority and Signature
I. Executive Summary and Request for Comment
A. Executive Summary
This ETS is based on the requirements of the Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSH Act or Act) and legal precedent arising under the Act. Under section 6(c)(1) of the OSH Act, 29 U.S.C. 655(c)(1), OSHA shall issue an ETS if the agency determines that employees are subject to grave danger from exposure to substances or agents determined to be toxic or physically harmful or from new hazards, and an ETS is necessary to protect employees from such danger. These legal requirements are more fully discussed in Pertinent Legal Authority (Section II. of this preamble). This ETS does not apply to workplaces subject to E.O. 14042 on Requiring Coronavirus Disease 2019 Vaccination for Federal Contractors. In addition, OSHA will treat federal agencies' compliance with E.O. 14043, and the Safer Federal Workforce Task Force guidance issued under section 4(e) of Executive Order 13991 and section 2 of Executive Order 14043, as sufficient to meet their obligations under the OSH Act and E.O. 12196.
COVID-19 has killed over 725,000 people in the United States in less than two years, and infected millions more (CDC, October 18, 2021—Cumulative US Deaths). The pandemic continues to affect workers and workplaces. While COVID-19 vaccines authorized or approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) effectively protect vaccinated individuals against severe illness and death from COVID-19, unvaccinated individuals remain at much higher risk of severe health outcomes from COVID-19. Further, unvaccinated workers are much more likely to contract and transmit COVID-19 in the workplace than vaccinated workers. OSHA has determined that many employees in the U.S. who are not fully vaccinated against COVID-19 face grave danger from exposure to SARS-CoV-2 in the workplace. This finding of grave danger is based on the severe health consequences associated with exposure to the virus along with evidence demonstrating the transmissibility of the virus in the workplace and the prevalence of infections in employee populations, as discussed in Grave Danger (Section III.A. of this preamble).
OSHA has also determined that an ETS is necessary to protect unvaccinated workers from the risk of contracting COVID-19 at work, as discussed in Need for the ETS (Section III.B. of this preamble). At the present time, workers are becoming seriously ill and dying as a result of occupational exposures to COVID-19, when a simple measure, vaccination, can largely prevent those deaths and illnesses. The ETS protects these workers through the most effective and efficient control available—vaccination—and further protects workers who remain unvaccinated through required regular testing, use of face coverings, and removal of all infected employees from the workplace. OSHA also concludes, based on its enforcement experience during the pandemic to date, that continued reliance on existing standards and regulations, the General Duty Clause of the OSH Act, 29 U.S.C. 654(a)(1), and workplace guidance, in lieu of an ETS, is not adequate to protect unvaccinated employees from the grave danger of being infected by, and suffering death or serious health consequences from, COVID-19.
OSHA will continue to monitor trends in COVID-19 infections and death as more of the workforce and the general population become fully vaccinated against COVID-19 and the pandemic continues to evolve. Where OSHA finds a grave danger from the virus no longer exists for the covered workforce (or some portion thereof), or new information indicates a change in measures necessary to address the grave danger, OSHA will update this ETS, as appropriate.
This ETS applies to employers with a total of 100 or more employees at any time the standard is in effect. In light of the unique occupational safety and health dangers presented by COVID-19, and against the backdrop of the uncertain economic environment of a pandemic, OSHA is proceeding in a stepwise fashion in addressing the emergency this rule covers. OSHA is confident that employers with 100 or more employees have the administrative capacity to implement the standard's requirements promptly, but is less confident that smaller employers can do so without undue disruption. OSHA needs additional time to assess the capacity of smaller employers, and is seeking comment to help the agency make that determination. Nonetheless, the agency is acting to protect workers now in adopting a standard that will reach two-thirds of all private-sector workers in the nation, including those working in the largest facilities, where the most deadly outbreaks of COVID-19 can occur.
The agency has also evaluated the feasibility of this ETS and has determined that the requirements of the ETS are both economically and technologically feasible, as outlined in Feasibility (Section IV. of this preamble). The specific requirements of the ETS are outlined and described in Summary and Explanation (Section VI. of this preamble).
B. Request for Comment
Although this ETS takes effect immediately, it also serves as a proposal under Section 6(b) of the OSH Act (29 U.S.C. 655(b)) for a final standard. Accordingly, OSHA seeks comment on all aspects of this ETS and whether it should be adopted as a final standard. OSHA encourages commenters to explain why they prefer or disfavor particular policy choices, and include any relevant studies, experiences, anecdotes or other information that may help support the comment. In particular, OSHA seeks comments on the following topics:
1. Employers with fewer than 100 employees. As noted above and fully discussed in the Summary and Explanation for Scope and Application (Section VI.B. of this preamble), OSHA has implemented a 100-employee threshold for the requirements of this standard to focus the ETS on companies that OSHA is confident will have sufficient administrative systems in place to comply quickly with the ETS. The agency is moving in a stepwise fashion on the short timeline necessitated by the danger presented by COVID-19 while soliciting stakeholder comment and additional information to determine whether to adjust the scope of the ETS to address smaller employers in the future. OSHA seeks information about the ability of employers with fewer than 100 employees to implement COVID-19 vaccination and/or testing programs. Have you instituted vaccination mandates (with or without alternatives), or requirements for regular COVID-19 testing or face covering use? What have been the benefits of your approach? What challenges have you had or could you foresee in implementing such programs? Is there anything specific to your industry, or the size of your business, that poses particular obstacles in implementing the requirements in this standard? How much time would it take, what types of costs would you incur, and how much would it cost for you to implement such requirements?
2. Significant Risk. If OSHA were to finalize a rule based on this ETS, it would be a standard adopted under 6(b) of the OSH Act, which requires a finding of significant risk from exposure to COVID-19. As discussed more fully in Pertinent Legal Authority (Section II. of this preamble), this is a lower showing of risk than grave danger, the finding required to issue a 6(c) emergency temporary standard. How should the scope of the rule change to address the significant risk posed by COVID-19 in the workplace? Should portions of the rule, such as face coverings, apply to fully vaccinated persons?
3. Prior COVID-19 infections. OSHA determined that workers who have been infected with COVID-19 but have not been fully vaccinated still face a grave danger from workplace exposure to SARS-CoV-2. This is an area of ongoing scientific inquiry. Given scientific uncertainty and limitations in testing for infection and immunity, OSHA is concerned that it would be infeasible for employers to operationalize a standard that would permit or require an exception from vaccination or testing and face covering based on prior infection with COVID-19. Is there additional scientific information on this topic that OSHA should consider as it determines whether to proceed with a permanent rule?
In particular, what scientific criteria can be used to determine whether a given employee is sufficiently protected against reinfection? Are there any temporal limits associated with this criteria to account for potential reductions in immunity over time? Do you require employees to provide verification of infection with COVID-19? If so, what kinds of verification do you accept ( i.e., PCR testing, antigen testing, etc.)? What challenges have you experienced, if any, in operationalizing such an exception?
4. Experience with COVID-19 vaccination policies. Should OSHA impose a strict vaccination mandate ( i.e., all employers required to implement mandatory vaccination policies as defined in this ETS) with no alternative compliance option? OSHA seeks information on COVID-19 vaccination policies that employers have implemented to protect workers. If you have implemented a COVID-19 vaccination policy:
(a) When did you implement it, and what does your policy require? Was vaccination mandatory or voluntary under the policy? Do you offer vaccinations on site? What costs associated with vaccination did you cover under the policy? What percentage of your workforce was vaccinated as a result? Do you offer paid leave for receiving a vaccination? If vaccination is mandatory, have employees been resistant and if so what steps were required to enforce the policy?
(b) How did you verify that employees were vaccinated? Are there other reliable means of vaccination verification not addressed by the ETS that should be included? Did you allow attestation where the employee could not find other proof, and if so, have you experienced any difficulties with this approach? Have you experienced any issues with falsified records of vaccination, and if so, how did you deal with them?
(c) Have you experienced a decrease in infection rates or outbreaks after implementing this policy?
(d) If you have received any requests for reasonable accommodation from vaccination, what strategies did you implement to address the accommodation and ensure worker safety ( e.g., telework, working in isolation, regular testing and the use of face coverings)?
5. COVID-19 testing and removal. OSHA seeks information on COVID-19 testing and removal practices implemented to protect workers.
(a) Do you have a testing and removal policy in your workplace and, if so, what does it require? How often do you require testing and what types of testing do you use ( e.g., at-home tests, tests performed at laboratories, tests performed at your worksites)? What costs have you incurred as part of your testing and removal policies? Do you have difficulty in finding adequate availability of tests? How often? Have you experienced any issues with falsified test results, and if so, how did you deal with them? Have you experienced other difficulties in implementing a testing and removal scheme, including the length of time to obtain COVID-19 test results? Do you offer paid leave for testing?
(b) How often have you detected and removed COVID-19 positive employees from the workplace under this policy? Do you provide paid leave and job protection to employees you remove for this reason?
(c) Should OSHA require testing more often than on a weekly basis?
6. Face coverings. As discussed in the Summary and Explanation for Face Coverings (Section VI.I. of this preamble), ASTM released a specification standard on February 15, 2021, to establish a national standard baseline for barrier face coverings (ASTM F3502-21). Should OSHA require the use of face coverings meeting the ASTM F3502-21 standard instead of the face coverings specified by the ETS? If so, should OSHA also require that such face coverings meet the NIOSH Workplace Performance or Workplace Performance Plus criteria (see CDC, September 23, 2021)? Are there particular workplace settings in which face coverings meeting one standard should be favored over another? Are there alternative criteria OSHA should consider for face coverings instead of the F3502-21 standard or NIOSH Workplace Performance or Workplace Performance Plus criteria? Is there sufficient capacity to supply face coverings meeting F3502-01 and/or NIOSH Workplace Performance or Workplace Performance Plus criteria to all employees covered by the ETS? What costs have you incurred as part of supplying employees with face coverings meeting the appropriate criteria?
7. Other controls. This ETS requires employees to either be fully vaccinated against COVID-19 or be tested weekly and wear face coverings, based on the type of policy their employer adopts. It stops short of requiring the full suite of workplace controls against SARS-CoV-2 transmission recommended by OSHA and the CDC, including distancing, barriers, ventilation, and sanitation. As OSHA explained in Need for the ETS (Section III.B. of this preamble), OSHA has determined that it needs more information before imposing these requirements on the entire scope of industries and employers covered by the standard. OSHA is interested in hearing from employers about their experience in implementing a full suite of workplace controls against COVID-19.
What measures have you taken to protect employees against COVID-19 in your workplace? Are there controls that you attempted to employ but found ineffective or infeasible? What are they? Why did you conclude that they were they ineffective or infeasible; for example, are there particular aspects of your workplace or industry that make certain controls infeasible? Do you require both fully vaccinated and unvaccinated employees to comply with these controls? Have you experienced a reduction in infection rates or outbreaks since implementing these controls?
8. Educational materials. Have you implemented any policies or provided any information that has been helpful in encouraging an employee to be vaccinated?
9. Feasibility and health impacts. Do you have any experience or data that would inform OSHA's estimates in its economic feasibility analysis or any of the assumptions or estimates used in OSHA's identification of the number of hospitalizations prevented and lives saved from its health impacts analysis (see OSHA, October 2021c)?
References
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, October 18). COVID Data Tracker. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/. (CDC, October 18, 2021)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, September 23). Types of Masks and Respirators. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/types-of-masks.html. (CDC, September 23, 2021)
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). (2021c, October). Health Impacts of the COVID-19 Vaccination and Testing ETS. (OSHA, October 2021c)
II. Pertinent Legal Authority
The purpose of the Occupational Safety and Health Act of 1970 (OSH Act), 29 U.S.C. 651 et seq., is “to assure so far as possible every working man and woman in the Nation safe and healthful working conditions and to preserve our human resources.” 29 U.S.C. 651(b). To this end, Congress authorized the Secretary of Labor (Secretary) to promulgate and enforce occupational safety and health standards under sections 6(b) and (c) of the OSH Act. 1 29 U.S.C. 655(b). These provisions provide bases for issuing occupational safety and health standards under the Act. Once OSHA has established as a threshold matter that a health standard is necessary under section 6(b) or (c)— i.e., to reduce a significant risk of material health impairment, or a grave danger to employee health—the Act gives the Secretary “almost unlimited discretion to devise means to achieve the congressionally mandated goal” of protecting employee health, subject to the constraints of feasibility. See United Steelworkers of Am. v. Marshall, 647 F.2d 1189, 1230 (D.C. Cir. 1981). A standard's individual requirements need only be “reasonably related” to the purpose of ensuring a safe and healthful working environment. Id. at 1237, 1241; see also Forging Indus. Ass'n v. Sec'y of Labor, 773 F.2d 1436, 1447 (4th Cir. 1985). OSHA's authority to regulate employers is hedged by constitutional considerations and, pursuant to section 4(b)(1) of the OSH Act, the regulations and enforcement policies of other federal agencies. See, e.g., Chao v. Mallard Bay Drilling, Inc., 534 U.S. 235, 241 (2002).
1 The Secretary has delegated most of his duties under the OSH Act to the Assistant Secretary of Labor for Occupational Safety and Health. Secretary's Order 08-2020, 85 FR 58393 (Sept. 18, 2020). This section uses the terms Secretary and OSHA interchangeably.
The OSH Act in section 6(c)(1) states that the Secretary “shall” issue an emergency temporary standard (ETS) upon a finding that the ETS is necessary to address a grave danger to workers. See 29 U.S.C. 655(c). In particular, the Secretary shall provide, without regard to the requirements of chapter 5, title 5, United States Code, for an emergency temporary standard to take immediate effect upon publication in the Federal Register if the Secretary makes two determinations: That employees are exposed to grave danger from exposure to substances or agents determined to be toxic or physically harmful or from new hazards, and that such emergency standard is necessary to protect employees from such danger. 29 U.S.C. 655(c)(1). A separate section of the OSH Act, section 8(c), authorizes the Secretary to prescribe regulations requiring employers to make, keep, and preserve records that are necessary or appropriate for the enforcement of the Act. 29 U.S.C. 657(c)(1). Section 8(c) also provides that the Secretary shall require employers to keep records of, and report, work-related deaths and illnesses. 29 U.S.C. 657(c)(2).
The ETS provision, section 6(c)(1), exempts the Secretary from procedural requirements contained in the OSH Act and the Administrative Procedure Act, including those for public notice, comments, and a rulemaking hearing. See, e.g., 29 U.S.C. 655(b)(3); 5 U.S.C. 552, 553.
The Secretary must issue an ETS in situations where employees are exposed to a “grave danger” and immediate action is necessary to protect those employees from such danger. 29 U.S.C. 655(c)(1); Pub. Citizen Health Research Grp. v. Auchter, 702 F.2d 1150, 1156 (D.C. Cir. 1983). The determination of what exact level of risk constitutes a “grave danger” is a “policy consideration that belongs, in the first instance, to the Agency.” Asbestos Info. Ass'n, 727 F.2d at 425 (accepting OSHA's determination that eighty lives at risk over six months was a grave danger); Indus. Union Dep't, AFL-CIO v. Am. Petroleum Inst., 448 U.S. 607, 655 n.62 (1980). However, a “grave danger” represents a risk greater than the “significant risk” that OSHA must show in order to promulgate a permanent standard under section 6(b) of the OSH Act, 29 U.S.C. 655(b). Int'l Union, United Auto., Aerospace, & Agr. Implement Workers of Am., UAW v. Donovan, 590 F. Supp. 747, 755-56 (D.D.C. 1984), adopted, 756 F.2d 162 (D.C. Cir. 1985); see also Indus. Union Dep't, AFL-CIO, 448 U.S. at 640 n.45 (noting the distinction between the standard for risk findings in permanent standards and ETSs).
In determining the type of health effects that may constitute a “grave danger” under the OSH Act, the Fifth Circuit emphasized “the danger of incurable, permanent, or fatal consequences to workers, as opposed to easily curable and fleeting effects on their health.” Fla. Peach Growers Ass'n, Inc. v. U. S. Dep't of Labor, 489 F.2d 120, 132 (5th Cir. 1974). Although the findings of grave danger and necessity must be based on evidence of “ actual, prevailing industrial conditions,” see Int'l Union, 590 F. Supp. at 751, when OSHA determines that exposure to a particular hazard would pose a grave danger to workers, OSHA can assume an exposure to a grave danger wherever that hazard is present in a workplace. Dry Color Mfrs. Ass'n, Inc. v. Dep't of Labor, 486 F.2d 98, 102 n.3 (3d Cir. 1973).
In demonstrating whether OSHA had shown that an ETS is necessary, the Fifth Circuit considered whether OSHA had another available means of addressing the risk that would not require an ETS. Asbestos Info. Ass'n, 727 F.2d at 426 (holding that necessity had not been proven where OSHA could have increased enforcement of already-existing standards to address the grave risk to workers from asbestos exposure). Additionally, a standard must be both economically and technologically feasible in order to be “reasonably necessary and appropriate” under section 3(8) and, by inference, “necessary” under section 6(c)(1)(B) of the Act. Cf. Am. Textile Mfrs. Inst., Inc. v. Donovan, 452 U.S. 490, 513 n.31 (1981) (noting “any standard that was not economically or technologically feasible would a fortiori not be `reasonably necessary or appropriate' ” as required by the OSH Act's definition of “occupational safety and health standard” in section 3(8)); see also Florida Peach Growers, 489 F.2d at 130 (recognizing that the promulgation of any standard, including an ETS, must account for its economic effect). However, given that section 6(c) is aimed at enabling OSHA to protect workers in emergency situations, the agency is not required to make a feasibility showing with the same rigor as in ordinary section 6(b) rulemaking. Asbestos Info. Ass'n, 727 F.2d at 424 n.18.
On judicial review of an ETS, OSHA is entitled to great deference on the determinations of grave danger and necessity required under section 6(c)(1). See, e.g., Pub. Citizen Health Research Grp., 702 F.2d at 1156; Asbestos Info. Ass'n, 727 F.2d at 422 (judicial review of these legislative determinations requires deference to the agency); cf. Am. Dental Ass'n v. Martin, 984 F.2d 823, 831 (7th Cir. 1993) (“the duty of a reviewing court of generalist judges is merely to patrol the boundary of reasonableness”). These determinations are “essentially legislative and rooted in inferences from complex scientific and factual data.” Pub. Citizen Health Research Grp., 702 F.2d at 1156. The agency is not required to support its conclusions “with anything approaching scientific certainty,” Indus. Union Dep't, AFL-CIO, 448 U.S. at 656, and has the “prerogative to choose between conflicting evidence.” Asbestos Info. Ass'n, 727 F.2d at 425.
The determinations of the Secretary in issuing standards under section 6 of the OSH Act, including ETSs, must be affirmed if supported by “substantial evidence in the record considered as a whole.” 29 U.S.C. 655(f). The Supreme Court described substantial evidence as “such relevant evidence as a reasonable mind might accept as adequate to support a conclusion.” Am. Textile Mfrs. Inst., 452 U.S. at 522-23 (quoting Universal Camera Corp. v. NLRB, 340 U.S. 474, 477 (1951)). The Court also noted that “the possibility of drawing two inconsistent conclusions from the evidence does not prevent an administrative agency's finding from being supported by substantial evidence.” Id. at 523 (quoting Consolo v. FMC, 383 U.S. 607, 620 (1966)). The Fifth Circuit, recognizing the size and complexity of the rulemaking record before it in the case of OSHA's ETS for organophosphorus pesticides, stated that a court's function in reviewing an ETS to determine whether it meets the substantial evidence standard is “basically [to] determine whether the Secretary carried out his essentially legislative task in a manner reasonable under the state of the record before him.” Fla Peach Growers Ass'n, 489 F.2d at 129.
Although Congress waived the ordinary rulemaking procedures in the interest of “permitting rapid action to meet emergencies,” section 6(e) of the OSH Act, 29 U.S.C. 655(e), requires OSHA to include a statement of reasons for its action when it issues any standard. Dry Color Mfrs., 486 F.2d at 105-06 (finding OSHA's statement of reasons inadequate). By requiring the agency to articulate its reasons for issuing an ETS, the requirement acts as “an essential safeguard to emergency temporary standard-setting.” Id. at 106. However, the Third Circuit noted that it did not require justification of “every substance, type of use or production technique,” but rather a “general explanation” of why the standard is necessary. Id. at 107.
ETSs are, by design, temporary in nature. Under section 6(c)(3), an ETS serves as a proposal for a permanent standard in accordance with section 6(b) of the OSH Act (permanent standards), and the Act calls for the permanent standard to be finalized within six months after publication of the ETS. 29 U.S.C. 655(c)(3); see Fla. Peach Growers Ass'n, 489 F.2d at 124. The ETS is effective “until superseded by a standard promulgated in accordance with” section 6(c)(3). 29 U.S.C. 655(c)(2).
Section 6(c)(1) states that the Secretary “shall” provide for an ETS when OSHA makes the prerequisite findings of grave danger and necessity. See Pub. Citizen Health Research Grp., 702 F.2d at 1156 (noting the mandatory language of section 6(c)). OSHA is entitled to great deference in its determinations, and it must also account for “the fact that `the interests at stake are not merely economic interests in a license or a rate structure, but personal interests in life and health.' ” Id. (quoting Wellford v. Ruckelshaus, 439 F.2d 598, 601 (D.C. Cir. 1971)).
When OSHA issues a standard pursuant to section 6—whether permanent or an ETS—section 18 of the OSH Act provides that OSHA's standard preempts any state occupational safety or health standard “relating to [the same] occupational safety or health issue” as the Federal standard. 29 U.S.C. 667(b); see also Gade v. Nat'l Solid Wastes Mgmt. Ass'n , 505 U.S. 88, 97 (1992). A state can avoid preemption only if it submits, and receives Federal approval for, a state plan for the development and enforcement of standards pursuant to section 18 of the Act, which must be “at least as effective” as the Federal standards. 29 U.S.C. 667; Indus. Truck Ass'n v. Henry , 125 F.3d 1305, 1311 (9th Cir. 1997). However, the OSH Act does not preempt state laws of “general applicability” that regulate workers and non-workers alike, so long as they do not conflict with an OSHA standard. Gade , 505 U.S. at 107.
As discussed in detail elsewhere in this preamble, OSHA has determined that a grave danger exists necessitating a new ETS (see Grave Danger and Need for the ETS , Sections III.A. and III.B. of this preamble), and that compliance with this ETS is feasible for covered employers (see Feasibility , Section IV. of this preamble). OSHA has also provided a more detailed explanation of each provision of this ETS in Summary and Explanation (Section VI. of this preamble). In addition, OSHA wishes to provide here some general guidance on its legal authority to regulate COVID-19 hazards, and for particular provisions of this ETS.
As a threshold matter, OSHA's authority to regulate workplace exposure to biological hazards like SARS-CoV-2 is well-established. Section 6(b)(5) of the OSH Act uses similar language to section 6(c)(1)(A): The former sets forth requirements for promulgating permanent standards addressing “toxic materials or harmful physical agents,” and the latter authorizes OSHA to promulgate an ETS addressing “substances or agents determined to be toxic or physically harmful” (as well as “new hazards”). OSHA has consistently identified biological hazards similar to SARS-CoV-2, as well as SARS-CoV-2 itself, to be “toxic materials or harmful physical agents” under the Act. Indeed, in its exposure and medical records access regulation, OSHA has defined “toxic materials or harmful physical agents” to include “any . . . biological agent (bacteria, virus, fungus, etc.)” for which there is evidence that it poses a chronic or acute health hazard. 29 CFR 1910.1020(c)(13). And in addition to previously regulating exposure to SARS-CoV-2 as a new and physically harmful agent in the Healthcare ETS (see, e.g. , 86 FR at 32381), OSHA has also previously regulated biological hazards like SARS-CoV-2 as health hazards under section 6(b)(5), for example in the Bloodborne Pathogens (BBP) standard, 29 CFR 1910.1030, which addresses workplace exposure to HIV and Hepatitis B. The BBP standard was upheld (except as to application in certain limited industries) in American Dental Association , which observed that “the infectious character” of the regulated bloodborne diseases might warrant “more regulation than would be necessary in the case of a noncommunicable disease.” 984 F.2d at 826. In addition, in the preamble to the respiratory protection standard, 29 CFR 1910.134, which was also promulgated under section 6(b)(5), “OSHA emphasize[d] that [the] respiratory protection standard does apply to biological hazards.” Respiratory Protection, 63 FR 1152-01, 1180 (Jan. 8, 1998) (citing Mahone Grain Corp. , 10 BNA OSHC 1275 (No. 77-3041, 1981)).
In addition to being a physically harmful agent covered by section 6(c)(1)(A), SARS-CoV-2 is also, without question, a “new hazard” covered by this provision, as discussed in more detail in Grave Danger (Section III.A. of this preamble). SARS-CoV-2 was not known to exist until January 2020, and since then more than 725,000 people have died from COVID-19 in the U.S. alone (CDC, October 18, 2021—Cumulative US Deaths).
Turning to specific provisions of this standard, the vaccination requirements in this ETS are also well within the bounds of OSHA's authority. Vaccination can be a critical tool in the pursuit of health and safety goals, particularly in response to an infectious and highly communicable disease. See, e.g. , Jacobson v. Commonwealth of Mass. , 197 U.S. 11, 27-28 (1905) (recognizing use of smallpox vaccine as a reasonable measure to protect public health and safety); Klaassen v. Trustees of Ind. Univ. , 7 F.4th 592, 593 (7th Cir. 2021) (citing Jacobson and noting that vaccination may be an appropriate safety measure against SARS-CoV-2 as “[v]accination protects not only the vaccinated persons but also those who come in contact with them”). And the OSH Act itself explicitly acknowledges that such treatments might be necessary, in some circumstances. 29 U.S.C. 669(a)(5) (providing in the Act's provisions on research and related activities conducted by the Secretary of Health and Human Services to aid OSHA in its formulation of health and safety standards that “[n]othing in this or any other provision of this Act shall be deemed to authorize or require medical examination, immunization , or treatment for those who object thereto on religious grounds, except where such is necessary for the protection of the health or safety of others .” (emphasis added)). In recognition of the health and safety benefits provided by vaccination, OSHA has previously exercised its authority to promulgate vaccine-related requirements in the COVID-19 Healthcare ETS (29 CFR 1910.502(m)) and the BBP standard (29 CFR 1910.1030(f)). The BBP standard illustrates congressional understanding that the statutory delegation of authority to OSHA to issue standards includes authority for vaccine provisions, where appropriate. See Public Law 102-170, Title I, Section 100, 105 Stat. 1107 (1991) (directing OSHA to complete the BBP rulemaking by a date certain, and providing that if OSHA did not do so, the proposed rule, which included a vaccine provision, would become the final standard).
Additionally, OSHA's authority to require employers to bear the costs of particular provisions of a standard is solidly grounded in the OSH Act. The Act reflects Congress's determination that the costs of compliance with the Act and OSHA standards are part of the cost of doing business and OSHA may foreclose employers from shifting those costs to employees. See Am. Textile Mfrs. Inst. , 452 U.S. at 514; Phelps Dodge Corp. v. OSHRC , 725 F.2d 1237, 1239-40 (9th Cir. 1984); see also Sec'y of Labor v. Beverly Healthcare-Hillview , 541 F.3d 193 (3d Cir. 2008). Consistent with this authority, OSHA has largely required employers to bear the costs of the provisions of this ETS, including the typical costs associated with vaccination. The allocation of vaccination costs to employers in this ETS is similar to OSHA's treatment of vaccine-related costs in the COVID-19 Healthcare ETS and the BBP standards. See 29 CFR 1910.502(m), (p); 29 CFR 1910.1030(f)(1)(ii)(A).
The OSH Act provides OSHA with discretion, however, to decide whether to impose certain costs—such as those related to medical examinations or other tests—on employers “[w]here [it determines that such costs are] appropriate.” 29 U.S.C. 655(b)(7). OSHA has determined that for purposes of this ETS, it would not be “appropriate” to impose on employers any costs associated with COVID-19 testing for employees who choose not to be vaccinated. For most of the agency's existing standards containing medical testing and removal provisions, OSHA has found it necessary to impose the costs of such provisions on employers in order to remove barriers to employee participation in medical examinations that are critical to effectuating the standards' safety and health protections. See United Steelworkers of Am. , 647 F.2d at 1229-31, 1237-38. However, as explained in greater detail elsewhere in this preamble (see Need for the ETS , Section III.B. of this preamble), the ETS's safety and health protections are best effectuated by employee vaccination, not testing. Accordingly, OSHA only requires employers to bear the costs of employee compliance with the preferred, and more protective, vaccination provision, but not costs associated with testing. The agency does not believe it appropriate to impose the costs of testing on an employer where an employee has made an individual choice to pursue a less protective option. For the same reasons, OSHA has also determined that it is not appropriate to require employers to pay for face coverings for employees who choose not to be vaccinated. 2
2 OSHA notes that while the ETS does not impose these testing or face covering costs on employers, in some circumstances employers may be required to pay for the costs related to testing and/or face coverings by other laws, regulations, or collectively negotiated agreements. OSHA has no authority under the OSH Act to determine whether such obligations under other laws, regulations, or agreements might exist.
Finally, the Act and its legislative history “both demonstrate unmistakably” OSHA's authority to require employers to temporarily remove workers from the workplace to prevent exposure to a health hazard. United Steelworkers of Am. , 647 F.2d at 1230. And again, this is an authority OSHA has repeatedly exercised in prior standards, including in: COVID-19 Healthcare ETS (29 CFR 1910.502); Lead (29 CFR 1910.1025); Cadmium (29 CFR 1910.1027); Benzene (29 CFR 1910.1028); Formaldehyde (29 CFR 1910.1048); Methylenedianiline (29 CFR 1910.1050); Methylene Chloride (29 CFR 1910.1052); and Beryllium (29 CFR 1910.1024). It is equally appropriate to impose that obligation here.
For all of these reasons, as well as those explained more fully in other areas of this preamble, OSHA has the authority—and obligation—to promulgate this ETS.
References
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, October 18). COVID Data Tracker. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/. (CDC, October 18, 2021)
III. Rationale for the ETS
A. Grave Danger
I. Introduction
Section 6(c)(1) of the OSH Act requires the Secretary to issue an ETS in situations where employees are exposed to a “grave danger” and immediate action is necessary to protect those employees from such danger (29 U.S.C. 655(c)(1)). Consistent with its legal duties, OSHA is issuing this ETS to address the grave danger posed by occupational exposure to SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. 3 OSHA has determined that occupational exposure to SARS-CoV-2, including the Delta variant (B.1.617.2 and AY lineages), presents a grave danger to unvaccinated workers in the U.S., with several exceptions explained below. 4 This finding of grave danger is based on the science of how the virus spreads, the transmissibility of the disease in workplaces, and the serious adverse health effects, including death, that can be suffered by those who are diagnosed with COVID-19. The protections of this ETS—which will apply, with some limitations, to a broad range of workplace settings where exposure to SARS-CoV-2 may occur—are designed to protect employees from infection with SARS-CoV-2 and from the dire, sometimes fatal, consequences of such infection.
3 OSHA is defining the grave danger as workplace exposure to SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes the development of COVID-19. COVID-19 is the disease that can occur in people exposed to SARS-CoV-2, and that leads to the health effects described in this section. This distinction applies despite OSHA's use of the terms SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 interchangeably in some parts of this preamble.
4 OSHA refers to the grave danger from occupational exposure to SARS-CoV-2 throughout this document. Those references are intended to encompass exposure to SARS-CoV-2 and all variants of SARS-CoV-2, including the Delta variant.
The fact that COVID-19 is not a uniquely work-related hazard does not change the determination that it is a grave danger to which employees are exposed, nor does it excuse employers from their duty to protect employees from the occupational transmission of SARS-CoV-2. The OSH Act is intended to “assure so far as possible every working man and woman in the Nation safe and healthful working conditions” (29 U.S.C. 651(b)), and there is nothing in the Act to suggest that its protections do not extend to hazards which might occur outside of the workplace as well as within. Indeed, COVID-19 is not the first hazard that OSHA has regulated that occurs both inside and outside the workplace. For example, the hazard of noise is not unique to the workplace, but the Fourth Circuit has upheld OSHA's Occupational Noise Exposure standard (29 CFR 1910.95) ( Forging Industry Ass'n v. Sec' of Labor , 773 F.2d 1437, 1444 (4th Cir. 1985)). Diseases caused by bloodborne pathogens, including HIV/AIDS and hepatitis B, are also not unique to the workplace, but the Seventh Circuit upheld the majority of OSHA's Bloodborne Pathogens standard (29 CFR 1910.1030) ( Am. Dental Ass'n v. Martin , 984 F.2d 823 (7th Cir. 1993)). OSHA's Sanitation standard, 29 CFR 1910.141, which requires measures such as cleaning, waste disposal, potable water, toilets, and washing facilities, addresses hazards that exist everywhere—both within and outside of workplaces. Moreover, employees have more freedom to control their environment outside of work, and to make decisions about their behavior and their contact with others to better minimize their risk of exposure. However, during the workday, while under the control of their employer, workers may have little ability to limit contact with coworkers, clients, members of the public, patients, and others, any one of whom could represent a source of exposure to SARS-CoV-2. OSHA has a mandate to protect employees from hazards they are exposed to at work, even if they may be exposed to similar hazards outside of work.
As described above in Pertinent Legal Authority (Section II. of this preamble), “grave danger” indicates a risk that is more than “significant” ( Int'l Union, United Auto., Aerospace, & Agr. Implement Workers of Am., UAW v. Donovan , 590 F. Supp. 747, 755-56 (D.D.C. 1984); Indus. Union Dep't, AFL-CIO v. Am. Petroleum Inst. , 448 U.S. 607, 640 n.45, 655 (1980) (stating that a rate of 1 worker in 1,000 workers suffering a given health effect constitutes a “significant” risk)). “Grave danger,” according to one court, refers to “the danger of incurable, permanent, or fatal consequences to workers, as opposed to easily curable and fleeting effects on their health” ( Fla. Peach Growers Ass'n, Inc. v. U.S. Dep't of Labor , 489 F.2d 120, 132 (5th Cir. 1974)). Fleeting effects were described as nausea, excessive salivation, perspiration, or blurred vision and were considered so minor that they often went unreported; these effects are in stark contrast with the adverse health effects of COVID-19 infections, which are formally referenced as ranging from “mild” to “critical,” 5 but which can involve significant illness, hospital stays, ICU care, death, and long-term health complications for survivors. Beyond this, however, “the determination of what constitutes a risk worthy of Agency action is a policy consideration that belongs, in the first instance, to the Agency” ( Asbestos Info. Ass'n/N. Am. v. OSHA , 727 F.2d 415, 425 (5th Cir. 1984)).
5 See the definitions for the different levels of severity of COVID-19 illness in the National Institutes of Health's COVID-19 treatment guidelines (NIH, October 12, 2021).
In the context of ordinary 6(b) rulemaking, the Supreme Court has said that the OSH Act is not a “mathematical straitjacket,” nor does it require the agency to support its findings “with anything approaching scientific certainty,” particularly when operating on the “frontiers of scientific knowledge” ( Indus. Union Dep't, AFL-CIO v. Am. Petroleum Inst. , 448 U.S. 607, 655-56 (1980)). Courts reviewing OSHA's determination of grave danger do so with “great deference” ( Pub. Citizen Health Research Grp. v. Auchter , 702 F.2d 1150, 1156 (D.C. Cir. 1983)). In one case, the Fifth Circuit, in reviewing an OSHA ETS for asbestos, declined to question the agency's finding that 80 worker lives at risk nationwide over six months constituted a grave danger ( Asbestos Info. Ass'n/N. Am. , 727 F.2d at 424). OSHA estimates that this ETS would save over 6,500 worker lives and prevent over 250,000 hospitalizations over the course of the next six months (OSHA, October 2021c). Here, the mortality and morbidity risk to employees from COVID-19 is so dire that the grave danger from exposures to SARS-CoV-2 is clear.
SARS-CoV-2 is both a physically harmful agent and a new hazard (see 29 U.S.C. 655(c)(1)(A)). The majority of OSHA's previous ETSs addressed toxic substances that had been familiar to the agency for many years prior to issuance of the ETS. OSHA's Healthcare ETS, issued in response to COVID-19 earlier this year, is one notable exception. In most cases, OSHA's ETSs were issued in response to new information about substances that had been used in workplaces for decades ( e.g. , Vinyl Chloride (39 FR 12342 (April 5, 1974)); Benzene (42 FR 22516 (May 3, 1977)); 1,2-Dibromo-3-chloropropane (42 FR 45536 (Sept. 9, 1977))). In some cases, the hazards of the toxic substance were already so well established that OSHA promulgated an ETS simply to update an existing standard ( e.g. , Vinyl cyanide (43 FR 2586 (Jan. 17, 1978))). The COVID-19 Healthcare ETS, which was issued in June 2021, was the sole instance in which OSHA issued an ETS to address a grave danger from a substance that had only recently come into existence. Although that action by the agency was challenged, the case has not gone to briefing (see United Food & Commercial Workers Int'l Union, AFL-CIO, CLC and AFL-CIO v. OSHA, Dep't of Labor , D.C. Circuit No. 21-1143). Thus, no court has had occasion to examine OSHA's authority under section (6)(c) of the OSH Act (29 U.S.C. 655(c)) to address a grave danger from a “new hazard.” Yet by any measure, SARS-CoV-2 is a new hazard. Unlike any of the hazards addressed in previous ETSs, there were no documented cases of SARS-CoV-2 infections in the United States until January 2020. Since then, more than 725,000 people have died in the U.S. alone (CDC, October 18, 2021—Cumulative US Deaths). The pandemic continues to affect workers and workplaces, with workplace exposures leading to further exposures among workers' families and communities. Clearly, SARS-CoV-2 is both a physically harmful agent and a new hazard that presents a grave danger to workers in the U.S.
Published on June 21, 2021, OSHA's Healthcare ETS (86 FR 32376) was written in response to the grave danger posed to healthcare workers in the United States who faced a heightened risk of infection from COVID-19. In the healthcare ETS, OSHA described its finding of grave danger for healthcare and healthcare support service workers (see 86 FR 32381-32412). OSHA now finds that all unvaccinated workers, with some exceptions, face a grave danger from the SARS-CoV-2 virus. 6
6 When OSHA refers to “unvaccinated” individuals in its grave danger finding, it means all individuals who are not fully vaccinated against COVID-19, i.e. , those who are completely unvaccinated and those who are partially vaccinated.
II. Nature of the Disease
The health effects of symptomatic COVID-19 illness can range from mild disease consisting of fever or chills, cough, and shortness of breath to severe disease. Severe cases can involve respiratory failure, blood clots, long-term cardiovascular and neurological effects, and organ damage, which can lead to hospitalization, ICU admission, and death (see 86 FR 32383-32388; NINDS, September 2, 2021). Even in the short time since the Healthcare ETS's publication in June 2021, the risk posed by COVID-19 has changed meaningfully. Since OSHA considered the impact of COVID-19 when promulgating the Healthcare ETS, over 135,000 additional Americans have died from COVID-19, and over 933,000 have been hospitalized, (CDC, October 18, 2021—Cumulative US Deaths; CDC, May 28, 2021; CDC, October 18, 2021—Weekly Review). In August 2021, COVID-19 was the third leading cause of death in the United States, trailing only heart disease and cancer (Ortaliza et al., August 27, 2021). By September 20, 2021, COVID-19 had killed as many Americans as the 1918-1919 flu pandemic (Johnson, September 20, 2021).
While the Healthcare ETS addresses the risk of illness and death from COVID-19 as the SARS-CoV-2 virus continues to change over time, it does not specifically address the increases in infectiousness and transmission, and the potentially more severe health effects, related to the Delta variant. The rapid rise to predominance of the Delta variant in the U.S. occurred shortly after the ETS was published. At this time, the widespread prevalence of the Delta variant and its increased transmissibility have resulted in increased risk of exposure and disease relative to the previously-dominant strains of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Adding to the information covered in the Healthcare ETS, the following sections provide a brief review of SARS-CoV-2 and describe the characteristics of the Delta variant that are different from previous versions of SARS-CoV-2 and have changed the risks posed by COVID-19. The agency specifically references the material presented in the Healthcare ETS, which is still relevant to this analysis, to support OSHA's finding of grave danger. Taken together, the information available to OSHA demonstrates that SARS-CoV-2 poses a grave danger to unvaccinated workers across all industry sectors.
a. Variants of SARS-CoV-2
Viral mutations have been a serious concern of scientists, public health experts, and policymakers from the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic. Viral mutations can affect how a virus interacts with a cell—altering the virus's transmissibility, infection severity, and sensitivity to vaccines. The U.S. government's SARS-CoV-2 Interagency Group has a variant classification scheme that defines four classes of SARS-CoV-2 variants: Variants Being Monitored (VBM), Variants of Interest (VOI), Variants of Concern (VOC), and Variants of High Consequence (VOHC). These variant designations are based on their “proportions at the national and regional levels and the potential or known impact of the constellation of mutations on the effectiveness of medical countermeasures, severity of disease, and ability to spread from person to person” (CDC, October 4, 2021), with VOIs considered less serious than VOCs and VOCs considered less serious than VOHCs. As of early October 2021, the CDC was monitoring 10 VBMs—Alpha (B.1.1.7, Q.1-Q.8), Beta (B.1.351, B.1.351.2, B.1.351.3), Gamma (P.1, P.1.1, P.1.2), Epsilon (B.1.427 and B.1.429), Eta (B.1.525), Iota (B.1.526), Kappa (B.1.617.1), B.1.617.3, Mu (B.1.621, B.1.621.1), and Zeta (P.2)—and one VOC—Delta (B.1.617.2 and AY.1 sublineages)—in the U.S. (CDC, October 4, 2021). CDC defines a VOC as “[a] variant for which there is evidence of an increase in transmissibility, more severe disease ( e.g. , increased hospitalizations or deaths), significant reduction in neutralization by antibodies generated during previous infection or vaccination, reduced effectiveness of treatments or vaccines, or diagnostic detection failures” (CDC, October 4, 2021).
While the proportions of SARS-CoV-2 variants in the United States have shifted over time (CDC, May 24, 2021c; CDC, October 18, 2021—Variant Proportions, July through October 2021), the primary variant that drove COVID-19 transmission in the late Winter and Spring of 2021 was the Alpha variant. The CDC noted that Alpha is associated with an increase in transmission, as well as potentially increased incidences of hospitalization and death, compared to the predominant variants before its emergence (CDC, October 4, 2021; Pascall et al., August 24, 2021; Julin et al., September 22, 2021). As Alpha transmission subsided in the United States during the late Spring and early Summer of 2021, Delta emerged and quickly became the predominant variant in the U.S. by July 3, 2021 (CDC, October 18, 2021—Variant Proportions, July through October 2021). Delta now accounts for more than 99% of circulating virus nationwide (CDC, October 18, 2021—Variant Proportions, July through October 2021).
FDA authorized and approved COVID-19 vaccines currently work well against all of these variants; however, there are differences in various variants' ability to spread and the likelihood of infection to cause severe illness. Data on the Beta and Gamma variants do not indicate that infections from these variants caused more severe illness or death than other VOCs. Data on the Alpha variant does indicate its ability to cause more severe illness and death in infected individuals. And some data on the Delta variant suggests that the Delta variant may cause more severe illness than previous variants, including Alpha, in unvaccinated individuals (CDC, October 4, 2021).
The emergence of the Delta variant, along with other VOCs, has resulted in a more deadly pandemic (Fisman and Tuite, July 12, 2021). While the Delta variant is the most transmissible SARS-CoV-2 variant to date, the possibility remains for the rise of future VOCs, and even more dangerous VOHCs, as the virus continues to spread and mutate. Inadequate vaccination rates and the abundance of transmission create an environment that can foster the development of new variants that could be similarly, or even more, disruptive (Liu and Rocklov, August, 4, 2021). In this context, it is critical that OSHA address the grave danger from COVID-19 that unvaccinated workers are currently facing by requiring vaccination and the other measures included in this rule, in order to significantly slow the transmission of COVID-19 in workers and workplaces and mitigate the rise of future variants.
b. Transmission
SARS-CoV-2 is a highly transmissible virus, regardless of variant. Since the first case was detected in the U.S., there have been close to 45 million reported cases of COVID-19, affecting every state and territory, with thousands more infected each day (CDC, October 18, 2021—Cumulative US Cases), and some indication that these numbers continue to underestimate the full burden of disease (CDC, July 27, 2021). According to the CDC, the primary way the SARS-CoV-2 virus spreads from an infected person to others is through the respiratory droplets that are produced when an infected person coughs, sneezes, sings, talks, or breathes (CDC, May 7, 2021). Infection could then occur when another person breathes in the virus. Most commonly this occurs when people are in close contact with one another in indoor spaces (within approximately six feet for at least fifteen minutes) (CDC, August 13, 2021). Additionally, airborne transmission may occur in indoor spaces without adequate ventilation where small respiratory particles are able to remain suspended in the air and accumulate (CDC, May 7, 2021; Fennelly, July 24, 2020). While scientists' understanding of the Delta variant's virology is evolving and remains at the frontier of science, current data shows that the routes of transmission remain the same for all currently-identified SARS-CoV-2 variants. In addition, all variants can be transmitted by people who are pre-symptomatic ( i.e. , people who are infected but do not yet feel sick) or asymptomatic ( i.e. , people who are infected but never feel any symptoms of COVID-19), as well as those who are symptomatic. Pre-symptomatic and asymptomatic transmission continue to pose serious challenges to containing the spread of COVID-19. For more extensive information on transmission routes, as well as pre-symptomatic and asymptomatic transmission, see the preamble to the Healthcare ETS (86 FR 32392-32396), which is hereby included in the record of this ETS. 7
7 This adoption includes the citations in the referenced section of the Healthcare ETS, which are also included in the docket for this ETS.
The Delta variant is transmitted from infectious individuals via the same routes as previous variants, but is much more transmissible. Specifically, Delta differs from previous dominant variants of SARS-CoV-2 in terms of the amplification of viral particles expelled from infected individuals. Testing of Delta-infected individuals indicates that their viral loads are—on average—approximately 1,000x greater than those of the SARS-CoV-2 variants from the first COVID-19 wave in early 2020. This finding suggests much faster replication of viral particles during early infection with the Delta variant, resulting in greater infectiousness (contagiousness) when compared to earlier versions of SARS-CoV-2 (Li et al., July 12, 2021).
The transmissibility of viruses is measured in part by the average number of subsequently-infected people (or secondary cases) that are expected to occur from each existing case (often referred to as R 0 ). Several comparisons of the transmissibility of the initial SARS-CoV-2 variants to the Delta variant have shown that Delta is approximately twice as transmissible (contagious) as previous versions of SARS-CoV-2 (CDC, August 26, 2021; Riou and Althaus, January 30, 2020; Li et al., July 12, 2021; Liu and Rocklov, August, 4, 2021), likely the result of higher initial viral loads during the pre-symptomatic phase (Li et al., July 12, 2021). In addition, as described further below, data on Delta shows that both unvaccinated and vaccinated individuals are more likely to transmit Delta than previous variants (Liu and Rocklov, August, 4, 2021; Eyre et al., September 29, 2021), making it especially dangerous to those who remain unvaccinated.
c. Health Effects
COVID-19 infections can lead to death. As reported in the Healthcare ETS, by May 24, 2021, there had been 587,432 deaths and 32,947,548 million infections in the U.S. alone (CDC, May 24, 2021a; CDC, May 24, 2021b). At that point in the pandemic, 1.8 out of every 1,000 people in the U.S. had died from COVID-19 (CDC, May 24, 2021a). Since then, reported cases have increased to 44,857,861 and the number of deaths has increased to 723,205 (CDC, October 18, 2021- Cumulative US Cases; Cumulative US Deaths). By September 2021, an astounding 1 in 500 Americans had died from COVID-19 (Keating, September 15, 2021). Updated mortality data 8 currently indicate that people of working age (18-64 years old) now have a 1 in 202 chance of dying when they contract the disease, with the risk much higher (1 in 72) for those aged 50-64 (CDC, October 18, 2021—Demographic Trends, Cases by Age Group; CDC, October 18, 2021—Demographic Trends, Deaths by Age Group). For a more in-depth description of the health effects resulting from SARS-CoV-2 infection, see the preamble to the Healthcare ETS (86 FR 32383-32392), which is hereby included in the record of this ETS. 9
8 Risk of death is based on averages from reported CDC data. Risks of hospitalization and death are much higher in unvaccinated individuals, as discussed further in Grave Danger , Section III.A.IV. Vaccines Effectively Reduce Severe Health Outcomes from and Transmission of SARS-CoV-2.
9 This adoption includes the citations in the referenced section of the Healthcare ETS, which are also included in the docket for this ETS.
Apart from fatal cases, COVID-19 can cause serious illness, including long-lasting effects on health. Many patients who become ill with COVID-19 require hospitalization. Indeed, updated CDC hospitalization and mortality data indicate that working age Americans (18-64 years old) now have a 1 in 14 chance of hospitalization when infected with COVID-19 (CDC, October 18, 2021—Demographic Trends, Cases by Age; Total Hospitalizations, by Age). Those who are hospitalized frequently need supplemental oxygen and treatment for the disease's most common complications, which include pneumonia, respiratory failure, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), acute kidney injury, sepsis, myocardial injury, arrhythmias, and blood clots. One study, which included 35,502 inpatients nationwide, determined that the median length of hospital stay was 6 days, unless the cases required ICU treatment. For those cases, ICU stays were on median 5 days in addition to the time spent hospitalized outside of the ICU (Rosenthal et al., December 10, 2020). Another study that assessed hospital length of stay for COVID-19 patients in England estimated that a non-ICU hospital stay averaged between 8 and 9 days, but those estimates ranged from approximately 12 to 18 days when patients were admitted to the ICU (Vekaria et al., July 22, 2021). Moreover, given that SARS-CoV-2 is still a novel virus, the severity of long-term health effects—such as “post-COVID conditions”—are not yet fully understood.
Many members of the workforce are at increased risk of death and severe disease from COVID-19 because of their age or pre-existing health conditions. The comorbidities that further exacerbate COVID-19 infections are common among adults of working age in the U.S. For instance, 46.1% of individuals with cancer are in the 20-64 year old age range (NCI, April 29, 2015), and over 40% of working age adults are obese (Hales et al., February 2020). Disease severity is also likely exacerbated by long-standing healthcare inequities experienced by members of many racial and economic demographics (CDC, April 19, 2021).
Recent data suggests that Delta variant infections may result in even more severe illness and a higher frequency of death than previous COVID-19 variants due to Delta's increased transmissibility, virulence, and immune escape (Fisman and Tuite, July 12, 2021). Symptomatic Delta variant infections do occur in fully vaccinated people (Mlcochova et al., June 22, 2021; Musser et al., July 22, 2021); however, as reported by the CDC (CDC, August 26, 2021), the vast majority of the continuing instances of severe and fatal COVID-19 infections are occurring in unvaccinated persons (discussed further in Grave Danger , Section III.A.IV. Vaccines Effectively Reduce Severe Outcomes from and Transmission of SARS-CoV-2). An assessment of Delta-related hospital admissions in Scotland found that hospitalizations were approximately doubled in patients with the Delta variant when compared to the Alpha variant (Sheikh et al., June 4, 2021). A similar study conducted using a retrospective cohort in Ontario, Canada compared the virulence of novel SARS-CoV-2 variants and found that the incidences of hospitalization, ICU admission, and death were more pronounced with the Delta variant than any other SARS-CoV-2 variant (Fisman and Tuite, July 12, 2021). A large national cohort study that included all Alpha and Delta SARS-CoV-2 patients in England between March 29 and May 23, 2021 found a “higher hospital admission or emergency care attendance risk for patients with COVID-19 infected with the Delta variant compared with the Alpha variant,” suggesting that Delta outbreaks—especially amongst unvaccinated populations—may lead to more severe health consequences and an equivalent or greater burden on healthcare services than the Alpha variant (Twohig et al., August 27, 2021). However, one more recent study examining data from several U.S. states demonstrated a significant increase in hospitalization from the pre-Delta to the Delta period, which may be related to increased transmissibility of Delta rather than more severe health outcomes (Taylor et al., October 22, 2021).
III. Impact on the Workplace
SARS-CoV-2 is readily transmissible in workplaces because they are areas where multiple people come into contact with one another, often for extended periods of time. When employees report to their workplace, they may regularly come into contact with co-workers, the public, delivery people, patients, and any other people who enter the workplace. Workplace factors that exacerbate the risk of transmission of SARS-CoV-2 include working in indoor settings, working in poorly-ventilated areas, and spending hours in close proximity with others. Full-time employees typically spend 8 hours or more at work each shift, more time than they spend anywhere else but where they live. Employees work in proximity to others in workplaces that were not originally designed to keep people six feet away from other people and that may make it difficult for employees to perform work tasks while maintaining a six-foot distance from others. Even in the cases where workers can do most of their work from, for example, a private office within a workplace, they share common areas like hallways, restrooms, lunch rooms and meeting rooms. Furthermore, many work areas are poorly ventilated (Allen and Ibrahim, May 25, 2021; Lewis, March 30, 2021). An additional factor that exacerbates the risk of transmission of SARS-CoV-2 is interacting with or caring for people with suspected or confirmed COVID-19; this was a primary driver of OSHA's determination of grave danger for healthcare workers in the Healthcare ETS (see 86 FR 32381-32383). In recent weeks, the majority of states in the U.S. have experienced what CDC defines as “high or substantial community transmission,” indicating that there is a clear risk of the virus being introduced into and circulating in workplaces (CDC, October 18, 2021—Community Transmission Rates).
Although COVID-19 is not exclusively an occupational disease, it is evident from research accrued since the beginning of the pandemic that SARS-CoV-2 transmission can and does occur in workplaces, affecting employees and their lives, health, and livelihoods. This continues to be true for the Delta variant, with its increased transmissibility and potentially more severe health effects. This section describes some of the clusters, outbreaks, and other occurrences of workplace COVID-19 cases that government agencies, researchers, and journalists have described, and the widespread effects of SARS-CoV-2 in industry sectors across the national economy. While the focus is on more recent data reflecting the impact of the Delta variant, evidence of workplace transmission that occurred prior to the emergence of the Delta variant is also presented.
The workplace-based clusters described below provide evidence that workplaces in a wide range of industries have been affected by COVID-19, that many employees face exposure to infected people in their workspaces, and that SARS-CoV-2 transmission is occurring in the workplace, including during the recent period where the Delta variant has predominated. Although the presence of a cluster on its own does not necessarily establish that the cluster is work-related ( i.e. , a result of transmission at the worksite), many state investigation reports and published studies provide evidence that transmission is work related by documenting that infections at a workplace occurred within 14-days (the incubation period for the virus) of each other and ruling out the possibility that transmission occurred outside the workplace. In addition, the information below demonstrates that exposures to SARS-CoV-2 happen regularly in a wide variety of different types of workplaces.
The basis for OSHA's grave danger finding is that employees can be exposed to the virus in almost any work setting; that exposure to SARS-CoV-2 can lead to infection (CDC, September 21, 2021); and that infection in turn can cause death or serious impairment of health, especially in those who are unvaccinated (see Section III.A.IV. Vaccines Effectively Reduce Severe Health Outcomes from and Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 ). The information described in this section supports OSHA's finding that employees who work in spaces shared by others are at risk of exposure to SARS-CoV-2. The degree of risk from droplet-based transmission may vary based on the duration of close proximity to a person infected with SARS-CoV-2, including the Delta variant, but the simple and brief act of sneezing, coughing, talking, or even breathing can significantly increase the risk of transmission if controls are not in place. SARS-CoV-2, including the Delta variant, might also be spread through airborne particles under certain conditions, particularly in enclosed settings with inadequate ventilation, which are common characteristics of some workplaces.
The peer-reviewed scientific journal articles, government reports, and news articles described below establish the widespread prevalence of COVID-19 among employees, beginning with a description of the recent impact from the Delta variant. OSHA's findings are based primarily on the evidence from peer-reviewed scientific journal articles and government reports. However, peer review for scientific journal articles and the assembly of information for government reports and other official sources of information take time, and therefore those sources do not always reflect the most up-to-date information (Chan et al., December 14, 2010). In addition, while state and local health departments can report workplace outbreaks to CDC, the agency does not provide summary statistics by workplace so that those outbreaks can be tracked on a national level. In the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, given the recent impacts due to the Delta variant and the emergence of new information on a daily basis, it is critical for OSHA to rely on the most up-to-date information available. Therefore, OSHA has occasionally supplemented peer-reviewed data and government reports with additional information on occupational outbreaks contained in other sources of media ( e.g. , newspapers, digital media, and information submitted to or obtained by private organizations). 10 The reported information from other sources can provide further evidence of the impact of an emerging and changing disease, especially for industries that are not well represented in the peer-reviewed scientific literature. Together, these sources of information represent the best available evidence of the impact on employees of the pandemic thus far.
10 OSHA did not make findings based solely on non-peer-reviewed sources such as news articles, but the agency found that those sources can sometimes provide useful information when considered with more robust sources.
The information described herein illustrates a significant number of infections among employees in a variety of industries, with virtually every state continuing to experience what CDC defines as high or substantial community transmission related to the recent surge of the Delta variant. The industries and types of workplaces described are not the only ones in which a grave danger exists. The science of transmission does not vary by industry or by type of workplace. OSHA therefore expects transmission to occur in diverse workplaces all across the country (see Dry Color Mfrs. Ass'n, Inc. v. Dep't of Labor , 486 F.2d 98, 102 n.3 (3d Cir. 1973) (holding that when OSHA determines a substance poses a grave danger to workers, OSHA can assume an exposure to a grave danger exists wherever that substance is present in a workplace)). In addition, the severity of COVID-19 does not depend on where an employee is infected; an employee exposed to SARS-CoV-2 might die whether exposed while working at a meat packing facility, a retail establishment, or an office (see Grave Danger , Section III.A.V.b. Employees Who Work Exclusively Outside, below, for a discussion of the risk of exposure in outdoor workplaces).
a. General Impact on Workers
Data on SARS-CoV-2 infections, illnesses, and deaths among employees in general industry, agriculture, construction, and maritime support OSHA's finding that COVID-19 poses a grave danger to employees in these sectors across the U.S. economy. This section summarizes studies and reports of COVID-19 illness and fatalities in a wide range of workplaces across those industry sectors. Not all workplace settings are discussed; nor is the data available to do so. However, the characteristics of the various affected workplaces—such as indoor work settings; contact with coworkers, clients, or members of the public; and sharing space with others for prolonged periods of time—indicate that exposures to SARS-CoV-2 are occurring in a wide variety of work settings across all industries. Therefore, most employees who work in the presence of other people ( e.g. , co-workers, customers, visitors) need to be protected.
While there is no comprehensive source of nationwide workplace infection data, reports from states and communities on outbreaks related to workplaces provide key, up-to-date data that illustrate the likelihood of employee exposure to SARS-CoV-2 at workplaces throughout the U.S. OSHA identified a number of recent reports from various regions of the country that together demonstrate the impact that SARS-CoV-2 can have on a variety of workplaces, including in service industries ( e.g. , restaurants, grocery and other retail stores, fitness centers, hospitality, casinos, salons), corrections, warehousing, childcare, schools, offices, homeless shelters, transportation, mail/shipping/delivery services, cleaning services, emergency services/response, waste management, construction, agriculture, food packaging/processing, and healthcare. Deaths are reported in many studies performed prior to the emergence of the Delta variant but, because the Delta outbreak is so recent and deaths can occur weeks after infection, the number of deaths from recent infections might be underestimated. Some of the reports include cumulative data representing various phases of the pandemic, beginning prior to the availability of vaccines and continuing through the recent surge of the Delta variant. In addition, some studies report investigations of recent outbreaks, which provide insight on the impact of the Delta variant as well as impacts associated with the current vaccination status of workers.
The Washington State Department of Health (WSDH) reports outbreaks occurring in non-healthcare workplaces (WSDH, September 8, 2021). In non-healthcare workplaces, outbreaks are defined as two or more laboratory confirmed cases of COVID-19, with at least two cases reporting symptom onset within 14 days of each other, and plausible epidemiological evidence of transmission in a shared location other than a household. As of September 4, 2021, WSDH reported 5,247 outbreaks in approximately 40 different types of non-healthcare work settings. During the week of August 29 through September 4, 2021, WSDH identified 137 separate workplace outbreaks. The types of non-medical workplace settings that represented more than 5% of the total outbreaks during that week included food service/restaurants, childcare, schools, retail, grocery, and shelter/homeless services. Other types of non-healthcare settings where outbreaks occurred recently included non-food and food manufacturing, construction, professional services/office based, agriculture/produce packing, transportation/shipping delivery, government agencies/facilities, leisure hospitality/recreation, corrections, utilities, warehousing, facility/domestic cleaning services, youth sports/activities, camps, and public safety. Over the course of the pandemic, outbreaks have also been observed at bars/nightclubs, hotels, and fishing/commercial seafood vessels.
The Oregon Health Authority (OHA) publishes a weekly report detailing outbreaks directly related to work settings. OHA epidemiologists consider cases to be part of a workplace outbreak when clusters form with respect to space and time, within a plausible incubation period for the virus, and their investigation does not uncover an alternative source for the outbreak. For privacy reasons, OHA only reports outbreaks with 5 or more cases in workplaces with 30 or more people. OHA reported a total of 26,013 cases and 135 deaths related to workplace outbreaks as of September 1, 2021. As of September 1, 2021, OHA was investigating more than 124 active workplace outbreaks (OHA, September 1, 2021). Those outbreaks occurred in a wide variety of industries including correctional facilities, emergency services, waste management, schools and child care, retail and grocery stores, restaurants, warehousing, agriculture, food processing/packaging, construction, healthcare, mail and delivery services, office locations, utilities, transportation, and others.
Tennessee Department of Health was investigating 557 active COVID-19 clusters as of September 8, 2021 (TDH, September 8, 2021). Clusters are defined as two or more laboratory confirmed COVID-19 cases linked to the same location or event that is not a household exposure. The clusters occurred in 13 types of settings, 10 of which were workplace settings. Outbreaks at workplaces represented more than half of the total active outbreaks in the state at that time. Settings comprising more than 5% of total clusters included assisted care living facilities, nursing homes, and correctional facilities. Other types of workplaces where outbreaks occurred included bars, construction, farms, homeless shelters, and industrial settings.
The North Carolina Department of Health and Human Services reports cumulative numbers of clusters, cases, and deaths for workers in poultry processing facilities (beginning in April of 2020) and other types of workplaces (beginning in May of 2020) (NCDHHS, August 30, 2021). Clusters are defined as a minimum of 5 cases with illness onset or initial positive results within a 14-day period and plausible epidemiological linkage between the cases. Plausible epidemiological linkage means that multiple cases were in the same general setting during the same time period ( e.g. , same shift, same physical area) and that a more likely source of exposure is not identified ( e.g. , household contact or close contact to a confirmed case in another setting). During that time period of April/May 2020 through August 30, 2021, workplaces 11 were associated with nearly 80% of the 1,969 clusters and 27,097 cases observed and nearly 40% of the 167 deaths related to the clusters. Cumulative numbers of cluster-associated deaths were highest in meat and poultry processing (25 of 5,351 cases), followed by healthcare (10 of 1,036 cases), government services and manufacturing (5 of 1,048 cases and 5 of 1,856 cases, respectively), and restaurants and childcare (3 of 421 cases and 3 of 1,943 cases, respectively). Recently, in July of 2021, the number of cases associated with workplace clusters began increasing in several different types of work settings, including meat processing, manufacturing, retail, restaurants, childcare, schools, and higher education.
11 NCDHHS identifies a “workplace” category in their report ( e.g. , agriculture, construction), but OSHA includes other settings where employees would be present ( e.g. , retail, restaurants, childcare, healthcare).
Colorado Department of Public Health & Environment/Colorado State Emergency Operations Center (CDPHE/CSEOC, September 8, 2021) reported 5,584 resolved workplace-related outbreaks involving 40,156 employee cases and 79 employee deaths since May of 2020. The agency's current investigations, as of September 8, 2021 included 291 active outbreaks (not defined), with 2,865 staff cases (assumed to be cases in employees). The majority of active outbreaks were reported in childcare, schools, healthcare, and corrections. Active outbreaks were also reported in construction, retail, homeless shelters, casinos, restaurants, hotels, offices, law enforcement, manufacturing, delivery services, and warehouses. Other types of work settings that were affected in resolved outbreaks included warehouses, bars, government locations, waste management, utilities, salons, emergency services, meat processing/packaging, and postal services. From June 21, 2021 (the date the healthcare ETS was published) through September 8, 2021, 1,469 staff cases associated with outbreaks were reported, for an average of approximately 19 cases per day.
Similar reporting is available from Louisiana's Department of Health (LDH, August 24, 2021), with 1,347 outbreaks and 9,130 cases reported as of August 24, 2021. LDH defines an outbreak as 2 or more cases among unrelated individuals who visited a site within a 14-day period. More than three quarters of outbreaks through that date were associated with workplaces. Workplace settings in Louisiana that experienced more than 5% of outbreaks included day care facilities, bars, restaurants, retail settings, industrial settings, and office spaces. Other types of workplace settings or industries where outbreaks occurred included casinos, gyms/fitness centers, banks, automotive services, construction, and ships/boats.
In addition to the state data above, some published studies and government reports provide information on recent workplaces outbreaks. For example, 47 people, including 3 of 11 staff members, 23 gymnasts, and 21 household contacts, contracted COVID-19 from an outbreak linked to an Oklahoma gymnastics facility during April 15 through May 3, 2021 (Dougherty et al., July 16, 2021). All 21 of the virus samples sequenced were determined to be the Delta variant. The majority of the infected individuals (85%) were unvaccinated. Infections were reported in 16 adults aged 20 years or older; two adults were hospitalized and one required intensive care.
The state of Hawaii defines clusters as three or more confirmed or probable cases linked to a site or event within 14 days, with no outside exposure of cases to each other (Hawaii State, August 19, 2021). The state reported a COVID-19 cluster in July associated with a concert at a bar that affected 16 people, including employees, band members, and concert attendees; infections also spread to 7 household members. Band members had performed while sick. Four of the initial 16 people and none of the household members who tested positive for COVID-19 were fully vaccinated. The concert cluster was linked to clusters at another workplace and another concert. The report lists additional clusters investigated in the two weeks prior to the report; those clusters were observed in workplace locations such as correctional facilities, bars and nightclubs, restaurants, construction/industrial sites, travel/lodging/tourism, schools, food suppliers, and gyms.
Additional evidence that employees are at risk of exposure to SARS-CoV-2 in the workplace is available from published, peer-reviewed studies that were conducted before the Delta variant emerged. Those studies demonstrate that employees have been at risk of infection, illness, and death throughout the COVID-19 pandemic. Because the Delta variant is more transmissible and likely causes more severe disease than previous variants, there is even greater potential for unvaccinated employees to become seriously ill or die as a result of exposure to the Delta variant.
Contreras et al. (July, 2021) examined workplace outbreaks (excluding healthcare settings, homelessness services, and emergency medical services) in Los Angeles county from March 19 through September 30, 2020. Workplace outbreaks were defined as 5 or more suspected or laboratory confirmed COVID-19 cases (prior to May 29) or 3 or more laboratory confirmed cases (after May 29) occurring within 14 days. Nearly 60% of the 698 identified outbreaks occurred in three sectors—manufacturing (184, 26.4%), retail trade (137, 19.6%), and transportation and warehousing (73, 10.5%). Also notable were the 71 outbreaks in the accommodation and food services industry, which represented 10.2% of the outbreaks. The study authors concluded that outbreaks were larger and lasted longer at facilities with more onsite staff.
Outbreaks in Wisconsin from March 4 through November 16, 2020 were also examined (Pray et al., January 29, 2021). Non-household outbreaks were defined as two or more confirmed COVID-19 cases that occurred within 14 days in persons who attended the same facility or event and did not share a household. During the period from March 4 through November 16, 2020, the largest percentages of cases were associated with outbreaks in long-term care facilities (26.8% of cases), correctional facilities (14.9% of cases), and colleges or universities (15% of cases). Also notable were the substantial number of cases associated with outbreaks in food production or manufacturing facilities (including meat processing and warehousing; 14.5% of cases) and schools and childcare facilities (10.6% of cases).
Bui et al. (August 17, 2020) analyzed data from the Utah Department of Health's COVID-19 case surveillance system, which included data on workplace outbreaks. Outbreaks were defined as two or more laboratory confirmed cases occurring within a 14 day period among coworkers in a common workplace ( e.g. , same facility). During the time period between March 6 and June 5, 2020, 277 COVID-19 outbreaks were reported, of which 210 (76%) occurred in workplaces. The 210 workplace outbreaks occurred in 15 of 20 industry sectors, and the industry sectors of manufacturing (43 outbreaks, 20%), construction (32 outbreaks, 15%), and wholesale trade (29 outbreaks, 14%) together represented nearly half of workplace outbreaks. Other sectors that represented more than 10% of total outbreaks were retail trade (28 outbreaks, 13%) and accommodation and food services (25 outbreaks, 12%). Incidence rates of COVID-19 over the period of March 6 through June 5, 2020 were 339/100,000 workers in manufacturing, 122/100,000 workers in construction, 377/100,000 workers in wholesale trade, 68/100,000 workers for retail trade, and 78/100,000 workers for accommodation and food services. For COVID-19 cases associated with workplace outbreaks in which hospitalization and severity status were known (1,382 and 1,155, respectively), the number in all sectors who were admitted to the hospital was 85 (6%) and the number with severe outcomes (intensive care unit admission, mechanical ventilation, or death) was 40 (3%).
The impact of SARS-CoV-2 exposures on employee infection, illness, and death has also been demonstrated in studies focusing on specific types of industries, such as those where employees have frequent contact with each other and the public ( e.g. , grocery stores, bars, fitness facilities, schools, and law enforcement/corrections). For example, a study by Lan et al. (September 26, 2020) demonstrates the risk of infection in service industries. The cross-sectional study examined the risks of SARS-CoV-2 exposure and infection for employees in a Boston, Massachusetts-area retail grocery store market. The study tested 104 grocery store employees, of whom 20% (21 employees) were positive for COVID-19; 76% of confirmed cases did not have symptoms. After adjusting for gender, smoking, age, and the prevalence of COVID-19 in the employees' residential communities, employees who had direct customer exposure ( e.g. , cashiers, sales associates, cart attendants) were 5.1 times more likely to have a positive test for COVID-19 than employees without direct face-to-face customer exposure ( e.g. , stockers, backroom, receiving and maintenance). The infection rate of 20% among all employees was significantly higher than the rate in the surrounding community.
In February of 2021, an event at an Illinois bar that accommodates approximately 100 people resulted in a COVID-19 outbreak that affected 46 people, including 3 (10%) staff members, 26 (90%) patrons, and 17 secondary cases (Sami et al., April 9, 2021). People at the event included an asymptomatic person diagnosed with COVID-19 on the previous day and 4 symptomatic people who were later diagnosed with COVID-19. The outbreak resulted in a school closure and the hospitalization of a resident at a long-term care facility.
In Minnesota, 47 COVID-19 outbreaks were detected at fitness facilities from August through November of 2020 (Suhs et al., July 23, 2021). One outbreak at a fitness facility during October through November of 2020 resulted in 23 COVID-19 cases including 5 (22%) employees and 18 (78%) members. A genetic analysis of specimens from 3 employees and 10 members identified 2 distinct genetic subclusters, indicating two distinct chains of transmission among members and employees.
School-related outbreaks were examined from December 1, 2020 through January 22, 2021 in eight public elementary schools of a Georgia school district (Gold et al., February 26, 2021). A COVID-19 case was determined to be school-related if (1) symptom onset or a positive test was consistent with the incubation period of the virus following contact with an index case or a school-associated case, (2) close contact occurred with the index case or school-associated case while that person was infected, and (3) no known contact occurred with an infected community or household contact in the two weeks prior to a positive test for COVID-19. The investigators identified nine clusters of three or more epidemiologically linked COVID-19 cases that involved 13 educators and 32 students in six of the eight elementary schools. Approximately half of the school-associated cases involved two clusters that began with probable transmission between educators, followed by educator to student transmission. Eighteen of 69 household members tested received positive results.
A number of studies demonstrate the impact of COVID-19 in law enforcement and related fields such as corrections. For example, a study examining COVID-19 antibodies in employees from public service agencies in the New York City area from May through July of 2020, found that 22.5% of participants had COVID-19 antibodies (Sami et al., March, 2021). The percentage of correctional officers found to have COVID-19 antibodies (39.2%) was the highest observed among all the occupations. The percentages of police dispatchers, traffic officers, security guards, and dispatchers found to have COVID-19 antibodies (29.8 to 37.3%) were among the highest levels observed in all the occupations. The study authors noted that those jobs involve frequent or close contact with the public or are done in places where employees work in close proximity to their coworkers.
Wallace et al. (May 15, 2020) evaluated data on COVID-19 cases and deaths among correctional facility employees and inmates from January 21 to April 21, 2020. Data were reported to CDC by 37 (69%) of 54 state and territorial health department jurisdictions. Of these 37 jurisdictions, 32 (86%) reported at least one COVID-19 case from a correctional facility. Of the 420 facilities with a case, 221 (53%) reported cases only among staff members. In total, 4,893 COVID-19 cases among incarcerated or detained persons and 2,778 cases among staff members were reported (total tested not provided). Among staff member cases, 79 hospitalizations (3%) and 15 deaths (1%) were reported. The study authors noted that “correctional and detention facilities face challenges in controlling the spread of infectious diseases because of crowded, shared environments and potential introductions by staff members and new intakes.”
Ward et al. (June 2021) analyzed COVID-19 prevalence among prisoners and staff in 45 states from March 31, 2020 through November 4, 2020. During that time period, COVID-19 cases in staff were 3 to 5 times higher compared to the U.S. population. Average daily increases in cases were 42 per 100,000 prison employees, 61 per 100,000 prisoners, and 13 per 100,000 U.S. residents. On November 4, 2020, COVID-19 prevalence for prison staff was 9,316 cases per 100,000 employees, which was 3.2 times greater than prevalence in the U.S. population (2,900 cases per 100,000).
Kirbiyik et al. (November 6, 2020) analyzed movement through a network-informed approach to identify likely high points of transmission within the Cook County Jail in Chicago, IL. At that facility, over 900 COVID-19 cases were reported across 10 housing divisions in 13 buildings from March 1-April 30, 2020. Staff members were required to report symptoms of COVID-19 (probable cases) or receipt of a positive test result (confirmed cases). A total of 2,041 staff members (77% of staff) were included in the network analysis because information was available about their shift and division assignments, and 198 (9.7%) of those staff members had COVID-19 during the two-month study period. Connections between staff members who had COVID-19 were higher than expected, suggesting likely transmission among staff members. Fewer connections than expected were observed among detained persons with SARS-CoV-2 infections, suggesting the effectiveness of medical isolation at reducing transmission.
The Officer Down Memorial Page, which tracks police officer fatalities determined to be occupationally related, reported that the majority of officer deaths for 2021 (157 of 269) were related to COVID-19 (ODMP, September 14, 2021). For the 269 officers who died, causes of death were not reported for each month, but the highest numbers of monthly deaths, 52 in January and 65 in August (compared to 16 to 34 deaths on other reported months), were consistent with the winter surge of COVID-19 and, more recently, the surge caused by the Delta variant.
The risk of COVID-19 has also been examined in industries where employees have little contact with the public, such as construction, and food processing, and where most exposure to SARS-CoV-2 likely comes from other workers. Pasco et al. (October 29, 2020) examined the association between construction work during the COVID-19 pandemic and community transmission and construction worker hospitalization rates in Austin, Texas from March 13 to August 20, 2020. A “Stay Home-Work Safe” order enacted on March 24, 2020, limited construction to only critical infrastructure and excluded commercial and residential work. One week later, the Texas governor lifted the restriction for essential workers and allowed all types of construction work to resume, while keeping the order in place for other workers. The authors found that resuming construction during the shelter-in-place order led to an increase in community transmission, an increase in hospitalizations among community members, and an increase in hospitalizations of construction workers. By mid-July, Austin Public Health identified at least 42 clusters (not defined) of COVID-19 cases in the construction industry; 515 individuals were hospitalized for COVID-19 illnesses acquired as part of these clusters, and 77 of those reported working in construction. The study found that construction workers had a nearly 5-fold increased risk of hospitalization in central Texas compared with workers in other occupations. The authors' model predicted that allowing unrestricted construction work would be associated with an increase in COVID-19 hospitalization rates from 0.38 per 1,000 residents to 1.5 per 1,000 residents overall, and from 0.22 per 1,000 construction workers to 9.3 per 1,000 construction workers for the construction industry specifically. The authors concluded that stringent workplace safety measures could significantly mitigate risks related to COVID-19 in the industry.
The meat packing and processing industries and related agricultural and food processing sectors have also been impacted by COVID-19. Waltenburg et al. (January, 2021) reported COVID-19 cases in employees from meat and poultry processing facilities in 31 states from March 1 through May 31, 2020. As reported in Table 2 of that report, 28,364 employees in those facilities were confirmed to have COVID-19 by laboratory testing and 132 died. Among the 20 states that reported total numbers of employees, 11.4% of the workers were diagnosed with COVID-19 (with a range of 3.1 to 27.7% of workers in individual states). For states that reported at least one COVID-19-related death, the percentages of employees who died in each state ranged from 0.1 to 2.4% of those with COVID-19. The authors found a high burden of disease in persons employed at these facilities who were racial or ethnic minorities. Higher incidence in these populations might be due to the likelihood of these employees working in areas in the plant where transmission risk is higher. Steinberg et al. (August 7, 2020) reported that attack rates (i.e., the number of individuals who are infected in comparison to the total number at risk) among production employees in the Cut (30.2%), Conversion (30.1%), and Harvest (29.4%) departments of a meat processing plant (where spacing between employees is less than 6 feet) were double that of salaried employees (14.8%) whose workstations had been modified to increase physical distancing from others.
Waltenburg et al. (January, 2021) also evaluated COVID-19 incidence in food manufacturing and agricultural settings ( e.g. , manufacturing or farming involving fruits, vegetables, dairy, baked goods, eggs, prepared foods), as reported in 30 states from March through May 2020. In food manufacturing and farming of fruits, vegetables, dairy, and other items, 742 workplaces were affected, including 8,978 infections and 55 fatalities. For states that reported total numbers of employees, the proportion of employees who developed COVID-19 in each state ranged from 2.0 to 43.5%. For states that reported at least one death, the percentages of deaths among cases ranged from 0.1 to 3.8%.
Porter et al. (April 30, 2021) reported that 13 COVID-19 outbreaks occurred at Alaska seafood processing facilities and vessels (both of which were described as high density workplaces) during the Summer and early Fall of 2020. The 13 outbreaks involved 539 COVID-19 cases, with 2-168 cases per outbreak. Attack rates in facilities and offshore vessels ranged from less than 5% to 75%. Outbreaks were also reported in entry quarantine groups. Because of these outbreaks, it was determined that vaccination of these essential workers is important and requirements for COVID-19 prevention were updated to include smaller quarantine groups, serial testing, and testing before transfers from one facility or vessel to another.
Finally, two published studies analyzed death records to determine how mortality rates among individuals in various types of workplaces had changed during the pandemic. Chen et al. (June 4, 2021) analyzed records of deaths occurring on or after January 1, 2016 in California and found that mortality rates in working aged adults (18-65 years) increased 22% during the COVID-19 pandemic period of March through November 2020 compared to pre-pandemic periods. Relative to pre-pandemic periods, the groups of employees experiencing the highest, statistically significant increases in relative excess mortality were those in food/agriculture (39% increase), transportation/logistics (31% increase), facilities (23% increase), and manufacturing (24% increase). Other groups that also experienced excess, statistically significant mortality compared to pre-pandemic periods were health or emergency workers (17% increase), retail workers (21% increase), and government and community workers (17% increase). The study authors concluded that certain occupational sectors were impacted disproportionally by mortality during the pandemic and that essential work conducted in-person is a likely avenue of infection transmission.
Hawkins et al. (January 10, 2021) examined death certificates of individuals who died in Massachusetts between March 1 and July 31, 2020. An age-adjusted mortality rate of 16.4 per 100,000 employees was determined from 555 death certificates that had useable occupation information. Employees in 11 occupational groups had particularly high mortality rates: healthcare support; transportation and material moving; food preparation and serving; building and grounds cleaning and maintenance; production, construction and extraction; installation/maintenance/repair; protective services; personal care services; arts/design/entertainment; sports/media; and community and social services. The study authors noted that occupational groups expected to have frequent contact with sick people, close contact with the public, and jobs that are not practical to do from home had particularly elevated mortality rates.
b. Healthcare Workers
As explained in the Healthcare ETS, COVID-19 presents a grave danger to workers in all U.S. healthcare settings where people with COVID-19 are reasonably expected to be present (86 FR 32381). Healthcare settings covered by the Healthcare ETS primarily include settings where people with suspected or confirmed COVID-19 are treated, exacerbating the risk present in most workplaces. To control the higher level of risk in those settings, OSHA determined that a suite of workplace controls was necessary to protect all employees, whether they are vaccinated or unvaccinated. As explained further below, OSHA now finds that unvaccinated healthcare workers in healthcare settings not covered by the Healthcare ETS are also at grave danger from exposure to SARS-CoV-2, just like unvaccinated workers in other industries. Data continue to be collected and reported for healthcare workers, and a small number of peer-reviewed studies demonstrate the potential impact of the Delta variant on healthcare workers.
CDC continues to provide updates for COVID-19 cases and deaths among healthcare personnel. However, information on healthcare personnel status continues to be reported for only a fraction (18.91%) of total reported cases, and death status was reported for only 82.16% of healthcare personnel cases as of October 18, 2021 (CDC, October 18, 2021—Healthcare Personnel). Given incomplete reporting, the data from this source represent only a fraction of actual healthcare cases and deaths. Nevertheless, CDC reported 666,707 healthcare personnel cases among the 6,754,306 reported cases that included information on healthcare personnel status (9.9%) and 2,229 fatalities among the 547,769 cases that included death status (0.4%) for healthcare employees as of October 18, 2021. This is a 26% increase in the number of cases and a 27% increase in the number of deaths since the May 24, 2021 data reported in the ETS (CDC, October 18, 2021—Healthcare Personnel). The Delta variant is likely responsible for the majority of those deaths. No healthcare worker deaths were reported by CDC during the weeks of May 30 through June 13, 2021; however, as the Delta variant's prevalence rose after June 20, healthcare worker deaths began increasing; they peaked during the period of August 15 through September 12, 2021, when 34 to 36 healthcare worker deaths were reported per week (CDC October 18, 2021—Healthcare Personnel, Deaths by Week). Independent reporting by Kaiser Health News and The Guardian reported more than 3,600 fatalities in health care workers as of April 2021 (Spencer and Jewett, April 8, 2021). That number is expected to be higher at this time since the earlier figure did not include the most recent 5 months of the pandemic, which includes the period of Delta variant predominance.
Published studies also demonstrate that healthcare workers, especially those who are unvaccinated, remain at risk of being infected with SARS-CoV-2 (see Section III.A.IV. Vaccines Effectively Reduce Severe Health Outcomes from and Transmission of SARS-CoV-2). Routine testing of health care personnel, first responders, and other frontline workers in eight U.S. locations in six states from December 14, 2020 through August 14, 2021 revealed 194 infections in 4,136 unvaccinated participants (89.7% symptomatic) and 34 infections in 2,976 fully vaccinated participants (80.6% symptomatic) (Fowlkes et al., August 27, 2021). During time periods when the Delta variant represented more than 50% of viruses sequenced, 19 infections were detected in 488 unvaccinated participants (94.7% symptomatic) and 24 infections were detected in 2,352 vaccinated participants (75% symptomatic).
Monthly COVID-19 cases in healthcare workers were reported during the period from March 1 to July 31, 2021 at the University of California San Diego (UCSD) health system, which is a healthcare provider that includes primary care services such as family medicine and pediatrics (Keehner et al., September 1, 2021; UCSD, 2021). During that time period, a total of 227 health care workers tested positive for COVID-19. One hundred and nine of 130 fully vaccinated workers who tested positive (83.8%) were symptomatic and 80 of 90 unvaccinated workers (88.9%) were symptomatic; one unvaccinated person was hospitalized for COVID-19 symptoms. By July of 2021, after the end of California's mask mandate on June 15 and after the Delta variant became dominant, the number of cases detected dramatically increased; the Delta variant accounted for more than 95% of SARS-CoV-2 viruses sequenced by the end of that month. During July of 2021, symptomatic infections were detected in 94 of 16,492 fully vaccinated workers and 31 of 1,895 unvaccinated workers. Attack rates in July of 2021 were 5.7 per 1,000 fully vaccinated workers and 16.4 per 1,000 unvaccinated workers.
In Finland, a Delta variant infection from a hospitalized patient spread throughout the hospital and to three primary care facilities, infecting 103 individuals, including 45 healthcare workers (Hetemäki et al., July 29, 2021). Twenty-six of the healthcare workers were infected at the hospital and 19 were infected at primary care facilities. The affected health care workers included 28 with direct patient contact (11 who were not fully vaccinated), 8 unvaccinated healthcare worker students, and 9 other staff, including hospital cleaners and secretaries (of whom 6 were not fully vaccinated). According to study authors, “There was high vaccine coverage among permanent staff in the central hospital, but lower for HCW in primary healthcare facilities. . .” Study authors estimated that vaccine effectiveness against the Delta variant in healthcare workers was approximately 88-91%, suggesting how much more extensive the outbreak could have been if a high percentage of healthcare workers were not fully vaccinated.
In the UK, a Delta variant infection in a healthcare worker resulted in an outbreak in a care home that affected 16 of 21 residents and 8 of 21 staff (Williams et al., July 8, 2021). One staff member was hospitalized. Attack rates were 35.7% in staff who were partially vaccinated ( i.e ., received their second dose of vaccine on the day that the index case was diagnosed with COVID-19 or had only received one vaccine dose) and 40% in staff who were not vaccinated.
Recent news stories demonstrate that outbreaks affecting staff members are still occurring in U.S. healthcare facilities. An outbreak that began in August, 2021 at a Washington State nursing center resulted in infections in 22 staff members and 52 residents. In an unrelated outbreak, a nursing facility in Hawaii reported infections in 24 employees and 54 patients (Wingate, September 24, 2021). Vaccination rates were reported at 64.5% of residents and 37.1% of staff in the Washington State facility and 91% of staff and more than 80% of patients at the Hawaii facility.
COVID-19 cases were also observed in staff at ambulatory care settings prior to emergence of the Delta variant. Over an 11-week period beginning on March 20, 2020, 254 tests for SARS-CoV-2 were performed on employees who had potential exposures at an outpatient urology center in New York State (Kapoor et al., 2020). Positive test rates in employees correlated with rates in New York State, declining over time, from 26.1% in the early stage to 7.3% in the late stage of the study. According to study authors, the positive test results coincided with the implementation of infection control procedures ( e.g. , symptom screening, masking, distancing, and hygiene). Positivity rates were similar in administrative and clinical staff and the study authors concluded that “administrative staff in an outpatient setting were equally—if not more—vulnerable to SARS-CoV-2 transmission when compared with clinical staff who were more directly exposed to patients.” The study authors speculated that possible reasons for the findings were that clinical staff were more familiar with PPE and that administrative staff, especially in check-in and check-out points, tend to work close to each other.
c. Conclusion for Employee Impact
The evidence described above provides examples of the impact that exposures from SARS-CoV-2, including those involving the Delta variant, have had on employees in general industry, agriculture, construction, maritime, and healthcare settings. It demonstrates that SARS-CoV-2 has spread to employees in these industries and, in many cases, infection was linked to exposure to infected persons at the worksite (WSDH, September 8, 2021; OHA, September 1, 2021; TDH, September 8, 2021; NCDHHS, August 30, 2021; Hawaii State, August 19, 2021; Pray et al., January 29, 2021; Sami et al., April 9, 2021; Suhs et al., July 23, 2021; Gold et al., February 26, 2021; Porter et al., April 30, 2021; Hetemäki et al., July 29, 2021; Williams et al., July 8, 2021). The documentation of so many workplace clusters suggests that exposures to SARS-CoV-2 occur regularly in workplaces where employees come into contact with others. This prevalence of clusters, combined with some evidence that many infections occurred within the 14-day incubation period for SARS-CoV-2 and that exposures to infected persons outside the workplace were frequently ruled out, supports the proposition that exposures to and transmission of SARS-CoV-2 occur frequently at work. Multiple studies demonstrate high rates of COVID infections, illnesses, and fatalities in the wide range of occupations that require frequent or prolonged close contact with other people, indoor work, and work in crowded and/or poorly ventilated areas The large numbers of infected employees suggest that SARS-CoV-2 is likely to be present in a wide variety of workplaces, placing unvaccinated workers at risk of serious and potentially fatal health effects.
IV. Vaccines Effectively Reduce Severe Health Outcomes From and Transmission of SARS-CoV-2
During the course of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, different variants have emerged with different characteristics that better enable transmission and potentially cause more severe outcomes. However, vaccines remain very effective at reducing the occurrence of COVID-19-related severe illness, disability and death. 12 The Delta variant is more transmissible than previous variants, might cause more severe illness than previous variants in unvaccinated people, and has led to hospitalization of individuals in numbers similar to those of the November 2020 to February 2021 surge. These changes in characteristics have provided a clearer realization of the continuing capacity for SARS-CoV-2 to present a grave danger to workers. However, it is well evident that even given these changed characteristics of Delta, serious disease and death continue to occur overwhelmingly in unvaccinated individuals while the vaccinated are afforded great protection. 13
12 A discussion of vaccination rates, as well as OSHA's rationale for why vaccination is a critical means of protecting workers from the grave danger described in this section, can be found in Need for the ETS (Section III.B. of this preamble).
13 While mild cases of COVID-19 are included in the grave danger presented by COVID-19, as stated in the Healthcare ETS (see 86 FR 32382), OSHA is focusing on the most severe health effects, i.e., cases requiring hospitalization and cases resulting in death, in this new rulemaking effort in order to prevent the gravest of consequences to workers.
a. Impact of Vaccination on Severe Health Outcomes
There are currently three vaccines that are approved or authorized for the prevention of COVID-19 in the U.S.: The Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine (FDA approved for ages 16 and above; authorized for ages 12 and above), the FDA-authorized Moderna COVID-19 vaccine (authorized for ages 18 and above), and the FDA-authorized Janssen COVID-19 vaccine (also known as the Johnson & Johnson vaccine; authorized for ages 18 and above.) Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna are mRNA vaccines that require two primary series doses administered three weeks and one month apart, respectively. Janssen is a viral vector vaccine administered as a single primary vaccination dose (CDC, September 15, 2021). The vaccines were shown to greatly exceed minimum efficacy thresholds in preventing COVID-19 in clinical trial participants (FDA, December 11, 2020; FDA, December 18, 2020; FDA, February 26, 2021). Data from clinical trials for all three vaccines and observational studies for the two mRNA vaccines clearly establish that fully vaccinated persons have a greatly reduced risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection compared to unvaccinated individuals. This includes severe infections requiring hospitalization and those resulting in death. For more information about the effectiveness of vaccines as of late Spring 2021, see 86 FR 32397, which OSHA hereby includes in the record for this ETS. 14
14 This adoption includes the citations in the referenced section of the Healthcare ETS, which are also included in the docket for this ETS.
Vaccines remain highly effective against hospitalization and death. A study evaluating vaccine effectiveness at preventing hospitalization among those with SARS-CoV-2 infections in New York found that effectiveness did not change from May 3 to July 25, 2021 as the Alpha variant gave way to the Delta variant (91.9-96.2% range; Rosenberg et al., August 27, 2021). Grannis et al. used data from 187 hospitals in nine states from June to August 2021 to evaluate the efficacy of vaccines against hospitalization when Delta had emerged as the predominant variant causing SARS-CoV-2 infections (September 17, 2021). This study found that vaccines were 89% effective at preventing hospitalization in individuals aged 18 to 74. Similarly, vaccines were also found to be 89% effective in preventing hospitalization in a study collecting data from five Veteran Affairs Medical Centers from July 1 to August 6, 2021, a time when most transmission was attributed to the Delta variant (Bajema et al., September 10, 2021).
Two other studies found that, although the level of protection provided by vaccination has decreased somewhat with the emergence of the Delta variant, vaccines continue to provide high levels of protection against hospitalization. In a U.S. study, researchers found that while the Moderna and Janssen vaccines mostly maintained their effectiveness at preventing hospitalization (going from 93% to 92% after more than 120 days post-vaccination and 71% to 68% after more than 28 days post-vaccination, respectively) from March to August 2021, the effectiveness of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine at preventing those severe outcomes decreased from 91% to 77% after more than 120 days post-vaccination (Self et al., September 17, 2021). An Israeli study on infections documented between July 11 and July 31, 2021 found a significant decrease in vaccine efficacy for the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine against severe outcomes in relation to when an individual was vaccinated, but the absolute difference was much less than what was observed in the U.S. study (e.g., 98% effective for 40-59 year olds vaccinated in March versus 94% effective for those in the same age group who were vaccinated in January) (Goldberg et al., August 30, 2021).
Vaccines also remain extremely effective at preventing death. A UK study evaluated the effectiveness of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine against death and found it to be 96.3% effective against the Alpha strain and 95.2% protective against the Delta strain (Andrews et al., September 21, 2021). Two Israeli studies, Haas et al. and Saciuk et al., performed during time periods where Alpha was predominant, found the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine to be 96.7% and 91.1% effective, respectively, against death (Haas et al., May 15, 2021; Saciuk et al., June 25, 2021). A California study found that the Moderna vaccine was 97.9% effective against death (Bruxvoort et al., September 2, 2021). A study on patients served by the Veterans Health Administration found that Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna vaccines provided 99% effectiveness against death (Young-Xu et al., July 14, 2021).
The risks of hospitalization and death appear to have increased for unvaccinated individuals since the Delta variant became a common source of infections. A study of Los Angeles County SARS-CoV-2 infections found that vaccinations reduced hospitalization risk by a factor of 10 on May 1, 2021, when the Alpha variant was dominant, but that the risk of hospitalization was even more greatly reduced (by a factor of 29.2) on July 25, 2021, when the Delta variant was dominant (Griffin et al., August 27, 2021). This difference suggests both that vaccines continue to provide a high level of protection against disease that results in hospitalization and that risk has increased for those who are unvaccinated. Similar increased risk for unvaccinated individuals was reported in a study that evaluated hospitalization and death data from 13 U.S. jurisdictions between June 20 and July 17, 2021, a period when the Delta variant gained prominence (Scobie et al., September 17, 2021). For unvaccinated 18 to 49 year olds, the risk of hospitalization was 15.2 times greater, and the risk of death was 17.2 times greater, than the risks for vaccinated people in the same age range. For unvaccinated 50 to 64 year olds, the risk of hospitalization was 10.9 times greater, and the risk of death was 17.9 times greater, than for those who are vaccinated. These studies illustrate that vaccination is an extremely effective control measure to minimize severe outcomes resulting from Delta variant infections.
b. Impact of Vaccination on Infection and Transmission
Vaccines continue to provide robust protection for vaccinated individuals against SARS-CoV-2 infections, even though several studies indicate that vaccine efficacy against infection may have decreased somewhat with the emergence of the Delta variant (Fowlkes et al., August 27, 2021; Rosenberg et al., August 27, 2021; Nanduri et al., August 27, 2021; Seppala et al., September 2, 2021; Bernal et al., August 12, 2021). For example, vaccination was observed to reduce the risk of infection by a factor of 8.4 on May 1, 2021, when the Alpha variant was predominant in Los Angeles county (Griffin et al., August 27, 2021). However, the level of protection had fallen to a factor of 4.9 by July 25, 2021, when Delta made up 88% of infections in the county. The findings from this study indicate that while vaccines maintain robust protection against severe outcomes, protection against infection has fallen with the increased circulation of the Delta variant. A broader study using data from 13 U.S. jurisdictions had similar findings, observing that the protection vaccines afforded against infection decreased from a factor of 11.1 ( i.e. , vaccinated people were 11.1 times less likely than unvaccinated people to become infected) between April 4 and June 19, 2021, to a factor of 4.6 between June 20 and July 17, 2021 (Scobie et al., September 17, 2021). An additional study noted, however, that the decrease in vaccine protectiveness against symptomatic infection from the Delta variant could be due to the waning of immunity specifically in older populations. Andrews et al. (September 21, 2021) found that while the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine effectiveness decreased from 94.1% to 67.4% in those 65 years old and older, vaccine effectiveness for those 40 to 64 years old only decreased from 92.9% to 80.6%.
While infections themselves do not normally result in serious illness for those who are vaccinated, evidence shows that vaccinated individuals who become infected with the Delta variant can transmit the disease more easily to others than with previous variants. This development poses a great concern for the unvaccinated, who generally do not have the protections against severe outcomes that vaccination affords. Before Delta, vaccinated individuals were shown to have lower estimated viral loads when infected than those who were unvaccinated, which suggested that infected vaccinated individuals were likely not a major concern for transmission (Levine-Tiefenbrun et al., March 29, 2021). Transmission studies prior to the emergence of Delta appear to bear this out. A Scottish study performed during a time period when the Alpha variant was predominant in the region, showed that a fully vaccinated individual was 3.2 times less likely than an unvaccinated individual to transmit the virus to unvaccinated family members (Shah et al., September 10, 2021; supplementary appendix). A population-based study from the Netherlands found that vaccination decreased secondary transmission to household members from 31% to 11% (de Gier et al., August 5, 2021). Additionally, a study from the UK found that household transmission decreased by as much as 50% when the infected individual was vaccinated (Harris et al., June 23, 2021).
More recent research suggests that the Delta variant may have reduced the level of protection vaccination affords against transmission of the virus to others, but still significantly reduces transmission risk in comparison to infected unvaccinated individuals. A UK study found that fully vaccinated individuals infected by the Delta variant are able to transmit the virus to both vaccinated and, to a greater degree, unvaccinated persons (Singanayagam et al., September 6, 2021). Still, the rate at which transmission to unvaccinated individuals occurred was nearly double the rate of transmission to vaccinated individuals (35.7% compared to 19.7%). Similarly, Eyre et al., (September 29, 2021) found that during the predominance of Alpha, full vaccination with the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines resulted in a significant reduction in transmission to others (an adjusted Odds Ratio (aOR) of 0.18, meaning that being unvaccinated increased the odds of transmission by over five times). With the rise of the Delta variant, that reduction in transmission to others was less than with the Alpha variant, but still significantly more than for unvaccinated individuals (aOR of 0.35, meaning that being unvaccinated increased the odds of transmission by almost three times).
The greater ability for vaccinated individuals to transmit the Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 to others (compared to previous variants) appears to be linked to the generation of similar viral loads (as estimated by Ct threshold) in the vaccinated compared to the unvaccinated (Ct threshold is the number of RT-PCR cycles that need to be run in order to amplify the RNA enough to be detected—fewer cycles means a greater initial amount of virus was collected) (Singanayagam et al., September 6, 2021). This observation has been made in several studies. A study from Israel observed that viral loads among those infected with the Delta variant were only decreased in people who had been vaccinated recently (within the past two months) or in those who had recently received a booster dose (Levine-Tiefenbrun et al., September 1, 2021). In a study of SARS-CoV-2 infections in Los Angeles County, performed when the Delta variant was predominant, vaccination status did not appear to affect the estimated viral loads, suggesting that infected individuals who are vaccinated may be just as likely to transmit the virus (Griffin et al., August 27, 2021). Additionally, estimated viral loads did not appear to be significantly different with respect to vaccination status in a Wisconsin study (Riemersma et al., July 31, 2021). Regardless of viral loads in vaccinated and unvaccinated individuals, the fact remains clear that unvaccinated people pose a higher risk of transmission to others than vaccinated people, simply because they are much more likely to get COVID-19 in the first place.
These studies, however, appear to overstate increases in transmission risk from vaccinated individuals related to the Delta variant. From May to July 2021, UK researchers tested individuals at random to better characterize viral load estimates in people with asymptomatic as well as symptomatic infections; they found that vaccination was associated with a significantly lower estimated viral load (Elliott et al., September 10, 2021). This more comprehensive study ( i.e. , Elliott et al., September 10, 2021) may have been able to better characterize the course of infection and to incorporate vaccinated individuals whose viral loads were decreasing quickly. The findings in Elliott et al. are consistent with studies observing that viral load may fall more quickly in vaccinated individuals, resulting in a shorter infectious period and possibly fewer transmission events (Chia et al., July 31, 2021; Eyre et al., September 29, 2021).
c. Conclusion for the Impact of Vaccines
The studies discussed above indicate that vaccines continue to effectively protect vaccinated individuals against SARS-CoV-2 infections, while the risk of infection, hospitalization, and death increased among unvaccinated people as the Delta variant became predominant in the U.S. The Delta variant is even more dangerous to unvaccinated individuals than previous variants because of the higher transmission potential from both unvaccinated and vaccinated people. Because unvaccinated individuals are at much higher risk of severe health outcomes from infection with SARS-CoV-2, and also pose a greater transmission risk to those around them, it is critical to assure that as many people as possible are fully vaccinated in order to prevent transmission at work.
V. Coverage of OSHA's Grave Danger Finding
Based on the information discussed above, OSHA finds that many unvaccinated workers across the U.S. economy are facing a grave danger of severe health effects or death from exposure to SARS-CoV-2. Fully vaccinated workers are not included in this grave danger finding because, as described throughout this section, those who are fully vaccinated are much better protected from the effects of SARS-CoV-2 and, in particular, the most severe effects, than are those who are unvaccinated. 15 Beyond that, OSHA's grave danger determination exempts several categories of workers based on characteristics of their work or workplace: (1) Workers who do not report to a workplace where other individuals are present or who telework from home; and (2) workers who perform their work exclusively outdoors. The basis for these exemptions is explained below. In this section, OSHA also addresses the basis for OSHA's grave danger finding for workers who are unvaccinated yet had a prior COVID-19 infection, and explains the Agency's more nuanced grave danger finding in the healthcare industry.
15 The exclusion of vaccinated workers from this grave danger finding does not mean that vaccinated workers face no risk from exposure to SARS-CoV-2. The best available evidence clearly shows that vaccination provides great protection from infection and severe outcomes, but breakthrough infections do occur and vaccinated individuals can still transmit the virus to others. In some cases, the level of risk to vaccinated workers may even rise to the level of a significant risk, the standard OSHA must meet for promulgation of a permanent standard under section 6(b)(5) of the OSH Act (29 U.S.C. 655(b)(5)).
a. Employees Who Telework and Employees Who Do Not Report to a Workplace Where Other People Are Present.
Employees who report to workplaces where no other people are present face no grave danger from occupational exposure to COVID-19 because such exposure requires the presence of other people. For those who work from their homes, or from workplaces where no other people are present (such as a remote worksite), the chances of being exposed to SARS-CoV-2 through a work activity are negligible. Therefore, OSHA is exempting those workers who do not come into contact with others for work purposes from its grave danger finding as well as the scope of the ETS (for more information, see the Summary and Explanation for Scope and Application, Section VI.B. of this preamble).
b. Employees Who Work Exclusively Outside
Employees who work exclusively outside face a much lower risk of exposure to SARS-CoV-2 at work, because their workplaces typically do not include any of the characteristics that normally enable transmission to occur ( e.g. , indoors, lack of ventilation, crowding). Bulfone et al. attributed the lower risk of transmission in outdoor settings ( i.e. , open air or structures with one wall) to increased ventilation with fresh air and a greater ability to maintain physical distancing (November 29, 2020). While the best available evidence firmly establishes a grave danger in indoor settings, the CDC has stated that the risk of outdoor transmission is “low” (CDC, September 1, 2021) and OSHA is unable to establish a grave danger in outdoor settings from exposure during normal work activities.
OSHA recognizes that outdoor transmission has been identified in a few specific incidents ( e.g. , 2 of 7,324 cases, Qian et al., October 27, 2020). However, general reviews of transmission studies that include large-scale and high-density outdoor gatherings indicate that indoor transmission overwhelmingly is responsible for SARS-CoV-2 transmission. Additionally, the lack of evidence tied to specific case studies illustrating outdoor transmission in comparison to the bevy of case studies on indoor transmission makes it difficult to support a conclusion that outdoor transmission rises to the level of a grave danger.
Bulfone et al. reviewed a collection of SARS-CoV-2 studies that evaluated infections in outdoor and indoor settings (November 29, 2020), and found that transmission is significantly less likely to occur in outdoor settings than in indoor settings. The studies overall found that the risk of outdoor transmission was less than 10% of the risk of transmission in indoor settings, with three of the studies concluding risk was 5% or less of the risk of transmission in indoor settings. While acknowledging significant gaps in knowledge, the authors of a different study suggested that increases in transmission related to large events such as the Sturgis motorcycle rally may be related to lack of local efforts to prevent transmission indoors (e.g., requiring the wearing of masks, closing indoor dining), rather than the outdoor setting for the rally (Dave et al., December 2, 2020). In contrast, transmission rates did not increase as expected following the Summer 2020 protests on racial injustice. This outcome was attributed, in part, to participants having been less likely to enter indoor commercial establishments.
