Ensuring safety: Machine guarding methods for portable powered tools
In September 2022, OSHA fined a Florida contractor $464,079 for three willful and one serious violation. In one of the violations, OSHA found the contractor failed to provide employees who use pneumatic nail guns, hammers, and portable circular saws with necessary eye protection.
Moving machine parts can cause severe workplace injuries, such as crushed fingers, amputations, or blindness. Safeguarding equipment is essential for protecting workers from these preventable injuries.
Portable powered tools are exactly the types of equipment that require proper safeguarding. While these tools help workers perform difficult or impossible tasks more efficiently, their use presents potential hazards. Proper machine guarding is one such action employers can take to reduce or eliminate hazards.
The requirements found at 1910.243, Guarding of portable powered tools, contain the information necessary to ensure these tools are properly safeguarded. Detailed requirements can be found for:
- Portable powered tools
- Pneumatic powered tools and hoses
- Portable abrasive wheels
- Explosive actuated fastening tools
- Power lawnmowers
Portable powered tools
Portable powered tools include circular saws and belt sanding machines. Portable circular saws are used for straight sawing. Per 1910.243(a)(1)(i), “All portable, power-driven circular saws having a blade diameter greater than 2 in. shall be equipped with guards above and below the base plate or shoe. The upper guard shall cover the saw to the depth of the teeth, except for the minimum arc required to permit the base to be tilted for bevel cuts. The lower guard shall cover the saw to the depth of the teeth, except for the minimum arc required to allow proper retraction and contact with the work.”
Portable belt sanders are used to smooth, level, and round and shape surfaces. 1910.243(a)(3) states, “Belt sanding machines shall be provided with guards at each nip point where the sanding belt runs onto a pulley. These guards shall effectively prevent the hands or fingers of the operator from coming in contact with the nip points. The unused run of the sanding belt shall be guarded against accidental contact.”
Pneumatic powered tools and hoses
Pneumatic powered tools, such as buffers, staple guns, and drills, run on compressed air. For this tool type, a tool retainer shall be installed on each piece of utilization equipment to prevent ejection of the tool. Hose and hose connections that are used for conducting compressed air to utilization equipment shall be designed for the pressure and service they are subjected to.
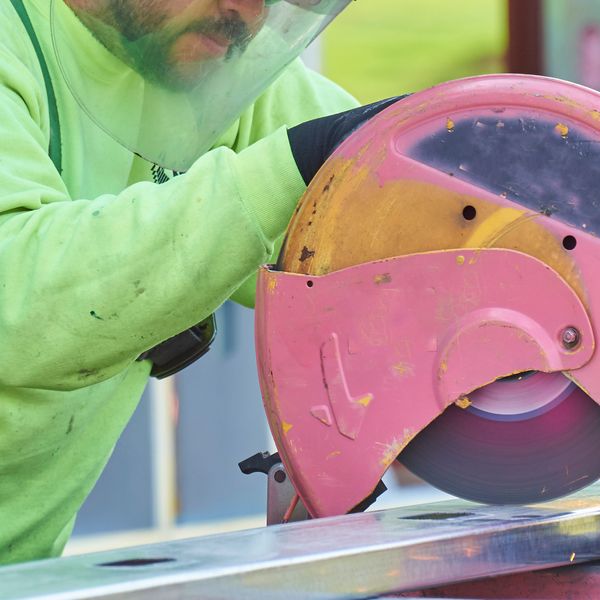
Portable abrasive wheels
General requirements state that abrasive wheels shall be used only on machines provided with safety guards as defined in 1910.243(c) (1) through (4), with a few exceptions. A safety guard shall cover the spindle end, nut, and flange projections and be mounted so as to maintain proper alignment with the wheel.
Cup wheels (Types 6 and 11) shall be protected by
- Safety guards as specified in 1910.243(c)(1),
- Special “revolving cup guards,” or
- Some other form of guard that will insure good protection.
Vertical portable grinders are used for grinding, cutting, and polishing surfaces. Safety guards shall have a maximum exposure angle of 180°, and the guard shall be located between the operator and the wheel during use.
Regarding other portable grinders, 1910.243(c)(4) says, “The maximum angular exposure of the grinding wheel periphery and sides for safety guards used on other portable grinding machines shall not exceed 180° and the top half of the wheel shall be enclosed at all times.”
Explosive actuated fastening tools
These tools use a small, controlled explosion to drive a nail, stud, or other specialized fastener into a solid base material such as steel, concrete, or masonry. Operators and assistants using these tools shall be safeguarded by means of eye protection. Additionally, head and face protection shall be used, as required by working conditions.
A high velocity tool requires the muzzle end of the tool to have a protective shield or guard at least 3 1⁄2 inches in diameter, mounted perpendicular to and concentric with the barrel, and designed to confine any flying fragments or particles that might otherwise create a hazard at the time of firing. Where a standard shield or guard cannot be used, a special shield, guard, fixture, or jig designed and built by the manufacturer of the tool being used shall be used as a substitute.
Power lawnmowers
Walk-behind, riding-rotary, and reel power lawnmowers shall be guarded in accordance with the machine guarding requirements in 29 CFR 1910.212, General requirements for all machines.
While safeguarding equipment is important for worker safety, proper training and inspection are equally important. Employers should ensure workers are trained on how to operate all equipment they will use as part of their job duties, and workers should carefully inspect tools before use. Any tool that is damaged or defective should be removed from service until it can be repaired or replaced.
Key to remember: Portable powered tools can cause workplace injuries, such as crushed fingers or amputations. The use of proper machine guards is essential for protecting workers from these preventable injuries.