Battle of the sniffles: Allergies vs. the common cold
What is the difference?
The common cold is caused by various respiratory viruses, with rhinoviruses being the most common. These viruses are highly contagious and spread simply through close personal contact with an infected person, respiratory droplets when they cough or sneeze, or even by touching contaminated surfaces and then touching your eyes, nose, or mouth.
The CDC emphasizes that colds are more frequent in colder months, but many cold viruses can spread effectively anytime of the year. Adults in the United States experience an average of two to three colds per year.
Allergies, on the other hand, are immune system reactions to substances known as allergens, such as pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and mold. The CDC clarifies that allergies are not contagious and are triggered by exposure to specific allergens.
OSHA highlights that workplace allergens can include chemicals, dust, mold, and other environmental factors. Approximately 31.8% of adults in the United States have some form of allergy.
What are the symptoms?
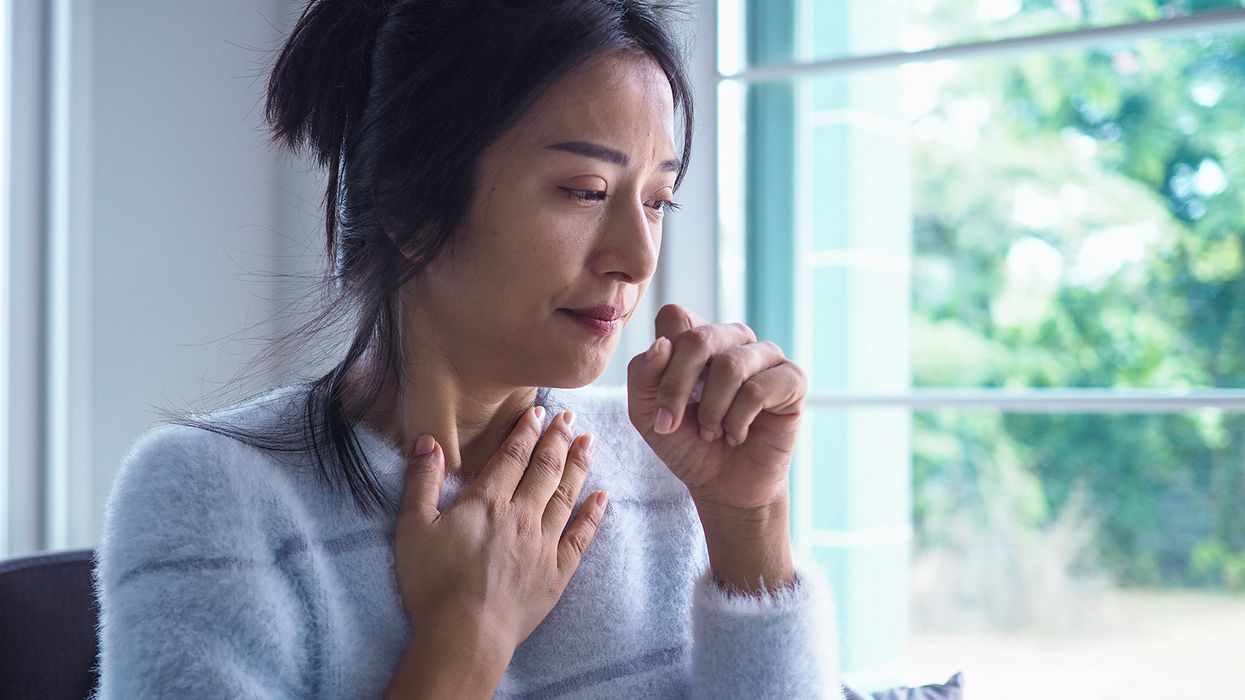
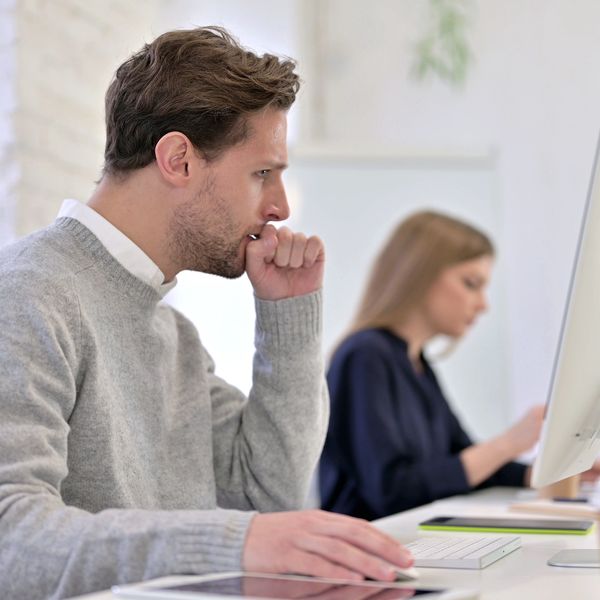
Cold symptoms typically include a runny or stuffy nose, sore throat, cough, sneezing, mild body aches, headache, and low-grade fever. These symptoms usually peak within two to three days of infection and typically last for about seven to ten days.
Allergy symptoms, as described by the CDC, include sneezing, runny or stuffy nose, itchy or watery eyes, itchy skin or throat, and cough. Unlike colds, allergy symptoms can persist as long as the person is exposed to the allergen. OSHA adds that workplace exposure to allergens can worsen these symptoms.
How can we prevent it from affecting the workplace?
To prevent the common cold from affecting the workplace, the CDC recommends good hygiene practices such as frequent hand washing, avoiding close contact with infected individuals, and disinfecting commonly touched surfaces.
OSHA supports these measures and encourages employers to provide hand sanitizers and promote a clean work environment. Additionally, employers can implement policies that encourage sick employees to stay home to prevent the spread of illness.
Preventing allergy symptoms requires minimizing exposure to allergens. The CDC suggests using air purifiers, keeping windows closed during high pollen seasons, regular cleaning to reduce dust and pet dander, and avoiding known food allergens.
OSHA highlights the importance of controlling workplace allergens through proper housekeeping and maintenance, including regular cleaning of ventilation systems and commonly touched surfaces.
Additionally, certain chemicals can cause allergic reactions, so reviewing your chemical inventory and minimizing chemicals that contain known allergens should be considered in workplaces.
Key to remember: While the common cold and allergies share some symptoms, they have distinct differences in their causes, duration, treatment, and prevention. Understanding these differences can help individuals manage their symptoms more effectively and ensure a healthier workplace.