Weed and Foad (September 10, 2020) found that transmission of SARS-CoV-2 related to large scale outdoor gatherings could be largely attributed to individual behaviors related to that event, such as communal travel and indoor congregation at other facilities ( e.g. , restaurants, shared accommodations), rather than to the time spent outdoors at those gatherings. Similarly, a Public Health England evaluation of the literature on SARS-CoV-2 and surrogate respiratory viruses (December 18, 2020) also concluded that when transmission does occur at outdoor events, outdoor activities were mixed with indoor setting use. Public Health England concluded that the vast majority of transmission happens in indoor settings, with very little evidence for outdoor transmission.
A systemic review of SARS-CoV-2 clusters identified 201 events through May 26, 2020 (Leclerc et al., April 28, 2021), only 4 of which occurred at predominantly outdoor settings. For those 4 clusters, the authors noted that they were not able to evaluate specific transmission events and attributed it to local health agencies being overwhelmed by the pandemic. OSHA notes that the designations of settings in this study are somewhat generic, as outdoor construction sites will often have indoor locations, such as mobile offices, or locations with reduced airflow, such as areas with a roof or ceiling and two or more walls. Regardless, this study illustrates the comparable abundance of evidence available to evaluate SARS-CoV-2 transmission in indoor settings versus outdoor settings.
Cevik et al. (August 1, 2021) reviewed studies on the transmission dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 infections from large scale, contact-tracing studies. The authors recommended that, based on the evidence that outdoor transmission dynamics resulted in significantly fewer infections than in indoor settings, public health entities should greatly encourage use of outdoor settings. The researchers highlighted a study by Nishiura et al. (April 16, 2020), who evaluated 110 cases in Japan at the beginning of the pandemic and found that outdoor settings reduced transmission risk by 18.7 times and reduced the risk of super-spreader events by 32.5 times.
Agricultural workplace settings have experienced significant SARS-CoV-2 infections. However, transmission in these settings is difficult to characterize because many jobs in this sector include both outdoor and indoor activities. Miller et al. (April 30, 2021) evaluated an outbreak among farmworkers in Washington State. The researchers found that 28% of workers with predominantly indoor tasks where they were unable to maintain physical distance were infected, compared to 6% of workers who performed predominantly outdoors tasks in the orchards. Conversely, a study on farmworkers in Monterey County, California found a significant correlation between evidence of infection and individuals who worked in the fields as opposed to indoor work (Mora et al., September 15, 2021). The paper noted that infections were predominant in individuals who lived in crowded conditions, commuted together to the fields, and spoke at home in indigenous languages, which is important as written health messages are often not available in all worker languages. These papers cannot identify where or when infections occurred in order to discern causation. The associations observed may indicate that SARS-CoV-2 infections may be more related to aspects related to indoor exposures outside of the work activities ( e.g. , crowded living conditions) or potentially overlooked indoor aspects connected to outdoor work ( e.g. , shared commuting).
Several studies discussed below in more detail have evaluated outdoors on-field transmission from infected participants during football, soccer, and rugby matches. These events include repeated close physical contact between players, without PPE or physical distancing, over the course of fairly long events, with increased exertion leading to greater respiratory effort and production of respiratory droplets. These events also include opposing cohorts who only interact during on-field activities. Therefore, these studies provide some evidence for the low likelihood of outdoor transmission in other workplace activities greatly impacted by the pandemic, such as in construction.
Mack et al. (January 29, 2021) detailed the National Football League's complex program to assess and prevent transmission, which included devices that recorded distance and duration of interactions with others, for the purpose of improving identification of individuals with high-risk exposures. Although 329 positive cases were identified among roughly 11,400 players and staff, there were no reported cases of on-field transmission by infected players. The results led the NFL to focus more on reducing transmission in indoor settings, including transportation.
Egger et al. (March 18, 2021) reviewed three soccer matches involving 18 players who had SARS-CoV-2; one match involved a team where 44% of the players were infected. Video analysis was used to determine the type of contact between players, such as contact to face or hand slaps. None of the existing cases were associated with on-field play and no secondary transmission from on-the-field contacts was observed. Jones et al. (February 11, 2021), evaluated four rugby Super League matches involving eight players who were found to be infected with SARS-CoV-2. Using video footage and global positioning data, the researchers were able to identify 28 players as high-risk contacts with the infected players. These high-risk players together had as many as 32 tackles and were within two meters of infected players as often as 121 times during the four matches. Of the 28 players noted as high-risk contacts, one became infected with SARS-CoV-2. However, researchers determined that the transmission resulted from internal team outbreaks and not from exposure on the field.
OSHA acknowledges that the risk of transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in outdoor settings is not zero, and that there may be some low risk to workers performing general tasks exclusively in outdoor settings. However, where studies have been able to differentiate between indoor and outdoor exposures, they indicate that indoor exposures are the much more significant drivers of SARS-CoV-2 infections. Therefore, the best available evidence at this time does not provide OSHA with the information needed to establish SARS-CoV-2 as a grave danger for general work activities in outdoor settings (see Int'l Union, United Auto., Aerospace, & Agr. Implement Workers of Am., UAW, 590 F. Supp. at 755-56, describing a “grave danger” as a risk that is more than “significant”). Therefore, OSHA has excluded employees who work exclusively outdoors from the scope of this ETS (see the Summary and Explanation for Scope and Application, Section VI.B. of this preamble).
c. Employees in Healthcare
Because OSHA issued a separate grave danger determination several months ago for some healthcare workers, some explanation of how its current finding applies to healthcare workers is necessary. In June 2021, OSHA issued its Healthcare ETS (86 FR 32376) after determining that some healthcare workers faced a grave danger of infection from SARS-CoV-2. This grave danger determination, along with the protections of the Healthcare ETS, applied to healthcare and healthcare support workers in settings where people with suspected or confirmed cases of COVID-19 are treated, and was based on the increased potential for transmission of the virus in such settings (see 86 FR 32411-32412). These workers are currently covered by the protections of the Healthcare ETS (29 CFR 1910.502). OSHA does not have data to demonstrate that unvaccinated workers in settings covered by the Healthcare ETS face a grave danger from SARS-CoV-2 when the requirements of that standard are followed. However, if the Healthcare ETS were no longer in effect, OSHA would consider the workers who were covered by it, and who remain unvaccinated, to be at grave danger for the reasons described in this ETS.
OSHA's new finding of grave danger applies to healthcare and healthcare support workers who are not covered by the Healthcare ETS, to the extent they remain unvaccinated. In this ETS, as discussed in this section, OSHA has made a broader determination of grave danger that applies to most unvaccinated workers, regardless of industry. OSHA's current finding of grave danger supporting this ETS does not depend on whether a workplace is one where people with suspected or confirmed COVID-19 are expected to be present. Therefore, the finding of grave danger applies to unvaccinated workers in healthcare settings that are not covered by 29 CFR 1910.502 to the same extent it applies to unvaccinated workers in all other industry sectors.
d. Employees Who Were Previously Infected With SARS-CoV-2
OSHA has carefully evaluated the effectiveness of previous SARS-CoV-2 infections in providing protection against reinfection. This section provides a detailed description of the current scientific information in order to ascertain what the best available scientific evidence on this topic indicates regarding the risk to individuals with previous COVID-19 infections from exposure to SARS-CoV-2. While the agency acknowledges that the science is evolving, OSHA finds that there is insufficient evidence to allow the agency to consider infection-acquired immunity to allay the grave danger of exposure to, and reinfection from, SARS-CoV-2.
To determine whether employees with infection-induced immunity from SARS-CoV-2 ( i.e. , those who were infected with SARS-CoV-2 but have not been vaccinated) face a grave danger, OSHA reviewed the scientific evidence on the protective effects of vaccine-induced SARS-CoV-2 immunity versus infection-induced immunity. Individual immunity to any infectious disease, including SARS-CoV-2, is achieved through a complex response to exposure by the immune system. This response consists of disease-specific antibody production guided and augmented by certain types of immune cells, such as T and B cells, which work together to neutralize or destroy the disease-causing agent. Immune responses to viruses like SARS-CoV-2 can be measured in several ways. For instance, blood serum can be taken and exposed to specific proteins found on the SARS-CoV-2 virus, in order to measure the presence of antibodies in the blood. Another antibody test, the neutralization test, measures the ability of the antibodies present in a serum to neutralize infectivity and prevent cells from being infected. T cell immunity can be measured using techniques that target a specific biomolecule that is specific to SARS-CoV-2.
A considerable number of individuals who were previously infected with SARS-CoV-2 do not appear to have acquired effective immunity to the virus (Psichogiou et al., September 13, 2021; Wei et al., July 5, 2021; Cavanaugh et al., August 13, 2021). The level of protection afforded by infection-induced immunity appears to depend on the severity of individuals' infections. In a study from Greece, immunogenicity was compared between healthcare workers who were vaccinated with Pfizer-BioNTech and unvaccinated patients who acquired a natural infection (Psichogiou et al., September 13, 2021). The researchers found that the immune response in unvaccinated individuals correlated to the severity of their disease. Fully vaccinated healthcare workers had immune responses (measured as antibody levels specific to SARS-CoV-2) that were 1.3 times greater than patients who had critical cases of COVID-19 cases, 2.5 times greater than patients who had moderate to severe cases, and 10.5 times greater than patients who had asymptomatic/mild illnesses. Similarly, another study found that 24.0% (1,742 of 7,256) of individuals who had a previous SARS-CoV-2 infection were seronegative ( i.e. , did not produce antibodies in response to the virus), suggesting that the previous infection provided insufficient protection against future infection (Wei et al., July 5, 2021). Individuals who were seronegative were typically older, had lower viral burdens when infected, and were more likely to be asymptomatic. The authors posited that the immunity of those who were seropositive ( i.e., did produce antibodies in response to the virus) would provide some measure of protection, but that these individuals would benefit from a vaccination booster. This position appears to be validated by a study that compared the reinfection rates of individuals in Kentucky based on their post-recovery vaccination status (Cavanaugh et al., August 13, 2021). Unvaccinated individuals with previous infection were found to be 2.3 times more likely to be reinfected than those who were vaccinated after their prior infection. These studies demonstrate not only that those with milder infections may not be protected against future infection, but that it is difficult to tell, on an individual level, which individuals might have had prior infections that conveyed protection equivalent to that provided by vaccination.
A number of other studies indicate that fully vaccinated individuals may be better protected against future infection than those with previous infections. A study in Massachusetts concluded that the immunity conveyed from a previous SARS-CoV-2 infection was effectively equivalent to the immunity of an uninfected individual who has had only one dose of an mRNA vaccine (Naranbhai et al., October 13, 2021). The authors found that fully vaccinated individuals have an immune response ( i.e., antibodies and neutralization) well above the levels observed in unvaccinated, previously-infected individuals. German researchers found that individuals who were fully vaccinated with Pfizer-BioNTech had a significantly greater immune response (as measured by antibody levels) than unvaccinated individuals who had infections, concluding that vaccination would be needed for those unvaccinated individuals to have similar protection against infection (Herzberg et al., June 13, 2021). Similarly, a Dutch study observed that vaccination greatly improved the immune response (as measured by antibodies and virus-specific T cells) of individuals who had recovered from COVID-19 (Geers et al., May 25, 2021). Planas et al. (August 12, 2021) also noted that immune response (as measured by neutralization) to the Alpha, Beta, and Delta (B.1.617.2) variants in unvaccinated, previously-infected individuals was considerably less than the immune response in individuals five weeks after their second Pfizer-BioNTech dose. When unvaccinated, previously-infected individuals were vaccinated, their immune response (as measured by neutralization) increased by more than an order of magnitude. Likewise, Wang et al. (July 15, 2021) found that the immune response (as measured by neutralization) of those with previous SARS-CoV-2 infection increased by more than an order of magnitude against Alpha (B.1.1.7), Beta (B.1.351), Iota (B.1.526), and Gamma (P.1) variants when they were vaccinated. These studies show that infection-induced immunity may not equal the protection afforded by vaccination and that vaccination greatly improves the immune response of those who were previously infected.
The aforementioned studies indicate that immunity acquired through infection appears to be less protective than vaccination. There are also a number of epidemiological studies that provide some evidence that infection-acquired immunity has the potential to provide a significant level of protection against reinfection. As OSHA discusses in greater detail below, these studies suffer from methodological limitations that render them inconclusive about the level of immunity conferred by infection, and therefore OSHA is unable to establish that such immunity eliminates grave danger. This determination is based in three parts.
First, the epidemiological literature OSHA reviewed generally suffers from selection bias to a degree that it serves as an unreliable basis on which to reach a robust conclusion on whether previous infection removes workers from grave danger. In general, the studies described below do not account for people who had mild COVID-19 infections, leading to study findings regarding the level of protection afforded by prior infection that are not generally applicable. Second, the tests employed in the studies are being used in ways that they were not originally designed to be employed. These tests are powerful tools, but there are limitations to their use in determining if a specific individual is, in fact, protected from the grave danger of SARS-CoV-2. Particularly problematic is the lack of established thresholds to determine full protection from reinfection or even a standardized methodology to determine infection severity or immune response. Thus, while these studies broadly establish some increase in protectiveness against SARS-CoV-2 among the studied populations, they as yet are unable to provide a reasonable degree of certainty on whether the degree of protection afforded any particular individual from their prior infection is sufficient to eliminate the grave danger from reinfection (see Milne, et al., October 21, 2021.) Third, while the research methodology itself creates difficulties in the context of OSHA's grave danger inquiry, the implications of trying to apply investigative research methodology to clinical practice are even more challenging. The need for the development of standardized methods and criteria for establishing sufficient immunity preclude the application of the studies' findings to robust and reliable clinical practice. These three rationales for OSHA's finding are described in more detail below.
Several epidemiological studies used previous RT-PCR positive cases to define previous infections (Hansen et al., March 27, 2021; Pilz et al., February 11, 2021; Vitale et al., May 28, 2021; Pouwels et al., October 14, 2021; Braeye et al., September 15, 2021; Hall et al., April 17, 2021). RT-PCR tests, particularly in the beginning of the pandemic, were given high priority to discern who seeking medical care was, in fact, infected. For instance, the progression of testing from medical needs to more of a community perspective is illustrated in Denmark (Vrangbaek et al., April 29, 2021). Denmark, considered one of the gold standard countries for its comprehensive testing program, missed five infections for every one it identified in the spring of 2020 (Espenhaim et al., August 22, 2021). Hansen et al. (March 27, 2021) depended greatly on these first surge infection definitions to determine that survivors had protection of 80.5% effectiveness during the second surge in Denmark from September through December, 2020. By only noting RT-PCR positives from the spring when testing was limited and highly focused on health care needs, it seems apparent that the study excluded many less severe cases (which are less likely to result in an effective immune response against reinfection), leading to results that may suggest greater protection is afforded by infection than in actuality. Even by December of 2020, it appears Denmark's gold standard comprehensive testing approach was only able to capture roughly half of all infections. Similar systemic undercounts have also been determined to be true in the United States where approximately three out of four infections have never been reported (CDC, July 27, 2021b).
It is important to recognize that RT-PCR testing was not implemented to find every infection, but was used instead to assist in determining when medical and community interventions were necessary. Infections without symptoms or with mild symptoms likely would not require medical intervention and, therefore, would likely not be identified via testing. The absence of this population that is more vulnerable to reinfection, in these studies, undercuts their usefulness in OSHA's grave danger analysis, because they may overestimate the protectiveness of immunity acquired through infection.
Several other studies in regions less known for their sampling approach than Denmark also were heavily dependent on early, limited pandemic RT-PCR testing. An Austrian study found a roughly ten-fold decrease in reinfection in survivors of reported infections from February to April 30, 2020 in comparison with the general public (Pilz et al., February 11, 2021). The authors noted that “infections in the first wave are likely to have been far more common than the documented ones” and referred to their results as a “rough estimate.” Researchers at the Cleveland Clinic also found a reduced rate of reinfection in those who had a reported previous infection compared with those with no prior infection (13.8% infection rate for those previously uninfected and 4.9% infection rate for those previously infected), but noted that testing was limited in that the “Cleveland Clinic did not test asymptomatic patients unless they were admitted to hospital or undergoing a procedure/surgery” (Sheehan et al., March 15, 2021). These criteria for testing create uncertainty in determining the level of effectiveness previous infection provides against SARS-CoV-2 because many individuals with asymptomatic infections would not have been tested. Similar issues are also found in studies on populations in Italy, Belgium, and the UK (Vitale et al., May 28, 2021; Braeye et al., September 15, 2021; Pouwels et al., October 14, 2021).
To avoid the well-known problems with RT-PCRs defining previous infection, other studies have defined previous infection as testing positive for antibodies specific for SARS-CoV-2 (Lumley et al., February 11, 2021; Abu-Raddad et al., April 28, 2021; Hall et al., April 17, 2021). As noted above, previous infection does not necessarily result in a seropositive outcome; one study indicated that nearly a quarter (24%) of those infected with SARS-CoV-2 subsequently showed no sign of an immune response in SARS-CoV-2-specific antibody testing (Wei et al., July 5, 2021). Therefore, studies only considering seropositive individuals are in essence studying only the individuals most likely to have protection from reinfection. Lumley et al. (February 11, 2021) found that those having a seropositive response had almost an order of magnitude fewer infections (e.g., 0.11 adjusted incidence rate ratio). Likewise, Abu-Raddad et al. (April 28, 2021) found that seropositive individuals were reinfected less (0.7%) during their study period in comparison to seronegative individuals (3.09%). In addition to the bias associated with using antibodies to determine previous infection, the authors also noted that there may have been issues with being able to document cases with mild or no symptoms.
Hall et al. (April 17, 2021) cast a wider net by defining previous infection to include both positive RT-PCR tests and seropositivity. The researchers found that those who were considered previously infected had an 84% lower risk of infection compared to those who were unvaccinated with no record of infection. While the study does attempt to capture as many previously-infected individuals as possible, this does not actually address the weaknesses of each method. Those with less severe infections were less likely to have sought out or been able to get an RT-PCR test during the first surge, which is when an overwhelming number of the previous infections were recorded in this study (March through May, 2020). Additionally, the less severe infections that are most likely underrepresented in the study appear to be the ones that are less likely to produce seropositivity. Shenai et al. (September 21, 2021) pooled several studies with the above issues and concluded that immunity acquired through a previous infection from SARS-CoV-2 may be as protective as, or more protective than, the immunity afforded by vaccination to an individual without previous infection. However, authors of several of those underlying studies used in the analysis noted that their studies were limited by not having the capability to fully account for asymptomatic infections (the aforementioned Lumley et al., July 3, 2021; Gazit et al., August 25, 2021; Shrestha et al., June 19, 2021). As noted earlier, infection severity appears to be correlated with the robustness of immunity acquired through that infection, so the failure to account for asymptomatic infections may mean that this finding is related to the protection afforded by more severe disease. While pooled analyses can be utilized to make powerful observations, those observations are highly dependent upon the underlying studies not sharing the same methodological weakness which, in this case, was the studies' exclusion of asymptomatic infections.
Moreover, while the evidence suggests that severe infection may provide significant protection against reinfection in some cases (Milne et al., October 21, 2021), the level of protection cannot be determined on an individual basis. The studies discussed above are based on tests that show only whether a person was or was not infected and provide no information about the severity of the infection. Because the studies are likely biased towards those who had a relatively serious infection, their findings cannot be generalized to all individuals with prior infections.
RT-PCR and antibody testing are powerful tools with many clinical and research applications. However, the application of these tools cannot determine what degree of protection a particular individual has against SARS-CoV-2 without a great deal of additional study concerning thresholds establishing individual immunity. Therefore, these tools are not yet able to assist OSHA in making more nuanced findings about which workers who had COVID-19 previously are at grave danger. There is no established threshold to determine full protection from reinfection or a standardized methodology to determine infection severity or immune response. Studies use Ct threshold to approximate viral loads and infer disease severity, but that metric depends on many variables (e.g. time of collection during infection, quality of collection, handling of sample, specifics of the test protocol and materials, precision in performing the protocol) that are often of far less importance when it is used as a crude diagnostic to determine the presence of an infection. In other words, it is reasonable to say that the lower the Ct count, the greater the likelihood that an individual is at a lower reinfection risk; however, the Ct count is greatly dependent on the RT-PCR test used, and how different laboratories may run that test, which cannot be discerned. Similarly, research needs to be done to better identify the minimum protective threshold of anti-SARS-CoV-2 serum neutralizing antibodies (Milne et al., October 21, 2021). Thus, these studies currently do not allow OSHA to determine, with a reasonable degree of certainty, how much protection employees with prior infections have against reinfection.
Furthermore, while the research methodology itself raises challenges in making the grave danger determination, the implications of trying to apply investigative research methodology to clinical practice are even more difficult. The lack of standardized methods and standardized measures for immunity preclude their application to robust and reliable clinical practice. One major drawback discussed above is that, in contrast to vaccine studies where researchers know who was vaccinated with a standardized dosing regime, scientific inquiries likely will not be able to identify most individuals who were infected, the degree of disease experienced for those with a confirmed infection, and the immunity against reinfection. As of October 18, 2021, several RT-PCR assays have been authorized without standardization or assessment with respect to measuring disease severity (FDA, October 18, 2021). As noted above, the use of the Ct threshold to approximate viral loads and infer disease severity is unreliable. As the FDA notes, the same is true about antibody tests, which are considered to be poor indicators for individuals to use to determine whether they are protected from reinfection (FDA, May 19, 2021). There are many different SARS-CoV-2-specific antibody tests that focus on different specificity. Not only are the outcomes of these tests not directly comparable to each other, but the specificity of these tests is not related to any notion of protection against reinfection. It can be reasonably said that a greater antibody response means a greater likelihood of protection against infection, but, again, the science is not clear what those thresholds are and whether a threshold would be comparable between laboratories. At this point in time, even if OSHA determined that some individuals with prior infections are not at grave danger from exposure to SARS-CoV-2, there is no agreement on what indicators of infection might be sufficient to confer this level of immunity or how a healthcare provider or employer could document that a certain level of immunity had been achieved.
Based on the best available evidence described above, OSHA concludes that while some individuals who were infected with SARS-CoV-2 may have significant protection from subsequent infections, the level of protection afforded by infection may be significantly impacted by the severity of the infection and some previously infected individuals may have no future protection at all. In addition, given the limitations of the studies described above, there is considerable uncertainty as to whether any given individual is adequately protected against reinfection. Furthermore, the level of protection, if any, provided by a given person's SARS-CoV-2 infection cannot be ascertained based on currently-available testing methods. Therefore, OSHA finds that the requirements of this ETS are necessary to protect unvaccinated individuals who had prior SARS-CoV-2 infections from the grave danger from exposure to SARS-CoV-2.
OSHA recognizes that its finding regarding infection-induced immunity is being made in an area of inquiry that is currently on the “frontiers of scientific knowledge” ( Indus. Union Dep't, AFL-CIO v. Am. Petroleum Inst. , 448 U.S. 607, 656 (1980)). For these reasons, OSHA finds that those who have previously been infected with SARS-CoV-2 and are not yet fully vaccinated are at grave danger from SARS-CoV-2 exposure and that it is necessary to protect these workers via vaccination, or testing and the use of face coverings, under this standard. OSHA will continue to follow developments on this issue, however, and make appropriate adjustments to this ETS if the evidence warrants.
VI. Conclusion.
OSHA finds that many employees in the U.S. who are not fully vaccinated against COVID-19 face a grave danger from exposure to SARS-CoV-2 in the workplace. OSHA's determination is based on the severe health consequences of exposure to the virus, including death; powerful lines of evidence demonstrating the transmissibility of the virus in the workplace; and the prevalence of infections in employee populations.
With respect to the grave health consequences of exposure to SARS-CoV-2, OSHA has found that regardless of where and how exposure occurs, COVID-19 can result in death. Even for those who survive a SARS-CoV-2 infection, the virus can cause serious, long-lasting, and potentially permanent health effects. Serious cases of COVID-19 require hospitalization and dramatic medical interventions, and might leave employees with permanent and disabling health effects. Both death and serious cases of COVID-19 requiring hospitalization provide independent bases for OSHA's finding of grave danger. The evidence is clear that the safe and effective vaccines authorized and/or approved for use in the United States greatly reduce the likelihood of these severe outcomes.
The best available evidence on the science of transmission of the virus makes clear that SARS-CoV-2 is transmissible from person to person in shared workplace settings. The likelihood of transmission can be exacerbated by common characteristics of many workplaces, including working indoors, working with others for extended periods of time, poor ventilation, and close contact with potentially infectious individuals. The likelihood of transmission in the workplace is also exacerbated by the presence of unvaccinated workers, who are more likely than those who are vaccinated to be infected and transmit the virus to others. Every workplace SARS-CoV-2 exposure or transmission has the potential to cause severe illness or even death, particularly in unvaccinated workers. Taken together, the severe health consequences of COVID-19 and the evidence of its transmission in environments characteristic of the workplaces covered by this ETS demonstrate that exposure to SARS-CoV-2 represents a grave danger to unvaccinated employees in many workplaces throughout the country.
The existence of a grave danger to employees from SARS-CoV-2 is further supported by the toll the pandemic has already taken on the nation as a whole and the number of workers who remain unvaccinated. Although OSHA cannot state with precision the total number of workers in our nation who have contracted COVID-19 at work and became sick or died, COVID-19 has killed 723,205 people in the United States as of October 18, 2021 (CDC, October 18, 2021—Cumulative US Deaths). That death toll includes 131,478 people who were 18 to 64 years old, prime working age (CDC, October 18, 2021—Demographic Trends, Deaths by Age Group). OSHA estimates that there are over 26 million workers subject to the rule who remain unvaccinated at present and therefore are in grave danger. As a result of this ETS, the agency estimates that 72% of them will be vaccinated (see OSHA, October 2021c).
Current mortality data shows that unvaccinated people of working age have a 1 in 202 chance of dying when they contract COVID-19 (CDC, October 18, 2021—Demographic Trends, Cases by Age Group; Demographic Trends, Deaths by Age Group). As of October 18, 2021, close to 45 million people in the United States have been reported to have infections, and thousands of new cases were being identified daily (CDC, October 18, 2021—Daily Cases).One in 14 reported cases of COVID-19 in people ages 18 to 64 becomes severe and requires hospitalization (CDC, October 18, 2021—Demographic Trends, Cases by Age; Total Hospitalizations, by Age). Moreover, public health officials agree that these numbers fail to show the full extent of the deaths and illnesses from this disease, and racial and ethnic minority groups are disproportionately represented among COVID-19 cases, hospitalizations, and deaths (CDC, December 10, 2020; CDC, May 26, 2021; Escobar et al., February 9, 2021; Gross et al., October 2020; McLaren, June 2020; CDC, October 6, 2021). Given this context, OSHA is confident in its finding that exposure to SARS-CoV-2 poses a grave danger to the employees covered by this ETS.
The above analysis fully satisfies the OSH Act's requirements for finding a grave danger. Although OSHA usually performs a quantitative risk assessment based on extrapolations among exposure levels before promulgating a health standard under section 6(b)(5) of the OSH Act (29 U.S.C. 655(b)(5)), that type of analysis is not necessary in this situation. OSHA has most often invoked section 6(b)(5) authority to regulate exposures to chemical hazards involving much smaller populations, many fewer cases, extrapolations from animal evidence, long-term exposure, and delayed effects. In those situations, mathematical modelling is necessary to evaluate the extent of the risk at different exposure levels. The gravity of the danger presented by a disease with acute effects like COVID-19, on the other hand, is made obvious by a straightforward count of deaths and illnesses caused by the disease, which reach sums not seen in at least a century. The evidence compiled above amply supports OSHA's finding that SARS-CoV-2 presents a grave danger in American workplaces. In the context of ordinary 6(b) rulemaking, the Supreme Court has said that the OSH Act is not a “mathematical straitjacket,” nor does it require the agency to support its findings “with anything approaching scientific certainty,” particularly when operating on the “frontiers of scientific knowledge” ( Indus. Union Dep't, AFL-CIO v. Am. Petroleum Inst. , 448 U.S. 607, 655-56 (1980)). This is true a fortiori in the current national crisis, where OSHA must act to ensure employees are adequately protected from the hazard presented by the COVID-19 pandemic (see 29 U.S.C 655(c)(1)).The grave danger from SARS-CoV-2 represents the biggest threat to employees in OSHA's more than 50-year history. The threat applies to employees in all sectors covered by OSHA, including general industry, construction, maritime, agriculture, and healthcare. Having made the determination of grave danger, as well as the determination that an ETS is necessary to protect employees from exposure to SARS-CoV-2 (see Need for the ETS , Section III.B. of this preamble), OSHA is required to issue this standard to protect employees from getting sick or dying from COVID-19 acquired at work (see 29 U.S.C. 655(c)(1)).
References
Allen JG and Ibrahim AM. (2021, May 25). Indoor air changes and potential implications for SARS-CoV-2 transmission. JAMA 325(20): 2112-2113. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.5053. (Allen and Ibrahim, May 25, 2021)
Abu-Raddad LJ et al. (2021, May 1). SARS-Cov-2 antibody-positivity protects against reinfection for at least seven months with 95% efficacy. EClinicalMedicine, 2021. 35: p. 100861. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100861 . (Abu-Raddad et al., May 1, 2021)
Andrews et al. (2021, September 21). Vaccine effectiveness and duration of protection of Comirnaty, Vaxzevria and Spikevax against mild and severe COVID-19 in the UK. medRxiv preprint. doi:10.1101/2021.09.15.21263583. (Andrews et al., September 21, 2021)
Bajema KL et al. (2021, September 10). Effectiveness of COVIF-19 mRNA Vaccines Against COVID-19—Associated Hospitzalization—Five Veteran Affairs Medical Centers, United States February 1-August 6, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2021; 70: early release. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/pdfs/mm7037e3-H.pdf . (Bajema et al., September 10, 2021)
Bernal JL et al. (2021, August 12). Effectiveness of Covid-19 Vaccines against the B.1.617.2 (Delta) Variant. N Eng J Med. 2021 Aug 12; 385(7): 585-594. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2108891. (Bernal et al., August 12, 2021)
Braeye T et al. (2021, September 15). Vaccine effectiveness against infection and onwards transmission of COVID-19: Analysis of Belgian contact tracing data, January-June 2021. Vaccine, 2021. 39(39): p. 5456-5460. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2021.08.060. (Braeye et al., September 15, 2021)
Bruxvoort et al. (September 2, 2021). Real-World Effectiveness of the mRNA-1273 Vaccine Against COVID-19: Interim Results from a Prospective Observational Cohort Study. Lancet preprint. https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3916094. (Bruxvoort et al., September 2, 2021)
Bui D et al. (2020, August 17). Racial and ethnic disparities among COVID-19 cases in workplace outbreaks by industry sector—Utah, March 6-June 5, 2020. MMWR: 69: 1133-1138. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/69/wr/mm6933e3.htm. (Bui et al., August 17, 2020)
Bulfone TC et al. (2020, November 29). Outdoor Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 and Other Respiratory Viruses: A Systematic Review. (2020). The Journal of Infectious Diseases 223: 550-561. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiaa742. (Bulfone et al., November 29, 2020)
Cavanaugh A et al. (2021, August 13). Reduced Risk of Reinfection with SARS-CoV-2 After COVID-19 Vaccination—Kentucky, May-June 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2021; 70: 32. 1081-1082. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7032e1.htm. (Cavanaugh et al., August 13, 2021)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2020, December 10). COVID-19 Racial and Ethnic Health Disparities. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/community/health-equity/racial-ethnic-disparities/index.html. (CDC, December 10, 2020)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, April 19). Health equity considerations and racial and ethnic minority groups. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/community/health-equity/race-ethnicity.html. (CDC, April 19, 2021)
Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, May 7). Scientific Brief: SARS-CoV-2 Transmission. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/science/science-briefs/SARS-cov-2-transmission.html#print. (CDC, May 7, 2021)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021a, May 24). COVID data tracker. Trends in number of COVID-19 cases and deaths in the US reported to CDC, by state/territory: Trends in Total COVID-19 Deaths in the United States Reported to CDC. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#trends_dailytrendscases. (CDC, May 24, 2021a)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021b, May 24). COVID data tracker. Trends in number of COVID-19 cases and deaths in the US reported to CDC, by state/territory: Trends in Total COVID-19 Cases in the United States Reported to CDC. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#trends_dailytrendscases. (CDC, May 24, 2021b)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021c, May 24). COVID data tracker. Variant proportions. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#variant-proportions. (CDC, May 24, 2021c)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, May 26). Health disparities: Race and Hispanic origin. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nvss/vsrr/covid19/health_disparities.htm. (CDC, May 26, 2021)
Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, May 28). COVID Data Tracker Weekly Review: What's Up, Doc? https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/covid-data/covidview/past-reports/05282021.html#print. (CDC, May 28, 2021)
Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, June 25). COVID Data Tracker Weekly Review: Keep Variants at Bay. Get Vaccinated Today. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/covid-data/covidview/past-reports/06252021.html. (CDC, June 25, 2021)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, July 27). Estimated COVID-19 Burden. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/cases-updates/burden.html. (CDC, July 27, 2021)
Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, August 13). How to Protect Yourself & Others. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/prevention.html. (CDC, August 13, 2021)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, August 26). Delta Variant: What we know about the science. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/variants/delta-variant.html?s_cid=11512:cdc%20delta%20variant:sem.ga:p:RG:GM:gen:PTN:FY21. (CDC. August 26, 2021)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, September 1). Interim Public Health Recommendations for Fully Vaccinated People. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/fully-vaccinated-guidance.html. (CDC, September 1, 2021)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, September 15). Science brief: background rationale and evidence for public health recommendations for fully vaccinated people. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/science/science-briefs/fully-vaccinated-people.html. (CDC, September 15, 2021)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, September 21). Appendix A—Glossary of key terms. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/php/contact-tracing/contact-tracing-plan/appendix.html#print. (CDC, September 21, 2021)
Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, October 1). COVID Data Tracker Weekly Review: Three Point Shot. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/covid-data/covidview/index.html. (CDC, October 1, 2021)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, October 4). SARS-CoV-2 Variant Classifications and Definitions. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/variants/variant-info.html. (CDC, October 4, 2021)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, October 6). Health Disparities: Provisional Death Counts for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nvss/vsrr/covid19/health_disparities.htm. (CDC, October 6, 2021)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, October 18). COVID Data Tracker. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/. (CDC, October 18, 2021)
Cevik M et al. (2021, August 1). Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Transmission Dynamics Should Inform Policy. Clinical Infectious Disease 73(S2): S170-S176. doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa1442. (Cevik et al., August 1, 2021)
Chan E et al. (2010, December 14). Global capacity for emerging infectious disease detection. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 107(50), 21701-21706. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1006219107. (Chan et al., December 14, 2010)
Chen YH et al. (2021, June 4). Excess mortality associated with the COVID-19 pandemic among Californians 18-65 years of age, by occupational sector and occupation: March through November 2020. PLoS One 16(6): e0252454. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0252454. (Chen et al., June 4, 2021)
Chia PY et al. (2021, July 31). Virological and serological kinetics of SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant vaccine-breakthrough infections: A multi-center cohort study. medRxiv preprint. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.07.28.21261295. (Chia et al., July 31, 2021)
Colorado Department of Public Health & Environment (CDPHE)/Colorado State Emergency Operations Center (CSEOC) (2021, September 8). COVID-19 Outbreak data. https://covid19.colorado.gov/covid19-outbreak-data. (CDPHE/CSEOC, September 8, 2021)
Contreras Z et al. (2021, July). Industry Sectors Highly Affected by Worksite Outbreaks of Coronavirus Disease, Los Angeles County, California, USA, March 19-September 30, 2020. Emerg Infect Dis. 2021; 27(7): 1769-1775. doi:10.3201/eid2707.210425. (Contreras et al., July, 2021)
Dave D et al. (2020, December 2). The Contagion Externality of a Superspreading Event: The Sturgis Motorcycle Rally and COVID-19. South Econ J 2020 Dec 2; 10. doi:10.1002/soej.12475. (Dave et al., December 2, 2020)
de Gier B et al. (2021, August 5). Vaccine effectiveness against SARS-CoV-2 transmission and infections among household and other close contacts of confirmed cases, the Netherlands, February to May 2021. Eurosurveillance 26(31): 7-13. doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.31.2100640. (de Gier et al., August 5, 2021)
Dougherty K et al. (2021, July 16). SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617.2 (Delta) variant COVID-19 outbreak associated with a gymnastics facility—Oklahoma, April-May 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 70: 1004-1007. http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7028e2external icon. (Dougherty et al., July 16, 2021)
Egger F et al. (2021, March 18). Does playing football (soccer) lead to SARS-CoV-2 transmission? A case study of 3 matches with 18 infected football players. Science and Medicine in Football. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/24733938.2021.1895442. (Egger et al., March 18, 2021)
Elliott P et al. (2021, September 10). REACT-1 round 13 final report: Exponential growth, high prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 and vaccine effectiveness associated with Delta variant in England during May to July 2021. medRxiv preprint. doi:10.1101/2021.09.02.21262979. (Elliott et al., September 10, 2021)
Escobar GJ et al. (2021, February 9). Racial disparities in COVID-19 testing and outcomes. Annals of Internal Medicine. doi:10.7326/M20-6979. (Escobar et al., February 9, 2021).
Espenhain L et al. (2021, August 22). Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in Denmark: Nationwide, population-based seroepidemiological study. European Journal of Epidemiology (2021) 36: 715-725. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-021-00796-8. (Espenhain et al., August 22, 2021)
Eyre DW et al. (2021, September 29). The impact of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination on Alpha and Delta variant transmission. medRxiv preprint. doi:10.1101/2021.09.28.21264260. (Eyre et al., September 29, 2021)
Fennelly K. (2020, July 24). Particle sizes of infectious aerosols: Implications for infection control. Lancet Respir Med 2020; 8: 914-24. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30323-4. (Fennelly, July 24, 2020)
Fisman DN and Tuite AR. (2021, July 12). Progressive Increase in Virulence of Novel SARS-CoV-2 Variants in Ontario, Canada. medRxiv 2021.07.05.21260050. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.07.05.21260050. (Fisman and Tuite, July 12, 2021)
Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2020, December 11). Emergency use authorization for an unapproved product review memorandum (Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine/BNT 162b2 mRNA-1273). https://www.fda.gov/emergency-preparedness-and-response/coronavirus-disease-2019-covid-19/pfizer-biontech-covid-19-vaccine. (FDA, December 11, 2020)
Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2020, December 18). Emergency use authorization for an unapproved product review memorandum (Moderna COVID-19 vaccine/mRNA-1273). https://www.fda.gov/emergency-preparedness-and-response/coronavirus-disease-2019-covid-19/moderna-covid-19-vaccine. (FDA, December 18, 2020)
Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2021, February 26). Janssen COVID-19 vaccine. Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee February 26, 2021 Meeting Briefing Document. https://www.fda.gov/media/146219/download. (FDA, February 26, 2021)
Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2021, May 19). Antibody testing is not currently recommended to assess immunity after COVID-19 vaccination: FDA safety communication. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/safety-communications/antibody-testing-not-currently-recommended-assess-immunity-after-covid-19-vaccination-fda-safety. (FDA, May 19, 2021)
Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2021, October 18). In vitro diagnostics EUAs—Molecular diagnostic tests for SARS-CoV-2. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/coronavirus-disease-2019-covid-19-emergency-use-authorizations-medical-devices/in-vitro-diagnostics-euas-molecular-diagnostic-tests-SARS-cov-2. (FDA, October 18, 2021)
Fowlkes A et al. (2021, August 27). Effectiveness of COVID-19 Vaccines in Preventing SARS-CoV-2 Infection Among Frontline Workers Before and During B.1.617.2 (Delta) Variant Predominance—Eight U.S. Locations, December 2020-August 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 70: 1167-1169. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7034e4external icon. (Fowlkes et al., August 27, 2021)
Gazit S et al. (2021, August 25, 2021). Comparing SARS-CoV-2 natural immunity to vaccine-induced immunity: Reinfection versus breakthrough infections. medRxiv preprint. doi:10.1101/2021.08.24.21262415. (Gazit et al., August 25, 2021)
Geers D et al. (2021, May 25). SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern partially escape humoral but not T cell responses in COVID-19 convalescent donors and vaccine recipients. Science Immunology 2021 May 25; 6(59). doi:10.1126/sciimmunol.abj1750. (Geers et al., May 25, 2021)
Gold JAW et al. (2021, February 26). Georgia K-12 School COVID-19 Investigation Team. Clusters of SARS-CoV-2 Infection Among Elementary School Educators and Students in One School District—Georgia, December 2020-January 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 70(8):289-292. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7008e4. Erratum in: MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021 Mar 12; 70(10): 364. PMID: 33630823; PMCID: PMC8344983. (Gold et al., February 26, 2021)
Goldberg Y et al. (2021, August 30). Waning immunity of the BNT162b2 vaccine: A nationwide study from Israel. medRxiv preprint. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.08.24.21262423. (Goldberg et al., August 30, 2021)
Grannis SJ et al. (2021, September 10). Interim Estimates of COVID-19 Vaccine Effectiveness Against COVID-19-Associated Emergency Department or Urgent Care Clinic Encounters and Hospitalizations Among Adults During SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617.2 (Delta) Variant Predominance—Nine States, June-August 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2021; 70: early release. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7037e2.htm. (Grannis et al., September 10, 2021)
Griffin JB et al. (2021, August 27). SARS-CoV-2 Infections and Hospitalizations Among Persons Aged >16 Years by Vaccination Stats—Los Angeles County, California, May 1-July 25, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2021; 70(34): 1170-1176. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/pdfs/mm7034e5-H.pdf. (Griffin et al., August 27, 2021)
Gross CP et al. (2020, October). Racial and ethnic disparities in population-level COVID-19 mortality. Journal of General Internal Medicine 35(10): 3097-3099. doi:10.1007/s11606-020-06081-w. (Gross et al., October 2020)
Haas EJ et al. (2021, May 15). Impact and effectiveness of mRNA BNT162b2 vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 infections and COVID-19 cases hospitalizations, and deaths following a nationwide vaccination campaign in Israel: An observational study using national surveillance data. Lancet; 397: 1819-1829. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00947-8. (Haas et al., May 15, 2021)
Hales CM et al. (2020, February). Prevalence of Obesity and Severe Obesity Among Adults: United States, 2017-2018. National Center for Health Statistics No. 30. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/products/databriefs/db360.htm. (Hales et al., February, 2020)
Hall VJ et al. (2021, April 17). SARS-CoV-2 infection reates of antibody-positive compared with antibody-negative health-care workers in England: A large, multicenter, prospective cohort study (SIREN). Lancet, 2021. 397(10283): p. 1459-1469. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00675-9. (Hall et al., April 17, 2021)
Hansen CH et al. (2021, March 27). Assessment of protection against reinfection with SARS-CoV-2 among 4 million PCR-tested individuals in Denmark in 2020: A population-level observsational study. Lancet, 2021. 397(10280): p. 1204-1212. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00575-4. (Hansen et al., March 27, 2021)
Harris RJ et al. (2021, June 23). Effect of Vaccination on Household Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in England. N Eng J Med. 2021 Jun 23. doi:10.1056/NEJMc2107717. (Harris et al., June 23, 2021)
Hawaii State. (2021, August 19). State of Hawaii Weekly COVID-19 Cluster Report. https://health.hawaii.gov/coronavirusdisease2019/files/2021/08/Hawaii_COVID-19_BiWeekly_Cluster_Report_19-August-2021_FINAL.pdf. (Hawaii State, August 19, 2021)
Hawkins D et al. (2021, January 10). COVID-19 deaths by occupation, Massachusetts, March 1-July 31, 2020. American Journal of Industrial Medicine 2021: 1-7. doi:10.1002/ajim.23227. (Hawkins et al., January 10, 2021)
Herzberg J et al. (2021, June 13). SARS-CoV-2-antibody response in health care workers after vaccination or natural infection in a longitudinal observational study. medRxiv preprint. doi:10.1101/2021.06.09.21258648. (Herzberg et al., June 13, 2021)
Hetemäki I et al. (2021, July 29). An outbreak caused by the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant (B.1.617.2) in a secondary care hospital in Finland, May 2021. Euro Surveill 26(30): 2100636. doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.30.2100636. (Hetemäki et al., July 29, 2021)
Johnson C. (2021, September 20). COVID has killed about as many Americans as the 1918-19 flu. AP News. https://apnews.com/article/science-health-pandemics-united-states-coronavirus-pandemic-c15d5c6dd7ece88d0832993f11279fbb. (Johnson, September 20, 2021)
Jones B et al. (2021, February 11). SARS-CoV-2 transmission during rugby league matches: Do players become infected after participating with SARS-CoV-2 positive players? Br J Sports Med. doi:10.1136/bjsports-2020-103714. (Jones et al., February 11, 2021)
Julin CH et al. (2021, September 22). Household transmission of SARS-CoV-2; a prospective longitudinal study showing higher viral load and transmissibility of the Alpha variant compared to previous strains. medRxiv preprint. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.08.15.21261478. (Julin et al., September 22, 2021)
Kapoor DA et al. (2020). The Impact of Systematic Safety Precautions on COVID-19 Risk Exposure and Transmission Rates in Outpatient Healthcare Workers. Rev Urol 22: 3. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33239968. (Kapoor et al., 2020)
Keating D et al. (2021, September 15). The pandemic marks another grim milestone: 1 in 500 Americans have died of covid-19. Washington Post. https://www.washingtonpost.com/health/interactive/2021/1-in-500-covid-deaths/. (Keating et al., September 15, 2021)
Keehner J et al. (2021, September 1). Resurgence of SARS-CoV-2i Infection in a highly vaccinated health system workforce. N Engl J Med. 2021 Sep 1. doi:10.1056/NEJMc2112981. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 34469645. (Keehner et al., September 1, 2021)
Kirbiyik U et al. (2020, November 6). Network Characteristics and Visualization of COVID-19 Outbreak in a Large Detention Facility in the United States—Cook County, Illinois. MMWR 69: 44. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/69/wr/pdfs/mm6944a3-H.pdf. (Kirbiyik et al., November 6, 2020)
Lan FY et al. (2020, September 26). Association between SARS-CoV-2 infection, exposure risk and mental health among a cohort of essential retail workers in the USA. Occup Environ Med. doi:10.1136/oemed-2020-106774. (Lan et al., September 26, 2020)
Leclerc et al. (2021, April 28). What settings have been linked to SARS-CoV-2 transmission clusters? Wellcome Open Research 5: 83. doi:10.12688/wellcomeopenres.15889.2. (Leclerc et al., April 28, 2021)
Levine-Tiefenburn M et al. (2021, March 29). Initial report of decreased SARS-CoV-2 viral load after inoculation with the BNT162b2 vaccine. Nature Medicine. 27: 790-792. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-021-01316-7. (Levine-Tiefenbrun et al., March 29, 2021)
Levine-Tiefenburn M et al. (2021, September 1). Viral loads of Delta-variant SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infections following vaccination and booster with the BNT162b2 vaccine. medRxiv preprint. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.08.29.21262798. (Levine-Tiefenbrun et al., September 1, 2021)
Lewis D. (2021 March 30). Why indoor spaces are still prime COVID hotspots. Nature 592(7852): 22-25. doi:10.1038/d41586-021-00810-9. PMID: 33785914. (Lewis, March 30, 2021)
Li B et al. (2021, July, 12). Viral Infection and Transmission in a Large Well-Traced Outbreak Caused by the Delta SARS-CoV-2 Variant. medRxiv 2021.07.07.21260122. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.07.07.21260122. (Li et al., July 12, 2021)
Liu Y and Rocklov J. (2021, August 4). The reproductive number of the Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 is far higher compared to the ancestral SARS-CoV-2 virus. J Travel Med 2021 Aug 9; taab124. https://doi.org/10.1093/jtm/taab124. (Liu and Rocklov, August, 4, 2021)
Louisiana Department of Health (LDH). (2021, August 24). COVID-19 outbreaks. https://ldh.la.gov/index.cfm/page/3997. (LDH, August 24, 2021)
Lumley SF et al. (2021, July 3). An observational cohort study on the incidence of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection and B.1.1.7 variant infection in healthcare workers by antibody and vaccination status. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2021; ciab608. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciab608. (Lumley et al., July 3, 2021)
Lumley SF et al. (2021, February 11). Antibody Status and Incidence of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Health Care Workers. New England Journal of Medicine, 2020. 384(6): p. 533-540. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2034545. (Lumley et al., February 11, 2021)
Mack CD et al. (2021, January 29). Implementation and evolution of mitigation measures, testing, contact tracing in the National Football League, August 9-November 21, 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2021; 70(4): 130-135. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7004e2.htm. (Mack et al., January 29, 2021)
McLaren J. (2020, June). Racial disparity in COVID-19 deaths: Seeking economic roots with Census data. NBER Working Paper Series. Working Paper 27407. doi:10.3386/w27407. (McLaren, June 2020).
Miller JS et al. (2021, April 30). COVID-19 Outbreak Among Farmworkers—Okanogan County, Washington, May-August 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2021; 70(17): 617-621. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7017a3.htm. (Miller et al., April 30, 2021)
Milne et al. (2021, October 21). Does infection with or vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 lead to lasting immunity? Lancet Respir Med 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00407-0. (Milne et al., October 21, 2021)
Mlcochova P et al. (2021, June 22). SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617.2 Delta Variant Emergence and Vaccine Breakthrough. Research Square Platform LLC. 2021 Jun 22; doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-637724/v1. (Mlcochova et al., June 22, 2021)
Mora AM et al. (2021, September 15). Risk Factors Assoicated with SARS-CoV-2 Infection Among Farmworkers in Monterey County, California. JAMA Network Open: 4(9): e2124116. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.24116. (Mora et al., September 15, 2021)
Musser JM et al. (2021, July 22). Delta Variants of SARS-CoV-2 Cause Significantly Increased Vaccine Breakthrough COVID-19 Cases in Houston, Texas. medRxiv 2021.07.19.21260808; doi:10.1101/2021.07.19.21260808. (Musser et al., July 22, 2021)
Nanduri S et al. (2021, August 27). Effectiveness of Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna Vaccines in Preventing SARS-CoV-2 Infection Among Nursing Home Residents Before and During Widespread Circulation of the SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617.2 (Delta) Variant—National Healthcare Safety Network, March 1-August 1, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2021; 70(34): 1163-1166. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7034e3.htm. (Nanduri et al., August 27, 2021)
Naranbhai V et al. (2021, October 13). Comparative immunogenicity and effectiveness of mRNA-1273, BNT162b2 and Ad26.COV2.S COVID-19 vaccines. medRxiv preprint. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.07.18.21260732. (Naranbhai et al., October 13, 2021)
National Cancer Institute (NCI). (2015, April 29). Age and Cancer Risk. https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/causes-prevention/risk/age. (NCI, April 29, 2015)
National Institutes of Health (NIH). (2021, October 12). Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Treatment Guidelines. https://files.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/guidelines/covid19treatmentguidelines.pdf. (NIH, October 12, 2021)
National Insitute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS). (2021, September 2). Coronovirus and the Nervous System. https://www.ninds.nih.gov/Current-Research/Coronavirus-and-NINDS/nervous-system#complications. (NINDS, September 2, 2021)
Nishiura H et al. (2020, April 16). Closed environments facilitate secondary transmission of coronavirus disease 2019. medRxiv preprint. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.02.28.20029272. (Nishiura et al., April 16, 2020)
North Carolina Department of Health and Human Services (NCDHHS). (2021, August 30). COVID-19 Clusters in North Carolina. https://covid19.ncdhhs.gov/media/725/download. (NCDHHS, August 30, 2021)
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). (2021c, October). Health Impacts of the COVID-19 Vaccination and Testing ETS. (OSHA, October 2021c)
Officer Down Memorial Page (ODMP) (2021, September 14). 2021 Honor Roll of Heroes. https://www.odmp.org/search/year/2021. (ODMP, September 14, 2021). (ODMP, September 14, 2021)
Oregon Health Authority (OHA) (2021, September 1). COVID-19 Weekly Outbreak Report—September 1, 2021. https://www.oregon.gov/oha/covid19/Documents/DataReports/Weekly-Outbreak-COVID-19-Report-2021-09-01-FINAL.pdf?utm_medium=email&utm_source=govdelivery. (OHA, September 1, 2021)
Ortaliza J et al. (2021, August 27). COVID-19 continues to be a leading cause of death in the U.S. in August 2021. Peterson-KFF Health System Tracker. https://www.healthsystemtracker.org/brief/covid-19-continues-to-be-a-leading-cause-of-death-in-the-u-s-in-august-2021/. (Ortaliza et al., August 27, 2021)
Pascall DJ et al. (2021, August 24). The SARS-CoV-2 Alpha variant causes increased clinical severity of disease. medRxiv preprint. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.08.17.21260128. (Pascall et al., August 24, 2021)
Pasco RF et al. (2020, October 29). Estimated association of construction work with risks of COVID-19 infection and hospitalization in Texas. JAMA Network Open 3(10): e2026373. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.26373. (Pasco et al., October 29, 2020)
Pilz S et al. (2021, February 11). SARS-CoV-2 re-infection risk in Austria. Eur J Clin Invest, 2021. 51(4): p. e13520. doi:10.1111/eci.13520. (Pilz et al., February 11, 2021)
Planas D et al. (2021, August 12). Reduced sensitivity of SARS_CoV-2 variant Delta to antibody neutralization. Nature 596: 276-280. doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03777-9. (Planas et al., August 12, 2021)
Porter KA et al. (2021, April 30). COVID-19 among workers in the seafood processing industry: Implications for prevention measures—Alaska, March-October 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep; 70: 622-626. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7017a4.htm. (Porter et al., April 30, 2021)
Pouwels KB et al. (2021, October 14). Effect of Delta variant on viral burden and vaccine effectiveness against new SARS-CoV-2 infections in the UK. Nat Med (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-021-01548-7. (Pouwels et al., October 14, 2021)
Pray IW et al. (2021, January 29). Trends in Outbreak-Associated Cases of COVID-19—Wisconsin, March-November 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 70(4): 114-117. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7004a2. Erratum in: MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021 Feb 05; 70(5): 183. (Pray et al., January 29, 2021)
Psichogiou M et al. (2021, September 13). Comparative Immunogenicity of BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccine with Natural SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Vaccines 9(1017). doi:10.3390/vaccines9091017. (Psichogiou et al., September 13, 2021)
Public Health England. (2020, December 18). Factors contributing to risk of SARS-CoV-2 transmission associated with various settings. https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/phe-factors-contributing-to-risk-of-SARS-cov2-transmission-in-various-settings-26-november-2020. (Public Health England, December 18, 2020)
Qian et al. (2020, October 27). Indoor transmission of SARS-CoV-2. Indoor Air 31: 639-645. doi:10.1111/ina.12766. (Qian et al., October 27, 2020)
Riemersma KK et al. (2021, July 31). Vaccinated and unvaccinated individuals have similar viral loads in communities with a high prevalence of the SARS_CoV-2 delta variant. medRxiv preprint. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.07.31.21261387 . (Riemersma et al., July 31, 2021)
Riou J and Althaus CL. (2020, January 30). Pattern of early human-to-human transmission of Wuhan 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV), December 2019 to January 2020. Eurosurveillance 25(4): pii=2000058. https://doi.org/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.4.2000058. (Riou and Althaus, January 30, 2020)
Rosenberg ES et al. (2021, August 27). New COVID-19 Cases and Hospitalizations Among Adults, by Vaccination Status—New York, May 3-July 25, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2021; 70(34): 1150-1155. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7034e1.htm. (Rosenberg et al., August 27, 2021)
Rosenthal N et al. (2020, December 10). Risk Factors Associated With In-Hospital Mortality in a US National Sample of Patients With COVID-19. JAMA Netw Open. 2020 Dec 1; 3(12): e2029058. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.29058. (Rosenthal et al., December 10, 2020)
Saciuk Y et al. (2021, June 25). Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine effectiveness against SARS_CoV-2 infection: Findings from a large observational study in Israel. Lancet preprint. https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3868853. (Saciuk et al., June 25, 2021)
Sami S et al. (2021, March). Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in first responders and public safety personnel, New York City, New York, USA, May-July 2020. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 27(3), 796-804. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid2703.204340. (Sami et al., March 2021)
Sami S et al. (2021, April 9). Community Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 Associated with a Local Bar Opening Event—Illinois, February 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 70(14): 528-532. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7014e3. (Sami et al., April 9, 2021)
Scobie HM et al. (2021, September 17). Monitoring Incidence of COVID-19 Cases, Hospitalizations, and Deaths, by Vaccination Status—13 U.S. Jurisdictions, April 4-July 17, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2021; 70: early release. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7037e1.htm. (Scobie et al., September 17, 2021)
Self WH et al. (2021, September 17). Comparative effectiveness of Moderna, Pfizer-BioNTech, and Janssen (Johnson and Johnson) vaccines in preventing COVID-19 hospitalizations among adults without immunocompromising conditions—United States, March-August 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2021; 70: early release. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7038e1.htm. (Self et al., September 17, 2021)
Seppala E et al. (2021, September 2). Vaccine effectiveness against infection with the Delta (B.1.617.2) variant, Norway, April to August 2021. 26(35): 1-7. doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.35.2100793. (Seppala et al., September 2, 2021)
Shah ASV et al. (2021, September 10). Effect of Vaccination on Transmission of SARS-CoV-2. N Enf J Med. doi:10.1056/NEJMc2106757. (Shah et al., September 10, 2021)
Sheehan MM et al. (2021, March 15). Reinfection rates among patients who previously tested positive for COVID-19: A retrospective cohort study. Clin Infect Dis, 2021. doi:10.1093/cid/ciab234. (Sheehan et al., March 15, 2021)
Sheikh A et al. (2021, June 4). SARS-CoV-2 Delta VOC in Scotland: Demographics, risk of hospital admission, and vaccine effectiveness. The Lancet. 2021; 397(10293): 2461-2462. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(21)01358-1. (Sheikh et al., June 4, 2021)
Shenai MB et al. (2021, September 21). Equivalency of protection from natural immunity in COVID-19 recovered versus fully vaccinated persons: A systematic review and pooled analysis. medRxiv preprint. doi:10.1101/2021.09.12.21263461. (Shenai et al., September 21, 2021)
Shrestha NK et al. (2021, June 19). Necessity of COVID-19 vaccination in previously infected individuals. medRxiv preprint. doi:10.1101/2021.06.01.21258176. (Shrestha et al., June 19, 2021)
Singanayagam A et al. (2021, September 6). Community transmission and viral load kinetics of SARS-CoV-2 Delta (B.1.617.2) variant in vaccinated and unvaccinated individuals. Lancet preprint. doi:10.2139/ssrn.3918287. (Singanayagam et al., September 6, 2021)
Spencer J and and Jewett C. (2021, April 8). Lost on the Frontline. 12 months of Trauma: More than 3,600 US health workers died in COVID's first year. https://khn.org/news/article/us-health-workers-deaths-covid-lost-on-the-frontline/. (Spencer and Jewett, April 8, 2020)
Steinberg J et al. (2020, August 7). COVID-19 Outbreak among employees at a meat processing facility — South Dakota, March-April 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 69: 1015-1019. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm6931a2. (Steinberg et al., August 7, 2020)
Suhs T et al. (2021, July 23). COVID-19 Outbreak Associated with a Fitness Center—Minnesota, September-November 2020. Clin Infect Dis. 2021 Jul 23: ciab653. doi:10.1093/cid/ciab653. Epub ahead of print. (Suhs et al., July 23, 2021)
Taylor et al. (2021, October 22). Severity of Disease Among Adults Hospitalized with Laboratory-Confirmed COVID-19 Before and During the Period of SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617.2 (Delta) Predominance—COVID-NET, 14 States, January-August 2021. MMWR Early Release/October 22, 2021/70. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7043e1.htm . (Taylor et al., October 22, 2021).
Tennessee Department of Health (TDH). (2021, September 8). COVID-19 critical indicators. https://www.tn.gov/content/dam/tn/health/documents/cedep/novel-coronavirus/CriticalIndicatorReport.pdf. (TDH, September 8, 2021)
Twohig K et al. (2021, August 27). Hospital admission and emergency care attendance risk for SARS-CoV-2 delta (B.1.617.2) compared with alpha (B.1.1.7) variants of concern: A cohort study. The Lancet Infectious Disease. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00475-8 . (Twohig et al., August 27, 2021)
University of California San Diego (UCSD). (2021). Better Primary Care for You and Your Family. https://health.ucsd.edu/specialties/primary-care/Pages/default.aspx . (UCSD, 2021)
Vekaria et al. (2021, July 22). Hospital length of stay for COVID-19 patients: Data-driven methods for forward planning. BMC Infect Dis 21, 700 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-021-06371-6 . (Vekaria et al., July 22, 2021)
Vitale J et al. (2021, May 28). Assessment of SARS-CoV-2 refinfection 1 year after primary infection in a population in Lombardy, Italy. JAMA Intern Med, 2021. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.2959. (Vitale et al., May 28, 2021)
Vrangbaek K et al. (2021, April 29). Transition Measures: Testing. COVD-19 Health System Response Monitor: Denmark. https://www.covid19healthsystem.org/countries/denmark/livinghit.aspx?Section=1.5%20Testing&Type=Section . (Vrangbaek et al., April 29, 2021)
Wallace M et al. (2020, May 15). COVID-19 in Correctional and Detention Facilities—United States, February-April 2020. MMWR 69: 587-590. http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm6919e1 . (Wallace et al., May 15, 2020)
Waltenburg MA et al. (2021, January). Coronavirus disease among workers in a food processing, food manufacturing, and agriculture workplaces. Emerg Infect Dis 27(1): 243-249. https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/27/1/20-3821_article . (Waltenburg et al., January 2021)
Wang Z et al. (2021, July 15). Naturally enhanced neutralizing breadth against SARS_CoV-2 one year after infection. Nature 595: 426-431. doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03696-9. (Wang et al., July 15, 2021)
Ward JA et al. (2021, June). COVID-19 cases among employees of U.S. federal and state prisons. Am J Prev Med. 60(6): 840-844. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2021.01.018. Epub 2021 Feb 22. (Ward et al., June, 2021)
Washington State Department of Health (WSDH). (2021, September 8). Statewide COVID-19 outbreak report. (WSDH, September 8, 2021)
Weed M and Foad A. (2020, September 10). Rapid Scoping Review of Evidence of Outdoor Transmission of COVID-19. medRxiv preprint. doi:10.1101/2020.09.04.20188417. (Weed and Foad, September 10, 2020)
Wei J et al. (2021, July 5). Anti-spike antibody response to natural SARS-CoV-2 infection in the general population. medRxiv preprint. doi:10.1101/2021.07.02.21259897. (Wei et al., July 5, 2021)
Williams SV et al. (2021, July 8). An outbreak caused by the SARS-CoV-2 Delta (B.1.617.2) variant in a care home after partial vaccination with a single dose of the COVID-19 vaccine Vaxzevria, London, England, April 2021. Euro Surveill. 26(27): 2100626. doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.27.2100626. (Williams et al., July 8, 2021)
Wingate K. (2021, September 24). Five dead and 74 infected after COVID-19 outbreak in Washington nursing home. USA Today. https://www.usatoday.com/story/news/nation/2021/09/24/covid-outbreak-nursing-home-washington-kills-infects-dozens/5848804001/ . (Wingate, September 24, 2021)
Young-Xu Y et al. (2021, July 14). Coverage and effectiveness of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines among veterans. medRxiv preprint. doi:10.1101/2021.06.14.21258906. (Young-Xu et al., July 14, 2021)
B. Need for the ETS
This ETS is necessary to protect unvaccinated workers from the risk of contracting COVID-19, including its more contagious variants, such as the B.1.617.2 (Delta), at work. The rule protects workers through the most effective and efficient workplace control available: Vaccination. Additionally, this ETS is necessary to protect workers who remain unvaccinated through required regular testing, use of face coverings, and removal of infected employees from the workplace.
I. Events Leading to the ETS
This section describes the evolution of OSHA's actions to protect employees from the grave danger posed by COVID-19 and the agency's reasons for issuing this ETS at this time.
a. OSHA's 2020 Actions Regarding COVID-19
Beginning in early 2020, OSHA began to monitor the growing cases of the SARS-CoV-2 virus that were occurring around the country. Because scientific information about the disease, its potential duration, and ways to mitigate it were undeveloped, OSHA decided to monitor the situation. As noted below, OSHA subsequently issued numerous guidance documents advising interested employers of steps they could take to mitigate the hazard arising from the virus.
Also beginning in early 2020, OSHA received numerous petitions and supporting letters from members of Congress, unions, advocacy groups, and one group of large employers urging the agency to take immediate action by issuing an ETS to protect employees from exposure to the virus that causes COVID-19 (Scott and Adams, January 30, 2020; NNU, March 4, 2020; AFL-CIO, March 6, 2020; Menendez et al., March 9, 2020; Wellington, March 12, 2020; DeVito, March 12, 2020; Carome, March 13, 2020; SMART, March 30, 2020; Blumenthal et al., April 8, 2020; Murray et al., April 29, 2020; Luong, April 30, 2020; Novoa, June 24, 2020; Solt, April 28, 2020; Castro et al., April 29, 2020; Talbott and Adely, May 4, 2020; Public Citizen, March 13, 2020; LULAC, March 31, 2020; Meuser, May 1, 2020; Raskin, April 29, 2020; Cartwright et al., May 7, 2020; Frosh et al., May 12, 2020; Pellerin, March 19, 2020; Yborra, March 19, 2020; Owen, March 19, 2020; Brown et al., April 30, 2020; Price et al., May 1, 2020; ORCHSE, October 9, 2020). These petitions and supporting letters argued that many employees had been infected because of workplace exposures to the virus that causes COVID-19, and that immediate, legally enforceable action is necessary for protection. OSHA quickly began issuing detailed guidance documents and alerts beginning in March 2020 that helped employers to determine employee risk levels of COVID-19 exposure and made recommendations for appropriate controls. As explained in detail in Section IV. of the Healthcare ETS, 86 FR 32376, 32412-13 (June 21, 2021) and hereby included in the record for this ETS, 16 at the time, OSHA leadership believed that implementing a combination of enforcement tools, including guidance, existing OSHA standards, and the General Duty Clause, would provide the necessary protection for workers. OSHA also expressed concern that an ETS might unintentionally enshrine requirements that are subsequently proven ineffective in reducing transmission.
16 This adoption includes the citations in the referenced section of the Healthcare ETS, which are also included in the docket for this ETS.
When it decided not to issue an ETS in the spring of 2020, OSHA determined that the agency could provide sufficient employee protection against COVID-19 through enforcing existing workplace standards and the General Duty Clause of the OSH Act, coupled with issuing industry-specific, non-mandatory guidance. However, in doing so OSHA indicated that its conclusion that an ETS was not necessary was specific to that time, and that the agency would continue to monitor the situation and take additional steps as appropriate (see, e.g., OSHA, March 18, 2020 Letter to Congressman Scott (stating “[W]e currently see no additional benefit from an ETS in the current circumstances relating to COVID-19. OSHA is continuing to monitor this quickly evolving situation and will take the appropriate steps to protect workers from COVID-19 in coordination with the overall U.S. government response effort.” (emphasis supplied); DOL May 29, 2020 at 20 (stating “OSHA has determined this steep threshold [of necessity] is not met here, at least not at this time.” (emphasis supplied))).
In addition to the various petitions for rulemaking that were submitted to OSHA, the AFL-CIO filed a petition for a writ of mandamus with the U.S. Court of Appeals for the D.C. Circuit, requesting that the court compel OSHA to issue an ETS. (AFL-CIO, May 18, 2020). In its administrative decision and filing in that case, OSHA explained that the determination not to issue an ETS was based on the conditions and information available to the agency at that time and was subject to change as additional information indicated the need for an ETS. On June 11, 2020, the U.S. Court of Appeals for the D.C. Circuit issued a one paragraph per curiam order denying the AFL-CIO's petition to require OSHA to issue an ETS. To be clear, nothing in OSHA's prior position or the D.C. Circuit's decision in In re Am. Fed'n of Labor & Cong. of Indus. Orgs., No. 20-1158, 2020 WL 3125324 (D.C. Cir. June 11, 2020); rehearing en banc denied (July 28, 2020) precludes OSHA's decision to promulgate an ETS now. To the contrary, at an early phase of the pandemic, when vaccines were not yet available and when it was not yet known how extensive the impact would be on illness and death, the court decided not to second-guess OSHA's decision to hold off on regulation in order to see if its nonregulatory enforcement tools could be used to provide adequate protection against the virus. “OSHA's decision not to issue an ETS is entitled to considerable deference,” the court explained, noting “the unprecedented nature of the COVID-19 pandemic” and concluding merely that “OSHA reasonably determined that an ETS is not necessary at this time.” (Id., with emphasis added).
Employers do not have a reliance interest in OSHA's prior decision not to issue an ETS on May 29, 2020, which did not alter the status quo or require employers to change their behavior. See Dep't of Homeland Security v. Regents of the Univ. of California , 140 S. Ct. 1891, 1913-14 (2020). As OSHA indicated when it made the decision, the determination was based on the conditions and information available to the agency at that time and was subject to change as additional information indicated the need for an ETS. In light of the agency's express qualifications and the surrounding context, any employer reliance would have been unjustified and cannot outweigh the countervailing urgent need to protect workers covered by this ETS from the grave danger posed by COVID-19.
b. OSHA's Decision To Promulgate a Healthcare ETS
OSHA subsequently issued the Healthcare ETS to protect healthcare workers. 86 FR 32376. (June 21, 2021), codified at 29 CFR 1910.502. Looking back on a year of experience, OSHA found that its enforcement efforts had encountered significant obstacles, demonstrating that existing standards, regulations, and the General Duty Clause were inadequate to address the grave danger faced by healthcare employees. 86 FR 32415. In promulgating that ETS, OSHA recognized that “the impact of [COVID-19] has been borne disproportionately by the healthcare and healthcare support workers tasked with caring for those infected by this disease.” 86 FR 32377. Furthermore, states and localities had taken increasingly divergent approaches to workplace protections against COVID-19, making it clear that a federal standard was needed to ensure sufficient protection in all states. 86 FR 32377. Therefore, OSHA focused on the unique situation experienced by healthcare industry workers as the frontline caregivers and support workers for those suffering from COVID-19. See 86 FR 32376, 32411-12.
The Healthcare ETS requires employers to institute a suite of engineering controls, administrative controls, work practices, and personal protective equipment to combat the COVID-19 hazard. In the Preamble to the Healthcare ETS, OSHA observed that the development of safe and highly effective vaccines is a critical milestone in the nation's response to COVID-19, and that fully vaccinated persons have a greatly reduced risk of death, hospitalization and other health consequences. 86 FR 32396. The Healthcare ETS therefore includes provisions intended to encourage employees to become vaccinated, including a requirement for employers to provide reasonable paid leave for vaccination and recovery from any side effects. 86 FR 32415, 29 CFR 1910.502(m).
In the Healthcare ETS OSHA found that employees who work in covered healthcare workplaces are exposed to grave danger. 86 FR 32411. The agency also stated that in light of the effectiveness of vaccines, there was “insufficient evidence in the record to support a grave danger finding for non-healthcare workplaces where all employees are vaccinated. ” 86 FR 32396 (emphasis supplied). OSHA made no finding at that time regarding unvaccinated workers in non-healthcare workplaces.
No employer challenged the Healthcare ETS in court. The United Food and Commercial Workers Union (UFCW) together with the AFL-CIO filed a petition for review asserting that the rule should have gone further and included more industries in its scope (UFCW and AFL-CIO, June 24, 2021). That case is being held in abeyance pending the issuance of this ETS.
c. Subsequent Developments
The preamble to the Healthcare ETS notes that new COVID-19 variants might emerge that are more transmissible and cause more severe illness, but does not specifically mention the Delta Variant. See 86 FR 32384. Since publication of the Healthcare ETS, the Delta Variant has become the dominant form of the virus in the United States, causing large spikes in transmission, and surges of hospitalizations, and deaths, overwhelmingly among the unvaccinated (CDC, August 26, 2021; CDC, October 18, 2021—Variant Proportions, July Through October, 2021). As discussed in more detail in Grave Danger (Section III.A. of this preamble), the Delta Variant is at least twice as contagious as previous COVID-19 variants, and research suggests that it also causes more severe illness in the unvaccinated population (CDC, August 26, 2021). More infections mean more potential for exposures, including in workplaces (see Grave Danger, Section III.A. of this preamble, for further discussion on workplace outbreaks, clusters, and the general impact of transmission in the workplace.). More infections also mean more opportunities for the virus to undergo mutations to its genetic code, resulting in genetic variants with the potential to infect or re-infect people.
Some variability in infection rates in a pandemic is to be expected. While the curves of new infections and deaths can bend down after peaks, they often reverse course only to reach additional peaks in the future (Moore et al., April 30, 2020). Last year experts expressed concern that one or more subsequent waves of COVID-19 were possible in 2021 (Moore et al., April 30, 2020), especially with new variants of COVID-19 in circulation (Doughton, February 9, 2021). That potential tragically became a reality with the spread of the Delta Variant.
In June 2021, when the Healthcare ETS was published, COVID-19 transmission rates in the United States were at a low point, with the 7-day moving average of reported cases to be about 12,000. (CDC, August 26, 2021) However, by the end of July, the 7-day moving average reached over 60,000 as the Delta Variant spread across the country. (CDC, August 26, 2021). The 7-day moving average of reported cases at the beginning of September, 2021 exceeded 161,000 (CDC, October 18, 2021—Daily Cases). The most recent 7-day moving average of reported cases, while lower than the peak in late August and early September, is still over 85,000. (CDC, October 18, 2021—Daily Cases). These rates are also far higher than the rate when OSHA first declined to issue an ETS. (CDC, August 27, 2020 (20,401 confirmed cases per day on May 29, 2020)). The jump in infections has resulted in increased hospitalizations and deaths for unvaccinated workers, as discussed in detail in Grave Danger (Section III.A. of this preamble). While the most current data reflect a decline in new cases from the peak, the level of new cases remains high. CDC data shows that, as of October 18, 2021, approximately 85% of U.S. counties were experiencing “high” rates of community transmission, and another 10% were experiencing “substantial” community transmission (CDC, October 18, 2021—Daily Cases). Although the number of new detected cases is currently declining nationwide (see CDC, October 18, 2021—Community Transmission Rates), the agency cannot assume based on past experience that nationwide case levels will not increase again. Indeed, many northern states are currently experiencing increases in their rate of new cases (see CDC, October 18, 2021—Cases, Deaths, and Laboratory Testing (NAATS) by State; Slotnik, October 18, 2021), including Vermont, which set a new record for new COVID-19 cases in mid-October 2021 (Murray, October 18, 2021). Unless vaccination rates increase, the experience of northern states during this fall could presage a greater resurgence in cases this winter as colder weather drives more individuals indoors (see Firozi and Dupree, October 18, 2021).
While it is important to recognize that the Delta Variant has caused a spike in hospitalization and death in the United States, the SARS-CoV-2 virus, and not just a particular variant of that virus, is the hazard that workers face (see Grave Danger, Section III.A. of this preamble). Like any virus, SARS-CoV-2 has the ability to mutate over time and produce variants that may be more or less severe. Indeed, the World Health Organization and the CDC both track new variants that have continued to arise, such as the Lamda and Mu Variants (WHO, October 12, 2021; CDC, October 4, 2021). At this time, the CDC is tracking 11 different variants of COVID-19 (CDC, October 4, 2021). The World Health Organization has classified the Lambda and Mu variants as “variants of interest,” meaning that they have genetic changes that affect transmissibility, disease severity, immune escape, diagnostic or therapeutic escape; and have been identified to cause significant community transmission or multiple COVID-19 clusters, in multiple countries with increasing relative prevalence alongside increasing number of cases over time, or other apparent epidemiological impacts to suggest an emerging risk to global public health (WHO, October 12, 2021). Medical experts have also explained that vaccination reduces the opportunities for the virus to continue to mutate by reducing transmission and length of infection. And, there is no indication that future variants of COVID-19 will not be equally or even more dangerous than Delta without a higher rate of vaccination (Bollinger and Ray, July 23, 2021).
Meanwhile, evidence on the power of vaccines to safely protect individuals from infection and especially from serious disease has continued to accumulate. (CDC, May 21, 2021). For example, as explained in more detail in Grave Danger (Section III.A. of this preamble), multiple studies have demonstrated that vaccines are highly effective at reducing instances of hospitalization and death. In September the CDC compiled data from various studies that demonstrated overall authorized vaccines reduced death and severe case rates by 91 and 92% respectively in the population studied between April and July (Scobie et al., September 17, 2021, Table 1.). Additionally, the FDA granted approval to the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine for individuals 16 years of age and older on August 23, 2021 (FDA, August 23, 2021). In announcing the decision, the FDA Commissioner explained that “[w]hile this and other vaccines have met the FDA's rigorous, scientific standards for emergency use authorization, as the first FDA-approved COVID-19 vaccine, the public can be very confident that this vaccine meets the high standards for safety, effectiveness, and manufacturing quality the FDA requires of an approved product.” (FDA, August 23, 2021.)
Despite this important milestone, and the demonstrated effectiveness of the approved and authorized vaccines available to the public, millions of employees remain unvaccinated, approximately 39% of workers who are covered by this ETS (See Economic Analysis, Section IV.B. of this ETS). The rate of vaccination in the United States has slowed significantly from its peak in April, when the daily number of vaccination doses administered exceeded three million at one point. In recent months, daily vaccination rates have hovered around one million doses administered, or lower (CDC, October 18, 2021—Daily Vaccination Rate). The shortfall in vaccination leaves the nation's working population vulnerable to sickness, hospitalization and death, whether today under the Delta Variant, or under future variants that may arise (CDC, October 18, 2021—Daily Vaccination Rate); see also Grave Danger (Section III.A. of this preamble).
Moreover, in recent months, an increasing number of states have promulgated Executive Orders or statutes that prohibit workplace vaccination policies that require vaccination or proof of vaccination status, thus attempting to prevent employers from implementing the most efficient and effective method for protecting workers from the hazard of COVID-19 (see, e.g., Texas Executive Order GA-40, October 11, 2021; Montana H.B. 702, July 1, 2021; Arkansas S.B. 739, October 4, 2021 and Arkansas H.B. 1977, October 1, 2021; AZ Executive Order 2021-18, August 16, 2021). While some States' bans have focused on preventing local governments from requiring their public employees to be vaccinated or show proof of vaccination, the Texas, Montana, and Arkansas requirements apply to private employers as well. Other states have banned local ordinances that require employers to ensure that customers who enter their premises wear masks, thus endangering the employees who work there, particularly those who are unvaccinated (see, e.g., Florida Executive Order 21-102, May 3, 2021; Texas Executive Order GA-34, March 2, 2021).
In short, at the present time, workers are becoming sick and dying unnecessarily as a result of occupational exposures, when there is a simple and effective measure, vaccination, that can largely prevent those deaths and illnesses (see Grave Danger , Section III.A. of this preamble). Congress charged OSHA with responsibility for issuing emergency standards when they are necessary to protect employees from grave danger. 29 U.S.C. 655(c). In light of the current situation, OSHA is issuing this emergency rule.
References
American Federation of Labor and Congress of Industrial Organizations (AFL-CIO). (2020, March 6). “To Address the Outbreak of COVID-19: A Petition for an OSHA Emergency Temporary Standard for Infectious Disease.” (AFL-CIO, March 6, 2020)
American Federation of Labor and Congress of Industrial Organizations (AFL-CIO). (2020, May 18). “Emergency Petition For A Writ Of Mandamus, and Request For Expedited Briefing And Disposition, No. 19-1158.” (AFL-CIO, May 18, 2020)
An Act Prohibiting Discrimination Based on a Person's Vaccination Status or Possession of an Immunity Passport; Montana H.B. 702. (2021, July 1). https://leg.mt.gov/bills/2021/billpdf/HB0702.pdf. (Montana H.B. 702 July 1, 2021)
Arizona Executive Order 2021-18. (2021, August 16). https://azgovernor.gov/sites/default/files/eo_2021-18.pdf. (AZ Executive Order 2021-18, August 16, 2021)
Arkansas H.B. 1977. (2021, October 1). To Provide Employee Exemptions From Federal Mandates and Employer Mandates Related to Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19); and to Declare an Emergency. https://www.arkleg.state.ar.us/Bills/FTPDocument?path=%2FAMEND%2F2021R%2FPublic%2FHB1977-H1.pdf. (Arkansas H.B. 1977, October 1, 2021)
Arkansas S.B. 739. (2021, October 4). An Act Concerning Employment Issues Related to Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19); To Provide Employee Exemptions From Federal Mandates and Employer Mandates Related to Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19); To Declare and Emergency; and For Other Purposes. https://www.arkleg.state.ar.us/Bills/FTPDocument?path=%2FBills%2F2021R%2FPublic%2FSB739.pdf. (Arkansas S.B. 739, October 4, 2021)
Blumenthal R, Murray P, Duckworth T, Casey RP, Baldwin B, Brown S, Menendez R. (2020, April 8). “COVID-19 ETS Petition.” (Blumenthal et al., April 8, 2020)
Bollinger R and Ray R. (2021, July 23). New Variants of the Coronavirus: What You Should Know. Johns Hopkins Medicine. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/coronavirus/a-new-strain-of-coronavirus-what-you-should-know. (Bollinger and Ray, July 23, 2021)
Brown S, Murray P, Baldwin T, Bennet MF, Casey Jr. RP, Whitehouse S, Hirono MK, Blumenthal R, Van Hollen C, Masto CC, Sanders B, Reed J, Harris KD, Wyden R, Durbin RJ, Booker CA, Warren E, Leahy PJ. (2020, April 30). “COVID-19 ETS Petition.” (Brown et al., April 30, 2020)
Carome M. (2020, March 13). “Letter requesting an immediate OSHA emergency temporary standard for infectious disease.” (Carome, March 13, 2020)
Cartwright M, Kaptur M, Roybal-Allard L, Foster B. (2020, May 7). “COVID-19 ETS Petition.” (Cartwright et al., May 7, 2020)
Castro J, Espaillat A, Cárdenas T, Ocasio-Cortez A, Sablan GKC, Garcia J, Gallego R, Escobar V, Vargas J, Trahan L, Torres NJ, Correa L, Barragán ND, Serrano JE, Cisneros Jr. GR, Napolitano GF, Velazquez NM, Garcia SR, Grijalva R. (2020, April 29). “COVID-19 ETS Petition.” (Castro et al., April 29, 2020)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2020, August 27). Previous U.S. Covid-19 Case Data. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/covid-data/previouscases.html. (CDC, August 27, 2020)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, May 21). Interim Estimates of Vaccine Effectivness of Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna COVID-19 Vaccines Among Health Care Personnel—33 U.S. Sites, January-March 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7020e2.htm. (CDC, May 21, 2021)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, August 26). Delta Variant: What We Know About the Science. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/variants/delta-variant.html?s_cid=11512:cdc%20delta%20variant:sem.ga:p:RG:GM:gen:PTN:FY21. (CDC, August 26, 2021)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, October 4). SARS-CoV-2 Variant Classifications and Definitions. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/variants/variant-info.html. (CDC, October 4, 2021)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, October 18). COVID Data Tracker. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/. (CDC, October 18, 2021)
DeVito J. (2020, March 12). “Grant OSHA emergency standard for COVID-19 to protect frontline workers.” (DeVito, March 12, 2020)
Doughton S. (2021, February 9). Can a fourth wave of COVID-19 be prevented? Not likely, says Fred Hutch model—but the curve could be flattened. The Seattle Times. https://www.seattletimes.com/seattle-news/health/can-a-fourth-wave-of-covid-19-be-prevented-not-likely-says-fred-hutch-model-but-the-curve-could-be-flattened/. (Doughton, February 9, 2021)
Firozee P and Dupree J. (2021, October 18). Coronavirus numbers are dropping. More vaccinations can prevent a winter surge, Fauci says. The Washington Post. https://www.washingtonpost.com/health/2021/10/18/faucis-americans-can-prevent-winter-pandemic-surge/. (Firozee and Dupree, October 18, 2021)
Florida Executive Order 21-102. (2021, May 3). https://www.flgov.com/wp-content/uploads/orders/2021/EO_21-102.pdf. (Florida Executive Order 21-102, May 3, 2021)
Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (2021, August 23). FDA Approves First COVID-19 Vaccine. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-first-covid-19-vaccine. (FDA, August 23, 2021)
Frosh BE, Becerra X, Weiser PJ, Jennings K, Racine KA, Raoul K., Frey AM, Healey M., Nessel D, Ellison K, Ford AD, Grewal GS, Balderas H, James L, Rosenblum EF, Shapiro J, Neronha P, Herring MP, Ferguson B, Kaul JL. (2020, May 12). “COVID-19 ETS Petition.” (Frosh et al., May 12, 2020)
League of United Latin American Citizens (LULAC). (2020, March 31). “COVID-19 ETS Petition.” (LULAC, March 31, 2020)
Luong M. (2020, April 30). “Petition for an OSHA Emergency Temporary Standard for Airborne Infectious Diseases.” (Luong, April 30, 2020)
Menendez R, Murray P, Baldwin T, Brown S, Duckworth T, Booker CA, Warren E. (2020). “Urge DOL to Direct OSHA to Issue Comprehensive Emergency Temporary Standard (ETS) To Protect Workers Against COVID-19.” (Menendez et al., March 9, 2020)
Meuser D. (2020, May 1). “COVID-19 ETS Petition.” (Meuser, May 1, 2020)
Moore KA et al. (2020, April 30). COVID-19: The CIDRAP Viewpoint. Part 1: The Future of the COVID-19 Pandemic: Lessons Learned from Pandemic Influenza. University of Minnesota Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy. https://www.cidrap.umn.edu/sites/default/files/public/downloads/cidrap-covid19-viewpoint-part1_0.pdf. (Moore et al., April 30, 2020)
Murray E. (2021, October 18). Vermont sets new positive COVID daily case record as delta surge continues. Burlington Free Press. https://www.burlingtonfreepress.com/story/news/local/2021/10/18/covid-vermont-new-daily-positive-case-record-set/8505021002/. (Murray, October 18, 2021)
Murray P, Brown S, Heinrich M, Brown S, Blumenthal R., Markey EJ, Van Hollen C, Durbin RJ, Smith T, Whitehouse S, Wyden R, King Jr. AS, Kaine T, Reed J, Menedez R, Gillibrand K, Duckworth T, Warren E, Hassan MW, Casey Jr. RP, Sanders B, Udall T, Hirono MK, Harris KD, Feinstein D, Klobuchar A, Booker CA, Shaheen J, Cardin B. (2020, April 29). “COVID-19 ETS Petition.” (Murray et al., April 29, 2020)
National Nurses United (NNU). (2020, March 4). “National Nurses United Petitions OSHA for an Emergency Temporary Standard on Emerging Infectious Diseases in Response to COVID-19.” (NNU, March 4, 2020)
Novoa M. (2020, June 24). “Direct OSHA to issue an emergency temporary standard to protect all workers from COVID-19 now!” (Novoa, June 24, 2020)
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). Letter from Loren Sweatt to Congressman Robert C. “Bobby” Scott. (OSHA, March 18, 2020)
ORCHSE Strategies. (2020, October 9). “Petition to the U.S. Department of Labor—Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) for an Emergency Temporary Standard (ETS) for Infectious Disease.” (ORCHSE, October 9, 2020)
Owen M. (2020, March 19). “Grant OSHA emergency standard to protect frontline workers from COVID-19.” (Owen, March 19, 2020)
Pellerin C. (2020, March 19). “Grant OSHA emergency standard to protect frontline workers from COVID-19.” (Pellerin, March 19, 2020)
Price D, Pocan M, Schakowsky J, DeLauro RL. (2020, May 1). “COVID-19 ETS Petition.” (Price et al., May 1, 2020)
Public Citizen. (2020, March 13). “Support for AFL-CIO's Petition for an OSHA Emergency Temporary Standard for Infectious Disease to Address the Epidemic of Novel Coronavirus Disease.” (Public Citizen, March 13, 2020)
Raskin J. (2020, April 29). “COVID-19 ETS Petition.” (Raskin, April 29, 2020)
Scobie HM et al. (2021, September 17). Monitoring Incidence of COVID-19 Cases, Hospitalizations, and Deaths, by Vaccination Status—13 U.S. Jurisdictions, April 4-July 17, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2021; 70: early release. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7037e1.htm. (Scobie et al., September 17, 2021)
Scott RC and Adams AS. (2020, January 30). “Prioritize OSHA's Work on Infectious Diseases Standard/Immediate Issue of Temporary Standard.” (Scott and Adams, January 30, 2020)
Slotnik D. (2021, October 18). Coronavirus cases rise in the northern U.S. amid lower temperatures. The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/live/2021/10/18/world/covid-delta-variant-vaccine#covid-cases-us-winter. (Slotnik, October 18, 2021)
International Association of Sheet Metal, Air, Rail and Transportation Workers (SMART). (2020, March 30). “Petition for Emergency Standards.” (SMART, March 30, 2020)
Solt BE. (2020, April 28). “COVID-19 ETS Petition” (Solt, April 28, 2020)
Talbott R and Adely R. (2020, May 4). “Rulemaking Petition to the United States Department of Labor Occupational Safety and Health Administration.” (Talbott and Adely, May 4, 2020)
Texas Executive Order GA-34. (2021, March 2). https://open.texas.gov/uploads/files/organization/opentexas/EO-GA-34-opening-Texas-response-to-COVID-disaster-IMAGE-03-02-2021.pdf. (Texas Executive Order GA-34, March 2, 2021)
Texas Executive Order GA-40. (2021, October 11). https://gov.texas.gov/uploads/files/press/EO-GA-40_prohibiting_vaccine_mandates_legislative_action_IMAGE_10-11-2021.pdf. (Texas Executive Order GA-40, October 11, 2021)
United Food and Commercial Workers International Union (UFCW) and American Federation of Labor and Congress of Industrial Organizations (AFL-CIO). (2021, June 24). “Petition for Review, filed with the D.C. Circuit on June 24, 2021.” (UFCW and AFL-CIO, June 24, 2021)
Wellington M. (2020, March 12). “Grant OSHA emergency standard for COVID-19 to protect front-line workers” (Wellington, March 12, 2020)
World Health Organization (WHO). (2021, October 12). Tracking SARS-CoV-2 variants. https://www.who.int/en/activities/tracking-SARS-CoV-2-variants/. (WHO, October 12, 2021)
Yborra G. (2020, March 19). “Grant OSHA emergency standard to protect frontline workers from COVID-19.” (Yborra, March 19, 2020)
II. This ETS Is Necessary To Protect Unvaccinated Employees From Grave Danger
As explained at length in the preceding section ( Grave Danger , Section III.A. of this preamble), OSHA has determined that most unvaccinated workers across the U.S. economy are facing a grave danger posed by the COVID-19 hazard. 17 This new hazard has taken the lives of more than 725,000 people—many of them workers—in the United States since it was first detected in this country in early 2020. As the federal agency tasked with protecting the safety and health of workers in the United States, OSHA is required to act when it finds that workers are exposed to a grave danger. 29 U.S.C. 655(c)(1). OSHA now finds that this emergency temporary standard is necessary to protect employees who are unvaccinated. Asbestos Info. Ass'n, 727 F.2d at 423 (“failure to act does not conclusively establish that a situation is not an emergency . . . [when there is a grave danger to workers,] to hold that because OSHA did not act previously it cannot do so now only compounds the consequences of the Agency's failure to act.”). As explained in detail below, OSHA has determined that vaccination is the most effective control for abating the grave danger that unvaccinated employees face from the COVID-19 hazard. And, for workers who are not vaccinated, the use of testing, face coverings, and removal from the workplace, while not as effective as vaccination, is still effective and necessary.
17 As explained in the Grave Danger section, this ETS focuses on protecting unvaccinated workers from the grave danger that COVID-19 poses in the workplace. OSHA did not include fully vaccinated workers in its finding of grave danger because such workers are generally much better protected from the effects of COVID-19, and, in particular, the most severe effects, than workers who are unvaccinated. OSHA's action in adopting this ETS for unvaccinated workers does not mean that vaccinated workers do not face a significant risk from COVID-19, or that the OSH Act's general duty clause poses no obligation on employers to protect their vaccinated workers from COVID-19. Indeed, symptomatic infections can occur in fully vaccinated people, and COVID-19 therefore poses at least some risk to vaccinated workers. OSHA has requested comment on the risks faced by vaccinated workers from COVID-19, and what additional measures, if any, should be taken to protect both vaccinated and unvaccinated workers (see Request for Comments, Section I.B. of this preamble).
OSHA has determined that the best method for addressing the grave danger that COVID-19 poses to unvaccinated workers is to strongly encourage the use of the single most effective and efficient protection available: Vaccination. OSHA has long recognized the importance of vaccinating workers against preventable illnesses to which they may be exposed on the job. See 56 FR 64004, 64152 (Dec. 6, 1991) (discussing requirement in Bloodborne Pathogens standard for employer to make hepatitis B vaccine available to any employees with occupational exposure to blood and other potentially infectious materials). As explained in Grave Danger (Section III.A. of this preamble), COVID-19 vaccines do not completely eliminate the potential for infection, but significantly reduce the likelihood of infection, and in turn, transmission of the virus to others. Data from clinical trials for all three vaccines and observational studies for the two mRNA vaccines clearly establish that fully vaccinated persons have a greatly reduced risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection compared to unvaccinated individuals (see FDA, December 11, 2020; FDA, December 18, 2020; FDA, February 26, 2021).
More importantly, vaccination is the single most effective method for protecting workers from the most serious consequences of a COVID-19 infection: Hospitalization and death. Although symptomatic infections can occur in fully vaccinated people, they are less likely to occur, and are far less likely to result in severe health outcomes or death. As discussed in Grave Danger (Section III.A. of this preamble), studies have established that the available COVID-19 vaccines are highly effective at preventing hospitalization, and even more effective at preventing death. For example, one study found that unvaccinated adults age 18 to 49 were 15.2 times more likely to be hospitalized and 17.2 times more likely to die of COVID-19 than fully vaccinated people in the same age range, and unvaccinated adults age 50 to 64 were 10.9 times more likely to be hospitalized and 17.9 times more likely to die than their fully vaccinated peers (Scobie et al., September 17, 2021). The New York Times reported on October 1, 2021, that of the approximately 100,000 individuals who died of COVID-19 since mid-June 2021, less than 3% had been identified by the CDC as vaccinated individuals (Boseman and Leatherby, October 1, 2021).
Vaccines are also uniquely effective when compared to non-pharmaceutical methods for controlling exposure to COVID-19 at the workplace. To be sure, non-pharmaceutical controls play an important role in employers' efforts to prevent exposure to the virus; as discussed in detail earlier, OSHA has, throughout the pandemic, advised employers to implement various administrative, engineering, and other controls to reduce workplace exposure to the virus. And, for certain work settings in the healthcare industry where people with COVID-19 are reasonably expected to be present, OSHA both encouraged vaccination and mandated a suite of protections, many of which involve physical controls (see 29 CFR 1910.502). Indeed, workers who work indoors and near others are best protected from COVID-19 when they are fully vaccinated and their exposure to COVID-19 is reduced (to the extent possible) by non-pharmaceutical controls.
Non-pharmaceutical controls, however, focus on preventing employee exposure to the virus, and do not directly affect an employee's immune response if exposure to the virus does occur. Additionally, non-pharmaceutical controls often rely on the actions of individuals and/or the integrity of equipment to be effective; for example, to use PPE to control exposure, a worker must correctly don appropriate PPE each time there is potential exposure, must properly clean, store, and maintain the PPE between uses, and must replace the PPE when it is no longer effective (see, e.g., 29 CFR 1910.132 (general PPE requirements in general industry workplaces)). Accordingly, OSHA standards have always followed the principle of the hierarchy of controls, under which employers must control hazards by means other than PPE whenever feasible, and PPE is a supplementary control. See e.g. , 29 CFR 1910.134(a); 29 CFR 1910.1030(d)(2).
Physical distancing requires workers to maintain constant awareness of their environment in order to avoid coming into close proximity with colleagues, customers, or other individuals, even though the realities of their jobs and/or the design of the workplace may be unaccommodating to that effort. Requiring employees to examine themselves for signs and symptoms consistent with SARS-CoV-2 infection before reporting to work is prone to human error and entirely ineffective when the employee is infected but asymptomatic or pre-symptomatic.
In contrast, a worker is considered fully vaccinated after completing primary vaccination with a COVID-19 vaccine, or the second dose of any combination of two doses of a COVID-19 vaccine that is approved, authorized, or listed as a two-dose primary vaccination by the FDA or WHO (see the Summary and Explanation for paragraph (c), Section VI.C. of this preamble). Once fully vaccinated, a worker enjoys automatic and long-lasting benefits; namely, a drastic reduction in the risk of severe health effects or death. The vaccine works by bolstering the worker's immune system and does not depend on the worker's acumen or actions to afford its protection. Moreover, where an employer implements one or more non-pharmaceutical controls at the workplace, vaccination provides workers with a backstop of protection that greatly reduces their risk of serious health effects if they are exposed to the virus despite the presence of other controls. Vaccination thus ensures that workers need not rely on other factors, be it the workplace environment, the effectiveness of equipment, or the actions of other individuals, to be substantially protected from the worst potential outcomes of a COVID-19 infection.
This ETS focuses on encouraging vaccination because it is the most efficient and effective method for addressing the grave danger. Vaccination is patently appropriate and feasible for almost every worker in all industries, and will drastically reduce the risk that unvaccinated workers will suffer the serious health outcomes associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection. As described in Section III.A. of this preamble ( Grave Danger ), employees who are unvaccinated are in grave danger from the SARS-CoV-2 virus, but employees who are fully vaccinated are not. Since it is the lack of vaccination that results in grave danger, vaccination will best allay the grave danger. This ETS, which is designed to strongly encourage vaccination, is thus “necessary to protect employees” from a grave danger. 29 U.S.C. 655(c).
OSHA continues to encourage employers to implement additional controls that may be appropriate to eliminate exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 virus at their workplace, but, as discussed further below, OSHA has not required employers to implement a comprehensive and multilayered set of COVID-19 exposure controls in this ETS. This decision reflects the extraordinary and exigent circumstances have required OSHA to immediately promulgate this emergency temporary standard. Although OSHA was able to design a comprehensive infection prevention program for the specific healthcare settings to which the June 2021 Healthcare ETS applied, this rule encompasses all industries covered by the OSH Act, and targets unvaccinated workers in any indoor work setting not covered by the Healthcare ETS where more than one person is present. Crafting a multi-layered standard that is comprehensive and feasible for all covered work settings, including mixed settings of vaccinated and unvaccinated workers, is an extraordinarily challenging and complicated undertaking, yet the grave danger that COVID-19 poses to unvaccinated workers obliges the agency to act as quickly possible. As discussed above, OSHA has identified vaccination as the single most efficient and effective means for removing an unvaccinated worker from the grave danger.
Given the urgency of the rulemaking, and the singular effectiveness of vaccination in removing unvaccinated workers from the grave danger, OSHA is promulgating this ETS to immediately address the grave danger that COVID-19 poses to unvaccinated workers by strongly encouraging vaccination. As discussed in Pertinent Legal Authority (Section II. of this preamble), a “grave danger” represents a risk greater than the “significant risk” that OSHA must show in order to promulgate a permanent standard under section 6(b) of the OSH Act, 29 U.S.C. 655(b). OSHA will consider whether it is necessary to require additional controls to avert a significant risk of harm in the rulemaking proceedings that follow this ETS. OSHA directs employers to its website, www.osha.gov/coronavirus , and the CDC's website, www.cdc.gov/coronavirus , for guidance on the engineering, administrative, and other exposure controls that may be effective and appropriate for their workplace.
OSHA expects that, by strongly encouraging vaccination, this ETS will have a positive impact on worker health. As discussed above, millions of workers remain unvaccinated and are presently exposed to risks of hospitalization and death many times higher than their vaccinated coworkers. Although predicting the health impact of this ETS is particularly challenging, given the ever-changing nature of the pandemic and the many factors that may motivate workers to become fully vaccinated, OSHA has attempted to quantify the potential number of hospitalizations and fatalities that this ETS could avert by increasing workforce vaccination rates (see OSHA, October 2021c). OSHA has estimated that, as a result of the ETS, over 6,500 fewer currently unvaccinated workers will die from COVID-19 over the next six months. OSHA also estimates that this ETS will prevent over 250,000 currently unvaccinated workers from being hospitalized during that same time period. Even if OSHA's estimate does not prove to be precisely accurate, OSHA is confident that this ETS will save hundreds of lives and prevent thousands of workers from becoming severely ill.
a. OSHA Finds It Necessary To Strongly Encourage Vaccination
Despite the proven safety and efficacy of the available COVID-19 vaccines, many workers remain unvaccinated and are currently exposed to a grave danger. As discussed in Grave Danger (Section III.A. of this preamble), countless COVID-19 outbreaks have occurred in myriad work settings where employees come into contact with others, and in recent weeks, the majority of states in the U.S. have experienced what CDC defines as high or substantial community transmission, indicating that there is a clear risk of the virus being introduced into and circulating in workplaces (CDC, October 18, 2021—Community Transmission Rates). As of October 18, 2021, more than 184 million people in the United States have been fully vaccinated, but only 68.5% of people ages 18 years or older are fully vaccinated (CDC, October 18, 2021—Fully Vaccinated). OSHA has estimated that approximately 62.4% percent of adults aged 18-74 within the scope of this ETS are either fully vaccinated or received their first vaccine dose during the previous two weeks, leaving approximately 31.7 million unvaccinated ( i.e. , not fully vaccinated and did not receive a first dose with in the past two weeks) (see Economic Analysis , Section IV.B. of this preamble, Table IV.B.7). Meanwhile, the rate of new vaccinations has slowed considerably; on October 15, 2021, the 7-day moving average number of administered vaccine doses reported to the CDC per day was 841,731 doses, a steep reduction from the peak 3,448,156 dose average that the CDC reported on April 11, 2021 (CDC, October 18, 2021—Weekly Review).
Given the pervasiveness of the virus in workplaces across the country and the unparalleled efficacy of vaccines at preventing serious health effects, OSHA finds it necessary to strongly encourage vaccination. Encouraging vaccination is principally necessary to reduce the likelihood that workers who are infected by the SARS-CoV-2 virus will suffer the worst outcomes of an infection (hospitalization and death). Put simply, the single best method for protecting an unvaccinated worker from the serious health consequences of a COVID-19 infection is for that worker to become fully vaccinated.
Additionally, encouraging vaccination is necessary to reduce the overall prevalence of the SARS-CoV-2 virus at workplaces. Because vaccinated workers are less likely than unvaccinated workers to be infected by the virus, they are less likely to spread the virus to others at their workplace, including to unvaccinated coworkers. Increasing workforce vaccination rates will therefore reduce the risk that unvaccinated workers will be infected by a coworker.
Evidence shows that mandating vaccination has proven to be an effective method for increasing vaccination rates, and that vaccination mandates have generally been more effective than merely encouraging vaccination. Significant numbers of workers would get vaccinated if their employers required it, and many workers who were vaccinated over the last four months were motivated by their employer requiring vaccination. The Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF) vaccine monitor, an ongoing research project tracking the public's attitudes and experiences with COVID-19 vaccinations, conducted a survey from September 13 to September 22, 2021, among a nationally representative random digit dial telephone sample of 1,519 adults ages 18 and older, and found that those who received their first dose of a COVID-19 vaccine after June 1, 2021 were motivated by mandates of various sorts, including one in five (19%) who say a major reason was that their employer required it (KFF, September 2021). A survey conducted by Change Research from August 30 to September 2, 2021 regarding Americans' views on COVID-19 vaccines found that among the 1,775 respondents, “one of the things that was most likely to lead someone to get vaccinated was if their employer required it” (Towey, September 27, 2021).
Vaccine mandates imposed by state governments and large employers have also demonstrated the effectiveness of mandates in increasing vaccination rates. For example, when Tyson Foods announced its vaccination requirement in early August 2021, only 45% of its workforce had received a vaccination dose, but as of September 30, 2021, the New York Times reported that has increased to 91% (White House, October 7, 2021; Hirsch, September 30, 2021). Similarly, United Airlines reported that 97% of its U.S.-based employees were fully vaccinated against COVID-19 within a week of the deadline of the company's vaccination mandate, and the 3% who were not fully vaccinated included several employees who sought a medical or religious exemption from vaccination (The Associated Press, September 22, 2021). In Washington State, the weekly vaccination rate increased 34% after the Governor announced vaccine requirements for state workers (White House, October 7, 2021). The success of these COVID-19 vaccination mandates comports with the National Safety Council's recent finding that employers that instituted a COVID-19 vaccination mandate produced a 35% increase in employee vaccination (NSC, September 2021). Similarly, the White House recently reported that its analysis of vaccination requirements imposed by healthcare systems, educational institutions, public-sector agencies, and private businesses demonstrated that such requirements increased their vaccination rates by more than 20 percentage points and have routinely seen their share of fully vaccinated workers rise above 90 percent (White House, October 7, 2021).
