Know your permit space air monitoring requirements
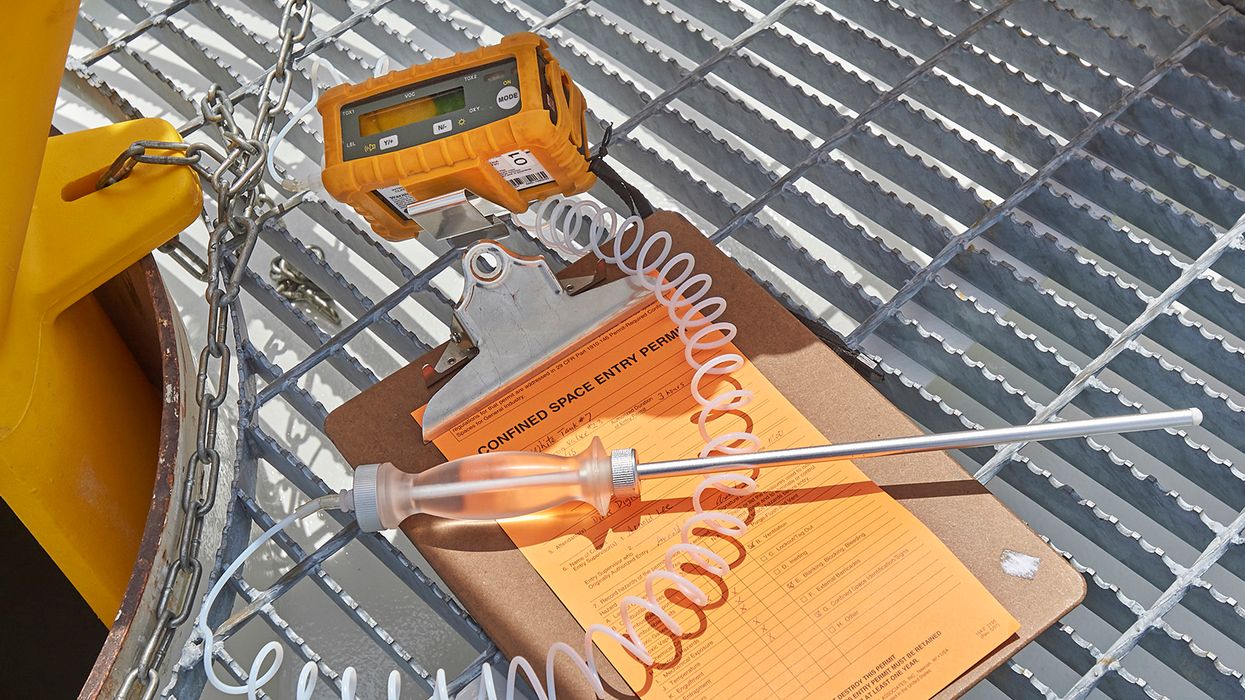
Atmospheres in permit-required confined spaces can be very unpredictable. That’s why OSHA has specific requirements to test the air and protect workers who enter permit spaces.
When should the air be monitored?
OSHA provides guidelines in 29 CFR 1910.146 for monitoring air in permit spaces. This must be done before entry is authorized, and as necessary to determine if acceptable entry conditions are being maintained during entry operations. If the space is too large to isolate, perform testing to the extent feasible before entry and continuously where entrants are working.
OSHA requires you test in this order:
- Test for oxygen first,
- Then for combustible gases and vapors, and
- Then for toxic gases and vapors.
Who monitors the air?
The rule states that:
- The person in charge must know the proper use and calibration of monitoring equipment and supervise its use.
- Authorized entrants must know how to use the testing and monitoring equipment.
- Employees entering the space must be allowed to observe the initial monitoring of the space.
What is required for employee training?
Provide the training specified in 1910.146(g). This requires employers to train workers so they have the understanding, knowledge, and skills necessary for the safe performance of the duties to assigned them . Retraining is needed when there are new or revised procedures. Finally, the employer must certify that training has taken place, and that the certification is available for inspection by employees and their authorized representatives.
Key to remember
Atmospheric testing is required to evaluate the air in the permit-required confined space, verify that conditions for entry are acceptable, and ensure conditions remain acceptable.