Avoiding costly mistakes: The most common RCRA hazardous waste violations
If your facility generates hazardous waste, compliance with the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) is not optional. Yet many businesses overlook key requirements, leading to violations that can cost thousands in fines and damage their reputation. Understanding the most common mistakes and how to prevent them can keep your operations safe and compliant.
The most frequent violations according to EPA
One of the most common errors is failing to determine whether a waste is hazardous. Businesses often assume leftover chemicals, contaminated rags, or spent filters are non-hazardous without testing or applying EPA criteria. Misclassification leads to improper storage and disposal, which can escalate into multiple violations.
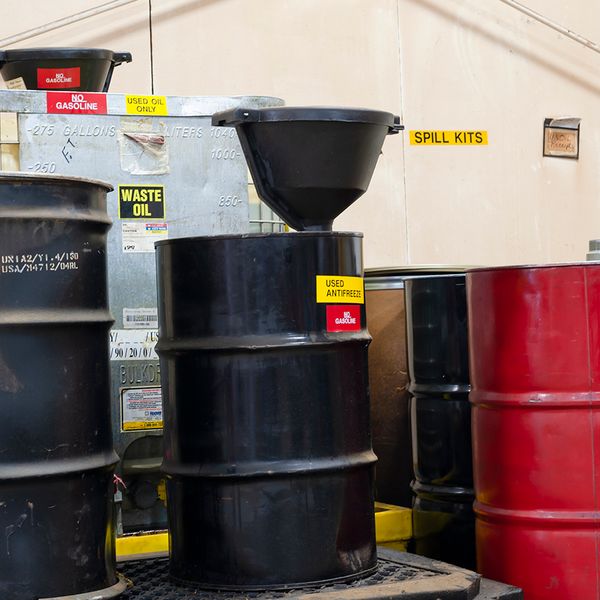
Container management is another frequent problem. Inspectors often find containers without the required “Hazardous Waste” label or missing the accumulation start date. Some containers are left open or improperly sealed, allowing leaks or vapors to escape. These issues are easy to fix but often overlooked in busy facilities.
Weekly inspections are mandatory for central accumulation areas, yet many companies skip them or fail to document them correctly. Missing dates, signatures, or inspection logs can result in citations even if the area is otherwise compliant.
Employee training is another weak spot. Large Quantity Generators must train staff on handling hazardous waste and emergency procedures and keep records of that training. Training should be job specific including emergency response specific to the facility. When training is incomplete or undocumented, it counts as a violation even if employees know what to do.
Improper disposal is a serious and costly mistake. Pouring hazardous waste down drains, tossing it in regular trash, or shipping it without a manifest violates federal law. These actions can lead to severe penalties and, in some cases, criminal liability.
Other common issues include exceeding accumulation time limits, 90 days for large quantity generators and 180 days for small quantity generators, without obtaining a permit. Facilities also forget to maintain a valid EPA identification number or fail to update contingency plans and emergency contact information.
How to stay compliant
Start with a thorough waste determination. Identify all materials that could be hazardous and classify them correctly and keep a record of the waste determination. Review container labeling and make sure every container is closed, dated, and marked “Hazardous Waste.” Establish a routine for weekly inspections and keep detailed records.
Invest in employee training and refresh it regularly. Document every session and keep those records accessible. Monitor accumulation times and set reminders to move waste before deadlines. Always use the Uniform Hazardous Waste Manifest when shipping waste off-site, and verify that your transporter and disposal facility are authorized.
Finally, maintain your EPA site ID number and update your contingency plan. Make sure emergency equipment is available, and local responders have your contact information.
Key to Remember: RCRA compliance is detailed, but most violations stem from simple oversights such as open containers, missing labels, skipped inspections, or forgotten paperwork. By building strong procedures and training your team, you can avoid costly mistakes and keep your facility safe and compliant.