Now hear this: OSHA Region 3 renews workplace noise REP
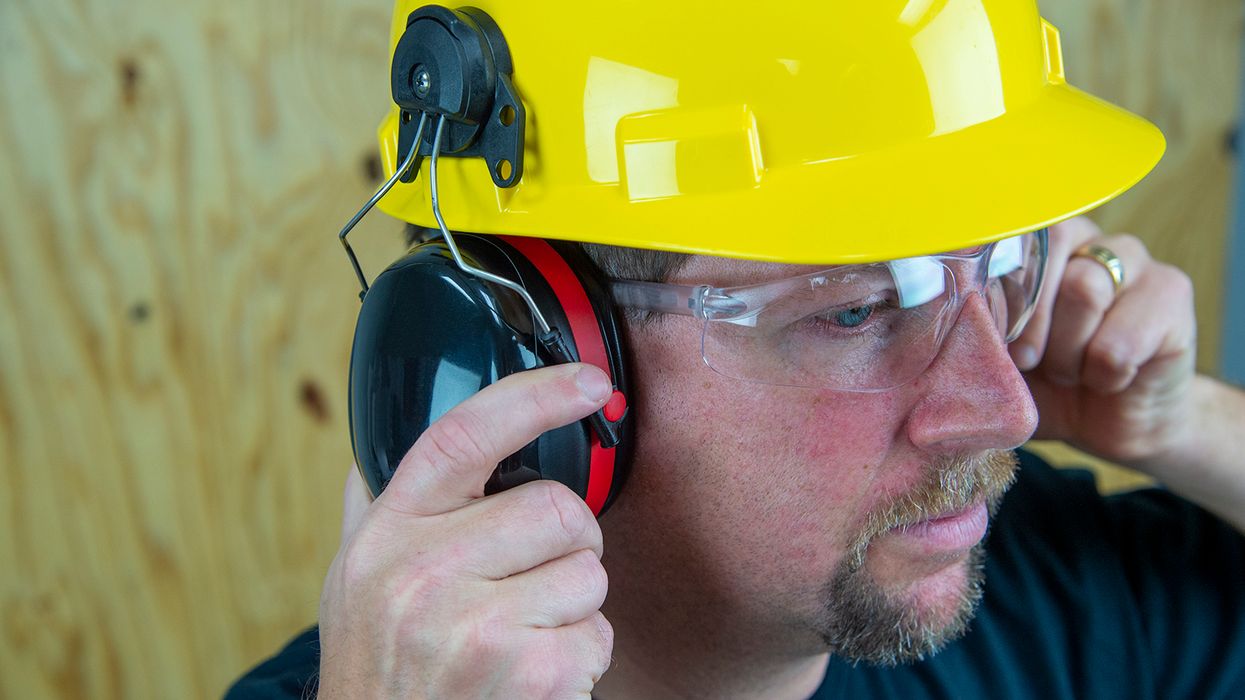
Potential hearing loss is a hazard for about 22 million workers, and those in the manufacturing industry face a greater risk. In 2021, about 12,000 workers suffered work-related hearing loss, the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) found, with 9,700 of those workers employed in manufacturing. For those reasons, OSHA Region 3 has renewed its workplace noise Regional Emphasis Program (REP). The REP was first established in 2018 and focuses inspections on industries with high levels of workplace noise to prevent permanent hearing loss.
OSHA Region 3 includes Delaware, the District of Columbia, Maryland, Pennsylvania, Virginia, and West Virginia.
Which industries are targeted?
As part of its renewal, OSHA added three manufacturing industry sectors to the REP after recent data showed higher risk of noise exposure in several industries:
- 32111 Sawmills and Wood Preservation,
- 32199 Other Wood Manufacturing, and
- 33232 Ornamental and Architectural Metal Products.
The REP also continues to include:
- 32192 Wood Container and Pallet Manufacturing,
- 32619 Other Plastics and Product Manufacturing,
- 32799 All Other Nonmetallic Mineral Product Manufacturing,
- 33231 Plate Work and Fabricated Structural Product Manufacturing,
- 33281 Coating, Engraving, Heat Treating, and Allied Activities,
- 33299 All Other Fabricated Metal Product Manufacturing, and
- 33661 Ship and Boat Building.
What will inspectors look for?
OSHA compliance officers will determine employee exposures to noise using methods such as sound level readings, full shift noise dosimetry, and a review of any third party noise sampling at the establishment.
They’ll review the employer’s hearing conservation program, including the use of appropriate hearing protection, training, and audiometric testing, as well as the employer’s efforts to evaluate employee noise exposures and implement engineering and administrative controls.
Employer records will be examined to determine if standard threshold shifts (STS) exist. This includes reviewing audiometric exams and the employer’s OSHA 300 logs to ensure recordable STS are properly recorded. Because employees in the industries listed in the REP are subject to multiple hazards, inspectors will also review the past five years of injury and illness records.
How to ensure you’re in compliance
You can be prepared before OSHA comes knocking. If your employees’ noise exposure equals or exceeds an 8-hour time-weighted average (TWA) of 85 decibels, you must:
- Implement a hearing conservation program;
- Conduct training for affected employees;
- Make copies of 1910.95, Occupational noise exposure, available to affected employees or their representatives, and post a copy in the workplace;
- Use feasible administrative or engineering controls;
- Establish and maintain an audiometric testing program;
- Develop and implement a noise monitoring program;
- Maintain records of employee exposure measurements;
- Provide hearing protectors at no cost to employees; and
- Evaluate hearing protector attenuation for the specific noise environments in which the protector will be used.
Key to Remember: OSHA Region 3 renewed its REP for workplace noise in certain manufacturing industries. Affected employers can be prepared by following the requirements in 1910.95.