Given the effectiveness of vaccination mandates in increasing vaccination rates, OSHA expects that, in most instances, an employer implementing a policy that requires all employees to be vaccinated will be the most effective approach for increasing the vaccination rate of its employees and ensuring that they have the best protection available against the worst consequences of a COVID-19 infection. Although OSHA may well have the authority to impose a vaccination mandate, OSHA has decided against pursuing strict vaccination requirement and has instead crafted the ETS to strongly encourage vaccination. Employers are in the best position to understand their workforces and the approach that will work most effectively with them to secure employee cooperation and protection. OSHA's traditional practice when including medical procedures, such as medical surveillance testing and vaccinations, in its health standards has been to require the employer to make the medical procedure available to employees, and has viewed mandating those procedures as a measure to avoid if possible. For example, when the agency promulgated its standard regulating occupational exposure to lead, OSHA considered mandating that employees participate in physical examinations and biological monitoring, but ultimately required employers to make them available to employees (see 43 FR 54354, 54450 (Nov. 21, 1978)). OSHA decided against mandating those procedures in part because it believed a voluntary approach would elicit more effective employee participation in the medical program and in part because of the agency's concerns about the Government intruding into a private and sensitive area of workers' lives (43 FR at 54450-51). OSHA has followed that same approach of requiring employers to “provide” or “make available” medical procedures to employees in numerous subsequent standards, such as the standards for asbestos (29 CFR 1910.1001), benzene (1910.1028), cotton dust (1910.1043), and formaldehyde (1910.1048).
OSHA adhered to this approach when it promulgated the Bloodborne Pathogens standard. The agency considered mandating a Hepatitis B vaccination, but instead required employers to make the Hepatitis B vaccination available to employees. 56 FR 64004, 64155 (Dec. 6, 1991); 29 CFR 1910.1030(f)(1)(i), (f)(2)(i). OSHA explained that the agency may have the legal authority to mandate vaccination, but believed that, under the circumstances, a voluntary vaccination program would “foster greater employee cooperation and trust in the system” and “enhance [ ] compliance while respecting individuals' beliefs and rights to privacy.” 56 FR at 64155.
In keeping with this traditional practice, the agency has stopped short of including a strict vaccination mandate with no alternative compliance option in this ETS. OSHA has never done so, and if it were to take that step, OSHA believes it more prudent to do so where the agency has ample time to fully assess the potential ramifications of imposing a vaccination mandate on covered employers and employees. Here, exigent circumstances demand that OSHA take immediate action to protect workers from the grave danger posed by COVID-19, but OSHA has not had a full opportunity to study the potential spectrum of impacts on employers and employees, including the economic and health impacts, that would occur if OSHA imposed a strict vaccination mandate with no alternative compliance option. Moreover, employers in their unique workplace settings may be best situated to understand their workforce and the strategies that will maximize worker protection while minimizing workplace disruptions. These considerations persuade the agency that this ETS should afford employers some flexibility in the form of an alternative option to strictly mandating vaccination. In light of the unique and grave danger posed by COVID-19, OSHA has requested comment on whether a strict vaccination mandate is warranted and the agency will consider all the information it receives as it determines how to proceed with this rulemaking (see Request for Comment , Section I.B. of this preamble).
Although this ETS does not impose a strict vaccination mandate, OSHA has determined that, to adequately address the grave danger that COVID-19 poses to unvaccinated workers, a more proactive approach is necessary than simply requiring employers to make vaccination available to employees. None of the standards that OSHA promulgated prior to this year concerned an infectious agent as readily transmissible as COVID-19. Standards like the Lead standard do not concern infectious agents that can be transmitted between individuals at a workplace; accordingly, the medical procedures that employers are required to make available under those standards are solely aimed at protecting the health of the worker who is undergoing the procedure. The Bloodborne Pathogens standard concerned exposure to infectious biological agents (Hepatitis B and HIV) that can be transmitted between individuals, but the potential for those agents to be transmitted between workers is minimal in comparison to the SARS-CoV-2 virus; Hepatitis B and HIV are transmitted through blood and certain body fluids, whereas the SARS-CoV-2 virus spreads through respiratory droplets that can travel through the air from worker-to-worker (see Grave Danger , Section III.A. of this preamble). Vaccination against COVID-19 is thus particularly important in reducing the potential for workers to become infected and spread the virus to others at the workplace, in addition to protecting the worker from severe health outcomes if they are infected. Moreover, the ease with which the SARS-CoV-2 virus spreads between workers makes it more urgent for workers to be vaccinated, and this urgency contributes to the agency's decision to strongly encourage vaccination.
Accordingly, to further the goal of increasing workforce vaccination rates, this ETS requires employers to implement a mandatory vaccination policy unless they adopt a policy in which employees may either be fully vaccinated or regularly tested for COVID-19 and wear a face covering in most situations when they work near other individuals. Employers have the duty under the OSH Act to provide safe workplaces to their employees, including protecting employees from known hazards by complying with occupational safety and health standards (see 29 U.S.C. 654), and this ETS therefore provides employers with two compliance options for protecting unvaccinated workers from the grave danger posed by COVID-19. But while this ETS offers employers a choice in how to comply, OSHA has presented implementation of a vaccination mandate as the preferred compliance option; as discussed above, vaccine mandates have proven to be effective in increasing vaccination rates, and OSHA expects that, in most instances, implementing a vaccination mandate will be the most effective method for increasing a workforce's vaccination rate. As discussed below, OSHA also recognizes that requiring that all employees be vaccinated provides more protection to vaccinated workers than regularly testing unvaccinated workers for COVID-19 and requiring them to wear face coverings when they work near others. This ETS will preempt inconsistent state and local requirements, including requirements that ban or limit employers' authority to require vaccination (see the Summary and Explanation for paragraph (a), Section VI.A. of this preamble), and will therefore provide the necessary legal authorization to covered employers to implement mandatory vaccination policies, if they choose to comply in this preferred manner.
Although the ETS does not require all covered employers to implement a mandatory vaccination policy, OSHA expects that employers that choose that compliance option will enjoy advantages that employers that opt out of the vaccination mandate option will not. Most obviously, employers with a mandatory vaccination policy will enjoy a dramatically reduced risk that their employees will become severely ill or die of a COVID-19 infection. In addition, employers who implement a vaccination mandate will likely have fewer workers temporarily removed from the workplace due to a COVID-19 positive test; this rule requires all covered employers to remove from the workplace any employee who tests positive for COVID-19 or receives a diagnosis of COVID-19 (see the Summary and Explanation for paragraph (h), Section VI.H. of this preamble), and because vaccinated workers are less likely than unvaccinated workers to be infected by the virus, OSHA expects employers with a mandatory vaccination policy will be statistically less likely to be obliged to remove a COVID-positive employee from the workplace in accordance with paragraph (h)(2). Additionally, only employers who decline to implement a mandatory vaccination program are required by the rule to assume the administrative burden necessary to ensure that unvaccinated workers are regularly tested for COVID-19 and wear face coverings when they work near others.
Where employers opt out of implementing a mandatory vaccination program, the ETS encourages employees to elect to be fully vaccinated. As discussed in the Summary and Explanation for paragraph (f) (Section VI.F. of this preamble), the ETS requires all covered employers to support vaccination by providing employees with reasonable time, including up to four hours of paid time, to receive each vaccination dose, and reasonable time and paid sick leave to recover from vaccination side effects. Many workers have been deterred from receiving vaccination by fears of missing work and/or losing pay to obtain vaccination and/or recover from side effects (see Section VI.F. of this preamble; see, e.g. , KFF, May 6, 2021; KFF, May 17, 2021), and OSHA finds that this employer support is necessary to ensure that employees can become fully vaccinated without concern that they will be sacrificing pay or their jobs to do so.
All covered employers are required by the ETS to bear the cost of providing up to four hours of paid time and reasonable paid sick leave needed to support vaccination, but where an employee chooses to remain unvaccinated, the ETS does not require employers to pay for the costs associated with regular COVID-19 testing or the use of face coverings (see the Summary and Explanation for paragraphs (g) and (i), Sections VI.G. and VI.I. of this preamble). In some cases, employers may be required to pay testing and/or face covering costs under other federal or state laws or collective bargaining obligations, and some may choose to do so even without such a mandate, but otherwise employees will be required to bear the costs if they choose to be regularly tested and wear a face covering in lieu of vaccination.
This ETS more strongly encourages vaccination than the June 2021 Healthcare ETS. OSHA designed the Healthcare ETS, which addresses the grave danger that COVID-19 poses workers in specific health care settings where COVID-19-positive individuals are reasonably likely to be present, to encourage vaccination (see 86 FR at 32415, 32423, 32565, 32597). Specifically, the Healthcare ETS encourages vaccination by requiring employers to provide employees reasonable and paid time to receive vaccination doses and recover from side effects (29 CFR 1910.502(m)), and by exempting from its scope “well-defined hospital ambulatory care settings where all employees are fully vaccinated” and all non-employees are screened and denied entry if they are suspected or confirmed to have COVID-19 (1910.502(a)(2)(iv)) and “home healthcare settings where all employees are fully vaccinated” and all nonemployees at that location are screened prior to employee entry so that people with suspected or confirmed COVID-19 are not present (1910.502 (a)(2)(v)).
Similar to the Healthcare ETS, this ETS requires employers to support vaccination by providing employees with reasonable time, including up to four hours of paid time, to receive vaccination, and reasonable time and paid sick leave to recover from vaccination side effects (see discussion above and the Summary and Explanation for paragraph (f), Section VI.F. of this preamble). However, as discussed above, this ETS goes further and expressly requires the implementation of a mandatory vaccination policy, unless the employer implements an alternative policy that requires unvaccinated workers to be regularly tested for COVID-19 and to wear face coverings in most situations when they work near others. While nothing in the Healthcare ETS prohibits covered employers from implementing a mandatory vaccination policy, this ETS presents the implementation of a mandatory vaccination policy as a preferred compliance option, and will preempt inconsistent state and local requirements that ban or limit employers' authority to require vaccination. Additionally, where the employer opts out of implementing a mandatory vaccination policy, and the employee opts out of vaccination, this ETS places no obligation on the employer to pay for costs associated with the regular testing of unvaccinated workers for COVID-19 or their use of face coverings, which will provide a financial incentive for some employees to be fully vaccinated.
OSHA finds it necessary to more strongly encourage vaccination in this ETS than in the Healthcare ETS in the manner described above. The Healthcare ETS's provisions that encouraged vaccination were packaged with a comprehensive infection prevention program that was tailored to the specific healthcare work settings to which the ETS applied, including a suite of layered and overlapping controls. In contrast, OSHA is promulgating this ETS to address the grave danger that COVID-19 now poses to all unvaccinated workers who work indoors and in the presence of others. As mentioned above, crafting a comprehensive and multi-layered standard that is comprehensive and feasible for the myriad work settings to which this ETS will apply, including workplaces as diverse as schools, restaurants, retail settings, offices, prisons, and factories, is an extraordinarily challenging and complicated undertaking.
Exigent circumstances require OSHA to immediately promulgate this ETS to protect unvaccinated workers, and vaccination is the single most efficient and effective method for removing unvaccinated workers from the grave danger. Given the urgency of the rulemaking and the singular efficacy of vaccination, OSHA has decided against including comprehensive and multilayered exposure controls in this ETS, and is instead focusing the ETS on strongly encouraging vaccination. Strongly encouraging vaccination is thus critical to the effectiveness of this ETS at protecting unvaccinated workers from the grave danger. In Request for Comment (Section I.B. of this preamble), OSHA seeks information on what additional measures, if any, should be required to protect employees against COVID-19.
Moreover, stronger encouragement of vaccination is needed in this ETS than in the Healthcare ETS because workers who are protected by the Healthcare ETS are more likely to be vaccinated and/or subject to a vaccination mandate. The Healthcare ETS, 29 CFR 1910.502, focused on healthcare work settings where COVID-19 is reasonably expected to be present, and, this ETS does not apply in settings where any employee provides healthcare services or healthcare support services while they are covered by the requirements of 29 CFR 1910.502 (see the Summary and Explanation for paragraph (b), Section VI.B. of this preamble). Evidence shows that workers in settings covered by §1910.502 already have a high rate of vaccination. As of July 2021, healthcare workers had a higher rate of vaccination than non-healthcare workers (Lazer et al., August, 2021), and many healthcare workers are currently subject to vaccination mandates. Twenty-two states and the District of Columbia have instituted vaccination mandates that are applicable to healthcare workers (NASHP, October 1, 2021), and nearly 300 hospitals and broader health systems have implemented vaccine mandates for their employees (Renton et al., October 14, 2021). The White House reported that almost 2,500 hospitals, 40% of all U.S. hospitals, across all 50 states, the District of Columbia, and Puerto Rico, have announced vaccination requirements for their workforce, and noted numerous examples of highly successful mandates in those workplaces (White House, October 7, 2021). News reports attest that many of these vaccination mandates have had great success in increasing the vaccination rate of the targeted healthcare workers (Goldberg, July 9, 2021; Otterman and Goldstein, September 28, 2021; Hubler, September 30, 2021; Beer, October 4, 2021). Even more healthcare workers covered by 29 CFR 1910.502 will be subject to a vaccination mandate under the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) rule published elsewhere in this issue of the Federal Register that requires COVID-19 vaccinations for workers in most healthcare settings that receive Medicare or Medicaid reimbursement, including but not limited to hospitals, dialysis facilities, ambulatory surgical settings, and home health agencies. This CMS rule applies to at least 76,000 providers (i.e., employers) and covers a majority of healthcare workers across the country. OSHA expects that the combination of incentives to vaccination in the Healthcare ETS and vaccination mandates applicable to healthcare workers will leave few healthcare workers within the scope of the Healthcare ETS unvaccinated.
b. Unvaccinated Workers Must Be Regularly Tested for COVID-19 and Use Face Coverings
As discussed above, this ETS presumptively requires employers to implement a mandatory vaccination policy, but permits employers to opt out of that requirement. Nonetheless, the grave danger that COVID-19 poses to unvaccinated workers demands that alternative protective measures be taken at workplaces where the employer does not implement a mandatory vaccination policy. Given that the SARS-CoV-2 virus is highly contagious, transmitted easily through the air, and can lead to severe and/or fatal outcomes in unvaccinated workers, it is critical that employers who do not require their employees to be vaccinated implement controls to mitigate the potential for COVID-19 outbreaks to occur. As discussed above, and in Grave Danger (Section III.A. of this preamble), unvaccinated workers are more likely than vaccinated workers to be infected with COVID-19 and transmit the virus to others, and thus pose a heightened risk of spreading the virus at the workplace, including to other unvaccinated workers.
To reduce the risk that unvaccinated workers will spread COVID-19 at the workplace, this rule requires employers that do not implement a mandatory vaccination policy to ensure that unvaccinated workers who report to a workplace where others are present are tested at least once a week for COVID-19. As discussed in the Summary and Explanation for paragraph (g) (Section VI.G. of this preamble), it is well-established that, by identifying and isolating infected individuals, regularly testing individuals for COVID-19 infection can be an effective method for reducing virus transmission. Regularly testing unvaccinated workers is essential because SARS-CoV-2 infection is often attributable to asymptomatic or presymptomatic transmission (Bender et al., February 18, 2021; Byambasuren et al., December 11, 2020; Johansson et al., January 7, 2021; Klompas et al., September 2021). In accordance with the CDC's recommendations, OSHA has set the minimum frequency of testing at 7 days because the agency expects that it will be effective in slowing the spread of COVID-19, while taking into account associated cost considerations (see the Summary and Explanation for paragraph (g), Section VI.G. of this preamble). As noted in the Request for Comment (Section I.B. of this preamble), OSHA is gathering additional information about whether OSHA should require testing more often than on a weekly basis.
The requirement for unvaccinated workers to be regularly tested for COVID-19 operates in tandem with paragraph (h)(2), which requires that all employers remove from the workplace any employee who receives a positive COVID-19 test, or a COVID-19 diagnosis (see the Summary and Explanation for paragraph (h), Section VI.H. of this preamble). Paragraph (h)(2) ensures that the COVID-19-positive employee will be isolated from the workplace until it is safe for the employee to return, and also allows the employee to seek medical care sooner and reduce the likelihood that they will suffer the most severe consequences of an infection ( e.g. , by seeking monoclonal antibody treatment). The combination of the testing and medical removal provisions will reduce the likelihood that an unvaccinated worker who has been infected with COVID-19, including those who are not experiencing symptoms of infection, will be permitted to spread the virus to others at the workplace, including unvaccinated coworkers.
Additionally, OSHA finds it necessary to require employers that do not implement a mandatory vaccination policy to ensure that unvaccinated workers wear face coverings in most situations when they are working near others. This reflects OSHA's recognition that regularly testing unvaccinated workers for COVID-19 will not be 100% effective in identifying infected workers before they enter the workplace. Most obviously, testing employees once a week will not prevent an unvaccinated worker from exposing others at the workplace if the worker becomes infected and reports to the workplace in between their weekly tests. And, even if the rule required unvaccinated workers to be tested more frequently than once a week, infected persons may still be missed, particularly in areas with high community spread (Chin et al., September 9, 2020).
Accordingly, requiring unvaccinated workers to wear face coverings in most situations when they are working near others will further mitigate the potential for unvaccinated workers to spread the virus at the workplace. As discussed in the Summary and Explanation for paragraph (i) (Section VI.I. of this preamble), it is well-established that face coverings provide effective source control; that is, they largely prevent respiratory droplets emitted by the wearer of the face covering from spreading to others, and thus make it significantly less likely that the person wearing the mask will transmit the virus, if they are infected. Face coverings are also believed to provide the wearer some limited protection from exposure to the respiratory droplets of co-workers and others (e.g., customers) (CDC, May 7, 2021), but the principal benefit of face coverings is to significantly reduce the wearer's ability to spread the virus. By requiring unvaccinated workers to wear face coverings, this rule significantly reduces the likelihood that an infected unvaccinated worker who enters the workplace despite the testing requirements will spread the virus to others, including unvaccinated coworkers.
OSHA acknowledges that regularly testing unvaccinated workers for COVID-19 and requiring them to wear face coverings when they work near others is less protective of unvaccinated workers than simply requiring all workers to be vaccinated. To be sure, OSHA strongly prefers that employers adopt a mandatory vaccination policy, as vaccination is singularly effective at protecting workers from the severe consequences that can result from a COVID-19 infection. And, where employers do not adopt a mandatory vaccination policy, employers may also consider alternative feasible measures that would remove employees who remain unvaccinated from the scope of this ETS, such as increasing telework (see the Summary and Explanation for paragraph (b), Section VI.B. of this preamble). Nonetheless, as discussed above, OSHA has not imposed a strict vaccination mandate on all covered employees who work in the presence of others and not exclusively outdoors, given that the agency has never previously used its authority to strictly mandate vaccination, and the exigent and extraordinary circumstances driving this emergency rulemaking have not afforded OSHA a full opportunity to assess the potential ramifications of including a strict vaccination mandate in this rule. Given these circumstances, and employers' unique understanding of the compliance approaches that will best increase vaccination rates among their workforce, OSHA has designed a rule that preserves a limited degree of employer flexibility, and strongly encourages, but does not strictly require, vaccination. OSHA has requested comment in this ETS on whether a strict vaccination mandate would be appropriate and the agency will consider those comments as it determines how to proceed with this rulemaking.
References
Beer T. (2021, October 4). COVID-19 Vaccine Mandates Are Working—Here's The Proof. Forbes. https://www.forbes.com/sites/tommybeer/2021/10/04/covid-19-vaccine-mandates-are-working-heres-the-proof/?sh=1a08d2e72305. (Beer, October 4, 2021)
Bender JK et al. (2021, February 18). Analysis of asymptomatic and presymptomatic transmission in SARS-CoV-2 outbreak, Germany, 2020. Emerging Infectious Diseases. 27(4). https://doi.org/10.3201/eid2704.204576 . (Bender et al., February 18, 2021)
Boseman J and Leatherby L. (2021, October 1). U.S. Coronavirus Death Toll Surpasses 700,000 Despite Wide Availability of Vaccines. The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/2021/10/01/us/us-covid-deaths-700k.html. (Boseman and Leatherby, October 1, 2021)
Byambasuren O et al., (2020, December 11). Estimating the extent of asymptomatic COVID-19 and its potential for community transmission: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Official Journal of the Association of Medical Microbiology and Infectious Disease Canada. 5(4): 223-234 doi:10.3138/jammi-2020-0030. (Byambasuren et al., December 11, 2020)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, May 7). Science brief: Community use of cloth masks to control the spread of SARS-CoV-2. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/science/science-briefs/masking-science-SARS-cov2.html. (CDC, May 7, 2021)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, October 18). COVID Data Tracker. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/ . (CDC, October 18, 2021)
Chin E et al. (2020, September 9). Frequency of routine testing for COVID-19 in high-risk healthcare environments to reduce outbreaks. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.04.30.20087015. (Chin et al., September 9, 2020)
Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2020, December 11). Emergency use authorization for an unapproved product review memorandum (Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine/BNT 162b2 mRNA-1273). https://www.fda.gov/emergency-preparedness-and-response/coronavirus-disease-2019-covid-19/pfizer-biontech-covid-19-vaccine. (FDA, December 11, 2020)
Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2020, December 18). Emergency use authorization for an unapproved product review memorandum (Moderna COVID-19 vaccine/mRNA-1273). https://www.fda.gov/emergency-preparedness-and-response/coronavirus-disease-2019-covid-19/moderna-covid-19-vaccine. (FDA, December 18, 2020)
Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2021, February 26). Janssen COVID-19 vaccine. Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee February 26, 2021 Meeting Briefing Document. https://www.fda.gov/media/146219/download. (FDA, February 26, 2021)
Goldberg C. (2021, July 9). Hospital Vaccine Mandates Suggest Success in Boosting U.S. Shots. Bloomberg News. https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2021-07-09/early-mandates-boost-worker-vaccine-rates-prompt-few-to-quit . (Goldberg, July 9, 2021)
Hirsch L. (2021, September 30). After Mandate, 91% of Tyson Workers Are Vaccinated. https://www.nytimes.com/2021/09/30/business/tyson-foods-vaccination-mandate-rate.html . (Hirsch, September 30, 2021)
Hubler S. (2021, September 30). `Mandates Are Working': Employer Ultimatums Life Vaccination Rates, So Far. The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/2021/09/30/us/california-vaccine-mandate-health-care.html . (Hubler, September 30, 2021)
Johansson MA et al., (2021, January 7). SARS-CoV-2 transmission from people without COVID-19 symptoms. JAMA Network Open. 4(1): e2035057. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.35057. (Johansson et al., January 7, 2021)
Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF). (2021, May 6). KFF COVID-19 Vaccine Monitor: April 2021. https://www.kff.org/coronavirus-covid-19/poll-finding/kff-covid-19-vaccine-monitor-april-2021/ . (KFF, May 6, 2021)
Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF). (2021, May 17). How employer actions could facilitate equity in COVID-19 vaccinations. https://www.kff.org/policy-watch/how-employer-actions-could-facilitate-equity-in-covid-19-vaccinations/ . (KFF, May 17, 2021)
Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF). (2021, September). Does The Public Want To Get A COVID-19 Vaccine? When? https://www.kff.org/coronavirus-covid-19/dashboard/kff-covid-19-vaccine-monitor-dashboard/?utm_source=web&utm_medium=trending&utm_campaign=COVID-19-vaccine-monitor#messagesandinformation . (KFF, September 2021)
Klompas M et al. (2021, September). The case for mandating COVID-19 vaccines for health care workers. Annals of Internal Medicine. https://doi.org/10.7326/M21-2366 . (Klompas et al., September 2021)
Lazer D et al. (2021, August). The COVID States Project: A 50-State COVID-19 Survey Report #62: COVID-19 Vaccine Attitudes Among Healthcare Workers. http://news.northeastern.edu/uploads/COVID19%20CONSORTIUM%20REPORT%2062%20HCW%20August%202021.pdf. (Lazer et al., August, 2021)
National Academy for State Health Policy (NASHP). (2021, October 1). State Efforts to Ban or Enforce COVID-19 Vaccine Mandates and Passports. https://www.nashp.org/state-lawmakers-submit-bills-to-ban-employer-vaccine-mandates/ . (NASHP, October 1, 2021)
National Safety Council (NSC). (2021, September). A Year in Review, and What's Next: COVID-19 Employer Approaches and Worker Experiences. https://www.nsc.org/faforms/safer-year-one-final-report . (NSC, September 2021)
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). (2021c, October). Health Impacts of the COVID-19 Vaccination and Testing ETS. (OSHA, October 2021c)
Otterman S and Goldstein J. (2021, September 28). Thousands of N.Y. Health Care Workers Get Vaccinated Ahead of Deadline. The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/2021/09/28/nyregion/vaccine-health-care-workers-mandate.html . (Otterman and Goldstein, September 28, 2021)
Renton B et al. (2021, October 14). New: Hospital Vaccine Mandate Tracker. Global Epidemics, Brown School of Public Health. https://globalepidemics.org/2021/07/24/new-hospital-vaccine-mandate-tracker/ . (Renton et al., October 14, 2021)
Scobie HM et al. (2021, September 17). Monitoring Incidence of COVID-19 Cases, Hospitalizations, and Deaths, by Vaccination Status—13 U.S. Jurisdictions, April 4-July 17, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2021; 70: early release. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7037e1.htm. (Scobie et al., September 17, 2021)
The Associated Press. (2021, September 22). United Airlines says 97% of US employees have been vaccinated. https://www.wifr.com/2021/09/22/united-airlines-say-97-us-employees-have-been-vaccinated/. (The Associated Press, September 22, 2021)
Towey R. (2021, September 27). CNBC poll shows very little will persuade unvaccinated Americans to get Covid shots. https://www.cnbc.com/2021/09/10/cnbc-poll-shows-very-little-will-persuade-unvaccinated-americans-to-get-covid-shots.html . (Towey, September 27, 2021)
White House. (2021, October 7). White House Report: Vaccination Requirements Are Helping Vaccinate More People, Protect Americans from COVID-19, and Strengthen the Economy. https://www.whitehouse.gov/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/Vaccination-Requirements-Report.pdf . (White House, October 7, 2021)
III. No Other Agency Action is Adequate To Protect Employees Against Grave Danger
OSHA's experience to date shows that the agency's existing tools are inadequate to meet the grave danger posed by COVID-19 to unvaccinated workers not covered by the Healthcare ETS. OSHA has determined that its existing standards, regulations, the OSH Act's General Duty Clause, and non-mandatory guidance will not adequately promote the most effective means to protect these workers: Vaccination. The agency has determined that this ETS is necessary to address these inadequacies. Multiple developments support this change in approach. First, large numbers of employees are continuing to contract COVID-19 and die. (See Grave Danger , Section III.A. of this preamble). Further, based on a thorough review of its existing approach to protecting employees from COVID-19 and the current state of the pandemic, OSHA finds that existing OSHA standards, regulations, the General Duty Clause, and non-mandatory guidance are not adequate to protect employees outside healthcare from COVID-19. The Preamble to the Healthcare ETS includes a detailed analysis demonstrating the inadequacy of existing tools in the healthcare industry. See 86 FR 32414-32423. In general, the same analysis applies here. The reasons existing tools were inadequate to protect healthcare workers apply in other industry sectors as well. The Healthcare ETS itself, while necessary to protect healthcare workers, of course applies only to that industry. Finally, the numerous guidance products published by other entities, such as CDC, are not adequate to protect employees because they are not enforceable; there is no penalty for noncompliance. 86 FR at 32415. Even as the CDC has increasingly recommended vaccination to protect from the dangers of transmission and severe illness related to the SARS-CoV-2 virus, vaccination rates remain uneven around the country. (CDC, September 9, 2021; Leonhardt, September 7, 2021; KFF, October 6, 2021; McPhillips and Cohen, May 19, 2021).
The need for this ETS is also reflected in the number of states and localities that have issued their own mandatory standards in recognition that OSHA's existing measures (including non-mandatory guidance, compliance assistance, and enforcement of existing standards) have failed to prevent the spread of the virus in workplaces. Additionally, as mentioned previously, other states have banned certain employers from implementing workplace vaccination mandates or from verifying an employee's vaccination status or from requiring face coverings. A national standard is necessary to establish clear requirements regarding vaccination, testing and face coverings that will protect employees in all states and preempt state or local ordinances that prevent employers from implementing necessary protections.
a. The Current Standards and Regulations Are Inadequate
In the Healthcare ETS, OSHA considered its enforcement efforts with regard to existing standards and regulations that OSHA had identified as potentially applicable to occupational exposure to SARS-CoV-2. OSHA's analysis in Section IV of the Healthcare ETS, 86 FR 32376, 32416-17 and hereby included in the record of this ETS, 18 is applicable here in considering the need for this ETS, which covers a much broader set of employers in all industries. There OSHA found that none of the existing OSHA standards could sufficiently abate the hazard posed by COVID-19 in healthcare settings. Here again OSHA concludes that the potentially applicable existing standards are insufficient to address the grave danger faced by workers covered by this ETS. None of the current standards, even if more rigorously enforced, can sufficiently address this cross-industry hazard of national proportions to abate the grave danger posed by COVID-19 or lead to the same benefits that this ETS will achieve. See Asbestos Info. Ass'n/N. Am. v. Occupational Safety & Health Admin. , 727 F.2d 415, 427 (5th Cir. 1984) (“[M]uch of the claimed benefit could be obtained simply by enforcing the current standard.”).
18 This adoption includes the citations in the referenced section of the Healthcare ETS, which are also included in the docket for this ETS.
Through its enforcement guidance, OSHA identified a number of current standards and regulations that might apply when workers have occupational exposure to SARS-CoV-2, most of which are the same standards OSHA considered in the Healthcare ETS. (Updated Interim Enforcement Response Plan for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)) (OSHA, July 7, 2021). OSHA has also cited the Hazard communication standard (29 CFR 1910.1200) during COVID-19 investigations. Accordingly, a list of potentially applicable standards and regulations follows:
• 29 CFR part 1904, Recording and Reporting Occupational Injuries and Illnesses. This regulation requires certain employers to keep records of work-related fatalities, injuries, and illnesses and report them to the government in specific circumstances.
• 29 CFR 1910.132, General requirements—Personal Protective Equipment (PPE). This standard requires that appropriate PPE, including PPE for eyes, face, head, and extremities, protective clothing, respiratory devices, and protective shields and barriers, be provided, used, and maintained in a sanitary and reliable condition.
• 29 CFR 1910.134, Respiratory protection. This standard requires that employers provide, and ensure the use of, appropriate respiratory protection when necessary to protect employee health.
• 29 CFR 1910.141, Sanitation. This standard applies to permanent places of employment and contains, among other requirements, general housekeeping and waste disposal requirements.
• 29 CFR 1910.145, Specification for accident prevention signs and tags. This standard requires the use of biological hazard signs and tags, in addition to other types of accident prevention signs and tags.
• 29 CFR Subpart U—COVID-19 Emergency Temporary Standard. The Healthcare ETS, promulgated on June 21, 2021 includes various controls (patient screening and management, respirators and other PPE, limiting exposure to aerosol-generating procedures, physical distancing, physical barriers, cleaning, disinfection, ventilation, health screening and medical management, access to vaccination, anti-retaliation provisions, and medical removal protection) to address the grave danger posed by COVID-19 to healthcare workers.
• 29 CFR 1910.1020, Access to employee exposure and medical records. This standard requires that employers provide employees and their designated representatives access to relevant exposure and medical records.
• 29 CFR 1910.1200, Hazard communication. This standard requires employers to keep Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for chemical hazards, provide SDSs to employees and their representatives when requested, and train employees about those hazards. The standard does not apply to biological hazards, but hazard communication becomes an issue for the SARS-CoV-2 virus when chemicals are used to disinfect surfaces.
OSHA again finds that none of these existing standards provide for the types of workplace controls that are necessary to combat the grave danger addressed by this ETS. First, none of the listed potentially applicable standards require vaccination against SARS-CoV-2, the most efficient and effective control to combat the grave danger posed by the virus. (The Bloodborne Pathogen Standard requires that the hepatitis B vaccine be made available to certain employees, but that is not that is not relevant here, since the hepatitis vaccine provides no protection against COVID-19). Nor are the additional safety measures included in this ETS—vaccination verification, screening testing, face coverings, and medical removal of COVID-19 positive workers— required by existing standards other than OSHA's Healthcare ETS (covering employees exempted from this new ETS while the Healthcare ETS is in effect).
Second, because existing standards do not contain provisions specifically targeted at the COVID-19 hazard, it may be difficult for employers and employees to determine what particular COVID-19 safety measures are required by existing standards, or how the separate standards are expected to work together as applied to COVID-19. An ETS that contains provisions specifically addressing COVID-19 hazards in covered workplaces will provide clear instructions. More certainty will lead to more compliance, and more compliance will lead to improved protection of employees covered by this standard.
Third, requirements in some standards may be appropriate for other situations but simply do not contemplate COVID-19 and fail to address important aspects of the hazard. For example, the general sanitation standard requires employers to provide warm water, soap, and towels that can be used in hand washing, but does not require disinfection or provision of hand sanitizer where handwashing facilities cannot be made readily available. See 86 FR 32417. Although the sanitation standard might appear at first glance to be relevant here, it simply does not require the types of controls that would, even if more rigorously enforced, sufficiently reduce the threat of COVID-19 in the workplace. As such, OSHA affirms its previous determination that some of the above-listed standards—including the sanitation standard—are in practice too difficult to apply to the COVID-19 hazard and have never been cited in COVID enforcement. 86 FR 32416.
Fourth, existing recordkeeping and reporting regulations do not adequately allow the employer or the agency to assess the full scope of COVID-19 workplace exposures and protection. OSHA's general recordkeeping regulations were not written with the nature of COVID-19 transmission or illness in mind. In order to adequately understand and thereby control the spread of COVID-19 in the workforce, it is critical that the employer has records of employees' vaccination status, and of the testing undergone by employees who do not receive vaccination, and that it knows of all cases of COVID-19 occurring among employees. However, such information is outside of the scope of OSHA's existing recordkeeping requirements, which are limited to injuries or illnesses that the employer knows to be work-related.
Moreover, existing reporting regulations do not adequately ensure that OSHA has the full picture of the impact of COVID-19 because those regulations only require employers to report in-patient hospitalizations that occur within 24 hours of the work-related incident and to report fatalities that occur within thirty days of the work-related incident. 86 FR at 32417. Many COVID-19 infections will not result in hospitalization or death until well after these limited reporting periods. Under existing regulations, such cases are not required to be reported to OSHA, which limits the agency's ability to fully understand the impact of COVID-19 on the workforce. 86 FR 32417. This ETS includes a provision, paragraph (k), that removes the time limitation on reporting for COVID-19 cases.
In conclusion, OSHA's experience has demonstrated that existing standards and regulations are inadequate to address the current COVID-19 hazard.
b. The General Duty Clause Is Inadequate To Meet the Current Crisis
Section 5(a)(1) of the OSH Act, or the General Duty Clause, provides the general mandate that each employer “furnish to each of [its] employees employment and a place of employment which are free from recognized hazards that are causing or are likely to cause death or serious physical harm to [its] employees.” 29 U.S.C. 654(a)(1). For General Duty Clause citations to be upheld, OSHA must demonstrate elements of proof that are supplementary to, and can be more difficult to show than, the elements of proof required for violations of specific standards, where a hazard is presumed. Specifically, to prove a violation of the General Duty Clause, OSHA needs to establish—in each individual case—that: (1) An activity or condition in the employer's workplace presented a hazard to an employee; (2) the hazard was recognized; (3) the hazard was causing or was likely to cause death or serious physical harm; and (4) feasible means to eliminate or materially reduce the hazard existed. BHC Nw. Psychiatric Hosp., LLC v. Sec'y of Labor , 951 F.3d 558, 563 (D.C. Cir. 2020). OSHA often relies on the General Duty Clause to fill gaps where specific standards do not address a hazard and OSHA enforces it through case-by-case adjudicative proceedings. See United States v. Strum , 84 F.3d 1, 5 (1st Cir. 1996).
OSHA has previously found the General Duty Clause to be inadequate to protect employees from dangers posed by infectious agents. In promulgating the bloodborne pathogens standard, OSHA explained that enforcement under the General Duty Clause was insufficient to protect employees from the serious hazards those pathogens present. 56 FR 64007 (December 6, 1991). In the recently promulgated Healthcare ETS, OSHA found that the General Duty Clause was insufficient to protect healthcare workers from the grave danger they faced as well. 86 FR 32418. While OSHA initially attempted to use the General Duty Clause to protect employees across all industries from COVID-19-related hazards, OSHA's experience has demonstrated that the Clause is grossly inadequate to protect employees covered by this ETS from the grave danger posed by COVID-19 in the workplace. As explained more fully below, OSHA finds this ETS is necessary to protect employees from the hazards of COVID-19.
As an initial matter, the General Duty Clause does not provide employers with specific requirements to follow or a roadmap for implementing appropriate abatement measures. The ETS, however, provides a clear statement of what OSHA expects employers to do to protect workers, thus facilitating better compliance. The General Duty Clause is so named because it imposes a general duty to keep the workplace free of recognized serious hazards; the ETS, in contrast, lays out clear requirements for employers to implement vaccination policies including vaccination verification, support for employee vaccination, screening testing and face coverings for unvaccinated workers, and medical removal of COVID-19 positive employees. Conveying obligations as clearly and specifically as possible makes it much more likely that employers will comply with those obligations and thereby protect workers from COVID-19 hazards. See, e.g., Integra Health Mgmt., Inc. , 2019 WL 1142920, at *7 n.10 (No. 13-1124, 2019) (noting that standards “give clear notice of what is required of the regulated community”); 56 FR 64007 (“because the standard is much more specific than the current requirements [general standards and the general duty clause], employers and employees are given more guidance in carrying out the goal of reducing the risks of occupational exposure to bloodborne pathogens”).
Moreover, several characteristics of General Duty Clause enforcement actions make them an inadequate means to address hazards associated with COVID-19. First, it would be virtually impossible for OSHA to require and enforce the most important worker-protective elements of the ETS (such as vaccination and testing) under the General Duty Clause. Second, OSHA's burden of proof for establishing a General Duty Clause violation is heavier than for standards violations. Third, promulgating an ETS will enable OSHA to issue more meaningful penalties for willful and egregious violations, thus creating effective deterrence against employers who intentionally disregard their obligations under the Act or demonstrate plain indifference to employee safety. As discussed in more detail below, all of these considerations demonstrate OSHA's need to promulgate this ETS in order to protect unvaccinated workers covered by this standard from hazards posed by COVID-19.
The General Duty Clause is ill-suited to requiring employers to adopt vaccination and testing policies, like those required by the ETS
Because the General Duty Clause requires OSHA to establish the existence and feasibility of abatement measures that can materially reduce a hazard, it is difficult for OSHA to use the clause to require specific control measures where an employer is doing something, but not what the Secretary has determined is needed to fully address the serious hazard. See, e.g., Waldon Health Care Center , 16 BNA OSHC 1052, 1993 WL 119662 at * (No. 89-2804, 1993) (vacating OSHA citation requiring pre-exposure hepatitis B vaccination under General Duty Clause by finding that although vaccination would more fully reduce the hazard, the employer's chosen means of abatement were sufficient); Brown & Root, Inc., Power Plant Div. , 8 BNA OSHC 2140, 1980 WL 10668 at *5 (No. 76-1296, 1980) (“[T]he employer may defend against a section 5(a)(1) citation by asserting that it was using a method of abatement other than the one suggested by the Secretary.”).
Further, even where OSHA establishes a violation of the General Duty Clause, the employer is under no obligation to implement the feasible means of abatement proven by OSHA as part of its prima facie case. Cyrus Mines Corp. , 11 OSH Cas. (BNA) 1063, 1982 WL 22717, at *4 (No. 76-616, 1983) (“[The employer] is not required to adopt the abatement method suggested by the Secretary, even one found feasible by the Commission; it may satisfy its duty to comply with the standard by using any feasible method that is appropriate to abate the violation.”); Brown & Root, Inc., Power Plant Div. , 1980 WL 10668 at *5. Thus, even in cases where OSHA prevails, the employer need not necessarily implement the specific abatement measure(s) OSHA established would materially reduce the hazard. The employer could select alternative controls and then it would be up to OSHA, if it wished to cite the employer again, to establish that the recognized hazard continued to exist and that its preferred controls could materially reduce the hazard even further.
Given the severity and pervasiveness of the COVID-19 hazard, OSHA has determined that the specific abatement measures provided in this ETS are necessary to protect workers from grave danger. Under the General Duty Clause alone, it would be nearly impossible to require employers to provide these specific measures, and even then, it could only be on a case-by-case enforcement basis. Considering the magnitude and ubiquity of the danger that SARS-CoV-2 poses to workers across the country, the case-by-case adjudicatory regime set up through the General Duty Clause is simply not adequate to combat the risk of severe illness and death caused by the virus.
General Duty Clause Citations Impose a Heavy Litigation Burden on OSHA
Under the General Duty Clause OSHA must prove that there is a recognized hazard, i.e., a workplace condition or practice to which employees are exposed, creating the potential for death or serious physical harm to employees. See SeaWorld of Florida LLC v. Perez , 748 F.3d 1202, 1207 (D.C. Cir. 2014); Integra Health Management, 2019 WL 1142920, at *5. Whether a particular workplace condition or practice is a “recognized hazard” under the General Duty Clause is a question of fact that must be decided in each individual case. See SeaWorld of Florida LLC , 748 F.3d at 1208. In the case of a COVID-19-related citation, this means showing not just that the virus is a hazard as a general matter—a fairly indisputable point—but also that the specific conditions in the cited workplace, such as unvaccinated, unmasked employees working in close proximity to other employees for extended periods, create a COVID-19-related hazard.
In contrast, an OSHA standard that requires or prohibits specific conditions or practices establishes the existence of a hazard. See Harry C. Crooker & Sons, Inc. v. Occupational Safety & Health Rev. Comm'n , 537 F.3d 79, 85 (1st Cir. 2008); Bunge Corp. v. Sec'y of Labor , 638 F.2d 831, 834 (5th Cir. 1981). Thus, in enforcement proceedings under OSHA standards, as opposed to the General Duty Clause, “the Secretary need not prove that the violative conditions are actually hazardous.” Modern Drop Forge Co. v. Sec'y of Labor , 683 F.2d 1105, 1114 (7th Cir. 1982). With OSHA's finding that the hazard of exposure to COVID-19 can exist for unvaccinated workers in all covered workplaces (see Grave Danger , Section III.A. of this preamble), the ETS will eliminate the burden to repeatedly prove, workplace by workplace, the existence of a COVID-19 hazard under the General Duty Clause.
One of the most significant advantages to standards like the ETS that establish the existence of the hazard at the rulemaking stage is that the Secretary can require specific abatement measures without having to prove that a specific cited workplace is already hazardous. 19 In contrast, as discussed above, under the General Duty Clause the Secretary cannot require abatement before proving in the enforcement proceeding that an existing condition at the workplace is hazardous. For example, in a challenge to OSHA's Grain Handling Standard, which was promulgated in part to protect employees from the risk of fire and explosion from accumulations of grain dust, the Fifth Circuit acknowledged OSHA's inability to effectively protect employees from these hazards under the General Duty Clause in upholding, in large part, the standard. See Nat'l Grain & Feed Ass'n v. Occupational Safety & Health Admin. , 866 F.2d 717, 721 (5th Cir. 1988) (noting Secretary's difficulty in proving explosion hazards of grain handling under General Duty Clause). Although OSHA had attempted to address fire and explosion hazards in the grain handling industry under the General Duty Clause, “employers generally were successful in arguing that OSHA had not proved that the specific condition cited could cause a fire or explosion.” Id. at 721 & n.6 (citing cases holding that OSHA failed to establish a fire or explosion hazard under the General Duty Clause). The Grain Handling Standard, in contrast, established specific limits on accumulations of grain dust based on its combustible and explosive nature, and the standard allowed OSHA to cite employers for exceeding those limits without the need to prove at the enforcement stage that each cited accumulation was likely to cause a fire or explosion. See id. at 725-26.
19 “The Act does not wait for an employee to die or become injured. It authorizes the promulgation of health and safety standards and the issuance of citations in the hope that these will act to prevent deaths and injuries from ever occurring.” Whirlpool Corp, v. Marshall, 445 U.S. 1, 12 (1980); see also Arkansas-Best Freight Sys., Inc. v. Occupational Safety & Health Rev. Comm'n , 529 F.2d 649, 653 (8th Cir. 1976) (noting that the “[OSH] Act is intended to prevent the first injury”).
The same logic applies to COVID-19 hazards. Given OSHA's burden under the General Duty Clause to prove that conditions at the cited workplace are hazardous, it is difficult for OSHA to ensure necessary abatement before individual employee lives and health are unnecessarily endangered by exposure to COVID-19, despite widespread evidence of the grave danger posed by worker exposure to COVID-19. Indeed, despite publishing a voluminous collection of COVID-19 guidance online and receiving and investigating thousands of complaints, OSHA did not believe it could justify the issuance of more than 20 COVID-19 related General Duty Clause citations over the entire span of the pandemic so far, because of the quantum of proof the Secretary must amass under the General Duty Clause. Unlike enforcement under the General Duty Clause, this ETS allows OSHA to cite employers for each protective requirement they fail to implement without the need to wait for employee infection or death to prove in an enforcement proceeding that the particular cited workplace was hazardous without that particular measure in place. Thus, this ETS, which covers millions of workers nation-wide, is significantly preferable to the General Duty Clause with respect to such a highly transmissible virus because the inability to prevent a single exposure can quickly result in an exponential increase in exposures and illnesses or fatalities even at a single worksite.
An additional limitation of the General Duty Clause is that proving that there are feasible means to materially reduce a recognized hazard typically requires testimony from an expert witness in each separate case, which limits OSHA's ability to prosecute these cases as broadly as needed to protect workers, in light of the expense involved. See, e.g., Integra Health Management , 2019 WL 1142920, at *13 (requiring expert witness to prove proposed abatement measures would materially reduce hazard). In contrast, where an OSHA standard specifies the means of compliance, the agency has already made the necessary technical determinations in the rulemaking and therefore does not need to establish feasibility of compliance as part of its prima facie case in an enforcement proceeding. See, e.g., A.J. McNulty & Co. v. Sec'y of Labor , 283 F.3d 328, 334 (D.C. Cir. 2002); S. Colorado Prestress Co. v. Occupational Safety & Health Rev. Comm'n , 586 F.2d 1342, 1351 (10th Cir. 1978). Preventing the initial exposure and protecting as many workers as quickly as possible is especially critical in the context of COVID-19 because, as explained in Grave Danger, Section III.A. of this preamble, it can spread so easily in workplaces.
The ETS will also permit OSHA to achieve meaningful deterrence when necessary to address willful or egregious failures to protect employees against the COVID-19 hazard
As described above, in contrast to the broad language of the General Duty Clause, this ETS will prescribe specific measures employers covered by this standard must implement. This specificity will make it easier for OSHA to determine whether an employer has intentionally disregarded its obligations or exhibited a plain indifference to employee safety or health. In such instances, OSHA can classify the citations as “willful,” allowing it to propose higher penalties, with increased deterrent effects. In promulgating the Healthcare ETS, OSHA noted that early in the pandemic, shifting guidance on the safety measures employers should take to protect their employees from COVID-19 created ambiguity regarding employers' specific obligations. Thus, OSHA could not readily determine whether a particular employer had “intentionally” disregarded obligations that were not yet clear. And, even as the guidance began to stabilize, OSHA's ability to determine “intentional disregard” or “plain indifference” was difficult, for example, when an employer took some steps address the COVID-19 hazard. 86 FR 32420. The Healthcare ETS largely resolved this issue for employers covered by that standard, by laying out clearly what parameters to put in place to protect healthcare workers. However, this general challenge persists in OSHA's attempts at enforcement in other industries.
Further, OSHA has adopted its “egregious violation” policy to impose sufficiently large penalties that achieve appropriate deterrence against bad actor employers who willfully disregard their obligation to protect their employees when certain aggravating circumstances are present, such as a large number of injuries or illnesses, bad faith, or an extensive history of noncompliance (OSHA Directive CPL 02-00-080 (October 21, 1990)). Its purpose is to increase the deterrent impact of OSHA's enforcement activity. This policy utilizes OSHA's authority to issue a separate penalty for each instance of noncompliance with an OSHA standard, such as each employee lacking the same required protections, or each workstation lacking the same required controls. It can be more difficult to use this policy under the General Duty Clause because the Fifth Circuit and the Occupational Safety and Health Review Commission have held that, under the General Duty Clause, OSHA may only cite a hazardous condition once, regardless of its scope or the number of workers affected. Reich v. Arcadian Corp. , 110 F.3d 1192, 1199 (5th Cir. 1997). Thus, even where OSHA finds that an employer willfully failed to protect a large number of employees from a COVID-19 hazard, OSHA might not be able to cite the employer on a per-instance basis for failing to protect each of its employees. The provisions of this ETS have been intentionally drafted to make clear OSHA's authority to separately cite employers for each instance of the employer's failure to protect employees and for each affected employee, where appropriate.
By providing needed clarity, the ETS will facilitate “willful” and “egregious” determinations that are critical enforcement tools OSHA can use to adequately address violations by employers who have shown a conscious disregard for the health and safety of their workers in response to the pandemic. Without the necessary clarity, OSHA has been limited in its ability to impose penalties high enough to motivate the very large employers who are unlikely to be deterred by penalty assessments of tens of thousands of dollars, but whose noncompliance can endanger thousands of workers. Indeed, OSHA has only been able to issue two COVID-19-related “willful” citations and no “egregious” citations since the start of the pandemic because of the challenges described above.
For all of the reasons described above, and after over a year of attempting to use the General Duty Clause to address this widespread hazard, OSHA finds that the General Duty Clause is not an adequate enforcement tool to protect employees covered by this standard from the grave danger posed by COVID-19.
c. OSHA and Other Entity Guidance Is Insufficient
OSHA has issued numerous non-mandatory guidance products to advise employers on how to protect workers from SARS-CoV-2 infection (see https://www.osha.gov/coronavirus ). Even the most comprehensive guidance makes clear, as it must, that the guidance itself imposes no new legal obligations, and that its recommendations are “advisory in nature.” (See OSHA's online guidance, Protecting Workers: Guidance on Mitigating and Preventing the Spread of COVID-19 in the Workplace (OSHA, Updated August 13, 2021); and OSHA's earlier 35-page booklet, Guidance on Preparing Workplaces for COVID-19, (OSHA, March 9, 2020)). This guidance, as well as guidance products issued by other government agencies and organizations, including the CDC, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), the Institute of Medicine (IOM), and the World Health Organization (WHO), help protect employees to the extent that employers voluntarily choose to implement the practices they recommend. Unfortunately, OSHA's experience and the continued spread of COVID-19 throughout the country shows that does not happen consistently or rigorously enough, resulting in inadequate protection for employees. For example, the CDC has strongly recommended vaccination since vaccines became widely available earlier in the year, but many employees have yet to take this simple step, which would protect themselves and their co-workers from the danger of COVID-19.
As documented in numerous peer-reviewed scientific publications, CDC, IOM, and WHO have recognized a lack of compliance with non-mandatory recommended infection-control practices (Siegel et al., 2007; IOM, 2009; WHO, 2009). As noted in the preamble to the Healthcare ETS, OSHA was aware of these findings when it previously concluded that an ETS was not necessary, but at the time of that conclusion, the agency erroneously believed that it would be able to effectively use the non-mandatory guidance as a basis for establishing the mandatory requirements of the General Duty Clause, and informing employers of their compliance obligations under existing standards. 86 FR 32421. As explained above, that has not proven to be an effective strategy. Moreover, when OSHA made its initial necessity determination at the beginning of the pandemic, it made an assumption that given the unprecedented nature of the COVID-19 pandemic, there would be an unusual level of widespread voluntary compliance by the regulated community with COVID-19-related safety guidelines. (See, e.g., DOL, May 29, 2020 at 20 (observing that “[n]ever in the last century have the American people been as mindful, wary, and cautious about a health risk as they are now with respect to COVID-19,” and that many “protective measures are being implemented voluntarily, as reflected in a plethora of industry guidelines, company-specific plans, and other sources”)).
Since that time, however, developments have led OSHA to conclude that the same uneven compliance documented by CDC, IOM, and WHO is also occurring for the COVID-19 guidance issued by OSHA and other agencies. For example, rising “COVID fatigue” or “pandemic fatigue” has been reported for nearly a year already— i.e., a decrease in voluntary use of COVID-19 mitigation measures over time (Meichtry et al., October 26, 2020; Silva and Martin, November 14, 2020; Belanger and Leander, December 9, 2020; Millard, February 18, 2021). Other reasons that people have not followed COVID-19 guidance include fear of financial loss; skepticism about the danger posed by COVID-19; and even a simple human tendency, called “psychological reactance,” to resist curbs on personal freedoms, i.e., an urge to do the opposite of what somebody tells you to do (Belanger and Leander, December 9, 2020; Markman, April 20, 2020). OSHA is seeing evidence of these trends in its COVID-19 enforcement. For example, although OSHA has issued guidance since the spring of 2020 encouraging the use of physical distancing and barriers as a means of protecting employees at fixed work locations, there have been a number of news reports indicating that employers ignore that guidance (Romo, November 19, 2020; Richards, May 5, 2020; Lynch, July 9, 2020). This was evidenced by a cross-sectional study performed from late summer to early fall of 2020 in New York and New Jersey that found non-compliance and widespread inconsistencies in COVID-19 response programs (Koshy et al., February 4, 2021). Indeed, OSHA continues to receive complaints and referrals attesting to such workplace practices. (OSHA, October 17, 2021). Worse, some employers must now deal with employees who not only have yet to be vaccinated but compound the danger by hiding their unvaccinated status and declining to wear source protection that would identify them as unvaccinated, even though it could provide some protection to their coworkers, in workplaces where there is a stigma attached to being unvaccinated. (Ember and Murphy Marcos, August 7, 2021). This ETS contains notification and vaccine verification requirements that address these avoidant behaviors and mitigate the hazard of undisclosed exposure and transmission (see the Summary and Explanation for paragraphs (e), (g), and (h), Sections VI.E., VI.G., and VI.H. of this preamble).
OSHA's more recent guidance update encourages employers to facilitate employee vaccination by providing paid time off and encourages testing and masks for unvaccinated workers. However, as discussed previously, vaccination rates remain inconsistent across the country and have slowed significantly since the spring of 2021. And infection rates remain high, especially among the unvaccinated. It is clear, as discussed previously, that voluntary self-regulation by employers will not sufficiently reduce the danger that COVID-19 poses in workplaces covered by this standard. As noted in the White House Report on vaccination requirements released on October 7, at this time only 25% of businesses have vaccine mandates in place (White House, October 7, 2021). Since this ETS and other federal efforts to require vaccination were announced more private and public sector institutions have begun to prepare to implement vaccination requirements, further demonstrating the need for this rule as an impetus for employer action (White House, October 7, 2021).
The high number of COVID-19-related complaints and reports that OSHA continues to receive on a regular basis suggests a lack of widespread compliance with existing voluntary guidance: From March 2020 to October 2021, OSHA has continued to receive hundreds of COVID-19-related complaints every month, including over 400 complaints during the month of August 2021, and over 450 complaints to date in the month of September (OSHA, October 11, 2021). And, as of October 17, OSHA has received 223 additional COVID-19-related complaints. (OSHA, October 17, 2021). If guidance were followed more strictly, or if there were enough voluntary compliance with steps to prevent illness, OSHA would expect to see a significant reduction in COVID-19-related complaints from employees.
The dramatic increases in the percentage of the population that contracted the virus during the summer of 2021 indicates a continued risk of COVID-19 transmission in workplace settings (for more information on the prevalence of COVID-19 see Grave Danger , Section III.A. of this preamble) despite OSHA's publication of numerous specific and comprehensive guidance documents. OSHA has found that neither reliance on voluntary action by employers nor OSHA non-mandatory guidance is an adequate substitute for specific, mandatory workplace standards at the federal level. Public Citizen v. Auchter , 702 F.2d 1150 at 1153 (voluntary action by employers “alerted and responsive” to new health data is not an adequate substitute for government action).
d. A Uniform Nationwide Response to the Pandemic Is Necessary To Protect Workers
As the pandemic has continued in the United States, there has been increasing recognition of the need for a more consistent national approach (GAO, September, 2020; Budryk, November 17, 2020; Horsley, May 1, 2020; DOL OIG, February 25, 2021). Many employers have advised OSHA that they would welcome a nationwide ETS. For example, in its October 9, 2020 petition for a COVID-19 ETS, ORCHSE Strategies, LLC explained that it is “imperative” that OSHA issue an ETS to provide employers one standardized set of requirements to address safety and health for their workers (ORCHSE, October 9, 2020). This group of prominent business representatives explained that an ETS would eliminate confusion and unnecessary burden on workplaces that are struggling to understand how best to protect their employees in the face of confusing and differing requirements across states and localities.
The lack of a national standard on this hazard has led to increasing imbalance in state and local regulation, a problem that OSHA already identified as concerning in its Healthcare ETS. See 86 FR 32413 (“The resulting patchwork of state and local regulations led to inadequate and varying levels of protection for workers across the country, and has caused problems for many employees and businesses.”) Since the Healthcare ETS was published, states and localities have taken increasingly more divergent approaches to COVID-19 vaccination, vaccination verification, screening testing, and the use of face coverings in the workplace. Currently, the spectrum ranges from states and localities requiring vaccine mandates and face coverings to states prohibiting or restricting them, with many states falling somewhere in between. Due to uneven approaches to vaccination across the country, states with the lowest rates of vaccination have COVID-19 infection rates four times as high as in states with the highest vaccine rates. (Leonhardt, September 7, 2021). Given that thousands of working age people continue to be infected with COVID-19 each week, many of whom will become hospitalized or die, OSHA recognizes that a patchwork approach to worker safety has not been successful in mitigating this infectious disease outbreak (CDC, October 18, 2021—Cases, By Age). It has become clear that a Federal standard, by way of this ETS, is necessary to provide clear and consistent protection to employees across the country. As explained in Pertinent Legal Authority (Section II. of this preamble) and the Summary and Explanation for paragraph (a) (Section VI.A. of this preamble), OSHA has the authority to comprehensively address the issue(s) described in this ETS, and the standard is intended to preempt conflicting state and local laws.
In sum, based on its enforcement experience during the pandemic to date, OSHA concludes that continued reliance on existing standards and regulations, the General Duty Clause, and guidance, in lieu of an ETS, is not adequate to protect unvaccinated employees from the grave danger of being infected by, and suffering death or serious health consequences from, COVID-19.
References
Belanger J and Leander P. (2020, December 9). What Motivates COVID Rule Breakers? Scientific American. https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/what-motivates-covid-rule-breakers/ . (Belanger and Leander, December 9, 2020)
Budryk Z. (2020, November 17). Fauci calls for `a uniform approach' to coronavirus pandemic. The Hill. https://thehill.com/policy/healthcare/526378-fauci-calls-for-a-uniform-approach-to-the-coronavirus-pandemic?rl=1. (Budryk, November 17, 2020)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, September 9). Your COVID-19 Vaccination. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/your-vaccination.html. (CDC, September 9, 2021)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, October 18). COVID Data Tracker. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/ . (CDC, October 18, 2021)
Ember S and Murphy Marcos C. (2021, August 7). They Don't Want the Shot. They Don't Want Colleagues to Know. The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/2021/08/07/business/workplace-vaccinations-coronavirus-reopenings.html. (Ember and Murphy Marcos, August 7, 2021)
Government Accountability Office (GAO). (2020, September). COVID-19: Federal Efforts Could Be Strengthened by Timely and Concerted Actions. https://www.gao.gov/assets/710/709934.pdf. (GAO, September 2020)
Horsley S. (2020, May 1). U.S. Workplace Safety Rules Missing in the Pandemic. National Public Radio. https://www.npr.org/2020/05/01/849212026/it-s-the-wild-west-u-s-workplace-safety-rules-missing-in-the-pandemic . (Horsley, May 1, 2020)
Institute of Medicine (IOM). (2009). Respiratory Protection for Healthcare Workers in a Workplace Against Novel H1N1 Influenza A: A letter report. The National Academies Press. http://www.nap.edu/catalog/12748.html . (IOM, 2009)
Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF). (2021, October 6). Latest Data on COVID-19 Vaccinations by Race/Ethnicity. https://www.kff.org/coronavirus-covid-19/issue-brief/latest-data-on-covid-19-vaccinations-by-race-ethnicity/ . (KFF, October 6, 2021)
Koshy K et al., (February 4, 2021). Perspectives of region II OSHA authorized safety and health trainers about initial COVID-19 response programs. Safety Science 138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2021.105193 . (Koshy et al., February 4, 2021)
Leonhardt D. (2021, September 7). One in 5,000. The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/2021/09/07/briefing/risk-breakthrough-infections-delta.html . (Leonhardt, September 7, 2021)
Lynch R. (2020, July 9). Orange County to crack down on gyms that ignore Covid-19 safety guidelines. Orlando Business Journal. https://www.bizjournals.com/orlando/news/2020/07/09/orange-county-gyms-could-face-scrutiny-for-not.html . (Lynch, July 9, 2020)
Markman A. (2020, April 20). Why are there still so many coronavirus skeptics? Fast Company. https://www.fastcompany.com/90492518/why-are-there-still-so-many-coronavirus-skeptics. (Markman, April 20, 2020)
McPhillips D and Cohen E. (2021, May 19). Uneven vaccination rates across the US linked to COVID-19 case trends, worry experts. CNN Health. https://www.cnn.com/2021/05/19/health/uneven-vaccination-rates-covid-19-trends/index.html . (McPhillips and Cohen, May 19, 2021)
Meichtry S et al. (2020, October 26). Pandemic Fatigue is Real—And It's Spreading; Collective exhaustion with coronavirus restrictions has emerged as a formidable adversary for governments. The Wall Street Journal. https://www.wsj.com/articles/pandemic-fatigue-is-realand-its-spreading-11603704601. (Meichtry et al., October 26, 2020)
Millard E. (2021, February 18). How to not let pandemic fatigue turn into pandemic burnout. Everyday Health. https://www.everydayhealth.com/coronavirus/how-to-not-let-pandemic-fatigue-turn-into-pandemic-burnout/ . (Millard, February 18, 2021)
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). (2020, March 9). Guidance on Preparing Workplaces for Covid-19. https://www.osha.gov/sites/default/files/publications/OSHA3990.pdf . (OSHA, March 9, 2020
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). (2021, July 7). Updated Interim Enforcement Response Plan for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). https://www.osha.gov/laws-regs/standardinterpretations/2021-07-07. (OSHA, July 7, 2021)
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). (2021, August 13). Guidance on Preparing Workplaces for Covid-19. https://www.osha.gov/sites/default/files/publications/OSHA3990.pdf. (OSHA, August 13, 2021)
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). (2021, August 13). Protecting Workers: Guidance on Mitigating and Preventing the Spread of COVID-19 in the Workplace. https://www.osha.gov/coronavirus/safework . (OSHA, Updated August 13, 2021)
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). (2021, October 17). Summary Data for Federal and State Programs—Enforcement. https://www.osha.gov/enforcement/covid-19-data#complaints_referrals . (OSHA, October 17, 2021)
ORCHSE Strategies. (2020, October 9). “Petition to the U.S. Department of Labor—Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) for an Emergency Temporary Standard (ETS) for Infectious Disease.” (ORCHSE, October 9, 2020)
Richards C. (2020, May 5). 2 Utah County businesses told staff to ignore COVID-19 guidelines, resulting in 68 positive cases. Daily Herald. https://www.heraldextra.com/news/local/2-utah-county-businesses-told-staff-to-ignore-covid-19-guidelines-resulting-in-68-positive/article_d8426991-a693-5879-9d88-f9e094aef5b5.html . (Richards, May 5, 2020)
Romo V. (2020, November 19). Tyson managers suspended after allegedly betting if workers would contract COVID. National Public Radio. https://www.npr.org/2020/11/19/936905707/tyson-managers-suspended-after-allegedly-betting-if-workers-would-contract-covid . (Romo, November 19, 2020)
Siegel J, Rhinehart E, Jackson M, Chiarello L, and the Healthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee. (2007). 2007 Guideline for isolation precautions: Preventing transmission of infectious agents in healthcare settings. https://www.cdc.gov/infectioncontrol/pdf/guidelines/isolation-guidelines-H.pdf . (Siegel et al., 2007)
Silva C and Martin M. (2020, November 14). U.S. Surgeon General Blames “Pandemic Fatigue” for Recent COVID-19 Surge. NPR. https://www.npr.org/sections/coronavirus-live-updates/2020/11/14/934986232/u-s-surgeon-general-blames-pandemic-fatigue-for-recent-covid-19-surge . (Silva and Martin, November 14, 2020)
United States Department of Labor (DOL) and Office of the Inspector General (OIG). (2021, February 25). COVID-19: Increased Worksite Complaints and Reduced OSHA Inspections Leave U.S. Workers' Safety at Increased Risk. http://www.oig.dol.gov/public/reports/oa/2021/19-21-003-10-105.pdf. (DOL OIG, February 25, 2021)
United States Department of Labor (DOL). (2020, May 29). In Re: American Federation Of Labor And Congress Of Industrial Organizations. Department Of Labor's Response to the Emergency Petition for a Writ of Mandamus, No. 20-1158 (D.C. Cir., May 29, 2020). (DOL, May 29, 2020)
White House. (2021, October 7). White House Report: Vaccination requirements are helping vaccinate more people, protect Americans from COVID-19, and strengthen the economy. https://www.whitehouse.gov/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/Vaccination-Requirements-Report.pdf . (White House, October 7, 2021)
World Health Organization (WHO). (2009). WHO Guidelines on Hand Hygiene in Health Care: A Summary—First Global Patient Safety Challenge Clean Care is Safer Care. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK144013/pdf/Bookshelf_NBK144013.pdf . (WHO, 2009)
IV. Conclusion
This pandemic continues to take a massive toll on American society, and addressing it requires a comprehensive national response. This ETS is part of that response. OSHA shares the nation's hope for the promise of recovery created by the vaccines. But in the meantime, it recognizes that we have not yet succeeded in defeating the virus, and that many workers across the country are in grave danger. Therefore, this ETS, with mitigation measures emphasizing worker vaccination, is necessary. Although OSHA finds it necessary to institute specific mitigation measures for the immediate future, the agency can adjust as conditions change. Even after issuing an ETS, OSHA retains the flexibility to update the ETS to adjust to the subsequent evolution of CDC workplace guidance. This ETS addresses (and incorporates as a main component) the major development in infection control over the last year—the development and growing implementation of COVID-19 vaccines. Going forward, further developments can be addressed through OSHA's authority to modify the ETS if needed, or to terminate it entirely if vaccination and other efforts end the current emergency. However, at this point in time, the available evidence indicates that the ETS is necessary to protect unvaccinated employees across the country from the grave danger of COVID-19.
IV. Feasibility
A. Technological Feasibility
This section presents an overview of the technological feasibility assessment for OSHA's Emergency Temporary Standard (ETS) for COVID-19 that requires all employers with 100 or more employees to ensure that all employees are fully vaccinated unless they implement a policy requiring employees to undergo testing for COVID-19 at least once every seven days and wear face coverings.
Technological feasibility has been interpreted broadly to mean “capable of being done” ( Am. Textile Mfrs. Inst. v. Donovan , 452 U.S. 490, 509-510 (1981)). A standard is technologically feasible if the protective measures it requires already exist, can be brought into existence with available technology, or can be created with technology that can reasonably be expected to be developed, i.e., technology that “looms on today's horizon” ( United Steelworkers of Am., AFL-CIO-CLC v. Marshall , 647 F.2d 1189, 1272 (D.C. Cir. 1980) ( Lead I )); Amer. Iron & Steel Inst. v. OSHA , 939 F.2d 975, 980 (D.C. Cir. 1991) ( Lead II ); American Iron and Steel Inst. v. OSHA , 577 F.2d 825 (3d Cir. 1978)). Courts have also interpreted technological feasibility to mean that a typical firm in each affected industry or application group will reasonably be able to implement the requirements of the standard in most operations most of the time (see Public Citizen v. OSHA , 557 F.3d 165 (3d Cir. 2009); Lead I , 647 F.2d at 1272; Lead II , 939 F.2d at 990).
OSHA issued an ETS in June 2021 to protect healthcare and healthcare support employees in covered healthcare settings from exposure to SARS-CoV-2. See 86 FR 32376 (June 21, 2021) (Healthcare ETS). OSHA found the requirements in that ETS to be technologically feasible, including a requirement for employers to pay for vaccination of employees that is very similar to the requirement in this new ETS. OSHA's finding that the Healthcare ETS was technologically feasible was primarily based on available evidence showing that most healthcare employers, and employers across all industry sectors, had already implemented, or were in process of implementing, procedures similar to those required by the Healthcare ETS. Similarly, OSHA's feasibility findings for this ETS are based on evidence that vaccination and testing policies, along with the use of face coverings consistent with recommendations from the CDC, have been implemented in multiple industry sectors as testing and vaccinations were made more widely available during the course of the pandemic.
As discussed in Summary and Explanation (Section VI. of this preamble), this ETS for vaccination and testing applies to all employers with 100 or more employees, except as noted here. It does not apply to workplaces covered under the Safer Federal Workforce Task Force COVID-19 Workplace Safety: Guidance for Federal Contractors and Subcontractors or settings where any employee provides healthcare services or healthcare support services when subject to the requirements of the Healthcare ETS (29 CFR 1910.502). It also does not apply to employees who do not report to a workplace where other individuals such as coworkers or customers are present, employees while they are working from home, or employees who work exclusively outdoors.
As noted above, OSHA has the legal duty to demonstrate that the average employer covered by this ETS can comply with that standard in most operations most of the time. This legal analysis is therefore focused solely on whether employers with 100 or more employees can comply with the standard. OSHA's rationale for that scope threshold of 100 or more employees is explained in the Summary and Explanation for paragraph (b), Section VI.B. of this preamble.
As discussed below, OSHA finds no technological feasibility barriers related to compliance with the requirements in the ETS. These requirements include establishing and implementing a written mandatory COVID-19 vaccination policy or alternative policy requiring testing and face coverings; determining employee vaccination status; supporting employee vaccination by providing paid time for vaccination and time off for recovery; ensuring that employees who are not fully vaccinated are tested for COVID-19 at least once every seven days and wear face coverings; and recordkeeping for employee vaccination status and testing.
OSHA reviewed numerous large-scale employer surveys and vaccination and testing policies developed by employers, public health organizations, trade association, and local, state, and federal governmental bodies. While OSHA discusses several examples of these plans and policies below, 20 OSHA's feasibility determination is based on all evidence in the rulemaking record. The majority of the survey data and other publicly available material that OSHA reviewed pertains to large employers with 100 or more employees.
20 While OSHA references several employers' policies, this is not intended to serve as an endorsement of those plans or an indication that those plans comply with the ETS. Rather, the plans and best practice documents show that developing and implementing policies to address employee COVID-19 vaccination in various workplaces is capable of being done in a variety of industries, and therefore, compliance with the ETS is technologically feasible.
Additionally, OSHA thoroughly reviewed current and future projections of the availability of COVID-19 tests, testing supplies, and laboratory capacity. Based on a review of vaccination and testing policies among large employers, OSHA has determined that most employers covered by this standard across a wide range of industries have either already implemented vaccination and testing programs and require unvaccinated employees to wear face coverings, or are capable of implementing programs that comply with the requirements in the ETS most of the time. OSHA therefore finds that the standard is technologically feasible.
I. Employer Policy on Vaccination
Paragraph (d)(1) of the ETS requires each covered employer to establish and implement a written mandatory vaccination policy unless the employer adopts an alternative policy requiring COVID-19 testing and face coverings for unvaccinated employees, which is discussed later. To meet the definition of “mandatory vaccination policy” under paragraph (c), the policy must require: Vaccination of all employees, including all new employees as soon as practicable, other than those employees (1) for whom a vaccine is medically contraindicated, (2) for whom medical necessity requires a delay in vaccination, or (3) those legally entitled to a reasonable accommodation under federal civil rights laws because they have a disability or sincerely-held religious beliefs, practices, or observances that conflict with the vaccination requirement.
OSHA requires employers to implement a mandatory vaccination requirement, but provides an exemption for an alternative policy that allows employees to choose either to be fully vaccinated or to be regularly tested and wear a face covering. This compliance options mean that the ETS is technologically feasible if employers across various industries are capable of implementing either policy, but nevertheless OSHA analyzes both employer policy options to demonstrate that there are no significant technological barriers to either approach.
OSHA reviewed several large-scale employer surveys related to vaccination policies across the country covering a wide range of industry sectors. Surveys conducted by Arizona State University (ASU) and the World Economic Forum (WEF), called COVID-19 Workplace Commons—Keeping Workers Well , show that most employers already have some type of vaccination policy, with more than 60 percent of surveyed employers requiring vaccinations for some or all employees. These survey results further support OSHA's determination that the vaccination policy requirement is feasible.
The ASU WEF workplace COVID-19 surveys collected information from employers across industry sectors about their response to the COVID-19 pandemic. The results and responses from more than 1,400 companies are publicly available through the ASU College of Health Solutions web page COVID-19 Diagnostics Commons (ASU, October 5, 2021). Case studies from employers are also available within the interactive dashboard on that web page. The surveys consisted of numerous questions about workplace pandemic response, including questions related to vaccination policies and testing unvaccinated employees.
The most recent COVID-19 survey data was collected between August 2, 2021 and August 20, 2021 and reported in September 2021 (accessible through the COVID-19 Workplace Commons). More than 1,400 companies operating 1143 facilities in 23 industry sectors were part of the survey, the majority of which are companies of the size covered by the ETS. Ninety percent of facilities surveyed had 100 or more employees at their facilities, and 56% had more than 100 but less than 1,000 employees at their facilities. The industry sectors surveyed include: Technology and software; business and professional services; manufacturing; construction; healthcare, hospitals, and clinics; retail stores; retail food stores; consumer retail service; energy and utilities; nonprofit organizations; education (colleges and universities); education (pre-K to 12); real estate and property management; agriculture and food production; healthcare services; media and entertainment; government and quasi-public; biotech, pharmaceuticals, and diagnostics; restaurants and food service; hotels and casinos; transportation, distribution, and logistics; consumer transportation; and recreation (ASU WEF, September 2021).
The survey responses related to vaccination policies support OSHA's determination that it is feasible for covered employers to implement mandatory COVID-19 vaccination policies. The survey results showed that 45% of employers surveyed require all employees to be vaccinated against COVID-19, and an additional 16% require some of its employees to be vaccinated against COVID-19. (ASU WEF, September 2021). Only three percent of employers surveyed did not have a vaccination policy at the time (ASU WEF, September 2021). While this survey covers a wide range of industries it may not represent the percentage of companies implementing mandatory vaccination policies in general populations but for the feasibility purposes it demonstrates that it has and can be done.
OSHA also reviewed slightly older survey data, which, even though it shows somewhat lower rates of employer vaccination mandates, still supports OSHA's finding that such vaccination polices are feasible. In late June 2021, the National Safety Council (NSC) conducted three national surveys, one organizational and two workforce, of private companies, nonprofits, legal experts, public health professionals, medical professionals and government agencies that have addressed workforce COVID-19 vaccinations based on best practices and proven workplace safety strategies. The survey results show that many employers and organizations are currently requiring employees to be vaccinated.
The three surveys were distributed to 300 employers and organizations across the country and from a wide range of industries to collect data on pandemic response, including implementation of COVID-19 vaccine policies and testing among their workforce. Of the employers and organizations surveyed in June 2021, the NSC found that 20% were implementing some form of a worker vaccination requirement. While OSHA believes that the ASU WEF surveys (which included more employers and are more recent) are better indicators of current employer vaccination policies, the NSC surveys also support the feasibility of employer vaccination mandates (NSC, September 2021)
The NSC, in partnership with the Health Action Alliance (HAA) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), have developed a multifaceted, comprehensive effort called SAFER, aimed at helping employers prioritize health and safety as they develop plans and polices for their employees to return to the workplace (NSC, May 17, 2021). Through SAFER, the NSC and HAA developed a web-based decision tool to guide employers on health, legal, and other considerations to prioritize the health and safety of workers. Due to the Delta Variant surge of new COVID-19 cases across the United States, the NSC and HAA revised the SAFER resources, including the online tool, to include information about employer requirements for COVID-19 vaccinations. These include guides for developing plans and policies to support employee vaccination through mandates and incentives; the collection and maintenance of COVID-19 vaccination records; and various considerations for testing unvaccinated workers. (HAA and NSC, September 17, 2021). The availability of these publicly-accessible tools to help employers develop vaccination policies further reduces any potential barriers for covered employers to establish and implement a written policy requiring each employee to be fully vaccinated against COVID-19, or alternatively to establish a policy allowing employees to choose whether to be fully vaccinated or tested for COVID-19 at least every seven days and wear face coverings.
The HAA maintains an online list of large companies requiring vaccinations for all or part of their workforce or customers. OSHA reviewed the list of companies, drawn from news reports and employer websites, with requirements for COVID-19 vaccination. Most of the companies listed require some or all employees to be vaccinated against COVID-19 while allowing medical exemptions or reasonable accommodations for disability or religious reasons. There are currently 188 listed companies across numerous industry sectors, including Amtrak, Deloitte, Google, The Walt Disney Company, Walmart, and the U.S. Chamber of Commerce. 21
21 https://www.healthaction.org/resources/vaccines/covid-19-vaccines-employer-requirements-health-action-alliance?0405d6f4_page=1 (last visited October 2, 2021).
While healthcare employers subject to 29 CFR 1910.502 are not covered by this ETS, a number of large healthcare employers have implemented mandatory vaccine policies. This also shows the feasibility of the employers implementing mandatory vaccination requirements, often on large scales. According to the American Hospital Association (AHA), over 1,800 hospitals have one or more vaccination requirements in place (Becker's Hospital Review, October 11, 2021). Large healthcare employers mandating that their employees be vaccinated include Kaiser Permanente, the nation's largest integrated, nonprofit health care organization with more than 216,000 employees and more than 23,000 physicians (Kaiser Permanente, August 2, 2021); Trinity Health, one of the largest multi-institutional Catholic health care delivery systems in the nation, with more than 123,000 employees and 90 hospitals in 22 states (Trinity Health, July 8, 2021); Sanford Health, which operates in 26 states and employs nearly 50,000 people (Sanford Health, July 22, 2021); and Genesis Health Care, a large U.S. nursing home chain with over 40,000 employees working in more than 250 centers across 23 states (Genesis Health Care, September 29, 2021).
Under paragraph (d)(2), if employers do not establish and implement a written mandatory vaccination policy, the employer must establish and implement a written policy allowing any employees not subject to a mandatory vaccination policy to either choose to be fully vaccinated or regularly tested for COVID-19 and wear a face covering. A substantial number of employers already have such policies in place. For example, the ASU WEF survey shows that 30% of employers surveyed require unvaccinated employees to participate in mandatory COVID-19 testing and 30% of employers require face coverings for unvaccinated employees (ASU WEF, September 2021).
OSHA also notes a number of state COVID-19 vaccination requirements. In response to the Delta Variant surge, 19 states have implemented written COVID-19 vaccination and testing policies for state employees and 23 states have done so for healthcare employees (NASHP, October 1, 2021). For example, on September 20, 2021, the Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment (CDPHE) implemented policies requiring state employees and personnel at health care facilities and hospitals to be fully vaccinated against COVID-19. All state employees must either be fully vaccinated against COVID-19 or participate in twice-weekly testing. Employees are allowed work time to get tested and administrative or Public Health Emergency Leave to get vaccinated. Employees who are not fully vaccinated must wear masks inside state facilities when they are around others. On August 30, 2021, the State Board of Health approved a vaccine requirement for personnel in health care settings with high-risk patients. All personnel affected by this rule needed to receive their first dose of COVID-19 vaccine by September 30, 2021, and must be fully vaccinated by October 31, 2021 (CDPHE, September 17, 2021).
A number of local governments have also implemented policies requiring COVID-19 vaccination or testing for employees. For example, the Fulton County Board of Commissioners in Georgia recently approved a “Vax or Test” policy requiring employees to get vaccinated or tested for COVID-19 each week. Since September 6, 2021, Fulton County has required all County employees, as a condition of employment, to either be vaccinated against COVID-19 or be tested weekly for COVID-19 unless an employee is granted a reasonable accommodation (Fulton County Government, September 03, 2021). The multitude of local, state, and employer vaccination or testing mandates across the country support OSHA's finding that such policies are feasible.
II. Determining Employee Vaccination Status
Paragraph (e) of the ETS requires employers to determine the vaccination status of each employee. Employers must require employees to provide an acceptable proof of vaccination status, including whether they are fully or partially vaccinated. As discussed in Summary and Explanation (Section VI. of this preamble), acceptable proof of vaccination status is: (i) The record of immunization from a health care provider or pharmacy; (ii) a copy of the COVID-19 Vaccination Record Card; (iii) a copy of medical records documenting the vaccination; (iv) a copy of immunization records from a public health, state, or tribal immunization information system; or a copy of any other official documentation that contains the type of vaccine administered, date(s) of administration, and the name of the health care professional(s) or clinic site(s) administering the vaccine(s). A signed and dated employee attestation is acceptable in instances when an employee is unable to produce proof of vaccination. Given the attestation option, there are no technological barriers to the provision for proof of vaccination status. As discussed below, many employers requiring proof of vaccination have successfully implemented such policies even without allowing the flexibility of the attestation option.
The employer must maintain a record and a roster of each employee's vaccination status. This information is subject to applicable legal requirements for confidentiality of medical information. These records must be preserved while the ETS is in effect. OSHA is not aware of any technological challenges that the large employers covered by this ETS would face with respect to collecting and maintaining records. This is a performance-based requirement, meaning that employers have the flexibility to structure their systems to fit within current systems, such as those relating to personnel records, tax records, and other sensitive or confidential records gathered and maintained by large employers.
A number of the surveys discussed above also show that most employers with vaccine mandates require proof of vaccination. For example, ASU WEF workplace COVID-19 survey from fall 2021 found that 60% of employers that required vaccinations also required proof of vaccination from employees. The NSC study from June 2021 found that 45% of employers with COVID-19 vaccination requirements required proof of vaccination, such as submitting a copy of the COVID-19 vaccination card. An additional 30% of employers surveyed verify employee vaccination status through self-reporting based on the honor system.
Additionally, a large-scale survey conducted by the Willis Towers Watson consulting firm between August 18 and 25, 2021, showed that a majority of employers currently track their employees' vaccination status. Nearly one thousand employers responded to this survey, and they collectively employ 9.7 million workers from industries across the public and private sectors including manufacturing, general services, wholesale and retail, IT and telecom, healthcare, financial services, energy and utilities, and public sector and education (Willis Towers Watson, June 23, 2021). Nearly six in 10 (59%) currently track their workers' vaccination status and another 19% are planning or considering doing so later this year. A majority (62%) of those employers who currently track their workers' vaccination status require proof of vaccination, such as CDC vaccination cards, while 36% rely on employees to self-report (Willis Towers Watson, September 1, 2021).
Other evidence in the record also supports the feasibility both of gathering proof of vaccination and determining employees' vaccination status. Many large employers with vaccination policies require employees to submit proof of vaccination. For example, Tyson Foods requires employees to submit proof of vaccination to Tyson Foods Vaccination Verification Program in order to qualify for the company's vaccination incentive (Tyson Foods, August 3, 2021). Similarly, Capital One bank requires all employees, contractors, vendors, and visitors to Capital One facilities to show proof of vaccination. (Capital One, August 11, 2021). The International Union of Painters and Allied Trades (IUPAT), which represents 140,000 craftspeople in the U.S. and Canada and has implemented vaccine requirements for its members, also requires all of its own non-bargaining unit office and field employees to show proof of vaccination. (IUPAT, May 10, 2021).
CVS Health, a health conglomerate with more than 300,000 employees, including more than 40,000 physicians, pharmacists, nurses and nurse practitioners, has mandated COVID-19 vaccination for its nurses, pharmacists and other employees who interact with patients and requires proof of vaccination for those employees (CVS Health, August 23, 2021).
The surveys and employer policies reviewed by OSHA all support the agency's finding that it is feasible for employers to determine their employees' vaccination status and collect proof of vaccination.
III. Providing Support for Vaccination
Paragraph (f) of the ETS requires employers to support COVID-19 vaccination for each employee by providing a reasonable amount of time to each employee for vaccination and reasonable time and paid sick leave to each employee for side effects experienced following vaccination. The feasibility of paying for the time is addressed in OSHA's economic analysis.
This technological feasibility determination focuses on whether employers would encounter obstacles in implementing payment policies that would make this requirement infeasible for the large employers covered by this ETS. OSHA has determined that there are no such obstacles. Most significantly, OSHA has already required this type of system for employers covered by the Healthcare ETS and nearly four months after that ETS took effect, OSHA is not aware that employers covered by that ETS experienced any technological compliance difficulties with respect to that requirement. In addition, many employers have already implemented policies such as those required to comply with this new ETS as a way of incentivizing employee vaccination. For example, the ASU WEF workplace COVID-19 survey from fall 2021 found that 60% of employers surveyed offered incentives for employees to be vaccinated. These incentives ranged from additional paid time off, cash, the ability to bypass regular testing and/or daily health screening requirements, and gifts. Eighteen percent of surveyed employers already provide additional time off for COVID-19 vaccination. Moreover, the NSC survey found that 86% of surveyed organizations had implemented policies such as paid time off, assistance with scheduling and transportation, and/or onsite vaccination.
OSHA's review of plans and best practice documents from the HAA registry and from other publicly-available sources also inform OSHA's finding that it is feasible for large employers to support employee vaccination (HAA, October 10, 2021). As part of this review, OSHA analyzed the ways that employers are currently supporting employee vaccination. One employer in the restaurant industry, the Fifty/50 Group, a Chicago-based restaurant group comprised of 14 establishments that requires employees to be fully vaccinated, offers paid time off for anyone getting a vaccine or feeling the mild after-effects. (Fifty/50 Group, May 18, 2021). Another employer in the animal slaughtering and processing industry, Tyson Foods, requires COVID-19 vaccinations for its U.S. workforce and also offers $200 and up to four hours of regular pay if employees are vaccinated outside of their normal shift or through an external source (Tyson Foods, August 3, 2021). In addition, Tyson Foods supports onsite vaccination events in collaboration with local health departments and healthcare providers to improve accessibility to vaccination. Tyson Foods has hosted more than 100 vaccination events at its locations across the country.
The evidence in the record demonstrates that many employers are already offering the types of vaccination support required by paragraph (f). Combined with OSHA's previous finding for a similar provision in the Healthcare ETS and the lack of compliance difficulties reported while that ETS has been in effect, OSHA therefore finds this requirement is technologically feasible.
IV. COVID-19 Testing for Employees Who Are Not Fully Vaccinated
Paragraph (g) of the ETS requires employers to ensure that employees who are not fully vaccinated and who report at least once every seven days to a workplace where other individuals such as coworkers or customers are present are: (1) Tested for COVID-19 at least once every seven days; and (2) provide documentation of the most recent COVID-19 test result to the employer no later than the seventh day following the date the employee last provided a test result. Employers must also ensure that employees who are not fully vaccinated and do not report during a period of seven or more days to a workplace where other individuals are present are: (1) Tested for COVID-19 within seven days prior to returning to the workplace; and (2) provide documentation of that test result upon return to the workplace.
Employees who are not fully vaccinated must be tested with a COVID-19 test, which is a test for SARS-CoV-2 that is: (i) Cleared, approved, or authorized, including in an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to detect current infection with the SARS-CoV-2 virus ( e.g., a viral test); (ii) administered in accordance with the authorized instructions; and (iii) not both self-administered and self-read unless observed by the employer or an authorized telehealth proctor. Examples of tests that satisfy this requirement include tests with specimens that are processed by a laboratory (including home or on-site collected specimens which are processed either individually or as pooled specimens), proctored over-the-counter tests, point of care tests, and tests where specimen collection is either done or observed by an employer.
COVID-19 testing has become more widely available throughout the pandemic and as of September 2021, the FDA has authorized approximately 250 tests and collection kits that diagnose current infection with the SARS-CoV-2 virus and may be acceptable under the ETS (FDA, September 10, 2021), and by October 1, 2021, the number of EUAs issued had grown to 324 (FDA, October 1, 2021). The ETS permits compliance through use of a wide range of FDA-authorized tests that are readily available, so there is little doubt that testing itself is technologically feasible.
This technological feasibility analysis therefore focuses on whether testing will continue to be readily available in quantities sufficient to meet the potential increase in testing demand while this ETS is in place. Given the wide variety of tests that can be used to comply with this ETS and OSHA's review of information about the existing manufacturing and distribution capabilities of test manufacturers, the agency does not anticipate feasibility issues related to ensuring that employees can get access to one of the acceptable tests within the time frames required by the ETS.
a. Brief Overview of Testing and Administration
COVID-19 tests that are cleared, approved, or authorized, including in an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA), by the FDA to detect current infection with the SARS-CoV-2 virus ( e.g., a viral test) satisfy the ETS. FDA-cleared, approved, or authorized molecular diagnostic tests and antigen tests are permitted under the ETS when used as authorized by the FDA and with a Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments of 1988 (CLIA) certification when appropriate. As described in the Summary and Explanation for paragraph (g) (Section VI.G. of this preamble), NAATs are a type of molecular test that detect genetic material. As of October 14, 2021, the FDA had issued EUAs for 264 molecular COVID-19 tests including tests specified to be used “with certain conditions of authorization required of the manufacturer and authorized laboratories”, 81 of which are authorized for home collection. Additionally, the FDA has issued EUAs for 2 OTC molecular COVID-19 test kits available without a prescription (FDA, October 14, 2021b).
NAATs, such as real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), have greater accuracy than antigen tests. However, most FDA-authorized NAATs need to be processed in a laboratory certified under the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments of 1988 (referred to as a “CLIA-certified laboratory”) with variable time to results (~1-2 days). While the NAAT test is a more reliable test, the antigen test is faster and less expensive.
An antigen test is an in vitro diagnostic test used to detect active SARS-CoV-2 infection. As of October 14, 2021, the FDA had issued 37 EUAs for COVID-19 antigen tests, including eight EUAs for over-the-counter (OTC) antigen tests that can be used without a prescription (FDA, October 14, 2021a).
Administration of an antigen test that meets the definition of COVID-19 test under this ETS falls into one of several categories: OTC employee self-tests that are observed by employers or authorized telehealth proctors; point-of-care (POC) or OTC tests performed by employers with a CLIA certificate of waiver; and other FDA cleared, approved, or authorized antigen tests that are analyzed in a CLIA certified laboratory setting (FDA, October 14, 2021a). The FDA has authorized POC tests that can be used at a place of employment when the facility is operating under a CLIA certificate of waiver. A CLIA certificate of waiver can be issued by CMS and may, when consistent with FDA's authorization, allow a laboratory to run a SARS-CoV-2 test outside a high or moderate complexity traditional clinical laboratory setting (CDC, September 9, 2021). In accordance with the CLIA certificate of waiver, the laboratory or POC testing site must use a test authorized for that location, like an FDA EUA POC test, and must adhere to the authorized test instructions to avoid human error. Certain COVID-19 antigen diagnostic tests can be analyzed on-site (where the person took the nasal swab) when that facility is operating under a CLIA certificate of waiver, while others must be analyzed in a CLIA certified high or moderate complexity laboratory setting. Some COVID-19 antigen diagnostic tests are authorized for use at home, without the need to send a sample to a laboratory. Antigen tests generally return results in approximately 15-30 minutes. The CDC provides training materials created by test manufacturers for POC antigen testing and reading of results for SARS-CoV-2 (CDC, July 8, 2021).
COVID-19 antigen diagnostic tests are found at physician offices; urgent care facilities; pharmacies, such as CVS or Walgreens; school health clinics; long-term care facilities and nursing homes; temporary locations, such as drive-through sites managed by local organizations; and other locations across the country (CDC, July 8, 2021; CVS Health, October 2021; Walgreens, October 8, 2021). The availability of government-offered antigen tests varies by state, and may be free or subsidized and accessible without a prescription or physician note (RiteAid, October 2021; Walgreens, October 2021; HHS, June 11, 2021). The Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) provides a publicly-available list of community-based testing locations in each state that offer free COVID-19 testing for insured and uninsured residents (HHS, August 17, 2021). Pharmacies and other locations often provide antigen tests by appointment, although some will allow testing for walk-ins (CVS Health, September 2021; Walgreens, October 8, 2021). COVID test kits are currently available from several on-line retailers (Amazon, October 12, 2021).
b. Testing Frequency
The ASU WEF survey data also supports OSHA's finding that the requirement for employees who are not fully vaccinated to be tested at least every seven days is feasible. The ASU WEF found that 73% of survey surveyed employers (797 employers) had testing policies for their workforce, and 76% of those employers had implemented mandatory testing requirements. Additionally, 25% of employers with testing polices had implemented requirements for routine testing of a portion of or the entire workforce, and 41% no longer require testing for fully vaccinated employees. Of the employers that test employees, 27% of those perform viral testing daily and 46% perform viral test once a week. Finally, 38% of companies exclusively administer polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests (PCR tests are a type of NAAT), 17% exclusively administer antigen tests, and 45% administer both. Companies administer a range of COVID-19 tests and conduct testing at a variety of locations (some companies use more than one location). Forty-two percent of companies test workers at health testing laboratories, 35% test onsite at work, 28% test at hospitals, 23% test at retail pharmacies, 13% test at universities, 9% test at home to be sent a lab for evaluation, and 5% test at home for immediate results (ASU WEF, September 2021).
OSHA also evaluated evidence of employers' current testing efforts by reviewing existing COVID-19 practices developed by employers, trade associations, and other organizations. Based on its review, OSHA concludes that it is feasible for most covered employees (and therefore their employers) to be tested in compliance with the ETS requirements for frequency of testing.
OSHA notes that there are several options for large employers to consider if they want to help facilitate testing for employees who are not vaccinated. Delta Airlines, for example, currently requires weekly COVID-19 testing for all of its employees who are not vaccinated, and the company has engaged the Mayo Clinic Laboratories to help design the employee testing program, assist in administering diagnostic and serology tests, and analyze the results to determine broader trends and provide recommendations to Delta's existing policies and procedures (Mayo Clinic Laboratories, June 30, 2020). Delta Airlines also operates onsite testing in cities with large employee populations including Atlanta, Minneapolis, and New York. It recently extended an at-home specimen collection option to all U.S. employees, through which Quest Diagnostics will send self-collection kits directly to an employee's doorstep upon request and support complete laboratory confirmation for results (Delta, August 25, 2021).
c. Availability of COVID-19 Tests
In the spring and early summer months of 2021, demand for tests decreased as vaccinations began to increase and the number of COVID-19 cases declined before the Delta surge and some manufacturers slowed production of COVID-19 tests. However, the number of tests performed daily has grown considerably over the summer due to the Delta Variant surge and re-openings of workplaces and schools. In parallel with the Delta surge, COVID-19 testing has increased from a daily average of about 450,000 in early July 2021 to about 1.8 million by mid-September 2021, or roughly 12.6 million per week (JHU, October 8, 2021). This data does not include any self-administered OTC tests, which will be discussed below.
OSHA's review of the evidence shows that the increasing rate of production of COVID-19 tests is more than adequate to meet rising demand related to compliance with the ETS testing option before the 60-day delayed testing compliance date (see paragraph (m)(2)(ii)). This determination is largely based on the number of tests with FDA EUAs actively being produced through the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Rapid Acceleration of Diagnostics (RADx) initiative described below.
According to the Johns Hopkins University of Medicine Coronavirus Resource Center, the total tests administered in August 2021 was approximately 44.4 million (or approximately 11.1 million per week). Id. During that same month, the total tests produced by the NIH RADx contracts was approximately 121 million (which would average to 30.25 million per week), resulting in a substantial surplus of available tests (NIBIB, September 28, 2021). As discussed in Economic Analysis , Section IV.B. of this preamble, Table IV.B.8, OSHA estimates that as many as 7.2 million tests may be administered weekly under this standard; however, 7.2 million is almost certainly an overestimate because it does not exclude employees who are already required to be tested by their employers and would continue to be tested at the same frequency after the ETS. Even if testing is increased by 7.2 million tests per week because of the ETS, that would still mean a surplus of nearly 12 million tests per week beyond what would be need to continue at current testing levels with the addition of ETS-related tests (30.25 − 11.1 − 7.2 = 11.95 million surplus per week).
The total number of tests administered during June, July, and August 2021, the period of the summer including the Delta Variant surge and other reasons for substantial testing increases such as re-opening of schools, was approximately 87 million tests, an average of approximately 6.7 million per week (JHU, October 8, 2021). During that period, more than 400 million COVID-19 tests were produced through the NIH RADx initiative, or roughly 33 million per week. OSHA anticipates that this surplus of tests will continue to increase the availability of tests that can be used to comply with the ETS.
The data from the Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center is collected from state and county government sources, so it does not include any self-administered OTC tests. Additionally, while all states report PCR testing, not all states report antigen testing. Nevertheless, the data from Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center is the best available evidence from which to estimate the total number of tests administered during a given period of time. Even though the number of administered tests reported through the Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center does not include unreported OTC tests, the NIH RADx program data shows a large surplus and sufficient additional COVID-19 test capacity relative to the number of administered tests reported. Additionally, the NIH RADx program will further allow for increased test distribution through retail markets and will address any increase in demand due to companies that may stockpile tests. This increased availability will strengthen test capacity, further enabling compliance with the ETS testing provision (NIBIB, September 28, 2021). OSHA has determined that even with an estimated additional 7.2 million tests administered weekly due to the ETS (see Economic Analysis (Section IV.B. of this preamble)), there are sufficient COVID-19 tests available to allow for both employers and employees to obtain COVID-19 tests through a variety of retail sources ( e.g., local pharmacies, on-line purchasing as discussed above).
Determinations of testing capacity are aggregate measures of domestic and global market and supply chains. Throughout the pandemic, diagnostic testing capacity has been stressed by the increased demand, as some products that are part of a global market cannot adapt by simply increasing manufacturing in one country ( e.g., laboratory instruments), and other products manufactured domestically require capital investments to address rising demands ( e.g., extraction kits) (CRS, February 25, 2021). As discussed below, because of the substantial investments made, OSHA projects that the diagnostic testing capacity can meet the increased demand due to this ETS.
OSHA evaluated multiple projections of current and future testing capacity and determined that projections related to the NIH initiatives discussed below are the most reliable estimates of current and future testing capacity for its technological feasibility assessment. Test manufacturers receiving NIH, FDA, and Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA) (a component of HHS) funding as part of these programs undergo a submission and authorization process where their production capacity and pipeline are assessed and production quantities are validated. As explained below, as of August 2021, the NIH data indicates testing capacity stands at about 30 million tests per week, and capacity continues to grow (NIBIB, September 28, 2021). OSHA notes that this number underestimates the total number of tests available each week, as it only includes companies that have received funding for tests and testing supplies through the NIH initiatives described below.
The NIH has identified constraints on testing capacity as an area of focus and investment since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, and OSHA examined potential constraints on testing capacity as part of its feasibility analysis. As described below, massive investments in testing capabilities, particularly in underserved areas, have largely mitigated issues with the availability of COVID-19 tests. Further, testing capacity continues to grow as new tests are developed and brought to market and manufacturers can ramp up supply to meet any future testing demands if need be.
The FDA has authorized more than 320 tests and collection kits that diagnose current infection with the SARS-CoV-2 virus and may be acceptable under the ETS (FDA, October 1, 2021). Among other criteria, the standard allows for the use of tests with specimens that are processed by a CLIA certified laboratory (including home or on-site collected specimens which are processed either individually or as pooled specimens), proctored over-the-counter tests, point of care tests, and tests where specimen collection and processing is either done or observed by an employer. As explained above, many employers across various industry sectors have already implemented policies for onsite testing. The use of FDA-authorized POC tests by these employers would be compliant with the testing provision of the ETS if the entity administering the test holds a CLIA certificate as required by the EUA. COVID-19 OTC tests that are both self-administered and self-read by employees do not satisfy the testing requirement unless observed by the employer or an authorized telehealth proctor. In the event that the employer is merely observing the employee conduct a test, a CLIA certificate would not be needed.
There have been extensive investments, including by the federal government, to help ensure that COVID-19 tests are widely available. Section 2401 of the American Rescue Plan appropriated $47,800,000 to the Secretary of the HHS, to remain available until expended, to carry out activities to detect, diagnose, trace, and monitor SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 infections and related strategies to mitigate the spread of COVID-19. Funds were made available to implement a national testing strategy; provide technical assistance, guidance, support, and awards grants or cooperative agreements to State, local, and territorial public health departments; and support the development, manufacturing, procurement, distribution, and administration of tests to detect or diagnose SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19; and establish federal, state, local and territorial testing capabilities.
On April 29, 2020, the NIH established the RADx initiative with a $1.5 billion investment. The RADx initiative has used this funding to speed development of rapid and widely-accessible COVID-19 testing (NIH, April 29, 2020). On October 6, 2020, the NIH and BARDA established the RADx Technology (RADx-Tech) and RADx Advanced Technology Platforms (RADx-ATP) programs to speed innovation in the development, commercialization, and implementation of technologies for COVID-19 testing specifically for late-stage scale-up projects. Through the RADx Tech and RADx-ATP programs, the NIH and BARDA have awarded a total of $476.4 million in manufacturing expansion contracts supporting a combined portfolio of 22 companies in the U.S. (NIH, October 6, 2020).
These programs have significantly increased testing capacity throughout the country. Since being established, RADx has worked closely with the FDA, the CDC, and BARDA to move more advanced diagnostic technologies swiftly through the development pipeline toward commercialization and broad availability. On April 28, 2021, the Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE) dedicated a special issue in the Journal of Engineering in Medicine and Biology exploring the innovative structure and operation of the RADx Tech program and determined that the initiatives had succeeded in dramatically increasing COVID-19 testing capacity in the United States. The IEEE report found that the RADx Tech/ATP programs, in conjunction with BARDA and the FDA, had streamlined and bolstered the national COVID-19 testing capacity. At the time of the report, the RADx Tech/ATP programs had increased the number of testing makers to 150 companies that, as a result of the NIH/BARDA investments, had the capacity to produce up to 1.9 million tests per day (IEEE, April 28, 2021).
The NIH RADx-TECH/ATP initiative entered its second phase on September 28, 2021, and at that time the supported companies had collectively produced over 500 million tests, received 27 FDA authorizations, and developed the first OTC COVID-19 test for use at home. These September 2021 investments are supporting late stage development of innovative point-of-care and home-based tests, as well as improved clinical laboratory tests that will increase the capacity of testing in the U.S. A full list of active contracts and supported U.S. COVID-19 testing manufacturers can be found on the NIH RADx-TECH/ATP programs: Phase 2 awards (NIBIB, October 14, 2021).
The following example shows the NIH RADx EUA pipeline process. On May 9, 2020, the FDA authorized the first EUA for a COVID-19 antigen test, a new category of tests for use in the ongoing pandemic. Quidel was awarded a contract under the NIH RADx TECH/ATP phase 1 initiative for the Sofia 2 SARS Antigen FIA for use in high and moderate complexity laboratories certified by CLIA, as well as for point-of-care testing by facilities operating under a CLIA certificate of waiver (FDA, May 9, 2020). On July 31, 2020, Quidel announced that it had received a contract for $71 million under the NIH RADx TECH/ATP program, phase 1, to accelerate the expansion of its manufacturing capacity for production of the SARS-CoV-2 rapid antigen test and quickly exceeded that capacity (Quidel Corp., July 31, 2020). On March 31, 2021, the FDA then authorized a second EUA from Quidel under contract with the NIH RADx initiative for the QuickVue At-Home OTC COVID-19 Test, another antigen test where certain individuals can rapidly collect and test their sample at home, without needing to send a sample to a CLIA certifed laboratory for analysis (FDA, March 31, 2021). Furthermore, based on the success of the Quidel for the Sofia 2 SARS Antigen FIA increasing production capacity, the NIH granted another $70 million contract for manufacturing Capacity Scale-Up for Sofia SARS Antigen and Sofia Influenza A B/SARS FIAs on June 11, 2021 (FDA, June 11, 2021).
The RADx-TECH/ATP initiative maintains a dashboard of manufacturer testing data from supported U.S. firms. OSHA reviewed the data available on the dashboard as part of its determination of feasibility. In August 2021, the data showed that U.S. manufacturers supported by the NIH RADx-TECH/ATP were producing approximately 30 million tests per week (NIBIB, September 28, 2021).
While consumers in some parts of the country have encountered difficulty obtaining rapid at-home tests, on October 4, 2021, the FDA granted EUA for the ACON Laboratories Flowflex COVID-19 Home Test, which is anticipated to double rapid at-home testing capacity in the United States within weeks (and well before compliance dates for testing required by this ETS) (FDA, October 4, 2021). By the end of the 2021 (ahead of the paragraph (g) compliance date), the manufacturer plans to produce more than 100 million tests per month and plans to produce more than 200 million tests per month by February 2022 (FDA, October 4, 2021). On October 6, 2021, the Administration announced a plan to buy $1 billion worth of rapid at-home COVID-19 tests; this purchase, coupled with the October 4 authorization of the Flowflex COVID-19 test, is expected to increase the number of available at-home COVID-19 tests to 200 million per month by December 2021 (Washington Post, October 6, 2021).
