MIS data affects DOT testing rates
Each year, the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) gathers data on positive Department of Transportation drug and alcohol tests to determine whether the current testing rates need adjusting.
A positive drug test is one that identifies marijuana, cocaine, opiates, amphetamines, or phencyclidine (PCP) in a urine specimen using the cutoff levels set by the Department of Health and Human Services.
A failed alcohol test is one that indicates a BAC of 0.04 or higher using an evidential breath alcohol testing device.
Random positivity rates
The positivity rate for random drug testing in 2021 was 1.2 percent, up from 0.9 percent in 2020 but down from a positivity rate of 1.6 percent in 2019.
The rate of those failing random alcohol tests in 2021 was 0.12 percent, slightly down from 2020’s 0.13 percent. The violation rate for 2019 was considerably higher at 0.3 percent.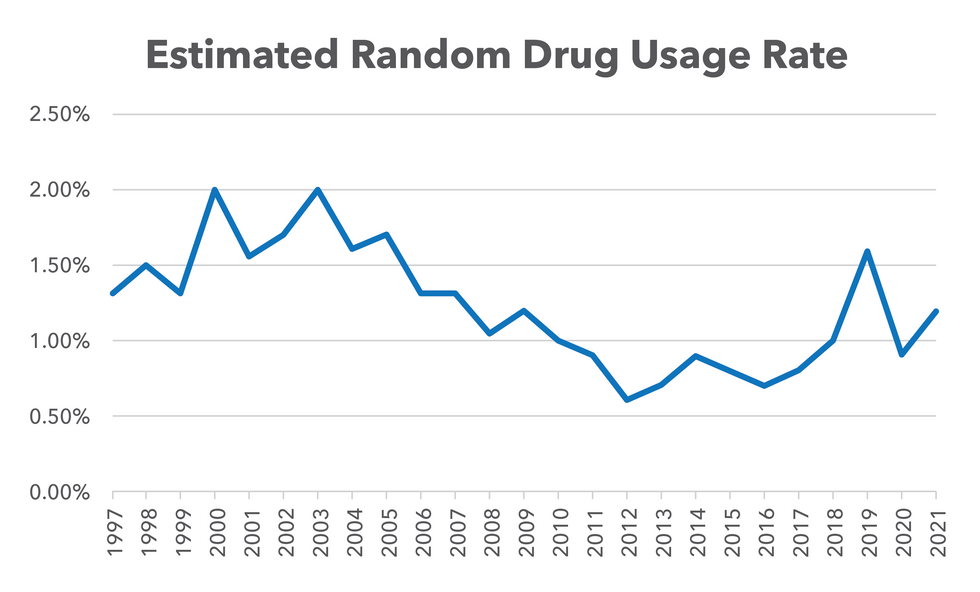
Non-random testing data
The survey also captured data on failed pre-employment and post-accident drug and alcohol tests.
The survey indicated a downward trend in failed pre-employment drug tests as noted below:
- 2019: 1.9%
- 2020: 1.1%
- 2021: 0.9%
Regarding post-accident drug tests, the positivity rate has declined as well:
- 2019: 5.8%
- 2020: 2.1%
- 2021: 1.5%
Failed post-accident alcohol testing increased slightly, returning to its 2019 level:
- 2019: 0.05%
- 2020: 0.03%
- 2021: 0.05%
How is data solicited from motor carriers?
The FMCSA’s 2021 testing data was based on survey results from nearly 9,500 motor carriers representing over 850,000 drivers.
Not all motor carriers are required to answer a drug-and-alcohol testing survey. Rather, FMCSA randomly selects motor carriers annually to complete the Management Information System (MIS) form.
Selected motor carriers are required to fill out the form by March 15 using drug and alcohol program records from the previous calendar year. They must enter result totals (negative, positive, canceled, refusal to test) by reason for testing (pre-employment, random, post-accident, etc.).
Maintaining accurate records throughout the year will assist in compiling the information. Motor carriers should have mechanisms in place to retrieve these data points, including use of lab summaries, spreadsheets, and/or software.
Motor carriers using a consortium or third-party administrator may ask their service provider to complete the form on their behalf, but someone from the motor carrier must still sign the form attesting to its accuracy.
How does the data affect testing rates?
The results of failed drug and alcohol tests determine whether FMCSA’s drug and/or alcohol testing rates are changed.
The current random alcohol testing rate is 10 percent. The rate will increase to 25 percent when the violation rate is 0.5-0.9 percent for the year. If the violation rate is 1.0 percent or greater, the testing rate will be increased to 50 percent.
The current drug testing rate is 50 percent. FMCSA lowers the rate to 25 percent in the event the data shows two consecutive years with an overall positivity rate of less than 1.0 percent.
Key to remember: The FMCSA Drug and Alcohol Testing Survey identifies trends to determine whether to change current FMCSA random testing rates. Maintaining complete records will assist motor carriers in providing accurate information for FMCSA to analyze.