Protecting solar energy workers from heat and electrical hazards
The solar boom is here. And with it, comes a surge in safety concerns. Are safety managers equipped to handle the challenges of this rapidly expanding workforce?
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the solar industry is expected to experience a 22% growth in the employment of solar installers between 2022 and 2032. That’s quite a difference from an average anticipated growth rate of 3% for all other occupations.
As the sector expands, the influx of new workers brings a heightened risk of injury, particularly from heat and electrical hazards.
Ensuring the safety of these workers is critical and requires a comprehensive approach that addresses equipment reliability, proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE), and extensive education and training.
Understanding the risks
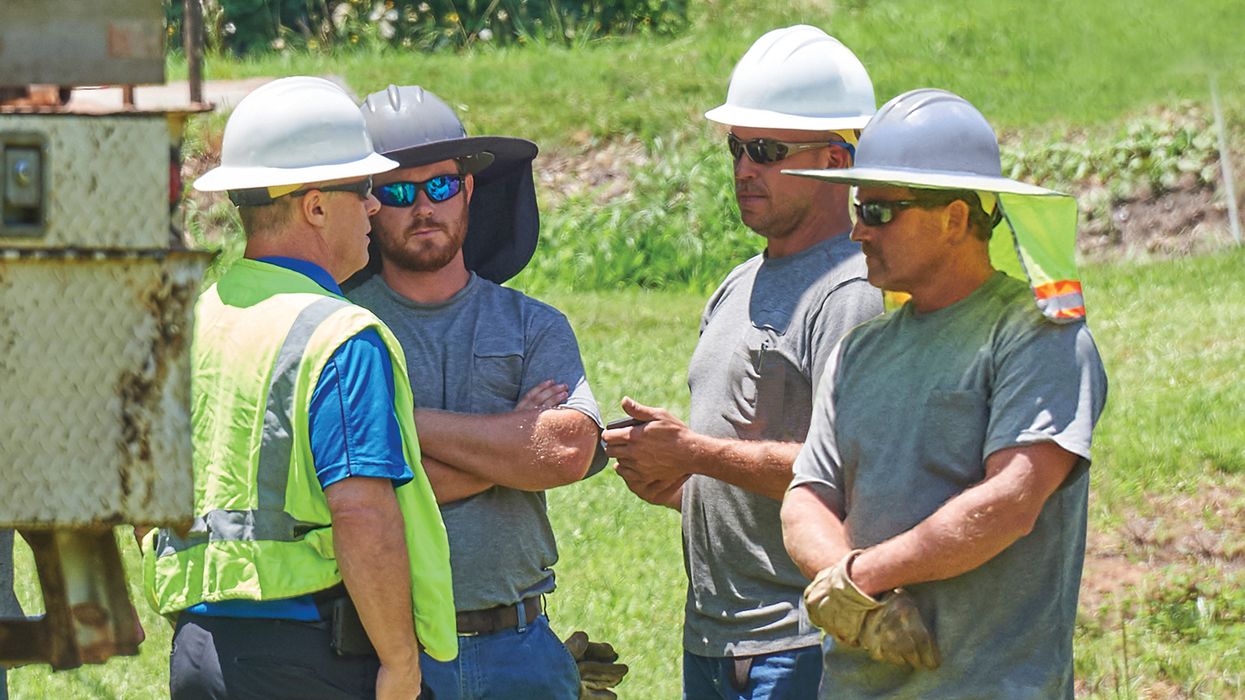
Solar energy workers face a variety of hazards, both during the manufacturing of solar components and the installation of solar panels. OSHA and the Bureau of Labor and Statistics (BLS) identify the primary risks as falls from ladders and roofs, shocks from electricity, arc flash, and burns from hot equipment and materials while installing and maintaining solar systems.
These dangers can result from several factors:
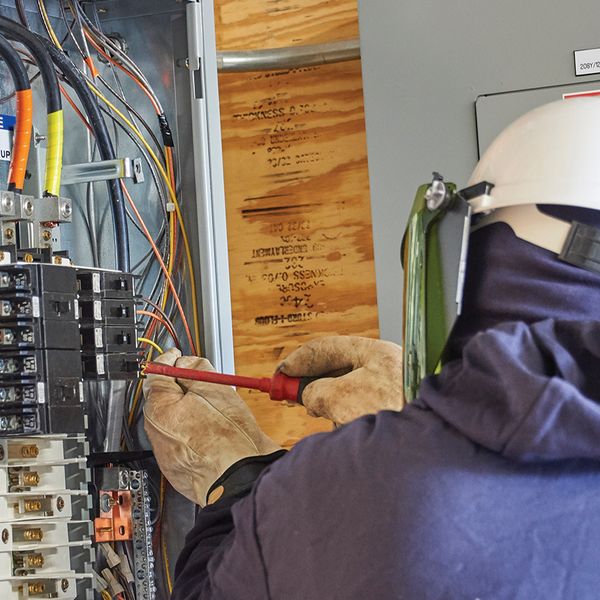
- Equipment Failures and Malfunctions: Electrical systems used in solar energy are complex and carry significant voltage. Malfunctions can lead to electrocution and burns. Regular maintenance and inspection of equipment are critical to prevent these incidents.
- PPE Issues: Workers in this industry often rely heavily on PPE, such as FR clothing, specialized footwear, ear and eye protection, and gloves. Failures or improper use of this equipment can lead to serious injuries.
- Inadequate Training and Education: A lack of proper training increases the likelihood of mistakes. New workers may be unfamiliar with the hazards and the correct procedures to mitigate them -- leading to falls, equipment malfunctions, and thermal burns.
Solar installers also face the risk of heat stress and other heat-related illnesses. Working outdoors for extensive periods of time, particularly in the summer months, can be extremely dangerous to workers.
Several states, including California, have recently implemented new requirements for protecting workers from heat-related illnesses. In addition, Federal OSHA announced a new proposed rule on heat illness prevention on July 1st, 2024. So, it’s definitely a hot topic right now!
Strategies for protecting workers
To safeguard solar energy workers from these hazards, several measures must be implemented:
- Rigorous Training Programs: Training is the cornerstone of safety in the solar industry. Workers must receive thorough education on the potential hazards and the proper use of equipment. This includes understanding the risks of electric shock, the importance of using fall protection systems, and the correct procedures for handling high-voltage components. Ongoing training sessions can keep safety practices top of mind.
- Regular Equipment Maintenance and Inspection: Preventing equipment failures is crucial. Regular maintenance and inspections should be conducted to ensure all tools and machinery are functioning correctly. Any faulty equipment should be repaired or replaced immediately to prevent accidents.
- Proper Use of PPE: Ensuring that workers have access to and correctly use PPE is essential. Employers should provide high-quality PPE and train workers on its proper use. Regular checks should be conducted to ensure that the PPE is in good condition and being used correctly.
- Heat Stress Management: Providing adequate hydration, rest breaks, and shaded areas can help mitigate the risk of heat-related illnesses. Training workers to recognize the signs of heat stress and how to respond is also important.
- Implementing Safety Protocols: Establishing and enforcing comprehensive safety protocols can help reduce the risk of accidents. This includes protocols for working at heights, handling electrical components, and emergency response procedures.
- Creating a Safety Culture: Encouraging a culture of safety within the workplace can have a significant impact. This involves promoting the importance of safety at all levels of the organization, from management to entry-level workers. Regular safety meetings and open communication about hazards can foster an environment where safety is a priority.
Key to remember: The solar industry is booming, and the future looks bright. However, as the solar industry continues to grow, protecting workers from heat and electrical hazards must remain a top priority.