These investments have had a pronounced impact on the availability of testing and employers' use of testing in the workplace. ASU's recent report, How Work has Changed: The Lasting Impact of COVID-19 on the Workplace , ascribed the jump in the percentage of employers that test their employees from 17% in the fall of 2020 to 70% in the fall of 2021 in large part to the increased availability of testing. In particular, the report noted that by the spring of 2021, “it became relatively easy to acquire tests and hire testing service providers. There are more labs and companies with EUA's and most have enough capacity that there are few shortages.” (ASU WEF, September 2021).
Moreover, to ensure a broad, sustained capacity for COVID-19 test production, multiple COVID-19 test manufacturers have been mobilized by authority of the Defense Production Act. Under the Administration's plan to increase COVID-19 testing, the federal government will directly purchase and distribute 280 million- rapid point-of-care and over-the-counter at-home COVID-19 tests, sending 25 million free at-home rapid tests to community health centers and food banks. These actions will provide tests for use by communities to build adequate stockpiles, as well as the sustained production to be able to scale up production as needed in the future. Additionally, to ensure convenient access to free testing, 10,000 pharmacies will be added to the Department of Health and Human Services free testing program.
In response to rising demands for testing, U.S. manufacturers have increased production of COVID-19 test kit, reagents, and supplies. Advanced Medical Technology Association (AdvaMed), a trade group for testing manufacturers, reported that its members are ramping up production of rapid point-of-care test supplies to meet demand and that laboratory-based testing capacity for test confirmation is strong. AdvaMed has created a national COVID-19 Diagnostic Supply Registry of COVID-19 test manufacturers that support state and federal governments in their pandemic responses. Registry participants are thirteen leading diagnostic manufacturers whose tests together comprise approximately 75-80% of the COVID-19 in vitro diagnostic devices (IVD) on the market in the U.S. While these manufacturers produce a majority of molecular COVID-19 tests, they do not produce a majority of the total COVID-19 tests manufactured. These COVID-19 test manufacturers collectively shipped approximately 3.8 million tests in July 2021, 8.2 million tests in August 2021, and 9.4 million molecular tests for the week ending September 4th, 2021 (AdvaMed, September 10, 2021). While these figures are not representative of the total weekly testing capacity in the U.S., this data demonstrates that testing capacity has grown significantly over the past few months and reflects the success manufacturers have had in ramping up production of tests.
While current test availability is sufficient to meet the increased testing demands due to the ETS, OSHA is also confident that the RADx-TECH/ATP initiatives will continue to spur testing capacity and growth. The RADx-TECH/ATP initiatives have focused on moving test makers' products through the late stage pipeline and securing FDA authorization for entry into the market. So far, there have been 27 such authorizations. As of September 2021, there were 824 eligible late-stage scale up proposals from various test makers up for review for NIH/BARDA funding. Furthermore, 517 of these submissions are for the authorization and production of multiple types of COVID-19 tests including one or more of the following: Blood, sputum, nasal swab, oral swab, fecal, saliva, or other types. OSHA considers this to be further support for its determination that testing capacity will continue to grow and that increased COVID-19 testing supplies are on the horizon (NIBIB, September 28, 2021).
Based on data from the Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center, which examined publicly-available data from multiple sources, approximately 12.4 million tests were conducted during the week of August 26-September 2, 2021. As noted earlier, in the economic analysis of this ETS, OSHA projects testing rates to increase by approximately 7.2 million tests per week starting 60 days after publication of the ETS. As described above, many employers are currently testing their workforce. This 7.2 million is almost certainly an overestimate because it does not exclude employees who are already required to be tested by their employers and would continue to be tested at the same frequency after the ETS. The data reviewed by OSHA on the RADx-TECH/ATP Dashboard shows that the manufacturers supported by the initiative are producing approximately 30 million tests per week, and capacity continues to grow. As explained above, it is expected that roughly 50 million at-home COVID-19 tests will be available each week by December 2021. OSHA therefore finds that there are (and will continue to be) sufficient COVID-19 tests available to meet the anticipated demand related to compliance with paragraph (g) by the 60-day delayed compliance date.
d. Availability of COVID-19 Test Supplies
OSHA has also analyzed the availability of COVID-19 test supplies for use by COVID-19 test kit manufacturers, diagnostic laboratories, and determined that there are sufficient supplies to allow compliance with the ETS testing option. The COVID-19 pandemic and recent Delta Variant surge have caused some disruptions in the availability of testing supplies such as swabs, viral transport medium, RNA extraction kits, serology consumables, diagnostic reagents, plastic consumables, and diagnostic instruments. The COVID-19 testing supply market is driven by the need to rapidly screen large segments of the population and deliver test results. The data presented throughout this assessment has shown demand for laboratory COVID-19 tests is rising across the country.
Testing for COVID-19 involves many different components that are manufactured, transported, and used independently ( e.g., bulk solvents, extracting reagents, packaging) or semi-independently ( e.g., test kits). Most of the supplies used in COVID-19 testing are disposable, requiring a constant sustained capacity for new supplies. Some distribution channels move supplies directly to medical and laboratory end-users and others move supplies through distributors. In either case, the combination of increased testing demand and the established supply chains indicate that testing kits will be available in sufficient quantities throughout the country, including in rural areas where large employers may be located.
There have been substantial investments from federal and state programs and private industry to stimulate the production and distribution of testing supplies to bolster testing capacity across the country. Many products, such as swabs and reagents for RNA extraction kits, exhibited rising demand and, at some point during the pandemic, were subject to shortages that threatened continued testing capacity. For example, there was only one domestic manufacturer of medical grade flocked swabs, Puritan Medical Products Company of Guilford, Maine, and the company's pre-pandemic capacity was insufficient to meet demand of increased testing in the early period of the COVID-19 pandemic (Puritan Products, April 20, 2020). On July 29, 2020, the Department of Defense (DOD), in coordination with the Department of Health and Human Services, awarded $51.15 million to Puritan to expand industrial production capacity of flock tip testing swabs (DOD, July 31, 2020). On March 26, 2021, Puritan was awarded another $146.77 million to increase the company's total production capacity to 250 million foam tip swabs per month at its Tennessee facility by February 2022 (DOD, March 29, 2021).
Other private sector companies were mobilized to change the products they manufactured to accelerate production of COVID-19 test components, such as swabs, reagents, and solvents for RNA extraction kits. For example, Microbrush, a U.S.-based manufacturer of sterile applicators for the dental industry, began production of a nasopharyngeal test swab to meet the growing demand for COVID-19 testing requirements in July 2020. The Microbrush test swabs are sterilized and individually packaged in a medical- grade pouch intended for nasopharyngeal sample collection such as in dental procedures and also COVID-19 testing (Microbrush, July 1, 2020).
RNA extraction kits are used by the majority of NAAT protocols. These kits are sets of consumable plastic laboratory materials (small centrifuge tubes, filters, and collection vials) and chemical reagents (solutions for breaking the virus apart and purification) assembled by a manufacturer. Each kit has enough materials to process several dozen samples. The use of RNA extraction kits is not exclusive to COVID-19 testing, meaning that a market existed pre-COVID-19, and manufacturers were able to adapt to fluctuations in demand spurred by the pandemic.
There are multiple companies with facilities in the United States that produce RNA extraction kits for the domestic market that have been awarded federal grants to increase the supply of COVID-19 test kits and reagent supplies. For example, in December 2020, the DOD and HHS identified several key reagents with the potential for supply chain bottlenecks and awarded a $4.8 million Indefinite Delivery/Indefinite Quantity contract to Anatrace Products, LLC to support increased production of key reagents for sample processing; Polyadenylic Acid (Poly A), Guanidinium Thiocyanate (GTC), and Proteinase K (Pro K) to process samples (DOD, December 21, 2020). Additionally, QIAGEN (based in Germany with U.S. manufacturing in Germantown, Maryland) produces extraction kits for authorized COVID-19 tests and has responded to the pandemic by scaling their production to around the clock production to strengthen testing kit capacity (Qiagen, October 2, 2021). On August 23, 2021, DOD, on behalf of and in coordination with HHS, awarded a $600,000 contract to QIAGEN to expand manufacturing capacity of enzymatic reagents and reagent kits used in COVID-19 molecular diagnostic tests, thereby allowing QIAGEN to increase its monthly production of reagent kits by 7,000 and enzymes by 5,100 milligrams by the end of February 2022 to support domestic laboratory testing for COVID-19 (DOD, August 23, 2021).
Additionally, manufacturers of raw materials and solvents for COVID-19 test kits have implemented strategies to strengthen their portions of the COVID-19 test supply chain. Millipore Sigma, a large producer of solvents and raw materials for tests, has created a global task force to actively evaluate the overall supply chain of products and key raw material suppliers to mitigate any potential disruption of COVID-19 testing capacity (Millipore Sigma, October 2021). In light of the foregoing, OSHA believes that there is sufficient—and increasing—availability of COVID-19 testing supplies to enable compliance with the ETS testing option.
e. Sufficiency of Laboratory Capacity
As noted above, a wide range of tests are acceptable under the ETS, including those that can be observed by employers without laboratory processing. Moreover, there has been rapid growth in the availability of OTC tests that do not require laboratory processing. Authorized OTC tests self-administered by employees and proctored by the employer do not require a CLIA certificate of waiver.
The Association of Public Health Laboratories (APHL) has conducted weekly surveys of its membership to monitor their current and projected capability and capacity to test for COVID-19. Data from this survey is used to inform HHS, FEMA, CDC, and other federal partners to support public health laboratory supply and reagent needs. OSHA reviewed the weekly COVID-19 survey results through the APHL COVID-19 Lab Testing Capacity and Capability Data Dashboard. The data comes from voluntary participation in the weekly surveys collected from approximately 100 state, local and territorial public health laboratories (PHLs) and reported to the CDC. The APHL weekly survey data supports OSHA's feasibility determination and demonstrates that COVID-19 testing demand will be met. For example, from August 15, 2021 to September 12, 2021, the APHL weekly survey data found that 96-100% of PHLs are meeting their current testing demand since the Delta Variant surge began (APHL, September 27, 2021).
Laboratory capacity for processing and confirmation of at-home COVID-19 rapid tests provided by manufacturer retailers such as Walmart has also increased. Laboratory and diagnostic service providers have implemented parallel strategies to strengthen laboratory capacity for confirmation of at-home COVID-19 rapid tests available on the market for employers and employees to utilize. For example, Quest Diagnostics, which is the laboratory processing the samples and delivering results to those tested at Walmart's drive-through and curbside testing sites, has scaled up laboratory testing capacity and rapid antigen test inventory should demand increase (Walmart, July 9, 2021). Quest Diagnostics has added COVID-19 testing platforms in laboratories in regions where demand is comparatively high and has implemented an online consumer-initiated test service for individuals and small businesses to request COVID-19 testing. In August 2021, Quest Diagnostics began to offer clinician-guided rapid COVID-19 antigen testing to employers through a guided telehealth visit using a self-administered, nasal swab antigen test that provides results in 15 minutes that is then shipped to a Quest Diagnostics lab for confirmation (Quest Diagnostics, September 28, 2021).
Based on the evidence reviewed, OSHA has determined that there is adequate laboratory capacity to enable compliance with the ETS testing option.
f. Access to Testing in Underserved Communities
Individuals in underserved communities (including Black, Latino, and Indigenous and Native American persons, Asian Americans and Pacific Islanders and other persons of color; members of religious minorities; lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer persons; persons with disabilities; persons who live in rural areas; and persons otherwise adversely affected by persistent poverty or inequality) are disproportionately burdened by the COVID-19 pandemic as many individuals in these communities are essential workers who cannot work from home, increasing their risk of being exposed to the virus. Access to COVID-19 testing in these communities has been identified as contributing factor to COVID-19 related health disparities in these communities. For example, the NSC June 2021 survey found that the most common barrier to testing for rural employers and workers is access to vaccination and testing sites (NSC, September 2021).
Several federal efforts have recently been implemented to strengthen testing capabilities in underserved communities. The NIH has invested heavily to improve COVID-19 testing in underserved communities throughout the COVID-19 pandemic. On September 30, 2020, the NIH received nearly $234 million to improve COVID-19 testing for underserved and vulnerable populations that have been disproportionately affected by this pandemic and launched the RADx Underserved Populations (RADx-UP) program (NIH, September 30, 2020).
The RADx-UP program has primary components supported by these NIH grants to increase availability, accessibility, and acceptance of testing among underserved and vulnerable populations. The RADx-UP program also provides overarching support and guidance on administrative operations and logistics, facilitating effective use of COVID-19 testing technologies, supporting community and health system engagement, and providing overall infrastructure for data collection, integration, and sharing from a coordination and data collection center (NIH, September 30, 2021). Through the RADx-UP program, the NIH has continued to support the needs of underserved populations and is currently funding 70 community-based projects across the country (NIH, September 30, 2021).
The CDC has also focused its efforts to improve COVID-19 testing in underserved communities throughout the COVID-19 pandemic. For example, on September 20, 2021, Maine Health, the largest health care organization in Maine and also serving northern New Hampshire, was awarded nearly $1 million for COVID-19 testing in higher risk communities (Maine Health, September 20, 2021). In March 2021, the CDC implemented a plan to invest $2.25 billion over two years to address COVID-19 related health disparities and advance health equity among populations that are at high-risk and underserved, including racial and ethnic minority groups and people living in rural areas. Since that time, the CDC has awarded grants to public health departments to improve testing capabilities; improve data collection and reporting; and build, leverage, and expand infrastructure support for testing (CDC, March 17, 2021). On September 30, 2021, the CDC awarded an $8.1 million grant to the Arizona Center for Rural Health (ACRH) to address COVID-19 disparities across Arizona by improving the delivery of COVID-19 testing to rural and underserved communities (ASU CRH, September 30, 2021). A number of other federal and state government agencies have been expanding support for COVID-19 testing in underserved communities as well. On June 11, 2021, HHS through the Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) provided $424.7 million in American Rescue Plan funding to over 4,200 Rural Health Clinics (RHCs) for COVID-19 testing (HHS, June 11, 2021).
Private industry has also mobilized considerably to increase access and testing capacity in rural and other underserved communities. The NSC June 2021 survey found that a common barrier to employers and employees in rural and other underserved communities is transportation and access to vaccination and testing sites (NSC, September 2021). In its final report, the NSC recommended employers in these communities host on-site vaccinations to increase worker access. Applications for mobile vaccination are available on most local and state health department websites (NSC, September 2021; ASU WEF, September 2021).
CVS has collaborated with several organizations, including the National Medical Association, to increase access to testing in underserved communities and has developed mobile solutions that allow health care professionals to bring testing capabilities to businesses in these communities as they re-open (CVS Health, September 2021). Walgreens has implemented efforts to increase access in underserved communities such as rural and/or lower socioeconomic communities as well, with now more than half of Walgreens testing sites currently located in areas the CDC has identified as socially vulnerable and underserved (Walgreens, October 2021). Because of these investments, OSHA concludes that employers and their employees in underserved communities, including those in rural areas, will have sufficient access to COVID-19 tests and will be able to comply with the ETS's testing requirements for employees who are not fully vaccinated.
V. Management of Confidential Medical Records, Including Employee COVID-19 Vaccination and Testing Records
The ETS requires employers to maintain a record of each employee's vaccination status. Employers must also maintain a record of each test result provided by each employee. These records must be maintained as confidential medical records and must not be disclosed except as required or authorized by this ETS or other federal law. The records are not subject to the retention requirements of 29 CFR 1910.1020(d)(1)(i) but must be maintained and preserved while the ETS is in effect.
Other OSHA rules have a similar requirement to maintain employee medical records, which could include vaccination records. See, e.g. , Bloodborne Pathogens (29 CFR 1910.1030), Respiratory Protection (29 CFR 1910.134), Respirable Crystalline Silica (29 CFR 1910.1053), Beryllium (29 CFR 1910.1024), Lead (29 CFR 1910.1025), and OSHA's requirements for employee access to medical and exposure records (29 CFR 1910.1020). OSHA is not aware of any potential technological feasibility issues related to recordkeeping.
The requirement under this ETS to maintain records of employees' COVID-19 vaccination status and COVID-19 test results is similar to requirements in the aforementioned OSHA standards, and OSHA therefore concludes that compliance is feasible. Employers subject to the ETS will be able to comply with the provisions in the ETS using straightforward recordkeeping systems that are already widely used by large employers as part of their usual and customary business practices. OSHA concludes that it is feasible for such employers to comply with the requirements in the ETS for maintaining records related to COVID-19 vaccination status and COVID-19 test results.
VI. Other Provisions
There are no technological feasibility barriers related to compliance with other requirements in the ETS ( e.g., face coverings, employee notification). As explained above, many of the employer plans and best practice documents reviewed by OSHA indicate that employers have implemented the measures in these provisions across industry sectors. OSHA highlights two of the ETS's other requirements below, which are explored in more depth in other sections of this preamble.
• Face Coverings. Paragraph (i) of the ETS requires the employer to ensure that all employees who are not fully vaccinated wear a face covering when indoors and when occupying a vehicle with another person for work purposes, except: (i) When an employee is alone in a room with floor to ceiling walls and a closed door; (ii) for a limited time while the employee is eating or drinking at the workplace or for identification purposes in compliance with safety and security requirements; (iii) when employees are wearing respirators or face masks; or (iv) where the employer can show that the use of face coverings is infeasible or creates a greater hazard. The definition of face covering allows various different types of masks, including clear face coverings or cloth face coverings with a clear plastic panel which may be used to facilitate communication with people who are deaf or hard-of-hearing or others who need to see a speaker's mouth or facial expressions to understand speech or sign language respectively. The types of face coverings permitted under this ETS are widely used and readily available. The results of the ASU WEF June 2021 survey found that 30% of employers required face coverings for unvaccinated employees, which demonstrates that this provision of the ETS is currently being implemented by a substantial number of employers and is “capable of being done.” (ASU WEF, September 2021). OSHA identifies no technological feasibility issues with this provision of the ETS.
• Notification. Paragraph (h) of the ETS contains COVID-19 notification requirements for both the employer and the employee. Under this provision, the employer must require each employee to promptly notify the employer if they receive a positive COVID-19 test or are diagnosed with COVID-19 by a licensed healthcare provider and must immediately remove any employee from the workplace who receives a positive COVID-19 test or is diagnosed with COVID-19 by a licensed healthcare provider. OSHA identifies no technological feasibility issues in connection with the ETS's notification requirements. It is the employer's responsibility to ensure that appropriate instructions and procedures are in place so that designated representatives of the employer (e.g., managers, supervisors) and employees conform to the rule's requirements.
VII. Conclusion
OSHA has determined that complying with this ETS is technologically feasible for typical firms covered by this standard, at least most of the time (see Public Citizen v. OSHA , 557 F.3d 165 (3d Cir. 2009); Lead I , 647 F.2d at 1272; Lead II , 939 F.2d at 990). OSHA reviewed extensive evidence across industries and did not identify any industry-specific compliance barriers. Evidence in the record that shows that the written workplace COVID-19 vaccination policy requiring each employee to be fully vaccinated against COVID-19 unless they establish and implement a written policy that permits an employee to choose to be tested for COVID-19 at least every seven days and wear a face covering is feasible. In fact, such policies have already been implemented by hundreds of large companies across industry sectors. OSHA has also determined that there are sufficient COVID-19 tests available and adequate laboratory capacity to meet the anticipated increased testing demand related to compliance with the ETS testing option.
Additionally, the ETS's requirements to determine employee vaccination status, support employee vaccination by providing time off for vaccination and time off for recovery, and maintain records of employee COVID-19 vaccination status and COVID-19 test results are also technologically feasible. As discussed above, that many employers and organizations have already implemented such requirements demonstrates that they are “capable of being done.” Moreover, the recordkeeping requirements in this ETS largely mirror the requirements for the collection and maintenance of similar employee medical records in OSHA's Bloodborne Pathogens standard (29 CFR 1910.1030) and the Respiratory Protection standard (29 CFR 1910.134). The ETS provides a flexible compliance option for employers to tailor their procedures and practices to the needs of their workplace. OSHA finds that employers in typical firms in all industry sectors can comply with the requirements of the ETS, and compliance with the ETS is therefore technologically feasible.
References
Advanced Medical Technology Association (AdvaMed). (2021, September 10). ADVAMED COVID-19 Diagnostic Supply Registry. https://www.advamed.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/AdvaMed-COVID-Testing-Supply-Registry-weekly-report-091021.pdf (AdvaMed, September 10, 2021)
Amazon.com (Amazon). (2021, October 12). Amazon.com product search results: FDA EUA covid-19 tests. https://www.amazon.com/s?k=FDA EUA covid-19 tests&ref=nb_sb_noss_2. (Amazon, October 12, 2021)
Arizona State University College of Health Solutions (ASU). (2021, October 5). COVID-19 Diagnostic Commons. https://chs.asu.edu/diagnostics-commons. (ASU, October 5, 2021)
Arizona State University (ASU) and the World Economic Forum (WEF). (2021, September). How work has changed: The Lasting Impact of COVID-19 on the Workplace. https://issuu.com/asuhealthsolutions/docs/asu_workplace_commons_sept2021_singles?fr=sNjBiNDE5NTg1NjM. (ASU WEF, September 2021)
Association of Public Health Laboratories (APHL). (2021, September 27). Lab Testing Capacity and Capability Data Dashboard. https://www.aphl.org/programs/preparedness/Crisis-Management/COVID-19-Response/Pages/COVID-19-Dashboard.aspx. (APHL, September 27, 2021)
Becker's Hospital Review. (2021, October 11). Hospitals, health systems mandating vaccines for workers. https://www.beckershospitalreview.com/workforce/hospitals-health-systems-mandating-vaccines-for-workersjune17.html. (Becker's Hospital Review, October 11, 2021)
Capital One. (2021, August 11). Capital One Announces Modifications to Workplace Return. https://www.capitalone.com/about/newsroom/return-to-office-update/. (Capital One, August 11, 2021)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, March 17). CDC Announces $2.25 Billion to Address COVID-19 Health Disparities in Communities that are at High-Risk and Underserved. https://www.cdc.gov/media/releases/2021/p0317-COVID-19-Health-Disparities.html. (CDC, March 17, 2021)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, July 8). Guidance for SARS-CoV-2 Point-of-Care and Rapid Testing. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/lab/point-of-care-testing.html. (CDC, July 8, 2021)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, September 9). Interim Guidance for Antigen Testing for SARS-CoV-2. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/lab/resources/antigen-tests-guidelines.html. (CDC, September 9, 2021)
Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment (CDPHE). (2021, September 17). Vaccine laws and regulations. https://covid19.colorado.gov/vaccine-laws-regulations. (CDPHE, September 17, 2021)
Congressional Research Service (CRS). (2021, February 25). COVID-19 Testing Supply Chain. https://crsreports.congress.gov/product/pdf/IF/IF11774. (CRS, February 25, 2021)
CVS Health. (2021, August 23). CVS Health will require COVID-19 vaccinations for clinical and corporate employees. https://cvshealth.com/news-and-insights/statements/cvs-health-will-require-covid-19-vaccinations-for-clinical-and-corporate-employees. (CVS Health, August 23, 2021)
CVS Health. (2021, September). COVID-19: Testing information. https://cvshealth.com/covid-19/testing-information. (CVS Health, September 2021)
Delta Airlines. (2021, August 25). Bastian memo to employees outlines COVID vaccine updates. https://news.delta.com/bastian-memo-employees-outlines-covid-vaccine-updates. (Delta, August 25, 2021)
Fifty/50 Group. (2021, May 18). Employee Vaccination Requirement Policy. https://www.thefifty50group.com/covidvaccines. (Fifty/50 Group, May 18, 2021)
Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2020, May 9). Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: FDA Authorizes First Antigen Test to Help in the Rapid Detection of the Virus that Causes COVID-19 in Patients. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-authorizes-first-antigen-test-help-rapid-detection-virus-causes. (FDA, May 9, 2020)
Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2021, March 31). Emergency Use Authorization QuickVue At-Home OTC COVID-19 Test. https://www.fda.gov/media/147247/download. (FDA, March 31, 2021)
Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2021, June 11). Emergency Use Authorization Sofia SARS Antigen FIA OTC COVID-19 Test. https://www.fda.gov/media/137886/download. (FDA, June 11, 2021)
Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2021, September 10). COVID-19 Tests and Collection Kits Authorized by the FDA: Infographic. https://www.fda.gov/ medical-devices/coronavirus-covid-19-and-medical-devices/covid-19-tests-and-collection-kits-authorized-fda-infographic. (FDA, September 10, 2021)
Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2021, September 22). Coronavirus Disease 2019 Testing Basics. https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/coronavirus-disease-2019-testing-basics. (FDA, September 22, 2021)
Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2021, October 1). Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: October 1, 2021. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-october-1-2021. (FDA, October 1, 2021)
Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2021, October 4). Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: FDA Authorizes Additional OTC Home Test to Increase Access to Rapid Testing for Consumers. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-authorizes-additional-otc-home-test-increase-access-rapid-testing. (FDA, October 4, 2021)
Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2021a, October 14). In Vitro Diagnostics EUAs—Antigen Diagnostic Tests for SARS-CoV-2. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/coronavirus-disease-2019-covid-19-emergency-use-authorizations-medical-devices/in-vitro-diagnostics-euas-antigen-diagnostic-tests-sars-cov-2. (FDA, October 14, 2021a)
Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2021b, October 14). In Vitro Diagnostics EUAs—Molecular Diagnostic Tests for SARS-CoV-2. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/coronavirus-disease-2019-covid-19-emergency-use-authorizations-medical-devices/in-vitro-diagnostics-euas-molecular-diagnostic-tests-sars-cov-2. (FDA, October 14, 2021b)
Fulton County, Georgia. (2021, September 3). Fulton Commissioners Approve Employee Vaccine Protocols. https://www.fultoncountyga.gov/news/2021/09/03/fulton-commissioners-approve-employee-vaccine-protocols. (Fulton County Government, September 3, 2021)
Genesis Health Care. (2021, September 29). Coronavirus Updates. https://www.genesishcc.com/coronavirus-updates. (Genesis Health Care, September 29, 2021)
Health Action Alliance (HAA). (2021, October 10). COVID-19 Vaccines: Employers & Requirements. A list of companies requiring vaccinations for all or part of their workforce or customers. https://www.healthaction.org/resources/vaccines/covid-19-vaccines-employer-requirements-health-action-alliance. (HAA, October 10, 2021)
Health Action Alliance (HAA) and the National Safety Council (NSC). (2021, September 17). COVID-19 Employer Policies: A Decision Tool for Business Leaders. https://www.healthaction.org/reopening-questions#Q. (HAA and NSC, September 17, 2021)
Institutes of Electrical and Electronics Engineers. (IEEE). (2021, April 28). RADxSM Tech: A New Paradigm for MedTech Development Overview of This Special Section. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9418526. (IEEE, April 28, 2021)
International Union of Painters and Allied Trades (IUPAT). (2021, May 10). IUPAT Supports Vaccine Mandates. https://www.iupat.org/press-room/vaccine-policy/. (IUPAT, May 10, 2021)
Johns Hopkins University. (2021, October 8). Coronavirus Resource Center: Testing Hub. https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/testing/individual-states. (JHU, October 8, 2021)
Kaiser Permanente. (2021, August 2). Protecting health and safety through vaccination. https://about.kaiserpermanente.org/our-story/news/announcements/protecting-health-and-safety-through-vaccination. (Kaiser Permanente, August 2, 2021)
MaineHealth. (2021, September 20). MaineHealth awarded nearly $1M by National Institutes of Health to study COVID-19 testing in higher risk communities. https://www.mainehealth.org/News/2021/09/MaineHealth-awarded-nearly-1M-by-NIH-to-study-COVID19-testing. (Maine Health, September 20, 2021)
Mayo Clinic Laboratories. (2020, June 30). Mayo Clinic experts to help guide Delta Air Lines COVID-19 safety measures. https://newsnetwork.mayoclinic.org/discussion/delta-engages-mayo-clinic-experts-to-advise-on-making-travel-even-safer/. (Mayo Clinic Laboratories, June 30, 2020)
Microbrush. (2020, July 1). Microbrush Introduces New Nasopharyngeal Test Swabs. https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/microbrush-introduces-new-nasopharyngeal-test-swabs-301087276.html. (Microbrush, July 1, 2020)
Millipore Sigma. (2021, October). Coronavirus COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) Detection, Characterization, Vaccine and Therapy Production. https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/US/en/life-science/covid. (Millipore Sigma, October 2021)
National Academy for State Health Policy (NASHP). (2021, October 1). State Efforts to Ban or Enforce COVID-19 Vaccine Mandates and Passports. https://www.nashp.org/state-lawmakers-submit-bills-to-ban-employer-vaccine-mandates/. (NASHP, October 1, 2021)
National Institutes of Health (NIH) National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB). (2021, September 28). RADx Tech/ATP Dashboard. https://www.nibib.nih.gov/covid-19/radx-tech-program/radx-tech-dashboard. (NIBIB, September 28, 2021)
National Institutes of Health (NIH) National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB). (2021, October 14). RADxSM Tech and ATP Programs: Phase 2 Awards. https://www.nibib.nih.gov/covid-19/radx-tech-program/radx-tech-phase2-awards. (NBIB, October14, 2021)
National Institutes of Health (NIH). (2020, October 6). NIH RADx initiative advances six new COVID-19 testing technologies. https://www.nih.gov/news-events/news-releases/nih-radx-initiative-advances-six-new-covid-19-testing-technologies. (NIH, October 6, 2020)
National Institutes of Health (NIH). (2020, September 30). NIH to assess and expand COVID-19 testing for underserved communities. https://www.nih.gov/news-events/news-releases/nih-assess-expand-covid-19-testing-underserved-communities. (NIH, September 30, 2020)
National Institutes of Health (NIH). (2020, April 29). NIH mobilizes national innovation initiative for COVID-19 diagnostics. https://www.nih.gov/news-events/news-releases/nih-mobilizes-national-innovation-initiative-covid-19-diagnostics. (NIH, April 29, 2020)
National Safety Council (NSC). (2021, May 17). SAFER: Safe Actions For Employee Returns. https://www.nsc.org/getmedia/f5dfd05d-83bf-4753-8903-538a24157725/safer-framework-summary.pdf. (NSC, May 17, 2021)
National Safety Council (NSC). (2021, September). SAFER Report: A Year in Review, and What's Next. https://www.nsc.org/workplace/safety-topics/safer/state-of-the-response-state-actions-to-address-the. (NSC, September 2021)
Puritan Products. (2020, April 20). Puritan Blog: Puritan at the Epicenter of COVID-19 Testing. https://blog.puritanmedproducts.com/puritan-at-epicenter-of-covid-19-testing. (Puritan Products, April 20, 2020)
Qiagen. (2021, October 2). COVID-19 Latest News. https://www.qiagen.com/us/customer-stories/latest-news-on-the-fight-against-coronavirus. (Qiagen, October 2, 2021)
Quest Diagnostics. (2021, September 28). Quest Diagnostics Media Statement about COVID-19 Testing. https://newsroom.questdiagnostics.com/COVIDTestingUpdates. (Quest Diagnostics, September 28, 2021)
Quidel Corporation. (2020, July 31). Press release, Quidel Corp. https://ir.quidel.com/news/news-release-details/2020/Quidel-Receives-Preliminary-Contract-Leading-to-Definitive-Agreement-for-71-Million-Under-NIHs-RADx-ATP-Program-to-Accelerate-the-Expansion-of-Its-Manufacturing-Capacity-for-Sofia-SARS-CoV-2-Antigen-Detection-Test-for-Rapid-Diagnosis-of-COVID-19/default.aspx. (Quidel Corp., July 31, 2020)
RiteAid. (2021, October). Free* COVID-19 Testing. https://www.riteaid.com/pharmacy/services/covid-19-testing. (RiteAid, October 2021)
Sanford Health. (2021, July 22). Sanford Health to require COVID-19 vaccine for employees. https://news.sanfordhealth.org/news-release/sanford-to-require-covid-19-vaccine-for-employees/. (Sanford Health, July 22, 2021)
Trinity Health. (2021, July 8). Trinity Health Announces COVID-19 Vaccine Requirement for All Colleagues. https://www.trinity-health.org/news/trinity-health-announces-covid-19-vaccine- requirement-for-all-colleagues. (Trinity Health, July 8, 2021)
Tyson Foods. (2021, August 3) Tyson Foods to Require COVID-19 Vaccinations for its U.S. Workforce. https://www.tysonfoods.com/news/news-releases/2021/8/tyson-foods-require-covid-19-vaccinations-its-us-workforce. (Tyson Foods, August 3, 2021)
University of Arizona Center for Rural Health (ASU CRH). (2021, September 30). ADHS-CDC COVID Disparities Initiative. https://crh.arizona.edu/programs/covid-disparities-initiative. (ASU CRH, September 30, 2021)
U.S. Department of Defense (DOD). (2021, March 29) DOD Awards $146.77 Million Contract to Puritan Medical Products to Increase Domestic Production Capacity of Foam Tip Swabs. https://www.defense.gov/News/Releases/Release/Article/2554073/dod-awards-14677-million-contract-to-puritan-medical-products-to-increase-domes/. (DOD, March 29, 2021)
U.S. Department of Defense (DOD). (2021, July 31). DOD Awards $51.15 Million Undefinitized Contract Action to Puritan Medical Products Company LLC to Increase Domestic Production Capacity of Flock Tip Testing Swabs. https://www.defense.gov/News/Releases/Release/Article/2295387/dod-awards-5115-million-undefinitized-contract-action-to-puritan-medical-produc/. (DOD, July 31, 2021)
U.S. Department of Defense (DOD). (2021, August 23). DOD Awards $0.6 Million Contract to QIAGEN to Increase Domestic Production Capacity of COVID-19 Diagnostic Test Kits and Reagents. https://www.defense.gov/News/Releases/Release/Article/2742967/dod-awards-06-million-contract-to-qiagen-to-increase-domestic-production-capaci/. (DOD, August 23, 2021)
U.S. Department of Defense (DOD). (2021, December 21). DOD Awards $4.8 Million Indefinite Delivery/Indefinite Quantity to a Calibre Scientific Subsidiary, Anatrace, to Increase Domestic Production Capacity of COVID-19 Testing Reagents. https://www.defense.gov/News/Releases/Release/Article/2454163/dod-awards-48-million-indefinite-deliveryindefinite-quantity-to-a-calibre-scien/. (DOD, December 21, 2020)
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. (HHS). (2021, June 11). HHS Provides $424.7 Million to Rural Health Clinics for COVID-19 Testing and Mitigation in Rural Communities. https://www.hhs.gov/about/news/2021/06/11/hhs-provides-424-million-to-rural-health-clinics-for-covid-19-testing.html. (HHS, June 11, 2021)
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). (2021, August 17). Community based testing sites. https://www.hhs.gov/coronavirus/community-based-testing-sites/index.html. (HHS, August 17, 2021)
Walgreens. (2021, October). Free Drive-Thru COVID-19 Testing for Ages 3 . https://www.walgreens.com/findcare/covid19/testing?ban=covid_hp_cause2. (Walgreens, October 2021)
Walgreens. (2021, October 8). COVID-19 FAQs. https://news.walgreens.com/our-stories/covid-19-stories/covid-19-faq.htm#testinghome. (Walgreens, October 8, 2021)
Walmart. (2021, July 9). Supporting COVID-19 Testing. https://corporate.walmart.com/covid19testing. (Walmart, July 9, 2021)
Washington Post. (2021, October 6). White House announces $1 billion purchase of rapid, at-home coronavirus tests. https://www.washingtonpost.com/health/2021/10/06/biden-rapid-at-home-covid-tests/. (Washington Post, October 6, 2021)
Willis Towers Watson. (2021, June 23) COVID-19 Vaccination and Reopening the Workplace Survey press release. https://www.willistowerswatson.com/en-US/News/2021/09/workplace-vaccine-mandates-expected-to-accelerate-wtw-survey-finds. (Willis Towers Watson, June 23, 2021)
Willis Towers Watson. (2021, September 1) Workplace vaccine mandates expected to accelerate, Willis Towers Watson survey finds. https://www.willistowerswatson.com/en-US/News/2021/09/workplace-vaccine-mandates-expected-to-accelerate-wtw-survey-finds. (Willis Towers Watson, September 1, 2021)
B. Economic Analysis
I. Introduction
This section presents OSHA's estimates of the costs and impacts, anticipated to result from the COVID-19 Vaccination and Testing ETS, 29 CFR 1910.501. The purpose of this ETS is to address the grave danger of COVID-19 in the workplace by promoting vaccination, while allowing an alternative for face covering and testing requirements, and also to remove COVID-19 positive workers from the workplace regardless of vaccination status. The estimated costs are based on employers achieving full compliance with the requirements of the ETS. They do not include prior costs associated with firms whose current practices are already in compliance with the ETS requirements. The purpose of this analysis is to:
• Identify the entities/establishments and industries affected by the ETS;
• Estimate and evaluate the costs and economic impacts that regulated entities/establishments will incur to achieve compliance with the ETS; and
• Evaluate the economic feasibility of the rule for affected industries.
In this analysis, OSHA is fulfilling the requirement under the OSH Act to show the economic feasibility of this ETS. This analysis is different from the cost portion of a regulatory impact analysis prepared in accordance with Executive Order 12866 in that the agency is focused only on costs to employers when evaluating economic feasibility. In a regulatory impact analysis, the costs to all parties ( e.g. , employers, employees, and governments) are included. While this is not the case for an economic feasibility analysis, it does not necessarily mean that the ETS imposes no costs or burdens on parties other than employers. For example, the rule imposes certain costs on employees who choose not to become vaccinated ( e.g. , for face coverings and testing. While these costs are not relevant for the purpose of establishing economic feasibility, these costs would be attributable to the ETS in a regulatory impact analysis. In addition, these costs are not mandatory because any employee who does not wish to pay them may choose to become vaccinated or leave employment (see discussion below on turnover), after which the costs would not be incurred. Some employees may also be entitled to a reasonable accommodation that may avoid additional cost ( e.g. , telework).
“[T]he Supreme Court has conclusively ruled that economic feasibility [under the OSH Act] does not involve a cost-benefit analysis.” Pub. Citizen Health Research Grp. v. U.S. Dept. of Labor , 557 F.3d 165, 177 (3d Cir. 2009); see also Asbestos Info. Ass'n , 727 F.2d at 424 n.18 (noting that formal cost benefit is not required for an ETS, and indeed may be impossible in an emergency). The OSH Act “place[s] the `benefit' of worker health above all other considerations save those making attainment of this `benefit' unachievable.” Cotton Dust , 452 U.S. at 509. Therefore, “[a]ny standard based on a balancing of costs and benefits by the Secretary that strikes a different balance than that struck by Congress would be inconsistent with the command set forth in” the statute. Id. While this case law arose with respect to health standards issued under section 6(b)(5) of the Act, which specifically require feasibility, OSHA finds the same concerns applicable to emergency temporary standards issued under section 6(c) of the Act. An ETS “serve[s] as a proposed rule” for a section 6(b)(5) standard, and therefore the same limits on any requirement for cost-benefit analysis should apply. Indeed, OSHA has also rejected the use of formal cost benefit analysis for safety standards, which are not governed by section 6(b)(5). See 58 FR 16,612, 16,622-23 (Mar. 30, 1993) (“in OSHA's judgment, its statutory mandate to achieve safe and healthful workplaces for the nation's employees limits the role monetization of benefits and analysis of extra- workplace effects can play in setting safety standards.”). 22 A standard must be economically feasible in order to be “reasonably necessary and appropriate” under section 3(8) and, by inference, “necessary” under section 6(c)(1)(B) of the OSH Act. Cf. Am. Textile Mfrs. Inst., Inc. v. Donovan , 452 U.S. 490, 513 n.31 (1981) (noting “any standard that was not economically . . . feasible would a fortiori not be `reasonably necessary or appropriate' ” as required by the OSH Act's definition of “occupational safety and health standard” in section 3(8)); see also Florida Peach Growers , 489 F.2d at 130 (recognizing that the promulgation of any standard, including an ETS, must account for its economic effect). A standard is economically feasible when industries can absorb or pass on the costs of compliance without threatening industry's long-term profitability or competitive structure, Cotton Dust , 452 U.S. at 530 n.55, or “threaten[ing] massive dislocation to, or imperil[ing] the existence of, the industry.” United Steelworkers of Am. v. Marshall , 647 F.2d 1189, 1272 (D.C. Cir. 1981) ( Lead I ). Given that section 6(c) is aimed at enabling OSHA to protect workers in emergency situations, the agency is not required to make the showing with the same rigor as in ordinary section 6(b) rulemaking. Asbestos Info. Ass'n/N. Am. v. OSHA , 727 F.2d 415, 424 n.18 (5th Cir. 1984). In Asbestos Information Association , the Fifth Circuit concluded that the costs of compliance were not unreasonable to address a grave danger where the costs of the ETS did not exceed 7.2% of revenues in any affected industry. Id. at 424.
22 To support its Asbestos ETS, OSHA conducted an economic feasibility analysis on these terms. 48 FR 51086, 51136-38 (Nov. 4, 1983). In upholding that analysis, the Fifth Circuit said that OSHA was required to show that the balance of costs to benefits was not unreasonable. Asbestos Info. Ass'n , 727 F.2d at 423. As explained above, OSHA does not believe that is a correct statement of the economic feasibility test. However, even under that approach this ETS easily passes muster.
The scope of judicial review of OSHA's determinations regarding feasibility (both technological and economic) “is narrowly circumscribed.” N. Am.'s Bldg. Trades Unions v. OSHA , 878 F.3d 271, 296 (D.C. Cir. 2017) ( Silica ). “OSHA is not required to prove economic feasibility with certainty, but is required to use the best available evidence and to support its conclusions with substantial evidence.” Amer. Iron & Steel Inst. v. OSHA , 939 F.2d 975, 980-81 (D.C. Cir. 1991) ( Lead II ); 29 U.S.C. 655(b)(5), (f). “Courts, [moreover], ‘cannot expect hard and precise estimates of costs.' ” Silica , 878 F.3d at 296 (quoting Lead II , 939 F.2d at 1006). Rather, OSHA's estimates must represent “a reasonable assessment of the likely range of costs of its standard, and the likely effects of those costs on the industry.” Lead I , 647 F.2d at 1266. The “mere ‘possibility of drawing two inconsistent conclusions from the evidence,' or deriving two divergent cost models from the data ‘does not prevent [the] agency's finding from being supported by substantial evidence.' ” Silica , 878 F.3d at 296 (quoting Cotton Dust , 452 U.S. at 523).
Executive Orders 12866 and 13563 direct agencies to assess the costs and benefits of the intended regulation and, if regulation is necessary, to select regulatory approaches that maximize net benefits (including potential economic, environmental, and public health and safety effects; distributive impacts; and equity). Executive Order 13563 emphasized the importance of quantifying both costs and benefits, of reducing costs, of harmonizing rules, and of promoting flexibility. Because of the continued impact of the pandemic on occupational safety and health, OSHA has prepared this ETS and the accompanying economic analysis on an extremely condensed timeline. Thus, in light of the Secretary's conclusion that the COVID-19 pandemic constitutes an emergency situation, the Secretary has notified OIRA that it is necessary for OSHA to promulgate this regulation more quickly than normal review procedures allow, pursuant to E.O. 12866 Sec. 6 (a)(3)(D). OIRA has waived compliance with Sec. 6(a)(3)(B) and (C) for this economically significant rule.
II. COVID-19 ETS Industry Profile
a. Introduction
In this section, OSHA provides estimates of the number of affected entities, establishments, and employees for the industries that have settings covered by this ETS. The term “entity” describes a legal for-profit business, a non-profit organization, or a local governmental unit, whereas the term “establishment” describes a particular physical site of economic activity. Some entities own and operate more than one establishment.
Throughout this analysis, where estimates were derived from available data those sources have been noted in the text. Estimates without sources noted in the text are based on agency expertise.
b. Scope of the COVID-19 ETS
This ETS applies to all employers with a total of 100 or more employees at any time this ETS is in effect. However, the requirements of this ETS do not apply to: (1) Workplaces covered under the Safer Federal Workforce Task Force COVID-19 Workplace Safety: Guidance for Federal Contractors and Subcontractors (Contractor Guidance); or (2) settings where any employee provides healthcare services or healthcare support services when subject to the requirements of 29 CFR 1910.502 ( i.e. , the Healthcare ETS). Furthermore, the requirements of this ETS do not apply to the employees of covered employers: (1) Who do not report to a workplace where other individuals, such as coworkers or customers, are present; or (2) while working from home; or (3) who work exclusively outdoors. Based on this scope, employers in nearly every sector are expected to be covered by this ETS.
OSHA's assumptions may result in an overestimate of the number of employees affected by the ETS. First, OSHA is not estimating the number and type of workplaces covered by the Safer Federal Workforce Task Force COVID-19 Workplace Safety: Guidance for Federal Contractors and Subcontractors or removing them from the profile of employers affected by this ETS. OSHA assumes for the purpose of this analysis that employers covered under the Contractor Guidance will also have contracts to perform work in workplaces where they are not covered under that Guidance ( i.e. , where the employer contracts with an entity other than the federal government), and so those employers are included in the scope here.
Second, OSHA estimates that all employers in all private sector industries are affected by this ETS to some extent. Although this ETS imposes no compliance burden on employers whose employees work remotely 100 percent of the time, in OSHA's analysis, no employers with 100 or more employees have all of their employees working remotely 100 percent of the time ( i.e. , at least some employees in each affected firm do not work remotely). Moreover, OSHA's analysis does not take into account that some employees may engage in part-time telework ( i.e. , it assumes that employees either work remotely full-time or do not work remotely at all). Finally, OSHA's analysis does not fully take into account the exemption for employees who do not report to a workplace where other individuals are present, meaning that this analysis may overestimate the number of employees affected by the rule.
As stated, the requirements of this ETS do not apply to the employees of covered employers who work exclusively outdoors. To determine the percentage of employees in occupations for which the exception is relevant, the agency uses data from the BLS's 2020 Occupational Requirements Survey (ORS) (BLS, 2020). This survey looks at various aspects of job requirements. In particular, the survey lists occupations where workers are outdoors “constantly,” which OSHA interprets as being nearly continuously outdoors. Because the majority of workers who work outdoors “constantly” likely work indoors at least some of the time, the agency judges that no more than 10 percent of the workers who are primarily outdoors are actually there exclusively. See Table IV.B.1 for the occupations, the ORS percentages, and final percentages for workers OSHA estimates are exempt from the scope of this ETS based on the outdoor work exemption.
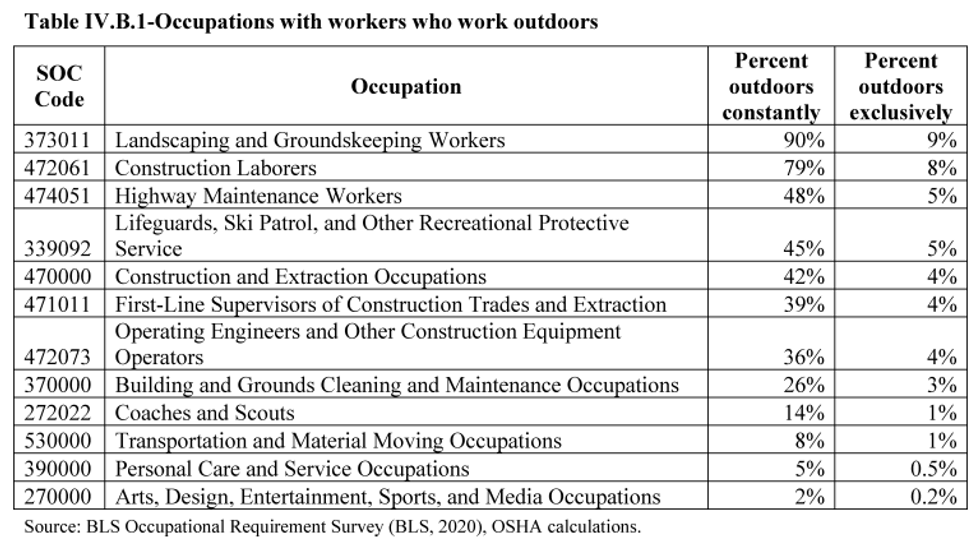
OSHA's estimate of employees who work exclusively outdoors does not account for employers who only need to make slight adjustments to their current work practices to ensure that their employees qualify for the outdoor exemption, such as by holding tool box talks outdoors instead of in a traditional indoor location. This may result in more employees falling within the exemption than estimated by OSHA; therefore, OSHA's cost analysis likely overestimates costs.
The requirements of the ETS also do not apply to settings where any employee provides healthcare services or healthcare support services when subject to the requirements of 29 CFR 1910.502 (the Healthcare ETS). The Healthcare ETS is a temporary standard that may not remain in effect for the entire period that 29 CFR 1910.501 remains in effect. This means that some employers or employees covered by the Healthcare ETS, those in firms that have 100 or more employees, may ultimately be covered by 29 CFR 1910.501 (because the exception in 29 CFR 1910.501 is limited to when employers are subject to the requirements of the Healthcare ETS). This potentially impacts two types of costs: Employer-based costs ( e.g. , employer policy on vaccination) and employee-based (periodic) costs ( e.g. , recordkeeping).
Employer-Based Costs: For the purpose of the economic analysis only, OSHA treats the Healthcare ETS as though it will no longer be in effect after December, 2021, because at that point the Healthcare ETS will have been in effect for the six months that OSHA had calculated costs for that ETS. Therefore, OSHA estimates that some employers including those with 100 or more employees subject to the 29 CFR 1910.502 exemption, will need to take employer-based costs because all these employers will ultimately be subject to 29 CFR 1910.501 under this assumption.
Employee-Based Costs: OSHA's estimates incorporate two assumptions for the purposes of this analysis only. First, for the purposes of assumptions for this analysis only, §1910.501 will remain in effect for 6 months. Second, many employers and employees currently covered only by the Healthcare ETS will be subject to the requirements of 29 CFR 1910.501 for approximately 4 months (4 months of the 6 month estimated lifespan of 29 CFR 1910.501). OSHA's estimate of those employees exempted by the Healthcare ETS was based on the Industry Profile of employees in firms with 100 employees or more covered by the Healthcare ETS, as estimated in Table VI.B.3 in the economic analysis for that rulemaking (see 86 FR 32488).
OSHA notes that some employees currently covered by the Healthcare ETS might also be currently covered by 29 CFR 1910.501 (albeit at different times or in different locations) because the Healthcare ETS is settings-based. For example, a pharmacist would normally not need to comply with the requirements of §1910.502 when just filling prescriptions in a retail pharmacy store (see 29 CFR 1910.502(a)(2)(ii)), but would need to comply when administering vaccinations within an embedded clinic inside that retail pharmacy. Thus, there are a number of variables that could impact the extent to which the pharmacist's employer might incur any costs. However, even to the extent that such costs might occur ( e.g. , recordkeeping for testing if the pharmacist works for an employer covered by 29 CFR 1910.501 and is unvaccinated), OSHA judges that they would be de minimis for several reasons. First, this pool of workers is likely to be very small, especially when compared to the population of workers covered by the Healthcare ETS. Second, most employees subject to both standards will have been fully vaccinated before OSHA takes costs for these employees under 29 CFR 1910.501 by operation of the CMS rule mandating vaccination or as a result of the voluntary vaccination incentives promoted by OSHA's Healthcare ETS (therefore negating most of the costs associated with vaccination and testing under 29 CFR 1910.501). Third, any underestimate of periodic costs will only apply during the first two months after 29 CFR 1910.501 goes into effect and the standard has a delayed compliance date of 30 days after the effective date for most provisions, except for testing, which has a delayed compliance date of 60 days. This will further lessen the periodic costs associated with any potential underestimate.
In all respects (other than the 4/6 share of employee-based costs), OSHA is taking the same approach in the Industry Profile and Cost Estimates for employers and employees currently covered by the Healthcare ETS as it does for all other industries. These employers and employees are fully integrated into Table IV.B.5, below, which contains a summary of covered entities and employees. Moreover, the same assumptions on outdoor work and other scope exemptions that OSHA explains earlier holds for these employers and employees. In addition, OSHA makes the same downward adjustment in telework for these employers and employees in accordance with the methodology it sets out below. Thus, the Healthcare ETS profile used in this ETS to account for employees exempted by the Healthcare ETS into the Profile in the event the Healthcare ETS expires (i.e., in Table IV.B.5, below) is an updated version of Table VI.B.3 in the Healthcare ETS (see 86 FR 32488). 23 OSHA notes that some firms may decide to proactively comply with certain 29 CFR 1910.501 requirements (such as mandating vaccination for all employees that were removed from the Industry Profile) before the end date of the Healthcare ETS based on the conclusion that 29 CFR 1910.501 will ultimately apply in full to them. Since these costs still occur due to 29 CFR 1910.501, OSHA is appropriately including them in this cost analysis.
23 The CMS rule published elsewhere in this issue of the Federal Register mandates vaccination for employees in facilities that receive Medicare or Medicaid. OSHA is ignoring this for the purpose of its cost analysis and taking costs into account as if the CMS rule were not promulgated. This creates a substantial overestimate.
There are 9.9 million employees who will newly be covered by 29 CFR 1910.501 starting in December whose employers will incur an additional $318 million in costs. These costs are integrated into the agency's main cost analysis, which is described later in this economic analysis.
Only some state- and local-government entities are included in this analysis. State- and local-government entities are specifically excluded from coverage under the OSH Act (29 U.S.C. 652(5)). Workers employed by these entities only have OSH Act protections if they work in states that have an OSHA-approved State Plan. (29 U.S.C. 667). Consequently, this analysis excludes public entities in states that do not have OSHA-approved State Plans. Table IV.B.2 presents the states that have OSHA-approved State Plans and their public entities are included in the analysis.
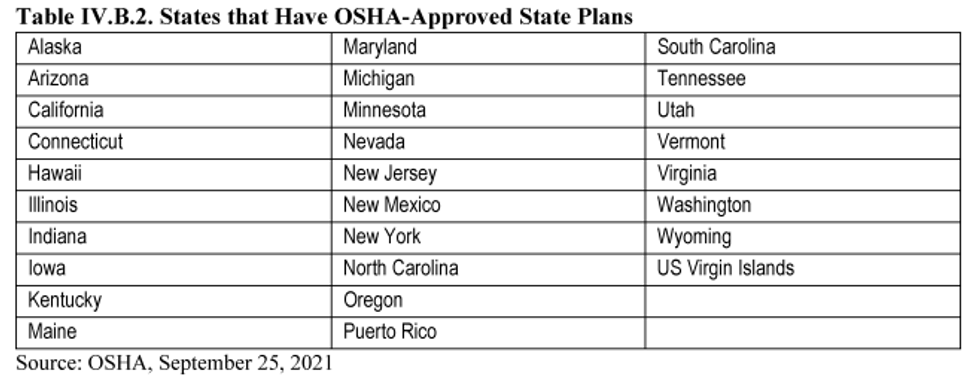
OSHA notes, finally, that the percentage of employers mandating vaccination, and hence the employee vaccination rate, would likely rise to some degree absent this ETS due to other federal actions, such as the vaccination mandate for federal contractors, the CMS rule published elsewhere in this issue of the Federal Register , and as a result of vaccination mandates that have been adopted at state and local levels. This analysis does not account for increases in vaccination that would occur absent the standard, resulting in a likely overestimate of the costs.
c. Teleworking
Dingel-Neiman Approach for Estimating Who Can Work Remotely
OSHA uses the estimates in a paper by J.I. Dingel and B. Neiman, “How Many Jobs Can be Done at Home?,” published in July 2020, as a starting point to determine the percentage of employees, by occupation, who are not expected to work remotely ( i.e. , the percentage of workers for whom employers have employee-based costs under this ETS) (Dingel and Neiman, July 2020).
In Dingel and Neiman's paper, the authors estimate the number of jobs in the U.S. economy that workers can feasibly perform remotely. The authors use two different surveys from the Occupational Information Network (O*Net) 24 to evaluate which occupations can be performed remotely and combine the O*Net estimates with the Bureau of Labor Statistics' (BLS) Occupational Employment and Wage Statistics (OEWS) data on employment by occupation to estimate the total number of workers nationally who can work remotely.
24 24 The O*Net Program is a major source of occupational information for the U.S. The O*NET database surveys ask both specific occupational experts and workers in those occupations questions covering multiple aspects of almost 1,000 occupations covering the entire U.S. economy. See https://www.onetonline.org/ for more information. The occupation definitions in the O*NET data are Standard Occupation Codes—the same definitions that are used in the BLS OEWS data. Dingel and Neiman use the responses to two surveys included in release 24.2 of the database administered by O*NET, the Worker Context Questionnaire and the Generalized Work Activities Questionnaire. The occupation with the median number of respondents had 26 respondents for each work context question and 25 respondents for each generalized work activities question per detailed-level SOC occupation code.
In the O*Net Questionnaires, survey respondents responded to statements about the nature and requirements of the daily tasks associated with their job on a 1-5 ordinal scale, where 5 represents the strongest agreement and 1 represents the strongest disagreement (see Table IV.B.3). The O*Net data contain the average response to each question for each occupation code. For instance, for occupation “Chief Executives” (SOC 11-1011), the average response to the prompt “Performing General Physical Activities is very important” was 1.39, indicating that performing general physical activity is not, on average, critical to the work of chief executives. The average responses by occupation for other prompts in the relevant surveys utilized by Dingel and Neiman are contained in those surveys.
To evaluate the survey responses, Dingel and Neiman first determined the occupations for which the average response to a given prompt met a preset threshold. Table IV.B.3 presents the Dingel and Neiman response threshold for each survey question as well as the percent of occupations that meet each respective predetermined threshold. For example, in 10.8 percent of occupations, the average response to the “Performing general physical activities” (4.A.3.a.1) question met the threshold, falling in the range of 4 to 5.
Dingel and Neiman determined that employees in a given occupation can telework full time if they did not meet the predetermined threshold for any of the questions highlighted in grey and denoted with a “Yes” in the column that reports whether that activity is used in determining whether a job can be done remotely in Table IV.B.3.
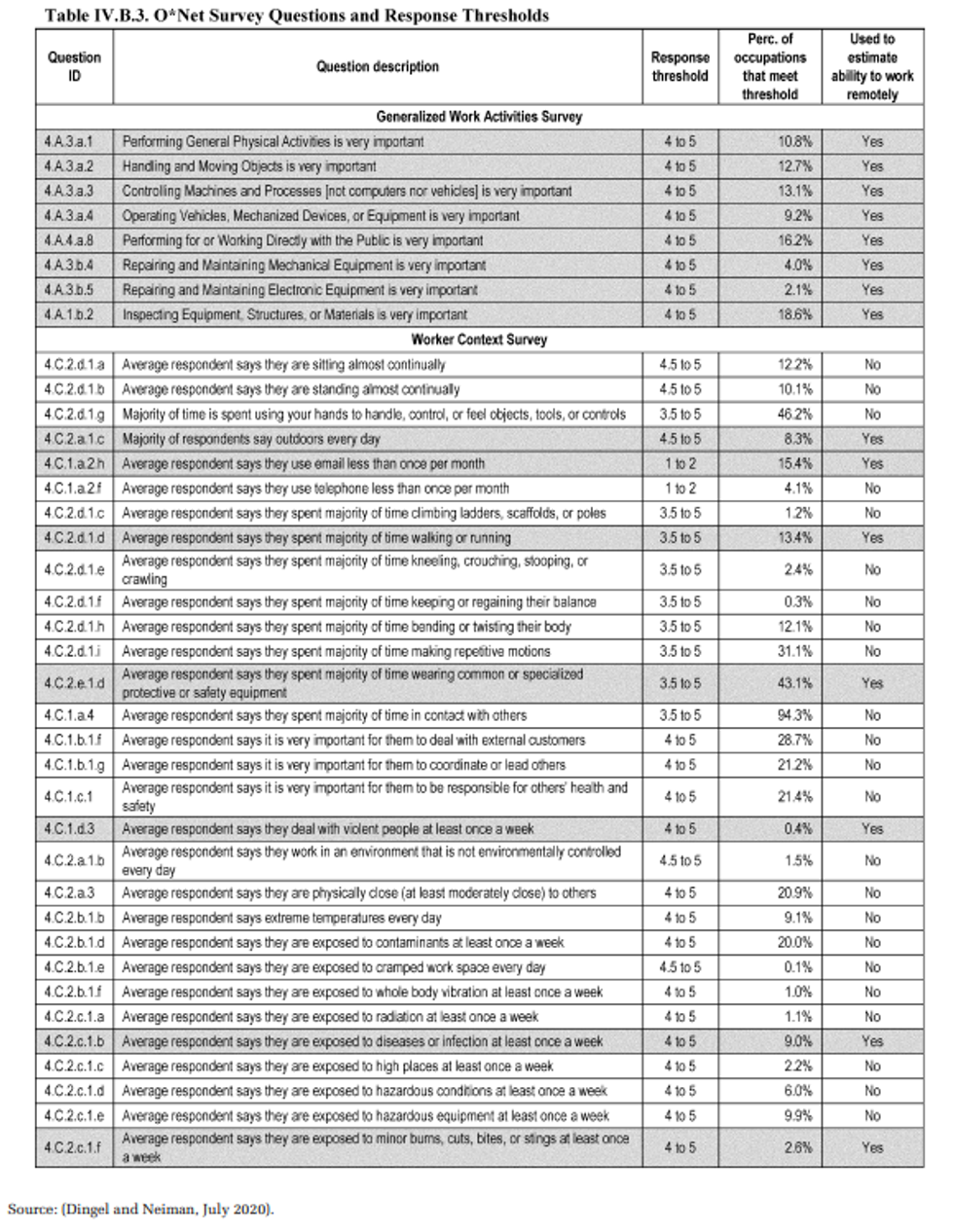
Source: (Dingel and Neiman, July 2020).
Adjusting Dingel and Neiman To Reflect Current Conditions
While many employees can and are working remotely, many have returned to their places of employment. This conclusion is borne out by BLS's Current Population Survey (CPS) (BLS, 2021c). To address the tendency toward employees returning to work on site and more accurately reflect current remote work conditions, OSHA made two adjustments to Dingel and Neiman's estimates. In the COVID-19 Healthcare ETS, OSHA also used Dingel and Neiman's paper to estimate the number of workers who teleworked in response to the pandemic and the ETS under the assumption that anyone who could work remotely would do so in response to the pandemic and the Healthcare ETS. Dingel and Neiman's estimates are therefore framed as the upper-bound of potential teleworking.
The adjustments OSHA made reflect changing circumstances. First, based on agency expertise, OSHA changed the status of certain occupations in its occupational list from working remotely to not working remotely. For example, when Dingel and Neiman published their study, many schools were operating virtually so the Dingel and Neiman finding that teachers were able to work remotely lined up with the situation where teachers were working remotely. At this point in the pandemic, on the other hand, in-person learning has mostly recommenced. To this end, OSHA changed the status of teachers and other employees in the education sector from working remotely to not working remotely in this analysis. As another example, many activities that ceased or were reduced significantly have now resumed and many locations that were closed to the public have reopened ( e.g. , athletic events, shows, gyms, casinos and places of worship), and, since more people have returned to the office, there is more need for childcare. Therefore, OSHA also changed the status of these employees and others from telework to non-telework. This has the ultimate effect of increasing costs estimates for the rule.
Appendix A (Table A-1), in the accompanying document in the docket, “Vaccination, and Testing ETS: Economic Profile and Cost Chapter Appendices” (OSHA, October 2021b), presents Dingel and Neiman's (July 2020) unmodified percentages of workers that can work remotely in each detailed occupation (based on BLS's Standard Occupation Code (SOC)). 25 Appendix A also presents, in separate columns, percentages reflecting the modifications OSHA made in those occupations where OSHA changed the results from telework to non-telework for the reasons stated, as well as percentages reflecting the modifications made in occupations where employees work exclusively outdoors.
25 Except for the adjustments to Dingel and Neiman discussed above, OSHA used the Dingel and Neiman estimates for telework by occupation without change. The agency recognizes that the authors' methodology ( i.e. , the use of 0-1 thresholds) led to a small number of results that may appear not to reflect real-world experiences within an occupation. However, Dingel and Neiman represents the best available evidence for determining the percentage of employees, by occupation, who are expected to work remotely. OSHA is aware of no other source for this information that contains the level of detail necessary to conduct this analysis. Moreover, as explained above, OSHA modified the results for individual occupations when it had a reasoned basis for doing so. In any event, every NAICS industry is comprised of many occupations, so for every occupation where OSHA suspects remote work is overestimated in Dingel and Neiman's results, there may be another where remote work is underestimated.
According to the OSHA-adjusted Dingel and Neiman estimates, 14 percent of the jobs in the United States are performed entirely at home, with significant variation across cities and industries. It should be noted that the Dingel and Neiman analysis does not specify a proportion of jobs that can be performed at home part of the time; under the analysis, employees are either working remotely full-time or are working on site full time.
The second adjustment OSHA made used monthly COVID-specific teleworking data from telework questions added during the pandemic to the CPS to estimate the reduction in teleworking since its peak and applied those estimates to further adjust downward the number of workers currently teleworking (BLS, 2021c). Specifically, the CPS questions asked respondents whether they were teleworking due to COVID-19 (as opposed to teleworking for other reasons) and OSHA estimated the difference in teleworking from the peak of COVID-related teleworking in all industries, which occurred in May 2020, through August 2021 (see Table IV.B.4). 26 The reduction in teleworking was then applied as the change in percentage points to the estimated overall level of employees covered by the ETS in each NAICS code estimated based on data from Dingel and Neiman (July 2020). OSHA's final teleworking estimates are provided in Appendix B in the accompanying document in the docket, “Vaccination, and Testing ETS: Economic Profile and Cost Chapter Appendices” (OSHA, October 2021b). Reductions due to employees working exclusively outdoors were applied to reduce the percentage of covered employees in Appendix B as well.
26 The CPS data were available only at the 2-digit NAICS level as shown in Table IV.B.4.
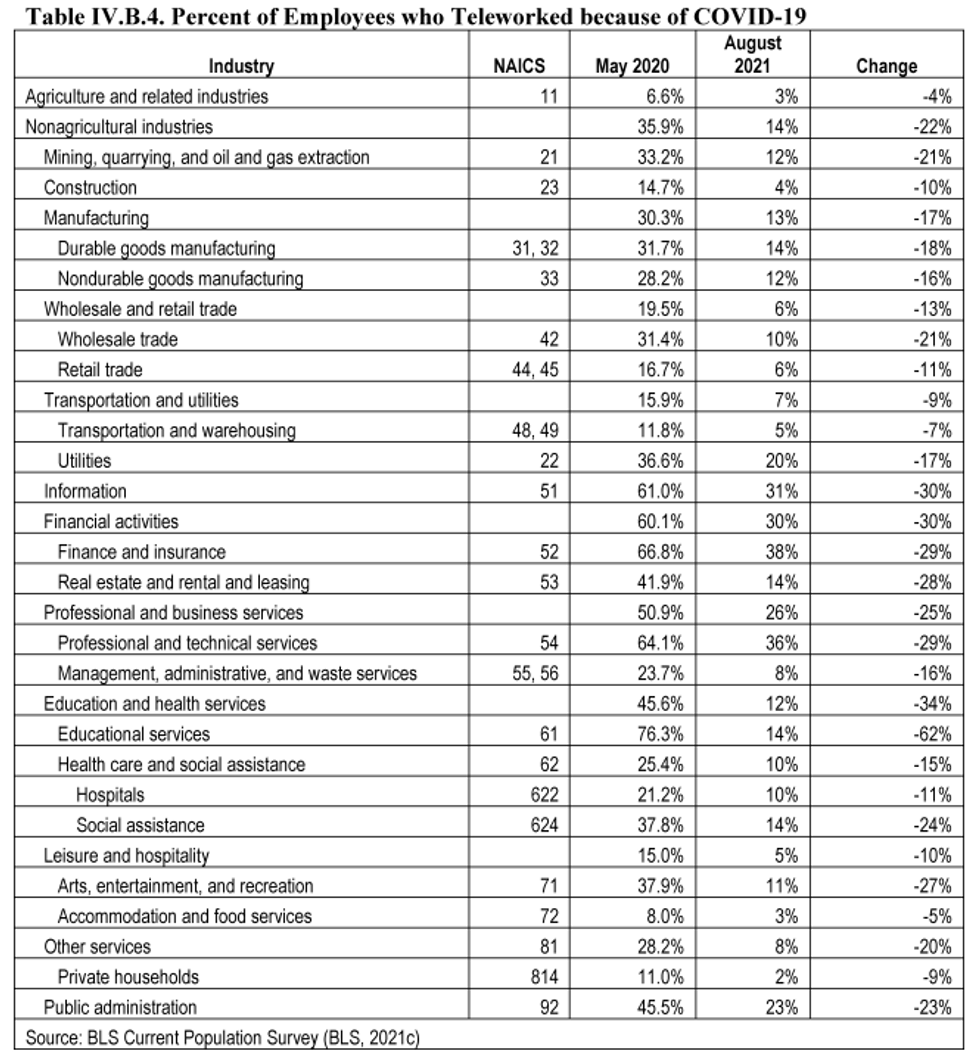
Other Teleworking Literature
A number of companies have announced plans to allow employees to work from home at least through the end of 2021—suggesting that the levels of remote work will not be returning to pre pandemic levels in the near future. Many technology and internet based companies, such as Dropbox, Coinbase, VMWare, and Slack, have announced a complete, permanent move to fully remote work (Courtney, September 27, 2021). Large employers such as Facebook, Amazon, and Siemens plan to maintain some physical workspace but now offer their employees who are telework eligible the option to work from home at least part of the time on a permanent basis (Id.). Google, Ford, Amazon, Apple and other large employers are expecting their telework eligible workers to return to on-site work (in some capacity) no earlier than January 2022 with Lyft anticipating a February 2022 return (Cerullo, August 31, 2021). As a final example, a survey of businesses in Massachusetts found that about 40 percent of teleworkers anticipate they will not be returning to the office in January 2022 or earlier (Chesto, June 22, 2021).
Additional studies provide qualitative support for the conclusion that a range of employees will “predictably” work from home both during the pandemic and beyond. In Bick, Blandin, and Martens's paper, “Work from Home Before and After the COVID-19 Outbreak” the authors use the following information to establish the physical location of employment (home or workplace) of workers: Data from the Real-Time Population Survey (RPS), a national labor market survey of adults between ages 18-64 that mirrors the Current Population Survey (CPS) and collects information used in pandemic analysis, such as commuting behavior before and after the World Health Organization declared a global pandemic; mobility data on commuting; and information from the CPS since May 2020 on `pandemic-related' telework (Bick et al., February 2021).
Based on these data, Bick et al., found that there was a sudden decline in commuting trips in the U.S. after the initial COVID-19 outbreak, and that even when these trips subsequently began increasing back toward the original number of commuting trips, the overall number of trips did not return to normal at the end of 2020 because many teleworking employees continued working from home. The authors found that the surge in work from home came almost entirely from employees working from home every workday in the reference week. The authors also suggest that, for some occupations, especially those occupations with more educated workers, the change to increased work from home appears to be a long-term change; the data showed that, as of December 2020, 12.5 percent of these workers reported they expect to be working from home full-time in the future, and 24.5 percent reported they expect to be working from home part-time.
In “COVID-19 and Remote Work: An Early Look At U.S. Data,” Brynjolfsson et al., noted that some of the shift to working from home seems to be a long-term phenomenon (Brynjolfsson et al., June 2020). The authors found, using an online survey, that 35.2 percent of workers had switched to working from home. Additionally, 15 percent of workers reported they were already working from home before COVID-19. Therefore, this study finds that about half of workers are now working from home—an even greater percentage than estimated by Dingel and Neiman.
Finally, in “Why Working from Home Will Stick,” Barrero et al. predict that 22 percent of all full workdays will be performed from home after the pandemic ends, compared to 5 percent before (Barrero et al., April 2021). The authors highlight five factors contributing towards the more permanent shift to telework: Diminished stigma, better-than-expected experiences working from home, investments in physical and human capital enabling work from home, reluctance to return to pre-pandemic activities, and innovation supporting work from home.
d. Affected Entities and Employees
OSHA used data from the U.S. Census' 2017 Statistics of U.S. Businesses (SUSB) to identify private sector entities and employees affected by this section of the ETS (U.S. Census Bureau, 2019), and used the BLS 2017 Quarterly Census of Employment and Wages (QCEW) to characterize state and local government entities (BLS, 2017). SUSB provides estimates of entities and employees by employer size range, which OSHA used to exclude employers with fewer than 100 employees. 27
27 SUSB with revenue data is only collected every 5 years. While OSHA could attempt to extrapolate these data to more recent years, the results would be imprecise because they would change the revenue-employee size distributions. Those distributions are crucial for measuring impacts so the agency has opted to use the data as is. The total number of employees in OSHA's estimate is fairly close to that of SUSB. The 2017 SUSB data includes a total of 128.6 million employees, while the more recent 2018 SUSB data includes a total of 130.9 million.
For rail transportation (NAICS 482), which is not included in SUSB or QCEW data, OSHA relied on Federal Railroad Administration and Association of American Railroads statistics reported in OSHA's 2020 final rule, Cranes and Derricks in Construction: Railroad Roadway Work. See 85 FR 57109 (September 15, 2020). OSHA used these data sources to identify public and private railroad employers with more than 100 employees. For agricultural NAICS (111 and 112), OSHA relies on the National Agricultural Statistics Service, 2017 Census of Agriculture (NASS, 2017) to obtain estimates of total entities, employees, and revenues. Since these data do not indicate the number of entities with more than 100 employees, OSHA assumes it is the same as the average proportion as the support activity sectors for crop and animal production (NAICS 114 and 115). OSHA similarly specifies teleworking conditions for NAICS 111 and 112 using the average result for support activities for agriculture (NAICS 114 and 115). For the postal service industry, NAICS 491110, which is not included in SUSB, OSHA obtains total entity and employment data for private postal services from the QCEW. Since these data do not indicate the number of entities with more than 100 employees, OSHA assumes it is the same as the average proportion as the related industries, couriers and express delivery (NAICS 492110), and local delivery (NAICS 492120).
OSHA used the BLS 2020 Occupational Employment and Wage Statistics (OEWS), which provides NAICS-specific estimates of employment and wages by occupation, along with the data in Appendix B (discussed earlier), to determine the subset of non-teleworking employees affected by the ETS.
Table IV.B.5 summarizes the set of entities covered by the ETS. OSHA estimates a total of approximately 263,879 entities and approximately 1.9 million establishments incur costs under the ETS. 28 OSHA estimates these entities employ approximately 102.7 million employees, and of these, OSHA estimates approximately 84.2 million employees are covered by the ETS and are not excluded from coverage by working remotely 100 percent of the time or exclusively outside. 29 For the purpose of this analysis, OSHA estimates that all employees that OSHA estimated will work remotely will continue to do so for the duration of this ETS. 30
28 This includes public entities only in states with an approved OSHA State Plan. See Table IV.B.2 above for further discussion of state plans.
29 OSHA's estimate of covered employees is based on the discussion in the text. For example, as OSHA writes above: OSHA assumes for the purpose of its analysis that employers covered under the Contractor Guidance will conduct work at least some of the time in workplaces not covered under that Guidance and so are fully integrated into the scope of the ETS; and the employers and employees covered by the Healthcare ETS are also fully integrated into the scope of the ETS.
30 Conditions are changing rapidly, and though many firms are planning to keep expanded telework to some extent, as the rate of vaccinated workers increases, there may be increased movement back to the workplace beyond what OSHA has estimated here.
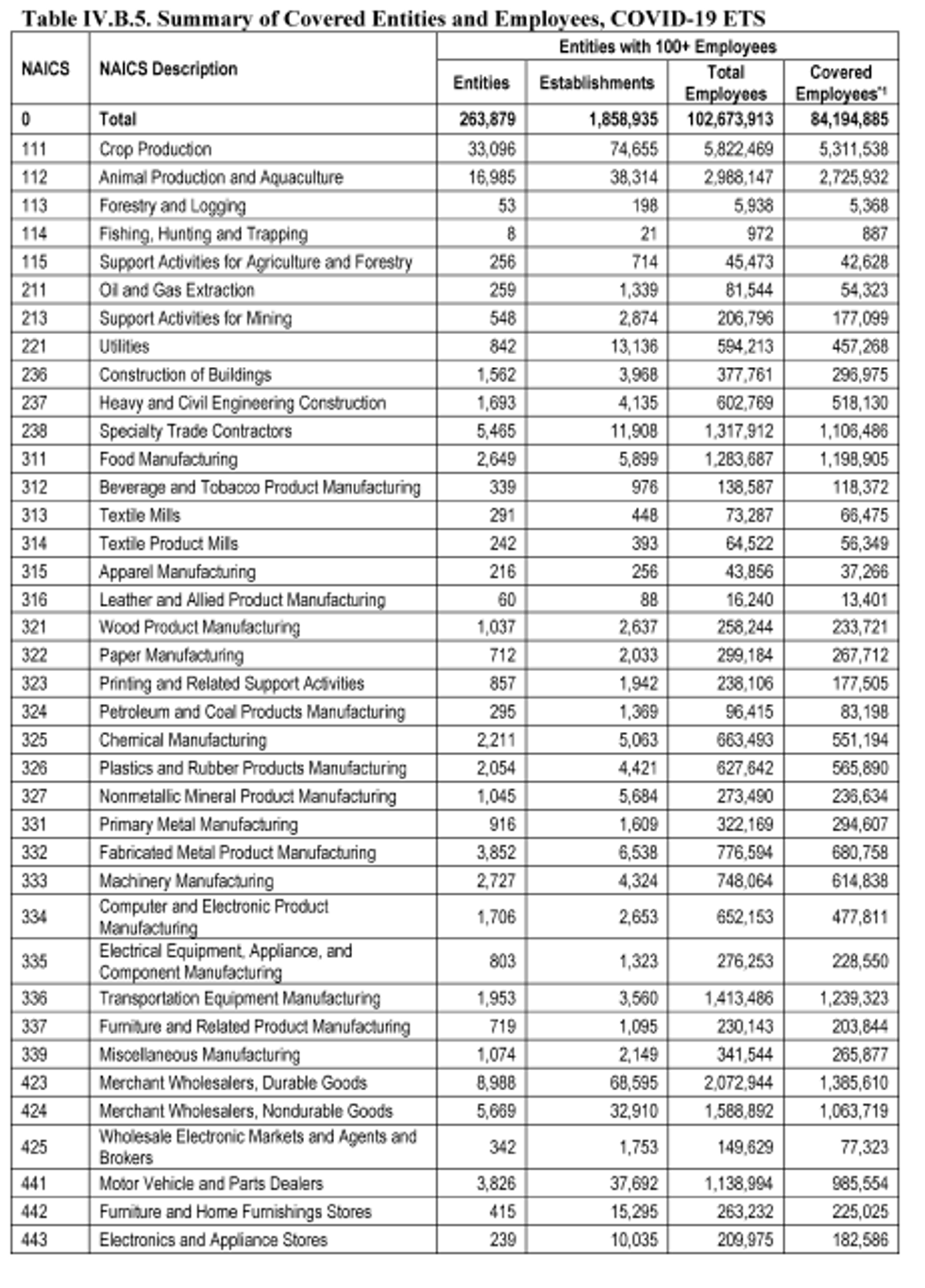
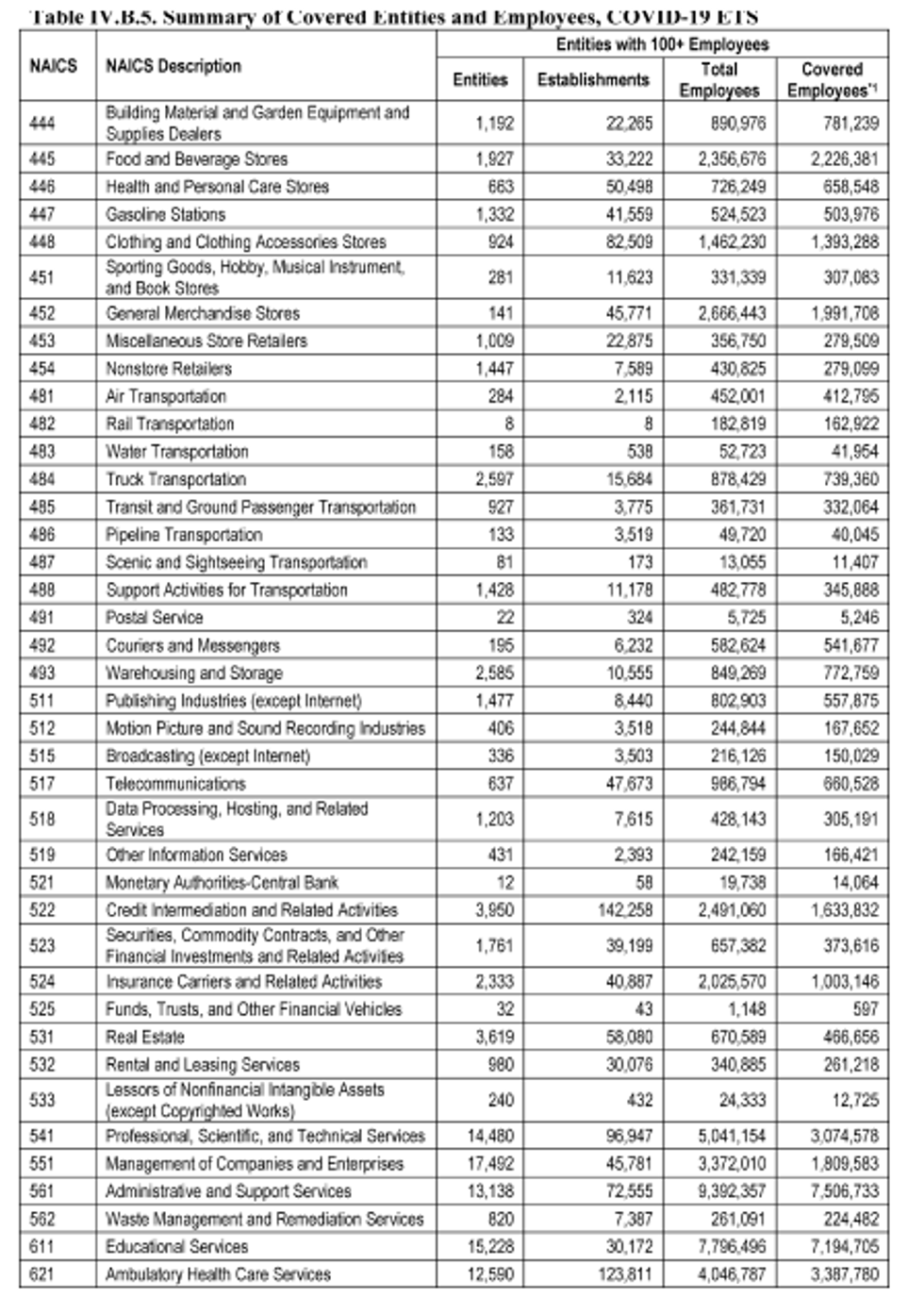
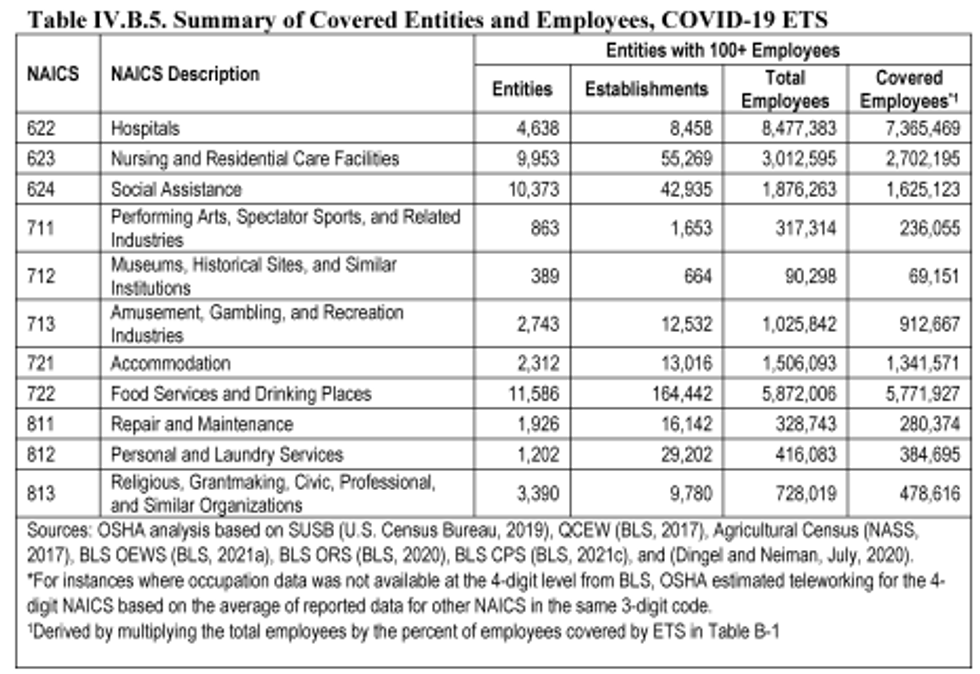
III. Baseline Vaccine Status for Covered Employees
To estimate the cost of the ETS, OSHA must first estimate the baseline vaccination status for the 84.2m covered employees (those who work for employers with 100 or more employees and are not otherwise excluded from coverage). OSHA recognizes that employees' current vaccination status continues to change on a daily basis. When specifying baseline vaccination rates, OSHA used the most recently available vaccination data from CDC, reflecting current conditions. For the remaining set of unvaccinated employees covered by the ETS, after accounting for baseline vaccinations, OSHA estimates the number of these employees who will be vaccinated and the number who will test under the ETS. OSHA's methodology for this analysis is detailed below.
a. Estimate the Current Vaccination Rate for Covered Employees
To estimate the current vaccinate rate for covered employees, OSHA obtained recent vaccination data by age group from the CDC COVID Data Tracker (CDC, October 4, 2021a). 31 For age groups covering 18-74 years old, these data include the number of people who are fully-vaccinated as well as the number of people of who have initiated their first shot in the past two weeks (relative to the October 4, 2021 data). 32 OSHA estimates the vaccination rate for each group (percent of total population in the age group who are vaccinated) based on the total number of people who are fully-vaccinated and had their first shot in the past two weeks, as a fraction of the population in each age group, obtained from the BLS Current Population Survey (CPS) (BLS, 2021d). Then, to estimate the overall average vaccination rate across age groups 18-74 years old, OSHA weighted each group based on the distribution of the labor force by age, also obtained from the BLS CPS (BLS, 2021d). As shown in Table IV.B.6, OSHA estimates an overall vaccination rate of 61.3 percent for covered employees (and 38.7 percent unvaccinated). The healthcare sector had an earlier push to get healthcare workers vaccinated and has a higher current rate, estimated to be 70 percent. 33
31 The data from the CDC website was retrieved on October 4, 2021.
32 Age groups included: 18-24, 25-39, 40-49, 50-64, and 65-74. OSHA had not included the group 65-74 in the economic analysis of the Healthcare ETS this past spring because for the healthcare sector, using the population wide average of workers in this age bracket was felt would overcount the number of such workers in this sector. OSHA is including this group now that more of the other age populations have been vaccinated and those concerns are no longer as relevant. This ETS will therefore indicate that a slightly higher percentage of universe of covered employees is vaccinated than if that age group of 65-74 was excluded altogether, but it also increases the number of employees for which additional compliance costs are factored in. OSHA interprets the ultimate result as a more accurate reflection of the workplace and notes that more costs are included than if the age group had been excluded from the analysis.
33 The agency takes a recent survey (Lazer et al., August 16, 2021) which breaks out rates for healthcare vaccination and non-healthcare, and rather than replacing the CDC base vaccination rate uses the CDC rate to make an adjustment upwards to the healthcare rate of 70 percent.
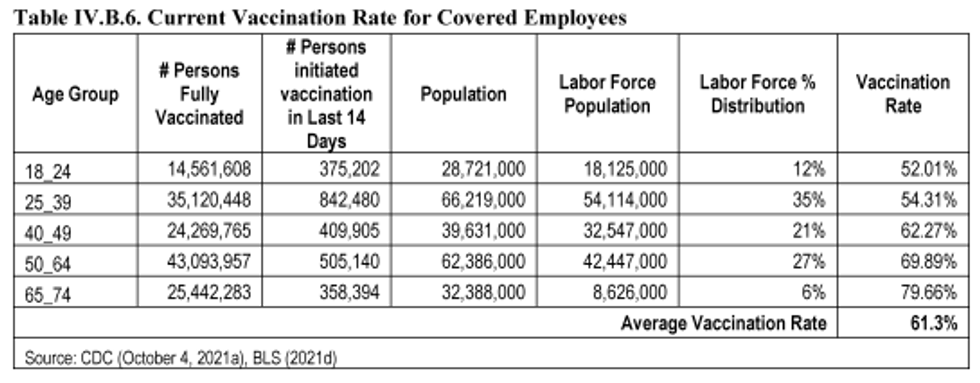
Based on the above, OSHA estimates that the 84.2m covered employees includes 52.5 million (62 percent) vaccinated employees and 31.7 million unvaccinated employees (38 percent).
b. Adjust Baseline Vaccination for Continuing Trends
OSHA adjusts the current vaccination rate to account for continuing trends in vaccinations among covered employees due to employers' continued implementation of vaccine mandates and other policies (described below), under the ETS. To make this adjustment, OSHA requires 1) further characterization of the set of unvaccinated employees in terms of their likelihood to receive the vaccine, and 2) specification of the extent of employer-mandated and other employer vaccination policies.
Based on vaccine confidence data from CDC (CDC, October 2021a), 13.8 percent of the population “probably or definitely will not” get the vaccine; hereafter referred to as “vaccine-hesitant”. Since this group is by definition part of the currently unvaccinated, OSHA characterizes the currently unvaccinated (37.6 percent) as being comprised of those who are vaccine—hesitant (13.8 percent) and the remainder, who while unvaccinated, are not hesitant because they are not in the “probably or definitely will not” group (23.8 percent).
Among those who are vaccine-hesitant, OSHA estimates that 5 percent of covered employees (or about 36 percent of the vaccine-hesitant), are hesitant due to a religious (4 percent) or medical (1 percent) exemption. The remaining 8.8 percent include those who are vaccine-hesitant for other reasons. For the 4 percent estimate for religious exemptions, OSHA relies on data from Vermont, which removed its vaccine exemption for nonreligious personal beliefs in 2016 and saw the proportion of kindergarten students with a religious exemption rise to about 4 percent (Graham, September 15, 2021). In analyzing this issue, the agency also reviewed other religious exemption data concerning state workers in Oregon and Washington; the agency decided not to rely on these data because the Vermont data is a more accurate measure of the correct religious exemption rate, although the data does represent parents deciding on whether to claim an exemption for their child, not for themselves. This is because, unlike the Vermont data, the Oregon and Washington data contain workers that have applied, but not yet been accepted, for a religious exemption (O'Sullivan, September 18, 2021; KEZI News, September 25, 2021). In Oregon, 5 percent and in Washington 8 percent of the employees have requested accommodations though only a fraction so far have been accepted. However, the data are not inconsistent with the Vermont data even though the process in both Oregon and Washington are not yet complete. For the 1 percent estimate for medical exemptions, OSHA relied on the Household Pulse Survey (HPS) conducted by the U.S. Census (U.S. Census Bureau, 2021). In Table 6a of the Health Tables for Week 31, September 1, 2021 through September 13, 2021, about 1% of the US population said they would not get the vaccine because “Doctor has not recommended it,” and OSHA uses this response as a proxy for all medical conditions. 34
34 Table 6a presents that 3,884,902 of the population will not take the vaccine because the “doctor has not recommended it” out of a total of 38,936,606 who will not get the vaccine for any reason. Medical reasons are then about 10% of the general population that will not get the vaccine, and the ones who won't get the vaccine are about 10% of the whole population, giving 1% (.10 * .10).
Table IV.B.7 presents the number of employees in each vaccination category, which informs OSHA's subsequent estimates of which currently unvaccinated employees may be vaccinated by employer-mandates, vaccinated under the ETS, or tested under the ETS.
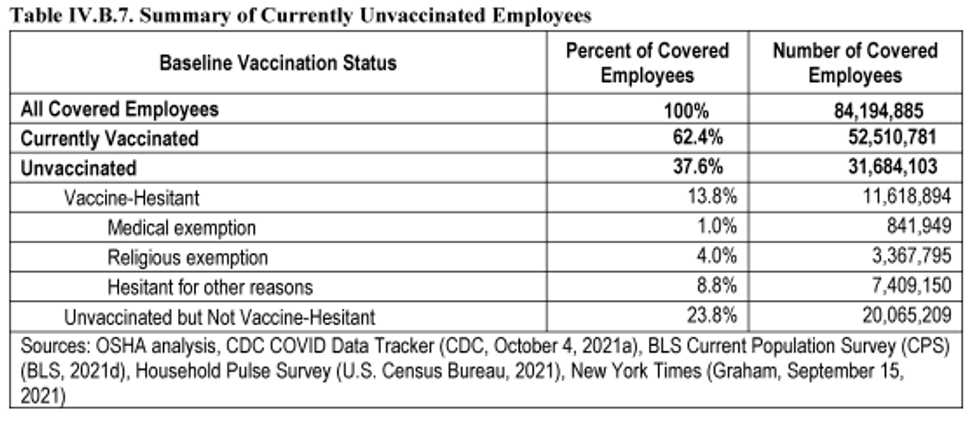
Next, OSHA estimates the number of currently unvaccinated employees that are likely to become vaccinated while the ETS is in effect, based on their employers' policies. Based on limited data on current vaccine mandate implementation and forecasts for future implementation (Mishra and Hartstein, August 23, 2021; ASU COVID-19 Diagnostic Commons, October 6, 2021), OSHA estimates that 25 percent of firms in scope currently have a mandate, and assumes that this will rise to 60 percent of employers after the ETS is in place. The baseline of 25 percent is based on recent surveys showing a range of approximately 13-45 percent of employers currently requiring or planning to require vaccination among employees (see Willis Towers Watson, June 23, 2021; Mishra and Hartstein, August 23, 2021; ASU COVID-19 Diagnostic Commons, October 6, 2021). Absent the ETS, OSHA assumes that the percentage of firms would remain 25 percent (with some measure of upward adjustment due to other federal vaccine mandates affecting select populations, as discussed above). To the extent more firms than OSHA estimates would mandate vaccination independent of the ETS and thereby increase the vaccination rate (again because of factors such as other federal vaccine mandates), then the agency's costs are overestimated because the agency's baseline vaccination rate is too low. The assumption of an increase from 25 to 60 percent is based on the same set of surveys that indicate that the share of employers who will mandate vaccinations after the ETS (including those that already mandate vaccinations) range from 25-75 percent, see above references. The agency also assumes that employees are distributed in the same proportion across employers with and without a vaccine mandate (e.g., if 60 percent of firms mandate vaccination, 60 percent of employees will be vaccinated due to the mandate (less those who remain unvaccinated due to religious or medical exemptions).
OSHA assumes that all unvaccinated employees subject to an employer mandate will be vaccinated under that employer mandate, except for those seeking a medical or religious exemption. For unvaccinated employees not subject to an employer mandate, OSHA assumes that they will also be vaccinated at their employer's request, except for employees who are vaccine-hesitant, which includes not only those who remain unvaccinated for medical and religious reasons, but also those who are hesitant for any other reason. OSHA carries through its assumptions and estimates into its total cost estimates. For example, OSHA estimates that the 25 percent of firms in scope that currently have a vaccination mandate will not need to implement a new written policy on vaccination in response to the ETS since they will already have implemented a policy that meets the requirements of the ETS.
In total, OSHA estimates that 27 percent of covered employees (22.7 million) will be vaccinated based on employer policies under the ETS; or 72 percent of covered employees who are currently unvaccinated. The resulting vaccination rate, adjusted for the ETS, is estimated based on the total of those who are currently vaccinated and those who will be vaccinated under employer policies, 89.4 percent as shown in Table IV.B.8. Calculations of this nature, while not discussed in more detail in this analysis, are contained fully in the spreadsheets supporting this analysis (OSHA, October 2021a). 35
35 OSHA notes that these estimates differ for employees covered by the Healthcare ETS. OSHA calculated these estimates separately because, as stated above, OSHA is only taking costs for these employees in the last four months of the assumed 6-month period while the ETS remains in effect. While OSHA does not describe in detail how it derived estimates for employees covered by the Healthcare ETS in this analysis, the derivation of those estimates run parallel to those described above. For more information, please see the spreadsheets supporting this analysis. (OSHA, October 2021a).
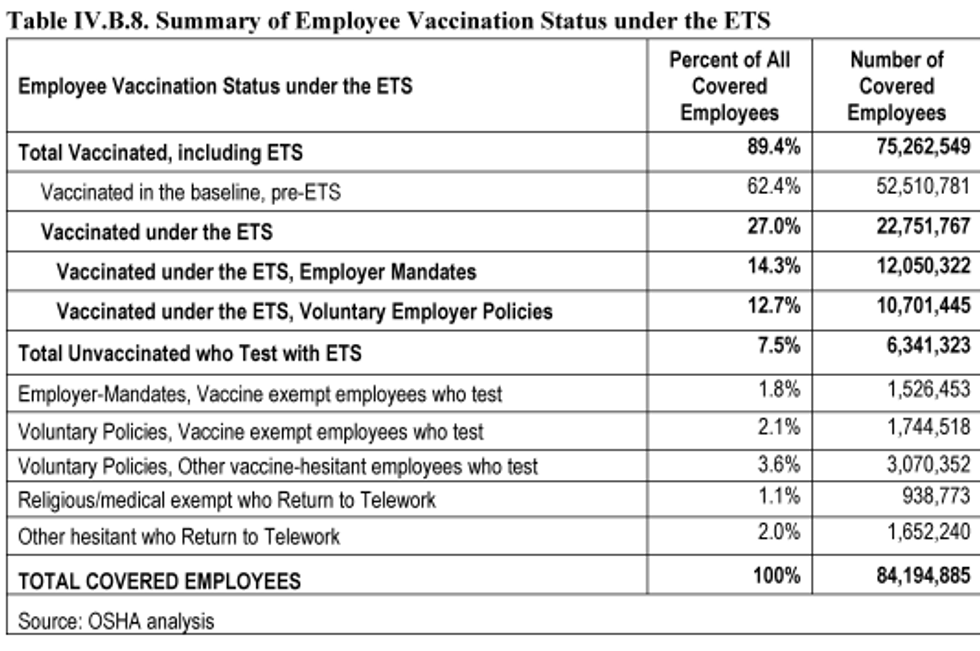
From Table IV.B.8, OSHA estimates that approximately 75.3 million (89.4 percent) of covered employees will be vaccinated when the ETS is in full effect, and that approximately 8.9 million employees (10.6 percent, made up of approximately 6.3 million covered employees who will be tested for COVID under the ETS and approximately 2.6 million employees who return to telework (see next paragraph)) will remain unvaccinated. This final set of unvaccinated employees includes all employees not vaccinated because of religious or medical accommodations or medical contraindication, plus the portion of those who are vaccine-hesitant for any other reason, who were not vaccinated because their employer has opted for a voluntary vaccination policy.
From the above, OSHA estimates that about 5 percent of all covered employees will seek and receive religious or medical accommodations or exemption for medical contraindication. While the agency encourages employers to consider the most protective accommodations such as telework, which would prevent the employee from being exposed at work or from transmitting the virus at work, for cost analysis purposes the agency assumes these workers will largely be tested in order for their employers to comply with the ETS. Consistent with the overall average 22 percent of those who returned to work after teleworking earlier in the pandemic (see teleworking discussion above), OSHA assumes for this cost analysis that only 22 percent of workers needing a reasonable accommodation will return to full time telework as a reasonable accommodation. OSHA also assumes that the 78 percent remainder will follow the testing/masking protocols in the ETS as a reasonable accommodation.
For hesitant employees who will not seek a religious or medical accommodation, and who work in a firm with a testing option, the agency assumes as above that those who were teleworking before (again on average 22 percent) will return to telework rather than being tested.
c. Cost of Absenteeism to Employers
Even mild cases of Covid-19 can be costly to employers as they can induce productivity losses due to work absences, both among those infected and their close contacts who may be subject to quarantine requirements. While many workers were able to engage in telework in March-April 2020, several occupational groups deemed essential, including childcare workers, personal care aids, healthcare support occupations, and food processing workers, exhibited significantly higher rates of absenteeism during that period, which the authors attributed to some workers contracting COVID-19 (Groenewold et al., July 10, 2020). Absenteeism can also affect the productivity of workers who are present, similar to how turnover can impose costs on incumbent workers (Kuhn and Yu, April 2021).
In aggregate, productivity losses from absences can be costly, as evidenced by the economic losses from seasonal influenza. One estimate found that the United States loses 20.1 million days of economic productivity every year due to influenza, an ongoing loss equivalent to 80,400 full-time worker-years (Putri et al., June 22, 2018). Another recent study found that higher influenza vaccination rates result in both fewer deaths and significantly reduced illness-related work absences (White, 2021).
OSHA recognizes that absenteeism has been a problem. However, as explained in other sections of the preamble, the ETS vaccination and testing and face covering requirements are necessary to reduce the spread of COVID-19 in the workplace, which may in part reduce absenteeism. The ETS might in a limited sense also increase absenteeism because the rule requires employers to temporarily remove from the workplace any employee who receives a positive COVID-19 test or is diagnosed with COVID-19 by a licensed healthcare provider. However, this provision will also help to further reduce absenteeism because, when an infected employee is promptly removed from the workplace, that can prevent one employee from infecting other employees in the workplace and potentially causing an outbreak or a super-spreader event. Thus, OSHA concludes that the ETS may, on net, help ameliorate absenteeism by reducing illnesses, but in any event will not increase absenteeism (see OSHA, October 2021c).
d. The Effect of Employee Turnover
One of the primary concerns among employers in imposing vaccination mandates is loss of staff, with 60 percent of employers selecting it as a concern with regard to mandating COVID-19 vaccination, according to one survey (Mishra and Hartstein, August 23, 2021). 36 To this end, employer vaccination mandates could lead to employee turnover; employees could either leave on their own volition or employers who have instituted strict vaccination policies may fire workers who are not vaccinated, or place them on unpaid leave.
36 This survey done in August, 2021, has 1,630 responses, reported by HR staff, attorneys, and executives. Described as being “from a variety of industries,” 83 percent of respondents were from companies with more than 100 employees.
On the other hand, there is countervailing evidence to suggest that employers who implement a vaccine mandate will be met with an influx of potential workers. Many employees would prefer a mandate in place, and would be more likely to stay with, or apply to, a firm that had a vaccine mandate in place. For example, although Inova health system in Northern Virginia, lost 89 workers for noncompliance with the system's vaccination mandate, that loss amounted to less than 0.5 percent of its workforce, (Portnoy, October 3, 2021), and, in any event, Inova's CEO stated that the vaccine mandate has helped with recruitment, and that its workers are concerned for their own safety and want to know they are working with vaccinated colleagues. This same article listed some other Virginia healthcare systems with higher rates of loss in connection with vaccine mandates. Valley Health terminated 1 percent of its employees, while Luminis Health had about 2 percent of its workers still unvaccinated at the time of its mandate deadline. As another example, although United Airlines had 593 employees (out of the company's 67,000 U.S. employees) who had not complied with the company's vaccination mandate at the end of September (a number that dropped below 240 employees by October 1), the company reported it has received 20,000 applications for 2,000 flight attendant positions, a much higher ratio than before the pandemic (Chokshi and Scheiber, October 2, 2021). In addition, one survey reports that among employee resignations due to COVID-19 workplace policies, 42 percent reported lack of workplace safety policies, 17 percent reported that existing workplace policies were not stringent enough, and only 39 percent reported overly restrictive workplace policies, suggesting that many employees will welcome vaccine mandates (ASU COVID-19 Diagnostic Commons, October 6, 2021). 37
37 This August 2021 global survey (all results presented here are for the US only) has 1,143 responses. It covers 28 industries, including: Technology and Software, Business and Professional Services, Manufacturing, Construction, and Healthcare. Ninety percent of respondents were from companies with more than 100 employees.
While employee turnover is a natural part of business in any industry, higher employee turnover rate than normal can have a direct impact on profit and revenue. The normal range of employee turnover differs widely by industry, with an average turnover rate of about 50 percent per year overall for the private sector. 38 For example, between 2016 and 2020, employee turnover ranged from 55 percent to 70 percent in the retail industry and from 40 percent to 60 percent in the transportation industry (the industry sectors with the highest employment). 39
38 BLS (March 11, 2021).
39 Id.
OSHA acknowledges that a vaccine mandate may result in increased employee turnover, but one recent survey 40 suggests it is very unlikely that this potential increase in employee turnover will exceed the ranges that industries have experienced over time. The survey, though limited because many respondents did not have mandates in place at that time, shows that there was no impact on turnover for 71 percent of those with mandates in place. Only 25 percent saw a slight increase in turnover (1 percent to 5 percent above normal) and only 4 percent saw a significant increase (more than 5 percent above normal). As such, OSHA does not anticipate that the potentially increased employee turnover attributable to vaccine mandates will be substantial enough to negate normal profit and revenue.
40 Umland, October 13, 2021. This October 2021 survey has 1,059 total respondents, though only 365 have implemented a vaccination mandate and answered this turnover question.
To this end, an important factor to consider in examining turnover in connection with vaccine mandates is the unquantified cost savings and other positive economic impacts accruing to employers that institute vaccine mandates. These include reduced absenteeism due to fewer COVID-19 illnesses and quarantines, as discussed above. Other positive economic impacts of a vaccine mandate are increased retail trade from customers that feel less at risk and better relations with suppliers and other business partners. These all would contribute to improved business and increased profits.
The existence of these cost savings and other positive economic impacts accruing to employers that comply with the ETS suggests that the actual net costs of the ETS could be much lower than the costs reported in this section of the economic analysis. As OSHA discusses above, OSHA has provided evidence to support its estimate that 25 percent of covered employers already voluntarily require that their employees be vaccinated and a much larger percentage are considering a vaccine mandate. This supports the conclusion that these businesses agree that doing so will ultimately save costs.
In addition, under the ETS, employers may implement a policy that allows for testing and face covering instead. Firms will have a tendency to self-select: If a large proportion of its work force has indicated concern about a vaccine mandate, the firm is more likely to choose the testing option to retain their workers. This is one factor that led the agency to estimate that approximately 40 percent of employers will allow employees to choose testing and face coverings in lieu of vaccination. To the extent employers are concerned about employee testing costs, employers can generally absorb testing costs or help employees reduce those costs through low-cost assistance such as employer proctoring of tests (even though that is not required by this ETS). Departure of personnel because of vaccine mandates is also likely to be less common when vaccine mandates are more prevalent across employers in a region or industry. One survey reports that 65 percent of employers state that actions of other companies in their industry are very, or at least moderately, important in deciding to mandate vaccination (Mishra and Hartstein, August 23, 2021).
Mandatory vaccinations for COVID-19 are still relatively new because vaccines only became available in quantities sufficient to support such mandates only about 6 months ago, and the FDA has only recently moved past emergency clearance to final clearance. While there is not an abundance of evidence about whether employees have actually left or joined an employer based on a vaccine mandate, particularly one with an alternative allowing for testing in lieu of vaccination, OSHA has examined the best available evidence it could locate in the timeline necessary to respond with urgency to the grave danger addressed in this ETS. Based on that, OSHA is persuaded that the net effect of the OSHA ETS on employee turnover will be relatively small, given the option for employers to implement a testing and face covering policy and the countervailing forces surrounding turnover that will limit those effects, as discussed above.
Finally, OSHA finds one line of evidence particularly persuasive because it involves data instead of polls: While different surveys may suggest different levels of worker intentions (joining or remaining with a safer employer versus leaving an employer to avoid vaccination), 41 the data suggests that the number of employees who actually leave an employer is much lower than the number who claimed they might: 1% to 3% or less actually leave, compared to the 48-50% who claimed they would. 42 As discussed earlier, this turnover number is well below the average turnover rate in most industries. Thus, OSHA concludes that whether or not the ETS proves helpful to recruitment efforts for some employers, it will not, on balance, add significant new costs to covered employers or threaten the economic feasibility of any industry during a six month period.
41 Two polls from June 2021, when the number of COVID-19 cases had dropped dramatically just before the Delta Variant led to a surge in cases, indicated that 50% of unvaccinated employees surveyed said that they would leave their job rather than accept a vaccination mandate from their employer. (KFF et al., June 30, 2021) (the same percentage also responded that “The number of cases is so low that there is no need for more people to get the vaccine.”). A separate poll from the same time also stated that 48% of “vaccine hesitant” employees claimed they would quit their jobs rather than be vaccinated. (Barry et al., September 24, 2021—citing yet unpublished June 2021 poll). In a more recent poll, about 44% of workers said that they would consider leaving their jobs if they were forced to get vaccinated, while around 38% of workers would consider leaving their current employer if the organization did not enact a vaccine mandate. (Kelly August 12, 2021). Interestingly, in that survey there was a direct correlation between the age of the worker and the desire to have a vaccinated workplace: Younger workers, usually the most mobile portion of the workforce, had a much higher desire for a vaccinated workforce (50% of Generation Z employees, as compared to 33% of Baby Boomers).
42 An article titled “Unvaccinated Workers Say They'd Rather Quit Than Get a Shot, but Data Suggest Otherwise” noted the 48%-50% threat to leave, but included hard data showing nothing close to those levels actually occurred: Houston Methodist Hospital required its 25,000 workers (including its 3,580 unvaccinated employees) to get a vaccine by June 7, and only 153 resigned or were fired (4% of the 3,580 unvaccinated employees; 0.6% of the total number of employees); other examples of the numbers of employees who left in response to their employers' mandatory vaccine policy involved 5 out of 527 (0.9%), 2 out of 250 (0.8%), 6 out of 260 (3%), and 125 out of 35,800 (0.3%). (Barry et al., September 24, 2021).
OSHA seeks comments on these estimates and conclusions, as well as further data that it could use to refine its estimates.
IV. Cost Analysis for COVID-19 Vaccination and Testing ETS, §1910.501
In this section, OSHA provides estimates of the per-entity and total costs for the requirements of this ETS. Section 6(c)(3) of the OSH Act states that the Secretary will publish a final standard “no later than six months after publication of the emergency standard.” Costs are therefore estimated over a six-month time period. Note that the estimates are presented in this section at the 3-digit NAICS level, but the analysis was conducted at the 6-digit NAICS level and aggregated to the 3-digit level for presentation purposes. The 6-digit NAICS level data is accessible in the supporting spreadsheet. It should be noted that this analysis deals strictly with averages. For any given entity, actual costs may be higher or lower than the point estimate shown here, but using an average allows OSHA to evaluate feasibility by industry as required by the OSH Act. In addition, OSHA has limited data on many of the parameters needed in this analysis and has estimated them based on the available data, estimates for similar requirements for other OSHA standards, consultation with experts in other government agencies, and internal agency judgment where necessary. OSHA's estimates are therefore based on the best evidence available to the agency at the time this analysis of costs and feasibility was performed.
As mentioned above, OSHA estimates that approximately 264,000 entities have employees who will be subject to the requirements of the ETS, including approximately 84.2 million employees. Many ETS requirements result in labor burdens that are monetized using the labor rates described next.
a. Wage Rates
OSHA used occupation-specific wage rates from BLS 2020 OEWS data (BLS, 2021a). Within each affected 6-digit NAICS industry, OSHA calculated the employee-weighted average wage to be used in the analysis. OSHA estimated loaded wages using the BLS' Employer Cost for Employee Compensation data (BLS, 2021b), as well as OSHA's standard estimate for overhead of 17 percent times the base wage.
Costs are estimated using three labor rates for each NAICS industry: The average labor rate for all employees, the labor rate for General and Operations Managers (SOC code 11-1021), and the labor rate for Office Clerks, General (SOC 43-9060). Industry-specific wage rates are presented in Appendix C in the accompanying document in the docket, “Vaccination and Testing ETS: Economic Profile and Cost Chapter Appendices (OSHA, October, 2021b).”
b. Rule Familiarization, Employer Policy on Vaccination, and Information Provided to Employees
ETS Requirements
Section 1910.501(d)(1) of the ETS specifies that the employer must establish and implement a written mandatory vaccination policy. The employer is exempted from the requirement in paragraph (d)(1) only if the employer establishes and implements a written policy allowing any employee not subject to a mandatory vaccination policy to either choose to be fully vaccinated against COVID-19 or to provide proof of regular testing for COVID-19 in accordance with paragraph (g) of the ETS and to wear a face covering in accordance with paragraph (i) of the ETS. 43
43 Note to paragraph (d): Under federal law, including the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) and Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964, some workers may be entitled to a reasonable accommodation from their employer, absent undue hardship. If the worker requesting a reasonable accommodation cannot be vaccinated against COVID-19 and/or wear a face covering because of a disability, as defined by the ADA, or if the vaccination, testing, and/or wearing a face covering conflicts with the worker's sincerely held religious belief, practice or observance, the worker may be entitled to a reasonable accommodation. For more information about evaluating requests for these types of reasonable accommodations for disability or sincerely held religious belief, employers should consult the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission's regulations, guidance, and technical assistance including at: https://www.eeoc.gov/wysk/what-you-should-know-about-covid-19-and-ada-rehabilitation-act-and-other-eeo-laws .
In addition, under §1910.501(j), information provided to employees, the ETS requires the employer to inform each employee, in a language and at a literacy level the employee understand about: (1) The requirements of the ETS as well as any employer policies and procedures established to implement the ETS; (2) COVID-19 vaccine efficacy, safety, and the benefits of being vaccinated; (3) the requirements of 29 CFR 1904.35(b)(1)(iv) and Section 11(c) of the OSH Act; and (4) the prohibitions of 18 U.S.C. 1001 and Section 17(g) of the OSH Act.
As stated, the ETS face covering requirements are contained in paragraph (i) of the ETS. Under that paragraph, the employer, with certain exceptions specified in the ETS, must ensure that each employee who is not fully vaccinated wears a face covering when indoors and when occupying a vehicle with another person for work purposes. The ETS does not require, nor does it prohibit, the employer to pay for any costs associated with face coverings (although employer payment for face coverings may be required by other laws, regulations, or collective bargaining agreements or other collectively negotiated agreements). However, the employer must permit the employee to wear a respirator instead of a face covering whether required or not. In addition, the employer may provide respirators or face coverings to the employee, even if not required. In such circumstances, where the employer provides respirators, the employer must also comply with §1910.504, Mini respiratory protection program.
OSHA estimates no costs associated with an employee voluntarily bringing in their own respirator to use instead of a face covering other than those costs that OSHA is estimating below in connection with 29 CFR 1910.501(j), information provided to employees. That section provides, again, that the employer must inform each employee, in a language and at a literacy level the employee understands about the requirements of the ETS as well as any employer policies and procedures established to implement the ETS. One policy the employer would need to establish to implement the ETS is a policy to comply with the requirements of 29 CFR 1910.504 when an employee voluntarily brings in their own respirator. Those requirements require only that the employer provide certain information to the employee (see 29 CFR 1910.504(c)).
OSHA is also estimating no costs in connection with the employer providing respirators to the employee. The ETS does not require the employer to provide respirators to employees. Therefore, any such provision is voluntary and not relevant to economic feasibility of this rule.
The face covering provisions in paragraph (i) contain several other requirements, none of which have costs associated with them.
Cost Analysis Assumptions
In this section, OSHA estimates the cost for establishing the employer policy on vaccination, providing required information to employees, and rule familiarization. OSHA assumes each entity will require an average one-time labor burden of 1 hour of management labor for rule familiarization. OSHA based this unit cost on that taken for rule familiarization in the Healthcare ETS (86 FR at 32496), but adjusted the time downward by a half-hour because this ETS is a simpler standard than the Healthcare ETS.
To establish a written policy in accordance with paragraph (d) of the ETS, OSHA assumes a one-time average labor burden of 5 hours of manager time per firm. OSHA bases this estimate on its cost estimates in the Healthcare ETS, where OSHA estimated that development of the COVID-19 Plan required by that standard would take between 5 and 40 hours (see 86 FR at 32496-32497). OSHA concludes that 5 hours is a reasonable estimate because the development of a written policy on vaccination will be much simpler than the development of the written COVID-19 Plan required by the Healthcare ETS (see 29 CFR 1910.502(c)). 44 OSHA notes, that like the Healthcare ETS (id.), the cost of implementing the plan for this ETS are included in the costs of implementing the corresponding requirements in the ETS, which are discussed below.
44 The estimates for the time to create the written vaccine policy plan under this ETS may differ from the time to create the various processes under the CMS rule published elsewhere in this issue of the Federal Register since the requirements of what is needed to be included in the plans differ. For example, the CMS plan requires a process for ensuring the implementation of additional precautions to mitigate the transmission and spread of COVID-19 while OSHA's vaccination policy requirements do not include this requirement.
To provide information to employees in accordance with paragraph (j) of the ETS, OSHA assumes a one-time average labor burden per firm of 10 minutes of manager time. The agency expects activities like posting the information on a community board, mass emailing, etc., will satisfy this requirement.
The total cost for rule familiarization, establishing an employer policy on vaccination and providing required information to employees is calculated as the product of:
• One-time labor burden for rule familiarization and establishing a policy (a total of 6 hours of manager time per entity) plus a one-time labor burden for providing information to employees (10 minutes of manager time per entity);
• The labor rate for General and Operations Managers (SOC code 11-1021, NAICS-specific wages); and,
• The total number of covered entities.
Cost for Employer Policy on Vaccination and Information Provided to Employees
Costs per entity and total costs for employer policy on vaccination and information provided to employees are shown below in Table IV.B.9.
BILLING CODE 4120-01-P
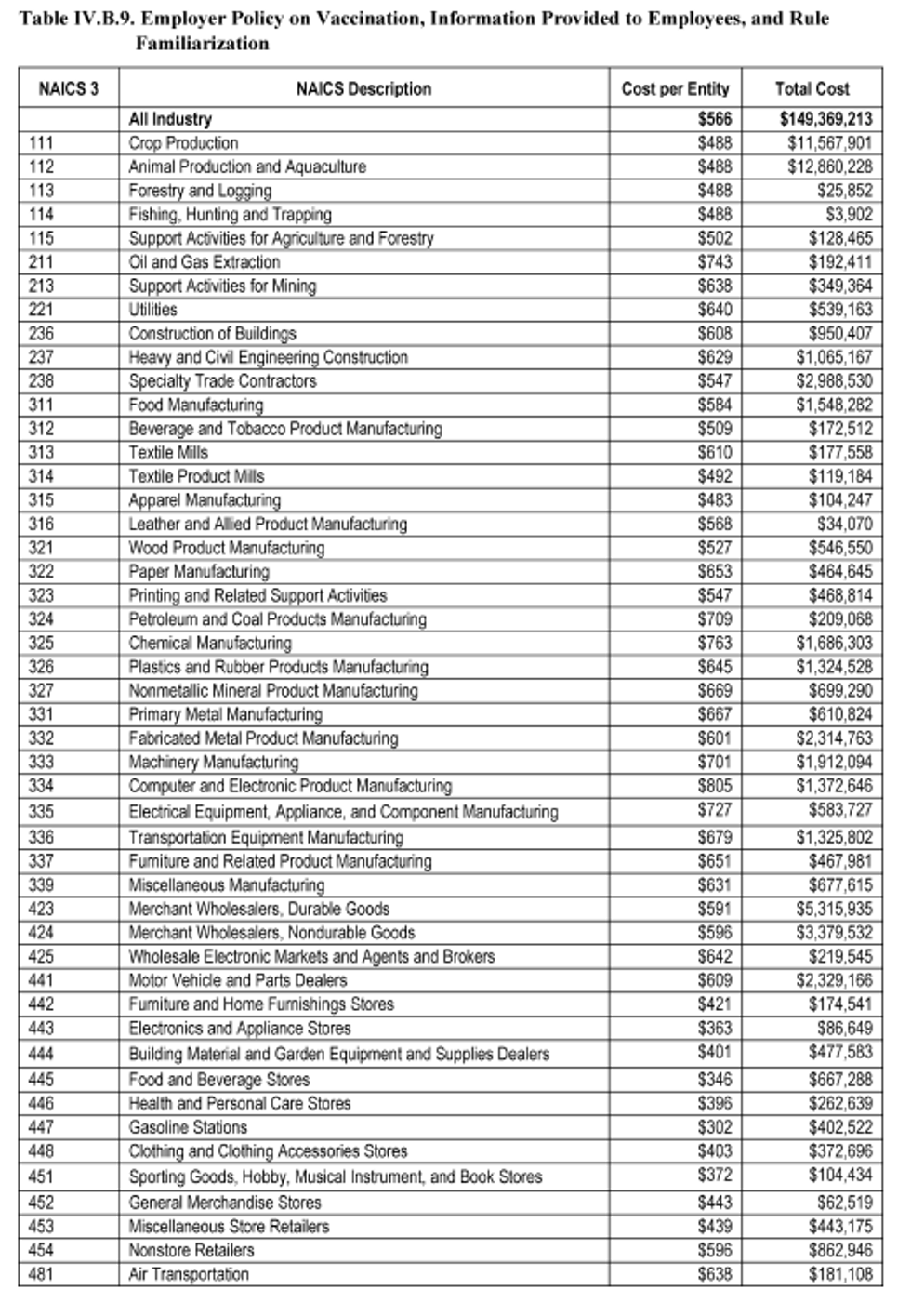
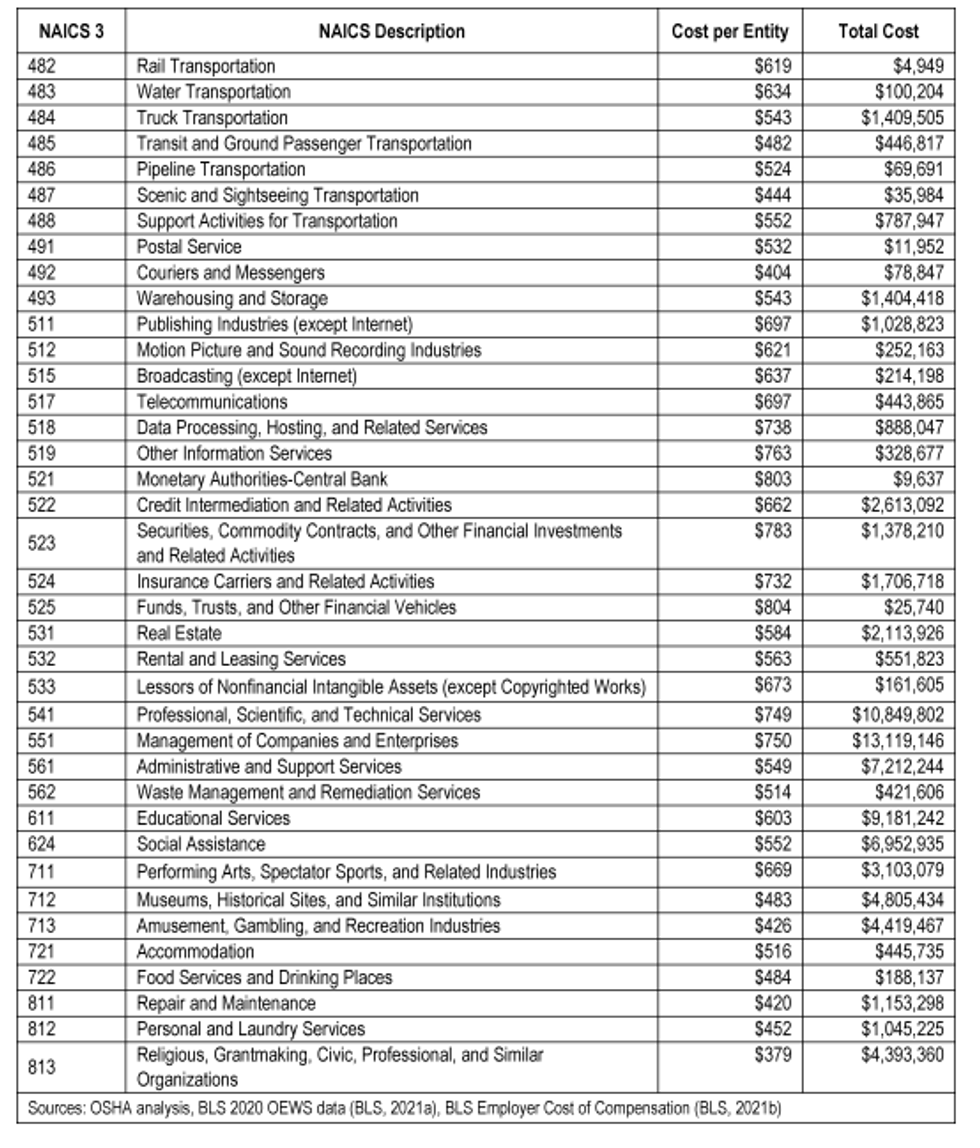
BILLING CODE 4120-01-C
c. Determining Employee Vaccination Status
ETS Requirements
Under §1910.501(e):
Paragraph (e)(1). The employer must determine the vaccination status of each employee. This determination must include whether the employee is fully vaccinated, which is 2 weeks after the full required vaccine course is completed.
Paragraph (e)(2). The employer must require each vaccinated employee to provide acceptable proof of vaccination status, including whether they are fully or partially vaccinated. Acceptable proof of vaccination status is:
• The record of immunization from a health care provider or pharmacy;
• A copy of the COVID-19 Vaccination Record Card;
• A copy of medical records documenting the vaccination;
• A copy of immunization records from a public health, state, or tribal immunization information system; or
• A copy of any other official documentation that contains the type of vaccine administered, date(s) of administration, and the name of the health care professional(s) or clinic site(s) administering the vaccine(s).
In instances where an employee is unable to produce acceptable proof of vaccination, per above, a signed and dated statement by the employee, subject to criminal penalties for knowingly providing false information:
• Attesting to their vaccination status (fully vaccinated or partially vaccinated); and
• Attesting that they have lost and are otherwise unable to produce proof required by the ETS.
Paragraph (e)(3). Any employee who does not provide one of the acceptable forms of proof of vaccination status in paragraph (e)(2) of the ETS to the employer must be treated as not fully vaccinated for the purpose of the ETS.
Paragraph (e)(4). The employer must maintain a record of each employee's vaccination status and must preserve acceptable proof of vaccination for each employee who is fully or partially vaccinated. The employer must maintain a roster of each employee's vaccination status. These records and roster are considered to be employee medical records and must be maintained as such records in accordance with 29 CFR 1910.1020 and must not be disclosed except as required or authorized by the ETS or other federal law. These records and roster are not subject to the retention requirements of 29 CFR 1910.1020(d)(1)(i) but must be maintained and preserved while the ETS remains in effect.
Paragraph (e)(5). Finally, when an employer has ascertained employee vaccination status prior to the effective date of this section through another form of attestation or proof, and retained records of that ascertainment, the employer is exempt from the requirements in paragraphs (e)(1)-(e)(3) only for each employee whose fully vaccinated status has been documented prior to the effective date of this section. For purposes of paragraph (e)(4), the employer's records of ascertainment of vaccination status for each such person constitute acceptable proof of vaccination.
The full costs for these provisions are taken under the costs for recordkeeping, discussed below, because determining vaccination status, providing acceptable proof of vaccination status, and creating and maintaining a roster of each employee's vaccination status will be part and parcel of the recordkeeping process.
d. Employer Support for Employee Vaccination
ETS Requirements
Under 29 CFR 1910.501(f):
The employer must support COVID-19 vaccination by providing:
• Time for vaccination. The employer must: (i) Provide a reasonable amount of time to each employee for each of their primary vaccination series dose(s); and (ii) provide up to 4 hours paid time, including travel time, at the employee's regular rate of pay for this purpose.
• Time for recovery. The employer must provide reasonable time and paid sick leave to recover from side effects experienced following any primary vaccination series dose to each employee for each dose.
Under the ETS, fully vaccinated means (i) a person's status 2 weeks after completing primary vaccination with a COVID-19 vaccine with, if applicable, at least the minimum recommended interval between doses in accordance with the approval, authorization, or listing that is: (A) Approved or authorized for emergency use by the FDA; (B) listed for emergency use by the World Health Organization (WHO); or (C) administered as part of a clinical trial at a U.S. site, if the recipient is documented to have primary vaccination with the “active” (not placebo) COVID-19 vaccine candidate, for which vaccine efficacy has been independently confirmed (e.g., by a data and safety monitoring board), or if the clinical trial participant from the U.S. site had received a COVID-19 vaccine that is neither approved nor authorized for use by FDA but is listed for emergency use by WHO; or (ii) a person's status 2 weeks after receiving the second dose of any combination of two doses of a COVID-19 vaccine that is approved or authorized by the FDA, or listed as a two-dose series by the WHO (i.e., heterologous primary series of such vaccines, receiving doses of different COVID-19 vaccines as part of one primary series). The second dose of the series must not be received earlier than 17 days (21 days with a 4-day grace period) after the first dose.
Cost Analysis Assumptions
OSHA assumes there will be no costs to employers or employees associated with the vaccine itself. 45 However, to provide support for vaccination of employees, OSHA estimates that it will take an average of 15 minutes of travel time, each way, per employee to travel to a vaccination site (for a total of 30 minutes). OSHA then estimates 5 minutes to wait, fill out any necessary paperwork, and receive the shot, and a post-shot wait time of 20 minutes, per employee. Some firms, particularly larger ones, will find it cheaper to have vaccines administered on site. They may have an on-site health clinic or may hire a 3rd party purveyor to come to the facility. 46 This will minimize travel and also allow the companies to mitigate some of the logistical issues that may be preventing employees from receiving a vaccine (finding a convenient appointment time, etc.). OSHA estimates that 10 percent of firms with employees between 100 to 500 employees will select this option, while, given decreased average costs associated with economies of scale, 25 percent of firms with over 500 employees will select this option. OSHA was unable to obtain an estimate of the cost savings associated with on-site vaccination in the time allotted to issue this emergency standard, so it is assuming that the costs for off-site vaccination are the same as the costs for on-site vaccination. This results in a likely over-estimate of costs given that the entities that choose the on-site option will do so as a cost-saving measure.
45 While there may be some administrative costs borne by the government, such costs are not germane to this analysis of whether the ETS is economically feasible for covered employers.
46 Prior to the effective date of this rule, some companies offered on-site vaccination according to a limited survey. (Willis Towers Watson, June 23, 2021). See also CDC on creating an on-site program (CDC, March 25, 2021; CDC, October 4, 2021b).
In OSHA's cost analysis, OSHA assumes that all employees will be vaccinated during working hours and employers would adjust the employee work schedule to ensure that the employee would not become eligible for overtime pay as a result of the vaccination time. However, it should be noted that, if an employee chooses to receive the vaccine outside of work hours, OSHA does not require employers to grant paid time to the employee for the time spent receiving the vaccine during non-work hours (although other laws may include additional requirements for employers, such as those addressing reasonable accommodations or exemptions). OSHA's analysis may be an overestimate as it reflects an assumption that all vaccinations are received during work hours.
CDC data indicated that 5 percent of employees vaccinated have received the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, and 95 percent have received either Pfizer or Moderna (CDC, October 2021b). OSHA applies the same allocation to employees being vaccinated under the ETS. For those receiving Pfizer or Moderna, the labor burden outlined above occurs twice, since vaccination requires two shots.
The employer must provide reasonable time and paid sick leave to recover from side effects experienced following any vaccination dose to each employee for each vaccination dose. Employers may require employees to use paid sick leave benefits otherwise provided by the employer to offset these costs, if available. The average amount of time off an employee may need for side effects while receiving the vaccine doses necessary to achieve full vaccination (one or two doses, depending on the vaccine) depends on several factors. First, the percentage of people who will have side effects that are severe enough to require time. Second, the average time duration for those who have such a severe reaction. For estimates of these parameters OSHA is using a recent study (Levi et al., September 29, 2021) which surveyed workers at a state-wide health care system who had been vaccinated. The study found that, for the first dose, 4.9% needed administrative leave, with an average length of absence of 1.66 days. For the second dose, 19.79% needed leave and their average length of absence was 1.39 days. Together, the average time on leave is .36 days (.049 * 1.66 .1979 * 1.39) for a person receiving two doses, which reflects the fact that many people who receive the vaccine do not have any side effects for either dose while others have more severe side effects.
In order to determine the amount of paid sick leave that would be available to employees, OSHA relied on data from BLS (BLS, 2021e). BLS estimates that for civilian workers in establishments with 100 employees, 88% have access to paid sick leave (Table 33). BLS states that the average number of paid sick leave available is 9 days (Table 36). Because there is the same number of days across all levels of employee tenure (1 year, 5 years, 10 years, and 20 years), OSHA used 9 days for all covered employees. The agency assumes that 75% of the available paid sick leave has been used by the current 4th quarter of the calendar year. So the average number of days available is 1.98 days: 9 (days) * 88% (employees with available paid sick leave) * 25% (amount of leave remaining in the year) = 1.98 days available. Given that the average overall time out due to side effects is 0.36 days (see above), OSHA concludes that, on average, employees should have sufficient existing paid sick leave available to cover the time needed as a result of vaccine-related side effects. As a result, OSHA is taking no costs to employers in connection with the ETS's requirement to provide time for recovery from vaccination (except as provided below), as these costs will have been incurred by the employer independent of the ETS.
While this analysis is entirely consistent with OSHA's standard procedure of strictly using averages in cost analysis, it nonetheless masks some significant effects resulting from the time for recovery requirements. From the BLS data, OSHA knows there are 12% of establishments that have 100 employees and do not provide paid sick leave. Correspondingly, there is a group of entities with no paid sick leave that will obviously incur costs that result directly from these requirements. In addition, some employees may not have, or some other entities may not offer, sufficient paid sick leave to cover these costs.
To account for the 12 percent of firms that do not offer paid sick leave, the agency uses the above estimate of average days for two doses, 0.36 days, and multiplies the average employee wage by NAICS to calculate the cost per employee. Since OSHA does not know which firms make up the 12 percent, the agency spreads this total cost across all firms by employee. Since firms without any sick leave are likely to be lower-wage firms, this will likely lead to a cost overestimate.
Therefore, the total cost for paid time off for vaccination is based on the costs for providing paid sick leave for the 12 percent of firms that do not offer paid sick leave and:
• Travel time per employee of covered firms of 15 minutes each way per vaccination dose (total of 30 minutes).
• Pre-shot wait time per employee of covered firms of 5 minutes per vaccination dose.
• Post-shot wait time per employee of covered firms of 20 minutes per vaccination dose. 47
47 According to the CDC, people with allergies require a wait time of 30 minutes, but they are a small group, and, in any event, the CDC recommends that routine wait time is 15 minutes, so the agency considers that its average of 20 minutes is probably an overestimate. (See CDC, October 4, 2021a; CDC, March 3,2021.)
• The average labor rate for employees (NAICS-specific wages).
• Total number of employees at covered firms getting vaccinated due to the ETS with the Johnson & Johnson vaccine.
• Total number of employees at covered firms getting vaccinated due to the ETS with the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines, multiplied by two to account for two shots.
Cost for Support for Employee Vaccination
Costs per firm and total costs for vaccination are shown below in Table IV.B.10.
BILLING CODE 4120-01-P



BILLING CODE 4120-01-C
e. COVID-19 Testing for Employees Who Are Not Fully Vaccinated
ETS Requirements
Section 1910.501(g)(1) of the ETS requires the employer to ensure that each employee who is not fully vaccinated do the following:
An employee who reports at least once every 7 days to a workplace where other individuals, such as coworkers or customers, are present:
• Must be tested for COVID-19 at least once every 7 days; and
• Must provide documentation of the most recent COVID-19 test result to the employer no later than the 7th day following the date on which the employee last provided a test result.
An employee who does not report during a period of 7 or more days to a workplace where other individuals, such as coworkers or customers, are present ( e.g., teleworking for two weeks prior to reporting to a workplace with others):
• Must be tested for COVID-19 within 7 days prior to returning to the workplace; and
• Must provide documentation of that test result to the employer upon return to the workplace.
Furthermore, if an employee does not provide documentation of a COVID-19 test result as required by paragraph (g)(1) of the ETS, the employer must keep that employee removed from the workplace until they provide a test result. In addition, when an employee has received a positive COVID-19 test, or has been diagnosed with COVID-19 by a licensed healthcare provider, the employer must not require that employee to undergo COVID-19 testing as required under paragraph (g) of this section for 90 days following the date of their positive test or diagnosis. Finally, the employer must maintain a record of each test result provided by each employee under paragraph (g)(1) of this section or obtained during tests conducted by the employer. These records are considered to be employee medical records and must be maintained as such records in accordance with 29 CFR 1910.1020 and must not be disclosed except as required or authorized by this section or other federal law. These records are not subject to the retention requirements of 29 CFR 1910.1020(d)(1)(i) but must be maintained and preserved while this section remains in effect.
OSHA addresses the costs associated with testing in the next section. The remaining costs required by paragraph (g) are taken under the costs for recordkeeping, discussed below, because providing documentation of test results to the employer will be part and parcel of the recordkeeping process.
Employees who are partially vaccinated are also required to be tested weekly until they are fully vaccinated. Those receiving the J&J vaccine will require two weeks of testing after the single shot, employees who received the Pfizer-BioNTech Vaccine will require 5 weeks of testing (3 weeks between shots and 2 weeks following the second shot), and Moderna recipients require 6 weeks of testing (4 weeks between shots and 2 weeks following the second shot) (CDC, October 4, 2021b). Notwithstanding this, in the agency's total cost estimate OSHA accounts for the fact that employers need not comply with the requirements of this section in paragraph (g) by 60 days after the rule's effective date, and that employees who have completed the entire primary vaccination series by that date do not have to be tested, even if they have not yet completed the 2 week waiting period.
There is no requirement in the rule that the employer pay for this testing so these testing-related costs are not included in the main analysis (although, as discussed below OSHA takes into account costs for testing in connection with the ETS's recordkeeping requirements). The agency estimates that 6.3 million weekly tests will need to be given due to this ETS (see Table IV.B.8). This 6.3 million is likely an overestimate of new costs because it encompasses tests for employees who were already required to conduct testing by their employers prior to this ETS.
OSHA also notes that its cost estimates for testing do not take into account the 90-day break in testing that occurs following the date of a positive test or diagnosis. OSHA's cost estimates are also potentially overcounting costs in that OSHA does not take into account that not all employees for whom testing is required will report at least once every 7 days to a workplace where other individuals, such as coworkers or customers, are present. Thus, OSHA's estimate assumes that employees for whom testing is required will need to be tested at least once every 7 days and not less frequently as will often be the case.
OSHA notes, in addition, that there are no costs associated with paragraph (g)'s removal provision. The ETS does not require the employer to provide paid time off to any employee for removal as a result of the employee's refusal/failure to provide documentation of a COVID-19 test result as required by paragraph (g)(1) of the ETS.
Finally, OSHA notes that a COVID-19 test under the ETS is a test for SARS-CoV-2 that is: (i) Cleared, approved, or authorized, including in an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA), by the FDA to detect current infection with the SARS-CoV-2 virus ( e.g., a viral test); (ii) Administered in accordance with the authorized instructions; and (iii) Not both self-administered and self-read unless observed by the employer or an authorized telehealth proctor. Examples of tests that satisfy this requirement include tests with specimens that are processed by a laboratory (including home or on-site collected specimens which are processed either individually or as pooled specimens), proctored over-the-counter tests, point of care tests, and tests where specimen collection and processing is either done or observed by an employer. Employers may have costs associated with doing, observing or proctoring employee testing, if employers choose to do so. However, for economic feasibility purposes, OSHA does not account for these costs in its estimates because they are not required for compliance with the ETS.
Costs Associated with Reasonable Accommodation: Testing, Face Coverings, and Determinations
The ETS does not require the employer to pay for any costs associated with testing; however employer payment for testing may be required by other laws, regulations, or collective bargaining agreements. Thus, while OSHA does not include any costs for reasonable accommodation requests in its main cost analysis in recognition that such costs would result from the application of other laws, OSHA notes that even if employers were to agree to pay for COVID-19 testing as part of a reasonable accommodation or some other reason required by law, such costs would not alter OSHA's findings regarding the economic feasibility of the rule. 48 OSHA reached this conclusion after conducting a separate analysis of reasonable accommodation costs that an employer might assume if they do not represent an undue hardship for the employer. This analysis is available in the docket at OSHA, October 2021d.
48 OSHA notes that while the testing required under this standard might be an option for employees who request a reasonable accommodation to avoid vaccination, other alternatives such as telework would be more protective to the employee by preventing COVID-19 exposure. These alternatives may also be available at no additional cost to the employer or employee.
OSHA notes that this separate analysis is limited to employees who request accommodation, and accounts for costs of reviewing medical and/or religious accommodation requests, as well as costs for COVID-19 testing and face coverings that would satisfy the requirements of this ETS. OSHA expects a reasonable accommodation request could lead to a review of the employee's request by a manager and then a conference between the manager and the employee. OSHA concludes that the combination of these costs would not alter OSHA's findings regarding the economic feasibility of the ETS.
f. Employee Notification to Employer of a Positive COVID-19 Test and Removal
ETS Requirements
Under §1910.501(h):
Regardless of COVID-19 vaccination status or any COVID-19 testing required under paragraph (g) of the ETS, the employer must:
• Require each employee to promptly notify the employer when they receive a positive COVID-19 test or are diagnosed with COVID-19 by a licensed healthcare provider; and
• Immediately remove from the workplace any employee who receives a positive COVID-19 test or is diagnosed with COVID-19 by a licensed healthcare provider and keep the employee removed until the employee: (i) Receives a negative result on a COVID-19 nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT) following a positive result on a COVID-19 antigen test if the employee chooses to seek a NAAT test for confirmatory testing; (ii) meets the return to work criteria in CDC's “Isolation Guidance” (incorporated by reference, §1910.509); or (iii) receives a recommendation to return to work from a licensed healthcare provider.
Costs Analysis Assumptions
The ETS does not require employers to provide paid time off to any employee for removal from the workplace as a result of a positive COVID-19 test or diagnosis of COVID-19; however paid time off may be required by other laws, regulations, or collective bargaining agreements or other collectively negotiated agreements. Therefore, there are no costs associated with paragraph (h)'s removal provision.
With respect to notification, to the extent employee notification is connected to the ETS's testing and documentation requirements in paragraph (g), those costs to the employer are taken under the costs for recordkeeping, discussed below, because, as explained above, receiving documentation of test results under paragraph (g) will be part and parcel of the recordkeeping process.
OSHA notes also that the costs associated with employee notification by vaccinated employees (not required by this ETS to undergo testing) should also be negligible because it will not occur with any real frequency. The very low breakthrough rates of infection among vaccinated persons suggests that the overwhelming majority of COVID-19 cases reported to a covered employer will be in the pool of unvaccinated employees.
g. Reporting COVID-19 Fatalities and Hospitalizations to OSHA
ETS Requirements
Under §1910.501(j):
The employer must report to OSHA:
• Each work-related COVID-19 fatality within 8 hours of the employer learning about the fatality.
• Each work-related COVID-19 in-patient hospitalization within 24 hours of the employer learning about the in-patient hospitalization.
When reporting COVID-19 fatalities and in-patient hospitalizations to OSHA in accordance with paragraph (j)(1) of the ETS, the employer must follow the requirements in 29 CFR part 1904.39, except for 29 CFR part 1904.39(a)(1) and (2) and (b)(6).
Cost Analysis Assumptions
OSHA estimates a total of 1,464 fatalities and 59,570 hospitalizations for employees of covered firms. 49 This analysis is broadly consistent, using updated data, with OSHA's analysis of a nearly identical provision in 29 CFR 1910.502, the Healthcare ETS. OSHA also estimates, based on the Healthcare ETS, that reporting of each fatality and hospitalization will require 45 minutes of an employer's time (86 FR at 32516). This includes hospitalizations and fatalities for employees that remain unvaccinated, as well as a small percentage of hospitalizations and fatalities of vaccinated employees due to breakthrough cases. Because of the timing requirements in the rule, the agency assumes that a hospitalization followed by a death will need two reports from the employer ( i.e., the agency assumes that reporting for hospitalizations will occur within 8 hours, before reporting for fatalities occurs, within 24 hours). This will result in a slight over-estimate.
49 These counts represent hospitalizations and fatalities that would occur to the in-scope labor force despite the ETS. The numbers are derived using methodology similar to that used in Health Impacts to generate hospitalizations and fatalities prevented. An infection rate and case fatality rate are multiplied by the number of unvaccinated workers to derive a total number of fatalities. That number is used to derive hospitalizations. The number of hospitalizations and fatalities to vaccinated employees is calculated in a similar fashion, but with a lower infection rate because vaccination makes it considerably less likely that an individual will be tested and found to be infected. See (OSHA, October 2021a and OSHA, October 2021c). One difference in methodology between these counts and the Health Impacts analysis is that these counts use a baseline of the last 19 months of CDC data to estimate the case fatality rate (similar to Alternative C in the Health Impacts analysis), rather than a baseline of the last 6 months (which OSHA used for the main Health Impacts analysis). This results in an estimate toward the upper bound for these counts ( i.e., an overestimate of costs).
The total cost for reporting COVID-19 fatalities and hospitalizations to OSHA is calculated as the product of:
• One-time labor burden of 45 minutes per report of hospitalization or fatality.
• Wage range for General and Operations Managers (SOC code 11-1021, NAICS-specific wages).
• Total number of fatalities for employees at covered firms.
• Total number of hospitalizations for employees at covered firms.
Cost for Reporting COVID-19 Fatalities and Hospitalizations to OSHA
Costs per entity and total costs for vaccination are shown below in Table IV.B.11.


h. Recordkeeping
ETS Requirements
As discussed above, the full costs for the requirements in paragraph (e) of the ETS are taken under the costs for recordkeeping because determining vaccination status, providing acceptable proof of vaccination status, and creating and maintaining a roster of each employee's vaccination status will be part and parcel of the recordkeeping process. Under paragraph (e)(4) of the ETS, the employer must maintain a record of each employee's vaccination status and must preserve acceptable proof of vaccination for each employee who is fully or partially vaccinated. The employer must also maintain a roster of each employee's vaccination status. These records and roster are considered to be employee medical records and must be maintained in accordance with 29 CFR 1910.1020 as such records and must not be disclosed except as required or authorized by the ETS or other federal law. These records and roster are not subject to the retention requirements of 29 CFR 1910.1020(d)(1)(i) but must be maintained and preserved while the ETS remains in effect.
With respect to vaccination, it should be noted that, under paragraph (e)(5) of the ETS, when an employer has ascertained employee vaccination status prior to the effective date of this section through another form of attestation or proof, and retained records of that ascertainment, the employer is exempt from the determination of vaccination requirements in paragraphs (e)(1)-(e)(3) only for each employee whose fully vaccinated status has been documented prior to the effective date of this section. For purposes of the recordkeeping requirements in paragraph (e)(4), the employer's records of ascertainment of vaccination status for each such person constitute acceptable proof of vaccination. OSHA estimates, based on this provision, that 60% of employees who were vaccinated prior to the promulgation of the ETS will not need to document vaccination status in connection with paragraph (e) (ASU COVID-19 Diagnostic Commons, October 6, 2021).
As also discussed above, the costs for the requirements for documenting test results in paragraph (g), including the timing for when recordkeeping costs for testing accrue under the ETS, are taken under the costs for recordkeeping because providing documentation of test results to the employer will be part and parcel of the recordkeeping process. Under paragraph (g)(4) of the ETS, the employer must maintain a record of each test result provided by each employee under paragraph (g)(1) of the ETS or obtained during tests conducted by the employer. These records must be maintained in accordance with 29 CFR 1910.1020 and must not be disclosed except as required or authorized by this section or other federal law. These records are not subject to the retention requirements of 29 CFR 1910.1020(d)(1)(i) but must be maintained and preserved while this section remains in effect.
With respect to testing, it should be noted that, under paragraph (m) of the ETS, employers are not required to comply with the requirements in paragraph (g) of the ETS until 60 days after the effective date of the ETS, meaning that for cost analysis purposes OSHA assumes that employers would not receive any testing records until the end of that 60-day period.
Finally, under paragraph 1910.501(l)(1) of the ETS, availability of records, by the end of the next business day after a request, the employer must make available, for examination and copying, the individual COVID-19 vaccine documentation and any COVID-19 test results for a particular employee to that employee and to anyone having written authorized consent of that employee. In addition, under paragraph 1910.501(l)(2) of the ETS, by the end of the next business day after a request by an employee or an employee representative, the employer must make available to the requester the aggregate number of fully vaccinated employees at a workplace along with the total number of employees at that workplace. Under paragraph 1910.501(l)(3) of the ETS, the employer must also provide to the Assistant Secretary for examination and copying: (i) Within 4 business hours of a request, the employer's written policy required by paragraph (d) of the ETS, and the aggregate numbers described in paragraph (l)(2) of the ETS; and (ii) By the end of the next business day after a request, all other records and other documents required to be maintained by the ETS.
Cost Analysis Assumptions
To fulfill the recordkeeping requirements in the ETS, OSHA estimates that it will take an average of 5 minutes of clerical time per employee record. OSHA bases this cost estimate on the estimate for recordkeeping in the Healthcare ETS (86 FR at 32515). While OSHA estimated an average of 10 minutes of clerical time per employee record in the Healthcare ETS, that standard includes more extensive recordkeeping requirements than what is being required under this ETS. See 29 CFR 1910.502(q)(2)(ii) (Healthcare ETS record must contain, for each instance, the employee's name, one form of contact information, occupation, location where the employee worked, the date of the employee's last day at the workplace, the date of the positive test for, or diagnosis of, COVID-19, and the date the employee first had one or more COVID-19 symptoms, if any were experienced).
In addition, OSHA includes in this estimate 5 minutes of employee time to provide documentation of vaccination status or testing, as applicable, to the employer. OSHA notes that, for an employee who is vaccinated, the employer will determine the vaccination status of that employees and obtain acceptable proof of vaccination status at the same time, thus negating the need to create two separate records for these requirements.
OSHA notes that there will be a cost associated with setting up the recordkeeping system ( e.g., a spreadsheet) used to comply with the ETS. OSHA takes these costs in connection with the costs for the employer policy on vaccination, which are described above.
Given the relative complexity of recordkeeping in the Healthcare ETS, OSHA has simplified its assumptions to reflect a variety of small costs in a combined estimate. As in the Healthcare ETS, the cost estimate of 5 minutes per event is likely much higher than necessary to account for just the actions of receiving and maintaining copies of records, so retaining this time will yield a tendency toward overestimation. However, this cost also reflects a margin to encompass additional outlier costs such as a second documentation of vaccination status for all employees who need to submit documentation twice (first for partial vaccination and then for full vaccination) under the ETS. This 5 minutes for recordkeeping also encompasses the marginal time for creating and maintaining a roster of each employee's vaccination status (paragraph (e)) and making aggregate employee data available (paragraph (l)). Since normally the system used for recordkeeping will be electronic in businesses with more than 100 employees, the time to create an aggregate report and a roster should be de minimis. Finally, this inflated recordkeeping cost encompasses time for employee notification to the employer of a positive COVID-19 test connected to the ETS's testing and documentation requirements in paragraph (g),which is a notification under paragraph (h). Finally, the burden of making available, for examination and copying, the individual COVID-19 vaccine documentation and any COVID-19 test results for a particular employee are included in this estimate because this documentation will normally be pulled from the electronic recordkeeping system described above. 50
50 The cost of providing to the Assistant Secretary for examination and copying the employer's written policy required by paragraph (d) of the ETS will be de minimis.
The total cost for these requirements is calculated based on:
• One-time labor burden of 5 minutes of employee labor to provide documentation and 5 minutes of clerk labor per employee record (one record per test administered and one record per documentation of vaccination status).
• The average labor rate for Office Clerks, General (SOC 43-9060, NAICS-specific wages) and employees providing documentation (average wage over all employees, NAICS-specific wages)
• Total number of employees at covered firms getting vaccinated due to the ETS with the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, who receive one shot.
• Total number of employees at covered firms getting vaccinated due to the ETS with the Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna vaccines, multiplied by two to account for two shots.
• Total number of tests for employees at covered firms who are unvaccinated and will get vaccinated by receiving the Johnson and Johnson vaccine.
• Total number of tests for employees at covered firms who are unvaccinated and will get vaccinated by receiving the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines.
• Total number of employees at covered firms who are unvaccinated and will be tested weekly.
Cost for Recordkeeping
Costs per entity and total costs for recordkeeping are shown below in Table IV.B.12.
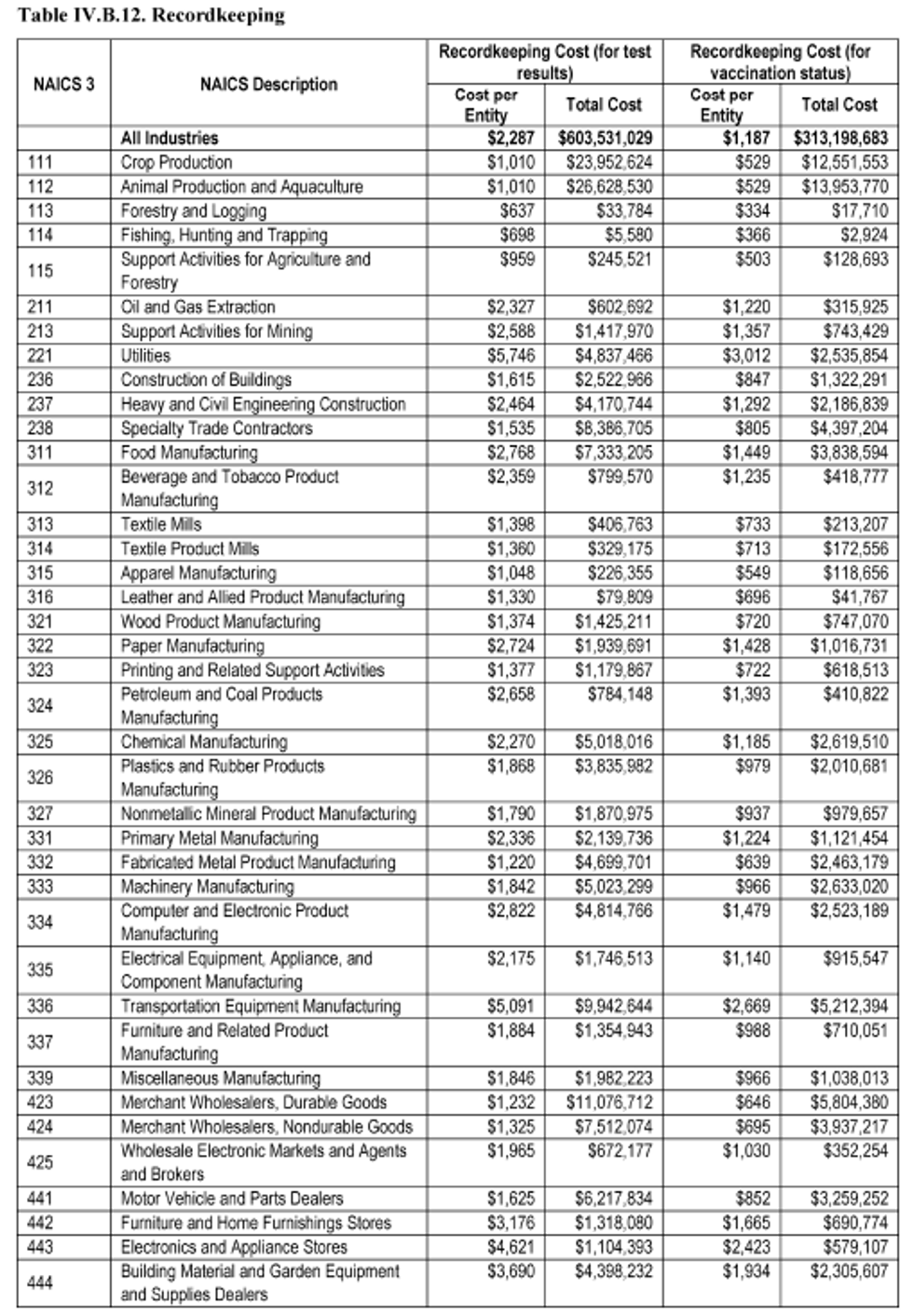
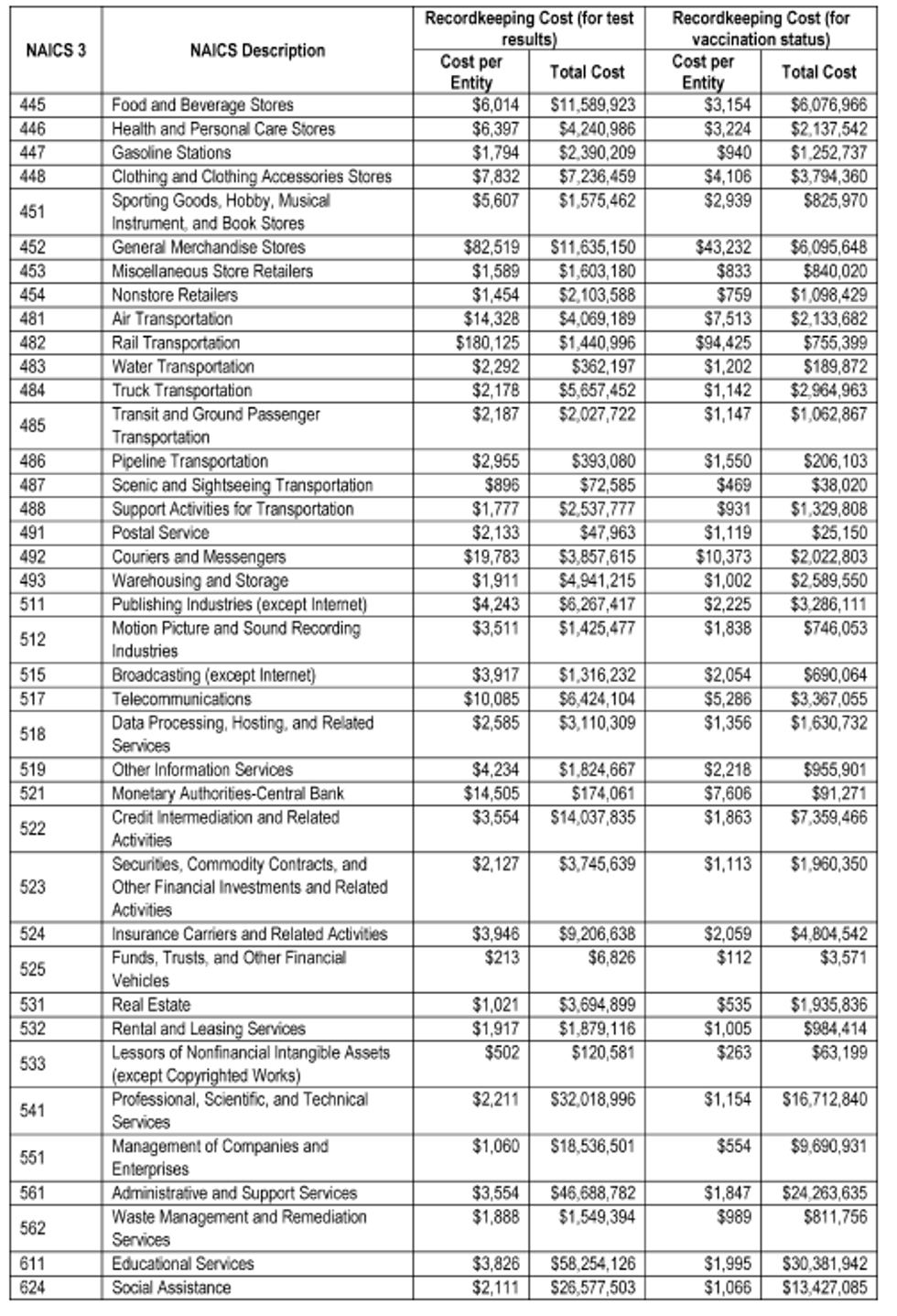
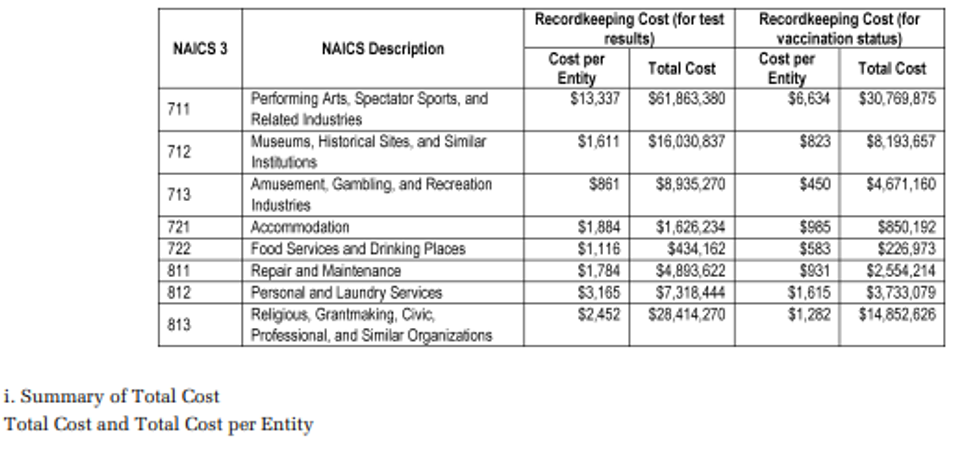
i. Summary of Total Cost
Total Cost and Total Cost per Entity
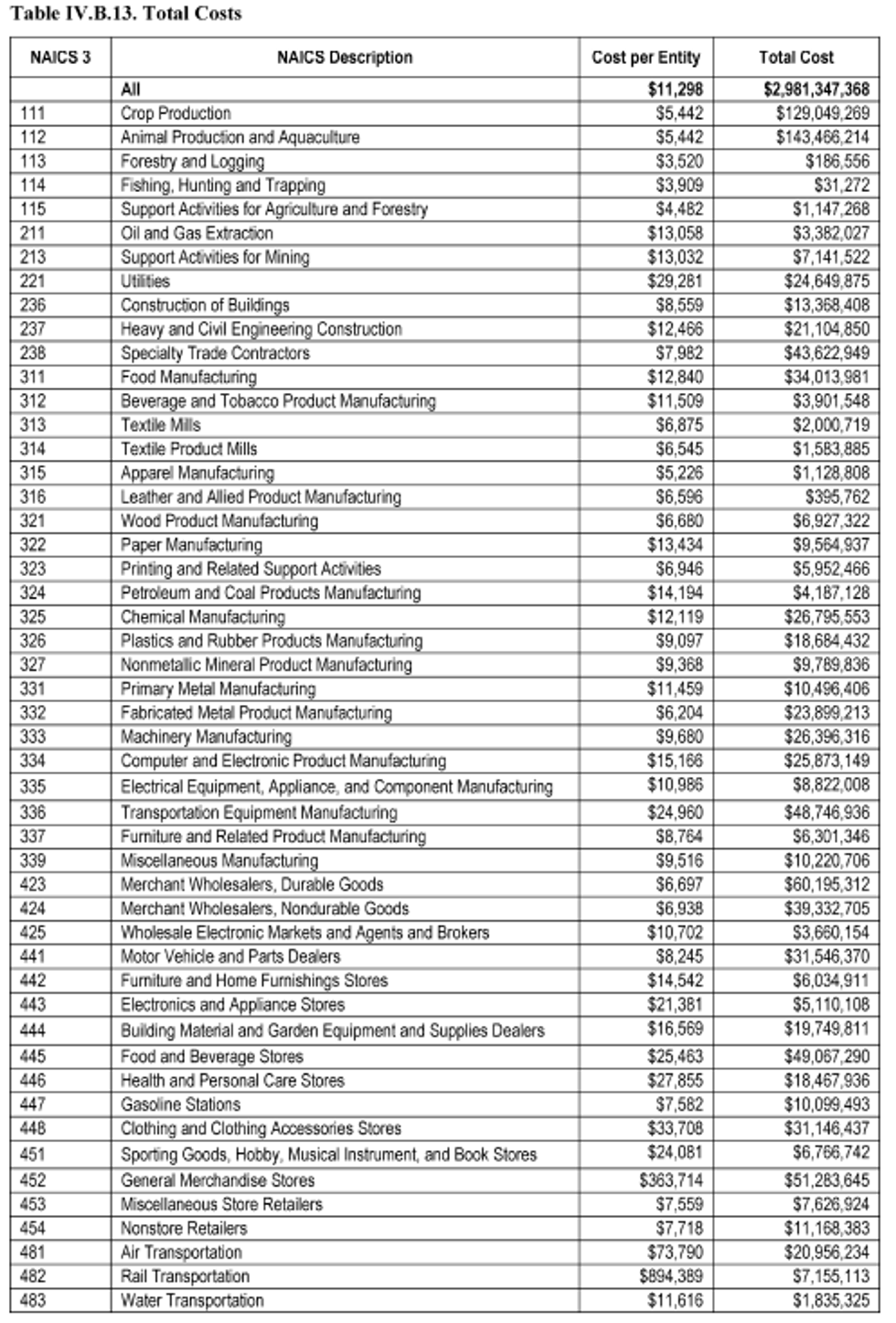
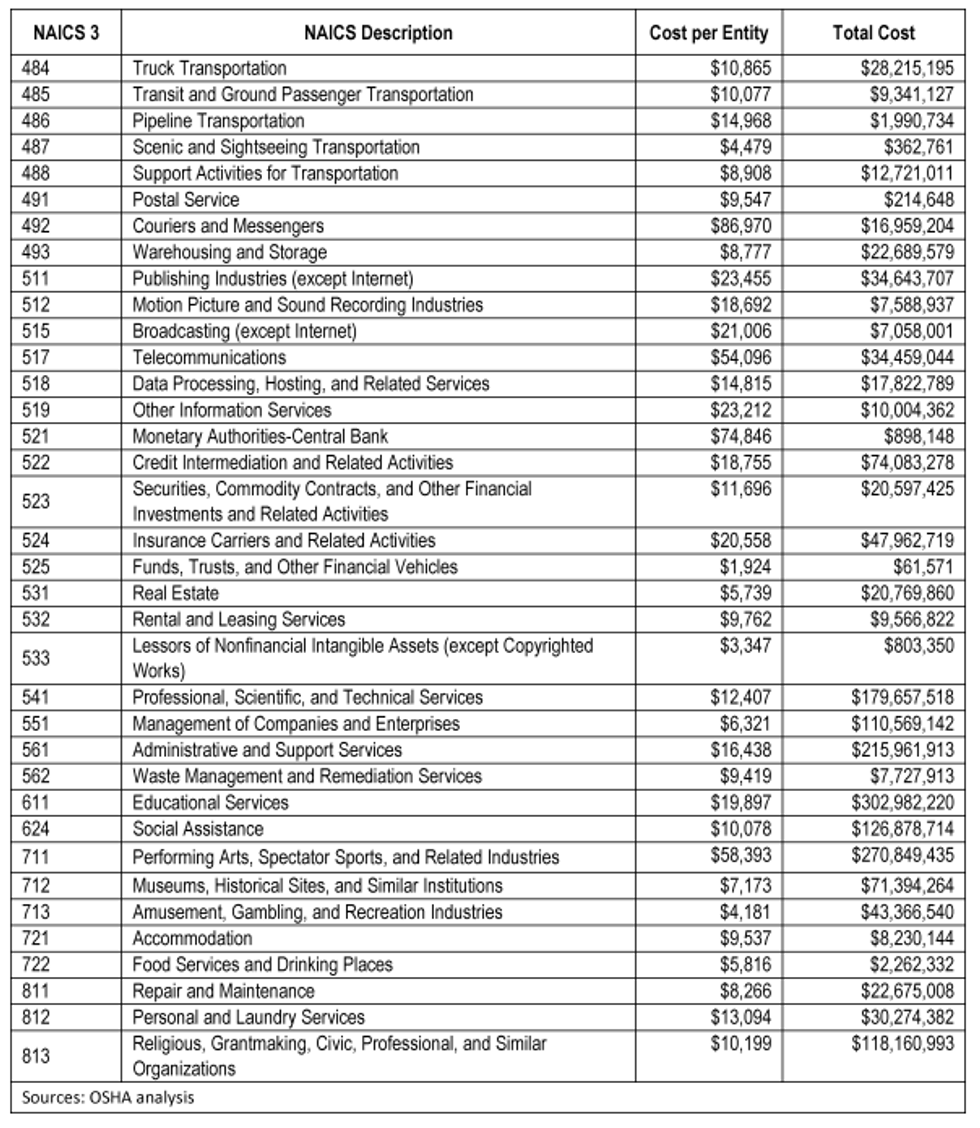
j. Sensitivity Analysis
As stated above, based on limited data on current vaccine mandate implementation and forecasts for future implementation (Mishra and Hartstein, August 23, 2021; ASU COVID-19 Diagnostic Commons, October 6, 2021), OSHA estimates that 25 percent of firms in scope currently have a vaccination mandate, and assumes that this will rise to 60 percent of covered employers after the ETS is in place. Because the agency has no historic reference on which to base its assumptions regarding vaccine mandates, the agency adjusted the percentage of firms that will institute a vaccine mandate because of the ETS as part of a sensitivity analysis. Along with the baseline estimate of 60 percent of firms having a mandate, the agency looked at a vaccine mandate rate of 40 percent and 80 percent for covered firms, which OSHA judged to be a reasonable range based on the data available. The total costs associated with a 40 percent vaccine mandate are $2.998 billion, and the total costs associated with an 80 percent vaccine mandate are $2.964 billion. This compares to the baseline costs associated with a 60 percent vaccine mandate of $2.981 billion. A higher vaccine mandate increases the share of employees who get vaccinated while reducing the share that must get weekly testing. It is this shift in shares that causes the costs to change because the total costs associated with weekly testing (recordkeeping) are more expensive than the total costs associated with vaccination under the ETS (employer support for vaccination, recordkeeping).
References
ASU COVID-19 Diagnostic Commons. (2021, October 6). https://chs.asu.edu/diagnostics-commons/workplace-commons . (ASU COVID-19 Diagnostic Commons, October 6, 2021)
Barrero J et al. (2021, April). Why Working From Home Will Stick. Becker Friedman Institute Working Paper No. 2020-174. https://bfi.uchicago.edu/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/BFI_WP_2020174.pdf . (Barrero et al., April 2021)
Barry J et al. (2021, September 24). Unvaccinated Workers Say They'd Rather Quit Than Get a Shot, but Data Suggest Otherwise. Scientific American. https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/unvaccinated-workers-say-theyd-rather-quit-than-get-a-shot-but-data-suggest-otherwise/ . (Barry et al., September 24, 2021)
Bick A et al. (2021, February). Work from Home Before and After the COVID-19 Outbreak. Federal Reserve Bank of Dallas No. 2017, Revised February 2021. https://doi.org/10.24149/wp2017r2 . (Bick et al., February 2021)
Brynjolfsson E et al. (2020, June). COVID-19 and Remote Work: An Early Look At US Data. National Bureau of Economic Research. https://www.nber.org/system/files/working_papers/w27344/w27344.pdf . (Brynjolfsson et al., June 2020)
Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). (2017). Quarterly Census of Employment and Wages (QCEW). https://www.bls.gov/cew/ . (BLS, 2017)
Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). (2020). Occupational Requirements Survey (ORS). https://www.bls.gov/ors/ . (BLS, 2020)
Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). (2021a). Occupational Employment and Wage Statistics (OEWS) Survey, May 2020. https://www.bls.gov/oes/ . (BLS, 2021a)
Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). (2021b). Employer Costs for Employee Compensation by Ownership, All 2018 Civilian Wages and Salaries, March 2021. https://www.bls.gov/news.release/archives/ecec_06172021.pdf . (BLS, 2021b)
Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). (2021c). Current Population Survey, Table 2. Employed persons who teleworked or worked at home for pay at any time in the last 4 weeks because of the coronavirus pandemic by usual full- or part-time status, occupation, industry, and class of worker; Persons who teleworked because of the coronavirus pandemic. https://www.bls.gov/cps/effects-of-the-coronavirus-covid-19-pandemic.htm#data . (BLS, 2021c)
Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). (2021d). Current Population Survey, Household Data, Annual Averages, Employment status of the civilian noninstitutional population by age, sex, and race, Civilian noninstitutional population. https://www.bls.gov/cps/cpsaat03.htm . (BLS, 2021d)
Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). (2021e). National Compensation Survey: Employee Benefits in the United States, March 2021. https://www.bls.gov/ncs/ebs/benefits/2021/employee-benefits-in-the-united-states-march-2021.pdf . (BLS, 2021e)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, March 3). Interim Considerations: Preparing for the Potential Management of Anaphylaxis after COVID-19 Vaccination. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/covid-19/clinical-considerations/managing-anaphylaxis.html . (CDC, March 3, 2021)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, March 25). Workplace Vaccination Program. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/recommendations/essentialworker/workplace-vaccination-program.html. (CDC, March 25, 2021)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021a, October). Trends in COVID-19 Vaccine Confidence in the US. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#vaccine-confidence. (CDC, October 2021a)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021b, October). COVID-19 Vaccinations in the United States. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#vaccinations_vacc-total-admin-rate-total. (CDC, October 2021b)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021a, October 4). Demographic Characteristics of People Receiving COVID-19 Vaccinations in the United States. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#vaccination-demographic. (CDC, October 4, 2021a)
Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021b, October 4). COVID-19 Vaccines That Require 2 Shots. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/second-shot.html. (CDC, October 4, 2021b)
Cerullo M. (2021, August 31). The New Return Office Date for Google? Try 2022. CBS News. https://www.cbsnews.com/news/return-to-office-big-companies-corporations-covid-pandemic/. (Cerullo, August 31, 2021)
Chesto J. (2021, June 22). Almost 40 percent of remote workers in Mass. won't be back in the office until January, at the earliest. Boston Globe. https://www.bostonglobe.com/2021/06/22/business/back-office-not-so-fast/. (Chesto, June 22, 2021)
Chokshi N and Scheiber N. (2021, October 2). Inside United Airlines' Decision to Mandate Coronavirus Vaccines. The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/2021/10/02/business/united-airlines-coronavirus-vaccine-mandate.html. (Chokshi and Scheiber, October 2, 2021)
Courtney E. (2021, September 27). 30 Companies Switching to Long-Term Remote Work. flexjobs. https://www.flexjobs.com/blog/post/companies-switching-remote-work-long-term/. Accessed September 27, 2021. (Courtney, September 27, 2021).
Dingel J and Neiman B. (2020, July). How many jobs can be done at home? Journal of Public Economics. Volume 189, July 2020, 104235. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0047272720300992. (Dingel and Neiman, July 2020)
Graham R. (2021, September 15). Vaccine Resistors Seek Exemptions. But What Counts as Religious? The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/2021/09/11/us/covid-vaccine-religion-exemption.html. (Graham, September 15, 2021)
Groenewold M et al., (2020, July 10). Increases in Health-Related Workplace Absenteeism Among Workers in Essential Critical Infrastructure Occupations During the COVID-19 Pandemic—United States, March-April 2020. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention MMWR Vol. 69, No. 27. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/69/wr/mm6927a1.htm. (Groenewold et al., July 10, 2020)
Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF). (2021, June 30). KFF COVID-19 Vaccine Monitor: June 2021. https://www.kff.org/coronavirus-covid-19/poll-finding/kff-covid-19-vaccine-monitor-june-2021/. (KFF, June 30, 2021)
Kelly J. (2021, August 12) Study Shows That 44% Of Employees Would Quit If Ordered To Get Vaccinated. https://www.forbes.com/sites/jackkelly/2021/08/12/study-shows-that-44-of-employees-would-quit-if-ordered-to-get-vaccinated/. (Kelly, August 12, 2021)
KEZI News. (2021, September 25). Here's How Many Oregon State Employees Have Requested a COVID Vaccine Exemption. https://www.kezi.com/content/news/Heres-how-many-Oregon-state-employees-have-requested-a-COVID-vaccine-exemption-575395141.html. (KEZI News, September 25, 2021)
Kuhn P and Yu L. (2021, April). How Costly is Turnover? Evidence from Retail. Journal of Labor Economics 39(2), 461-496. https://doi.org/10.1086/710359. (Kuhn and Yu, April, 2021)
Lazer D et al. (2021, August 16). The COVID States Project: A 50-State Survey, Report #62: COVID-19 Vaccine Attitudes Among Healthcare Workers. The COVID States Project Report 62. https://covidstates.org/reports. (Lazer et al., August 16, 2021)
Levi M et al. (2021, September 29). COVID-19 mRNA vaccination, reactogenicity, work-related absences and the impact on operating room staffing: A cross-sectional study. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8479312/. (Levi et al., September 29, 2021).
Mishra D and Hartstein B. (2021, August 23). Littler COVID-19 Vaccine Employer Survey Report—Delta Variant Update. https://www.littler.com/publication-press/press/littler-survey-employers-increasingly-consider-vaccine-mandates-covid-19. (Mishra and Hartstein, August 23, 2021)
National Agricultural Statistics Service (NASS). (2017). Census of Agriculture. https://www.nass.usda.gov/Quick_Stats/CDQT/chapter/1/table/1. (NASS, 2017)
O'Sullivan J. (2021, September 18). Washington state workers are getting exemptions to avoid the COVID-19 vaccine—but will they keep their jobs? Seattle Times. https://www.seattletimes.com/seattle-news/politics/washington-state-workers-are-getting-exemptions-to-avoid-the-covid-19-vaccine-but-will-they-keep-their-jobs/. (O'Sullivan, September 18, 2021).
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). (2021, September 25). State Plans. https://www.osha.gov/stateplans/faqs. (OSHA, September 25, 2021)
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). (2021a, October). Analytical Spreadsheets in Support of the COVID-19 Vaccination and Testing ETS. (OSHA, October 2021a)
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). (2021b, October). COVID-19 Vaccination and Testing ETS: Economic Profile and Cost Chapter Appendices. (OSHA, October 2021b)
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). (2021c, October). Health Impacts of the COVID-19 Vaccination and Testing ETS. (OSHA, October 2021c)
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). (2021d, October). Costs Associated with Reasonable Accommodation: Testing, Face Coverings, and Determinations. (OSHA, October 2021d)
Portnoy J. (2021, October, 3). Several hundred Virginia health-care workers have been suspended or fired over coronavirus vaccine mandates. The Washington Post. https://www.washingtonpost.com/local/covid-vaccine-mandate-hospitals-virginia/2021/10/01/b7976d16-21ff-11ec-8200-5e3fd4c49f5e_story.html. (Portnoy, October 3, 2021)
Putri W et al. (2018, June, 22). Economic burden of seasonal influenza in the United States. Vaccine 36(27), 3960-3966. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0264410X18306777?via%3Dihub. (Putri et al., June 22, 2018)
Umland B. (2021, October 13). Survey Looks at Vaccine Mandates and Employee Turnover. Mercer. https://www.mercer.us/our-thinking/healthcare/survey-looks-at-vaccine-mandates-and-employee-turnover.html. (Umland, October 13, 2021)
U.S. Census Bureau. (2019). Statistics of U.S. Businesses (SUSB). https://www.census.gov/programs-survey/susb.html. (U.S. Census Bureau, 2019)
U.S. Census Bureau. (2021). Household Pulse Survey (HPS), Week 37 Table 6A. https://www.census.gov/programs-surveys/household-pulse-survey/data.html. (U.S. Census Bureau, 2021)
White C. (2021). Measuring Social and Externality Benefits of Influenza Vaccination. Journal of Human Resources Vol 56 Number 3, pp. 749-785. https://muse.jhu.edu/article/798143. (White, 2021)
Willis Towers Watson. (2021, June 23). COVID-19 Vaccination and Reopening the Workplace Survey. https://www.willistowerswatson.com/en-US/Insights/2021/06/covid-19-vaccination-and-reopening-the-workplace-survey. (Willis Towers Watson, June 23, 2021)
V. ETS Economic Feasibility Determination
a. OSHA's Screening Tests for Economic Feasibility
As noted in the introduction to the economic analysis, an OSHA standard is economically feasible when industries can absorb or pass on the costs of compliance without threatening industry's long-term profitability or competitive structure, Cotton Dust , 452 U.S. at 530 n.55, or “threaten[ing] massive dislocation to, or imperil[ing] the existence of, the industry.” United Steelworkers of Am. v. Marshall (Lead I), 647 F.2d 1189, 1272 (D.C. Cir. 1981).
To determine whether a rule is economically feasible, OSHA typically begins by using two screening tests to determine whether the costs of the rule are beneath the threshold level at which the economic feasibility of an affected industry might be threatened. The first screening test is a revenue test. While there is no hard and fast rule on which to base the threshold, OSHA generally considers a standard to be economically feasible for an affected industry when the annualized costs of compliance are less than one percent of annual revenues. The one-percent revenue threshold is intentionally set at a low level so that OSHA can confidently assert that the rule is economically feasible for industries that are below the threshold ( i.e., industries for which the costs of compliance are less than one percent of annual revenues). To put the one-percent threshold into perspective, OSHA calculated the average compounded annual rate of growth or decay in average revenues over the 15-year period from 2002 to 2017 (inflated to 2005 to 2020 dollars) for firms with 100 or more employees in the 479 NAICS (out of 546) industries covered by this ETS for which Census data were available and found that the average annual real rate of change in revenues in absolute terms for the average firm was 2.2 percentage points a year. 51 In other words, revenues are generally observed to change by well more than one percent per year, on average, for firms with 100 or more employees in covered industries, indicating that changes of this magnitude are normal in these industries and that covered firms are typically able to withstand such changes over the course of a year, much less six months. As discussed below, the average percentage change due to this ETS for all covered NAICS is a fraction of this fluctuation in revenues.
51 These results are presented in the Excel ETS Revenue Threshold Test Tables available in the Docket for this ETS. The data used for six-digit NAICS were from the Bureau of the Census, available every five years (2002, 2007, 2012, 2107).
The second screening test that OSHA traditionally uses to consider whether a standard is economically feasible for an affected industry is if the costs of compliance are less than ten percent of annual profits (see, e.g., OSHA's economic analysis of its Silica standard, 81 FR 16286, 16533 (March 25, 2016); upheld in N. Am.'s Bldg. Trades Unions v. OSHA, 878 F.3d 271, 300 (D.C. Cir. 2017)). The ten-percent profit test is also intended to be at a sufficiently low level so as to allow OSHA to identify industries that might require further examination. Specifically, the profit screen is primarily used to alert OSHA to potential impacts on industries where the price elasticity of demand does not allow for ready absorption of new costs in higher prices ( e.g., industries with foreign competition where the American firms would incur costs that their foreign competitors would not because they are not subject to OSHA requirements). In addition, setting the threshold for the profit test low permits OSHA to reasonably conclude that the rule would be economically feasible for industries below the threshold. To put the ten-percent profit threshold test into perspective, evidence used by OSHA in its 2016 OSHA silica rule indicates that, for the combined affected manufacturing industries in general industry and maritime from 2000 through 2012, the average year-to-year fluctuation in profit rates (both up and down) was 138.5 percent (81 FR 16545). 52
52 Profits are subject to the dynamics of the overall economy. Many factors, including a national or global recession, a downturn in a particular industry, foreign competition, or the increased competitiveness of producers of close domestic substitutes are all easily capable of causing a decline in profit rates in an industry of well in excess of ten percent in one year or for several years in succession (See OSHA, March 24, 2016).
When an industry “passes” both the “cost-to-revenue” and “cost-to-profit” screening tests, OSHA is assured that the costs of compliance with the rule are economically feasible for that industry. The vast majority of the industries covered by the ETS fall into this category.
A rule is not necessarily economically infeasible, however, for the industries that do not pass the initial revenue screening test ( i.e., those for which the costs of compliance with the rule are one percent or more of annual revenues), the initial profit screening test ( i.e, those for which the costs of compliance are ten percent or more of annual profits), or both. Instead, OSHA normally views those industries as requiring additional examination as to whether the rule would be economically feasible (see N. Am.'s Bldg. Trades Unions v. OSHA, 878 F.3d at 291). OSHA therefore conducts further analysis of the industries that “fail” one or both of the screening tests in order to evaluate whether the rule would threaten the existence or competitive structure of those industries (see United Steelworkers of Am., AFL-CIO-CLC v. Marshall, 647 F.2d 1189, 1272 (D.C. Cir. 1980)).
Time Parameters for Analysis
OSHA's economic analyses almost always measure the costs of a standard on an annual basis, conducting the screening tests by measuring the cost of the standard against the annual profits and annual revenues for a given industry. One year is typically the minimum period for evaluating the status of a business; for example, most business filings for tax or financial purposes are annual in nature.
Some compliance costs are up-front costs and others are spread over the duration of the ETS; regardless, the costs of the rule overall will not typically be incurred or absorbed by businesses all at once. However, OSHA does not expect that the ETS will require employers to incur initial capital costs for equipment to be used over many years (which would typically be addressed through installments over a year or a longer period to leverage loans or payment options to allow more time to marshal revenue and minimize impacts on reserves).
The compliance costs for this ETS are for a temporary rule for a period of six months (which, again, is the time period that OSHA assumes this ETS will last, solely for economic purposes). While OSHA believes the most appropriate screens would be based on annual profits and revenue, it has followed the more cautious route of basing the screens on 6 months of profits and revenues to avoid any potential uncertainty about whether the ETS is economically feasible for the industries covered by this ETS. Using one year of revenues and profits as the denominators in the cost-to-revenue and cost-to-profit ratios would have resulted in ratios that are half of the estimated ratios presented in this analysis. It is therefore unsurprising that businesses in some number of NAICs have edged above the profit-thresholds using a 6 month screen (as will be discussed later), and OSHA believes that edging above the screening thresholds is less of an indicator of economic peril in this context than in the context of a permanent rulemaking analysis. Nevertheless, OSHA has examined each of the NAICS that did not clear either of these conservative screening tests and has concluded that the ETS is economically feasible for each one.
Data Used for the Screening Tests
The estimated costs of complying with the ETS, which OSHA relied upon to examine feasibility is based on the two tests described above (see OSHA, October 2021a). The revenue numbers used to determine cost-to-revenue ratios were obtained from the 2017 Economic Census for firms with 100 or more employees in covered industries. This is the most current information available from this source, which OSHA considers to be the best available source of revenue data for U.S. businesses. 53 OSHA adjusted these figures to 2020 dollars using the Bureau of Economic Analysis's GDP deflator, which is OSHA's standard source for inflation and deflation analysis.
53 For information regarding the standards and practices used by the Census Bureau to ensure the quality and integrity of its data, see (US Census Bureau, October 8, 2021a; US Census Bureau, October 8, 2021b).
The profit screening test for feasibility ( i.e., the cost-to-profit ratio) was calculated as ETS costs divided by profits. Profits were calculated as profit rates multiplied by revenues. The before-tax profit rates that OSHA used were estimated using corporate balance sheet data from the Internal Revenue Service (IRS), 2013 Corporation Source Book (IRS, 2013). The IRS discontinued the publication of these data after 2013, and therefore the most current years available are 2000-2013. 54 The most recent version of the Source Book represents the best available evidence for these data on profit rates. 55
54 See IRS, 2013.
55 OSHA also investigated Bizminer and RMA as potential sources of profit information and determined that they do not represent adequate and random samples of the affected industries.
For each of the years 2000 through 2013, OSHA calculated profit rates by dividing the “net income” from all firms (both profitable and unprofitable) by total receipts from all firms (both profitable and unprofitable) for each NAICS. 56 OSHA then averaged these rates across the 14-year (2000 through 2013) period. Since some data provided by the IRS were not available at disaggregated levels for all industries and profit rates, data at more highly aggregated levels were used for some industries; that is, where data were not available for each six-digit NAICS code, data for the corresponding four- or five-digit NAICS codes were used. Data were used for all firms in the NAICS (as opposed to just firms with 100 or more employees) since data disaggregated by employment size-class were not available. Profit rates are expressed as a percentage (see OSHA, October 2021a). Profits themselves were used to calculate the cost-to-profit estimates for all firms contained in a particular NAICS code (see OSHA, October 2021a).
56 There is one code reported per tax entity and it may not be representative to the six-digit level. See Corporation Sourcebook on limitations of the industry classification for details. (IRS, 2013).
OSHA has estimated costs over a 6-month timeframe for this ETS. As discussed above, OSHA has therefore used six months of revenue to conduct the cost-to-revenue tests and six months of profit to conduct the cost-to-profit tests.
General Use of Revenues and Profits To Measure Economic Feasibility
As with other OSHA rulemaking efforts, the agency relies on the two screening tests (costs less than one percent of revenue and costs less than ten percent of profit) as an initial indicator of economic feasibility. OSHA has generally found that the cost-to-revenue test is a more reliable indicator of feasibility simply because the revenue data are more accurate than the profit data. There are several reasons for this.
First, OSHA has been using corporate balance sheet data from the IRS as the best available evidence for estimating corporate profits for years. 57 Nevertheless, because firms typically have an incentive to minimize their tax burden, it is reasonable to expect that some of the reported accounting data may have been strategically adjusted to reduce reported profits and their associated tax implications. Business profits are much more likely to reflect such strategic accounting than business revenues; accordingly, revenues are a more accurate measure than profits for evaluating economic feasibility for a multitude of reasons. 58
57 OSHA funded and accepted a final report by Contractor Henry Beale (Beale Report, 2003) that reviewed alternative financial data sources and concluded that the IRS data were the best. Since then OSHA has been relying on IRS data to provide the financial data to support its rulemaking analyses. See, for example, Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) (2016), Final Economic and Regulatory Flexibility Analysis for OSHA's Rule on Occupational Exposure to Respirable Crystalline Silica, Chapter VI, pp. VI-2 to VI-3, Docket No. OSHA-2010-0034-4247 (OSHA, March 24, 2016), which includes a more recent review of data sources for corporate financial profit data and further support for OSHA's choice of IRS data.
58 In fact, all other Department of Labor agencies rely solely on revenues to assess economic impacts, such as Regulatory Flexibility Act certifications, in their rulemakings (see, e.g., Employment and Training Administration, Final Rule on Strengthening Wage Protections for the Temporary and Permanent Employment of Certain Aliens in the United States, https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/FR-2021-01-14/pdf/2021-00218.pdf; Wage and Hour Division, Tip Regulations Under the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA), https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/FR-2020-12-30/pdf/2020-28555.pdf ).
Second, because OSHA is using data from both profitable and unprofitable firms, the average profit rate for a small number of industries is negative (as described above, using 14 years of data that predate the pandemic). This result could have occurred because of the way profits are calculated, which unnaturally skews average profit rates downward by including firms that have large losses (negative profits) or subnormal profits and have already closed or are in the process of closing, irrespective of any action by OSHA. The negative rates could also be the result of macroeconomic fluctuations during the 14-year period used to determine the average, a period in which some of these industries may have experienced unusually adverse financial impacts (see, e.g., the explanation in Chapter VI, pp. VI-20 of the Final Economic and Regulatory Flexibility Analysis for OSHA's Rule on Occupational Exposure to Respirable Crystalline Silica, Docket No. OSHA-2010-0034-4247, which notes the skew from negative impacts during recession years (OSHA, March 24, 2016)). Or they could result from tax-related incentives, as previously noted.
Whatever the reason, the cost-to-profit calculations for NAICS with negative profit rates fail to provide reliable information about the long-term profitability of these industries, independent of the ETS. Companies and industries that consistently lose money do not typically stay in business, and would almost certainly not still be in business in 2021 if that loss continued at the same level for each of the 8 years since the profit data was published in 2012. Revenue streams are a more dependable measure for those firms because those streams tend to be more stable and more indicative of the actual capabilities of sustainable firms than reported negative profit margins. As a result, for the purposes of this analysis, OSHA has relied more heavily on its cost-to-revenue estimates, in lieu of cost-to-profit estimates, as the more reliable indicator for economic feasibility for the industries with negative profit rates.
Third, and similarly, profit rates that are only slightly positive ( i.e., less than one percent) are inconclusive and not useful for the purpose of OSHA's cost-to-profit test. In economics terms, profit entails a reasonable rate of return on investment, and long-term profits of less than one percent a year are not generally reasonable for firms that expect to remain in business. Thus data showing industry-wide profits in this range do not measure the true ability of companies to pay for the ETS costs. As previously stated, revenue streams tend to be more stable and more indicative of the actual capabilities of sustainable firms. Therefore, where possible, OSHA prefers to rely on the cost-to-revenue test to evaluate economic feasibility for industries that have a less than one percent profit rate.
The qualification, and by far the most important reason for the general primacy of revenues versus profits as the appropriate metric for determining economic feasibility, for most OSHA rules, is that the regulated firms are able to pass on the costs of the rule in the form of higher prices. When they cannot, the profit test functions primarily as a screen for a limited purpose: Alerting OSHA to potential impacts where unregulated competitors can prevent firms from passing costs along to customers.
To understand this point, some economic background is needed. The price elasticity of demand refers to the relationship between the price charged for a product or service and the quantity demanded for that product or service: The more elastic the relationship, the larger the decrease in the quantity demanded for a product when the price goes up. When demand is elastic, establishments have less ability to pass compliance costs on to customers in the form of a price increase and must absorb such costs in the form of reduced profits. In contrast, when demand is relatively inelastic, the quantity demanded for the product or service will be less affected by a change in price. In such cases, establishments can recover most of the variable costs of compliance ( i.e., costs that are highly correlated with the amount of output) by raising the prices they charge; under this scenario, if costs are variable rather than fixed, business activity and profit rates are largely unchanged for small changes in costs. Ultimately, where demand is relatively inelastic, any impacts are primarily borne by those customers who purchase the relevant product or service for a slightly higher price. Most of the costs of this ETS are variable costs because they depend primarily on the level of production or the number of employees at an establishment. For example, under the ETS, a firm with 500 employees must determine and record the vaccination status of 500 employees, while a firm with 250 employees need determine and record the vaccination status of only 250 employees. 59
59 While fixed cost can be more limiting in terms of options for businesses, most of the costs of this rule are not fixed. Instead, most of the compliance costs vary with the level of output or employment at a facility.
In general, “[w]hen an industry is subjected to a higher cost, it does not simply swallow it; it raises its price and reduces its output, and in this way shifts a part of the cost to its consumers and a part to its suppliers” ( Am. Dental Ass'n v. Sec'y of Labor, 984 F.2d 823, 829 (7th Cir. 1993)). A reduction in output could happen in a variety of ways: Individual establishments could reduce their levels of service ( e.g., retail firms) or production ( e.g., manufacturing), both of which could take the form of a reduction of worker hours; some marginal establishments could close; or, in the case of an industry with high turnover of establishments, new entry could be delayed until demand equals supply. In many cases, a decrease in overall output for an industry will be a combination of all three kinds of reductions. The primary means of achieving the reduction in output most likely depends on the rate of turnover in the industry and on the form that the costs of the regulation take. Further, the temporary nature of the ETS and its associated costs suggests that firms may have more flexibility to respond than when facing a permanent increase in costs. For example, firms may be able to temporarily increase prices or temporarily defer planned capital expenditures or other maintenance to cover compliance costs.
There are two situations typically mentioned when an industry subject to regulatory costs might be unable to pass those costs on: (1) Foreign competition not subject to the regulation, or (2) domestic competitors in other industries, not subject to the regulation, that produce goods or services that are close substitutes. Otherwise, when all affected domestic industries are covered by a rule and foreign businesses must also comply with the rule or are unable to compete effectively, the ability of a competing industry to offer a substitute product or service at a lower price is greatly diminished.
There is a third situation that is relevant to this ETS—when only some firms in a domestic industry (in this case, only employers with 100 or more employees) are subject to the ETS and its regulatory costs. In principle, competition from smaller employers in a NAICS could prevent the larger employers from passing on their costs in the form of higher prices and instead require them to absorb the costs in the form of lost profits. There are, however, several important caveats:
1. As a practical matter, it is implausible to expect that covered employers (with 100 or more employees) would feel constrained by smaller competitors in their industry so as not to pass on costs for a rule lasting 6 months that imposes costs equal to 0.02 percent of revenues, on average across all NAICS, over that time period (see OSHA, October 2021a). This time period would likely be too short for small firms to expand to take business away from the larger firms or for new firms to form to take advantage of such minor and transitory business opportunities. Furthermore, smaller firms (particularly very small firms—those with fewer than 20 employees) typically can't compete on price with large firms that have cost advantages due to various economies of scale; as a result, smaller firms often serve a specialized niche market rather than compete directly with larger firms. To the extent that this ETS creates new business opportunities for these smaller uncovered firms, they would also be covered by the ETS as soon as they reached 100 employees. 60
60 This cost advantage may be exaggerated or non-existent in many cases (see the discussion directly below in the text in Caveat 2).
2. An important factor to consider in calculating the costs and impacts and economic feasibility of this ETS is the unquantified and unmonetized cost savings and other positive economic impacts accruing to employers that comply with the ETS. These include reduced absenteeism due to COVID-19 illnesses 61 and quarantine. 62 Other positive economic impacts that compliant employers would enjoy from a safer business environment are increased retail trade from customers that feel less at risk and better relations with suppliers and other business partners. These all would contribute to improved business and increased profits.
61 Several occupational groups less able to avoid exposure to SARS-CoV-2 infection exhibited significantly higher rates of absenteeism in March-April 2020 compared to earlier periods (Groenewold et al., July 10, 2020).
62 For a discussion of turnover ( i.e. whether the ETS could affect the likelihood that an employee will remain with an employer, either because the imposition of a vaccine requirement will lead some employees to leave and find employment at an establishment not subject to the ETS, or, alternatively, to stay due to a preference for enhanced COVID-19 safety procedures), please see the cost section (Section III.d.) of this economic analysis.
3. The existence of these cost savings and other positive economic impacts accruing to employers that comply with the ETS suggests that the actual net costs of the ETS will be much lower than the costs reported in the supporting economic analysis for this ETS used to estimate cost impacts and demonstrate economic feasibility. In fact, for some share of covered employers, the net costs of the ETS may well be negative. Indeed, this is being confirmed by revealed preference in the market. Elsewhere in the economic analysis for this ETS (Cost Analysis section 4.2), OSHA has provided evidence to support its estimate that 25 percent of covered employers already voluntarily require that their employees be vaccinated and a much larger percentage are considering a vaccine mandate. This strongly supports the conclusion that these businesses agree that doing so will ultimately save costs.
b. Economic Feasibility Analysis and Determination
This section summarizes OSHA's feasibility findings for industries covered by the ETS. As stated previously, the agency uses two screening tests (costs less than one percent of revenue and costs less than ten percent of profit) as an initial indicator of economic feasibility. In this section, OSHA discusses the industries that fall above the threshold level for either screening test.
The overall effect of compliance with the general section of the ETS on covered industries is very small (see OSHA, October 2021a). The vast majority of the covered NAICS have very low cost-to-revenue and cost-to-profit ratios, with the overall averages being 0.02 percent of revenues and 0.49 percent of profits. To put this into perspective, if the average firm decided to raise prices to cover the costs of the ETS, the price of a $100 product or service, for example, would have to be increased by 2 cents (during the six-month period).
Based on the information presented here, the costs of the ETS are below both the threshold revenue test (1 percent of revenues) and the threshold profit test (10 percent of profits) for the vast majority of NAICS industries. 63 This indicates that the average firm in these industries will be able either to raise prices to cover ETS costs or to absorb the costs of the ETS out of available profits. In either case, OSHA concludes that the ETS is economically feasible for all of these industries.
63 By OSHA's calculation, 524 out of the 546 six-digit NAICS covered by the ETS.
Critically, there are no industries covered by the general section of the ETS that are above OSHA's cost-to-revenue threshold level of one percent and most are a small fraction of this level. Because OSHA is using data from both profitable and unprofitable firms, the average profit rate for a small number of industries is negative. There are 14 NAICS with negative cost-to-profit ratios, resulting from negative average profit rates. These industries with negative profit rates are domestic service industries that are not subject to international competition.
There are eight six-digit NAICS industries, covering all establishments in those industries covered by the general section of the ETS, with cost-to-profit ratios above 10 percent:
1. NAICS 221118—Other Electric Power Generation, 23.97 percent;
2. NAICS 488119—Other Airport Operations, 18.41 percent;
3. NAICS 488410—Motor Vehicle Towing, 15.75 percent;
4. NAICS 488490—Other Support Activities for Road Transportation, 14.32 percent;
5. NAICS 713920—Skiing Facilities, 13.16 percent; and
6. NAICS 713940—Fitness and Recreational Sports Centers, 12.33 percent;
7. NAICS 713120—Amusement Arcades, 11.18 percent; and
8. NAICS 488320—Marine Cargo Handling, 10.03 percent.
The average profit rate reported over the 14 years for which OSHA has profit data for all the NAICS affected by the ETS is 4.2 percent. All of the eight NAICS industries with a cost-to-profit ratio above the 10 percent threshold report an annual profit rate below one percent—75 percent or more below the overall average for all NAICS covered by the ETS. These eight industries all provide domestic services and are not subject to international competition.
The fact that the covered firms in these 22 NAICS industries (the 14 with negative cost-to-profit ratios and the 8 with more sustainable cost-to-profit ratios) exceeded the profit screen suggests that they might in theory have difficulty paying for the costs of the ETS out of profits gained over the six-month duration of the ETS if they had no savings or access to capital, but even if that were true it would be highly unlikely to place the firms in financial jeopardy. OSHA examines these industries more closely below, but before even considering the reasons in NAICs-specific analysis it is important to consider the larger context. For the ETS to threaten the economic solvency of these firms, the following 3 conditions must apply:
1. These firms must not enjoy certain cost savings and positive economic impacts from the ETS that would partially or totally offset their costs. This condition is questionable because of the estimated 25 percent of employers sampled that reported voluntarily imposing a vaccine mandate and the substantial number more contemplating the voluntary adoption of such a mandate. They can be expected to base their decisions, partly or entirely, on anticipated cost savings or positive economic impacts (which would reduce or eliminate their risk of insolvency due to the ETS).
2. These firms (all with 100 or more employees) must not be able to raise prices to cover ETS costs because of the threat that smaller firms in their NAICS industry, not covered by the ETS, could underprice them and take away their business. This condition is unlikely or limited because of the economies of scale the larger firms enjoy and the fact that the smaller firms out of necessity tend to serve a market niche not in direct competition with the larger firms. Also, there is a severe limit to the extent that firms with fewer than 100 employees can take away significant portions of business from the larger firms without becoming subject to the requirements of the rule themselves. If the larger firms do not feel threatened by being underpriced by smaller firms in these NAICS industries, then they could raise prices an average of less than 0.05 percent 64 to cover the cost of the ETS—a small fraction of the 1.0 percent of revenues threshold (beneath which OSHA has determined that economic feasibility is not a concern).
64 If not underpriced by smaller firms, covered firms in the 8 NAICS industries reporting ETS costs above 10 percent of profits could cover these costs by raising prices an average of 0.08 percent (highest, 0.11 percent); covered firms in the 14 NAICS industries reporting negative profits could cover ETS costs with a price increase of 0.01 percent (highest, 0.02 percent).
3. These firms must not generate sufficient profits or have adequate borrowing capacity during the six months the ETS is in force to cover the costs of the ETS. There are several reasons to doubt that this condition broadly applies. First, the estimates of business profits come from corporate balance sheet data that firms report to the IRS. But, as previously noted, it is generally the case that firms have an incentive to minimize their tax burden, and it is reasonable to expect that some of the reported accounting data may have been strategically adjusted to reduce reported profits and their associated tax implications. Another point concerning the IRS data is that they include the negative profits of firms that are going out of business or have since gone out of business. To the extent that these points are true, many or most of the covered firms in these NAICS industries (still in business) actually would generate sufficient profit to cover the cost of the ETS. A related point is that for this condition to apply, the firms must not be able to borrow the money to pay for the costs of the ETS. Recall, however, that these are all large firms with 100 employees. It is reasonable to expect that many or most firms of this size in the 22 NAICS industries at issue either have available funds or could obtain a short-term loan to cover costs equal to the 0.01 to 0.11 percent of revenues that these firms would incur over the six-month period that OSHA assumes the ETS will remain in effect. Firms of this size normally have banking relationships and some unencumbered assets. They also have access to national and international capital markets. If these firms can borrow funds to pay for the ETS, then the profit restriction doesn't matter.
Finally, OSHA anticipates concern that limiting the scope of the ETS to employers with 100 or more employees will somehow put these larger firms in economic jeopardy from the smaller firms to which the ETS does not currently apply. This is highly improbable for several reasons discussed earlier, including the fact that these are large employers with advantages of economies of scale and access to capital and the fact that this is a temporary standard that would result, at most, in marginal impacts over 6 months (on average, equal to costs of 0.02 percent of revenues, which, again, translates to a cost increase of a penny on a fifty dollar item).
But even that misses the main point: Economic feasibility refers to the industry, not to the firm. OSHA must construct a reasonable estimate of compliance costs and demonstrate a reasonable likelihood that these costs will not threaten the existence or competitive structure of an industry, even if it does portend disaster for some marginal firms ( Lead I, 647 F.2d at 1272). In the (again) highly unlikely event that individual firms exit an industry and are replaced by other firms in the industry, then the ETS would preserve the economic feasibility of the covered industries. If an employer covered by this standard actually had to increase its prices slightly to account for the cost of this standard, there are two potential groups of smaller businesses that could seek to supplant the covered firms. The first group of businesses are much smaller than the covered firms. Those businesses, however, will typically have higher costs and prices to begin with due to their scale disadvantages to the larger firms. The larger firm's small price increases attributable to this ETS would not be likely to create an actionable competitive advantage for this group of smaller businesses. The second group of businesses are those closer in size to the 100-employee cutoff. If the marginal price increases did actually cause some of the larger firms to fail and the slightly smaller firms to take their place, the industry itself would not suffer a massive dislocation or be imperiled. And, of course, if all of the firms in an industry are large employers with 100 or more employees, no competitive disadvantage from within the industry would exist (even hypothetically), and there would be no question that they could cover the cost of ETS by raising prices to customers accordingly.
Although the preceding discussion demonstrates that the ETS is economically feasible, OSHA has provided an additional examination of each of the NAICS that have crossed the profit screen (again noting that none of these failed the revenue screen): The eight NAICS industries with positive profit ratios but profit rates below 1 percent.
1. NAICS 221118—Other Electric Power Generation, 23.97 Percent
This U.S. industry comprises establishments primarily engaged in operating electric power generation facilities (except hydroelectric, fossil fuel, nuclear, solar, wind, geothermal, biomass). These facilities convert other forms of energy, such as tidal power, into electric energy. The electric energy produced in these establishments is provided to electric power transmission systems or to electric power distribution systems.
Using tides to generate power is not yet economically viable, according to one source, because “[t]otal availability of tidal power is restricted by its relatively high cost and limited number of sites having high flow velocities and tidal ranges,” although “with [ ] recent advancements in tidal technologies, the total availability of tidal power in terms of turbine technology as well as design may be higher than before, and the economic costs may be reduced significantly to competitive levels.” In support, in the same article, “recent reports state that the UK, which has the largest tidal and wave resource in Europe, is capable of harnessing up to 153GW of tidal power capacity with the help of three types of technologies and thus meeting 20% of current UK electricity demand and reducing carbon emissions. Hence it is evident that wave and tidal energy could contribute more to the increasing electricity demands across the globe.” 65
65 See Walker, January 22, 2013.
At the time OSHA obtained the most recent NAICS data, there were 7 affected entities in this NAICS industry. The entities in this NAICS industry include firms like Berkshire Hathaway Energy Company, (with annual sales of $19.8 billion, whose “portfolio consists of locally managed business that share a vision for a secure and sustainable energy future”); Dominion Energy (with annual sales of $13.4 billion); and other leading firms in this industry including some of the largest power generation companies in the US (See NAICS Association, 2018a; NAICS Association 2018d; and NAICS Association 2018e).
As this NAICS industry is not yet viable, (in the United States, at least), it is to be expected that revenues and profits would be low. In fact, OSHA believes the best way to view this industry is as a series of incredibly well-funded start-up companies during the investment phase of the business, where short-term losses are expected and offset with the anticipation of enormous revenue growth potential (in an acknowledged very limited energy market.) Given these factors, OSHA's typical revenue and profit screen are a poor predictor of future viability with respect to this NAICS industry (although, as pointed out, this NAICS industry, like all other NAICS industries, falls well below the revenue screen threshold). The estimated cost of this ETS per firm is $866 in this NAICS industry, which equals about 11 cents per hundred dollars of revenue over a limited six-month duration. OSHA concludes that this industry will be able to withstand this small cost in order to keep its workers protected during the pandemic.
2. NAICS 488119—Other Airport Operations, 18.41 Percent 66
66 This U.S. industry comprises establishments primarily engaged in (1) operating international, national, or regional airports, or public flying fields or (2) supporting airport operations, such as rental of hangar space, and providing baggage handling and/or cargo handling services.
The services this industry offers are integrated into a particular geographic location and entail specific tasks, such as parking and baggage handling services, that must be done to ensure the proper functioning of airports, thus negating the potential for substitution during the 6 month period that OSHA is assuming the ETS will be in effect for economic purposes. In addition, because these are services that need to be done in particular domestic locations ( i.e., airports), there is no risk of international competition.
3. NAICS 488410—Motor Vehicle Towing, 15.75 Percent 67
67 This industry comprises establishments primarily engaged in towing light or heavy motor vehicles, both local and long-distance. These establishments may provide incidental services, such as storage and emergency road repair services.
The actual cost impacts on this industry are likely significantly overstated to the extent that most employees performing towing services ride alone in their trucks and their services do not typically require exposure to others. In the event that individual large towing firms are concerned about economic impacts, it would not be difficult to structure their employee interactions with the company and customers to take advantage of the scope restrictions. Moreover, the primary services this industry offers involve the use of specialized vehicles designed uniquely for towing, thus lowering the risk of substitution. In addition, because these services are geographically based, there is no risk of international competition.
4. NAICS 488490—Other Support Activities for Road Transportation, 14.32 Percent 68
68 This industry comprises establishments primarily engaged in providing services (except motor vehicle towing) to road network users.
This industry offers services that must be done to ensure proper operation of roadways (for example, bridge, tunnel, and highway operations, pilot car services ( i.e., wide load warning services), driving services ( e.g., automobile, truck delivery), and truck or weighing station operations), thus negating the potential for substitution. In addition, because these services need to be done in particular domestic locations ( i.e., roadways), there is no risk of international competition.
5. NAICS 713920—Skiing Facilities, 13.16 Percent 69
69 This industry comprises establishments engaged in (1) operating downhill, cross country, or related skiing areas and/or (2) operating equipment, such as ski lifts and tows. These establishments often provide food and beverage services, equipment rental services, and ski instruction services. Four season resorts without accommodations are included in this industry.
This industry caters to a wealthy clientele who ensure an inelastic demand easily capable of absorbing any fractional increases attributable to this ETS. 70 In addition, skiing is done outdoors, which will incentivize clientele to continue engaging in this particular activity in lieu of indoor substitutions, during the pandemic. Finally, there is little to no risk of international competition from foreign ski resorts because the added and substantial costs of international travel outweigh the costs associated with marginally higher prices resulting from the ETS.
70 See Brown, January 19, 2017, “[o]f the 9.4 million skiers in the U.S., more than half earn a salary higher than $100,000. For some context, only 20 percent of American households have a combined income of $100K. . . .”)
6. NAICS 713940—Fitness and Recreational Sports Centers, 12.33 Percent 71
71 This industry comprises establishments primarily engaged in operating fitness and recreational sports facilities featuring exercise and other active physical fitness conditioning or recreational sports activities, such as swimming, skating, or racquet sports.
As these settings are generally located close to where clients live or work, there is no risk of international competition. Some of the largest employers in this industry have already responded to customer feedback by not only requiring employees to be vaccinated, but also members. 72 This suggests both that the costs estimates attributed to the ETS are overstated for these employers because higher levels of compliance may have already occurred than projected in OSHA's analysis, and that the ETS requirements reflect more of an industry trend than a threat to the existence of the industry.
72 See Jackson, August 2, 2021 “Equinox also noted in the press release that `an overwhelming majority of members' have expressed support for a vaccination requirement for entry to Equinox clubs.”
7. NAICS 713120—Amusement Arcades, 11.18 Percent 73
73 This industry comprises establishments primarily engaged in operating amusement (except gambling, billiard, or pool) arcades and parlors.
This industry caters to a select clientele who have chosen to engage in leisure activities in the unique settings offered by the industry, thus negating the likelihood for substitution. In addition, because these settings are localized, there is no risk of international competition.
8. NAICS 488320—Marine Cargo Handling, 10.03 Percent 74
74 This industry comprises establishments primarily engaged in providing stevedoring and other marine cargo handling services (except warehousing).
The services this industry offers are integrated into a particular location and entail specific tasks, such as loading and unloading services at ports and harbors, longshoremen services, marine cargo handling services, ship hold cleaning services, and stevedoring services, that must be done to ensure the proper movement of cargo off of and onto ships, thus negating the potential for substitution. In addition, because these are services that need to be done in particular domestic locations ( e.g., docks), there is no risk of international competition.
As with towing, the actual cost impacts on this industry are likely significantly overstated to the extent that some of the employees may be able to perform their work exclusively outdoors.
The Fourteen NAICS Industries With Negative Profit Ratios
1. Air Transportation 75
75 NAICS 481111 (Scheduled Passenger Air Transportation) provides air transportation of passengers or passengers and freight over regular routes and on regular schedules, including commuter and helicopter carriers (except scenic and sightseeing). NAICS 481112 (Scheduled Freight Air Transportation) provides air transportation of cargo without transporting passengers over regular routes and on regular schedules, including scheduled air transportation of mail on a contract basis. NAICS 481211 (Nonscheduled Chartered Passenger Air Transportation) provides air transportation of passengers or passengers and cargo with no regular routes and regular schedules. NAICS 481212 (Nonscheduled Chartered Freight Air Transportation) provides air transportation of cargo without transporting passengers with no regular routes and regular schedules. NAICS 481219 (Other Nonscheduled Air Transportation) provides air transportation with no regular routes and regular schedules (except nonscheduled chartered passenger and/or cargo air transportation). These establishments provide a variety of specialty air transportation or flying services based on individual customer needs using general purpose aircraft.
NAICS 481111 (Scheduled Passenger Air Transportation), NAICS 481112 (Scheduled Freight Air Transportation), NAICS 481211 (Nonscheduled Chartered Passenger Air Transportation), NAICS 481212 (Nonscheduled Chartered Freight Air Transportation), NAICS 481219 (Other Nonscheduled Air Transportation).
This group of NAICS industries is comprised of U.S. industries that primarily engage in providing air transportation. There is little to no risk of substitution for this group of NAICS industries. Air transportation provides unique and important benefits that cannot be substituted via other forms of transportation (e.g., rail, freight, bus). (See ATAG, September 2005). To this end, air transportation is often the speediest means of transporting passengers and cargo, giving it a unique purpose that cannot be met by other forms of transport. It should be noted that the five NAICS in this group of industries are the only NAICS in NAICS 4811 (Scheduled Air Transportation) and 4812 (Nonscheduled Air Transportation). The other industries in NAICS 48 (Transportation) do not provide air transportation (See NAICS Association, 2018b). This further reduces the risk of substitution, as all five NAICS at issue have a negative profit ratio and therefore face similar challenges that appear to be endemic to air transportation. Firms in this industry that have been able to weather the pandemic this long are typically highly capitalized or have access to loans, so it is highly likely that they could also weather the temporary marginal costs of OSHA's ETS.
There is also no risk of international competition with respect to this group of NAICS industries because any workers, whether they work for an international company or not, who are in the US, are subject to US laws, including the ETS, and foreign air carriers will need to follow the ETS for those workers. In addition, OSHA suspects that any smaller foreign air carriers will not have an incentive to expand their routes significantly or change their routes to domestic US routes to take advantage of the 100-employee cutoff in the ETS in the 6-months the ETS is assumed to be in effect.
2. Telecommunications 76
76 NAICS 517311 (Wired Telecommunications Carriers) comprises establishments primarily engaged in operating and/or providing access to transmission facilities and infrastructure that they own and/or lease for the transmission of voice, data, text, sound, and video using wired telecommunications networks. Establishments in this industry use the wired telecommunications network facilities that they operate to provide a variety of services, such as wired telephony services, including VoIP services; wired (cable) audio and video programming distribution; wired broadband internet services; and, by exception, establishments providing satellite television distribution services using facilities and infrastructure that they operate are included in this industry. NAICS 517312 (Wireless Telecommunications Carriers (except Satellite)) comprises establishments primarily engaged in operating and maintaining switching and transmission facilities to provide communications via the airwaves. Establishments in this industry have spectrum licenses and provide services using that spectrum, such as cellular phone services, paging services, wireless internet access, and wireless video services. NAICS 517410 (Satellite Telecommunications) comprises establishments primarily engaged in providing telecommunications services to other establishments in the telecommunications and broadcasting industries by forwarding and receiving communications signals via a system of satellites or reselling satellite telecommunications. NAICS 517911 (Telecommunications Resellers) comprises establishments engaged in purchasing access and network capacity from owners and operators of telecommunications networks and reselling wired and wireless telecommunications services (except satellite) to businesses and households. Establishments in this industry resell telecommunications; they do not operate transmission facilities and infrastructure. NAICS 517919 (All Other Telecommunications) comprises establishments primarily engaged in providing specialized telecommunications services, such as satellite tracking, communications telemetry, and radar station operation, and also includes establishments primarily engaged in providing satellite terminal stations and associated facilities connected with one or more terrestrial systems and capable of transmitting telecommunications to, and receiving telecommunications from, satellite systems, as well as establishments providing internet services or Voice over internet protocol (VoIP) services via client-supplied telecommunications connections.
NAICS 517311 (Wired Telecommunications Carriers), NAICS 517312 (Wireless Telecommunications Carriers (except Satellite), NAICS 517410 (Satellite Telecommunications), NAICS 517911 (Telecommunications Resellers), NAICS 517919 (All Other Telecommunications).
This group of NAICS industries is entirely comprised of U.S. industries, except for NAICS 517410 (Satellite Telecommunications). All of these industries provide specialized unique services in the telecommunications industry that require specialized unique knowledge and are thus resistant to substitution. While it is perhaps possible that different forms of telecommunications might be substituted for one another (e.g., the substitution of wired telecommunications carriers for wireless telecommunications carriers), the reality is that these different forms exist separately and feed different markets and customer needs that are independent of the ETS. Moreover, the five NAICS in this group of industries are the only NAICS in NAICS 5173 (Wired and Wireless Telecommunications Carriers), NAICS 5174 (Satellite Telecommunications), and NAICS 5179 (Other Telecommunications). The other industries in NAICS 51 (Information) are not engaged in telecommunications (NAICS Association, 2018c). This further reduces the risk of one industry substituting for the others, as all five NAICS at issue have a negative profit ratio and therefore face similar challenges that appear to be endemic to telecommunications.
Moreover, three of the five NAICS industries in this group (NAICS 517311, 517312, 517410) operate or control the infrastructure needed for engaging in the particular type of telecommunications in which those industries engage. This not only fully negates the risk of substitution, but also negates the risk of international competition for these industries.
The other two industries in the group apparently do not operate or control the infrastructure needed for telecommunications. However, the telecommunications industry faces strict state and federal licensing requirements, which severely limit the risk of competition both internationally and from smaller firms seeking to take advantage of the ETS's 100-employee cutoff. (See FCC, 2014; FCC, October 12, 2021a; FCC, October 12, 2021b; Caltrans, October 12, 2021; and UTC, October 12, 2021).
3. Car and Equipment Rental 77
77 NAICS 532111 (Passenger Car Rental) comprises establishments primarily engaged in renting passenger cars without drivers, generally for short periods of time. NAICS 532112 (Passenger Car Leasing) comprises establishments primarily engaged in leasing passenger cars without drivers, generally for long periods of time. NAICS 532120 (Truck, Utility Trailer, and RV (Recreational Vehicle) Rental and Leasing comprises establishments primarily engaged in renting or leasing, without drivers, one or more of the following: Trucks, truck tractors, buses, semi-trailers, utility trailers, or RVs (recreational vehicles). NAICS 532310 (General Rental Centers) comprises establishments primarily engaged in renting a range of consumer, commercial, and industrial equipment. Establishments in this industry typically operate from conveniently located facilities where they maintain inventories of goods and equipment that they rent for short periods of time. The type of equipment that establishments in this industry provide often includes, but is not limited to: Audio visual equipment, contractors' and builders' tools and equipment, home repair tools, lawn and garden equipment, moving equipment and supplies, and party and banquet equipment and supplies.
NAICS 532111 (Passenger Car Rental), NAICS 532112 (Passenger Car Leasing), NAICS 532120 (Truck, Utility Trailer), and RV (Recreational Vehicle) Rental and Leasing) NAICS 532310 (General Rental Centers).
This group of industries rent motor vehicles (NAICS 532111, 532112, 532120) or equipment (NAICS 532310), for example, audio visual equipment, contractors' and builders' tools and equipment, home repair tools, lawn and garden equipment, moving equipment and supplies, and party and banquet equipment and supplies, to individuals and businesses, for personal and professional use. There is no risk of substitution with respect to these industries, as these industries rent specific items to those who want to use them. There is also no risk of foreign competition with respect to these industries, as consumers and businesses rent and pick up vehicles, as well as the type of equipment offered for rent by NAICS 532310, from specific locations, including car rental and other rental centers.
These industries have not been hard hit by the pandemic, as many consumers have turned from group travel to individual transportation. For example, RV rentals and leasing has soared during the pandemic, which is not reflected in the pre-pandemic profit and revenue data available for this analysis. 78
78 See Park, January 23, 2021.
References
Air Transport Action Group (ATAG). (2005, September). The economic & social benefits of air transport. https://www.icao.int/meetings/wrdss2011/documents/jointworkshop2005/atag_socialbenefitsairtransport.pdf. (ATAG, September 2005)
Beale HBR. (2003). Financial Data Sources. Microeconomic Applications Inc. (Beale Report, 2003)
Brown J. (2017, January 19). Bring More Diversity to Skiing. https://www.powder.com/stories/opinion/extend-the-family/. (Brown, January 19, 2017)
Caltrans. (2021, October 12). Wireless Licensing Program, California Department of Transportation. https://dot.ca.gov/programs/right-of-way/wireless-licensing-program. (Caltrans, October 12, 2021)
Federal Communications Commission (FCC). (2021, October 12a) Licensing. https://www.fcc.gov/licensing-databases/licensing. (FCC, October 12, 2021a)
Federal Communications Commission (FCC). (2021, October 12b) Satellite. https://www.fcc.gov/general/satellite. (FCC, October 12, 2021b)
Groenewold M et al., (2020, July 10). Increases in Health-Related Workplace Absenteeism Among Workers in Essential Critical Infrastructure Occupations During the COVID-19 Pandemic—United States, March-April 2020. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention MMWR Vol. 69, No. 27. (Groenewold et al., July 10, 2020)
Internal Revenue Service (IRS). (2013). 2013 Corporation Source Book. https://www.irs.gov/statistics/soi-tax-stats-corporation-source-book-us-total-and-sectors-listing. (IRS, 2013)
Jackson S. (2021, August 2). Gyms like Equinox and SoulCycle will soon require members to show proof of vaccination to use their clubs and studios. https://www.businessinsider.com/equinox-soulcycle-will-require-covid-19-vaccines-for-members-staff-2021-8. (Jackson, August 2, 2021)
NAICS Association. (2018a). NAICS Codes Description, 2018: 221118—Other Electric Power Generation. https://www.naics.com/naics-code-description/?code=221118. Last accessed October 12, 2021. (NAICS Association, 2018a)
NAICS Association. (2018b). Six Digit NAICS Codes and Titles, 2018: Codes 48-49. https://www.naics.com/six-digit-naics/?code=48-49. Last accessed October 12, 2021. (NAICS Association, 2018b)
NAICS Association. (2018c). Six Digit NAICS Codes and Titles, 2018: Code 51. https://www.naics.com/six-digit-naics/?code=51. Last accessed October 12, 2021. (NAICS Association, 2018c)
NAICS Association. (2018d). NAICS Profile Page, 2018: Berkshire Hathaway Energy Co. https://www.naics.com/company-profile-page/?co=4973. Last accessed October 12, 2021. (NAICS Association, 2018d)
NAICS Association. (2018e). NAICS Profile Page, 2018: Dominion Energy Inc. https://www.naics.com/company-profile-page/?co=11715. Last accessed October 12, 2021. (NAICS Association, 2018e)
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). (2016, March 24). Final Economic and Regulatory Flexibility Analysis for OSHA's Rule on Occupational Exposure to Respirable Crystalline Silica, Chapter VI, pp. VI-20. Docket No. OSHA-2010-0034-4247. (OSHA, March 24, 2016)
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). (2021a, October). Analytical Spreadsheets in Support of the COVID-19 Vaccination and Testing ETS. (OSHA, October 2021a)
Park S. (2021, January 23). RV sales soar during coronavirus pandemic. https://www.foxbusiness.com/lifestyle/rv-sales-soar-during-pandemic-travel-road-trip. (Park, January 23, 2021)
U.S. Census Bureau. (2021, October 8a). Scientific Integrity. https://www.census.gov/about/policies/quality/ scientific_integrity.html. (US Census Bureau, October 8, 2021a)
U.S. Census Bureau. (2021, October 8b). Statement of Commitment to Scientific Integrity by Principal Statistical Agencies. https://www.census.gov/content/dam/Census/about/about-the-bureau/policies_and_notices/scientificintegrity/Scientific_Integrity_Statement_of_the_Principal_Statistical_Agencies.pdf. (US Census Bureau, October 8, 2021b)
Walker C. (2013, January 22). Is Tidal Power a Viable Source of Energy? https://www.azocleantech.com/article.aspx?ArticleID=350. (Walker, January 22, 2013)
Washington Utilities and Transportation Commission (UTC). (2021, October 12). Eligible Telecommunications Carriers. https://www.utc.wa.gov/regulated-industries/utilities/telecommunications/federal-universal-service-funds/eligible-telecommunications-carriers. (UTC, October 12, 2021)
V. Additional Requirements
A. Regulatory Flexibility Act
Whenever an agency is required by the Administrative Procedure Act, 5 U.S.C. 553, or another law, to publish a general notice of proposed rulemaking, the Regulatory Flexibility Act (RFA), 5 U.S.C. 601 et seq., requires the agency to prepare an initial regulatory flexibility analysis (IRFA). 5 U.S.C. 601(2), 603(a). Since this ETS “shall serve as a proposed rule” for a final standard under section 6(c)(3) of the OSH Act, it is treated as a general notice of proposed rulemaking under the RFA. An agency may waive or defer the IRFA in the event a rule is promulgated in response to an emergency that makes compliance with the requirements of section 603 impracticable. 5 U.S.C. 608(a). The agency hereby certifies that compliance with the IRFA requirement is impracticable under the circumstances. OSHA prepared this ETS on an expedited basis in response to a national emergency affecting the lives and health of the nation's workers; the IRFA is inherently a relatively lengthy process that would be impracticable to undertake for a standard of such broad applicability in the limited time available. Because OSHA is not preparing an IRFA for the ETS, the agency is also not required to convene a small entity panel under section 609(b).
B. Unfunded Mandates Reform Act (UMRA), 2 U.S.C. 1501 et seq.
Section 202 of the Unfunded Mandates Reform Act of 1995 (UMRA), 2 U.S.C. 1532, requires agencies to assess the anticipated costs and benefits of a rule before issuing “any general notice of proposed rulemaking” that includes a Federal mandate that may result in expenditures in any one year by state, local, or Tribal governments, or by the private sector, of at least $100 million, adjusted annually for inflation. The assessment requirement also applies to “any final rule for which a general notice of proposed rulemaking was published.” Although no general notice of proposed rulemaking was published, the agency has analyzed the ETS's economic feasibility and health impacts in Section IV.B. of this preamble ( Economic Analysis ) and Health Impacts Appendix (OSHA, October 2021c).
C. Executive Order 13175
Section 5 of E.O. 13175, on Consultation and Coordination with Indian Tribal Governments, requires agencies to consult with tribal officials early in the process of developing regulations that: (1) Have tribal implications, that impose substantial direct compliance costs on Indian governments, and that are not required by statute; or (2) have tribal implications and preempt tribal law. 65 FR 67249, 67250 (Nov. 6, 2000). E.O. 13175 requires that such consultation occur to the extent practicable. Given the expedited nature of issuing the ETS, it was not practicable for OSHA to consult and incorporate non-federal input prior to promulgation of the standard. OSHA commits to meaningful consultation with tribal representatives after publication of the ETS and during the comment period before finalizing any permanent standard. Such consultation will be consistent with the Administrative Procedure Act.
D. National Environmental Policy Act
OSHA has reviewed this ETS according to the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) of 1969, 42 U.S.C. 4321 et seq., the regulations of the Council on Environmental Quality, 40 CFR chapter V, subchapter A, and the Department of Labor's NEPA procedures, 29 CFR part 11. As a result of this review, the agency has determined that the rule will have no significant impact on air, water, or soil quality; plant or animal life; the use of land; or other aspects of the external environment. Although the ETS contains testing requirements, and test kits and supplies can generate some additional materials that will enter the waste stream, the impact of this ETS will be minimal. As discussed in more detail in Technological Feasibility (Section IV.A. of this preamble), there is already a surplus of available tests, and projected production of COVID-19 tests will be more than sufficient to meet demands for testing created as a result of the rule. Therefore, tests used for purposes of or for compliance with this ETS are not being produced as a result of this standard, and the standard will not generate significant new streams of waste beyond what would be generated in the absence of the standard.
E. Congressional Review Act
This ETS is considered a major rule under the Congressional Review Act (CRA), 5 U.S.C. 801 et seq. Section 801(a)(3) of the CRA normally requires a 60-day delay in the effective date of a major rule. 5 U.S.C. 801(a)(3), 804(2). However, section 808(2) of the CRA allows the issuing agency to make a rule effective sooner than otherwise provided by the CRA if the agency makes a good cause finding that notice and public procedure are impracticable, unnecessary, or contrary to the public interest. 5 U.S.C. 808(2). OSHA finds that there is good cause to make this rule effective upon publication because notice and public procedure with respect to this ETS are both impracticable and contrary to the public interest, given the expedited timeline on which this standard was developed and the grave danger threatening workers' lives and health (see Grave Danger and Need for the ETS , both in Section III. of this preamble). Congress authorized OSHA to take swift action in promulgating an ETS to address this type of grave danger, and provided explicitly that an ETS is effective upon publication, 29 U.S.C. 655(c)(1); delaying the effective date of such an expedited process would thwart that purpose. It is specifically because of the emergency nature of this rulemaking that the OSH Act allows for OSHA to proceed without the extensive public input the agency normally solicits in issuing occupational safety and health standards. 29 U.S.C. 655(c)(1). For rules to which section 808(2) applies, the agency may set the effective date. In this case, consistent with the OSH Act requirement cited above, the ETS takes immediate effect upon publication in the Federal Register .
F. Administrative Procedure Act
The Administrative Procedure Act (APA) normally requires notice and comment, and a 30-day delay of the effective date of a final rule, for recordkeeping and reporting regulations promulgated under section 8(c) of the OSH Act. 29 U.S.C. 657(c); 5 U.S.C. 553(b), (d). This ETS contains recordkeeping and reporting requirements tailored to address COVID-19 illness. To the extent that these requirements are not already exempt from the APA's requirements for notice and comment under section 6(c) of the Act (29 U.S.C. 655(c)), OSHA invokes the “good cause” exemption to the APA's notice requirement because the agency finds that notice and public procedure are impracticable and contrary to the public interest under 5 U.S.C. 553(b)(B). As explained in more detail in Grave Danger and Need for the ETS (both in Section III. of this preamble), this finding is based on the critical importance of implementing the requirements in this ETS, including the recordkeeping and reporting provisions, as soon as possible to address the grave danger that COVID-19 presents to workers.
As noted above, the ETS is required by the OSH Act to take immediate effect upon publication. 29 U.S.C. 655(c)(1). For that reason, and the underlying public health emergency that prompted this ETS as discussed above, OSHA finds good cause to waive the normal 30-day delay in the effective date of a final rule from the date of its publication in the Federal Register . See 5 U.S.C. 553(d)(3). OSHA notes, however, that OSHA does not require compliance with any provision of the ETS within the first 30 days after it becomes effective.
G. Consensus Standards
OSHA must consider adopting an existing national consensus standard that differs substantially from OSHA's standard if the consensus standard would better effectuate the purposes of the Act. See section 12(d)(1) of the National Technology Transfer and Advancement Act of 1995 (15 U.S.C.A. 272 Note); see also 29 U.S.C. 655(b)(8).
OSHA considered incorporation of ASTM F3502-21 in this ETS, as required. However, the agency has insufficient evidence to make a general finding of feasibility at this time. The agency notes that face coverings that meet ASTM F3502-21 criteria also meet the definition of “face coverings” in this ETS (see the discussion of this issue in Summary and Explanation , Section VI. of this preamble). The agency has asked questions about this topic to gather additional information.
H. Executive Order 13045
Executive Order 13045, on Protection of Children from Environmental Health Risks and Safety Risks, requires that Federal agencies submitting covered regulatory actions to OIRA for review pursuant to Executive Order 12866 must provide OIRA with (1) an evaluation of the environmental health or safety effects that the planned regulation may have on children, and (2) an explanation of why the planned regulation is preferable to other potentially effective and reasonably feasible alternatives considered by the agency (62 FR 19885 (April 23, 1997)). Executive Order 13045 defines “covered regulatory actions” as rules that may (1) be economically significant under Executive Order 12866, and (2) concern an environmental health risk or safety risk that an agency has reason to believe may disproportionately affect children. Because OSHA has no reason to believe that the risk from COVID-19 disproportionately affects children, the ETS is not a covered regulatory action and OSHA is not required to provide OIRA with further analysis under section 5 of the executive order. However, to the extent children are exposed to COVID-19 either as employees or at home as a result of family members' workplace exposures to COVID-19, the ETS should provide some protection for children.
I. Federalism
The agency reviewed this ETS according to Executive Order 13132, on Federalism, which requires that Federal agencies, to the extent possible, refrain from limiting State policy options, consult with States before taking actions that would restrict States' policy options, and take such actions only when clear constitutional authority exists and the problem is of national scope. 64 FR 43255 (August 10, 1999). The Executive Order generally allows Federal agencies to preempt State law only as provided by Congress or where State law conflicts with Federal law. In such cases, Federal agencies must limit preemption of State law to the extent possible.
The Occupational Safety and Health Act is an exercise of Congress's Commerce Clause authority, and under Section 18 of the Act, 29 U.S.C. 667, Congress expressly provided that States may adopt, with Federal approval, a plan for the development and enforcement of occupational safety and health standards. OSHA refers to States that obtain Federal approval for such plans as “State Plans.” Occupational safety and health standards developed by State Plans must be at least as effective in providing safe and healthful employment and places of employment as the Federal standards. As discussed below, State Plans must submit to Federal OSHA for approval, standards that differ from Federal standards addressing the same issues, in order for such standards to become part of the OSHA-approved State Plan. Subject to these requirements, State Plans are free to develop and enforce their own occupational safety and health standards.
This ETS complies with E.O. 13132. The problems addressed by this ETS for COVID-19 are national in scope. As explained in Grave Danger (Section III.A. of this preamble), employees face a grave danger from exposure to COVID-19 in the workplace. Employees across the country face the danger of exposure to COVID-19 at work, and as explained in Need for the ETS (Section III.B. of this preamble), a national standard is needed to protect workers from the grave danger of COVID-19 by strongly encouraging vaccination and limiting the presence of COVID-19 positive workers in the workplace through testing and to ensure that a clear and consistent baseline approach is taken across the country to protect them. The SARS-CoV-2 virus is highly communicable and infects workers without regard to state borders, making a national approach necessary. Accordingly, the ETS establishes minimum requirements for employers in every State to protect employees from the risks of exposure to COVID-19.
In States without OSHA-approved State Plans, Congress provides for OSHA standards to preempt State occupational safety and health standards for issues addressed by the Federal standards. In these States, this ETS limits State policy options in the same manner as every standard promulgated by the agency. Furthermore, as discussed in the Summary and Explanation for Purpose , nothing in the ETS is intended to limit generally applicable public health measures instituted by state or local governments that go beyond, and are not inconsistent with, the requirements of the ETS. (See Summary and Explanation for Purpose , Section VI.A. of this preamble); Gade v. National Solid Wastes Management Ass'n , 505 U.S. 88, 107 (1992). In States with OSHA-approved State Plans, this ETS does not significantly limit State policy options. Any special workplace problems or conditions in a State with an OSHA-approved State Plan may be dealt with by that State's standard, provided the standard is at least as effective as this ETS.
As discussed in the Summary and Explanation for Purpose in this preamble, OSHA has included a provision that states the purpose of this ETS, as well as OSHA's intent to preempt all inconsistent State and local requirements that relate to the issues addressed by this ETS. (See section 1910.501(a); Summary and Explanation for Purpose , Section VI.A. of this preamble). This includes State and local requirements banning or limiting the authority of employers to require vaccination, face covering, or testing. As discussed in that section, such State and local bans would be preempted by this ETS, even in States with OSHA-approved State Plans, because such bans are not approved by federal OSHA as part of the State Plan and could not be approved, because such bans are clearly not as effective—and, indeed, are contrary to—the federal ETS. See Indust. Truck Ass'n v. Henry , 125 F.3d 1305, 1311 (9th Cir. 1997).
J. State Plans
When Federal OSHA promulgates an emergency temporary standard, States and U.S. Territories with their own OSHA-approved occupational safety and health plans (“State Plans”) must either amend their standards to be identical or “at least as effective as” the new standard, or show that an existing State Plan standard covering this area is “at least as effective” as the new Federal standard. 29 CFR 1953.5(b). This ETS imposes new requirements to protect workers across the nation from COVID-19. Adoption of this ETS, or an ETS that is at least as effective as this ETS, by State Plans must be completed within 30 days of the promulgation date of the final Federal rule, and State Plans must notify Federal OSHA of the action they will take within 15 days. The State Plan standard must remain in effect for the duration of the Federal ETS. As noted above in Federalism (Section V.I. of this preamble), this ETS preempts all State and local requirements, including in States with State Plans, that ban or limit the authority of employers to require vaccination, face covering, or testing. (See also the Summary and Explanation for Purpose , Section VI.A. of this preamble). As with all non-identical State Plan standards, OSHA will review any comparable State standards to determine whether they are at least as effective as this ETS. A State Plan standard that prohibits employers from requiring vaccination would not be at least as effective as this ETS because OSHA has recognized in this ETS that vaccination is the most protective policy choice for employers to adopt to protect their workplaces.
Of the 28 States and Territories with OSHA-approved State Plans, 22 cover both public and private-sector employees: Alaska, Arizona, California, Hawaii, Indiana, Iowa, Kentucky, Maryland, Michigan, Minnesota, Nevada, New Mexico, North Carolina, Oregon, Puerto Rico, South Carolina, Tennessee, Utah, Vermont, Virginia, Washington, and Wyoming. The remaining six States and Territories cover only state and local government employees: Connecticut, Illinois, Maine, New Jersey, New York, and the Virgin Islands.
K. Paperwork Reduction Act
I. Overview
The Emergency Temporary Standard (ETS) for COVID-19 Vaccination and Testing contains collection of information requirements that are subject to review by the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) under the Paperwork Reduction Act of 1995 (PRA), 44 U.S.C. 3501, et seq., and OMB's regulations at 5 CFR part 1320. The PRA defines a collection of information to mean the obtaining, causing to be obtained, soliciting, or requiring the disclosure to third parties or the public, of facts or opinions by or for an agency, regardless of form or format (44 U.S.C. 3502(3)(A)). OSHA has determined an ETS is necessary to protect workers from the grave danger posed by COVID-19 and is issuing an ETS that amends 29 CFR 1910 subpart U to provide COVID-19 protections to workers of employers with 100 or more employees. Section 1910.501 contains collections of information necessary to effectuate the purpose of the ETS. The collections of information appear in paragraphs 1910.501(d), (e)(2), (e)(4), (f)(1), (g)(1), (g)(4), (h)(1), (j), (k)(1), (k)(2), (l)(1), and (l)(2). For a more comprehensive discussion of these provisions, see the sectional analysis earlier in this preamble. These information collections are applied by cross reference to other industries in regulations 29 CFR 1915.1501 (Shipyard Employment), 1917.31 (Marine Terminals), 1918.110 (Longshoring), 1926.58 (Construction), 1928.21 (Agriculture). 79
79 The ETS applies to agricultural establishments with 11 or more employees engaged on any day in hand-labor occupations in the field and agricultural establishments that maintain a temporary labor camp, regardless of how many employees are engaged on any day in hand-labor occupations in the field).
Under the PRA, a Federal agency cannot conduct or sponsor a collection of information unless OMB approves it and the agency displays a currently valid OMB control number (44 U.S.C. 3507). Notwithstanding any other provision of law, if a collection of information does not display a currently valid control number, an employer shall not be subject to penalty for failing to comply with the collection of information (44 U.S.C. 3512). The PRA has special provisions for emergency situations that are applicable to this ETS. OMB may authorize a collection of information without regard to the normal clearance procedures if either (a) the relevant agency determines that the collection of information is essential to the mission of the agency and public harm is reasonably likely to result if normal clearance procedures are followed, or (b) the use of normal clearance procedures is reasonably likely to cause a statutory or court ordered deadline to be missed (44 U.S.C. 3507(j) and 5 CFR 1320.13). Because COVID-19 presents an ongoing public health threat to workers and American businesses, OSHA has requested the use of these emergency procedures for this ETS. In accordance with 44 U.S.C. 3507(j)(1), OMB approved the request and assigned this ETS an OMB control number that is valid for 180 days. Therefore, the information collection provisions contained within this ETS will take effect at the same time as all other provisions.
II. Summary of Information Collection Requirements
This information collection is summarized as follows.
1. Title: COVID-19 Vaccination and Testing Emergency Temporary Standard (29 CFR 1910, subpart U; 1915, subpart Z; 1917, subpart B; 1918, subpart K; 1926, subpart D; 1928, subpart B).
2. Type of Review: Emergency.
3. OMB Control Number: 1218-0278.
4. Affected Public: This rule applies to employers with a total of 100 or more employees except where the workplace is covered under the Safer Federal Workforce Task Force COVID-19 Workplace Safety: Guidance for Federal Contractors and Subcontractors; or in setting where the employee provides healthcare services or healthcare support services that falls under the requirements of 29 CFR 1910.502. This rule does not apply to employees of covered employers who work from home, exclusively outdoors, or who do not report to a workplace where other individuals such as coworkers or customers are present.
5. Description of the ICR. This ICR contains collections of information requirements for employers with 100 or more employees. The employer must establish, implement, and enforce a written mandatory vaccination policy that requires each employee to be fully vaccinated against COVID-19 unless the employer implements a policy that allows employees to choose between being fully vaccinated or both tested and wearing a face covering. Employers must determine employee vaccination status, and must require than any employees who are not vaccinated be tested for COVID-19 at least once every 7 days. Employers must provide specified information to employees regarding COVID-19 vaccine efficacy, safety, and the benefits of being vaccinated, and must maintain a record of the COVID-19 vaccination status, proof of vaccination, and copies of employee COVID-19 test results, and the aggregate number of fully vaccinated employees at a workplace along with the total number of employees at that workplace.
6. Number of respondents: 1,858,935.
7. Frequency: Varies.
8. Number of Responses: 205,262,803.
9. Estimated Burden Hours: 79,720,444.
10. Estimated Cost (Capital-operation and maintenance): $1,383,751,520.
These totals are explained and supported in the agency's Supporting Statement as required by the PRA.
III. Request for Comment
Although the ETS takes effect immediately, with implementation dates specified in the Dates provision of this publication, it also serves as a temporary standard that can only be made permanent following an opportunity for public notice and comment. OSHA therefore invites the public to submit comments to OSHA on the proposed collections of information with regard to the following.
• Whether the proposed collections of information are necessary for the proper performance of the Agency's functions, including whether the information is useful.
• The accuracy of OSHA's estimate of the burden (time and cost) of the collections of information, including the validity of the methodology and assumptions used.
• The quality, utility, and clarity of the information collected.
• Ways to minimize the compliance burden on employers, for example, by using automated or other technological techniques for collecting and transmitting information.
Please submit comments related to the Paperwork Act analysis to OSHA in the PRA docket (Docket Number OSHA-2021-0008). Comments related to other parts of the ETS should be submitted to the rulemaking docket (Docket Number OSHA-2021-0007). OSHA will accept comments for 60 days on the information collection aspects of the rule. For instructions on submitting these comments to the rulemaking and/or PRA docket, see the sections of this Federal Register notice titled DATES and ADDRESSES .
References
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). (2021c, October). Health Impacts of the COVID-19 Vaccination and Testing ETS. (OSHA, October 2021c)
VI. Summary and Explanation
A. Purpose
The ETS includes a sentence that states the purpose of the rule. The first part of the sentence in the paragraph indicates that the standard addresses the grave danger of COVID-19 in the workplace by establishing workplace vaccination, vaccination verification, face covering and testing requirements.
The second part of the sentence addresses the preemption of State and local laws, regulations, executive orders, and other requirements, by this Federal standard. It indicates OSHA's intention that the ETS address comprehensively the occupational safety and health issues of vaccination, wearing face coverings, and testing for COVID-19, and thus that the standard is intended to preempt States, and political subdivisions of States, from adopting and enforcing workplace requirements relating to these issues, except under the authority of a Federally-approved State Plan. In particular, OSHA intends to preempt any State or local requirements that ban or limit an employer's authority to require vaccination, face covering, or testing.
Preemption of such State and local requirements derives from section 18 of OSH Act and general principles of conflict preemption. See Gade v. National Solid Wastes Management Ass'n , 505 U.S. 88 (1992). 80 Gade clarified two important principles. First, section 18 expresses Congress' intent to preempt State workplace safety or health laws relating to issues on which Federal OSHA has promulgated occupational safety and health standards. Under section 18, a State can avoid preemption of such laws only if it submits and receives Federal approval for a State Plan for the development and enforcement of standards. OSHA-approved State Plans operate under authority of State law and must adopt occupational safety and health standards which, among other things, must be at least as effective in providing safe and healthful employment and places of employment as Federal standards. 29 U.S.C. 667.
80 The Court held that the dual impact licensing statutes were preempted; however, no rationale commanded a majority. A four-justice plurality found that supplementary State regulation is impliedly preempted. Id. at 98-99. Justice Kennedy's concurrence would have found express preemption rather than implied preemption, Id. at 110-111, but otherwise agreed that “in the OSH statute Congress intended to pre-empt supplementary state regulation.” Id. at 113.
Second, State and local laws that do not constitute occupational safety or health laws because they are “laws of general applicability” that regulate workers and nonworkers alike are preempted only if they conflict with the federal standard. Laws of general applicability that are consistent with the federal standard are not preempted. Gade , 505 U.S. at 107.
While section 18 applies to every occupational safety and health standard that OSHA promulgates, this ETS raises particular concerns because of the current landscape of existing State and local requirements that may overlap with, or directly conflict with, the requirements of this ETS. As discussed in Need for the ETS (Section III.B. of this preamble), OSHA is adopting this ETS in response to an unprecedented health crisis that has resulted in a global pandemic severely impacting the health and wellbeing of people in the United States, and globally. This ETS is issued based on OSHA's determination that employees in the United States face a grave danger from workplace exposures to SARS-CoV-2, that the ETS is necessary to protect those workers, and that the measures for vaccination, vaccine verification, face coverings, and testing that this ETS requires will help ensure that workers covered by the ETS are protected from severe illness and death resulting from contracting COVID-19 in the workplace.
As explained in Need for the ETS (Section III.B. of this preamble), the lack of a national standard on this hazard has led to disparate State and local requirements, and this underscores the need for OSHA's ETS to provide clear and consistent protection to employees across the country. Over the past months, an increasing number of States have passed laws or enacted other requirements banning workplace vaccination policies that would mandate vaccination or require proof of vaccination status, thus prohibiting employers operating in those jurisdictions from implementing this proven method of protecting workers from the hazard of COVID-19 that is at the core of this ETS (see, e.g., Texas Executive Order GA-40, October 11, 2021; Montana H.B. 702, July 1, 2021; Arkansas S.B. 739, October 4, 2021 and Arkansas H.B. 1977, October 1, 2021; AZ Executive Order 2021-18, Aug. 16, 2021). While some States' bans have focused on preventing local governments from requiring their public employees to be vaccinated or show proof of vaccination, the Texas, Montana, and Arkansas requirements apply to private employers as well. Likewise, some States and localities have enacted requirements that prohibit businesses, government offices, schools or other public spaces from requiring that face coverings be worn (see, e.g., Florida Executive Order 21-102, May 3, 2021; Texas Executive Order GA-34, March 2, 2021; Texas Executive Order GA-36, May 18, 2021). State and local requirements that prohibit employers from implementing employee vaccination mandates, or from requiring face coverings in workplaces, serve as a barrier to OSHA's implementation of this ETS, and to the protection of America's workforce from this deadly virus.
As discussed below, state restrictions of this kind are clearly preempted whether they take the form of direct workplace regulation or are part of a law of general applicability because they relate to the issues addressed by this standard and conflict with it. Gade , 505 U.S. at 99, 107. As is also discussed below, this is true even for State or local requirements that may not prevent employers from compliance with the ETS, but that prescribe or limit the employer's ability to mandate vaccination for its workforce as the employer's chosen means of compliance. See Gade , 505 at 107; see also Geier v. American Honda , 529 U.S. 861, 869, 875-886 (2000) (finding Department of Transportation (DOT) regulations preempted a State tort action where the state action “upset the careful regulatory scheme established by federal law” and placing weight on DOT's interpretation that such tort suit would be “an obstacle to the accomplishment and execution” of Agency objectives). An employer's choice to mandate vaccination is a critical aspect of this ETS, and state laws that remove that choice conflict with it.
Thus, to ensure that the ETS supplants the existing State and local vaccination bans and other requirements that could undercut its effectiveness, and to foreclose the possibility of future bans, OSHA has clearly defined the issues addressed by this section to encompass vaccination, face covering, and testing needed to protect against transmission of COVID-19 to employees in the workplace. To avoid ambiguity, OSHA has stated expressly that it intends this ETS to preempt all State and local workplace requirements that “relate” to these issues, except pursuant to a State Plan. 29 U.S.C. 667(b).
The “unavoidable implication” of section 18 is that because OSHA has adopted this ETS, States may no longer regulate these issues except with OSHA's approval and the authority of a Federally-approved State Plan. Gade , 505 U.S. at 99. As the Court explained, section 18 preempts States without approved plans from adopting or enforcing any laws that constitute, “in a direct, clear and substantial way regulation of worker health and safety” relating to an issue addressed by an OSHA standard. Id. at 107.
State and local requirements that ban or otherwise limit workplace vaccination, face covering, or testing clearly “relate” to the occupational safety and health “issues” that OSHA is regulating in this ETS. 29 U.S.C. 667(b). Such bans regulate key workplace COVID-19 protections that are encompassed by this ETS “in a direct, clear and substantial way.” Gade , 505 U.S. at 107. The direct effect of such bans is to prohibit employers from requiring employees to implement measures, such as vaccination requirements, face coverings, or testing. These workplace protective measures are covered by, and, in many circumstances required by, this ETS. For example, vaccination mandate bans directed at employers specifically bar them from requiring employee vaccination requirements for the purposes of protecting their workforce. Prohibitions on face covering mandates likewise directly prohibit individuals in positions of authority, including employers, from requiring face covering use.
Although the expressly stated purposes for State and local requirements banning or limiting employers from requiring vaccinations, face coverings, or testing may not be occupational safety and health, 81 this does not control their preemption under section 18 of the OSH Act. In assessing State and local requirements' impact on a federal statutory scheme, courts “have refused to rely solely on the legislature's professed purpose and have looked as well to the effects of the law.” Gade , 505 U.S. at 105; see also, e.g., Perez v. Campbell , 402 U. S. 637, 651-652 (1971) (“[A]ny state legislation which frustrates the full effectiveness of federal law is rendered invalid by the Supremacy Clause”); Napier v. Atlantic Coast Line R. Co. , 272 U.S. 605, 612 (1926) (pre-emption analysis does not depend on whether federal and State laws “are aimed at distinct and different evils” but whether they “operate upon the same object”).
81 The express purposes of such requirements banning or limiting employers from requiring vaccination, face coverings, or testing may often not relate to occupational safety and health. For example, Governor Greg Abbott's Texas face covering mandate ban in Executive Order GA-16, is based on alleged decreasing COVID-19 rates and the need to alleviate “confusion,” (Texas Executive Order GA-36, May 18, 2021); the stated purpose of Montana's vaccination mandate ban is to address health care privacy interests (Montana H.B. 702, July 1, 2021).
That a State has articulated a purpose other than, or in addition to, workplace health and safety would not divest the OSH Act of its preemptive force, because preemption law looks to the effects as well as the purpose of a State law, and thus a dual-impact State law cannot avoid OSH Act preemption simply because the regulation serves several objectives. Gade , 505 U.S. at 107 (holding “a law directed at workplace safety is not saved from pre-emption simply because the State can demonstrate some additional effect outside of the workplace” and “[t]hat such law may also have a nonoccupational impact does not render it any less of an occupational standard for purposes of pre-emption analysis”). Thus, to the extent that the stated purpose of a requirement that bans or limits employers from requiring vaccinations, face coverings, or testing is something other than, or in addition to, occupational health, such laws, which have a specific and direct impact on worker health, are nevertheless preempted.
Further, section 18 preempts even “nonconflicting” State and local occupational safety and health requirements relating to the issues addressed by this standard. Gade , 505 U.S. at 98-99, 103; see id. at 100 (“state laws regulating the same issue as federal laws are not saved, even if they merely supplement the federal standard”). This is because OSHA “'pre-empts the field' for any nonapproved State law regulating the same safety and health issue.” See Gade , 505 U.S. at 104, n. 2, citing English v. General Electric. Co. , 496 U.S. 72, 79-80, n.5 (“[F]ield preemption may be understood as a species of conflict pre-emption: A State law that falls within a pre-empted field conflicts with Congress' intent (either express or plainly implied) to exclude state regulation”); see also id. at 105 (discussing effect of field preemption). See generally Geier , 529 U.S. at 869, 875-886 (finding State law preemption where it “upset the careful regulatory scheme established by federal law”); Williamson v. Mazda Motor of Am., Inc. , 562 U.S. 323, 330-36 (2011) (affirming the conflict pre-emption principle that “a state law that stands as an obstacle to the accomplishment and execution of the full purposes and objectives of a federal law is pre-empted” and finding preemption where State law interfered with “significant objective” of the federal regulation).
For example, the ETS would preempt State or local governments from dictating that employers adopt a scheme of testing and face coverings that complies with 1910.501(g) and (i) of the ETS, but that bars employers from electing the preferred vaccine mandate alternative in paragraph (d), because this interferes with OSHA's significant regulatory objectives and its preemption of the field. 82 ( See Need for the ETS (Section III.B. of this preamble) discussing that vaccination is the preferred compliance option under this rule because it is the most effective method of protecting workers from COVID-19). Likewise, the ETS would preempt such State or local occupational requirements, even to the extent that they may regulate employers with fewer than 100 employees, notwithstanding that the requirements in this ETS only apply to employers with more than 100 employees.
82 OSHA is aware that some States have adopted or are considering adopting such requirements, which this ETS would preempt (see, e.g., Arkansas S.B. 739, October 4, 2021 and Arkansas H.B. 1977, October 1, 2021, which Arkansas Governor Asa Hutchinson allowed to became law without his signature, and which require employers in Arkansas to allow employees to opt out of vaccination for purposes of complying with federal vaccination requirements; see also Governor Hutchinson, October 13, 2021; Marr, October 7, 2021 (describing the Arkansas legislation and noting that other states may contemplate similar legislation)).
Case law is instructive on this point. In Gade, the Supreme Court found regulations implementing a State statute that required training for workers handling hazardous waste that went beyond, but did not conflict with, OSHA's hazardous waste training requirements to be preempted by the OSHA requirements. Id. Likewise, in Industrial Truck Association Incorporated v. Henry , the Ninth Circuit found that OSHA's hazard communication standard preempted California's Hazard Communication regulations that were not submitted to OSHA for approval through its State Plan, even to the extent that California's Hazard Communication rule regulated manufacturers and distributers who were excluded from coverage under federal OSHA's rule. Indust. Truck Ass'n v. Henry , 125 F.3d 1305, 1311-14 (9th Cir. 1997). In the same way, the ETS preempts all State and local requirements that bar or limit the ability of an employer to require workplace vaccination, testing, and face coverings to protected employees against COVID-19 in any respect, since OSHA has occupied the entire field of regulation on these issues.
OSHA's definition of the “issue” in this rule should be afforded weight, since the OSH Act vests OSHA with standard-setting responsibility and, therefore, the authority to determine which “issues” to address with occupational safety and health standards. See Indust. Truck , 125 F.3d at 1311 (relying on OSHA's regulation and statements in the preamble to identify the relevant “issue” for preemption purposes in OSHA's Hazard Communication standard).
Importantly, although OSHA's stated intention is to preempt conflicting State and local requirements relating to the issues addressed by this standard, OSHA recognizes that the OSH Act does not allow, and OSHA does not intend, for the ETS to preempt non-conflicting State or local requirements of general applicability. In Gade , the Supreme Court qualified its ruling by saving from preemption non-conflicting State and local “laws of general applicability (such as laws regarding traffic safety or fire safety) that do not conflict with OSHA standards and that regulate the conduct of workers and nonworkers alike.” Gade , 505 U.S. at 107. The Majority reasoned that, “[a]lthough some laws of general applicability may have a `direct and substantial' effect on worker safety, they cannot fairly be characterized as `occupational' standards, because they regulate workers simply as members of the general public.” Id.
During the pandemic, many States and municipal governments have adopted requirements intended to protect public health by helping to prevent the spread of COVID-19 in public spaces. These have included requirements mandating face coverings in indoor public spaces, including businesses, government buildings, and schools (see, e.g., Baltimore City Health Department, August 10, 2021; Illinois Executive Order 2021-20, August 26, 2021; Hawai'i Emergency Proclamation, October 1, 2021). In addition, in recent months, some States and municipal governments have adopted requirements mandating that members of the public provide proof of vaccination or recent COVID-19 testing in order to enter restaurants, bars, or other businesses or public spaces (see, e.g., NYC Emergency Executive Order 225, August 16, 2021 (mandating COVID-19 vaccination for most individuals for indoor entertainment, recreation, dining and fitness settings)). Requirements such as these apply to “workers and nonworkers alike” and “regulate workers simply as member of the general public” and are accordingly not preempted. Gade , 505 U.S.at 107.
Based on OSHA's observations and experience during the past year and a half that the pandemic has been ongoing, OSHA is confident that protective State and local regulations of general applicability that mandate face coverings or vaccination will complement, rather than interfere with OSHA's enforcement of the ETS, and also does not intend to preempt such requirements. Indeed, OSHA believes that such measures have significantly reduced the harmful effects of the pandemic and total fatalities. See Steel Institute of NY v. The City of NY , 716 F.3d 31, 38 (affording some weight to OSHA's view that municipal regulations governing construction cranes did not interfere with OSHA's regulatory scheme in its crane standards and ultimately adopted OSHA's view in finding these municipal regulations were not preempted by OSHA crane standards). 83
83 OSHA's Cranes and Derricks in Construction rule directly discussed its expectations and intent regarding the preemptive effect of the rule, including that it was not intended to preempt generally applicable municipal regulations, such as building codes, which serve public safety purposes. Cranes and Derricks in Construction, 75 FR 47,906, 48,128 (August 9, 2010). This rule also includes a provision that requires employers to comply with State crane operator licensing requirements that meet the federal floor for crane operator certification in the rule. 29 CFR 1926.1427(c)(1). OSHA has also indicated that its rule would not preempt State or local requirements in other rulemakings. See e.g., 72 FR 7136, 7188 (Feb. 14, 2007) (Preamble to OSHA's most recent electrical safety standard) (“State and local fire and building codes, which are designed to protect a larger group of persons than employees,” are not preempted); 29 CFR 1910.134(e) (requiring compliance with State and local laws by requiring “a licensed health care professional” to perform a medical evaluation of an employee's ability to use a respirator).
In Steel Institute , the Second Circuit held that OSHA's crane regulations did not preempt New York City municipal regulations governing construction cranes, finding that such regulations were requirements of general applicability, notwithstanding their direct bearing on worker safety, because their primary purpose and effect was to preserve the safety of the general public, and they regulated workers and nonworkers alike. Id. The Steel Institute court noted the “strong presumption against preemption when states and localities “exercise[ ] their police powers to protect the health and safety of their citizens.” Id. at 36, citing Medtronic, Inc. v. Lohr , 518 U.S. 470, 475 (1996). The Second Circuit was also influenced by the clear danger presented to the public by unsafe crane operation. This is analogous to the situation here, because exposure to COVID-19 is a hazard that directly impacts everyone. Thus, generally applicable State and local mandates requiring face coverings or vaccination should not be preempted and should remain in effect, notwithstanding this ETS. 84
84 In addition, some State and local governments have adopted vaccination mandates directed at State and/or local government employees. The OSH Act and OSHA's standards would not preempt such requirements since State or local government employers and employees are exempt from OSHA coverage under the OSH Act. 29 U.S.C. 652 (5) (defining employer to exclude “any State or political subdivision of a State”). However, many State and local government employers in States with OSHA-approved State Plans will be covered by State occupational safety and health requirements, and State Plans must adopt requirements for State and local government employers, as well as covered private sector employers, that are at least as effective as federal OSHA's requirements; State Plans may also choose to adopt more protective occupational safety and health requirements. 29 U.S.C. 667(c).
On the other hand, as noted above, this standard will preempt requirements that conflict with it, regardless of whether the requirements are part of a law of general applicability. 85
85 As previously discussed, bans on mandating vaccinations or face coverings have not typically been generally applicable, but even the least workplace-specific, most generally applied bans will not survive preemption because they directly interfere with the ETS's regulatory scheme.
The effect of the ETS on State law requirements in State Plan States works somewhat differently. As previously noted, under section 18 of the OSH Act States that wish to assume responsibility for the development and enforcement of “occupational safety and health standards relating to any occupational safety or health issue with respect to which a Federal standard has been promulgated” may submit a State Plan to OSHA for approval. Id. section 667(b); see also id. section 667(c) (describing requirements for OSHA approval of State Plans on issues for which OSHA has adopted standards). There are 22 States and territories that have OSHA-approved State Plans for private employers, and 6 additional States and territories that have OSHA-approved State Plans for public employers only.
Under section 18(c)(2) of the OSH Act, State Plans are required to adopt and enforce occupational safety and health standards that are at least as effective as federal OSHA's requirements. Id. section 667(c)(2). In addition, the OSH Act requires that State Plans must cover State and local government employees (including, e.g., State and local school systems within the scope of this rule), even though federal OSHA does not have coverage over such employees in States without OSHA-approved State Plans.
Once OSHA promulgates an ETS, OSHA's regulations provide that those States have “30 days after the date of promulgation of the Federal standard to adopt a State emergency temporary standard,” or to demonstrate “that promulgation of an emergency temporary standard is not necessary because the State standard is already the same or at least as effective as the Federal standard change.” 29 CFR 1953.5(b)(1). The new ETS becomes part of the OSHA-approved State Plan through the State Plan's submission to OSHA documentation showing it adopted an identical ETS or a “Plan Change Supplement” showing that it has adopted requirements that are “at least as effective” as federal OSHA's ETS. 29 CFR 1953.5(b)(3); 1953.4.
Even in States with OSHA-approved State Plans, any State law relating to an occupational safety and health issue that OSHA regulates is preempted unless it is submitted for OSHA's approval as a supplement to the State Plan. Indust. Truck Ass'n , 125 F.3d at 1311 (“If a State wishes to regulate an issue of worker safety for which a federal standard is in effect, its only option is to obtain the prior approval of the Secretary of Labor . . . [and] [i]t would make the state plan approval requirement superfluous if a state could pick and choose which occupational health and safety regulations to submit to OSHA”). Thus, a State or local requirement banning or limiting employer vaccine mandates would similarly be preempted because it has not been approved by federal OSHA as part of the State Plan. And, indeed, it could not be approved by federal OSHA, because such bans or limitations undercut the ETS's requirements and are clearly not as effective as the federal ETS. See 29 U.S.C. 667(c)(2). 86
86 For example, Arizona has an OSHA-approved State Plan, but its vaccination ban, which is not part of its State Plan, is preempted by this ETS (see AZ Executive Order 2021-18, Aug. 16, 2021).
Finally, this provision includes a note that this section establishes minimum requirements for employers, that nothing in this section prevents employers from agreeing with their employees to implement additional measures, and that this section does not supplant collective bargaining agreements or other collectively negotiated agreements in effect that may have negotiated terms that exceed the requirements herein. It also references the National Labor Relations Act of 1935, which protects most private-sector employees' right to take collective action. The purpose of this note is to remind employers and employees that OSHA's ETS establishes a floor for protections, and that it does not preclude bargaining for additional protective measures. For example, employers might agree to cover the costs of face coverings or medical removal, or to a requirement that all employees, regardless of vaccination status, wear face coverings while working indoors.
References
An Act Prohibiting Discrimination Based on a Person's Vaccination Status or Possession of an Immunity Passport; Montana H.B. 702. (2021, July 1). https://leg.mt.gov/bills/2021/billpdf/HB0702.pdf . (Montana H.B. 702, July 1, 2021)
Arizona Executive Order 2021-18. (2021, August 16). https://azgovernor.gov/sites/default/files/eo_2021-18.pdf . (AZ Executive Order 2021-18, August 16, 2021)
Arkansas H.B. 1977. (2021, October 1). To Provide Employee Exemptions From Federal Mandates and Employer Mandates Related to Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19); and to Declare an Emergency. https://www.arkleg.state.ar.us/Bills/FTPDocument?path=%2FAMEND%2F2021R%2FPublic%2FHB1977-H1.pdf . (Arkansas H.B. 1977, October 1, 2021)
Arkansas S.B. 739. (2021, October 4). An Act Concerning Employment Issues Related to Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19); To Provide Employee Exemptions From Federal Mandates and Employer Mandates Related to Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19); To Declare and Emergency; and For Other Purposes. https://www.arkleg.state.ar.us/Bills/FTPDocument?path=%2FBills%2F2021R%2FPublic%2FSB739.pdf . (Arkansas S.B. 739, October 4, 2021)
Arkansas Governor Asa Hutchinson. (2021, October 13). Press Release: Governor Hutchinson Allows Vaccine Mandate, Redistricting Bills to Become Law Without His Signature. https://governor.arkansas.gov/news-media/press-releases/governor-hutchinson-allows-vaccine-mandate-redistricting-bills-to-become-la . (Governor Hutchinson, October 13, 2021)
Baltimore City Health Department. (2021, August 10). Health Commissioner Updated Directive and Order for Face Coverings. https://www.baltimorecity.gov/sites/default/files/HEALTH%20COMMISSIONER%20AUGUST%2010,%202021%20DIRECTIVE%20AND%20ORDER%20FOR%20FACE%20COVERINGS_FINAL.pdf . (Baltimore City Health Department, August 10, 2021)
Emergency Executive Order 225. (2021, August 16). Key to NYC: Requiring COVID-19 Vaccination for Indoor Entertainment, Recreation, Dining and Fitness Settings. https://www1.nyc.gov/office-of-the-mayor/news/225-001/emergency-executive-order-225 . (NYC Emergency Executive Order 225, August 16, 2021)
Florida Executive Order 21-102. (2021, May 3). https://www.flgov.com/wp-content/ uploads/orders/2021/EO_21-102.pdf . (Florida Executive Order 21-102, May 3, 2021)
Hawai'i Emergency Proclamation Related to the State's COVID-19 Delta Response. (2021, October 1). https://governor.hawaii.gov/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/2109152-ATG_Emergency-Proclamation-Related-to-the-States-COVID-19-Delta-Response-distribution-signed.pdf . (Hawai'i Emergency Proclamation, October 1, 2021)
Illinois Executive Order 2021-20. (2021, August 26). https://www.illinois.gov/government/executive-orders/executive-order.executive-order-number-20.2021.html . (Illinois Executive Order 2021-20, August 26, 2021)
Marr C. (2021, October 7). Workplace Vaccine Exemption Bills Sent to Arkansas Governor. Bloomberg Law. https://news.bloomberglaw.com/daily-labor-report/workplace-vaccine-exemption-bills-sent-to-arkansas-governor . (Marr, October 7, 2021)
Texas Executive Order GA-34. (2021, March 2). Executive Order No. GA-34 relating to the opening of Texas in response to the COVID-19 disaster. https://open.texas.gov/uploads/files/organization/opentexas/E.O.-GA-34-opening-Texas-response-to-COVID-disaster-IMAGE-03-02-2021.pdf . (Texas Executive Order GA-34, March 2, 2021)
Texas Executive Order GA-36. (2021, May 18). Executive Order No. GA-36 relating to the prohibition of governmental entities and officials from mandating face coverings or restricting activities in response to the COVID-19 disaster. https://gov.texas.gov/uploads/files/press/E.O.-GA-36_prohibition_on_mandating_face_coverings_response_to_COVID-19_disaster_IMAGE_05-18-2021.pdf . (Texas Executive Order GA-36, May 18, 2021)
Texas Executive Order GA-40. (2021, October 11). Executive Order No. GA-40 relating to prohibiting vaccine mandates, subject to legislative action. https://gov.texas.gov/uploads/files/press/E.O.-GA-40_prohibiting_vaccine_mandates_legislative_action_IMAGE_10-11-2021.pdf . (Texas Executive Order GA-40, October 11, 2021)
B. Scope and Application
Paragraph (b)(1) of this ETS provides that the ETS applies to all employers that have a total of at least 100 employees at any time the ETS is in effect. OSHA has determined that the unvaccinated employees of these employers face a grave danger of exposure to SARS-CoV-2, including the Delta variant, while they are at work (see Grave Danger , Section III.A. of this preamble). Because this grave danger finding applies to all unvaccinated employees who come into contact with other people in indoor work settings as part of their employment, this ETS is not limited by industrial sector or NAICS code. Therefore, this standard generally covers employers in all workplaces that are under OSHA's authority and jurisdiction, including industries as diverse as manufacturing, retail, delivery services, warehouses, meatpacking, agriculture, construction, logging, maritime, and healthcare.
I. Decision To Limit Coverage of This ETS to Employers With 100 or More Employees
This ETS applies to employers with a total of 100 or more employees at any time the standard is in effect. In light of the unique occupational safety and health dangers presented by COVID-19, and against the backdrop of the uncertain economic environment of a pandemic, OSHA established this coverage threshold for four reasons. First, OSHA is confident that employers with 100 or more employees will be able to meet the standard's requirements promptly, as the emergency addressed by the standard necessitates. OSHA is less confident that smaller employers can do so without undue disruption. Second, this coverage threshold will enable the standard to reach two-thirds of all private-sector workers in the nation, providing them with prompt protection. Third, the standard will reach the largest facilities, where the most deadly outbreaks of COVID-19 can occur. Fourth, the 100-employee threshold in this standard is comparable with the size thresholds established by congressional and agency decisions in analogous contexts.
a. Challenges to Feasibility Analysis for Small Businesses
An OSHA standard, including an ETS, must be both economically and technologically feasible. A standard is economically feasible under the OSH Act if it neither threatens “massive dislocation to” nor upsets the “competitive stability of” the regulated industries. United Steelworkers of Am., AFL-CIO-CLC v. Marshall , 647 F.2d 1189, 1265 (D.C. Cir. 1980). Technological feasibility has been interpreted broadly to mean “capable of being done” Am. Textile Mfrs. Inst. v. Donovan , 452 U.S. 490, 509-510 (1981).
As shown in Economic Analysis , Section IV.B. of this preamble, OSHA is confident that this standard is feasible for employers with 100 or more employees. OSHA is not at this time making any determination about whether it would be appropriate to extend the ETS to cover smaller employers. Put simply, the agency is requiring that employers it is confident can implement the provisions of the standard without delay do so. At the same time, the agency is soliciting public comment and seeking additional information to assess the ability of smaller employers to do so in the rulemaking commenced by this ETS. OSHA will determine the issue on the basis of the record, after receiving public comment. 87 The SARS-CoV-2 virus continues to spread rapidly, and each day that passes, tens of thousands more people are infected. The employees of larger firms should not have to wait for the protections of this standard while OSHA takes the additional time necessary to assess the feasibility of the standard for smaller employers.
87 If OSHA receives information suggesting that a broader scope would be appropriate, the agency could expand the scope of the ETS quickly through a supplemental action. Fla. Peach Growers Ass'n, Inc. v. U. S. Dep't of Labor , 489 F.2d 120, 127 (5th Cir. 1974) (“It is inconceivable that Congress, having granted the Secretary the authority to react quickly in fast-breaking emergency situations, intended to limit his ability to react to developments subsequent to his initial response.”)
The pandemic has presented special challenges for small businesses. According to a survey conducted during its early stages, 66% of businesses with fewer than 100 employees had suffered revenues losses exceeding 30%. (SHRM, May 6, 2020a). By contrast, only 27% of larger businesses with more than 100 employees had seen revenue drops of more than 30% (SHRM, May 6, 2020b). More recently, 61% of the members of the National Federation of Independent Businesses, mostly very small businesses, responded to a survey reported that they were experiencing staff shortages, with half of that group reporting a moderate to significant loss of sales because of unfilled positions (NFIB, July 12, 2021).
The requirements of the ETS could have a differential impact on small businesses compared with larger firms. Many small businesses lack separate human resources departments and struggle to carry out HR functions. A study found that some 70% of small businesses (with 5 to 49 employees) handle HR tasks in an ad hoc way. (ADP, December 2016). Only 23% of ad hoc managers believed they had the tools and resources necessary to perform HR tasks well, and only 19% were fully confident in their ability to handle HR tasks without making mistakes (ADP, December 2016). Another survey found that HR functions are proportionally far more expensive for smaller firms than for larger (small firms defined as up to 250 workers) (SHRM, 2015). The ETS requires employers to establish new systems to track vaccination status among workers, to keep related records, and for firms that allow the testing option, to keep records of each test. These records must be treated as confidential medical records subject to detailed regulations, which is not something most smaller employers typically need to do or have existing systems in place to address. 29 CFR 1910.1020. While OSHA has imposed similar requirements on smaller employers before, it has typically done so in highly regulated industries, such as healthcare, or in industries involving complicated industrial processes, which already require a certain degree of administrative capacity even when not responding to a grave danger, through a rulemaking process that provides additional time for notice and implementation, and when there is more time to assess the impact that the standard would have on small business. This emergency standard by contrast applies across the board to all industries, including less regulated retail and service sectors.
Moreover, OSHA estimates that some 5% of employees may have a medical contraindication or request an accommodation from the rule's requirements for disability or sincerely held religious belief reasons. (Please see Economic Analysis , Section IV.B. of this preamble). Assessing these requests may require more resources for smaller firms with less experience in this area, particularly if they lack HR staff. By the same token, a delay in applying the ETS to businesses with fewer than 100 employees would allow those businesses the benefit of learning from the models established by larger businesses with respect to accommodations. Similarly, implementing the ETS's testing provisions in a stepwise fashion will allow OSHA the time necessary to assess any impact the new requirements may have on the testing infrastructure and related supply chains before considering extending those requirements to additional employers.
b. The ETS Provides Prompt Protection for Most of America's Workforce
The 100 employee threshold means the ETS will reach two-thirds of the nation's private sector workforce, providing protection to millions of workers while issues regarding smaller firms are reviewed. OSHA considered that a 100 employee threshold was superior to a 150 employee threshold in this respect, because it would protect more employees: 67% rather than 63%, which is a difference of 4.856 million workers. (U.S. Census Bureau, May 2021). And while a 50 employee threshold would have covered more employees (78%), it would have required additional feasibility analysis, while still leaving many employees outside the standard. (U.S. Census Bureau, May 2021).
c. The ETS Will Help Prevent Large Outbreaks of COVID-19
The ETS's focus on employers with more than 100 employees will also help prevent large-scale outbreaks. As addressed in more detail in the discussion of Grave Danger (Section III.A. of this preamble), all unvaccinated employees who work in indoor settings face a grave danger from COVID-19, which is why the scope of the ETS is not limited to worksites of a specific size. The standard is based on employer size primarily because administrative capacity is more closely related to employer size. In addition, employer size provides a clear measure that is easy for employers (and OSHA) to track, as opposed to an alternative such as a workplace-based approach, which could fluctuate from day to day and mean more places and information for the employer to track. But OSHA also chose the 100 employee size threshold in recognition of the fact that larger employers are more likely to have many employees gathered in the same location. For employers with 100 or more employees, the median number of employees at any one location is approximately 50 (the average is also 50). (U.S. Census Bureau, May 2021). For employers with fewer than 100 employees, the median number of any one location is approximately 2 (with an average number of 7) (U.S. Census Bureau, May 2021).
Employees at larger locations are statistically more likely to be exposed to someone with COVID-19 during the course of their shifts, and thus face a heightened risk of virus transmission. Studies indicate that introduction of infection and the risk of infection transmission is increased with the size of a gathering (Champredon et al., April, 2021), and with larger populations (Shacham et al., July 5, 2021). See also (Contreras et al., July, 2021) (concluding that outbreaks were larger and lasted longer at facilities with more onsite staff). It is therefore not surprising that significant COVID-19 outbreaks have occurred at large facilities of employers with 100 or more employees 88 (Oregon Health Authority, October 6, 2021; CDPHE, October 6, 2021). A study of outbreaks in Los Angeles County found that the median number of employees in an establishment in which an outbreak occurred was 95, well above the 50 employee median for locations of employers covered by this rule, indicating that the rule will protect employees in the places where outbreaks are most likely to occur. (Contreras et al., July, 2021). And those outbreaks occurred even before the emergence of the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant, which the CDC says “causes more infections and spreads faster than early forms of SARS-CoV-2.” (CDC, August 26, 2021) In fact, the studies noted earlier in this paragraph were published just as the Delta variant was emerging, meaning that the risk of transmission cited in those studies has likely increased.
88 See, e.g., Oregon Health Authority, October 6, 2021, (publishing data on outbreaks in large workplaces including two Amazon facilities, several hospitals, and a Walmart distribution center); CDPHE, Oct. 6, 2021, (identifying an active Covid outbreak in Cargill's Fort Morgan, CO meat processing plant, which employs more than 2,000 workers). While some have speculated that clusters of infections among employees at the same facility might result initially from shared exposures outside of work, the original source of the infection would have little bearing on the statistical probability of exposure and transmission once the infected people are together in the workplace with unvaccinated co-workers. The most effective way to prevent further transmission is to protect the other workers through vaccination or, when that is not possible, identify and remove the infected workers from the workplace as quickly as possible.
While virus transmission is certainly not limited to large facilities, the potential scope of an outbreak is inherently more limited when fewer employees are present. In limiting the scope of the ETS to employers with 100 or more employees, OSHA is prioritizing coverage of those businesses in which the spread of the virus could potentially affect the largest number of employees and for which the agency is most confident that it is feasible to apply the standard.
d. Analogous Regulatory Regimes Use Comparable Employee Size Thresholds
Congress and federal agencies have frequently recognized that an employee size threshold may be appropriate in different regulatory contexts. They have not settled on any one number as the most appropriate, presumably because that depends on balancing different considerations that are relevant to the particular context, as OSHA has done here. But several analogous regulatory regimes use employee size thresholds comparable to the one selected here, in light of similar concerns about administrative feasibility.
For example, the EEOC has issued regulations requiring employers with 100 or more employees to submit annual reports related to equal employment opportunity in their workforce, in recognition that larger employers are better equipped to absorb the types of administrative burdens imposed by surveying, tracking and recordkeeping requirements. See 42 U.S.C. 2000e-8(c), 29 CFR 1602.7-.14 and 41 CFR 60-1.7(a). In earlier measures adopted in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, Congress adopted special protections and exemptions based on employee counts. The Families First Coronavirus Response Act, Public Law 116-127 (2020), sections 7001 and 7003 provided tax credits to businesses with fewer than 500 employees to assist compliance with the Act's expansion of paid sick and family leave, in recognition of the challenges facing smaller employers. Congress again relied on the same 500 employee threshold when it later extended tax credits only to employers who granted employees paid time off to be vaccinated, implicitly acknowledging the financial obstacles that can exist for smaller employers for the same activity that this ETS promotes (and without the vaccine policy and verification requirement in this ETS). American Rescue Plan Act, Public Law 117-2, Sec. 9641 (2021).
In the Affordable Care Act, Congress set the maximum size of a “small employer” at 100 employees for purposes of allowing greater flexibility to these employers. 42 U.S.C.A. 18024(b)(3). Likewise, private employers with fewer than 50 employees are exempt from complying with the Family and Medical Leave Act, in recognition of smaller employers' decreased administrative capacity, as well as their inability to easily accommodate employee absences. 29 U.S.C.A. 2611(2)(b)(2).
e. The 100 Employee Coverage Provision Is a Reasonable Exercise of the Secretary's Authority
OSHA's choice of a 100 employee threshold is based on balancing the fundamentally incommensurable considerations described above. Under the statute OSHA “shall” issue an ETS when employees are exposed to grave danger, and is not to follow normal notice and comment procedures to build a record. 29 U.S.C. 655(e). But OSHA may not issue an ETS unless it shows that the rule is feasible for the employers covered, and it has not yet made a feasibility determination for smaller employers. In the circumstances of this case, OSHA considered that an ETS was urgently needed to protect employees, that a 100 employee threshold would protect the great majority of them and prevent the largest outbreaks, that it would avoid the delays that would be needed if the agency were required to gather information and analyze feasibility for smaller employers, and that a comparable size threshold has been found appropriate in similar contexts. Where employees are dying every day, it is not unreasonable for the agency to prioritize doing what it can to address the problem quickly, regardless of whether there are further actions it might be able to take later.
Doing so implements the statutory delegation of authority to the agency to establish priorities for issuing standards by giving “due regard to the urgency of the need” for standards for particular workplaces. 29 U.S.C. 655(g). The courts have recognized that this provision authorizes the Secretary to make reasonable decisions limiting the scope of a standard, particularly where as here the agency has said it will address the reserved issue in subsequent rulemaking. Forging Indus. Assoc. v. Donovan, 773 F.2d 1436, 1454 (4th Cir. 1985) (hearing conservation standard); United Steelworkers of Am. v. Marshall, 647 F.2d 1189, 1309-1310 (D.C. Cir. 1980) (lead standard).
Where competing considerations are in play and there is no clear perfect choice, OSHA has a degree of discretion to draw a reasonable line. Courts have consistently recognized that agencies have discretion to draw reasonable lines. As the D.C. Circuit has explained: An agency has “wide discretion” in making line-drawing decisions and “[t]he relevant question is whether the agency's numbers are within a zone of reasonableness, not whether its numbers are precisely right.” WorldCom, Inc. v. FCC, 238 F.3d 449, 462 (D.C. Cir. 2001) (quotation marks omitted). An agency “is not required to identify the optimal threshold with pinpoint precision. It is only required to identify the standard and explain its relationship to the underlying regulatory concerns.” Id. at 461-62. Nat'l Shooting Sports Found. v. Jones, 716 F.3d. 200, 214-215 (D.C. Cir 2013). See also Providence Yakima Med. Ctr. v. Sebelius , 611 F.3d 1181, 1190-1191 (9th Cir. 2010).
For the reasons discussed above, the balance the agency struck here falls well within this zone of reasonableness.
II. Explanation of Who Is Included in the 100-Employee Threshold
The applicability of this ETS is based on the size of an employer, in terms of number of employees, rather than on the type or number of workplaces. In determining the number of employees, employers must include all employees across all of their U.S. locations, regardless of employees' vaccination status or where they perform their work. Part-time employees do count towards the company total, but independent contractors do not. As discussed above, OSHA has not found that the standard is feasible for firms with fewer than 100 employees, because it needs additional time to assess the impact of the standard on these employers, particularly as many smaller firms lack separate human resources departments and may face additional challenges when carrying out human resources functions. In contrast, OSHA has determined that the standard is feasible for firms with 100 or more employees, regardless of where those employees report to work. These firms generally have greater administrative capacities, and including all such employers in the scope of this ETS ensures that OSHA can cover two-thirds of all workers in the private sector as quickly as possible.
For a single corporate entity with multiple locations, all employees at all locations are counted for purposes of the 100-employee threshold for coverage under this ETS. In a traditional franchisor-franchisee relationship in which each franchise location is independently owned and operated, the franchisor and franchisees would be separate entities for coverage purposes, such that the franchisor would only count “corporate” employees, and each franchisee would only count employees of that individual franchise. In other situations, two or more related entities may be regarded as a single employer for OSH Act purposes if they handle safety matters as one company, in which case the employees of all entities making up the integrated single employer must be counted.
In scenarios in which employees of a staffing agency are placed at a host employer location, only the staffing agency would count these jointly employed workers for purposes of the 100-employee threshold for coverage under this ETS. Although the staffing agency and the host employer would normally share responsibility for these workers under the OSH Act, this ETS raises unique concerns in that OSHA has set the threshold for coverage based primarily on administrative capacity for purposes of protecting workers as quickly as possible, as discussed above, and the staffing agency would typically handle administrative matters for these workers. Thus, for purposes of the 100-employee threshold, only the staffing agency would count the jointly employed employees. The host employer, however, would still be covered by this ETS if it has 100 or more employees in addition to the employees of the staffing agency. For enforcement purposes, traditional joint employer principles would apply where both employers are covered by the ETS, as illustrated further by the examples below. See also https://www.osha.gov/temporaryworkers/.
On a typical multi-employer worksite such as a construction site, each company represented—the host employer, the general contractor, and each subcontractor—would only need to count its own employees, and the host employer and general contractor would not need to count the total number of workers at each site. That said, each employer must count the total number of workers it employs regardless of where they report for work on a particular day. Thus, for example, if a general contractor has more than 100 employees spread out over multiple construction sites, that employer is covered under this ETS even if it does not have 100 or more employees present at any one worksite. Covering the employees of larger employers at multi-employer worksites would mitigate the spread of COVID-19 at the workplace even where not all employees are covered by this ETS because fully vaccinated employees (or unvaccinated employees wearing face coverings and submitting to weekly testing) would be less likely to spread the virus to unvaccinated workers at the site who are not covered by this ETS.
The determination as to whether a particular employer is covered by the standard should be made separately from whether individual employees are covered by the standard's requirements, as described by paragraph (b)(3) ( e.g., some employers may be covered but have no duties with respect to some of their employees under this standard). Some additional examples include:
• If an employer has 75 part-time employees and 25 full-time employees, the employer would be within the scope of this ETS because it has 100 employees.
• If an employer has 150 employees, 100 of whom work from their homes full-time and 50 of whom work in the office at least part of the time, the employer would be within the scope of this ETS because it has more than 100 employees.
• If an employer has 102 employees and only 3 ever report to an office location, that employer would be covered.
• If an employer has 150 employees, and 100 of them perform maintenance work in customers' homes, primarily working from their company vehicles ( i.e., mobile workplaces), and rarely or never report to the main office, that employer would also fall within the scope.
• If an employer has 200 employees, all of whom are vaccinated, that employer would be covered.
• If an employer has 125 employees, and 115 of them work exclusively outdoors, that employer would be covered.
• If a single corporation has 50 small locations ( e.g., kiosks, concession stands) with at least 100 total employees in its combined locations, that employer would be covered even if some of the locations have no more than one or two employees assigned to work there.
• If a host employer has 80 permanent employees and 30 temporary employees supplied by a staffing agency, the host employer would not count the staffing agency employees for coverage purposes and therefore would not be covered. (So long as the staffing agency has at least 100 employees, however, the staffing agency would be responsible for ensuring compliance with the ETS for the jointly employed workers.)
• If a host employer has 110 permanent employees and 10 temporary employees from a small staffing agency (with fewer than 100 employees of its own), the host employer is covered under this ETS and the staffing agency is not.
• If a host employer has 110 permanent employees and 10 employees from a large staffing agency (with more than 100 employees of its own), both the host employer and the staffing agency are covered under this standard, and traditional joint employer principles apply.
• Generally, in a traditional franchisor-franchisee relationship, if the franchisor has more than 100 employees but each individual franchisee has fewer than 100 employees, the franchisor would be covered by this ETS but the individual franchises would not be covered.
As explained earlier, part of OSHA's rationale in adopting the 100-employee threshold is to focus the ETS on companies that OSHA is confident will have sufficient administrative systems in place to comply quickly with the ETS. Thus, the ETS applies to all employers who have the requisite number of employees at any time this ETS is in effect. Along with employers that always have more than 100 employees, OSHA intends to cover employers that fluctuate above and below the 100-employee threshold during the term of the ETS because those employers will typically have already developed systems and capabilities for compliance; a decrease in the number of employees is therefore unlikely to make them less capable of compliance.
The determination of whether an employer falls within the scope of this ETS based on number of employees should initially be made as of the effective date of the standard, as set out in paragraph (m)(1). If the employer has 100 or more employees on the effective date, this ETS applies for the duration of the standard. If the employer has fewer than 100 employees on the effective date of the standard, the standard would not apply to that employer as of the effective date. However, if that same employer subsequently hires more workers and hits the 100-employee threshold for coverage, the employer would then be expected to come into compliance with the standard's requirements. Once an employer has come within the scope of the ETS, the standard continues to apply for the remainder of the time the standard is in effect, regardless of fluctuations in the size of the employer's workforce. For example, an employer that has 103 employees on the effective date of the standard, but then loses four within the next month, would continue to be covered by the ETS. OSHA is confident that employers with 100 or more employees at any point while this ETS is in effect have the administrative capacity to comply with the ETS, even if the number of employees fluctuates somewhat above and below 100.
Paragraph (b)(2) of this ETS sets forth two exemptions to the standard. 89 Under paragraph (b)(2)(i), this ETS does not apply to workplaces covered by the Safer Federal Workforce Task Force COVID-19 Workplace Safety: Guidance for Federal Contractors and Subcontractors (see Safer Federal Workforce Task Force, September 24, 2021). With limited exceptions, such as where a medical contraindication, disability, or sincerely held religious belief would prevent an employee from complying with certain provisions, those guidelines require covered contractors to ensure that all covered contractor employees (1) are fully vaccinated by December 8, 2021; (2) follow CDC guidelines for masks and physical distancing, including masking and distancing requirements based on the employee's vaccination status and the level of community transmission of COVID-19 where the workplace is located; and (3) designate a person to coordinate COVID-19 workplace safety efforts at covered workplaces. Because covered contractor employees are already covered by the protections in those guidelines, OSHA has determined that complying with this standard in addition to the federal contractor guidelines is not necessary to protect covered contractor employees from a grave danger posed by COVID-19. Although there may be some respects in which the OSHA standard is somewhat more protective, such as providing paid leave for vaccination, the federal contractor guidelines are somewhat more protective in other respects, such as requiring vaccination for everyone who does not have a right to an accommodation rather than allowing employees to submit to testing in lieu of vaccination. In essence, they are similar but slightly different schemes that provide roughly equivalent protection, and OSHA has determined that imposing a second set of similar protections on covered federal contractors by subjecting them to this ETS in addition to the federal contractor guidance is not necessary at this time to reduce a grave danger to covered contractor employees from COVID-19.
89 Note that, in addition to the scope exceptions contained in the ETS itself, which are discussed in this section, there may be situations where the ETS does not apply by operation of the OSH Act. For example, the OSH Act does not apply to working conditions of employees with respect to which other Federal agencies have exercised their statutory authority to prescribe or enforce standards or regulations affecting occupational safety or health (see 29 U.S.C. 653(b)(1)). Moreover, the ETS does not apply where states with OSHA-approved occupational safety and health programs (“State Plans”) have coverage (see 29 U.S.C. 667). State Plans must adopt and enforce COVID-19 requirements that are at least as effective as this ETS. Finally, the ETS does not apply to state and local government employers in states without State Plans (see 29 U.S.C. 652(5)).
Under Executive Order 14043, every federal agency must implement a program requiring each of its federal employees to be vaccinated against COVID-19, except as required by law. 86 FR 50989. OSHA will regard a federal agency's compliance with this requirement, and the related Safer Federal Workforce Task Force guidance issued under section 4(e) of Executive Order 13991 and section 2 of Executive Order 14043 (including guidance on employer support in the form of paid time for vaccination and paid leave for post-vaccination recovery), as sufficient to meet its obligation to comply with this ETS under Section 19 of the OSH Act and Executive Order 12196. In essence, the federal government has chosen the mandatory vaccination option of this rule, and all federal employees are required to be fully vaccinated by the compliance date of this standard, except where entitled to a reasonable accommodation. The Safer Federal Workforce Task Force's guidelines for vaccination verification are consistent with the ETS's (see Safer Federal Workforce Task Force, October 11, 2021). Note, however, that under the OSH Act, the U.S. Postal Service is treated as a private employer, see 29 U.S.C. 652(5), and it is therefore required to comply with this ETS in the same manner as any other employer covered by the Act.
For similar reasons, paragraph (b)(2)(ii) provides that this ETS does not apply in settings where any employee provides healthcare services or healthcare support services while they are covered by the requirements of 29 CFR 1910.502. Section 1910.502 requires a multi-layered suite of protections for employees covered by its requirements, including patient screening and management, facemasks or respirators, other personal protective equipment (PPE), limiting exposure to aerosol-generating procedures, physical distancing, physical barriers, cleaning, disinfection, ventilation, health screening and medical management, access to vaccination, and medical removal protection. Section 1910.502 was carefully tailored to the healthcare workplaces it covers and, given the full suite of protections it requires, including (like this ETS) the provision of paid time for vaccination, OSHA has determined that it adequately protects the employees covered by its requirements from the grave danger posed by COVID-19. Therefore, complying with the additional requirements of this ETS is not necessary to protect those employees while they are covered by that standard's protections.
OSHA's intent was to leave no coverage gaps between section 1910.502 and this ETS. In other words, the purpose of paragraph (b)(2)(ii) is to ensure that all workers in healthcare and healthcare support jobs who are at grave danger from exposure to SARS-CoV-2 are protected by either section 1910.502 or this ETS while performing their jobs. Therefore, it will be necessary for employers with employees covered by section 1910.502 to determine if they also have employees covered by this ETS. For example, a healthcare employer with more than 100 employees that has non-hospital ambulatory care facilities that are exempt under section 1910.502(a)(2)(iii) (for non-hospital ambulatory care settings where all non-employees are screened prior to entry and those with suspected or confirmed COVID-19 are prohibited from entry) would be required to protect the employees in those ambulatory care facilities under this ETS. Similarly, a retail pharmacy chain that operates a series of ambulatory care clinics embedded in its stores, where those embedded clinics are the only areas in the store that are covered under 1910.502 (see section 1910.502(a)(3)(i)), would have to ensure that the remainder of its employees in other parts of its stores are protected under this ETS if the company has 100 or more employees company-wide, including those covered under 1910.502.
Paragraph (b)(3) provides that, even where the standard applies to a particular employer, its requirements do not apply to employees: (i) Who do not report to a workplace where other individuals such as coworkers or customers are present; (ii) while working from home; or (iii) who work exclusively outdoors. OSHA intends these provisions to exempt workplace settings where workers do not interact indoors with other individuals, and to exempt work performed in the employee's home regardless of whether other individuals may be present in the home.
OSHA has determined that the provisions of this ETS are not necessary to protect employees from COVID-19 when they are working alone, or when they are working from home (see Grave Danger, Section III.A. of this preamble). These two provisions may overlap in some cases, but also can apply to slightly different situations. Paragraph (b)(3)(i) would apply to work in a solitary location, such as a research station where only one person (the employee) is present at a time. In that situation, the employee is not exposed to any potentially infectious individuals at work. Paragraph (b)(3)(ii) would apply to employees working in their homes, regardless of whether other individuals who are not employees of the same employer are present. In a home telework environment, many factors—such as the presence of family members and other individuals unrelated to the employee's work, who may not be fully vaccinated or wearing face coverings—may be beyond the employer's control. Employees are typically in the best position to manage COVID-19 risks in their homes. Note that the exemption in paragraph (b)(3)(ii) only applies to employees while they are working from home. An employee who switches back and forth from teleworking to working in a setting where other people are present ( e.g., an office) is covered by this ETS and must be vaccinated if required by the employer. If the employer does not require vaccination, the teleworking employee must either be vaccinated or complete testing and wear a face covering in accordance with their employer's policy under paragraph (d). How often such an employee must be tested for COVID-19 and wear a face covering, however, depends on how often they report to the office (see, e.g., paragraph (g)(1)(ii)).
Paragraph (b)(3)(iii) provides that, even if a particular employer is covered by the standard, the requirements of the standard do not apply to employees who work exclusively outdoors. OSHA has determined that COVID-19 does not pose a grave danger to employees who work exclusively outdoors because of the significantly reduced likelihood of transmission in outdoor settings. As discussed in more detail in Grave Danger (Section III.A. of this preamble), the record contains very little evidence of COVID-19 transmission in outdoor settings. And, in studies where clusters were identified in worksites characterized as being outdoors, the study authors were not able to identify specific incidents that led to transmission. In addition, workplaces characterized as “outdoors” may in fact involve significant time spent indoors. For example, on a construction site, workers inside a partially complete structure are not truly outdoors, and some individuals on a construction site may spend significant amounts of time in a construction trailer where other individuals are present. Workers at outdoor locations may also routinely share work vehicles. These indoor exposures could account for COVID-19 clusters among employees at worksites otherwise characterized as being outdoors. And employees whose outdoor time is interrupted by the indoor periods will still be subject to the requirements in this ETS.
Studies of athletic teams further indicate that evidence of COVID-19 clusters among workers characterized as working outdoors could actually be caused by indoor exposures. Even where athletes were in very close contact during outdoor exposures on the playing field, the study authors could not identify a single case of COVID-19 transmission between teams that occurred outdoors (see Mack et al., January 29, 2021; Egger et al., March 18, 2021; Jones et al., February 11, 2021). For all of these reasons, and as discussed more fully in Grave Danger (Section III.A. of this preamble), OSHA has determined that COVID-19 does not pose a grave danger to employees who work exclusively outdoors.
As a practical matter, determining the applicability of paragraph (b)(3)(iii) depends on the working conditions of individual employees. For example, if a landscaping contractor has at least 100 employees and is not covered by the exemptions in paragraph (b)(2), the standard applies to that employer even if a majority of the company's employees work exclusively outdoors. The standard's protections would only apply to employees working in indoor settings around other individuals (other than telework in their own homes), not to those employees working exclusively outdoors. In some cases, it may be true that the standard applies to an employer but the employer would not have to implement its provisions at all because all of its employees fall within exemptions in paragraph (b)(3). Going back to the example of the large landscaping contractor, if all indoor workers either work from home or in locations where no other individuals are present, and all outdoors workers work exclusively outdoors and do not drive to worksites together in a company vehicle, the employer would be covered by the ETS but not required to comply with its provisions.
An employee will only be covered by the exemption in paragraph (b)(3)(iii) if the employee works exclusively outdoors. Thus, an employee who works indoors on some days and outdoors on other days would not be exempt from the requirements of this ETS. Likewise, if an employee works primarily outdoors but routinely occupies vehicles with other employees as part of work duties, that employee is not covered by the exemption in paragraph (b)(3)(iii). However, if an employee works outdoors for the duration of every workday except for de minimis use of indoor spaces where other individuals may be present—such as a multi-stall bathroom or an administrative office—that employee would be considered to work exclusively outdoors and covered by the exemption under paragraph (b)(3)(iii) as long as time spent indoors is brief, or occurs exclusively in the employee's home ( e.g., a lunch break at home). Extremely brief periods of indoor work would not normally expose employees to a high risk of contracting COVID-19; however, OSHA will look at cumulative time spent indoors to determine whether that time is de minimis. Thus, if there are several brief periods in a day when an employee goes inside, OSHA will total those periods of time when determining whether the exception for exclusively outdoors work applies.
Finally, to qualify for this exception, the employee's work must truly occur “outdoors,” which would not include buildings under construction where substantial portions of the structure are in place, such as walls and ceiling elements that would impede the natural flow of fresh air at the worksite. Workplaces that are truly outdoors typically do not include any of the characteristics that normally enable transmission of SARS-CoV-2 to occur, such as poor ventilation, enclosed spaces, and crowding. As discussed in Bulfone et al. (November 29, 2020), the lower risk of transmission in outdoor settings ( i.e., open air or structures with only one wall) is likely due to increased ventilation with fresh air and a greater ability to maintain physical distancing (see Grave Danger, Section III.A. of this preamble, for more information on risk of transmission outdoors).
References
Always Designing for People (ADP). (2016, December). Opportunity is calling. Answer it. Insights and solutions for moving beyond risky ad hoc HR management. (ADP, December 2016)
Bulfone TC et al. (2020, November 29). Outdoor Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 and Other Respiratory Viruses: A Systematic Review. (2020). The Journal of Infectious Diseases 223: 550-561. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiaa742. (Bulfone et al., November 29, 2020)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, August 26). Delta Variant: What We Know About the Science. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/variants/delta-variant.html?s_cid=11512:cdc%20delta%20variant:sem.ga:p:RG:GM:gen:PTN:FY21. (CDC, August 26, 2021)
Champredon D et al. (2021, May 12). Modelling approach to assessing risk of transmission of SARS-CoV-2 at gatherings. https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/reports-publications/canada-communicable-disease-report-ccdr/monthly-issue/2021-47/issue-4-april-2021/assessing-risk-transmission-sars-cov-2-gatherings.html. (Champredon et al., May 12, 2021)
Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment (CDPHE). (2021, October 6). CDPHE COVID-19 outbreak map updated October 6, 2021. https://cdphe.maps.arcgis.com/apps/webappviewer/index.html?id=dcc0b993632a4bc68dc7b9a1dd015cfe. (CDPHE, October 6, 2021)
Contreras Z et al. (2021, July). Industry Sectors Highly Affected by Worksite Outbreaks of Coronavirus Disease, Los Angeles County, California, USA, March 19-September 30, 2020. Emerg Infect Dis. 2021; 27(7): 1769-1775. doi:10.3201/eid2707.210425. (Contreras et al., July, 2021)
Egger F et al. (2021, March 18). Does playing football (soccer) lead to SARS-CoV-2 transmission?—a case study of 3 matches with 19 infected football players. Science and Medicine in Football. doi:10.1080/24733938.2021.1895442. (Egger et al., March 18, 2021)
Jones B et al. (2021, February 11). SARS-CoV-2 transmission during rugby league matches: do players become infected after participating with SARS-CoV-2 positive players? Br J Sports Med doi:10.1136/bjsports-2020-103714. (Jones et al., February 11, 2021)
Mack CD et al. (2021, January 29). Implementation and evolution of mitigation measures, testing, and contact tracing in the national football league, August 9-November 21, 2020. MMWR 70: 130-135. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7004e2. (Mack et al., January 29, 2021)
National Federation of Independent Business (NFIB) Research Center. (2021, July 12). Covid-19 small business survey (18): federal small business programs, the vaccine, labor shortage, and supply chain disruptions. https://assets.nfib.com/nfibcom/Covid-19-18-Questionnaire.pdf. (NFIB, July 12, 2021)
Oregon Health Authority. (2021, October 6). COVID-19 weekly outbreak report—October 6, 2021. https://www.oregon.gov/oha/covid19/Documents/DataReports/Weekly-Outbreak-COVID-19-Report.pdf. (Oregon Health Authority, October 6, 2021)
Safer Federal Workforce Task Force. (2021, September 24). COVID-19 Workplace Safety: Guidance for Federal Contractors and Subcontractors. https://www.saferfederal/workforce./gov/downloads/Draft%/20contractor%/20guidance%/20doc_20210922.pdf. (Safer Federal Workforce Task Force, September 24, 2021)
Safer Federal Workforce Task Force. (2021, October 11). Vaccinations: Vaccination Documentation and Information. https://www.saferfederalworkforce.gov/faq/vaccinations/. (Safer Federal Workforce Task Force, October 11, 2021)
Shacham E et al. (2021, July 5). Examining the relationship between COVID-19 vaccinations and reported incidence. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.06.30.21259794. (Shacham et al., July 5, 2021)
Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM). (2015). How organizational staff size influences HR metrics. https://www.shrm.org/resourcesandtools/business-solutions/documents/organizational%20staff%20size.pdf. (SHRM, 2015)
Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM). (2020a, May 6). Navigating COVID-19: impact of the pandemic on small businesses. https://shrm.org/hr-today/trends-and-forecasting/research-andsurveys/Documents/SHRM%20CV19%20SBO%20Research%20Presentation%20v1.1.pdf. (SHRM, May 6, 2020a)
Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM). (2020b, May 6). Survey: COVID-19 could shutter most small businesses. https://www.shrm.org/about-shrm/press-room/press-releases/pages/survey-covid-19-could-shutter-most-small-businesses.aspx. (SHRM, May 6, 2020b)
United States (US) Census Bureau. (2021, May). 2017 SUSB Annual Data Tables by Establishment Industry, The annual data table titled “U.S. & states, NAICS, detailed employment sizes U.S., 6-digit and states, NAICS sector,” https://www.census.gov/data/tables/2017/econ/susb/2017-susb-annual.html. (US Census Bureau, May 2021)
C. Definitions
Paragraph (c) of the ETS provides definitions of terms used in the section.
“Assistant Secretary” means the Assistant Secretary of Labor for Occupational Safety and Health, U.S. Department of Labor, or designee. This definition provides clarification about who can request and receive records specified in paragraph (l)(3) of this section. A designee includes a representative conducting an inspection or an investigation.
“COVID-19 (Coronavirus Disease 2019)” means the disease caused by SARS-CoV-2 (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2). SARS-CoV-2 is a highly transmissible virus that spreads primarily through the respiratory droplets that are produced when an infected person coughs, sneezes, sings, talks, or breathes. The nature of the disease, variants of SARS-CoV-2, disease transmission, and associated health effects are all described in great detail in Grave Danger (Section III.A. of this preamble). For clarity and ease of reference, the ETS also uses the term “COVID-19” when describing exposures or potential exposures to SARS-CoV-2. The requirements of the ETS are intended to address the grave danger of exposure to COVID-19 in the workplace.
A “COVID-19 test” means a test for SARS-CoV-2 that is: (1) Cleared, approved, or authorized, including in an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA), by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to detect current infection with the SARS-CoV-2 virus ( e.g., a viral test); (2) administered in accordance with the authorized instructions; and (3) not both self-administered and self-read unless observed by the employer or an authorized telehealth proctor. Examples of tests that satisfy this requirement include tests with specimens that are processed by a laboratory (including home or on-site collected specimens which are processed either individually or as pooled specimens), proctored over-the-counter tests, point of care tests, and tests where specimen collection and processing is either done or observed by an employer.
Under paragraph (g), employees who are not fully vaccinated must be tested for COVID-19. When an employee must be tested, the test is considered acceptable only if the test and the administration of the test satisfy the definition of COVID-19 test in this standard.
COVID-19 tests can broadly be divided into two categories, diagnostic tests and antibody tests. Diagnostic tests detect parts of the SARS-CoV-2 virus and can be used to diagnose current infection. On the other hand, antibody tests look for antibodies in the immune system produced in response to SARS-CoV-2, and are not used to diagnose an active COVID-19 infection. Antibody tests do not meet the definition of COVID-19 test for the purposes of this ETS.
Diagnostic tests for current infection fall into two categories: Nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs) and antigen tests. NAATs are a type of molecular test that detect genetic material (nucleic acids); NAATs for COVID-19 identify the ribonucleic acid (RNA) sequences that comprise the genetic material of the virus. NAATs can reliably detect small amounts of SARS-CoV-2 and are unlikely to return a false-negative result. NAATs use many different methods to detect the virus, including reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), which is a high-sensitivity, high-specificity 90 test for diagnosing SARS-CoV-2 infection. Other types of NAATs that use isothermal amplification methods include nicking endonuclease amplification reaction (NEAR), transcription mediated amplification (TMA), loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP), helicase-dependent amplification (HDA), clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR), and strand displacement amplification (SDA) (CDC, June 14, 2021).
90 Test sensitivity indicates the ability of a test to correctly identify people who have a disease. Test specificity indicates the ability of a test to correctly identify people who do not have a disease. A test with high sensitivity and high specificity minimizes inaccurate results.
Most NAATs need to be processed in a laboratory with variable time to receive results (approximately 1-2 days), but some NAATs are point-of-care tests with results available in about 15-45 minutes. As of October 14, 2021, 264 molecular tests (NAATs) and collection devices have EUA from the FDA for COVID-19 (FDA, October 14, 2021b). These tests may be acceptable under the ETS.
Antigen tests may also meet the definition of COVID-19 test under this standard. Antigen tests indicate current infection by detecting the presence of a specific viral antigen. Most can be processed at the point of care with results available in about 1530 minutes. Antigen tests generally have similar specificity to, but are less sensitive than, NAATs (CDC, October 7, 2021). As of October 14, 2021, thirty-seven antigen tests have EUA from the FDA for COVID-19 (FDA, October 14, 2021a). These tests may be acceptable under the ETS.
Most antigen tests and some NAATs are conducted at the point of care, which means the test processing and result reading is performed at or near the place where a specimen is collected so that results can be obtained within minutes rather than hours or days. Rapid point-of-care tests are administered in various settings operating under a Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments of 1988 (CLIA) certificate of waiver, such as physician offices, urgent care facilities, pharmacies, school health clinics, workplace health clinics, long-term care facilities and nursing homes, and at temporary locations, such as drive-through sites managed by local health organizations (FDA, November 16, 2020).
To be a valid COVID-19 test under this standard, a test may not be both self-administered and self-read unless observed by the employer or an authorized telehealth proctor. OSHA included the requirement for some type of independent confirmation of the test result in order to ensure the integrity of the result given the “many social and financial pressures for test-takers to misrepresent their results” (Schulte et al., May 19, 2021). This independent confirmation can be accomplished in multiple ways, including through the involvement of a licensed healthcare provider or a point-of-care test provider. If an over-the-counter (OTC) test is being used, it must be used in accordance with the authorized instructions. The employer can validate the test through the use of a proctored test that is supervised by an authorized telehealth provider. Alternatively, the employer could proctor the OTC test itself.
Employers have the flexibility to select the testing scenario that is most appropriate for their workplace. Some employees and employers may rely on testing that is conducted by a healthcare provider ( e.g., doctor or nurse) who arranges for the specimen to be analyzed at a laboratory or at a point-of-care testing location ( e.g., a pharmacy). The involvement of licensed or accredited healthcare providers allows employers to have a high degree of confidence in the suitability of the test and the test results. Some large employers who set up their own on-site testing program may partner with a healthcare organization ( e.g., a local hospital or clinic) or rely on a licensed healthcare provider to help obtain a CLIA certificate of waiver. Other employers may simply require that employees perform and read their own OTC test while an authorized employee observes the administration and reading of the test to ensure that a new test kit was used and that the test was administered properly ( e.g., nostrils were swabbed), and to witness the test result.
Due to the potential for employee misconduct ( e.g., falsified results), tests that are both self-administered and self-read are not acceptable unless they are observed by the employer or an authorized telehealth proctor. Some COVID-19 tests are authorized by the FDA to be performed only with the supervision of a telehealth proctor, which is someone who is trained to observe sample collection and provide instructions and result interpretation assistance to individuals using the test. The term “authorized telehealth proctor” refers to proctors who follow the requirements for proctoring specified by the FDA authorization. For a more detailed discussion on COVID-19 testing requirements under this ETS, see the Summary and Explanation for paragraph (g) (Section VI.G. of this preamble).
A “face covering” means a covering that: (1) Completely covers the nose and mouth; (2) is made with two or more layers of a breathable fabric that is tightly woven (i.e., fabrics that do not let light pass through when held up to a light source); (3) is secured to the head with ties, ear loops, or elastic bands that go behind the head. If gaiters are worn, they should have two layers of fabric or be folded to make two layers; (4) fits snugly over the nose, mouth, and chin with no large gaps on the outside of the face; and (5) is a solid piece of material without slits, exhalation valves, visible holes, punctures, or other openings. This definition includes clear face coverings or cloth face coverings with a clear plastic panel that, despite the non-cloth material allowing light to pass through, otherwise meet this definition and which may be used to facilitate communication with people who are deaf or hard-of-hearing or others who need to see a speaker's mouth or facial expressions to understand speech or sign language respectively. Face coverings can be manufactured or homemade, and they can incorporate a variety of designs, structures, and materials. Face coverings provide variable levels of protection based on their design and construction.
As explained in paragraph (i), face covering use is required based on an employee's vaccination status. The criteria in the definition help to ensure that face coverings that are worn by workers who are not fully vaccinated will provide effective source control and some degree of personal protection. Source control means reducing the spread of large respiratory droplets to others by covering a person's mouth and nose. The personal protection afforded by face coverings, as well as the benefits and necessity, are described in the Summary and Explanation for paragraph (i) (Section VI.I. of this preamble).
Face coverings differ from facemasks and respirators, which are also defined in paragraph (c) of this section. Face coverings, unlike facemasks and respirators, are not considered to be personal protective equipment (PPE) under OSHA's general PPE standard (29 CFR 1910.132), as discussed in the Summary and Explanation for paragraph (i) (Section VI.I. of this preamble).
Lastly, face coverings as required by this standard do not have to meet a consensus standard, although face coverings that adhere to such consensus standards, with design and construction specifications, meet the definition and may offer both greater protection and the confidence that at least a minimum level of protection has been provided. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) recommends that employers and workers who want a face covering that provides a known level of protection use face coverings that meet a new standard, called Workplace Performance and Workplace Performance Plus masks, for workplaces. As discussed in the Summary and Explanation for paragraph (i) (Section VI.I. of this preamble), the new NIOSH criteria and the ASTM Specification for Barrier Face Coverings, F3502-21 (ASTM Standard) provide a greater level of source control performance for workers when wearing the face covering according to manufacturer's instructions. The NIOSH criteria require that face coverings conform to the ASTM Standard and meet additional quantitative leakage criteria. Although not required by the standard, OSHA notes that face coverings that meet ASTM F3502-21 requirements and the new NIOSH criteria may offer a higher level of source control and wearer protection than those face coverings that do not meet a consensus standard.
A “facemask” means a surgical, medical procedure, dental, or isolation mask that is FDA-cleared, authorized by an FDA EUA, or offered or distributed as described in an FDA enforcement policy. Facemasks may also be referred to as “medical procedure masks.” This definition provides clarification about the exception to the face covering requirement under paragraph (i)(1)(iii) that permits facemask use in lieu of face coverings. OSHA notes that facemasks are not respirators, which are also defined in this section.
Facemasks provide protection against exposure to splashes, sprays, and spatter of body fluids. Facemasks offer both source control, as defined in this section under face coverings, and protection for the wearer. OSHA has previously established that facemasks are essential PPE for employees in healthcare, under both the general PPE standard (29 CFR part 1910.132) and the Bloodborne Pathogens standard (29 CFR part 1910.1030). Although not required, the Summary and Explanation for paragraph (i) (Section VI.I. of this preamble) addresses their inclusion in this standard. Additional information on such facemasks can be found in relevant FDA guidance.
“Fully vaccinated” means (i) a person's status 2 weeks after completing primary vaccination with a COVID-19 vaccine with, if applicable, at least the minimum recommended interval between doses in accordance with the approval, authorization, or listing that is: (A) Approved or authorized for emergency use by the FDA; (B) listed for emergency use by the World Health Organization (WHO); or (C) administered as part of a clinical trial at U.S. site, if the recipient is documented to have of primary vaccination with the “active” (not placebo) COVID-19 vaccine candidate, for which vaccine efficacy has been independently confirmed ( e.g. , by a data and safety monitoring board) or if the clinical trial participant from the U.S. sites had received a COVID-19 vaccine that is neither approved nor authorized for use by the FDA but is listed for emergency use by the WHO. Currently-authorized FDA vaccines include Janssen (Johnson & Johnson), which is a single-dose primary vaccination, and Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna, which have a two-dose primary vaccination series. This definition is consistent with the CDC definition of fully vaccinated (CDC, September 16, 2021).
The definition of “fully vaccinated” also means a person's status 2 weeks after receiving the second dose of any combination of two doses of a COVID-19 vaccine that is approved or authorized by the FDA, or listed as a two-dose series by the WHO ( i.e., heterologous primary series of such vaccines, receiving doses of different COVID-19 vaccines as part of one primary series). The second dose of the series must not be received earlier than 17 days (21 days with a 4-day grace period) after the first dose (CDC, October 15, 2021). OSHA has included this because people who have received a heterologous primary vaccination series (including mixing of mRNA, adenoviral, and mRNA plus adenoviral products) are considered by the CDC to also meet this definition. OSHA considers a vaccination series that meets the definition in subparagraph (ii) to be a primary vaccination for purposes of the requirements to support vaccination in paragraph (f).
The employer obligations under the ETS differ based on whether each employee is fully vaccinated. This definition is relevant to the definition of mandatory vaccination policy, in this paragraph (c), as well as the provisions under paragraph (d) regarding written vaccination policy requirements and relevant procedures for workers who are fully vaccinated. Paragraph (e)(2) also addresses fully vaccinated employees, including the determination of vaccination status and acceptable forms of proof. Lastly, the definition provides clarity with regard to the requirements of paragraphs (g) and (i) respectively, which contain requirements for regular COVID-19 testing and face covering use among employees who are not fully vaccinated.
Paragraph (e) requires employers to determine each employee's vaccination status, including whether they are fully or partially vaccinated. By “partially vaccinated,” OSHA means someone who has started a primary vaccination series but not completed it ( e.g., has received one dose of a two-dose series) or has completed their primary vaccination and two weeks have not elapsed since the last dose of the primary vaccination.
A “mandatory vaccination policy” is an employer policy requiring each employee to be fully vaccinated. To meet the definition of a mandatory vaccination policy, the policy must require: Vaccination of all employees, including vaccination of all new employees as soon as practicable, other than those employees (1) for whom a vaccine is medically contraindicated, (2) for whom medical necessity requires a delay in vaccination, 91 or (3) who are legally entitled to a reasonable accommodation under federal civil rights laws because they have a disability or sincerely held religious beliefs, practices, or observances that conflict with the vaccination requirement. OSHA intends that “employee,” as used in this definition, includes only employees that are covered by this ETS and does not include employees who are excluded from coverage under paragraph (b)(3).
91 As defined by CDC's informational document, Summary Document for Interim Clinical Considerations for Use of COVID-19 Vaccines Currently Authorized in the United States (CDC, September 29, 2021).
Paragraph (d)(1) of the standard requires an employer to establish, implement, and enforce a written mandatory vaccination policy that meets this definition. The benefits of vaccination, including the effectiveness of vaccination mandates, are discussed in Grave Danger (Section III.A. of this preamble) and Need for the ETS (Section III.B. of this preamble).
OSHA recognizes that vaccination policies may vary, as indicated in paragraph (d)(2). Any policy that permits the employee to choose between vaccination and COVID-19 testing and face covering use would not be considered a mandatory vaccination policy under paragraph (d)(1), although such policy is permissible under paragraph (d)(2). In some cases, employers may implement vaccination policies that differ by location or type of business operation and thus the application of paragraph (d)(2) might vary across an employer's workforce. This is discussed in greater detail in the Summary and Explanation for paragraph (d) (Section VI.D. of this preamble).
A “respirator” is a type of PPE that is certified by NIOSH under 42 CFR part 84 or is authorized under an EUA by the FDA. These specifications are intended to ensure some consistent level of testing, approval, and protection and to prevent the use of counterfeit respirators that will not offer adequate protection, which is important because respirators are intended to protect the wearer when directly exposed to hazards. Respirators protect against airborne hazards by removing specific air contaminants from the ambient (surrounding) air or by supplying breathable air from a safe source. Common types of respirators include filtering facepiece respirators ( e.g., N95), elastomeric respirators, and powered air-purifying respirators (PAPRs). Face coverings, facemasks, and face shields are not respirators.
As stated above, there are various types of respirators that would fall within this definition. A filtering facepiece respirator (FFR) is a negative-pressure particulate respirator with a non-replaceable filter as an integral part of the facepiece or with the entire facepiece composed of the non-replaceable filtering medium. N95 FFRs are the most common type of FFR and are the type of respirator most often used to control exposures to infections transmitted via the airborne route. When properly worn, N95 FFRs filter at least 95% of airborne particles. An elastomeric respirator is a tight-fitting respirator with a facepiece that is made of synthetic or rubber material that permits it to be disinfected, cleaned, and reused according to the manufacturer's instructions. Elastomeric respirators are equipped with replaceable cartridges, canisters, or filters. Lastly, a powered air-purifying respirator (PAPR) is an air-purifying respirator that uses a blower to force the ambient air through air-purifying elements to the inlet covering.
This standard does not require the use of respirators. This definition is included because it relates to paragraph (i)(1)(iii), which exempts employees from wearing face coverings when they are wearing respirators or facemasks. In addition, paragraph (i)(4) requires employers to permit employees to wear a respirator instead of a face covering and permits employers to provide respirators to their employees, instead of face coverings. When respirators are used pursuant to paragraph (i)(4), the employer must also comply with §1910.504, the Mini Respiratory Protection Program.
NIOSH has developed a set of regulations in 42 CFR part 84 for testing and certifying non-powered, air-purifying, particulate-filter respirators. To help address concerns about availability during the COVID-19 pandemic, the FDA has issued EUAs for certain PPE products, including respiratory protective devices such as respirators. For the purposes of this standard, respirators certified by NIOSH, under 42 CFR part 84 or authorized under an EUA by the FDA meet the definition. Additional information on such respirators can be found in relevant FDA and NIOSH guidance.
A “workplace” is a physical location ( e.g. , fixed, mobile) where the employer's work or operations are performed. It does not include an employee's residence, even if the employee is teleworking from their residence. Examples of fixed locations include: Offices, retail establishments, co-working facilities, and factories or manufacturing facilities. A workplace includes the entire site (including outdoor and indoor areas, a structure or a group of structures) or an area within a site where work or any work-related activity occurs ( e.g., taking breaks, going to the restroom, eating, entering or exiting work). The workplace includes the entirety of any space associated with the site ( e.g., workstations, hallways, stairwells, breakrooms, bathrooms, elevators) and any other space that an employee might occupy in arriving, working, or leaving. Examples of employees who have mobile workplaces include maintenance and repair technicians who go to homes or businesses to provide repair services, or those who provide delivery services.
References
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, June 14). Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/lab/naats.html. (CDC, June 14, 2021).
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, September 16). When You've Been Fully Vaccinated: How to Protect Yourself and Others. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/fully-vaccinated.html. (CDC, September 16, 2021)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, September 29). Summary Document for Interim Clinical Considerations for Use of COVID-19 Vaccines Currently Authorized in the United States. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/covid-19/downloads/summary-interim-clinical-considerations.pdf. (CDC, September 29, 2021)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, October 7). Interim Guidance for SARS-CoV-2 Testing in Non-Healthcare Workplaces. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/community/organizations/testing-non-healthcare-workplaces.html. (CDC, October 7, 2021)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, October 15). Interim Public Health Recommendations for Fully Vaccinated People. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/fully-vaccinated-guidance.html. (CDC, October 15, 2021)
Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC). (2021, October 25). What You Should Know About COVID-19 and the ADA, the Rehabilitation Act, and Other EEO Laws. https://www.eeoc.gov/wysk/what-you-should-know-about-covid-19-and-ada-rehabilitation-act-and-other-eeo-laws. (EEOC, October 25, 2021)
Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2020, November 16). COVID-19 Test Settings: FAQs on Testing for SARS-CoV-2. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/coronavirus-covid-19-and-medical-devices/covid-19-test-settings-faqs-testing-sars-cov-2. (FDA, November 16, 2020)
Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2021a, October 14). In Vitro Diagnostics EUAs—Antigen Diagnostic Tests for SARS-CoV-2. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/coronavirus-disease-2019-covid-19-emergency-use-authorizations-medical-devices/in-vitro-diagnostics-euas-antigen-diagnostic-tests-sars-cov-2. (FDA, October 14, 2021a)
Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2021b, October 14)). In Vitro Diagnostics EUAs—Molecular Diagnostic Tests for SARS-CoV-2. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/coronavirus-disease-2019-covid-19-emergency-use-authorizations-medical-devices/in-vitro-diagnostics-euas-molecular-diagnostic-tests-sars-cov-2. (FDA, October 14, 2021b)
Schulte P et al. (2021, May 19). Proposed Framework for Considering SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Testing of Unexposed Asymptomatic Workers in Selected Workplaces. J Occup Environ Med. 2021 Aug; 63(8): 646-656. Published online 2021, May 19. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8327768/. (Schulte et al., May 19, 2021)
D. Employer Policy on Vaccination
Vaccination is a vital tool to reduce the presence and severity of COVID-19 cases in the workplace, in communities, and in the nation as a whole. Despite the robust protection against COVID-19 that vaccination affords, millions of eligible individuals have not yet been vaccinated. Current efforts to increase the proportion of the U.S. population that is fully vaccinated against COVID-19 are critical to ending the COVID-19 pandemic (CDC, September 15, 2021). As described more fully in Need for the ETS (Section III.B. of this preamble), mandatory vaccination policies work. Therefore, OSHA has determined that requiring or strongly encouraging vaccination—the most effective and efficient control for reducing COVID-19—is key to ensuring the protection of workers against the grave danger of exposure to SARS-CoV-2 in the workplace (see Grave Danger, Section III.A. of this preamble). Therefore, this ETS requires employers to adopt mandatory vaccination policies for their workplaces, with an exception for employers that instead adopt a policy allowing employees to elect to undergo regular COVID-19 testing and wear a face covering at work in lieu of vaccination. In Need for the ETS (Section III.B of this preamble), OSHA explains its rationale for providing the exception.
Paragraph (d) of this ETS is a critical element in ensuring employees' protection, as it requires covered employers to develop, implement, and enforce written policies on COVID-19 vaccination for their workforces. Paragraph (d)(1) requires the employer to establish, implement, and enforce a written mandatory vaccination policy. As defined in paragraph (c), a mandatory vaccination policy is an employer policy requiring each employee to be fully vaccinated. Such a policy must require vaccination of all employees, other than those employees who fall into one of three categories: (1) Those for whom a vaccine is medically contraindicated, (2) those for whom medical necessity requires a delay in vaccination, or (3) those who are legally entitled to a reasonable accommodation under federal civil rights laws because they have a disability or sincerely held religious beliefs, practices, or observances that conflict with the vaccination requirement. The policy must also require all new employees to be vaccinated as soon as practicable.
Paragraph (d)(2) is a limited exemption from the mandatory vaccination policy requirement. As discussed in Need for the ETS (Section III.B. of this preamble), vaccination mandates are effective at increasing overall vaccination rates and protecting employees and, therefore, the agency encourages all employers to implement a mandatory vaccination policy. Under paragraph (d)(2), however, employers can avoid the mandate in paragraph (d)(1) if the employer establishes, implements, and enforces a written policy allowing any employee not subject to a mandatory vaccination policy to choose either to: (1) Be fully vaccinated against COVID-19 or (2) provide proof of regular testing for COVID-19 in accordance with paragraph (g) of this section and wear a face covering in accordance with paragraph (i). An employer who chooses to operate under paragraph (d)(2), however, must still offer the support for vaccination required under paragraph (f) and may not prevent employees from getting vaccinated. Adopting a policy under paragraph (d)(2) simply means that employees themselves may choose not to get vaccinated, in which case they must get tested and wear face coverings per the requirements of the standard.
OSHA recognizes there may be employers who develop and implement partial mandatory vaccination policies, i.e., that apply to only a portion of their workforce. An example might be a retail corporation employer who has a mixture of staff working at the corporate headquarters, performing intermittent telework from home, and working in stores serving customers. In this type of situation, the employer may choose to require vaccination of only some subset of its employees ( e.g., those working in stores), and to treat vaccination as optional for others ( e.g., those who work from headquarters or who perform intermittent telework). This approach would comply with the standard so long as the employer complies in full with paragraph (d)(1) and (d)(2) for the respective groups.
OSHA uses the terms establish, implement, and enforce in paragraph (d) to emphasize that it is necessary for an employer to first determine its policy and create a written record of that policy. After determining the policy, an employer must then ensure that it is following the policy, as laid out in its written plan. Finally, employers must ensure that they enforce the requirements of their policies with respect to their workforce, through training and the use of such mechanisms as work rules and the workplace disciplinary system, if necessary. These requirements apply to the written policy required under paragraph (d), whether employers choose to implement the mandatory vaccination policy under paragraph (d)(1) or utilize the exemption under paragraph (d)(2) for all or a portion of their workforce.
To ensure that employers' vaccination policies under paragraph (d) are comprehensive and effective, the policies should address all of the applicable requirements in paragraphs (e)-(j) of this standard, including: Requirements for COVID-19 vaccination; applicable exclusions from the written policy ( e.g., medical contraindications, medical necessity requiring delay in vaccination, or reasonable accommodations for workers with disabilities or sincerely held religious beliefs); information on determining an employee's vaccination status and how this information will be collected (as described in paragraph (e)); paid time and sick leave for vaccination purposes (as described in paragraph (f)); notification of positive COVID-19 tests and removal of COVID-19 positive employees from the workplace (as described in paragraph (h)); information to be provided to employees (pursuant to paragraph (j)— e.g., how the employer is making that information available to employees); and disciplinary action for employees who do not abide by the policy. In addition to addressing the requirements of paragraphs (e)-(j) of this standard, the employer should include all relevant information regarding the policy's effective date, who the policy applies to, deadlines ( e.g., for submitting vaccination information, for getting vaccinated), and procedures for compliance and enforcement, all of which are necessary components of an effective plan. Having a comprehensive written policy will provide a solid foundation for an effective COVID-19 vaccination program, while making it easier for employers to inform employees about the program-related policies and procedures, as required under paragraph (j)(1).
If an employer utilizes the exemption under paragraph (d)(2), its workplace may contain employees who are vaccinated and unvaccinated. This might be the case even for employers who establish a mandatory vaccination policy under paragraph (d)(1); for example, an employer with a mandatory vaccination policy might have employees who cannot be vaccinated for medical reasons. Given the additional safety protocols under this standard for individuals who are not fully vaccinated (see paragraphs (g) and (i)), an employer who has both vaccinated and unvaccinated employees will have to develop and include the relevant procedures for two sets of employees in the written policy. The procedures for those who are fully vaccinated should contain all the information previously discussed relevant to establishing, implementing, and enforcing a comprehensive written policy. However, the procedures applicable to employees who are not fully vaccinated ( i.e., those who decline vaccination, those who are unable to receive vaccination and are, absent undue hardship to their employers, entitled to reasonable accommodation) and those who are unable to provide proof of vaccination as required by paragraph (e) (who must be treated as not fully vaccinated), must include COVID-19 testing and face covering use as required by paragraphs (g) and (i), respectively, unless the reasonable accommodation from vaccination removes the employee from the scope of §1910.501 ( e.g., full time telework consistent with one of the exceptions in §1910.501(b)(3)). OSHA intends that such an employer will develop one written plan that includes different policies and procedures for vaccinated and unvaccinated employees. The requirements of paragraphs (e), (f), (h), and (j) should be addressed in the policy regardless of the vaccination requirements adopted by the employer.
As with all elements of the written plan, an effective written plan will explain the testing requirements contained in paragraph (g) for unvaccinated employees, and how the employer will implement and enforce those policies. As described in paragraph (g)(1), the testing requirements differ for employees who report at least once every 7 days to a workplace compared to those who do not. Thus, the policy may describe different testing procedures for those different groups of employees, depending on how often they physically report to a workplace where other individuals are present. As described in paragraph (g)(3), the testing requirements are temporarily suspended for 90 days following a positive COVID-19 test or diagnosis. Thus, the employer's policy and procedures to implement this temporary suspension of testing should be included in their written workplace policy. In addition to the testing requirements in paragraph (g), an effective policy must address mandatory face covering use as described in paragraph (i), including procedures for employee compliance. Employers can get more information on the requirements for paragraphs (e) through (j), and what they must do to comply with those provisions of the standard, in the relevant Summary and Explanation sections (see Section VI. of this preamble).
As an employer develops their written policy, they must address how the policy will apply to new employees. Although many new hires will be fully vaccinated, there should be procedures within the plan to collect information about the new employee's vaccination status, and determine when an unvaccinated new hire must be vaccinated and, for employers using a plan under paragraph (d)(2), when COVID-19 testing and face covering use will commence if an employee remains unvaccinated. All new hires should be treated similarly to any employee who has not entered the workplace in the last seven days and will need to be fully vaccinated or provide proof of a negative COVID-19 test within the last seven days prior to entering the workplace for the first time. It is not OSHA's intention to discourage employers from hiring new employees, but rather to ensure that new employees are as well-protected from COVID-19 hazards in the workplace as current employees and are less likely to spread the virus to other employees.
An employer may have already developed and implemented a written policy on vaccination, testing, and/or face covering use to protect employees from COVID-19. It is not OSHA's intent for employers to duplicate current effective policies covering the requirements of this ETS; however, each employer with a current policy must evaluate that policy to ensure it satisfies all of the requirements of this rule. Employers with existing policies must modify and/or update their current policies to incorporate any missing required elements, and must provide information on these new updates or modifications to all employees in accordance with paragraph (j)(1). Once the employer has developed its policy pursuant to paragraph (d), the policy must be reduced to writing in order to be compliant with paragraph (d).
The note to paragraph (d) was included in recognition that, under federal law, some employees may be entitled to a reasonable accommodation from their employer, absent undue hardship. If the worker requesting a reasonable accommodation cannot be vaccinated and/or wear a face covering because of a disability, as defined by the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), that worker may be entitled to a reasonable accommodation. In addition, if the vaccination, and/or testing for COVID-19, and/or wearing a face covering conflicts with a sincerely held religious belief, practice or observance, a worker may be entitled to a reasonable accommodation. Such accommodations exist independently of the Occupational Safety and Health Act and, therefore, OSHA does not administer or enforce these laws. Examples of relevant federal laws under which an accommodation can be requested include the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) and Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964.
For more information, the note refers to a resource produced by the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC), which is responsible for enforcing federal laws that prohibit employment-related discrimination based on a person's race, color, religion, sex (including pregnancy, gender identity, and sexual orientation), national origin, age (40 or older), disability, or genetic information. The EEOC resource listed in the note, What You Should Know About COVID-19 and the ADA, the Rehabilitation Act, and Other EEO Laws, available at https://www.eeoc.gov/wysk/what-you-should-know-about-covid-19-and-ada-rehabilitation-act-and-other-eeo-laws, should be helpful to employers in navigating employees' requests for accommodations, including the process for determining a reasonable accommodation and information on undue hardship (EEOC, October 25, 2021). An additional resource that might be helpful is the CDC's informational document, Summary Document for Interim Clinical Considerations for Use of COVID-19 Vaccines Currently Authorized in the United States (CDC, September 29, 2021), which lists the recognized clinical contraindications to receiving a COVID-19 vaccine.
References
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, September 15). Science Brief: Background rationale and evidence for public health recommendations for fully vaccinated people. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/science/science-briefs/fully-vaccinated-people.html. (CDC, September 15, 2021)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, September 29). Summary Document for Interim Clinical Considerations for Use of COVID-19 Vaccines Currently Authorized in the United States. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/covid-19/downloads/summary-interim-clinical-considerations.pdf. (CDC, September 29, 2021)
Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC). (2021, October 25). What You Should Know About COVID-19 and the ADA, the Rehabilitation Act, and Other EEO Laws. https://www.eeoc.gov/wysk/what-you-should-know-about-covid-19-and-ada-rehabilitation-act-and-other-eeo-laws. (EEOC, October 25, 2021)
E. Determination of Employee Vaccination Status
To comply with the requirements of the standard, it is essential that employers are aware of each employee's vaccination status. As discussed in the Summary and Explanation for paragraph (d) (Section VI.D. of this preamble), effective implementation and enforcement of a written vaccination policy requires the employer to know the vaccination status of all employees. Furthermore, the employer must know each employee's vaccination status in order to ensure that the vaccination, testing, and face covering requirements of the standard are met. As such, paragraph (e) includes provisions for determining each employee's vaccination status. The standard requires employers to determine the vaccination status of each employee (paragraph (e)(1)), and also to maintain records of each employee's vaccination status, preserve acceptable proof of vaccination for each employee who is fully or partially vaccinated, and maintain a roster of each employee's vaccination status (paragraph (e)(4)). As discussed more fully below, maintenance of records in accordance with this paragraph is subject to applicable legal requirements for confidentiality of medical information. Additional provisions in paragraph (e) define acceptable proof of vaccination status for vaccinated employees (paragraph (e)(2)) and provide that any employee who does not submit an acceptable form of proof of vaccination status must be treated as not fully vaccinated (paragraph (e)(3)).
Paragraph (e)(1) requires the employer to determine the vaccination status of each employee, including whether the employee is fully vaccinated. Under paragraph (e)(2), the employer must require each vaccinated employee to provide acceptable proof of vaccination status, including whether they are fully or partially vaccinated. This is an ongoing requirement for the employer ( i.e., the employer needs to update this information as employees proceed through the vaccination process).
Paragraph (e)(2) defines what “acceptable proof of vaccination status” means for purposes of the ETS, and employers must accept any of the proofs listed in accordance with the terms of the standard and as explained more fully below. Under paragraph (e)(2), the following are acceptable for proof of vaccination: (i) The record of immunization from a health care provider or pharmacy; (ii) a copy of the U.S. CDC COVID-19 Vaccination Record Card (CDC Form MLS-319813_r, published on September 3, 2020) (CDC, October 5, 2021); (iii) a copy of medical records documenting the vaccination; (iv) a copy of immunization records from a public health, state, or tribal immunization information system; or (v) a copy of any other official documentation that contains the type of vaccine administered, date(s) of administration, and the name of the health care professional(s) or clinic site(s) administering the vaccine(s).
To be acceptable as proof of vaccination, any documentation should generally include the employee's name, type of vaccine administered, date(s) of administration, and the name of the health care professional(s) or clinic site(s) administering the vaccine(s). In some cases, state immunization records may not include one or more of these data fields, such as clinic site; in those circumstances, an employer can still rely upon the State immunization record as acceptable proof of vaccination. OSHA notes that clinic sites can include temporary vaccination facilities used during large vaccine distribution campaigns, such as schools, churches, or sports stadiums. Copies, including digital copies, of the listed forms of proof are acceptable means of documentation so long as they clearly and legibly display the necessary information. Digital copies can include, for example, a digital photograph, scanned image, or PDF of an acceptable form of proof. Some state governments are utilizing digital COVID-19 vaccine records showing the same information as the U.S. CDC COVID-19 Vaccination Record Card (CDC Form MLS-319813_r, published on September 3, 2020) and providing quick response (QR) codes that when scanned will provide the same information (see, e.g., New York State Government, n.d., Retrieved October 4, 2021). In certain states, the QR code confirms the vaccine record as an official record of the state (see, e.g., State of California, n.d., Retrieved October 7, 2021) and therefore would provide acceptable proof of vaccination under the ETS (see paragraph (e)(2)(iv)). However, as discussed later, the employer must retain a copy of the vaccination information retrieved when the QR code is scanned, not just the QR code itself, to comply with paragraph (e)(4). In requesting proof of vaccination, the employer must take care to comply with any applicable Federal laws, including requirements under the Privacy Act, 5 U.S.C. 552a, and the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), 42 U.S.C. 12101 et seq.
Each employee who has been partially or fully vaccinated should be able to provide one of the forms of acceptable proof listed above (paragraphs (e)(2)(i)-(e)(2)(v)). An employee who does not possess their COVID-19 vaccination record ( e.g., because it was lost or stolen) should contact their vaccination provider ( e.g., local pharmacy, physician's office) to obtain a new copy or utilize their state health department's immunization information system. In instances where an employee is unable to produce acceptable proof of vaccination under paragraphs (e)(2)(i)-(e)(2)(v), paragraph (e)(2)(vi) provides that a signed and dated statement by the employee will be acceptable. The employee's statement must: (A) Attest to their vaccination status (fully vaccinated or partially vaccinated); (B) attest that they have lost or are otherwise unable to produce proof required by the standard; and (C) include the following language: “ I declare (or certify, verify, or state) that this statement about my vaccination status is true and accurate. I understand that knowingly providing false information regarding my vaccination status on this form may subject me to criminal penalties. ” The note to paragraph (e)(2)(vi) explains that an employee who attests to their vaccination status should, to the best of their recollection, include the following information in their attestation: The type of vaccine administered; date(s) of administration; and the name of the health care professional(s) or clinic site(s) administering the vaccine(s). For example, some of the information may be easier to recall, such as receiving a vaccine at a mass vaccination site or local pharmacy, while the dates of administration might only be remembered as falling within a particular month or months. OSHA understands that employees may not be able to recall certain information, such as the type of vaccine received. Employees providing attestations should include as much of this information as they can remember to the best of their ability.
Any statement provided under paragraph (e)(2)(vi) must include an attestation that the employee is unable to produce another type of proof of vaccination (paragraph (e)(2)(vi)(B)). Thus, before an employee statement will be acceptable for proof of vaccination under paragraph (e)(2)(vi), the employee must have attempted to secure alternate forms of documentation via other means ( e.g., from the vaccine administrator or their state health department) and been unsuccessful in doing so. The agency recognizes that securing vaccination documentation may be challenging for some members of the workforce, such as migrant workers, employees who do not have access to a computer, or employees who may not recall who administered their vaccines ( e.g., if the vaccination was provided at a temporary location, such as a church, or during a state or local mass vaccination campaign). Thus, for employees who have no other means of obtaining proof of vaccination, the standard permits employers to accept attestations meeting the requirements in paragraph (e)(2)(vi) as proof of vaccination. However, employers should explain to their employees that they need to produce vaccination proof through the other means listed in paragraph (e)(2), such as by contacting the vaccination administrator, if they are able to do so. Once the employee has provided a signed and dated attestation that meets the requirements of paragraph (e)(2)(vi), the employer no longer needs to seek out one of the other forms of vaccination proof for that employee and, depending on the content of the attestation, the employer may consider that employee either fully or partially vaccinated for purposes of the ETS.
Recently, there has been evidence of fraud associated with people attesting to their vaccination status (Bergal, September 16, 2021). While employers may not invite or facilitate fraud, the ETS does not require employers to monitor for or detect fraud. By defining what constitutes acceptable proof of vaccination under the ETS, OSHA is ensuring that employers can accept proof meeting the requirements of paragraph (e) for purposes of compliance with the standard. However, the standard's requirements for proof of vaccination are integral to ensuring that employees are protected appropriately, either through vaccination (the preferred and most effective workplace control in this ETS), or through regular testing and use of face coverings. Thus, it is paramount that employees provide truthful information regarding their vaccination status.
As discussed in more detail in the Summary and Explanation for paragraph (j) (Section VI.J. of this section), 18 U.S.C. 1001(a), which provides for fines or imprisonment of generally up to 5 years for any person who “in any matter within the jurisdiction” of the executive branch U.S. Government “knowingly and willfully” engages in any of the following:
(1) Falsifies, conceals, or covers up by any trick, scheme, or device a material fact;
(2) makes any materially false, fictitious, or fraudulent statement or representation; or
(3) makes or uses any false writing or document knowing the same to contain any materially false, fictitious, or fraudulent statement or entry.
Similarly, the OSH Act recognizes that OSHA's ability to protect workers' safety and health hinges on truthful reporting. For that reason section 17(g) of the OSH Act subjects anyone who “knowingly makes any false statement, representation, or certification in any application, record, report, plan, or other document filed or required to be maintained pursuant to this chapter” to criminal penalties. 29 U.S.C. 666(g). False statements made in any proof submitted under paragraph (e)(2) of the standard could fall under either or both of 18 U.S.C. 1001 or section 17(g) of the OSH Act. And by requiring a specific declaration about the truth and accuracy of employee statements provided under paragraph (e)(2)(vi), employees who are unable to provide any means of proof other than their own attestation are being made aware that their words are being held to the same standard of truthfulness as any other record presented for proof of vaccination.
OSHA notes that these same prohibitions on false statements and documentation can apply to employers. If an employer knows that proof submitted by an employee is fraudulent, and even with this knowledge, accepts and maintains the fraudulent proof as a record of compliance with this ETS, it may be subject to the penalties in 18 U.S.C. 1001 and 17(g) of the OSH Act.
Paragraph (e)(3) provides the mechanism for employers to determine vaccination status for employees who do not submit any of the acceptable forms of proof of vaccination status. Under paragraph (e)(3), any employee who does not provide their employer with one of the acceptable forms of proof of vaccination status in paragraph (e)(2) must be treated as not fully vaccinated for the purpose of the standard. An unvaccinated employee does not need to provide any documentation regarding vaccination status under this ETS; however, failing to provide acceptable proof of vaccination status will signal the employer to consider the employee as not fully vaccinated and to note that as their status in the roster. For employers that include COVID-19 testing in their written policies under paragraph (d), employees without acceptable proof of vaccination status must submit to weekly tests (as required by paragraph (g)) and wear a face covering (as required by paragraph (i)).
Paragraph (e)(4) requires the employer to maintain a record of each employee's vaccination status and preserve acceptable proof of vaccination for each employee who is fully or partially vaccinated. As discussed previously, the employer has various options for acquiring proof of vaccination from each employee. An employer may allow employees to provide a digital copy of acceptable records, including, for example, a digital photograph, scanned image, or PDF of such a record that clearly and legibly displays the necessary vaccination information. However, to be in compliance with paragraph (e)(4), the employer must ensure they are able to maintain a record of each employee's vaccination status. Therefore, obtaining an employee's vaccination information verbally would not comply with paragraph (e)(2) or satisfy the record maintenance requirements of the standard. Similarly, the record maintenance requirements of paragraph (e)(4) cannot be fulfilled by an employee merely showing the employer their vaccination status ( e.g., by bringing the CDC COVID-19 vaccination card to the workplace and showing it to an employer representative or showing an employer representative a picture of the immunization records on a personal cellphone). To satisfy paragraph (e)(4), the employer must retain a copy of the documentation. As mentioned above, some states and local governments utilize QR codes to facilitate proof of vaccination. This can be an acceptable form of proof for compliance with the standard so long as the employer retains a copy of the information retrieved by scanning the QR code and maintains that record. Required records of vaccination status can be maintained physically or electronically, but the employer must ensure they have access to the records at all times.
In addition to obtaining and maintaining individual records of each employee's vaccination status and preserving acceptable proof of vaccination for each employee who is partially or fully vaccinated, under paragraph (e)(4) the employer must maintain a roster of each employee's vaccination status, subject to applicable confidentiality requirements. The roster must list all employees and clearly indicate for each one whether they are fully vaccinated, partially (not fully) vaccinated, not fully vaccinated because of a medical or religious accommodation (see Note to paragraph (d)), or not fully vaccinated because they have not provided acceptable proof of their vaccination status. As noted previously, any employee that has not provided acceptable proof of their vaccination status must be treated as not fully vaccinated. Although unvaccinated employees will not have proof of vaccination status, the standard requires the employer to include all employees, regardless of vaccination status, on the roster.
The roster allows the employer to easily access the vaccination status for any employee quickly and easily. This will be useful should the employer need to respond to a request from an employee or employee representative for the aggregate number of fully vaccinated employees at a workplace (along with the total number of employees at that workplace), as required under paragraph (l)(2). Additionally, the roster will help the employer implement the written policy developed in accordance with paragraph (d) and comply with other requirements of the ETS. And finally, the roster, which must be provided to OSHA on request (paragraph (l)(3)), will aid OSHA's ability to effectively and efficiently enforce this ETS.
The records and roster required by paragraph (e)(4) are considered to be employee medical records and must be maintained as such records in accordance with 29 CFR 1910.1020 and must not be disclosed except as required or authorized by this ETS or other federal law, including the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), 42 U.S.C. 12101 et seq. These records and roster are not subject to the retention requirements of 29 CFR 1910.1020(d)(1)(i) but must be maintained and preserved while this ETS remains in effect. OSHA considers vaccination records required by paragraphs (e)(2) and (e)(4) of the ETS to be employee medical records concerning the health status of an employee and is requiring this personally identifiable medical information to be maintained in a confidential manner. OSHA notes that under paragraph (e)(4), vaccination records and rosters are employee medical records, and must be treated as employee medical records under 29 CFR 1910.1020, without regard to whether the records satisfy the definition of employee medical record at 29 CFR 1910.1020(c)(6)(i).
Paragraph (e) in 29 CFR 1910.1020 includes requirements for access to employee medical records by employees, their designated representatives, and OSHA. However, as discussed in more detail below, paragraph (l) of the ETS includes specific timeframes within which employers must make vaccine records available to employees, OSHA, and other specified individuals. Accordingly, the timeframes for providing access to employee medical records in 29 CFR 1910.1020(e) do not apply, and employers must follow the specific timeframes set forth in paragraph (l) of the ETS for providing access to vaccination records.
Additionally, 29 CFR 1910.1020(d) addresses the preservation of employee exposure and medical records. Paragraph (d)(1)(i) in section 1910.1020 generally provides that unless a specific occupational safety and health standard provides a different period of time, each employer must preserve and maintain employee medical records for at least the duration of employment plus thirty (30) years. Paragraph (e)(4) of the ETS specifically provides that the vaccination records required by the ETS are not subject to the retention requirements of 29 CFR 1910.1020(d)(1)(i). Instead, paragraph (e)(4) states that vaccination records must be maintained and preserved only so long as the ETS remains in effect.
Finally, while the provisions on timeframes for access to records and the retention provisions of 29 CFR 1910.1020 do not apply to vaccine records required by the ETS, other provisions in that regulation can still apply. For example, 29 CFR 1910.1020(h) includes requirements for the transfer of employee medical records when an employer ceases to do business.
OSHA recognizes the possibility that an employer may have already collected information about the vaccination status of employees, including proof of vaccination, prior to the effective date of this ETS. Under paragraph (e)(5), when an employer has ascertained employee vaccination status prior to the effective date of the ETS through another form of attestation or proof, and retained records of that ascertainment, the employer is exempt from the requirements in paragraphs (e)(1)-(e)(3). The exemption applies only for each employee whose fully vaccinated status has been documented prior to the effective date of the standard. For example, an employer may have asked each employee to self-report their vaccination status without requiring the employee to provide any form of proof. If that self-reporting was through oral conversation only, and not documented in some way, the employer is not considered to have retained records of that ascertainment for the purposes of this ETS. However, if, for example, the employer had the employees provide their vaccine information on a dated form, or through individual emails retained by the employer, or on an employer portal specifically created for employees to provide documentation status, or the employer created and retained some other means of documentation, the employer is considered to have retained records of ascertainment for the purposes of this ETS. Even if the record does not have all of the elements of the acceptable forms of proof listed in paragraph (e)(2), so long as the employer has ascertained employee vaccination status prior to the effective date of the ETS through another form of attestation or proof, and retained records of that ascertainment, the employer does not need to re-determine vaccination status (paragraph (e)(1)) or obtain proof of vaccination status (paragraph (e)(2)) for fully vaccinated employees. For purposes of paragraph (e)(4), the employer's records of vaccination status for each employee whose fully vaccinated status was previously documented constitute acceptable proof of vaccination. However, the employer must still develop a roster of each employee's vaccination status and include on that roster the employees for whom it had previously determined and retained records of vaccination status. OSHA notes that if the employer has not ascertained employee vaccination status for employees prior to the effective date of the ETS, then all requirements of paragraph (e) would apply. And all requirements of paragraph (e) also apply with respect to employees for whom the employer ascertained only partial vaccination status prior to the effective date of the ETS.
References
Bergal J. (2021, September 16). Fake Vaccine Card Sales Have Skyrocketed Since Biden Mandate. https://www.pewtrusts.org/en/research-and-analysis/blogs/stateline/2021/09/16/fake-vaccine-card-sales-have-skyrocketed-since-biden-mandate . (Bergal, September 16, 2021).
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, October 5). Getting Your CDC COVID-19 Vaccination Record Card. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/vaccination-card.html . (CDC, October 5, 2021).
New York State Government. (n.d.) Excelsior Pass and Excelsior Pass Plus. Retrieved October 4, 2021 from https://covid19vaccine.health.ny.gov/excelsior-pass-and-excelsior-pass-plus . (New York State Government, n.d., Retrieved October 4, 2021).
State of California. (n.d.) Frequently Asked Questions. Retrieved October 7, 2021 from https://myvaccinerecord.cdph.ca.gov/faq . (State of California, n.d., Retrieved October 7, 2021).
F. Employer Support for Employee Vaccination
As discussed in the Summary and Explanation for paragraph (d) (Section VI.D. of this preamble), as well as in Grave Danger and Need for the ETS (Sections III.A. and III.B. of this preamble), vaccination is the single most efficient and effective method for protecting unvaccinated workers from the grave danger posed by COVID-19. This emergency temporary standard is therefore designed to strongly encourage vaccination. As discussed in detail below, paragraph (f) requires employers to support vaccination by providing employees reasonable time, including up to four hours of paid time, to receive each primary vaccination dose, and reasonable time and paid sick leave to recover from side effects experienced following each primary vaccination dose. For purposes of the requirements to support vaccination in paragraph (f), OSHA considers a vaccination series that meets the criteria in subparagraph (ii) of the definition of “fully-vaccinated” ( i.e., a heterologous primary series of such vaccines, receiving doses of different COVID-19 vaccines as part of one primary series) to be a primary vaccination series, along with the primary vaccination described in subparagraph (i) of that definition (see the Summary and Explanation for paragraph (c), Section VI.C. of this preamble, for more information on the definition of fully vaccinated).
Removing logistical barriers to obtaining vaccination is essential to increasing workforce vaccination rates, and one such barrier for many employees is their lack of time off of work to receive the vaccine and recover from any potential side effects (SEIU Healthcare, February 8, 2021). Employees' concerns about missing work to obtain and recover from a COVID-19 vaccination dose are well documented. In a McKinsey survey, 12% of respondents stated that the time spent away from work to get vaccinated or due to vaccine side effects was a barrier to vaccination (Azimi et al., April 9, 2021). In a survey conducted of unvaccinated adults in April 2021, a fifth of respondents said they were very or somewhat concerned that they may need to take time off to go and get the vaccine, and 48% of respondents said that they were very or somewhat concerned that they might miss work if the vaccine side effects make them feel sick (KFF, May 6, 2021). Black and Hispanic adults were particularly worried about the potential time necessary to receive the vaccine and to recover from vaccine side effects; 64% of unvaccinated Hispanic adults and 55% of unvaccinated Black adults expressed concern that they might have to miss work due to the side effects of a COVID-19 vaccine, and 30% of Hispanic adults and 23% of Black adults were concerned that they might need to take time off work to get a COVID-19 vaccine (KFF, May 6, 2021; KFF, May 17, 2021). News and journal articles further evince this concern (Roy et al., December 29, 2020; Cleveland Documenters, 2021; Rosenberg and Stein, August 18, 2021).
This concern reflects the fact that many workers do not have access to paid time off to receive vaccination or to recover from side effects. A KFF survey found that only half of all workers reported that their employer provided them with paid time off either to get a COVID-19 vaccine or to recover from any side effects (KFF, June 30, 2021). A subsequent KFF survey found that only about one-third of workers were sure that their employer offered them paid time off to get a COVID-19 vaccine and recover from side effects (KFF, September 28, 2021). Although employee access to paid sick leave is less of a concern for employers with 100 or more employees, approximately 12% of employees in these situations do not have paid sick leave (BLS, September 2021) and in some cases, employees may have already exhausted paid sick leave they have received and would need additional time from their employers to recover from vaccine side effects.
The scarcity of paid time off for vaccination and side effect recovery is particularly acute for certain demographic groups. The June 2021 KFF survey found that only 38% of Black workers reported getting either paid time off to get a COVID-19 vaccine or to recover from side effects, and that only 41% of workers with household incomes less than $40,000 annually had access to such paid time off (KFF, June 30, 2021). Similarly, the September 2021 KFF survey found that lower-wage workers were particularly unlikely to report access to paid time off for vaccination or recovery, with only 23% of workers whose household incomes was less than $40,000 reporting that they could take paid time off to get vaccinated, and only 28% of that group reporting that they could take paid time off to recover from side effects (KFF, September 28, 2021). Lower-wage workers' lack of access to paid time off for vaccination comports with a different report indicating that, before the pandemic, about 65% of the lowest-wage workers had no access to paid sick leave, meaning that any time off for vaccination or recovery would result in lost wages for those who can least afford those losses (BLS, September 2021). The need for paid time off to receive vaccination is also particularly important for workers with disabilities and workers in rural areas because travel to and from vaccination sites may take more time or be more logistically difficult for those populations (National Safety Council, 2021).
Paying workers for the time spent to receive vaccination and to recover from side effects has proven to be an effective method for increasing vaccination rates. In June 2021, KFF found that approximately 75% of employed adults surveyed who received paid time off to get the vaccine or to recover from side effects had received at least one dose of the vaccine compared to only 51% of those surveyed who did not receive paid time off from their employer (KFF, June 30, 2021). KFF also found that employees who are provided paid time off and are encouraged by their employers to get vaccinated are more likely to get vaccinated, even after controlling for demographic characteristics that may impact vaccination uptake (KFF, June 30, 2021). Another KFF survey found that 28% of unvaccinated respondents who did not want to get the vaccine as soon as possible said that they would be more likely to obtain vaccination if their employer gave them paid time off to get vaccinated and recover from any side effects (KFF, May 6, 2021). KFF has also found that increasing access to paid leave for vaccination or recovery from side effects can also help further reduce disparities in vaccination by age and income (KFF, September 28, 2021).
In a different survey, paid time off for vaccination and the recovery period post-vaccination was the single most-influential action for encouraging employee vaccination, with 75% of respondents indicating that such paid time off would significantly or moderately increase the likelihood that they would get vaccinated (Azimi et al., April 9, 2021). Another survey of nearly 9,000 service workers across large grocery, retail, food service, pharmacy, and delivery firms, found that vaccination rates were lower than other frontline workers who also regularly work in-person and indoors, and when employers supported and facilitated vaccination, such as through providing paid time off or paid sick leave for vaccination or for recovery from side effects, employee vaccination rates were higher than if no support was provided, and in May 2021, workers with paid sick leave were 15% more likely to have gotten the vaccine than workers without such leave (Bellew et al., June 2021).
To address this barrier to vaccination, paragraph (f) requires employers to support COVID-19 vaccination by providing each employee with reasonable time, including up to four hours of paid time, to receive each primary vaccination dose, and reasonable time and paid sick leave to recover from side effects experienced following any primary vaccination dose. Providing this time is essential for all unvaccinated employees who are covered by this rule to ensure that they can receive primary vaccination dose(s) and recover from side effects without sacrificing pay or their jobs. In workplaces where employers implement a mandatory vaccination policy in accordance with paragraph (d)(1) of this rule, the requirements of paragraph (f) ensure that employees are able to comply with the mandatory vaccination policy without concern about missing work to do so. In workplaces where the employer opts out of implementing a mandatory vaccination policy in accordance with paragraph (d)(2), the requirements of paragraph (f) encourage employees to choose vaccination, and ensure that employees who choose to obtain vaccination, rather than be regularly tested for COVID-19 and wear a face covering in most situations when they work near others, are not penalized for making that choice.
Paragraph (f)(1) requires employers to support COVID-19 vaccination for each employee by providing reasonable time to each employee during work hours for each of their primary vaccination dose(s), including up to four hours of paid time, at the employee's regular rate of pay, for the purposes of vaccination. Reasonable time may include, but is not limited to, time spent during work hours related to the vaccination appointment(s), such as registering, completing required paperwork, all time spent at the vaccination site ( e.g., receiving the vaccination dose, post-vaccination monitoring by the vaccine provider), and time spent traveling to and from the location for vaccination (including travel to an off-site location ( e.g., a pharmacy), or situations in which an employee working remotely ( e.g., telework) or in an alternate location must travel to the workplace to receive the vaccine).
Employers are not, however, obligated by this ETS to reimburse employees for transportation costs ( e.g., gas money, train/bus fare, etc.) incurred to receive the vaccination. This could include the costs of travel to an off-site vaccination location ( e.g., a pharmacy) or travel from an alternate work location ( e.g., telework) to the workplace to receive a vaccination dose.
Because employers are required to provide reasonable time for vaccination during work hours, if an employee chooses to receive a primary vaccination dose outside of work hours, employers are not required to grant paid time to the employee for the time spent receiving the vaccine during non-work hours. However, even if employees receive a primary vaccination dose outside of work hours, employers must still afford them reasonable time and paid sick leave to recover from side effects that they experience during scheduled work time in accordance with paragraph (f)(2).
An employer may make other efforts to facilitate vaccination of its employees by, for example, hosting a vaccine clinic at the workplace ( e.g., mobile trailer) or partnering with another entity, such as a pharmacy or healthcare provider, so that employees can be vaccinated at the workplace or at an off-site location. If an employer chooses to make the vaccine available to its employees, it must support full vaccination ( i.e., provide all doses in a primary vaccination, as applicable), and assure the availability of reasonable time and paid time to each employee to receive the full primary vaccination, and reasonable time and paid sick leave to recover from side effects that they may experience. Any additional costs incurred by the employer to bring vaccination on-site would be covered by the employer, though such an approach would likely reduce the amount of paid time needed for vaccine administration (but not side effects) because of reduced employee travel time.
Paragraph (f)(1) specifies that the amount of paid time that an employer is required to provide each employee to receive each primary vaccination dose is capped at four hours. OSHA has determined that four hours would provide reasonable time for most employees to get each vaccination dose. Vaccines are widely available to the public at clinics, pharmacies, and other locations across the country (see CDC, October 8, 2021). Providing four hours of paid time to receive each primary vaccination dose is consistent with OSHA's presumption of the amount of time needed to receive a vaccination dose in the June 2021 Healthcare ETS (86 FR 32598), and with the U.S. Office of Personnel Management's guidance to federal government agencies on the use of the emergency paid leave created for federal employees in the American Rescue Plan Act of 2021 (Public Law 117-2), which encouraged agencies to offer up to four hours of administrative leave per dose to cover time spent getting a vaccine dose, plus additional time if reasonably necessary, instead of having employees use emergency paid leave (OPM, April 29, 2021). OSHA expects that most employees will need less than four hours to receive a vaccination dose.
The maximum of four hours of paid time that employers must provide under paragraph (f)(1)(ii) for the administration of each primary vaccination dose cannot be offset by any other leave that the employee has accrued, such as sick leave or vacation leave. OSHA is concerned that employees forced to use their sick leave or vacation leave for vaccination would have a disincentive to gaining the health protection of vaccination. Employers must pay employees for up to four hours of time at the employee's regular rate of pay. This may be achieved by paying for the time to be vaccinated as work hours for up to four hours. Requiring employers to pay for vaccine administration is consistent with OSHA's normal approach of requiring employers to bear the costs of compliance with safety and health standards.
OSHA understands that employees may need much less than four hours to receive a primary vaccination dose, for example, if vaccinations are offered on-site. However, OSHA also understands that, in some circumstances, an employee may need more than four hours to receive a primary vaccination dose, in which case the additional time, as long as it is reasonable, would be considered unpaid but protected leave. The employer cannot terminate the employee if they use a reasonable amount of time to receive their primary vaccination doses. The employee may use other leave time that they have available ( e.g., sick leave or vacation time) to cover the additional time needed to receive a vaccination dose that would otherwise be unpaid.
Paragraph (f)(2) also requires employers to support COVID-19 vaccination for each employee by providing reasonable time and paid sick leave to recover from side effects experienced following any primary vaccination dose to each employee for each dose. The paid sick leave can be in the form of an employee's accrued sick leave, if available. If the employee does not have available sick leave, leave must be provided for this purpose.
Although some individuals experience no side effects from COVID-19 vaccination doses, the CDC has identified a range of side effects that other individuals may experience following a vaccination dose (CDC, April 2, 2021; CDC, September 30, 2021). Side effects may affect individuals' ability to engage in daily activities, are typically mild-to-moderate in severity, and usually go away in a few days. Common side effects include pain, redness, and swelling at the site of injection, and systemic side effects throughout the body, including tiredness, headache, muscle pain, chills, fever, and nausea. Side effects may be sufficiently severe to require the employee to take sick leave from work, but will rarely extend beyond a few days. One study found that “unanticipated paid administrative leave was only required for 4.9% and 19.79% of individuals after the first and second doses of vaccine, respectively” (Levi et al., September 25, 2021). Employees would not typically be expected to need leave solely to address redness or swelling at the site of injection, but it is not uncommon for vaccine recipients to require some recovery time for many of the other side effects. The CDC notes, however, that cough, shortness of breath, runny nose, sore throat, or loss of taste or smell are not consistent with post-vaccination symptoms and instead may be symptoms of COVID-19 or another infection (CDC, April 2, 2021).
If an employee already has accrued paid sick leave, an employer may require the employee to use that paid sick leave when recovering from side effects experienced following a primary vaccination dose. Additionally, if an employer does not specify between different types of leave ( i.e., employees are granted only one type of leave), the employer may require employees to use that leave when recovering from vaccination side effects. If an employer provides employees with multiple types of leave, such as sick leave and vacation leave, the employer can only require employees to use the sick leave when recovering from vaccination side effects. Employers cannot require employees to use advanced sick leave to cover reasonable time needed to recover from vaccination side effects under paragraph (f)(2). An employer may not require an employee to accrue negative paid sick leave or borrow against future paid sick leave to recover from vaccination side effects. In other words, the employer cannot require an employee to go into the negative for paid sick leave if the employee does not have accrued paid sick leave when they need to recover from side effects experienced following a primary vaccination dose. Neither the paid time required to receive any vaccine dose(s) nor the paid sick leave required to recover from side effects experienced following any vaccination dose are retroactive requirements for vaccine dose(s) received prior to the promulgation of this ETS.
Paragraph (f)(2) requires employers to provide reasonable time and paid sick leave to employees to recover from side effects experienced following a primary vaccination dose, but does not specify the amount of paid sick leave that the employer is required to provide for that purpose. Employers may set a cap on the amount of paid sick leave available to employees to recover from any side effects, but the cap must be reasonable. CDC notes that although some people have no side effects, side effects, if experienced, should go away in a few days (CDC, September 30, 2021). Another study found that the average unanticipated paid administrative leave required by individuals experiencing side effects was around two days (1.66 days for the first dose and 1.39 days for the second dose) (Levi et al., September 25, 2021). Generally, OSHA presumes that, if an employer makes available up to two days of paid sick leave per primary vaccination dose for side effects, the employer would be in compliance with this requirement. When setting the cap, an employer would not be expected to account for the unlikely possibility of the vaccination resulting in a prolonged illness in the vaccinated employee ( e.g., a severe allergic reaction).
OSHA is aware that other federal, state, or local laws, or collective bargaining agreements, may require employers to provide employees additional paid time for vaccination and/or paid sick leave to recover from vaccination side effects. Where such an overlap exists, the requirements of this standard are satisfied so long as the employer provides each employee reasonable time and four hours of paid time to receive each primary vaccination dose, and reasonable time and paid sick leave to recover from side effects experienced following a primary vaccination dose.
References
Azimi T et al. (2021, April 9). Getting to work: Employers' role in COVID-19 vaccination. 1 (Azimi et al., April 9, 2021)
1 Azimi T et al. (2021, April 9). Getting to work: Employers' role in COVID-19 vaccination. https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/pharmaceuticals-and-medical-products/our-insights/getting-to-work-employers-role-in-covid-19-vaccination# (Azimi et al., April 9, 2021)
Bellew E et al. (2021, June). Half of service sector workers are not yet vaccinated for COVID-19: What gets in the way? The Shift Project: Research Brief. https://shift.hks.harvard.edu/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/Vax_Brief_6.28.21-2.pdf . (Bellew et al., June 2021)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, April 2). Post-vaccination considerations for workplaces. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/community/workplaces-businesses/vaccination-considerations-for-workplaces.html . (CDC, April 2, 2021)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, September 30). Possible side effects after getting a COVID-19 vaccine. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/expect/after.html . (CDC, September 30, 2021)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, accessed October 8). We can do this: Vaccines.gov website. https://www.vaccines.gov/ . (CDC, October 8, 2021)
Cleveland Documenters. (2021). Why some Clevelanders are still on the fence or not getting vaccinated: Voices on the vaccine. The Cleveland Observer. https://www.freshwatercleveland.com/street-level/VaccineVoice050521.aspx . (Cleveland Documenters, 2021)
Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF). (2021, May 6). KFF COVID-19 Vaccine Monitor: April 2021. https://www.kff.org/coronavirus-covid-19/poll-finding/kff-covid-19-vaccine-monitor-april-2021/ . (KFF, May 6, 2021)
Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF). (2021, May 17). How employer actions could facilitate equity in COVID-19 vaccinations. https://www.kff.org/policy-watch/how-employer-actions-could-facilitate-equity-in-covid-19-vaccinations/ . (KFF, May 17, 2021)
Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF). (2021, June 30). KFF COVID-19 Vaccine Monitor: June 2021. https://www.kff.org/report-section/kff-covid-19-vaccine-monitor-june-2021-findings/ . (KFF, June 30, 2021)
Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF). (2021, September 28). KFF COVID-19 Vaccine Monitor: September 2021. https://www.kff.org/coronavirus-covid-19/poll-finding/kff-covid-19-vaccine-monitor-september-2021/ . (KFF, September 28, 2021)
Levi ML et al. (2021, September 25). COVID-19 mRNA vaccination, reactogenicity, work-related absences and the impact on operating room staffing: A cross-sectional study. Perioperative Care and Operating Room Management preprint. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcorm.2021.100220 . (Levi et al., September 25, 2021)
National Safety Council. (2021). A Year in Review, and What's Next: COVID-19 Employer Approaches and Worker Experiences. https://www.nsc.org/faforms/safer-year-one-final-report . (National Safety Council, 2021)
Rosenberg E and Stein J. (2021, August 18). America's failure to pay workers time off undermines vaccine campaign, according to surveys, policy experts. Washington Post. https://www.washingtonpost.com/us-policy/2021/08/16/paid-leave-covid-vaccine/ . (Rosenberg and Stein, August 18, 2021)
Roy B et al. (2020, December 29). Health Care Workers' Reluctance to Take the COVID-19 Vaccine: A Consumer-Marketing Approach to Identifying and Overcoming Hesitancy.NEJM Catalyst. https://catalyst.nejm.org/doi/pdf/10.1056/CAT.20.0676 . (Roy et al., December 29, 2020)
SEIU Healthcare. (2021, February 8). Research shows 81% of healthcare workers willing to take COVID-19 vaccines but personal financial pressures remain a significant barrier for uptake. https://www.newswire.ca/news-releases/research-shows-81-of-healthcare-workers-willing-to-take-covid-19-vaccines-but-personal-financial-pressures-remain-a-significant-barrier-for-uptake-888810789.html . (SEIU Healthcare, February 8, 2021)
United States Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). (2021, September). National Compensation Survey: Employee Benefits in the United States, March 2021. https://www.bls.gov/ncs/ebs/benefits/2021/employee-benefits-in-the-united-states-march-2021.pdf . (BLS, September, 2021)
United States Office of Personnel Management (OPM). (2021, April 29). American Rescue Plan: COVID-19 Emergency Paid Leave for Federal Employees. https://chcoc.gov/sites/default/files/Attachment%205%20COVID-19%20Emergency%20Paid%20Leave%20Questions%20and%20Answers_0.pdf . (OPM, April 29, 2021)
G. COVID-19 Testing for Employees Who Are Not Fully Vaccinated
Paragraph (g) of this ETS addresses employers' obligations with respect to employees who are not fully vaccinated, including the requirement to ensure unvaccinated employees are tested for COVID-19. As explained in Need for the ETS (Section III.B. of this preamble), OSHA strongly prefers that employers implement written mandatory vaccination policies because that is the most effective and efficient workplace control available for preventing the spread of COVID-19. However, this ETS is also necessary to protect workers who remain unvaccinated through required regular testing, use of face coverings, and removal of infected employees from the workplace, and to protect other workers from the greater likelihood that unvaccinated workers may spread COVID-19 in the workplace. People who are unvaccinated are at increased risk of becoming infected with COVID-19 and are more likely to spread the disease when compared to people who are fully vaccinated (CDC, September 15, 2021). Additionally, people who are unvaccinated are more likely to experience severe clinical outcomes if they become infected than people who are vaccinated (Lopez Bernal et al., July 21, 2021). Therefore, routine COVID-19 testing of unvaccinated employees is necessary to identify employees with COVID-19 so they can be removed from the workplace to prevent transmission to other employees and to facilitate early medical intervention for infected employees when appropriate.
Routine testing of unvaccinated employees is necessary regardless of whether the unvaccinated employees have symptoms because SARS-CoV-2 infection is often attributable to asymptomatic and/or pre-symptomatic transmission ( i.e., individuals who are not exhibiting symptoms) (Bender et al., February 18, 2021; Klompas, September 2021; Johansson et al., January 7, 2021; Byambasuren et al., December 11, 2020). Although less effective and efficient than vaccination, the CDC has recognized regularly testing unvaccinated employees for COVID-19 as a useful tool for identifying asymptomatic and/or pre-symptomatic infected individuals so that they can be isolated (CDC, May 4, 2021; CDC, October 7, 2021). In contrast, the CDC recommends that fully vaccinated employees with no symptoms and no known exposure should be exempt from routine testing programs (CDC, May 4, 2021). Additional information about the risks of COVID-19 transmission in vaccinated and unvaccinated workers is discussed in Grave Danger (Section III.A. of this preamble).
Testing for COVID-19 can broadly be divided into two categories: diagnostic testing and screening testing. The purpose of diagnostic testing is to identify current infection when a person has signs or symptoms consistent with COVID-19, or when a person is asymptomatic but has recent known or suspected exposure to SARS-CoV-2. The information provided by diagnostic testing can be used by a healthcare provider to diagnose or treat a patient. The purpose of screening testing is to identify infected people who are asymptomatic and do not have known, suspected, or reported exposure to COVID-19. Screening testing helps to identify unknown cases both so that measures can be taken to prevent further transmission to others ( e.g., removal from the workplace and home isolation) and also to allow infected, but asymptomatic, people to begin medical treatment, as appropriate, so they can better avoid the most severe outcomes of COVID-19 ( e.g., high risk individuals seeking monoclonal antibody treatment or anti-viral medication). Although the testing required in paragraph (g)(1) of this ETS is screening testing, both screening and diagnostic testing can help prevent the spread of COVID-19. Paragraph (g) does not preclude additional diagnostic testing if an employee shows signs or symptoms consistent with COVID-19 or has recent known or suspected exposure to SARS-CoV-2.
Both screening and diagnostic testing involve the use of viral COVID-19 tests to detect current infection, as opposed to antibody COVID-19 tests, which are used to detect whether a person has antibodies for COVID-19. A positive antibody test indicates someone has antibodies to SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, which could either be the result of a prior infection with the virus or vaccination against COVID-19 (FDA, May 19, 2021; CDC, September 10, 2021). Viral tests for current infection fall into two categories: Nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs) and antigen tests. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (October 6, 2021) has issued a number of Emergency Use Authorizations (EUAs) for viral COVID-19 tests. It is important to note that OSHA's definition of “COVID-19 test” requires that COVID-19 tests be cleared, approved, or authorized by the FDA and administered in accordance with authorized instructions, with the noted exception of not allowing tests that are both self-administered and self-read by the employee unless observed by the employer or an authorized telehealth proctor. In this regard, OSHA recognizes that it is within FDA's authority and jurisdiction to help to assure the appropriate safety, efficacy, and accuracy of COVID-19 tests. The definition of “COVID-19 test” has previously been discussed in the Summary and Explanation for paragraph (c) (Section VI.C. of this preamble). Additional information about the type of COVID-19 tests that would satisfy the requirements of paragraph (g) are available in that section of this preamble.
As explained above, the most effective and efficient workplace control for preventing the spread of COVID-19 is vaccination and OSHA strongly prefers that employers implement written mandatory vaccination policies. However, where employers have unvaccinated employees, regular COVID-19 screening tests are necessary so infected employees can be identified and removed from the workplace to prevent workplace transmission and to facilitate early medical intervention, when appropriate. In addition to being more likely to become infected with COVID-19, people who are unvaccinated are more likely to experience severe clinical outcomes from COVID-19 than fully vaccinated people (see Grave Danger , Section III.A. of this preamble). In a recent CDC Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR) out of Los Angeles County, the SARS-CoV-2 infection rate among unvaccinated persons was 4.9 times and the hospitalization rate was 29.2 times the rates among fully vaccinated persons (Griffin et al., August 27, 2021). As explained below, regular screening testing of individuals for COVID-19 is an effective method of identifying asymptomatic and pre-symptomatic infections. Screening testing of unvaccinated employees is necessary because symptom and temperature checks will miss both asymptomatic and pre-symptomatic infections, which is a serious problem because pre-symptomatic and asymptomatic transmission are significant drivers of the continued spread of COVID-19 (Johansson et al., January 7, 2021). Once infected employees are identified, they can be removed from the workplace, thereby reducing virus transmission to other employees.
Several studies have indicated that the time from exposure to becoming contagious for COVID-19 is shorter than the time for symptoms to develop (incubation period), meaning that individuals can transmit SARS-CoV-2 before they begin to feel ill ( i.e., pre-symptomatic transmission) (Nishiura et al., March 4, 2020; Tindale et al., June 22, 2020). Pre-symptomatic individuals can transmit the virus to others before they know they are sick. These individuals should isolate but would not know to do so if they are unaware of their infection. It is also possible for individuals to be infected and subsequently transmit the virus without ever exhibiting symptoms. This is called asymptomatic transmission. A meta-analysis of 351 studies from January 1, 2020, to April 2, 2021, estimated that 42.8% of those infected with the SARS-CoV-2 virus exhibited no symptoms at the time of testing and so had either asymptomatic or pre-symptomatic infections (Sah et al., August 10, 2021). In another meta-analysis of studies, which included people of all ages at risk of contracting COVID-19 who were tested regardless of presence or absence of symptoms, seventeen percent of cases never developed symptoms during entire COVID-19 infection ( i.e., asymptomatic infection). In those studies, a diagnosis was confirmed with a positive result on a RT-PCR and all positive cases had a follow-up period of at least seven days to distinguish asymptomatic cases from pre-symptomatic cases (Byambasuren et al., December 11, 2020). In another study, researchers used a decision analytical model to assess the proportion of SARS-CoV-2 transmission from pre-symptomatic, never symptomatic, and symptomatic individuals in the community. Based on their modeling, they predicted that 59% of transmission came from asymptomatic transmission, including 35% from pre-symptomatic individuals and 24% from individuals who never develop symptoms (Johansson et al., January 7, 2021).
The existence of pre-symptomatic and asymptomatic infections pose serious challenges to containing the spread of SARS-CoV-2. Although the risk of asymptomatic transmission is 42% lower than from symptomatic COVID-19 patients (Byambasuren et al., December 11, 2020), asymptomatic transmission may result in more transmissions than symptomatic cases because asymptomatic persons are less likely to be aware of their infection and can unknowingly continue to spread the disease to others (Sah et al., August 10, 2021). The challenge of containing pre-symptomatic and asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 transmission is amplified among unvaccinated individuals because, as explained above, they are more likely to become infected with COVID-19 in the first place.
Because unvaccinated employees are at higher risk of COVID-19 infection and COVID-19 transmission among individuals without symptoms is a significant driver of the spread of COVID-19, OSHA has determined it is necessary to prevent the pre-symptomatic and asymptomatic transmission of COVID-19 from unvaccinated workers, through a requirement for weekly screening testing. Screening testing with antigen tests is a rapidly evolving and important tool that can be used to reduce the spread of SARS-CoV-2 in the workplace, particularly when coupled with other COVID-19 prevention and control measures ( e.g., workplace removal of infected persons, proper use of face coverings) (Schulte et al., May 19, 2021). The CDC recommends screening testing of unvaccinated asymptomatic workers as a useful tool to detect COVID-19 and stop transmission quickly. Screening testing is particularly useful in areas with moderate to high community transmission of COVID-19, which is currently the overwhelming majority of the United States (CDC, October 7, 2021). In a study with a well-defined population of SARS-CoV-2 infected individuals, researchers found that frequent testing ( i.e., at least twice per week) maximizes the likelihood of detecting infected individuals. However, even when used weekly, rapid antigen tests still had a 76% probability of detection ( i.e., weekly rapid antigen tests correctly identified 76% of true positive infected COVID-19 individuals) (Smith et al., September 15, 2021). By identifying pre-symptomatic and asymptomatic unvaccinated employees, employers can remove them from the workplace to prevent those employees from spreading SARS-CoV-2 to other employees. More information about the removal requirements in this ETS is available in the Summary and Explanation for paragraph (h) (Section VI.H. of this preamble).
Since the incubation period for COVID-19 can be up to 14 days, the CDC recommends that screening testing be conducted at least weekly in non-healthcare workplaces (CDC, October 7, 2021; CDC, May 4, 2021). Other researchers also recognize the effectiveness of weekly screening testing to control surges of COVID-19 infections (Larremore, January 1, 2021). Consequently, in workplaces with unvaccinated employees, OSHA has set the minimum frequency of testing unvaccinated workers at seven days because the agency expects that it will be effective in slowing the spread of COVID-19 in those workplaces, when used in tandem with face coverings (paragraph (i)) and removal of infected individuals (paragraph (h)). OSHA emphasizes that each of these infection controls provides some protection from COVID-19 by itself, but that they work best when used together, layering their protective impact to boost overall effectiveness. Although some studies have shown that more regular screening testing ( e.g., twice weekly) would identify even more cases, OSHA has decided to require testing only on a weekly basis. This is in line with the CDC recommendations, and as noted above the evidence shows that this frequency is effective in detecting asymptomatic and pre-symptomatic cases. A more frequent testing schedule would result in significant additional costs, and OSHA is hesitant to impose these costs and depart from CDC recommendations without a fuller record generated through the benefit of notice and comment rulemaking. OSHA seeks comment on this issue. Nonetheless, it should be noted that nothing in this rule prevents screening testing from being conducted more frequently based on factors such as the level of community transmission, workplace experience with outbreaks, and type of workplace ( e.g., specific workplace factors such as high volume retail or critical infrastructure sector).
Early detection of COVID-19-positive employees through screening testing of unvaccinated employees also facilitates early medical intervention, when appropriate, to avoid the most severe health outcomes associated with COVID-19. Early effective treatment of disease can help avert progression to more serious illness, especially for patients at high risk of disease progression and severe illness, with the additional benefit of reducing the burden on healthcare systems (CDC, December 4, 2021). For example, anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibodies have been shown to reduce the risk of hospitalization and death in the outpatient setting in those with mild to moderate COVID-19 symptoms and certain risk factors for disease progression. Treatment should be started as soon as possible after the patient receives a positive result on a COVID-19 test and within 10 days of symptom onset (NIH, September 24, 2021). Any COVID-19 medical treatment should be used in accordance with a licensed healthcare provider. The screening tests required by this rule will facilitate such treatment.
Pursuant to paragraph (g)(1)(i), covered employers must ensure that each employee who is not fully vaccinated and reports at least once every seven days to a workplace where other individuals ( e.g., coworkers, customers) are present: (A) Is tested for COVID-19 at least once every seven days; and (B) provides documentation of the most recent COVID-19 test result to the employer no later than the 7th day following the date on which the employee last provided a test result. Employers must ensure these unvaccinated employees are tested at least once every seven calendar days, regardless of their work schedule. For example, an unvaccinated part-time employee who is scheduled to work only every Monday and Tuesday must still be tested at least once every seven days. Because employees must provide documentation of their most recent COVID-19 test results to their employers no later than the 7th day following the date on which they last provided a test result, employees may want to set a schedule for their testing ( e.g., get a COVID-19 test every Wednesday). A consistent testing day may help employees ensure their documentation is provided every seven calendar days.
Paragraph (g)(1)(ii) addresses situations where an employee does not report to a workplace where other individuals, such as coworkers or customers, are present during a period of seven or more days ( e.g., when an employee is teleworking for an extended period of time). In such cases, the employer must ensure the employee is tested for COVID-19 within seven days prior to returning to the workplace and provides documentation of that test result to the employer upon return to the workplace. For example, if an unvaccinated office employee has been teleworking for two weeks but must report to the office, where other employees will be present ( e.g., coworkers, security officers, mailroom workers), on a specific Monday to copy and fax documents, that employee must receive a COVID-19 test within the seven days prior to the Monday and provide documentation of that test result to the employer upon return to the workplace. The employee's test must occur within the seven days before the Monday the employee is scheduled to report to the office, but it also must happen early enough to allow time for the results to be received before returning to the workplace. Similarly, unvaccinated new hires would need to be tested for COVID-19 within seven days prior to reporting to a workplace where other employees will be present and provide documentation of their test results no later than arrival on their first day of work. Since point-of-care testing that uses an antigen test allows for results within minutes, OSHA does not expect that scheduling tests or providing results to employers will be an impediment.
OSHA chose the seven-day period for employees returning to work after more than a week away from the workplace based on the evidence noted above about the effectiveness of testing at seven-day intervals. While it considered using a shorter time period in this situation, OSHA concluded that it would be less confusing for employers to use a uniform time period for both situations. OSHA was concerned that requiring different time periods in the two situations would cause confusion among both employees and supervisors implementing the program that would undermine the effectiveness of the testing scheme. OSHA seeks comment on this issue.
An employer has some discretion regarding how to satisfy its obligations under paragraph (g)(1), but those policies and procedures must be detailed in the employer's written policy pursuant to paragraph (d)(2) of this ETS. For example, the employer must specify how testing will be conducted ( e.g., testing provided by the employer at the workplace, employees independently scheduling tests at point-of-care locations, etc.). The employer must also specify in their policy how employees should provide their COVID-19 test results to the employer ( e.g., an online portal, to the human resources department). The Summary and Explanation for paragraph (d) (Section VI.D. of this preamble) provides additional information regarding the requirements of paragraph (d)(2) of this ETS. Test results given to the employer must contain information that identifies the worker ( i.e., full name plus at least one other identifier, such as date of birth), the specimen collection date, the type of test, the entity issuing the result ( e.g., laboratory, healthcare entity), and the test result.
If an employer is notified that an employee has a positive screening test, the employer must remove that employee from the workplace pursuant to paragraph (h)(2) of this ETS. The employee should quarantine and the employer must not allow the employee to return to the workplace until they meet the requirements in paragraphs (h)(2)(i) through (iii). More discussion of employee notification to their employer of a COVID-19 positive status and removal requirements is available in the Summary and Explanation for paragraph (h) (Section VI.H. of this preamble).
OSHA expects that most screening testing will be antigen testing that is conducted at point-of-care locations due to the reduced cost and faster processing time when compared to NAAT testing in laboratories. Most NAATs need to be processed in a laboratory with variable time to results (approximately 1-2 days). In contrast, most antigen tests can be processed at the point of care with results available in about 15-30 minutes (CDC, October 7, 2021). Rapid point-of-care tests are administered in various settings, such as: Physician offices, urgent care facilities, pharmacies, school health clinics, workplace health clinics, long-term care facilities and nursing homes, and at temporary locations, such as drive-through sites managed by local organizations. As explained above, COVID-19 tests that are both self-administered and self-read do not meet the definition of “COVID-19 test” in this ETS (unless observed by the employer or an authorized telehealth proctor) and therefore do not satisfy the testing requirements of paragraph (g).
Because antigen testing in point-of-care locations will typically produce results within minutes, the use of antigen testing should not result in an inability to provide the employer with test results in a timely fashion. However, the agency recognizes that where the employee or employer uses an off-site laboratory for testing, there may be delays beyond the employee's or employer's control. In the event that there is a delay in the laboratory reporting results and the employer permits the employee to continue working, OSHA will look at the pattern and practice of the individual employee or the employer's testing verification process and consider refraining from enforcement where the facts show good faith in attempting to comply with the standard.
OSHA has determined that employers may use pooling procedures to satisfy the requirements of screening testing under paragraph (g)(1). Pooling (also referred to as pool testing or pooled testing) means combining the same type of specimen from several people and conducting one laboratory test on the combined pool of specimens to detect SARS-CoV-2 ( e.g., four samples may be tested together, using only the resources needed for a single test). The advantages of pooling include preserving testing resources, reducing the amount of time required to test large numbers of specimens (increasing throughput), and lowering the overall cost of testing (CDC, June 30, 2021).
If pooling procedures are used and a pooled test result comes back negative, then all the specimens can be presumed negative with the single test. In other words, all of the employees who provided specimens for that pool test can be assumed to have a negative test result for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Therefore, documentation of the negative pooled test result would satisfy the paragraph (g)(1) documentation requirement for each employee in the pool and no additional testing is necessary. However, if the pooled test result is positive, immediate additional testing would be necessary to determine which employees are positive or negative. Each of the original specimens collected in the pool must be tested individually to determine which specimen(s) is (are) positive. If original specimens from the workers in a pooled test with a positive result are insufficient to be subsequently tested individually, those workers in the positive pool would need to be immediately re-swabbed and tested. The individual employee test results would be necessary to satisfy the employee documentation requirements of paragraph (g)(1). Where pooled testing is used (in accordance with paragraph (g)(1)), CDC and FDA procedures and recommendations for implementing screening pooled tests should be followed (CDC, June 30, 2021; FDA, August 24, 2020). OSHA notes that only some tests are authorized for pooled testing, and should be performed per the authorization.
In a note to paragraph (g)(1), OSHA explains that this section does not require the employer to pay for any costs associated with testing. As explained in Pertinent Legal Authority, Section II. of this preamble, the OSH Act authorizes OSHA to require employers to bear the costs of compliance with occupational safety and health standards, but OSHA has discretion to decide whether to impose certain costs—such as those related to medical examinations or other tests—on employers “[w]here [it determines that such costs are] appropriate.” 29 U.S.C. 655(b)(7). OSHA has commonly required employers to bear the costs of compliance with standards as a cost of doing business, including requiring employers to bear the costs of medical examinations and procedures (see, e.g., 29 CFR 1910.1018(n)(1)(i) (inorganic arsenic standard requires employers to ensure that medical examinations and procedures are provided “without cost to the employee”); see also United Steelworkers, 647 F.2d at 1229-31 (discussing Lead standard's medical removal provisions and OSHA's authority for imposing cost of medical removal on employers)). Requiring employers to bear the costs of compliance makes it more likely that employees will take advantage of workplace protections (see 86 FR 32605). For example, employees are more likely to use personal protective equipment (PPE) when employers provide the PPE to their employees at no cost (see 72 FR 64342, 64344).
In this ETS, OSHA has largely required employers to bear the costs of compliance, including the typical costs associated with vaccination, but has determined that it would not be appropriate to impose on employers any costs associated with COVID-19 testing for employees who choose not to be vaccinated. As explained in Need for the ETS, Section III.B. of this preamble, this ETS is designed to strongly encourage vaccination because vaccination is the most efficient and effective control for protecting unvaccinated workers from the grave danger posed by COVID-19. COVID-19 testing is only required under the ETS where an employee has made an individual choice to forgo vaccination and pursue a less protective option. Given the superior protectiveness of vaccination, and OSHA's intent for this ETS to strongly encourage vaccination, requiring employers to bear the costs of COVID-19 testing would be counter-productive. As mentioned above, requiring employers to pay for workplace protections makes it more likely that employees will take advantage of that protection, and in this ETS, OSHA intends to strongly encourage employees to choose vaccination, not regular COVID-19 testing. Because employees who choose to remain unvaccinated will generally be required to pay for their own COVID-19 testing, this standard creates a financial incentive for those employees to become fully vaccinated and avoid that cost.
Although this ETS does not require employers to pay for testing, employer payment for testing may be required by other laws, regulations, or collective bargaining agreements or other collectively negotiated agreements. This section also does not prohibit the employer from paying for costs associated with testing required by paragraph (g)(1) of this section. Otherwise, the agency leaves the decision regarding who pays for the testing to the employer. Because OSHA does not specify who pays for the testing, OSHA expects that some workers and/or their representatives will negotiate the terms of payment. OSHA has also considered that some employers may choose to pay for some or all of the costs of testing as an inducement to keep employees in a tight labor market. Other employers may choose to put the full cost of testing on employees in recognition of the employee's decision not to become fully vaccinated. It is also possible that some employers may be required to cover the cost of testing for employees pursuant to other laws or regulations. OSHA notes, for instance, that in certain circumstances, the employer may be required, under the Fair Labor Standards Act, to pay for the time it takes an employee to be tested ( e.g., if employee testing is conducted in the middle of a work shift). The subject of payment for the costs associated with testing pursuant to other laws or regulations not associated with the OSH Act is beyond OSHA's authority and jurisdiction. As explained in a note to paragraph (d) of this ETS, under various anti-discrimination laws, workers who cannot be tested because of a sincerely held religious belief may ask for a reasonable accommodation from their employer. For more information about evaluating requests for reasonable accommodation for a sincerely held religious belief, employers should consult the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission's website: https://www.eeoc.gov/wysk/what-you-should-know-about-covid-19-and-ada-rehabilitation-act-and-other-eeo-laws.
Pursuant to paragraph (g)(2), if an employee does not provide the result of a COVID-19 test as required by paragraph (g)(1), the employer must keep the employee removed from the workplace until the employee provides a test result. This provision is imperative because workers with asymptomatic or pre-symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection are significant contributors to COVID-19 transmission, and screening testing will help to identify and remove those individuals from the workplace. Employees providing accurate and weekly test results to their employer is of utmost importance for preventing and reducing the transmission of COVID-19 in the workplace.
Paragraph (g)(3) provides that when an employee has received a positive COVID-19 test, or has been diagnosed with COVID-19 by a licensed healthcare provider, the employer must not require that employee to undergo COVID-19 testing for 90 days following the date of their positive test or diagnosis. This provision is specifically intended to prohibit screening testing for 90 days because of the high likelihood of false positive results that do not indicate active infection but are rather a reflection of past infection. Studies of patients who were hospitalized and recovered indicate that SARS-CoV-2 RNA can be detected in upper respiratory tract specimens for up to three months (90 days) after symptom onset (CDC, August 2, 2021; CDC, September 14, 2021). If employees were to be subjected to screening tests in such a situation it would both undermine the confidence in the COVID-19 screening tests and could result in a harm to the worker of being unnecessarily removed from the workplace and subjected to the additional burden of unnecessary tests. Where employers implement a vaccination policy that allows employees to choose to provide proof of regular testing and wear a face covering rather than getting vaccinated, the employer's policy and procedures to implement this temporary suspension of testing must be included in their written workplace policy as required by paragraph (d)(2) of this ETS.
Paragraph (g)(4) provides that the employer must maintain a record of each test result required to be provided by each employee under paragraph (g)(1) of this ETS or obtained during tests conducted by the employer. These records must be maintained in accordance with 29 CFR 1910.1020 as an employee medical record and must not be disclosed except as required by this ETS or other federal law. However, these records are not subject to the retention requirements of 29 CFR 1910.1020(d)(1)(i) (Employee medical records), but must be maintained and preserved while this ETS remains in effect.
Additionally, paragraph (l) of this ETS includes specific timeframes for providing access to records, including the COVID-19 test results required by paragraph (g)(1). As a result, the timeframes for providing access to employee medical records in 29 CFR 1910.1020(e) do not apply. Instead, when providing access to an employee, anyone with written authorized consent from that employee, and OSHA, employers must follow the access timeframes set forth in paragraph (l) of this ETS. The Summary and Explanation for paragraph (l) (Section VI.L. of this preamble) contains additional information about accessing records gathered pursuant to paragraph (g)(1).
Finally, while the access timeframes in 29 CFR 1910.1020(e) and retention requirements of 29 CFR 1910.1020(d)(1)(i) do not apply to test result records required by this ETS, the other provisions in 29 CFR 1910.1020 do apply. For example, 29 CFR 1910.1020(h) includes requirements for the transfer of employee medical records when an employer ceases to do business. Like the vaccine records required by paragraph (e)(4) of this ETS, and because they concern the health status of an employee, test result records required by paragraph (g)(1) are employee medical records for purposes of 29 CFR 1910.1020. These test result records contain personally identifiable medical information and must be maintained in a confidential manner. The Summary and Explanation for paragraph (e) (Section VI.E. of this preamble) contains additional information about the interplay between this ETS and OSHA's regulation at 29 CFR 1910.1020.
References
Bender et al., (2021, February 18). Analysis of Asymptomatic and Presymptomatic Transmission in SARS-CoV-2 Outbreak, Germany, 2020. https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/27/4/20-4576_article. (Bender et al., February 18, 2021).
Byambasuren O et al. (2020, December 11). Estimating the extent of asymptomatic COVID-19 and its potential for community transmission: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Official Journal of the Association of Medical Microbiology and Infectious Disease Canada. 5(4): 223-234 doi:10.3138/jammi-2020-0030. (Byambasuren et al., December 11, 2020).
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2020, December 4). Information for Clinicians on Investigational Therapeutics for Patients with COVID-19. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/therapeutic-options.html. (CDC, December 4, 2020).
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, May 4). Antigen Testing for Screening in Non-Healthcare Workplaces: A tool to prevent the spread of COVID-19. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/community/workplaces-businesses/antigen-testing.html. (CDC, May 4, 2021).
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, June 30). Interim Guidance for Use of Pooling Procedures in SARS-CoV-2 Diagnostic and Screening Testing. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/lab/pooling-procedures.html. (CDC, June 30, 2021).
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, August 2). COVID-19 Testing Overview. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/symptoms-testing/testing.html. (CDC, August 2, 2021).
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, September 10). Using Antibody Tests for COVID-19. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/lab/resources/antibody-tests.html. (CDC, September 10, 2021).
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, September 14). Ending Isolation and Precautions for People with COVID-19: Interim Guidance. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/duration-isolation.html. (CDC, September 14, 2021).
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, September 15). Science Brief: COVID-19 Vaccines and Vaccination. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/science/science-briefs/fully-vaccinated-people.html. (CDC, September 15, 2021).
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, October 7) Interim Guidance for SARS-CoV-2 Testing in Non-Healthcare Workplaces. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/community/organizations/testing-non-healthcare-workplaces.html. (CDC, October 7, 2021).
Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2020, August 24). Pooled Sample Testing and Screening Testing for COVID-19. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/coronavirus-covid-19-and-medical-devices/pooled-sample-testing-and-screening-testing-covid-19. (FDA, August 24, 2020).
Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2021, May 19). Antibody Testing Is Not Currently Recommended to Assess Immunity After COVID-19 Vaccination: FDA Safety Communication. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/safety-communications/antibody-testing-not-currently-recommended-assess-immunity-after-covid-19-vaccination-fda-safety. (FDA, May 19, 2021).
Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2021, October 6). In Vitro Diagnostics EUAs. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/coronavirus-disease-2019-covid-19-emergency-use-authorizations-medical-devices/in-vitro-diagnostics-euas. (FDA, October 6, 2021).
Griffin JB et al. (2021, August 27). SARS-CoV-2 infections and hospitalizations among persons aged ≥16 years, by vaccination status—Los Angeles County, California, May 1-July 25, 2021. MMWR 70: 1170-1176. http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7034e5. (Griffin et al., August 27, 2021).
Johansson MA et al. (2021, January 7). SARS-CoV-2 transmission from people without COVID-19 symptoms. JAMA Network Open. 4(1): e2035057. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.35057. (Johansson et al., January 7, 2021).
Klompas M et al., (2021, September). The case for mandating COVID-19 vaccines for health care workers. Annals of Internal Medicine. https://doi.org/10.7326/M21-2366. (Klompas et al., September 2021).
Larremore DB et al. (2021, January 1). Test sensitivity is secondary to frequency and turnaround time for COVID-19 screening. Sci Adv 2021; 7(1): eabd5393. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abd5393. (Larremore, January 1, 2021).
Lopez Bernal et al. (2021, July 21). Effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines against the B.1.617.2 (Delta) variant. The New England Journal of Medicine, 385(7), 585-594. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2108891. (Lopez Bernal, July 21, 2021).
National Institutes of Health (NIH). (2021, September 24). Therapeutic Management of Nonhospitalized Adults With COVID-19. https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/management/clinical-management/nonhospitalized-adults--therapeutic-management/. (NIH, September 24, 2021).
Nishiura H et al. (2020, March 4). Serial interval of novel coronavirus (COVID-19) infections. Int J Infect Dis. 2020 Apr; 93: 284-286. doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.02.060. Epub 2020 Mar 4. PMID: 32145466; PMCID: PMC7128842. (Nishiura et al., March 4, 2020).
Sah P et al. (2021, August 10). Asymptomatic SARS-COV-2 infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 118(34), 1-12. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2109229118. (Sah et al., August 10, 2021).
Schulte P et al. (2021, May 19). Proposed Framework for Considering SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Testing of Unexposed Asymptomatic Workers in Selected Workplaces. J Occup Environ Med. 2021 Aug; 63(8): 646-656. Published online 2021, May 19. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8327768/. (Schulte et al., May 19, 2021).
Smith R et al. (2021, September 15). Longitudinal assessment of diagnostic test performance over the course of acute SARS-CoV-2 infection. The Journal of Infectious Diseases; 224(6), 976-982. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiab337. (Smith et al., September 15, 2021).
Tindale LC et al. (2020, June 22). Evidence for transmission of COVID-19 prior to symptom onset. Elife. 2020; 9: e57149. Published 2020 Jun 22. doi:10.7554/eLife.57149. (Tindale et al., June 22, 2020).
H. Employee Notification to Employer of a Positive COVID-19 Test and Removal
Employers can substantially reduce disease transmission in the workplace by removing employees who are confirmed to have COVID-19 based on a COVID-19 test or diagnosis by a healthcare provider. It is necessary that employees who are confirmed to have COVID-19 be removed from the workplace to prevent transmission to other employees. Several studies have focused on the impact of isolating persons with COVID-19 from others during their likely known infectious period, and those studies show that isolation is a strategy that reduces the transmission of infections. For example, Kucharski et al. (2020) found that transmission of SARS-CoV-2 would decrease by 29% with self-isolation within the household, which would extend to 37% if the entire household quarantined. Similarly, Wells et al. (2021) found that isolation of individuals at symptom onset would decrease the reproductive rate (R0) of COVID-19 from 2.5 to 1.6. Lastly, Moghadas et al. (2020) reported results that highlight the role of silent transmission, from a combination of the pre-symptomatic stage and asymptomatic infections, as the primary driver of COVID-19 outbreaks and underscore the need for mitigation strategies, including those that detect and isolate infectious individuals prior to the onset of symptoms. Isolating contagious employees from their co-workers can prevent further spread at the workplace and safeguard the health of other employees.
Paragraph (h) provides that employers must require each employee to promptly notify the employer when the employee receives a positive COVID-19 test or is diagnosed with COVID-19 by a licensed healthcare provider. This notification must occur regardless of employee vaccination status. As discussed in Grave Danger (Section III.A. of this preamble), exposure to SARS-CoV-2 in the workplace presents a grave danger to employees; removing those who are confirmed to have COVID-19 from the workplace mitigates that grave danger. This is true even for fully vaccinated employees since they also have the potential to transmit COVID-19 to other individuals, including other employees. Because the goal of this ETS, and the notification requirements in this paragraph, is to reduce transmission of COVID-19 in the workplace, employees are required to notify the employer of any COVID-19 positive test or diagnosis that they receive, not just positive results that are received from testing required under paragraph (g) of this ETS.
Paragraph (h)(1) states that the employer must require each employee who is COVID-19 positive to notify the employer of their COVID-19 test result or diagnosis “promptly.” For employees who are not at the workplace when they receive a positive COVID-19 test result or diagnosis, “promptly” notifying the employer means notifying the employer as soon as practicable before the employee is scheduled to start their shift or return to work. In the event that the employee is in the workplace when they receive a positive COVID-19 test result or diagnosis of COVID-19, “promptly” notifying the employer means notifying the employer as soon as safely possible while avoiding exposing any other individuals in the workplace.
The employer should establish notification procedures and inform employees about these procedures (see paragraph (j)(1)), so that employees are aware of the appropriate method for providing this notification to their employer. These notification procedures can be based on the employer's current protocols for employees to notify the employer if they are not able to come to work or need to leave work because of illness or injury. However the employer chooses to implement its notification procedures, it must ensure that an employee notification of a positive COVID-19 test or diagnoses results in the employee's immediate removal from the workplace, as required under paragraph (h)(2). For example, the employer may require employees to report any positive COVID-19 test or diagnosis to a company supervisor with the authority to temporarily remove the employee from the workplace. If an employer takes all steps required under this paragraph but an employee fails to report required information, the ETS does not dictate that any disciplinary action be taken against the employee. If an employer is cited by OSHA under this provision under such circumstances, the employer is entitled to contest the citation if it can establish an employee misconduct defense in accordance with applicable case law.
The notification requirement in paragraph (h)(1) is an important measure to ensure employers can take adequate steps to protect their employees from the hazard of COVID-19 because it is connected to a parallel requirement in paragraph (h)(2) to remove, from the workplace, any employee who receives a positive COVID-19 test or is diagnosed with COVID-19. It is important to remove employees who test positive or are diagnosed with COVID-19 from the workplace as soon as possible to prevent the transmission of COVID-19 to other employees. Therefore, the requirement that employees promptly inform their employer of a positive COVID-19 test result or COVID-19 diagnosis is necessary because this information allows the employer to take actions to protect other employees, including most critically by removing employees whose illness poses a direct threat of infection to other employees in the workplace.
Paragraph (h)(2) requires employers to immediately remove from the workplace any employee, regardless of vaccination status, who receives a positive COVID-19 test or is diagnosed with COVID-19 by a licensed healthcare provider. OSHA determined that directing an employee who tests positive or is diagnosed with COVID-19 to stay home until return to work criteria are achieved is critical to preventing the transmission of COVID-19 in the workplace. Similar to the notification required in paragraph (h)(1), this removal must occur regardless of employee vaccination status since someone who is fully vaccinated can still transmit COVID-19 to others, including other employees (see Grave Danger, Section III.A. of this preamble).
OSHA notes that, in most circumstances, any positive COVID-19 test would result in removal. However, this is not necessarily the case where an employer uses pooled COVID-19 testing, a method where one laboratory test is conducted using the specimens of several people to detect the virus that causes COVID-19 (CDC, June 30, 2021). If an employer conducts pooled testing for COVID-19, a positive pooled test result would trigger a need to immediately re-test those employees in the pool using an individual COVID-19 test because the positive pooled result would not satisfy the requirements of paragraph (g). Only those employees who test positive on their individual re-test would need to be removed from the workplace.
OSHA intends “removal” under paragraph (h)(2) to refer only to the temporary removal from the workplace of an employee while that employee is infectious. The requirement in paragraph (h)(2) to temporarily remove a COVID-19 positive employee from the workplace does not mean permanent removal of an employee from their position. Any time an employee is required to be removed from the workplace under paragraph (h)(2) of this section, the employer can require the employee to work remotely or in isolation if suitable work is available and if the employee is not too ill to work. In cases where working remotely or in isolation is not possible, OSHA encourages employers to consider flexible and creative solutions, such as a temporary reassignment to a different position that can be performed by telework. However, if an employee is too ill to work, remote work should not be required, and sick leave or other leave should be made available as consistent with the employer's general policies and practices, and as may be required under applicable laws.
After an employee has been removed from the workplace as required by paragraph (h)(2), the employer must ensure that they do not return to the workplace until the employee meets one of three criteria outlined in paragraphs (h)(2)(i) through (h)(2)(iii). The purpose of these provisions is to ensure that an employee who has COVID-19 does not return to work until the risk that they will transmit the disease to others in the workplace has been minimized. Each of these provisions is based on the best scientific evidence available on when a person with COVID-19 is no longer likely to transmit the virus.
Under paragraph (h)(2)(i), the employee can return to work if they receive a negative result on a COVID-19 nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT) following a positive result on a COVID-19 antigen test (the most common screening test). There is a small possibility for employees to receive false positive test results when conducting regular screening with an antigen test. Positive results are usually highly accurate at moderate-to-high peak viral load, but false positives can occur, depending on the course of infection (FDA, April 2021). OSHA recognizes that an employee might choose to seek a NAAT test for confirmatory testing. NAATs are considered the “gold standard” for clinical diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 and may have a higher sensitivity ( i.e., ability to correctly generate a positive result) than antigen tests (CDC, September 9, 2021). If an employee tested positive for COVID-19 via an antigen test, but then received follow-up confirmatory testing via a NAAT and the NAAT was negative, the positive antigen test can be considered a false positive and the employee can return to work (CDC, September 9, 2021). For a more detailed discussion of COVID-19 tests, see the Summary and Explanation for paragraph (c) (Section VI.C. of this preamble).
The employee may also return to work if they meet the return to work criteria in CDC's “Isolation Guidance” (incorporated by reference, §1910.509) (CDC, February 18, 2021) as described in paragraph (h)(2)(ii). CDC's guidance states that a COVID-19 positive person can stop isolating when three criteria are met: (1) At least ten days have passed since the first appearance of the person's symptoms; (2) the person has gone at least 24 hours without a fever (without the use of fever-reducing medication); and (3) the person's other symptoms of COVID-19 are improving (excluding loss of taste and smell). If a person has tested positive but never experiences symptoms, then the person can stop isolating after ten days from the date of their positive test. These recommendations are based on scientific evidence reviewed by CDC, which indicates that levels of viral RNA in upper respiratory tract samples begin decreasing after the onset of symptoms (CDC, September 14, 2021). The rationale for including CDC's “Isolation Guidance” in the ETS was addressed in detail in Need for Specific Provisions in the agency's prior rulemaking on 1910.502 (see 86 FR 32376, 32455).
Finally, the employee may return to work, per paragraph (h)(2)(iii), if the employee receives a return-to-work recommendation from a licensed healthcare provider. The appropriate duration of removal from work for any given individual may differ depending on factors such as disease severity or the health of the employee's immune system. For this reason, the ETS permits employers to make decisions about an employee's return to work in accordance with guidance from a licensed healthcare provider (who would be better acquainted with a particular employee's condition). If a licensed healthcare provider recommends a longer period of isolation for a particular employee than the CDC's “Isolation Guidance” would otherwise recommend, then the employer would need to abide by that longer period rather than returning the employee to work after ten days.
OSHA's removal requirements as outlined in paragraph (h)(2) are intended to set the floor for what is required; however, OSHA encourages employers who are able to do so to have a more robust program of medical removal, as indeed some employers have already done. In addition to removal from the workplace based on a positive COVID-19 test or diagnosis of COVID-19, employers may consider removal based on COVID-19 symptoms or certain exposure or close contacts employees have had outside of the workplace. Similarly, employers may consider removing employees from the workplace if the employer learns that the employee was notified by a state or local public health authority to quarantine or isolate; the employer might even be contacted by such an authority directly. Although this ETS does not require removal from the workplace in those situations, the employer might choose to remove employees from the workplace, above and beyond what is required by this ETS.
Finally, the note to paragraph (h)(2) clarifies that this ETS does not require employers to provide paid time to any employee for removal as a result of a positive COVID-19 test or diagnosis of COVID-19; however, paid time may be required by other laws, regulations, or collective bargaining agreements or other collectively negotiated agreements. On the other hand, the ETS does not preclude employers from choosing to pay employees for time required for removal under this standard. Additionally, employers should allow their employees to make use of any accrued leave in accordance with the employer's policies and practices on use of leave. This provision, while not placing the burden on the employer to provide paid time, should not be read as depriving employees of the benefits they are normally entitled to as part of their employment.
Because it does not require employers to provide paid time to employees who are removed for a positive COVID-19 test or diagnosis of COVID-19, this ETS differs from OSHA's COVID-19 Healthcare ETS, which applies to employees in the healthcare industry who are expected to be exposed to COVID-19, and requires paid medical removal protection benefits (§1910.502(l)(5)) for most employees. This difference reflects the structure and focus of this ETS relative to the Healthcare ETS. The Healthcare ETS requires employees to report symptoms of COVID-19 to their employers, as well as positive COVID-19 tests or diagnoses (see §1910.502(l)(2)), but does not require employees to be regularly tested for COVID-19. A primary function of the payment for medical removal in that standard is, therefore, to remove the potential for financial disincentives that might deter employees from reporting any signs or symptoms of COVID-19 that they experience. Because this ETS already requires testing for unvaccinated workers, which should result in employers learning of cases of COVID-19 in unvaccinated workers, and does not otherwise require employees to report signs and symptoms of COVID-19 to their employers, OSHA found that requiring employer payment for removal was not necessary in this standard.
As the note to paragraph (h) indicates, the employer may be required to follow other laws or regulations that would require paid medical removal. For example, if an employee covered by this ETS believes they were exposed to COVID-19 in the workplace and then tested positive, that employee may be entitled to workers' compensation benefits. Workers' compensation is a system already in place to provide benefits to employees who get sick or injured on the job from occupational disease or a work-related injury. Some states have expressly clarified or expanded their workers compensation rules to allow for COVID-19 claims during the pandemic (see, e.g., Industrial Commission of Arizona, May 15, 2020; Connecticut Executive Order No. 7JJJ, July 24, 2020; Minn. Stat. Ann. §176.011 Subd. (15)(f), 2020)).
Finally, the ETS does not contain specific requirements under this paragraph for the employer to establish or maintain records of employee notifications of a positive COVID-19 test or diagnosis of COVID-19 by a licensed healthcare provider. However, should an employer determine that a reported case of COVID-19 is work-related, the employer must continue to record that information on the OSHA Forms 300, 300A, and 301, or on equivalent forms, if required to do so under 29 CFR part 1904. This also includes confirmed cases of COVID-19 identified under paragraph (h) that an employer determines are work-related. Under 29 CFR part 1904, COVID-19 is a recordable illness and employers are responsible for recording cases of COVID-19 if: (1) The case is a confirmed case of COVID-19 as defined by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC); (2) the case is work-related as defined by 29 CFR part 1904.5; and (3) the case involves one or more of the general recording criteria in set forth in 29 CFR part 1904.7 ( e.g., medical treatment beyond first aid, days away from work). Under 29 CFR part 1904, employers must generally provide access to the 300 log to employees, former employees, and their representatives with the names of injured or ill employees included on the form. If, however, the employee requests that their name not be entered on the 300 log, the employer must treat their illness as a privacy concern case and may not enter their name on the log (see 29 CFR 1904.29(b)(6), (b)(7)(vi)).
References
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, February 18). Isolate if you are sick. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/if-you-are-sick/isolation.html. (CDC, February 18, 2021).
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, June 30). Interim Guidance for Use of Pooling Procedures in SARS-CoV-2 Diagnostic and Screening Testing. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/lab/pooling-procedures.html. (CDC, June 30, 2021)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, September 9). Interim Guidance for Antigen Testing for SARS-CoV-2. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/lab/resources/antigen-tests-guidelines.html. (CDC, September 9, 2021).
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, September 14). Ending Isolation and Precautions for People with COVID-19: Interim Guidance. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/duration-isolation.html. (CDC, September 14, 2021).
Connecticut Executive Order No. 7JJJ. (2020, July 24). Executive Order No. 7JJJ Protection of public health and safety during COVID-19 pandemic and response—rebuttable presumption regarding workers compensation benefits related to contraction of COVID-19. https://portal.ct.gov/-/media/Office-of-the-Governor/Executive-Orders/Lamont-Executive-Orders/Executive-Order-No-7JJJ.pdf. (Connecticut Executive Order No. 7JJJ, July 24, 2020).
Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2021, April). Coronavirus Disease 2019 Testing Basics. https://www.fda.gov/media/140161/download. (FDA, April 2021).
Industrial Commission of Arizona. (2020, May 15). COVID-19 Workers' Compensation Claims. https://www.azica.gov/sites/default/files/SPS%20-COVID-19%20FINAL.pdf. (Industrial Commission of Arizona, May 15, 2020).
Kucharski AJ et al. (2020). Effectiveness of isolation, testing, contact tracing, and physical distancing on reducing transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in different settings: a mathematical modelling study. The Lancet Infectious Disease. 2020 Oct; 20(10): 1151-1160. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30457-6. Epub 2020 Jun 16. PMID: 32559451; PMCID: PMC7511527. (Kucharski et al., 2020)
Minnesota Statutes Annotated, Section 176.011 Definitions. Subd. 15(f). (2020). https://www.revisor.mn.gov/statutes/cite/176.011/pdf. (Minn. Stat. Ann. §176.011 Subd. (15)(f), 2020)
Moghadas S et al. (2020, July 6). The implications of silent transmission for the control of COVID-19 outbreaks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 117(30), 17513-17515. doi: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2008373117. (Moghadas et al., July 6, 2020)
Wells CR et al. (2021). Optimal COVID-19 quarantine and testing strategies. Nature Communications 2021 Jan 7; 12(1): 356. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-20742-8. PMID: 33414470; PMCID: PMC7788536. (Wells et al., 2021)
I. Face Coverings
Paragraph (i) of this standard addresses the use of face coverings. As previously discussed in Grave Danger (Section III.A. of this preamble), COVID-19 spreads when an infected person breathes out droplets and very small particles that contain the virus. These droplets and particles can be breathed in by other people or land on their eyes, noses, or mouth. Face coverings reduce the risk of droplet transmission of COVID-19. The CDC recommends that people who are not fully vaccinated wear a face covering ( e.g., a mask) in indoor public places. (CDC, July 14, 2021). Additional discussion on the efficacy of face coverings is provided below.
Face coverings are simple bi-directional barriers that tend to keep droplets, and to a lesser extent airborne particulates, on the side of the filter from which they originate. An explanation of the term “face covering”, as used in this ETS, can be found in the Summary and Explanation for paragraph (c) (Section VI.C. of this preamble). The CDC (August 13, 2021) recommends unvaccinated people wear face coverings when indoors to prevent getting and spreading COVID-19 mostly by blocking large respiratory droplets from either leaving the face covering of the wearer (source control) or by preventing someone else's droplets from reaching the wearer (personal protection). The need for face coverings in workplaces applies particularly to unvaccinated workers due to their increased potential for asymptomatic and pre-symptomatic transmission of COVID-19.
The CDC Healthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee's (HICPAC) “Isolation Guidance” for healthcare settings has long recommended facemasks, among other controls, to prevent the transmission of viruses that cause respiratory illnesses (Siegel et al., 2007). Face coverings play an important dual role in protecting workers from droplet transmission of COVID-19. One of their key purposes is to function as source control. In this role, the face covering helps protect people around the wearer by reducing the number of infectious droplets released into the air by the wearer and limiting the distance traveled by any particles that are released. As a result, anyone near the wearer is exposed to fewer (if any) droplets and the transmission risk is lowered (OSHA, January 28, 2021; Siegel et al., 2007). Face coverings also provide a degree of particulate filtration to reduce the amount of inhaled particulate matter, meaning face coverings can help protect the wearer themselves, by reducing their inhalation of droplets produced by an infected person nearby (CDC, May 7, 2021; Brooks et al., February 10, 2021).
The efficacy of any given face covering in either functioning as source control or protecting the wearer will depend on the construction, design, and material used for the face covering. The CDC has stated that “masks are primarily intended to reduce the emission of virus-laden droplets (“source control”), which is especially relevant for asymptomatic or presymptomatic infected wearers who feel well and may be unaware of their infectiousness to others, and who are estimated to account for more than 50% of transmissions” (CDC, May 7, 2021). The CDC has also stated that: “Multi-layer cloth masks block release of exhaled respiratory particles into the environment, along with the microorganisms these particles carry. Cloth masks not only effectively block most large droplets ( i.e., 20-30 microns and larger) but they can also block the exhalation of fine droplets and particles (also often referred to as aerosols) smaller than 10 microns; which increase in number with the volume of speech and specific types of phonation. Multi-layer cloth masks can both block up to 50-70% of these fine droplets and particles and limit the forward spread of those that are not captured. Upwards of 80% blockage has been achieved in human experiments that have measured blocking of all respiratory droplets, with cloth masks in some studies performing on par with surgical masks as barriers for source control” (CDC, May 7, 2021). Thus, the construction of the face covering is a significant factor in determining its efficacy at reducing COVID-19 transmission.
While face coverings are generally effective as source control, because of the potential variations in protective properties, OSHA has not considered face coverings that are not certified to a consensus standard to be personal protective equipment (PPE) under OSHA's general PPE standard (29 CFR 1910.132), as there is insufficient assurance that any given face covering is of safe design and construction for the work to be performed, which is required by the PPE standard. Despite these limitations, many of the available face coverings have proven to be effective at providing source control, and where a face covering is also effective in providing personal protection, the wearer will be at reduced risk of, and could be protected from, infection. Accordingly, over the course of the pandemic, through its guidance, OSHA has strongly encouraged workers to wear face coverings when they are in close contact with others to reduce the risk of spreading COVID-19 despite the shortcomings that have prevented the agency from considering them to be PPE that complies with the requirement of the PPE standard. To enhance the effectiveness of any face covering required by this standard, this ETS imposes certain minimum design criteria, consistent with CDC recommendations. Thus, the face covering must consist of at least two layers of material that is either tightly woven or non-woven, and the face covering must not have visible holes or openings. CDC has found face coverings that are tightly woven and made with at least two layers are more effective at filtering droplets than face coverings that are loosely woven or consist of a single layer of fabric (CDC, May 7, 2021; Ueki et al., June 25, 2020).
OSHA's determination on the importance of face coverings is supported by a substantial body of evidence. As described in further detail below, consistent and correct use of face coverings is widely recognized and scientifically supported as an important evidence-based strategy for COVID-19 control. Accordingly, with specific exceptions relevant to outdoor areas and vaccinated persons, the CDC recommends everyone two years of age and older wear a face covering in public settings and when around people outside of their household (CDC, August 13, 2021). And, on January 21, 2021, President Biden issued Executive Order 13998, which recognizes the use of face coverings or facemasks as a necessary, science-based public health measure to prevent the spread of COVID-19, and therefore directed regulatory action to require that they be worn in compliance with CDC guidance while traveling on public transportation ( e.g., buses, trains, subway) and while at airports (Executive Order 13998, 86 FR 7205, 7205 (Jan. 21, 2021); CDC, February 2, 2021). Similarly, the World Health Organization (WHO) has recognized face coverings as a key measure in suppressing COVID-19 transmission, and thus, saving lives. The WHO observes that face coverings serve two purposes, to both protect healthy people from acquiring COVID-19 and to prevent sick people from further spreading it. Since December of 2020, the WHO has recommended that the general public wear face coverings in indoor settings and in outdoor settings where physical distancing cannot be maintained (WHO, December 1, 2020).
In the United States, several states have imposed statewide face covering mandates in order to mitigate the spread of COVID-19. One study examined data on statewide face covering mandates during March 1-October 22, 2020, and found that statewide face covering mandates were associated with a decline in weekly COVID-19-associated hospitalization growth rates by up to 5.6 percentage points for adults aged 18-64 years after mandate implementation, compared with growth rates during the 4 weeks preceding implementation of the mandate (Joo et al., February 12, 2021). Similarly, another study examined the association of state-issued face covering mandates with COVID-19 cases and deaths during March 1-December 31, 2020, and found mandating face coverings was associated with a decrease in daily COVID-19 case and death growth rates within 20 days of implementation (Guy et al., March 12, 2021).
School face covering policies for students, staff members, faculty, and visitors are associated with a reduction in COVID-19 outbreaks. Between July 15 and August 31, 2021, schools in Arizona were analyzed for school mask policies, which provided that all persons, regardless of vaccination status, were required to wear a mask indoors. The odds of a school-associated COVID-19 outbreak in schools without a mask requirement were 3.5 times higher than those in schools with an early mask requirement (Odds Ratio = 3.5; 95% Confidence Interval = 1.8-6.9) (Jehn et al., October 1, 2021).
The effectiveness of face coverings in limiting the emission and spread of droplets has also been demonstrated in numerous studies. For example, multiple studies in which droplets were visualized while individuals were talking or a manikin was used to simulate coughs and sneezes demonstrated that two-layer face coverings limited the number of droplets released into the air, and limited the forward spread of those not captured (Fischer et al., September 2, 2020; Verma et al., June 30, 2020; CDC, May 7, 2021).
The effectiveness of face coverings in preventing infections was also observed in a number of epidemiological studies. For example, in June of 2020 an outbreak was studied aboard the USS Theodore Roosevelt , an environment notable for congregate living quarters, close working environments, and a sample of mostly young, healthy adults. The investigation found that use of face coverings on board was associated with a 70% reduced risk of transmission, which demonstrates that the use of face coverings, especially among asymptomatic cases, can help mitigate future transmission (Payne et al., June 12, 2020). Another publication, released in July of 2020, included an investigation of a high-exposure event among 139 clients exposed to two symptomatic hair stylists with confirmed cases of COVID-19. Both of the stylists and all of their clients wore face coverings during their interactions. Among 67 clients subsequently tested for COVID-19, all test results were negative; no symptomatic secondary cases were reported by any clients, including those who were not tested. The study concluded that the strict use of face coverings likely mitigated the spread of COVID-19 (Hendrix et al., July 17, 2020).
Several other observational epidemiological studies have reviewed data regarding the “real-world” effectiveness of face covering usage. First, in a study of 124 Beijing households with one or more laboratory-confirmed case of COVID-19, face covering use by both the index patient and all family contacts before the index patient developed symptoms reduced secondary transmission ( i.e., infections occurring within two weeks of symptom onset in the index case) within the households by 79% (Wang et al., May 11, 2020). Second, a retrospective case-control study from Thailand documented that, among more than 1,000 persons interviewed as part of contact tracing investigations, those who reported having always worn a face covering during high-risk exposures experienced a greater than 70% reduced risk of infection compared with persons who did not wear face coverings under these circumstances. The risk for infection was not significantly lower in those who reported only sometimes wearing face coverings compared to those who did not wear face coverings at all. This evidence supports the conclusion that face coverings must be worn consistently and correctly to meaningfully reduce the risk of infection (Doung-ngern et al., September 14, 2020).
Community-level analyses have also confirmed the benefit of universal face covering use in: A unified hospital system (Wang et al., July 14, 2020); a German city (Mitze et al., June 1, 2020); a U.S. state (Gallaway et al., October 6, 2020); a panel of 15 U.S. states and Washington, DC (Lyu and Wehby, June 16, 2020; Hatzius et al., June 29, 2020); as well as both Canada (Karaivanov et al., October 1, 2020) and the U.S. (Chernozhukov et al., September 15, 2020) nationally. Each community analysis demonstrated that, following universal face covering directives from both organizational and political leadership, new infections were shown to fall significantly. These analyses have also shown reductions in mortality and the need for lockdowns, with their associated monetary/gross domestic product losses (Leffler et al., December 2, 2020; Hatzius et al., June 29, 2020). Additionally, multiple investigations involving infected passengers aboard flights longer than ten hours strongly suggest that face covering usage prevented in-flight transmissions, as demonstrated by the absence of infection developing in other passengers and crew in the 14 days following exposure (Schwartz et al., April 14, 2020; Freedman and Wilder-Smith, September 25, 2020).
Researchers from the COVID-19 Systematic Urgent Review Group Effort investigated the effects of face coverings and eye protection on virus transmission in both healthcare and non-healthcare settings. They identified 172 observational studies for their systematic review and 44 comparative studies for their meta-analysis, including data on 25,697 COVID-19, SARS, or MERS patients. They concluded for the general public, based mainly on evidence from face covering use within households and among contacts of cases, that disposable surgical masks or face coverings (reusable multi-layer cotton face coverings) are associated with protection from viral transmission. Through the meta-analysis, combining 39 of the studies' results, they found a 14.3% reduction in the difference of anticipated absolute effect ( e.g., the chance of viral infection or transmission) between no face covering and face covering groups (Chu et al., June 27, 2020).
Ueki et al. (June 25, 2020) evaluated the effectiveness of cotton face coverings, facemasks, and N95s (a commonly used respirator) in preventing transmission of SARS-CoV-2 using a laboratory experimental setting with manikins. The researchers found that all offerings provided some measure of protection as source control, limiting droplets expelled from both infected and uninfected wearers. For instance, when spaced roughly 20 inches apart, an uninfected person can reduce inhalation of infectious virus by 37% by wearing a cotton face covering. If only the infected person wears a cotton face covering, the amount breathed in by the uninfected recipient is reduced by 57%. However, if both individuals wear a cotton face covering, the exposure is reduced 67%. If both are wearing facemasks, exposure is reduced by 76%. When an infected individual wore an N95 respirator, exposure was reduced by 96% or, when the seams were taped, 99.7%.
As demonstrated by the studies above, proper face covering usage leads to a substantial reduction in the emission of virus-containing droplets and consequent transmission of the virus. This is especially critical for asymptomatic or pre-symptomatic infected wearers who feel well and may not be taking other preventative measures—like self-isolation—because they are unaware of their infectiousness to others. Combined, these individuals are estimated to account for more than 50% of COVID-19 transmissions (Honein et al., December 11, 2020; Moghadas et al., July 6, 2020; Johansson et al., January 7, 2021). This figure could be substantially reduced if face coverings are required, even for individuals who do not feel sick. Face covering use is also especially important in indoor spaces (Honein et al., December 11, 2020). The studies reviewed above show that face coverings reduce the release of droplets but do not completely eliminate them. CDC guidance affirms that COVID-19 pandemic control requires face covering use (Honein et al., December 11, 2020; CDC, May 7, 2021). Similarly, the WHO advises face covering use as a critical measure of a comprehensive package of prevention and control measures to limit the spread of COVID-19 (WHO, December 1, 2020).
Although increasing COVID-19 vaccination coverage remains the most effective means to achieve control of the pandemic, additional layered prevention strategies will be needed in the short term to minimize preventable morbidity and mortality among unvaccinated individuals. Unvaccinated individuals remain at substantial risk for infection, severe illness, and death, especially in areas where the level of SARS-CoV-2 community transmission is high (discussed in detail in Grave Danger (Section III.A. of this preamble)). Among strategies to prevent COVID-19, CDC recommends all unvaccinated individuals wear face coverings in public indoor settings. A proven effective strategy against SARS-CoV-2 transmission, beyond vaccination, includes using face coverings consistently and correctly (Christie et al., July 30, 2021).
The agency is not requiring the use of face coverings by workers who are fully vaccinated because vaccination is sufficient to reduce the grave danger to themselves or others. While vaccination is sufficient to reduce grave danger to the workers themselves, the agency recognizes that there may still be residual risk ( e.g., breakthrough infections); severe health outcomes among vaccinated workers, however, are unlikely. Vaccination is also sufficient to reduce the grave danger that fully vaccinated workers present to others given the reduced likelihood of transmission (see Grave Danger in Section III.A. of this preamble). Nonetheless, the use of face coverings by fully vaccinated workers, while not required by this ETS, is strongly encouraged in a wide range of circumstances to reduce the overall risk of transmitting COVID-19, particularly in areas of substantial or high transmission, when indoors and when in crowded outdoor areas. The use of face coverings by customers and visitors to workplaces is also beneficial in reducing the overall risk of workplace transmission of COVID-19.
OSHA has always considered recognized consensus standards, with design and construction specifications, when determining the PPE requirements of the agency's standards. The OSH Act (29 U.S.C. 655(b)(8)) requires the agency to generally give deference to consensus standards unless setting its own specifications would better effectuate the purposes of the Act. The agency's standards generally require PPE to conform to the specifications in consensus standards through incorporation by reference ( e.g., eye and face protection, head protection, foot protection). ASTM released a specification standard on February 15, 2021, to establish a national standard baseline for barrier face coverings (ASTM F3502-21). OSHA considered, as required, incorporation of ASTM F3502-21 in this ETS. However, the agency has determined that it is infeasible for the timeframe of this ETS to incorporate this consensus standard or to otherwise establish additional criteria for face coverings beyond that already recommended by the CDC due to the time needed to manufacture and distribute any new product. OSHA notes the CDC's guidance on types of masks, including those that meet ASTM F3502-21 requirements, and respirators as helpful to employers and workers in selecting an appropriate product (CDC, September 23, 2021).
Relatedly, OSHA has previously established that medical facemasks are essential PPE for workers in healthcare and associated industries, and are already used by workers under both the general PPE standard (29 CFR 1910.132), and more specifically, the Bloodborne Pathogens standard (29 CFR 1910.1030). Facemasks are intended for a medical purpose, such as prevention of infectious disease transmission (including uses related to COVID-19). Facemasks can function as a barrier to protect the wearer from hazards such as splashes or large droplets of blood and bodily fluids. Facemasks, such as surgical masks, must be FDA-cleared or authorized by FDA, including under an EUA and provide a similar or greater level of protection when serving the purposes of a face covering. Respirators are another type of personal protective device that OSHA has regulated under the Respiratory Protection standard (29 CFR 1910.134).
The best available experimental and epidemiological data support consistent use of face coverings by unvaccinated workers in work settings to reduce the spread of COVID-19 through droplet transmission. As discussed in Need for the ETS (Section III.B. of this preamble), adopting face covering policies is necessary, as part of a strategy combined with testing, to protect employees from exposure to COVID-19. Requiring unvaccinated workers to wear face coverings in the workplace will reduce the likelihood that, in conjunction with the testing (paragraph (g)) and removal, of infected workers, (paragraph (h)) requirements, they will spread the virus to others, including other unvaccinated coworkers. Based on the proven effectiveness of face covering use, OSHA's COVID-19 ETS includes necessary provisions for required use of face coverings by unvaccinated workers and provisions to allow vaccinated workers and customers and visitors to wear face coverings or respirators as a component of reducing the overall risk of COVID-19 transmission in the workplace.
The benefits that result from the use of face coverings for preventing transmission of COVID-19 are derived from the combination of source control ( i.e., reducing the spread of large respiratory droplets to others by covering an infected person's mouth and nose) and some personal protection for the wearer, as was discussed above in the Need for Face Coverings section. Face coverings are a vital layer of protection, and the benefit to any given individual increases with increasing community use. Paragraph (i) contains requirements for the use of face coverings by each employee who is not fully vaccinated, as well as alternatives to face coverings ( e.g., facemasks, respirators) that may be acceptable in some situations (described in detail below). As defined in paragraph (c), a face covering means a covering that completely covers the nose and mouth of the wearer, excluding face shields, which is made with two or more layers of a breathable fabric that is tightly woven, is secured to the wearer's head with ties, ear loops, or elastic bands that go behind the head, and is a solid piece of material without slits, exhalation valves, visible holes, or other openings in the material. This definition encompasses face coverings that otherwise meet the definition of face covering under paragraph (c), but include clear plastic windows, such as those utilized by persons communicating with those who are deaf or hard-of-hearing or when seeing a person's mouth is otherwise important. Face coverings can be manufactured or homemade, and they can incorporate a variety of designs, structures, and materials. Face coverings can be disposable or reusable. Face coverings do not have to meet a consensus standard, although they might. Apart from any applicable FDA or NIOSH regulatory requirements that might otherwise apply, such requirements are not required solely for the purposes of meeting the requirements of this standard.
As a general rule, OSHA has authority to, and does, require employers to bear the costs for protective equipment, among other worker protections, required by an OSHA standard. See, e.g., 29 CFR 1910.1018(j) (requiring the employer to provide protective clothing at no cost to the employee). However, in limited circumstances, OSHA has chosen not to require employers to pay for some forms of non-specialized protective equipment, such as every-day clothing, products providing weather-related protection, and non-specialized equipment that the employee wears off the job site. See 29 CFR 1910.132(h)(2)-(5). Like the analogous situations listed above, here employees may use their personal face coverings in a variety of circumstances on and off the job site as part of their every-day protection. Because the types of face coverings permitted under this ETS are widely used and readily available, (see Technological Feasibility (Section IV.A. of this preamble)), employees will have no difficulty obtaining them. OSHA is requiring employers to bear the costs for employee vaccination, because it is the more protective control, ( Need for the ETS (Section III.B. of this preamble). OSHA does not believe it appropriate to impose the costs of personal face coverings on an employer where an employee has made an individual choice to pursue a less protective option. For these reasons, OSHA has determined not to impose the costs of face coverings on the employer as a requirement under this ETS.
Paragraph (i)(1) requires employers to ensure that each employee who is not fully vaccinated wears a face covering when indoors or when occupying a vehicle with another person for work purposes, except (i) when an employee is alone in a room with floor to ceilings windows and a closed door. However, if that employee exits the room or another individual enters the room, they are required to wear a face covering. The second exception is (ii) for a limited time while an employee is eating or drinking at the workplace or for identification purposes in compliance with safety and security requirements. Under this exception, employees are not required to wear face coverings during the limited time while eating or drinking at the workplace. Employers may also let employees eat or drink outside where there may be more space and reduced risk of transmission. Additionally, under the exception in paragraph (i)(1)(ii), employees are not required to wear a face covering for a limited time for identification purposes in compliance with safety and security requirements. This means that an unvaccinated employee can temporarily remove their face covering when at a security checkpoint within their worksite and when identification is otherwise required.
Another exception for required face coverings is under paragraph (i)(1)(iii) for when an employee is wearing a respirator or facemask in accordance with other OSHA standards ( e.g., 1910.134, 1910.504, 1910.1030, 1910.502). Facemask or respirator use in accordance with other OSHA standards takes precedence over face covering use in this ETS. For example, OSHA standard 1910.1030 has requirements for facemasks in healthcare settings and requires that workers should continue to use the required facemask appropriate for that setting. Another example may include a worker who is required to use a respirator under 1910.134 for workplace exposure to harmful dusts, where effective engineering controls are not feasible; that worker should continue to use the required respirator. Employees must resume wearing a face covering when not engaged in the activity where a facemask or respirator is required as an essential part of their job. The last exception, contained in paragraph (i)(1)(iv), is for a very limited set of circumstances where employers can show that the use of the face covering is infeasible or creates a greater hazard. Situations where it is important to see an employee's mouth for reasons related to their job duties, or their job requires the use of their uncovered mouth, or when the use of a face covering presents a risk of serious injury or death to the employee, would also be covered under this provision. As has been previously discussed in Summary and Explanation for paragraph (d) (Section VI.D. of this preamble), OSHA recognizes that there may be certain workers who may not be able to wear a face covering due to a disability or sincerely held religious belief and are entitled to an accommodation.
If employers receive accommodation requests relating to face coverings or other protective gear, for example due to disability or religious garb or grooming, they should evaluate those requests under applicable laws (EEOC, October 25, 2021).
Paragraph (i)(2) requires that employers ensure that any face covering required to be worn by this section is: (i) Worn by the employee to fully cover the employee's nose and mouth; and (ii) replaced when wet, soiled, or damaged ( e.g., is ripped, has holes, or has broken ear loops). To be worn properly, face coverings must completely cover the wearer's mouth and nose and must fit snugly against the sides of the face without gaps. Gaps can let air with respiratory droplets leak in and out around the edges of the mask. Face coverings with a nose wire help to avoid issues with glasses fogging and create a snug fit. Workers can also use a mask fitter or brace over a disposable mask or a cloth mask to prevent air from leaking around the edges of the mask. To ensure face coverings are worn properly, an employer might appoint a manager or senior employee to check that each unvaccinated employee is properly wearing a face covering at the start of and throughout each shift. Many aspects of proper mask use are easily observable ( e.g., covering the mouth and nose, as well as no observable gaps). Additionally, employers may consider utilizing workplace announcements (email messages, safety talks, etc.) or displaying signs or posters throughout the facility about proper face covering usage.
The employer must ensure that employees replace face coverings when wet, soiled, or damaged (paragraph (i)(2)(ii)). Face coverings can become soiled by splashes, sprays, or splatters, from contact with a contaminated surface, or by touching/adjusting them with contaminated hands. Damaged face coverings may not fit properly and thus will have reduced effectiveness. Employees who work where there is potential for spills, sprays, or splashes may need to change or replace their face coverings more frequently ( e.g., in food, meat, or poultry processing plants; water, sanitation, or wastewater treatment facilities; or restaurants). As note 1 to paragraph (i) addresses, face shields may be worn in addition to face coverings to prevent them from getting wet and soiled. For work where face coverings are expected to become dirty or soiled less frequently, employees may only need to replace their face coverings daily ( e.g., in retail or office buildings). Regardless of work location, reusable face coverings can become soiled after each use and may be contaminated with bacteria and viruses, including the virus that causes COVID-19. To ensure performance and minimize the risk of contaminating employees after contact with a soiled face covering, as described previously, the CDC recommends washing them whenever they get dirty, but at least once a day. The CDC also has guidance on the selection, proper wearing, cleaning, and storage of face coverings (CDC, August 13, 2021).
The employer must not prevent any employee, regardless of vaccination status, from voluntarily wearing a face covering or facemask unless the employer can demonstrate that doing so would create a hazard (paragraph (i)(3)). While vaccination greatly reduces the risk of the most severe consequences of COVID-19 ( e.g. hospitalizations and fatalities) to workers, it does not reduce the risk to zero and thus workers must be permitted to wear face coverings or facemasks even when not required to in order to allow the workers to further address residual risk. The agency has determined this provision is necessary because employees may themselves have additional medical risk factors that employers may or may not be aware of, and which require enhanced precautions. Similarly, employees may live with or have frequent contact with family members or others who have enhanced risk if infected with COVID-19 and thus justify assuring the employees' ability to take reasonable precautions to protect their own health and safety or that of loved ones.
Paragraph (i)(4) states that the employer must permit the employee to wear a respirator instead of a face covering whether required or not ( i.e., without regard to vaccination status), and the employer may provide respirators to the employee, even if not required. This means that when a face covering is not required by paragraph (i)(1), the employer must permit the employee to wear a respirator or the employer may even provide a respirator; in such circumstances, the employer must also comply with 1910.504 (the mini respiratory protection program). Respirators, as defined in paragraph (c), are a type of PPE that are certified by NIOSH or authorized under an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) by the FDA, and protect against airborne hazards by removing specific air contaminants from the ambient (surrounding) air or by supplying breathable air from a safe source. Respirator use can provide an additional level of comfort and protection beyond that provided by face coverings for employees in circumstances that do not require a respirator to be used. As discussed previously, the agency has determined that workers need the ability to wear PPE, even when it is not required, in order to address residual risk and due to health conditions that either they or their close contacts may have that warrant enhanced precautions. For a more in-depth description of the mini respiratory protection program, see the preamble to the Healthcare ETS (86 FR 32615-32617). OSHA intends the mini respirator protection program to be preserved for the duration of this ETS, and any references relied upon by OSHA in those sections of the Healthcare ETS are also incorporated explicitly into the rulemaking docket for this ETS.
The mini respiratory protection program is designed to strengthen employee protections with a small set of provisions for the safe use of respirators designed to be easier and faster to implement than the more comprehensive respiratory protection program under 29 CFR 1910.134. This ETS is addressing an emergency health crisis, so it is critical for employers to be able to get more employee protection in place quickly. OSHA expects that this approach will facilitate additional employee choice for the additional protection provided by respirators while reducing disincentives that may have discouraged employers from allowing or voluntarily providing respirators. A mini respirator program is therefore an important control to protect employees from the hazard posed by COVID-19.
The mini respiratory protection program is primarily intended to be used for addressing circumstances where employees are not exposed to suspected or confirmed sources of COVID-19, but where respirator use could offer enhanced protection to employees. Examples include when a respirator could offer enhanced protection in circumstances where a less protective (in terms of filtering and fit) face covering is required under the ETS (See 29 CFR 1910.501(i)(1)). The decision to use a respirator in place of a face covering could be due to the higher filter efficiency and better sealing characteristics of respirators when compared to face coverings. For additional discussion, the rationale for the mini respiratory protection program was addressed in detail in Need for Specific Provisions in the agency's prior rulemaking on 1910.504, and the requirements of the mini respiratory protection program section are discussed in Summary and Explanation in the agency's prior rulemaking on 1910.504.
As required by paragraph (i)(5), the employers must not prohibit customers or visitors from wearing face coverings. Face coverings are a vital layer of protection against the risk of COVID-19. (See the discussion earlier in this section on the benefits to individuals associated with increased community use.) This provision is necessary because increased use of face coverings also reduces the overall risk of COVID-19 transmission from the customers and visitors to workers, both unvaccinated and vaccinated alike. Additionally, it allows customers and visitors to protect their own health and safety. Employers may even want to create a policy encouraging the use of face coverings by anyone who enters the business; they are encouraged to coordinate with state and local health officials to obtain and respond appropriately to timely and accurate information ( e.g., level of community transmission, health system capacity, vaccination coverage, capacity for early detection of increases in COVID-19 cases, and populations at risk for severe outcomes from COVID-19). Local conditions will influence the decisions that public health officials make regarding community-level strategies. Additionally, workers and their representatives may also negotiate additional face covering measures not required by the ETS through collective bargaining agreements or other collectively negotiated agreements.
Lastly, for the reasons explained above, note 2 to paragraph (i) clarifies that this section does not require the employer to pay for any costs associated with face coverings. However, the note also makes clear that this section does not prohibit the employer from paying for costs associated with face coverings required by this section. OSHA notes that employer payment for face coverings may be required by other laws, regulations, or collective bargaining agreements or other collectively negotiated agreements. Additionally, workers and their representatives may also negotiate employer payment for face coverings not required by the ETS through collective bargaining agreements or other collectively negotiated agreements.
References
Brooks J et al. (2021, February 10). Maximizing fit for cloth and medical procedure masks to improve performance and reduce SARS-CoV-2 transmission and exposure. MMWR. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7007e1. (Brooks et al., February 10, 2021)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, February 2). Order under Section 361 of the Public Health Service Act (42 U.S.C. 264) and 42 Code of Federal Regulations 70.2, 71.31(b), 71.32(b). Federal Register notice: Wearing of face masks while on conveyances and at transportation hubs. https://www.cdc.gov/quarantine/masks/mask-travel-guidance.html. (CDC, February 2, 2021)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, May 7). Scientific brief: Community Use of Cloth Masks to Control the Spread of SARS-CoV-2. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/more/masking-science-sars-cov2.html. (CDC, May 7, 2021)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, July 14). How COVID-19 spreads. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/how-covid-spreads.html. (CDC, July 14, 2021)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, August 13). Your Guide to Masks. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/about-face-coverings.html. (CDC, August 13, 2021)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, September 23). Types of Masks and Respirators. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/types-of-masks.html. (CDC, September 23, 2021)
Chernozhukov V et al. (2020, September 15). Causal impact of masks, policies, behavior on early COVID-19 pandemic in the U.S. Journal of Econometrics. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeconom.2020.09.003. (Chernozhukov et al., September 15, 2020)
Christie A et al. (2021, July 30). Guidance for implementing COVID-19 prevention strategies in the context of varying community transmission levels and vaccination coverage. MMWR 70: 1044-1047. http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7030e2. (Christie et at., July 30, 2021).
Chu DK et al. (2020, June 27). Physical Distancing, Face Masks, and Eye Protection to Prevent Person-to-Person Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. The Lancet. 395: 1973-1987. https://doi.org/10.1016/. (Chu et al., June 27, 2020)
Doung-ngern P et al. (2020). Case-control study of use of personal protective measures and risk for SARS-CoV-2 infection, Thailand. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 26(11), 2607-2616. doi: https:// dx.doi.org/10.3201/eid2611.203003. (Doung-ngern et al., September 14, 2020).
Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC). (2021, October 25). What You Should Know About COVID-19 and the ADA, the Rehabilitation Act, and Other EEO Laws. https://www.eeoc.gov/wysk/what-you-should-know-about-covid-19-and-ada-rehabilitation-act-and-other-eeo-laws. (EEOC, October 25, 2021)
Fischer E et al. (2020, September 2). Low-cost measurement of face mask efficacy for filtering expelled particles during speech. Science Advances, 6(36). doi: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abd3083. (Fischer et al., September 2, 2020)
Freedman D and Wilder-Smith A. (2020, September 25). In-flight transmission of SARS-CoV-2: A review of the attack rates and available data on the efficacy of face masks. Journal of Travel Medicine. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/jtm/taaa178. (Freedman and Wilder-Smith, September 25, 2020)
Gallaway S et al. (2020, October 6). Trends in COVID-19 incidence after implementation of mitigation measures—Arizona, January 22-August 7, 2020. MMWR, 69, 1460-1463. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm6940e3. (Gallaway et al., October 6, 2020)
Guy GP Jr et al. (2021, March 12). Association of State-Issued Mask Mandates and Allowing On-Premises Restaurant Dining with County-Level COVID-19 Case and Death Growth Rates—United States, March 1-December 31, 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2021; 70: 350-354. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7010e3. (Guy et al., March 12, 2021)
Hatzius J et al. (2020, June 29). Face masks and GDP. Goldman Sachs Research. https://www.goldmansachs.com/insights/pages/face-masks-and-gdp.html. (Hatzius et al., June 29, 2020)
Hendrix J et al. (2020, July 17). Absence of apparent transmission of SARS-CoV-2 from two stylists after exposure at a hair salon with a universal face covering policy—Springfield, Missouri, May 2020. MMWR, 69, 930-932. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm6928e2. (Hendrix et al., July 17, 2020)
Honein MA et al. (2020, December 11). Summary of Guidance for Public Health Strategies to Address High Levels of Community Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 and Related Deaths, December 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2020; 69: 1860-1867. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm6949e2. (Honein et al., December 11, 2020)
Jehn M et al. (2021, October 1). Association between K-12 school mask policies and school-associated COVID-19 outbreaks—Maricopa and Pima Counties, Arizona, July-August 2021. MMWR 70: 1372-1373. http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7039e1. (Jehn et al., October 1, 2021).
Johansson MA et al. (2021, January 7). SARS-CoV-2 transmission from people without COVID-19 symptoms. JAMA Network Open, 4(1), e2035057. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.35057. (Johansson et al., January 7, 2021)
Joo H, Miller GF, Sunshine G, et al. (2021, February 12). Decline in COVID-19 Hospitalization Growth Rates Associated with Statewide Mask Mandates—10 States, March-October 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2021; 70: 212-216. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7006e2. (Joo et al., February 12, 2021)
Karaivanov A et al. (2020, October 1). Face masks, public policies and slowing the spread of COVID-19: Evidence from Canada. National Bureau of Economic Research. http://www.nber.org/papers/w27891. (Karaivanov et al., October 1, 2020)
Leffler C et al. (2020, December 2). Association of country-wide Coronavirus mortality with demographics, testing, lockdowns, and public wearing of masks. The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 103(6), 2400-2411. https://doi.org/10.4269/ajtmh.20-1015. (Leffler et al., December 2, 2020)
Lyu W and Wehby G. (2020, June 16). Community use of face masks and COVID-19: Evidence from a natural experiment of state mandates in the U.S. Health Affairs, 39(8), 1419-1425. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.2020.00818. (Lyu and Wehby, June 16, 2020)
Mitze T et al. (2020, June 1). Face masks considerably reduce COVID-19 cases in Germany: A synthetic control method approach. IZA—Institute of Labor Economics (Germany). http://ftp.iza.org/dp13319.pdf. (Mitze et al., June 1, 2020)
Moghadas S et al. (2020, July 6). The implications of silent transmission for the control of COVID-19 outbreaks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 117(30), 17513-17515. doi: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2008373117. (Moghadas et al., July 6, 2020)
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). (2021, January 28). Frequently asked questions COVID-19. https://www.osha.gov/coronavirus/faqs. (OSHA, January 28, 2021)
Payne D et al. (2020, June 12). SARS-CoV-2 infections and serologic responses from a sample of U.S. Navy Service Members—USS Theodore Roosevelt. MMWR, 69(23), 714-721. doi: https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm6923e4. (Payne et al., June 12, 2020)
Schwartz K et al . (2020, April 14). Lack of COVID-19 transmission on an international flight. Canadian Medical Association Journal, 192(15), E410. doi: https://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.75015. (Schwartz et al., April 14, 2020)
Siegel J, Rhinehart E, Jackson M, Chiarello L, and the Healthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee. (2007). 2007 Guideline for isolation precautions: Preventing transmission of infectious agents in healthcare settings. https://www.cdc.gov/infectioncontrol/pdf/guidelines/isolation-guidelines-H.pdf. (Siegel et al., 2007)
Ueki H et al. (2020, October 21). Effectiveness of Face Masks in Preventing Airborne Transmission of SARS-CoV-2. mSphere 5: e00637-20. https://doi.org/10.1128/mSphere.00637-20. (Ueki et al., October 21, 2020)
Verma S et al. (2020, June 30). Visualizing the effectiveness of face masks in obstructing respiratory jets. Physics of Fluids, 32(6), 061708. doi: https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0016018. (Verma et al., June 30, 2020)
Wang X et al. (2020, July 14). Association between universal masking in a health care system and SARS-CoV-2 positivity among health care workers. Journal of the American Medical Association, 324(7), 703-704. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.12897. (Wang et al., July 14, 2020)
Wang Y et al. (2020, May 11). Reduction of secondary transmission of SAR-CoV-2 in households by face mask use, disinfection and social distancing: A cohort study in Beijing, China. BMJ Global Health, 5, e002794. doi: 10.1136/bmjgh-2020-002794. (Wang et al., May 11, 2020)
World Health Organization (WHO). (2020, December 1). Mask use in the context of COVID-19. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/advice-for-public/when-and-how-to-use-masks. (WHO, December 1, 2020)
J. Information Provided to Employees
In order to successfully implement the provisions of the ETS, it is critical that employers provide relevant information to employees. Employers must provide employees with the information specified in paragraph (j), an essential part of this ETS, because it helps to ensure that employees understand both their rights and responsibilities under the ETS and their employer's policies and procedures. The ETS cannot be effective if employees do not have sufficient knowledge and understanding of the requirements of the ETS, their employers' policies and procedures, information about available COVID-19 vaccines, their protections against retaliation and discrimination, and the potential penalties for knowingly providing false information to their employer.
Paragraph (j) provides that employers must provide the required information to each employee in a language and at a literacy level the employee understands. This means that if an employer has employees that speak different languages or are at different literacy levels, the employer must present information in a way that ensures each employee can understand it. This may require an employer to create different materials for different groups of employees ( e.g., materials in different languages). When information must be translated into different languages, employers must ensure the translation is one the employees can understand. When an employer provides employees with the required information in a manner employees understand, they help ensure that their implementation of this ETS is successful.
The manner in which employers provide the required information to employees may vary based on the size and type of workplace. Employers have flexibility to communicate this information to employees using any effective methods that are typically used in their workplaces, and may choose any method of informing employees so long as each employee receives the information specified in the standard in a language and at a literacy level they understand. For example, an employer may provide this information to employees through email communications, printed fact sheets, or during a discussion at a regularly scheduled team meeting. To ensure comprehension of the information provided, employers can identify a point-of-contact for employees who have questions about the information provided.
Paragraphs (j)(1)-(4) specify the information that employers must provide to employees. Paragraph (j)(1) requires employers to provide each employee with information regarding the requirements of §1910.501 and any policies and procedures the employer establishes to implement this ETS. The information provided to employees must cover any employer policies under paragraph (d), including the details of the employer's vaccination policy. Employers must also inform employees about the process that will be used to determine employee vaccination status, as required under paragraph (e). In addition, employers must inform employees about the time and pay/leave they are entitled to for vaccinations and any side effects experienced following vaccinations, as required by paragraph (f). And employers must also inform employees about the procedures they need to follow to provide notice of a positive COVID-19 test or diagnosis of COVID-19 by a licensed healthcare provider, as required under paragraph (h), as well as the procedures to be used for requesting records under paragraph (l). Employers must provide additional information to unvaccinated employees, including information about the employer's policies and procedures for COVID-19 testing and face coverings, as required by paragraphs (g) and (i), respectively.
Some employers may have informed employees about their COVID-related workplace-specific policies, e.g., policies on vaccination, testing, and face coverings, prior to the effective date of this ETS. Employers may rely on any such prior communications for purposes of complying with paragraph (j)(1) to the extent that the prior communications meet the relevant requirements of paragraph (j) and there have been no changes to the relevant policies. Employers must review and evaluate the information already provided to determine whether it covers all of the information necessary under paragraph (j)(1). If previous information provided to employees did not cover all of the required elements, the employer must provide employees the information on those missing elements to come into compliance with the ETS. For example, if an employer has a mandatory vaccination policy and has already provided information to the employees on the policies and procedures the employer has established to implement that policy, and provided that information in a language and at a literacy level each employee can understand, the employer would not need to expend resources to provide that information again to meet the requirements under this ETS. However, the employer would still need to provide information to its employees about other new policies and procedures established to implement the ETS.
When an employer's policies or procedures change, the employer must provide any updated or supplemental information to employees. For example, an employer may initially opt to allow only paper copies as proof of COVID-19 test results. Over time, however, the employer may decide that it wants to accept electronic proof of test results. If that employer modifies its policy to permit employees to submit electronic proof of test results, the employer must inform employees of any new or altered policies and procedures that the employer implements as a result.
Paragraph (j)(2) requires employers to provide information to each employee about COVID-19 vaccine efficacy, safety, and the benefits of being vaccinated. To meet this requirement, employers must provide the CDC's document, “Key Things to Know About COVID-19 Vaccines,” available at https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/keythingstoknow.html (CDC, October 7, 2021), to each employee. The employer may choose to provide this information to employees in either an electronic or print format. The CDC currently provides this document in multiple languages; however, employers may need to provide additional translations if necessary to inform each employee of the contents of the document in a language they understand. Employers do not have any further obligations to create or provide information on vaccine efficacy, safety, or the benefits of being vaccinated beyond providing the aforementioned CDC document to each employee.
Paragraph (j)(3) requires employers to inform each employee about the requirements of 29 CFR 1904.35(b)(1)(iv) and section 11(c) of the OSH Act. These two provisions work together to protect employees from retaliation for engaging in activities protected by OSHA statute or regulation. The first of these provisions, section 1904.35(b)(1)(iv), prohibits employers from discharging or in any manner discriminating against any employee for reporting a work-related injury or illness. The second provision, section 11(c) of the OSH Act, prohibits employers from discriminating against employees for exercising rights under, or as a result of actions required by, the ETS. Section 11(c) also protects employees from retaliation for filing an occupational safety or health complaint, reporting a work-related injury or illness, or otherwise exercising any rights afforded by the OSH Act.
Retaliation takes many forms; it occurs when an employer (through a manager, supervisor, or administrator) fires an employee or takes any other type of adverse employment action against an employee for engaging in a protected activity. Adverse employment actions include discipline, reducing pay or hours, reassignment to a less desirable position, denying overtime or promotion, intimidation or harassment, and any other action that would dissuade a reasonable employee from raising a concern about a possible violation or engaging in other protected activity (see Burlington Northern & Santa Fe Railway Co. v. White, 548 U.S. 53, 57 (2006) holding, in the Title VII context, that the test for determining whether a particular employment action is materially adverse is whether it “could well dissuade” a reasonable person from engaging in protected activity).
The ETS does not change employers' substantive obligations under either 29 CFR 1904.35(b)(1)(iv) or section 11(c) of the OSH Act. Rather, it simply requires employers to make employees aware of these provisions and their requirements. By increasing awareness, OSHA believes that paragraph (j)(3) will prevent acts of retaliation from occurring in the workplace, encourage employees to exercise their right to the protections of the ETS, and engage employees in actions required by the ETS.
It is critically important for employees to be aware of, and to be able to exercise, their rights under the ETS. Employee participation is essential to mitigating the spread of COVID-19 in the workplace, and fear of retaliation would undermine the effectiveness of the ETS. For example, per paragraph (f) of this ETS, employers must provide employees up to 4 hours of paid time at the employee's regular rate of pay for each vaccination dose, as well as reasonable time and paid sick leave for employees to recover from side effects experienced following any vaccination dose. If an employer fails to comply with paragraph (f) and then retaliates against employees who object, employees may be deterred from being vaccinated. Similarly, if employees fear retaliation, they will be less likely to voice concerns about unvaccinated co-workers who do not wear required face coverings (see paragraph (i)(1)). A workplace free from the threat of retaliation promotes collaboration between employers and employees and allows employers to more effectively implement the various requirements of this ETS.
OSHA has received a record number of complaints of retaliation during the COVID-19 pandemic. The agency's website shows that, as of September 26, 2021, OSHA had received 5,788 complaints of retaliation related to workplace protections from COVID-19 (OSHA, September 29, 2021). These figures indicate that some employers need to be reminded that they are legally prohibited from engaging in retaliatory actions. Additionally, employees likely need reassurance of their legal right to engage in protected activity without fear of suffering from adverse employment actions. As such, it is critical for employers to inform employees of the prohibitions against retaliation in 29 CFR 1904.35(b)(1)(iv) and section 11(c) after the effective date of the ETS, without regard to any information they may have provided previously on these anti-retaliation provisions. As with the other parts of paragraph (j), employers have flexibility regarding how they will provide the required information.
Paragraph (j)(4) requires employers to provide each employee with information regarding the prohibitions of 18 U.S.C. 1001 and Section 17(g) of the OSH Act, which provide for criminal penalties associated with knowingly supplying false statements or documentation. The first of these two provisions, 18 U.S.C. 1001(a) is described earlier in this preamble and provides for fines or imprisonment for persons who “knowingly and willfully” (1) falsifies, conceals, or covers up by any trick, scheme, or device a material fact; (2) makes any materially false, fictitious, or fraudulent statement or representation; or (3) makes or uses any false writing or document knowing the same to contain any materially false, fictitious, or fraudulent statement or entry. And section 17(g) of the OSH Act provides for fines up to $10,000, and imprisonment for not more than six months, or both, for anyone who “knowingly makes any false statement, representation, or certification” in any application, record, report, plan, or other document “filed or required to be maintained pursuant to this chapter.” False statements or documents made or submitted for purposes of complying with policies required by this ETS could fall under either or both of these statutory provisions.
This ETS requires that each employee provide their employer either COVID-19 vaccination documentation (paragraph (e)), or, if applicable, regular COVID-19 test results (paragraph (g)). There is a significant public health interest in ensuring employees provide this information truthfully to the employer. Employers cannot effectively implement the requirements of this ETS based on false information. By increasing awareness of the possible penalties an employee may face for misrepresenting their vaccination status or test results, OSHA intends to discourage such behavior. Employers can satisfy the requirement of paragraph (j)(4) by providing each employee with the text of the two statutory provisions in hard copy or via electronic communication ( e.g. , email), translated as necessary into other languages, emphasizing the importance of providing truthful information about vaccine status and test results, and explaining that providing false information could be punishable under the two provisions. Employers are not required to provide further explanation of the statutory provisions or to provide legal advice.
Information requirements are routine components of OSHA standards. The inclusion of information requirements in this ETS reflects the agency's conviction, as noted above, that informed employees are essential to the implementation of any effective occupational safety and health policy or procedure. OSHA believes that informing employees about their rights and responsibilities under the ETS; the employer's policies and procedures; and the safety, efficacy, and benefits of vaccination will help increase the number of employees vaccinated and will facilitate effective implementation of the standard by employers.
References
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, October 7). Key Things to Know About COVID-19 Vaccines. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/keythingstoknow.html. (CDC, October 7, 2021).
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). (2021, September 29). COVID-19 Response Summary: Summary Data for Federal Programs—Whistleblower Data. https://www.whistleblowers.gov/covid-19-data. (OSHA, September 29, 2021).
K. Reporting COVID-19 Fatalities and Hospitalizations to OSHA
OSHA has required employers to report work-related fatalities and certain work-related hospitalizations under its recordkeeping regulation since 1971. These requirements have been an important part of the agency's statutory mission to assure safe and healthful working conditions for all working people. All employers covered by the OSH Act, including employers who are partially exempt from maintaining injury and illness records, are required to comply with OSHA reporting requirements at 29 CFR 1904.39. Under OSHA's current reporting regulation, employers are required to report each work-related fatality to OSHA within 8 hours of the event, and each work-related in-patient hospitalization, amputation, and loss of an eye within 24 hours of the event.
The purpose of the reporting requirement in §1904.39 is to provide OSHA with information to determine whether it is necessary for the agency to conduct an immediate investigation at a specific establishment. Employer reports of work-related COVID-19 fatalities and in-patient hospitalizations are an important element of the agency's efforts to reduce occupational exposure to the virus. After receiving an employer report, OSHA decides whether an inspection is needed to determine the cause of a work-related COVID-19 fatality or in-patient hospitalization, and whether any OSHA standards may have been violated. These reports are critical for the agency to respond quickly to COVID-19 exposure that may pose an ongoing risk to other employees at the worksite. Timely investigation also allows OSHA to view evidence at a workplace soon after a work-related COVID-19 fatality or in-patient hospitalization has occurred, and can make it easier for the agency to gather relevant information from others at the worksite that might be useful in protecting other employees. Moreover, prompt inspection enables OSHA to gather information to evaluate whether its current standards adequately address the workplace hazard presented from COVID-19. The information gathered from employer reports is also used by the agency to form the basis of statistical data on the causes and remediation of work-related COVID-19 fatalities and in-patient hospitalizations.
In order to address the unique circumstances presented by COVID-19, and to facilitate OSHA investigation and better workplace health surveillance, paragraph (k)(1) requires covered employers to report each work-related COVID-19 fatality to OSHA within 8 hours of the employer learning about the fatality, and each work-related COVID-19 in-patient hospitalization to OSHA within 24 hours of the employer learning about the in-patient hospitalization. As described in more detail in the following discussion, OSHA is adding these additional COVID-19 reporting requirements because the delay in the manifestation and progression of symptoms of COVID-19 can lead to hospitalization or fatality outside the normal window for reporting those workplace events.
Paragraph (k)(1)(i) provides that employers must report each work-related COVID-19 fatality to OSHA within 8 hours of the employer learning about the fatality. Under this paragraph, an employer must make a report to OSHA within 8 hours of learning both (1) that an employee has died from a confirmed case of COVID-19, and (2) that the cause of death was the result of a work-related exposure to COVID-19. Employers are only required to report confirmed cases of COVID-19 as defined by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) (CDC, May 20, 2020). Typically, the cause of death is determined by the physician who was responsible for a patient who died in a hospital, although the cause of death can also be determined by others such as medical examiners or coroners (Pappas, May 19, 2020).
The requirement in paragraph (k)(1)(i) is similar to the fatality reporting requirement in OSHA's regulation at 29 CFR 1904.39(a)(1), which requires an employer to report to OSHA within 8 hours after the death of any employee as the result of a work-related incident. However, 29 CFR 1904.39(b)(6) requires employers to report a work-related fatality to OSHA only if the fatality occurs within 30 days of “the work-related incident.” Prior to this ETS, for purposes of reporting events involving COVID-19, OSHA interpreted the phrase “the work-related incident” to mean “exposure” in the work environment. Therefore, in order to be reportable under 29 CFR 1904.39(a)(1), a work-related fatality due to COVID-19 needed to have occurred within 30 days of an employee's exposure in the work environment. Given the possibility of long-term illness before death, the 30-day limitation for reporting fatalities to OSHA could restrict OSHA's ability to receive information about work-related COVID-19 fatalities.
To address these issues, OSHA has chosen not to apply the 30-day limitation period from 29 CFR 1904.39(b)(6) to the reporting provision in paragraph (k) (see paragraph (k)(2)). Therefore, the requirement to report these fatalities is not limited by the length of time between workplace exposure and death. The reporting of work-related COVID-19 fatalities that occur beyond 30 days from the time of exposure will enable the agency to evaluate more work-related COVID-19 fatalities to determine whether immediate investigations are needed to prevent other employees at the same worksite from being exposed to the virus. The report of these fatalities to OSHA facilitates the agency's timely tracking of this data. Accordingly, paragraph (k)(1)(i) requires employers to report each work-related COVID-19 fatality to OSHA within 8 hours of the employer learning about the fatality regardless of when the exposure in the work environment occurred.
Paragraph (k)(1)(ii) of the standard requires an employer to report each work-related COVID-19 in-patient hospitalization to OSHA within 24 hours of the employer learning about the in-patient hospitalization. Under this paragraph, and similar to OSHA's reporting regulation at 29 CFR 1904.39, an employer must make a report to OSHA within 24 hours of learning that (1) an employee has been in-patient hospitalized due to a confirmed case of COVID-19, and (2) the reason for the hospitalization was the result of a work-related exposure to the illness.
OSHA's current reporting regulation at 29 CFR 1904.39(a)(2) provides that, within 24 hours after the in-patient hospitalization of one or more employees, as the result of a work-related incident, an employer must report the in-patient hospitalization to OSHA. 29 CFR 1904.39(b)(6) requires employers to only report in-patient hospitalizations to OSHA if the hospitalization occurs within 24 hours of the work-related incident. For example, if an employee trips in the workplace and sustains an injury on Monday, but is not hospitalized until Thursday, the employer does not need to report the event. In this example, “the work-related incident” occurred on Monday when the employee tripped and was injured in the workplace. Also, under §1904.39, employers must report in-patient hospitalizations to OSHA within 24 hours of knowing both that the employee has been in-patient hospitalized and that the reason for the hospitalization was the result of “the work-related incident” (see 29 CFR 1904.39(a)(2), (b)(7)-(b)(8)). In non-COVID cases, the work-relatedness of the injury is typically apparent immediately.
Since the beginning of the pandemic, the reporting of work-related COVID-19 in-patient hospitalizations under 29 CFR 1904.39 has presented unique challenges. As noted above, for purposes of reporting COVID-19 fatalities and in-patient hospitalizations, OSHA has interpreted the phrase “the work-related incident” in 29 CFR 1904.39(b)(6) to mean an employee's “exposure” to COVID-19 in the work environment. Thus, in order to be reportable, an in-patient hospitalization needed to occur within 24 hours of an employee's exposure to COVID-19 in the work environment. Given the incubation period of the virus, and the typical timeframe between exposure and the emergence of symptoms serious enough to require hospitalization, it is extremely unlikely for an in-patient hospitalization to occur within 24 hours of an employee's exposure to the virus.
To address these issues, paragraph (k)(1)(ii) does not limit the COVID-19 reporting requirement to only those hospitalizations that occur within 24 hours of exposure, as in 29 CFR 1904.39(b)(6). This change in the reporting requirement will result in OSHA making more determinations as to whether immediate investigations are needed at additional worksites. Given the severity of the disease, and how quickly it can spread, it is essential that remediation efforts at a workplace be undertaken immediately. As noted above, it is critical for OSHA to respond quickly to hazardous conditions where employees have been hospitalized. The elimination of the 24-hour limitation period will not only allow OSHA to receive more employer reports about work-related COVID-19 in-patient hospitalizations and, as a result, shed light on where severe COVID-19 events are occurring, but it will also enable the agency to respond more quickly and effectively to these situations. Accordingly, employers must report each work-related COVID-19 in-patient hospitalization to OSHA regardless of when the employee's exposure in the workplace occurred (paragraph (k)(1)(ii)). But consistent with OSHA's normal reporting requirements, when hospitalization for a work-related case of COVID-19 does occur, the employer must report it within 24 hours of learning about the hospitalization.
Additionally, for purposes of this section, OSHA defines in-patient hospitalization as a formal admission to the in-patient services of a hospital or clinic for care or treatment (see 29 CFR 1904.39(b)(9) and (b)(10)). The determination as to whether an employee is formally admitted into the in-patient service is made by the hospital or clinic. Treatment in an Emergency Room only is not reportable.
I. Work-Relatedness Determinations
Given the nature of the disease, and the extent of community spread, in some cases, it may be difficult for an employer to determine whether an employee's COVID-19 illness is work-related, especially when an employee has experienced potential exposure both in and out of the workplace. For purposes of this ETS, when evaluating whether a fatality or in-patient hospitalization is the result of a work-related case of COVID-19, employers must follow the criteria in OSHA's recordkeeping regulation at 29 CFR 1904.5 for determining work-relatedness. Applying the criteria in 29 CFR 1904.5 under paragraph (k) of this ETS is consistent with how employers make work-relatedness determinations when reporting fatalities and other serious events under 29 CFR 1904.39.
Under §1904.5, employers must consider an injury or illness to be work-related if an event or exposure in the work environment either caused or contributed to the resulting condition, or significantly aggravated a pre-existing injury or illness. An injury or illness is presumed work-related if it results from events or exposures occurring in the work environment, unless an exception in §1904.5(b)(2) specifically applies. Under this language, an injury or illness is presumed work-related if an event or exposure in the work environment is a discernable cause of the injury or illness (see 66 FR 66,943 (December 27, 2001)).
According to 29 CFR 1904.5(b)(3), the “work environment” includes the employer's establishment and any other location where work is performed or where employees are present as a condition of their employment. Under 29 CFR 1904.5(b)(3), employers should evaluate the employee's work duties and environment and determine whether it is more likely than not that exposure at work caused or contributed to the illness (see 66 FR 5958-59 (January 19, 2001)).
Because of the typical incubation period of 3 to 14 days, an employee's exposure to COVID-19 will usually be determined after the fact. Employers must make reasonable efforts to acquire the necessary information to make good-faith work-relatedness determinations under this section. In addition, the employer should rely on information that is reasonably available at the time of the fatality or in-patient hospitalization.
A work-related exposure in the work environment would likely include close contact with a person known to be infected with COVID-19. For example, although work-relatedness must be determined on a case-by-case basis, if a number of COVID-19 illnesses develop among coworkers who work closely together without an alternative explanation, it is reasonable to conclude that an employee's fatality or in-patient hospitalization is work-related. On the other hand, if there is not a known exposure to COVID-19 that would trigger the presumption of work-relatedness, the employer must evaluate the employee's work duties and environment to determine whether it is more likely than not that the employee was exposed to COVID-19 during the course of their employment. Employers should consider factors such as:
• The type, extent, and duration of contact the employee had at the work environment with other people, particularly the general public.
• Physical distancing and other controls that impact the likelihood of work-related exposure.
• The extent and duration of time spent in a shared indoor space with limited ventilation.
• Whether the employee had work-related contact with anyone who exhibited signs and symptoms of COVID-19.
Since 1971, under OSHA's recordkeeping system, employers have been making work-relatedness determinations regarding workplace fatalities, injuries, and illnesses. In general, employers are in the best position to obtain information, both from the employee and the workplace, necessary to make a work-relatedness determination. Although employers may rely on experts and healthcare professionals for guidance, the determination of work-relatedness ultimately rests with the employer.
Finally, OSHA wishes to emphasize that, under OSHA's recordkeeping regulation at 29 CFR 1904, employers must record on the OSHA 300 log each work-related fatality, injury, and illness reported to OSHA under §1904.39. The work-relatedness determination for fatality and in-patient hospitalization is no different than the requirement to determine work-relatedness when entering fatalities, injuries and illness on the OSH 300 log. Accordingly, the work-relatedness determination for reporting COVID-19 fatalities and in-patient hospitalizations is a determination that is already required to be made by the employer.
II. Time Periods for Reporting COVID-19 Fatalities and In-Patient Hospitalizations
As noted above, under paragraph (k), employers must report each work-related COVID-19 fatality or hospitalization to OSHA within the specified timeframes based on when any agent or employee of the employer becomes aware of the reportable event. For example, an employer “learns” of a COVID-19 fatality or in-patient hospitalization when a supervisor, receptionist, or other employee at the company receives information from a family member or medical professional about an employee fatality or in-patient hospitalization. It is the employer's responsibility to ensure that appropriate instructions and procedures are in place so that managers, supervisors, medical personnel, as well as other employees or agents of the company, who learn of an employee's death or in-patient hospitalization due to COVID-19 know that the company must make a report to OSHA.
Consistent with OSHA's regulation at 29 CFR 1904.39, the reporting clock begins to run with the occurrence of the reportable event. Under paragraph (k), in situations where the employer or the employer's agent does not learn about the work-related COVID-19 fatality or in-patient hospitalization right away, the employer must make the report to OSHA within 8 hours for a fatality, or 24 hours for an in-patient hospitalization, from the time the employer (or the employer's agent) learns about the reportable event. For example, if an employee dies from a work-related case of COVID-19 on Sunday at 6:00 a.m., but the employer does not learn about the death until Monday at 8:00 a.m., the employer has until 4:00 p.m. that day to make the report to OSHA. Similarly, if an employee is in-patient hospitalized for a work-related case of COVID-19 at 8:30 p.m. on Monday, but the employer or the employer's agent(s) does not learn about the hospitalization until 9:00 a.m. the next day (Tuesday), then the employer would be required to make the report to OSHA within 24 hours of learning of the in-patient hospitalization (i.e., by 9:00 a.m. on Wednesday) (see 29 CFR 1904.39(b)(7)).
Likewise, if an employer does not learn right away that a reportable fatality or in-patient hospitalization is work-related, the employer must make the report to OSHA within 8 hours or 24 hours of learning that the death or in-patient hospitalization was the result of a work-related COVID-19 exposure. For example, if an employee is in-patient hospitalized for a case of COVID-19 at 9:00 a.m. on Monday, but the employer does not have enough information to make a work-relatedness determination until 11:00 a.m. on Monday, then the employer would be required to report the hospitalization within 24 hours of learning that the hospitalization was work-related ( i.e., by 11:00 a.m. on Tuesday) (see 29 CFR 1904.39(b)(8)).
Finally, if an employer makes a report to OSHA concerning a work-related COVID-19 in-patient hospitalization and that employee subsequently dies from the illness, the employer does not need to make an additional fatality report to OSHA.
III. How To Report COVID-19 Fatalities and In-Patient Hospitalizations and What Information Must Be Included in the Report
Paragraph (k)(2) of the standard provides that when reporting work-related COVID-19 fatalities and in-patient hospitalizations to OSHA in accordance with paragraph (k)(1), the employer must follow the requirements in 29 CFR 1904.39, except for 29 CFR parts 1904.39(a)(1)-(2) and (b)(6). As explained above, OSHA has included specific provisions for the reporting of work-related COVID-19 fatalities and in-patient hospitalizations that differ from 29 CFR 1904.39. However, when making COVID-19 fatality and in-patient hospitalization reports to OSHA, employers must follow the other reporting procedures set forth in §1904.39. Specifically, under §1904.39(a)(3), employers have three options for reporting work-related fatalities and in-patient hospitalizations to OSHA:
1. By telephone to the OSHA Area Office that is nearest to the site of the incident;
2. by telephone to the OSHA toll-free central telephone number, 1-800-321-OSHA (1-800-321-6742);
3. by electronic submission using the reporting application located on OSHA's public website at www.osha.gov .
Section 1904.39(a)(3) also allows employers to report work-related fatalities and in-patient hospitalizations to OSHA in person to the OSHA Area Office that is nearest to the site of the incident. However, because many OSHA Area Offices are closed to the public during the COVID-19 pandemic, employers must use one of the three options listed above. In addition, §1904.39(b)(1) makes clear that, if the OSHA Area Office is closed, an employer may not report a work-related fatality or in-patient hospitalization by leaving a message on OSHA's answering machine, faxing the Area Office, or sending an email. Instead, the employer must make the report by using the 800 number or the reporting application located on OSHA's public website at www.osha.gov.
The other provisions in 29 CFR 1904.39 (except for 29 CFR 1904.39(a)(1)-(2) and (b)(6)) also apply to the reports required by paragraph (k). For example, employers should consult 29 CFR 1904.39(b)(2) to determine what information employers must give to OSHA when making COVID-19 fatality or in-patient hospitalization reports. Per that provision, employers must give OSHA the following information for each fatality or in-patient hospitalization: The establishment name, the location of the work-related incident, the time of the work-related incident, the type of reportable event ( i.e., fatality or in-patient hospitalization), the number of employees who suffered a fatality or in-patient hospitalization, the names of the employees who suffered a fatality or in-patient hospitalization, the employer's contact person and his or her phone number, and a brief description of the work-related incident.
References
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2020, May 20). Reporting and Coding Deaths Due to COVID-19. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/covid19/coding-and-reporting.htm. (CDC, May 20, 2020).
Pappas, S. (2020, May 19). How COVID-19 Deaths are Counted. Scientific American. https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/how-covid-19-deaths-are-counted1/. (Pappas, May 19, 2020).
L. Availability of Records
Section 8(c)(1) of the Act requires employers to “make, keep and preserve, and make available to the Secretary [of Labor] or the Secretary of Health and Human Services, such records regarding his activities relating to this Act as the Secretary, in cooperation with the Secretary of Health and Human Services, may prescribe by regulation as necessary or appropriate for the enforcement of this Act or for developing information regarding the causes and prevention of occupational accidents and illnesses.” Section 8(c)(2) of the Act specifically directs the Secretary of Labor to promulgate regulations requiring employers to maintain accurate records of work-related injuries and illnesses. Section 8(c)(3) of the Act requires employers to “maintain accurate records of employee exposures to potentially toxic materials or harmful physical agents which are required to be monitored or measured under section 6 [of the Act.]” In accordance with section 8(c), paragraph (l) of the ETS includes availability of records requirements for certain COVID-19-related records required to be created and maintained by the ETS. This paragraph provides a right of access to records by employees, employee representatives, and OSHA.
Paragraph (l)(1) specifies that the employer must make available, for examination and copying, the individual COVID-19 vaccine documentation and any COVID-19 test results required by the ETS for a particular employee to that employee and to anyone having written authorized consent of that employee by the end of the next business day after a request. Prompt employee access to this information ensures that employees have the information necessary to take an active role in their employers' efforts to prevent COVID-19 transmission in the workplace. In particular, in circumstances where employers or employees choose to have the employee's COVID-19 test results go directly to the employer, paragraph (l)(1) gives the employee access to their own records. Access to COVID-19 test results may be helpful for a requesting employee in evaluating information relevant to COVID-19 exposure, including if that exposure occurred at the workplace. Prompt production of these records can also assist employees in making personal medical decisions and seeking care from a licensed healthcare provider if necessary.
Employers should note that employee privacy is protected under the access to records provisions in paragraph (l)(1). Specifically, as noted above, paragraph (l)(1) requires employers to provide access to the vaccination records or COVID-19 test results for a particular employee to that employee or to anyone having that employee's written permission. However, it does not authorize employers to allow anyone other than the particular employee to access their records or results without the written consent of that employee (except as provided for under paragraph (l)(3)).
Paragraph (l)(2) requires the employer to make the following information available to an employee or an employee representative on request: (1) The aggregate number of fully vaccinated employees at a workplace and (2) the total number of employees at that workplace. This information must be made available to these individuals by the end of the next business day after a request. Employers will be able to utilize the roster of each employee's vaccination status they are required to maintain under paragraph (e)(4) of this section to provide this information promptly to a requester.
Since the aggregate totals of fully vaccinated employees and total employees made available by request in paragraph (l)(2) do not contain any personal identifiable information or personal medical information, OSHA does not believe that access to these records raises any serious confidentiality or privacy concern if disclosed to employees or their representatives.
OSHA believes that access to this information will allow employees and employee representatives to calculate a percentage of fully vaccinated employees at a workplace, evaluate the efficacy of the employer's vaccination policy, raise any concerns identified to OSHA, and actively participate in the employer's vaccination efforts. Without the provision of this information to employees and their representatives, the only potential check on whether the employer is complying with the requirements of the ETS would be OSHA inspections. The agency believes that making this information available to employee representatives will help ensure compliance with the requirements of the ETS and thereby protect workers.
Consistent with 29 CFR 1904.35(a)(3), OSHA interprets the term “employee” as used in paragraph (l) to include former employees. In addition, for purposes of paragraph (l)(2), the term “representative” is intended to have the same meanings as in 29 CFR 1904.35(b)(2), which encompasses two types of employee representatives. The first is a personal representative of the employee, who is a person the employee designates, in writing, as his or her personal representative, or is a legal representative of a deceased or legally incapacitated employee. The second is an authorized representative, which is defined as an authorized collective bargaining agent of one or more employees working at the employer's worksite. In accordance with these interpretations, OSHA also interprets the phrase “employee representative,” as used in paragraph (l)(2), to include the personal and authorized representatives of former employees. These interpretations are limited to these provisions.
Under paragraphs (l)(1) and (l)(2), requesters are entitled to one free copy of each requested record, which is consistent with OSHA's recordkeeping regulation at 29 CFR 1904.35. The cost of providing one free copy to employees, former employees, and/or their representatives is minimal, and these individuals are more likely to access the records if it is without cost. Allowing the employer to charge for a copy of the record would only delay the production of the information. After receiving an initial, free copy of a requested record or document, an employee, former employee, or representative may be charged a reasonable fee for copying duplicative records. However, no fee may be charged for an update to a previously requested record. It should be noted that each COVID-19 test is a separate record, and, as such, the employee or the representative is entitled to one free copy of each COVID-19 test record.
Paragraph (l)(3) provides OSHA with a specific right of access. Under paragraph (l)(3)(i), employers must provide the written policy required by paragraph (d), and the aggregate numbers described in paragraph (l)(2) of this section (both the aggregate number of fully vaccinated employees at a workplace and the total number of employees at that workplace), to the Assistant Secretary for examination and copying within 4 business hours of a request. Consistent with the requirements in 29 CFR 1904.40(b)(2), if the records are maintained at a location in a different time zone, the employer may use the business hours of the establishment at which the records are located when calculating the deadline.
Providing OSHA with prompt access to the written policy and the aggregate numbers allows the agency to more rapidly focus inspections on employers that may not be in compliance with the requirements of this ETS. In addition, this information will help OSHA determine what to focus on in an investigation. For example, if an employer has established, implemented, and is enforcing a written mandatory vaccination policy under paragraph (d)(1) and their aggregate numbers indicate that their entire workforce is fully vaccinated against COVID-19, the agency might approach the investigation differently than in a workplace where the employer's written policy (under paragraph (d)(2)) allows employees to provide proof of regular testing for COVID-19 in accordance with paragraph (g) and wear a face covering in accordance with paragraph (i), instead of being fully vaccinated. This information also provides OSHA representatives with the ability to quickly check any vaccination claims made by an employer without undertaking an employee-by-employee assessment and assists OSHA representatives in their evaluation of the effectiveness of the employer's written policy.
Having this information within 4 business hours of the request helps the agency act more quickly to protect employees and preserves agency resources. In addition, the 4-hour response time is consistent with similar obligations under other OSHA recordkeeping requirements, such as the recordkeeping requirement in 29 CFR 1904.40(a).
Paragraph (l)(3)(ii) requires employers to provide all other records and other documents that are required to be maintained by this section to the Assistant Secretary for examination and copying by the end of the next business day after a request. This means that employers must allow OSHA representatives to examine and copy each employee's COVID-19 vaccine documentation (required to be maintained under paragraph (e)(4)), the roster of employee vaccination status (required to be maintained under paragraph (e)(4)), and each employee's COVID-19 test results (required to be maintained under paragraph (g)(4)), upon request.
As indicated in paragraph (c), the term Assistant Secretary includes the Assistant Secretary's designees. Consequently, the records and information required to be provided to the Assistant Secretary under paragraph (l)(3) must be given to the Assistant Secretary or their representatives, such as OSHA's Compliance Safety and Health Officers.
As noted above, section 8 of the OSH Act recognizes OSHA's right of access to records relating to employer compliance with occupational safety and health standards and regulations, including access to relevant employee medical records. OSHA does not believe that its inspectors need to obtain employee permission to access and review personally identifiable information. Gaining this permission would essentially make it impossible to obtain full access to the records in a timely manner, which is needed by OSHA to perform a meaningful workplace investigation. OSHA also has policies and procedures in place to ensure the privacy and confidentiality of employee records it accesses during inspections. Finally, without complete and timely access to the vaccine and testing records, agency efforts to conduct immediate interventions to ensure employees are protected from COVID-19 at a specific workplace would be limited.
OSHA does not prescribe specific methods for requests for records in this ETS. Employees, employee representatives, and the Assistant Secretary and designees can submit requests in any manner that provides adequate notice of the request to the employer. This may include requests by in writing ( e.g., email, fax, letter), by phone, or in person.
M. Dates
To minimize transmission of COVID-19 in the workplace, it is essential that employers ensure that the provisions of this ETS are implemented as quickly as possible, but no later than the dates outlined in paragraph (m). This paragraph sets forth the effective date of the section and the compliance dates for specific requirements of the standard. The effective date for this ETS, as required by section 6(c)(1) of the OSH Act (29 U.S.C. 655(c)(1)), is the date of publication in the Federal Register . The compliance date for all provisions in the ETS is 30 days after the effective date, except for paragraph (g) (COVID-19 testing for employees who are not fully vaccinated), which requires compliance within 60 days of the effective date. Given the grave danger to employees from occupational exposure to COVID-19, as previously described, the effective date and compliance dates provided for this ETS are reasonable and appropriate.
For over a year and a half—since at least January 2020, when the Secretary of Health and Human Services declared COVID-19 to be a public health emergency for the entire United States—all employers have been made acutely aware of the importance of minimizing employees' exposure to COVID-19 and many have willingly joined the global response to stop the spread of COVID-19 and to protect their employees. Therefore, many employers have already been encouraging their employees to get vaccinated against COVID-19. Many employers have also instituted vaccination mandates (see Technological Feasibility, Section IV.A. of this preamble, for more information).
OSHA has published this ETS because there is great urgency in instituting the workplace protections OSHA has found to be necessary as quickly as possible. Unvaccinated workers are being hospitalized with COVID-19 every day, and many are dying, so it is particularly critical to remove obstacles as soon as possible for those who wish to be vaccinated. At the same time, OSHA has set the compliance dates to allow enough time for employers to obtain and read the standard, become knowledgeable about the standard's requirements, and undertake the necessary steps for compliance.
OSHA anticipates that employers will be able to implement measures to comply with most provisions of the ETS well within 30 days, pursuant to paragraph (m)(2)(i). Even in situations where an employer has not previously taken the required actions to address COVID-19 hazards in the workplace, steps such as developing a vaccination policy, determining employee vaccination status, providing support for employee vaccination, ensuring employees who are not fully vaccinated wear face coverings, and most other measures required under the standard can readily be completed within the 30-day time period. These measures do not require extensive lead times for large employers to implement. The scope of the standard is limited to employers with more than 100 employees largely because OSHA is especially confident that these employers will have the ability to implement the standard.
Paragraph (m)(2)(ii) of the ETS provides a longer period of time—60 days—for employers to comply with the requirements for COVID-19 testing in paragraph (g). Paragraph (g) requires employers to implement COVID-19 testing and reporting of results for employees who are not fully vaccinated. One reason for this extended period of time for testing is that employers may need additional time to develop policies and procedures regarding COVID-19 testing and associated recordkeeping.
Perhaps more critically, this ETS is intended to incentivize vaccination, so this delayed compliance date was established to allow sufficient time for employees to complete a COVID-19 primary vaccination before it is necessary to comply with the testing requirements in paragraph (g). The 60-day compliance period in paragraph (m)(2)(ii) provides employees with sufficient time to receive one dose of a single-dose primary vaccination ( e.g., Janssen (Johnson & Johnson)) or both doses of a two-dose primary vaccination series ( e.g., Pfizer-BioNTech, Moderna). For the Janssen COVID-19 vaccine, the primary vaccination takes 1 day to complete (CDC, August 10, 2021). Employees who receive the Janssen vaccine could therefore begin their primary vaccination at any time up to and including the 60th day from the date of publication in the Federal Register in order to be exempt from the testing requirements of paragraph (g). For the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine, the primary vaccination series takes 21 days to complete (CDC, August 25, 2021). Employees receiving the Pfizer-BioNTech series could begin their primary vaccination series up to 39 days from the date of publication in the Federal Register . Finally, for the Moderna COVID-19 vaccine, the primary vaccination series takes 28 days to complete (CDC, August 23, 2021). Employees receiving the Moderna series could therefore begin their primary vaccination series up to 32 days from the date of publication in the Federal Register .
As specified in paragraph (m)(2)(ii), if an employee completes the entire primary vaccination within 60 days following publication in the Federal Register , that employee does not have to be tested under paragraph (g), even if they have not yet completed the two week waiting period that is required to meet the definition of fully vaccinated in paragraph (c). Employers must begin compliance with the testing requirements of paragraph (g) only for employees who have not yet completed primary vaccination ( i.e., employees who have not received any doses, employees who have received only one dose of a two-dose series) within 60 days from the date of publication in the Federal Register . And because employers must have their vaccination support processes (as required by paragraph (f)) in place before employees would need to initiate their primary vaccination in time to avoid testing under this section, employees will be able to avoid all testing costs required by this ETS.
Compliance with the requirements of the ETS within the specified dates is achievable. Many employers are likely already in compliance with at least some of the provisions of the ETS. Resources are also readily available to help employers achieve compliance. These resources include guidance issued by OSHA, the CDC, state and local governments, trade associations, and other organizations to help employers successfully implement vaccination, testing, and face covering requirements to minimize the transmission of COVID-19 in the workplace. OSHA therefore concludes that the compliance dates in this ETS strike a reasonable balance between incentivizing vaccination and allowing enough time for employers to comply.
Although employers are not required to comply with the requirements of this ETS until 30 days from the date of publication in the Federal Register (60 days for paragraph (g)), OSHA strongly encourages employers to implement the required measures to support employee vaccination as soon as practicable. Providing support for employees to receive the COVID-19 vaccine and recover from side effects, as required in paragraph (f) of the ETS, prior to the compliance date may encourage employees to receive a COVID-19 vaccination at the earliest possible date. This would not only reduce the grave danger of COVID-19 in the workplace but also reduce burdens on both employers and employees when the compliance dates for the additional requirements for employees who are not fully vaccinated arrive.
References
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, August 10). Janssen COVID-19 Vaccine (Johnson & Johnson). https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/covid-19/info-by-product/moderna/index.html. (CDC, August 10, 2021)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, August 23). Moderna COVID-19 Vaccine. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/covid-19/info-by-product/moderna/index.html. (CDC, August 23, 2021)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, August 25). Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/covid-19/info-by-product/pfizer/index.html. (CDC, August 25, 2021)
N. Severability
OSHA's amendment to its COVID-19 ETS, Part 1910, Subpart U, includes a republication of §1910.505, Severability. Section 1910.505 contains a severability clause, the primary purpose of which is to express OSHA's intent that if any section or provision of the COVID-19 ETS is held invalid or unenforceable or is stayed or enjoined by any court of competent jurisdiction, the remaining sections or provisions should remain effective and operative. OSHA is including 29 CFR 1910.505 as part of this ETS for the same reasons the agency included the provision in the Healthcare ETS, and OSHA intends for it to have the same purposes and effects as those expressed in the preamble to the Healthcare ETS (86 FR 32617-32618), which is hereby included in the record for this ETS.
Because subpart U is the result of two separate ETSs published at different times and subject to different time frames, but OSHA intends for both ETSs to be subject to the same principles of severability, OSHA has relied on the same centralized severability section for both for efficiency. For the benefit of the reader and for administrative convenience, this centralized severability section is located in the same subpart as the other provisions of the ETS. While either ETS remains in effect, it is OSHA's intent that 29 CFR 1910.505 remain in subpart U and operative as to either ETS still in effect. If both ETSs are not made permanent, 29 CFR 1910.505 will cease to have effect along with the rest of subpart U. If either ETS is made permanent, OSHA will provide notice at that time of the agency's intended application of 29 CFR 1910.505 to the newly permanent standard. For example, if 29 CFR 1910.502 becomes permanent because it has been finalized, but 29 CFR 1910.501 remains a temporary requirement because it is not yet finalized, 29 CFR 1910.505 would remain in subpart U and operative as to 29 CFR 1910.501 and the agency would separately provide notice of how severability is intended to apply to the newly permanent 29 CFR 1910.502.
O. Incorporation by Reference
OSHA's amendment to its COVID-19 ETS, Part 1910, Subpart U, includes the addition of §1910.501, Vaccination, Testing, and Face Coverings. This section incorporates by reference CDC's “Isolation Guidance.”
This document, listed below, will be fixed in time and made publicly available. OSHA had previously incorporated this same document into 29 CFR 1910.502 and listed it in subpart U's incorporation by reference (IBR) section, 29 CFR 1910.509. Because subpart U is the result of two separate ETSs published at different times and subject to different time frames, but both incorporate documents by reference, OSHA has relied on the same centralized IBR section for both. For the benefit of the reader and for administrative convenience, this centralized IBR section is located in the same subpart as the other provisions of the ETS.
While either ETS remains in effect, it is OSHA's intent that 29 CFR 1910.509 remain in subpart U. If both ETSs are not made permanent, 29 CFR 1910.509 will cease to have effect along with the rest of subpart U. If either ETS is made permanent, OSHA intends to recodify the relevant standards for that ETS from 29 CFR 1910.509 into 29 CFR 1910.6, the centralized IBR section for part 1910. For example, if 29 CFR 1910.502 becomes permanent because it has been finalized, but 29 CFR 1910.501 remains a temporary requirement because it is not yet finalized, OSHA would relocate all of 29 CFR 1910.502's incorporated documents into 29 CFR 1910.6, but 29 CFR 1910.509 would remain in subpart U and would list the one document incorporated by reference into 29 CFR 1910.501.
In this section, OSHA includes a list of the titles, editions/versions, and years of the incorporated documents. Stakeholders may consult 29 CFR 1910.509 both to locate all of the documents incorporated by reference in subpart U (the paragraph in which the document is incorporated is listed there) and to find more details regarding how to locate the specific consensus standard and guidelines that have been incorporated by reference in the ETS.
OSHA recognizes that the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) may update their guidelines based on the most current available scientific evidence, but OSHA is only requiring compliance with CDC's “Isolation Guidance” as incorporated by reference, which is fixed in time as of February 18, 2021.
As discussed in the preamble of the Healthcare ETS at 86 FR 32619, CDC's guidance, including its “Isolation Guidance,” is not expressed in mandatory terms. As such, OSHA has determined it is not sufficiently protective or a meaningful alternative to a mandatory standard. OSHA has reviewed this guidance and determined that compliance with the safety measures and specific instructions in CDC's “Isolation Guidance” is important to protect workers who work for employees with over 100 employees. For the same reasons as described in the Healthcare ETS (86 FR 32619), OSHA is incorporating this guidance by reference, and compliance with the recommendations will be mandatory. OSHA will be able to cite employers who do not follow them. Compliance with all applicable provisions of the incorporated document is required where the provisions into which they are incorporated are mandatory, whether the incorporated document sets out its directions in mandatory language or recommendations. OSHA recognizes that this document incorporated by reference into the ETS may become outdated when newer versions are published or other entities revise those documents. In that case, OSHA will work quickly to update the ETS through a new rulemaking or issue enforcement guidance, as appropriate. But OSHA also has a longstanding de minimis enforcement policy to allow employers to rely on documents that are at least as protective.
OSHA is incorporating by reference (in 29 CFR 1910.509) the material below. A brief description of the guidance is provided in the text below. A description of its use can be found in the Regulatory Text, and Summary and Explanation (Section VI. of this preamble), where the guidance is referenced.
Regulatory Text—§§1910.501(h); 1910.502(l)
CDC's Isolation Guidance (2021): This guidance provides steps to take when someone is experiencing COVID-19 symptoms and/or tested positive for COVID-19. This document is available at www.osha.gov/coronavirus/ets/ibr.
The CDC document is available at no cost through the contact information listed above. In addition, in accordance with §1910.509(a)(1), this guidance is available for inspection at any Regional Office of the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), or at the OSHA Docket Office, U.S. Department of Labor, 200 Constitution Avenue NW, Room N-3508, Washington, DC 20210; telephone: 202-693-2350 (TTY number: 877-889-5627). Due to copyright issues, OSHA cannot post consensus standards on the OSHA website or through www.regulations.gov.
List of Subjects
29 CFR Part 1910
COVID-19, Disease, Health, Health care, Health facilities, Incorporation by reference, Occupational safety and health, Public health, Quarantine, Reporting and recordkeeping requirements, Respirators, SARS-CoV-2, Telework, Vaccines, Viruses.
29 CFR Parts 1915, 1917, 1918, 1926, and 1928
COVID-19, Disease, Health, Health care, Health facilities, Occupational safety and health, Public health, Quarantine, Reporting and recordkeeping requirements, Respirators, SARS-CoV-2, Telework, Vaccines, Viruses.
Authority and Signature
James S. Frederick, Acting Assistant Secretary of Labor for Occupational Safety and Health, U.S. Department of Labor, authorized the preparation of this document pursuant to the following authorities: Sections 4, 6, and 8 of the Occupational Safety and Health Act of 1970 (29 U.S.C. 653, 655, 657); Secretary of Labor's Order 8-2020 (85 FR 58393 (Sept. 18, 2020)); 29 CFR part 1911; and 5 U.S.C. 553.
James S. Frederick,
Acting Assistant Secretary of Labor for Occupational Safety and Health.
For the reasons set forth in the preamble, chapter XVII of title 29 of the Code of Federal Regulations is amended as follows:
PART 1910—OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY AND HEALTH STANDARDS
Subpart U—COVID-19
1. Revise the heading for Subpart U to read as set forth above.
2. The authority citation for subpart U continues to read as follows:
Authority:
29 U.S.C. 653, 655, and 657; Secretary of Labor's Order No. 8-2020 (85 FR 58393); 29 CFR part 1911; and 5 U.S.C. 553.
3. Add §1910.501 to subpart U to read as follows:
§1910.501 Vaccination, testing, and face coverings.
(a) Purpose. This section is intended to establish minimum vaccination, vaccination verification, face covering, and testing requirements to address the grave danger of COVID-19 in the workplace, and to preempt inconsistent state and local requirements relating to these issues, including requirements that ban or limit employers' authority to require vaccination, face covering, or testing, regardless of the number of employees.
Note 1 to paragraph (a):
This section establishes minimum requirements that employers must implement. Nothing in this section prevents employers from agreeing with workers and their representatives to additional measures not required by this section and this section does not supplant collective bargaining agreements or other collectively negotiated agreements in effect that may have negotiated terms that exceed the requirements herein. The National Labor Relations Act of 1935 (NLRA) protects the right of most private-sector employees to take collective action to improve their wages and working conditions.
(b) Scope and application. (1) This section covers all employers with a total of 100 or more employees at any time this section is in effect.
(2) The requirements of this section do not apply to:
(i) Workplaces covered under the Safer Federal Workforce Task Force COVID-19 Workplace Safety: Guidance for Federal Contractors and Subcontractors; or
(ii) Settings where any employee provides healthcare services or healthcare support services when subject to the requirements of §1910.502.
(3) The requirements of this section do not apply to the employees of covered employers:
(i) Who do not report to a workplace where other individuals such as coworkers or customers are present;
(ii) While working from home; or
(iii) Who work exclusively outdoors.
(c) Definitions. The following definitions apply to this section.
Assistant Secretary means the Assistant Secretary of Labor for Occupational Safety and Health, U.S. Department of Labor, or designee.
COVID-19 (Coronavirus Disease 2019) means the disease caused by SARS-CoV-2 (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2). For clarity and ease of reference, this section also uses the term “COVID-19” when describing exposures or potential exposures to SARS-CoV-2.
COVID-19 test means a test for SARS-CoV-2 that is:
(i) Cleared, approved, or authorized, including in an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA), by the FDA to detect current infection with the SARS-CoV-2 virus ( e.g., a viral test);
(ii) Administered in accordance with the authorized instructions; and
(iii) Not both self-administered and self-read unless observed by the employer or an authorized telehealth proctor. Examples of tests that satisfy this requirement include tests with specimens that are processed by a laboratory (including home or on-site collected specimens which are processed either individually or as pooled specimens), proctored over-the-counter tests, point of care tests, and tests where specimen collection and processing is either done or observed by an employer.
Face covering means a covering that:
(i)(A) completely covers the nose and mouth;
(B) Is made with two or more layers of a breathable fabric that is tightly woven ( i.e., fabrics that do not let light pass through when held up to a light source);
(C) Is secured to the head with ties, ear loops, or elastic bands that go behind the head. If gaiters are worn, they should have two layers of fabric or be folded to make two layers;
(D) Fits snugly over the nose, mouth, and chin with no large gaps on the outside of the face; and
(E) Is a solid piece of material without slits, exhalation valves, visible holes, punctures, or other openings.
(ii) This definition includes clear face coverings or cloth face coverings with a clear plastic panel that, despite the non-cloth material allowing light to pass through, otherwise meet this definition and which may be used to facilitate communication with people who are deaf or hard-of-hearing or others who need to see a speaker's mouth or facial expressions to understand speech or sign language respectively.
Facemask means a surgical, medical procedure, dental, or isolation mask that is FDA-cleared, authorized by an FDA EUA, or offered or distributed as described in an FDA enforcement policy. Facemasks may also be referred to as “medical procedure masks.”
Fully vaccinated means:
(i) A person's status 2 weeks after completing primary vaccination with a COVID-19 vaccine with, if applicable, at least the minimum recommended interval between doses in accordance with the approval, authorization, or listing that is:
(A) Approved or authorized for emergency use by the FDA;
(B) Listed for emergency use by the World Health Organization (WHO); or
(C) Administered as part of a clinical trial at a U.S. site, if the recipient is documented to have primary vaccination with the active (not placebo) COVID-19 vaccine candidate, for which vaccine efficacy has been independently confirmed ( e.g., by a data and safety monitoring board) or if the clinical trial participant at U.S. sites had received a COVID-19 vaccine that is neither approved nor authorized for use by FDA but is listed for emergency use by WHO; or
(ii) A person's status 2 weeks after receiving the second dose of any combination of two doses of a COVID-19 vaccine that is approved or authorized by the FDA, or listed as a two-dose series by the WHO ( i.e., a heterologous primary series of such vaccines, receiving doses of different COVID-19 vaccines as part of one primary series). The second dose of the series must not be received earlier than 17 days (21 days with a 4-day grace period) after the first dose.
Mandatory Vaccination Policy is an employer policy requiring each employee to be fully vaccinated. To meet this definition, the policy must require: Vaccination of all employees, including vaccination of all new employees as soon as practicable, other than those employees:
(i) For whom a vaccine is medically contraindicated;
(ii) For whom medical necessity requires a delay in vaccination; or
(iii) Who are legally entitled to a reasonable accommodation under federal civil rights laws because they have a disability or sincerely held religious beliefs, practices, or observances that conflict with the vaccination requirement.
Respirator means a type of personal protective equipment (PPE) that is certified by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) under 42 CFR part 84 or is authorized under an EUA by the FDA. Respirators protect against airborne hazards by removing specific air contaminants from the ambient (surrounding) air or by supplying breathable air from a safe source. Common types of respirators include filtering facepiece respirators ( e.g., N95), elastomeric respirators, and powered air purifying respirators (PAPRs). Face coverings, facemasks, and face shields are not respirators.
Workplace means a physical location ( e.g., fixed, mobile) where the employer's work or operations are performed. It does not include an employee's residence.
(d) Employer policy on vaccination. (1) The employer must establish, implement, and enforce a written mandatory vaccination policy.
(2) The employer is exempted from the requirement in paragraph (d)(1) of this section only if the employer establishes, implements, and enforces a written policy allowing any employee not subject to a mandatory vaccination policy to choose either to be fully vaccinated against COVID-19 or provide proof of regular testing for COVID-19 in accordance with paragraph (g) of this section and wear a face covering in accordance with paragraph (i) of this section.
Note 1 to paragraph (d):
Under federal law, including the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) and Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964, workers may be entitled to a reasonable accommodation from their employer, absent undue hardship. If the worker requesting a reasonable accommodation cannot be vaccinated and/or wear a face covering because of a disability, as defined by the ADA, the worker may be entitled to a reasonable accommodation. In addition, if the vaccination, and/or testing for COVID-19, and/or wearing a face covering conflicts with a worker's sincerely held religious belief, practice or observance, the worker may be entitled to a reasonable accommodation. For more information about evaluating requests for reasonable accommodation for disability or sincerely held religious belief, employers should consult the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission's regulations, guidance, and technical assistance including at: https://www.eeoc.gov/wysk/what-you-should-know-about-covid-19-and-ada-rehabilitation-act-and-other-eeo-laws.
(e) Determination of employee vaccination status. (1) The employer must determine the vaccination status of each employee. This determination must include whether the employee is fully vaccinated.
(2) The employer must require each vaccinated employee to provide acceptable proof of vaccination status, including whether they are fully or partially vaccinated. Acceptable proof of vaccination status is:
(i) The record of immunization from a health care provider or pharmacy;
(ii) A copy of the COVID-19 Vaccination Record Card;
(iii) A copy of medical records documenting the vaccination;
(iv) A copy of immunization records from a public health, state, or tribal immunization information system; or
(v) A copy of any other official documentation that contains the type of vaccine administered, date(s) of administration, and the name of the health care professional(s) or clinic site(s) administering the vaccine(s);
(vi) In instances where an employee is unable to produce acceptable proof of vaccination under paragraphs (e)(2)(i) through (v) of this section, a signed and dated statement by the employee:
(A) Attesting to their vaccination status (fully vaccinated or partially vaccinated);
(B) Attesting that they have lost and are otherwise unable to produce proof required by this section; and
(C) Including the following language: “I declare (or certify, verify, or state) that this statement about my vaccination status is true and accurate. I understand that knowingly providing false information regarding my vaccination status on this form may subject me to criminal penalties.”
Note 1 to paragraph (e)(2)(vi):
An employee who attests to their vaccination status should, to the best of their recollection, include the following information in their attestation: The type of vaccine administered; date(s) of administration; and the name of the health care professional(s) or clinic site(s) administering the vaccine(s).
(3) Any employee who does not provide one of the acceptable forms of proof of vaccination status in paragraph (e)(2) of this section to the employer must be treated as not fully vaccinated for the purpose of this section.
(4) The employer must maintain a record of each employee's vaccination status and must preserve acceptable proof of vaccination for each employee who is fully or partially vaccinated. The employer must maintain a roster of each employee's vaccination status. These records and roster are considered to be employee medical records and must be maintained as such records in accordance with §1910.1020 and must not be disclosed except as required or authorized by this section or other federal law. These records and roster are not subject to the retention requirements of §1910.1020(d)(1)(i) but must be maintained and preserved while this section remains in effect.
(5) When an employer has ascertained employee vaccination status prior to the effective date of this section through another form of attestation or proof, and retained records of that ascertainment, the employer is exempt from the requirements in paragraphs (e)(1) through (3) of this section only for each employee whose fully vaccinated status has been documented prior to the effective date of this section. For purposes of paragraph (e)(4) of this section, the employer's records of ascertainment of vaccination status for each such person constitute acceptable proof of vaccination.
(f) Employer support for employee vaccination. The employer must support COVID-19 vaccination as described in this paragraph.
(1) Time for vaccination. The employer must:
(i) Provide a reasonable amount of time to each employee for each of their primary vaccination dose(s); and
(ii) Provide up to 4 hours paid time, including travel time, at the employee's regular rate of pay for this purpose.
(2) Time for recovery. The employer must provide reasonable time and paid sick leave to recover from side effects experienced following any primary vaccination dose to each employee for each dose.
(g) COVID-19 testing for employees who are not fully vaccinated. (1) The employer must ensure that each employee who is not fully vaccinated complies with paragraph (g)(1)(i) or (ii) of this section:
(i) An employee who reports at least once every 7 days to a workplace where other individuals such as coworkers or customers are present:
(A) Must be tested for COVID-19 at least once every 7 days; and
(B) Must provide documentation of the most recent COVID-19 test result to the employer no later than the 7th day following the date on which the employee last provided a test result.
(ii) An employee who does not report during a period of 7 or more days to a workplace where other individuals such as coworkers or customers are present ( e.g., teleworking for two weeks prior to reporting to a workplace with others):
(A) Must be tested for COVID-19 within 7 days prior to returning to the workplace; and
(B) Must provide documentation of that test result to the employer upon return to the workplace.
Note 1 to paragraph (g)(1):
This section does not require the employer to pay for any costs associated with testing; however employer payment for testing may be required by other laws, regulations, or collective bargaining agreements or other collectively negotiated agreements. This section also does not prohibit the employer from paying for costs associated with testing required by paragraph (g)(1) of this section.
(2) If an employee does not provide documentation of a COVID-19 test result as required by paragraph (g)(1) of this section, the employer must keep that employee removed from the workplace until the employee provides a test result.
(3) When an employee has received a positive COVID-19 test, or has been diagnosed with COVID-19 by a licensed healthcare provider, the employer must not require that employee to undergo COVID-19 testing as required under paragraph (g) of this section for 90 days following the date of their positive test or diagnosis.
(4) The employer must maintain a record of each test result provided by each employee under paragraph (g)(1) of this section or obtained during tests conducted by the employer. These records are considered to be employee medical records and must be maintained as such records in accordance with §1910.1020 and must not be disclosed except as required or authorized by this section or other federal law. These records are not subject to the retention requirements of §1910.1020(d)(1)(i) but must be maintained and preserved while this section remains in effect.
(h) Employee notification to employer of a positive COVID-19 test and removal. Regardless of COVID-19 vaccination status or any COVID-19 testing required under paragraph (g) of this section, the employer must:
(1) Require each employee to promptly notify the employer when they receive a positive COVID-19 test or are diagnosed with COVID-19 by a licensed healthcare provider; and
(2) Immediately remove from the workplace any employee who receives a positive COVID-19 test or is diagnosed with COVID-19 by a licensed healthcare provider and keep the employee removed until the employee:
(i) Receives a negative result on a COVID-19 nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT) following a positive result on a COVID-19 antigen test if the employee chooses to seek a NAAT test for confirmatory testing;
(ii) meets the return to work criteria in CDC's “Isolation Guidance” (incorporated by reference, §1910.509); or
(iii) Receives a recommendation to return to work from a licensed healthcare provider.
Note 1 to paragraph (h)(2):
This section does not require employers to provide paid time to any employee for removal as a result of a positive COVID-19 test or diagnosis of COVID-19; however, paid time may be required by other laws, regulations, or collective bargaining agreements or other collectively negotiated agreements.
(i) Face coverings. (1) The employer must ensure that each employee who is not fully vaccinated wears a face covering when indoors and when occupying a vehicle with another person for work purposes, except:
(i) When an employee is alone in a room with floor to ceiling walls and a closed door.
(ii) For a limited time while the employee is eating or drinking at the workplace or for identification purposes in compliance with safety and security requirements.
(iii) When an employee is wearing a respirator or facemask.
(iv) Where the employer can show that the use of face coverings is infeasible or creates a greater hazard that would excuse compliance with this paragraph ( e.g., when it is important to see the employee's mouth for reasons related to their job duties, when the work requires the use of the employee's uncovered mouth, or when the use of a face covering presents a risk of serious injury or death to the employee).
(2) The employer must ensure that any face covering required to be worn by this section:
(i) Is worn by the employee to fully cover the employee's nose and mouth; and
(ii) Is replaced when wet, soiled, or damaged ( e.g., is ripped, has holes, or has broken ear loops).
(3) The employer must not prevent any employee from voluntarily wearing a face covering or facemask unless the employer can demonstrate that doing so would create a hazard of serious injury or death, such as interfering with the safe operation of equipment.
(4) The employer must permit the employee to wear a respirator instead of a face covering whether required or not. In addition, the employer may provide respirators to the employee, even if not required. In such circumstances, the employer must also comply with §1910.504.
(5) The employer must not prohibit customers or visitors from wearing face coverings.
Note 1 to paragraph (i)(5):
Nothing in this section precludes employers from requiring customers or visitors to wear face coverings.
Note 1 to paragraph (i):
Face shields may be worn in addition to face coverings to prevent them from getting wet and soiled.
Note 2 to paragraph (i):
This section does not require the employer to pay for any costs associated with face coverings; however employer payment for face coverings may be required by other laws, regulations, or collective bargaining agreements or other collectively negotiated agreements. This section also does not prohibit the employer from paying for costs associated with face coverings required by this section.
(j) Information provided to employees. The employer must inform each employee, in a language and at a literacy level the employee understands, about:
(1) The requirements of this section as well as any employer policies and procedures established to implement this section;
(2) COVID-19 vaccine efficacy, safety, and the benefits of being vaccinated, by providing the document, “Key Things to Know About COVID-19 Vaccines,” available at https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/keythingstoknow.html;
(3) The requirements of 29 CFR 1904.35(b)(1)(iv), which prohibits the employer from discharging or in any manner discriminating against an employee for reporting a work-related injuries or illness, and section 11(c) of the OSH Act, which prohibits the employer from discriminating against an employee for exercising rights under, or as a result of actions that are required by, this section. Section 11(c) also protects the employee from retaliation for filing an occupational safety or health complaint, reporting a work-related injuries or illness, or otherwise exercising any rights afforded by the OSH Act; and
(4) The prohibitions of 18 U.S.C. 1001 and of section 17(g) of the OSH Act, which provide for criminal penalties associated with knowingly supplying false statements or documentation.
(k) Reporting COVID-19 fatalities and hospitalizations to OSHA. (1) The employer must report to OSHA:
(i) Each work-related COVID-19 fatality within 8 hours of the employer learning about the fatality.
(ii) Each work-related COVID-19 in-patient hospitalization within 24 hours of the employer learning about the in-patient hospitalization.
(2) When reporting COVID-19 fatalities and in-patient hospitalizations to OSHA in accordance with paragraph (j)(1) of this section, the employer must follow the requirements in 29 CFR part 1904.39, except for 29 CFR part 1904.39(a)(1) and (2) and (b)(6).
(l) Availability of records. (1) By the end of the next business day after a request, the employer must make available, for examination and copying, the individual COVID-19 vaccine documentation and any COVID-19 test results for a particular employee to that employee and to anyone having written authorized consent of that employee.
(2) By the end of the next business day after a request by an employee or an employee representative, the employer must make available to the requester the aggregate number of fully vaccinated employees at a workplace along with the total number of employees at that workplace.
(3) The employer must provide to the Assistant Secretary for examination and copying:
(i) Within 4 business hours of a request, the employer's written policy required by paragraph (d) of this section, and the aggregate numbers described in paragraph (l)(2) of this section; and
(ii) By the end of the next business day after a request, all other records and other documents required to be maintained by this section.
(m) Dates—(1) Effective date. This section is effective as of November 5, 2021.
(2) Compliance dates. (i) Employers must comply with all requirements of this section, except for requirements in paragraph (g) of this section, by December 6, 2021.
(ii) Employers must comply with the requirements of this section in paragraph (g) by January 4, 2022, but employees who have completed the entire primary vaccination by that date do not have to be tested, even if they have not yet completed the 2-week waiting period.
4. Amend §1910.504 by revising paragraph (a) to read as follows:
§1910.504 Mini Respiratory Protection Program.
(a) Scope and application. This section applies only to respirator use in accordance with §§1910.501(i)(4) and 1910.502(f)(4).
* * * * *
5. Republish §1910.505 to read as follows:
§1910.505 Severability.
Each section of this subpart U, and each provision within those sections, is separate and severable from the other sections and provisions. If any provision of this subpart is held to be invalid or unenforceable on its face, or as applied to any person, entity, or circumstance, or is stayed or enjoined, that provision shall be construed so as to continue to give the maximum effect to the provision permitted by law, unless such holding shall be one of utter invalidity or unenforceability, in which event the provision shall be severable from this subpart and shall not affect the remainder of the subpart.
6. Amend §1910.509 by revising paragraph (b)(5) to read as follows:
§1910.509 Incorporation by reference.
* * * * *
(b) * * *
(5) Isolation Guidance. COVID-19: Isolation If You Are Sick; Separate yourself from others if you have COVID-19, updated February 18, 2021, IBR approved for §§1910.501(h) and 1910.502(l).
* * * * *
PART 1915—OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY AND HEALTH STANDARDS FOR SHIPYARD EMPLOYMENT
7. The authority citation for part 1915 is revised to read as follows:
Authority:
33 U.S.C. 941; 29 U.S.C. 653, 655, 657; Secretary of Labor's Order No. 12-71 (36 FR 8754); 8-76 (41 FR 25059), 9-83 (48 FR 35736), 1-90 (55 FR 9033), 6-96 (62 FR 111), 3-2000 (65 FR 50017), 5-2002 (67 FR 65008), 5-2007 (72 FR 31160), 4-2010 (75 FR 55355), 1-2012 (77 FR 3912), or 8-2020 (85 FR 58393); 29 CFR part 1911; and 5 U.S.C. 553, as applicable.
Subpart Z—Toxic and Hazardous Substances
8. Add §1915.1501 to subpart Z to read as follows:
§1915.1501 COVID-19.
The requirements applicable to shipyard employment under this section are identical to those set forth at 29 CFR 1910.501.
PART 1917—MARINE TERMINALS
9. The authority citation for part 1917 is revised to read as follows:
Authority:
33 U.S.C. 941; 29 U.S.C. 653, 655, 657; Secretary of Labor's Order No. 12-71 (36 FR 8754), 8-76 (41 FR 25059), 9-83 (48 FR 35736), 1-90 (55 FR 9033), 6-96 (62 FR 111), 3-2000 (65 FR 50017), 5-2002 (67 FR 65008), 5-2007 (72 FR 31160), 4-2010 (75 FR 55355), 1-2012 (77 FR 3912), or 8-2020 (85 FR 58393), as applicable; and 29 CFR part 1911.
Sections 1917.28 and 1917.31 also issued under 5 U.S.C. 553.
Section 1917.29 also issued under 49 U.S.C. 1801-1819 and 5 U.S.C. 553.
Subpart B—Marine Terminal Operations
10. Add §1917.31 to subpart B to read as follows:
§1917.31 COVID-19.
The requirements applicable to marine terminal work under this section are identical to those set forth at 29 CFR 1910.501.
PART 1918—SAFETY AND HEALTH REGULATIONS FOR LONGSHORING
11. The authority citation for part 1918 is revised to read as follows:
Authority:
33 U.S.C. 941; 29 U.S.C. 653, 655, 657; Secretary of Labor's Order No. 12-71 (36 FR 8754), 8-76 (41 FR 25059), 9-83 (48 FR 35736), 1-90 (55 FR 9033), 6-96 (62 FR 111), 3-2000 (65 FR 50017), 5-2002 (67 FR 65008), 5-2007 (72 FR 31160), 4-2010 (75 FR 55355), 1-2012 (77 FR 3912), or 8-2020 (85 FR 58393), as applicable; and 29 CFR 1911.
Sections 1918.90 and 1918.110 also issued under 5 U.S.C. 553.
Section 1918.100 also issued under 49 U.S.C. 5101 et seq. and 5 U.S.C. 553.
12. Add subpart K to part 1918 to read as follows:
Subpart K—COVID-19.
Sec.
1918.107-1918.109 [Reserved]
1918.110 COVID-19.
1918.107 through 1918.109 [Reserved]
§1918.110 COVID-19.
The requirements applicable to longshoring work under this section are identical to those set forth at 29 CFR 1910.501.
PART 1926—SAFETY AND HEALTH REGULATIONS FOR CONSTRUCTION
13. The authority citation for part 1926 is revised to read as follows:
Authority:
40 U.S.C. 3704; 29 U.S.C. 653, 655, and 657; and Secretary of Labor's Order No. 12-71 (36 FR 8754), 8-76 (41 FR 25059), 9-83 (48 FR 35736), 1-90 (55 FR 9033), 6-96 (62 FR 111), 3-2000 (65 FR 50017), 5-2002 (67 FR 65008), 5-2007 (72 FR 31159), 4-2010 (75 FR 55355), 1-2012 (77 FR 3912), or 8-2020 (85 FR 58393), as applicable; and 29 CFR part 1911.
Sections 1926.58, 1926.59, 1926.60, and 1926.65 also issued under 5 U.S.C. 553 and 29 CFR part 1911.
Section 1926.61 also issued under 49 U.S.C. 1801-1819 and 5 U.S.C. 553.
Section 1926.62 also issued under sec. 1031, Public Law 102-550, 106 Stat. 3672 (42 U.S.C. 4853).
Section 1926.65 also issued under sec. 126, Public Law 99-499, 100 Stat. 1614 (reprinted at 29 U.S.C.A. 655 Note) and 5 U.S.C. 553.
Subpart D—Occupational Health and Environmental Controls
14. Add §1926.58 to read as follows:
§1926.58 COVID-19.
The requirements applicable to construction work under this section are identical to those set forth at 29 CFR 1910.501 Subpart U.
PART 1928—OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY AND HEALTH STANDARDS FOR AGRICULTURE
15. The authority citation for part 1928 is revised to read as follows:
Authority:
Sections 4, 6, and 8 of the Occupational Safety and Health Act of 1970 (29 U.S.C. 653, 655, 657); Secretary of Labor's Order No. 12-71 (36 FR 8754), 8-76 (41 FR 25059), 9-83 (48 FR 35736), 1-90 (55 FR 9033), 6-96 (62 FR 111), 3-2000 (65 FR 50017), 5-2002 (67 FR 65008), 4-2010 (75 FR 55355), or 8-2020 (85 FR 58393), as applicable; and 29 CFR 1911.
Section 1928.21 also issued under 49 U.S.C. 1801-1819 and 5 U.S.C. 553.
Subpart B—Applicability of Standards
16. Amend §1928.21 by adding paragraph (a)(8) to read as follows:
§1928.21 Applicable standards in 29 CFR part 1910.
(a) * * *
(8) COVID-19—§1910.501, but only with respect to—
(i) Agricultural establishments where eleven (11) or more employees are engaged on any given day in hand-labor operations in the field; and
(ii) Agricultural establishments that maintain a temporary labor camp, regardless of how many employees are engaged on any given day in hand-labor operations in the field.
* * * * *
[FR Doc. 2021-23643 Filed 11-4-21; 8:45 am]
BILLING CODE 4510-26-P