Don’t blast away arc flash safety
Despite the numerous safety standards and resources to protect employees from arc flash blasts, many employees continue to get seriously injured or killed by these lethal hazards. In early 2022, Congress met with OSHA and other stakeholders to discuss improvements to OSHA’s electrical personal protective equipment (PPE) requirements. During the meeting, stakeholders agree that between 500,000 and 800,000 workers regularly work without adequate PPE, including arc flash protection.
If you have two energized points which are not contacting each other solidly, the current can jump from one point to the other. This is called an electric arc or arc flash. Arc flashes occur by an electrical equipment failure (like a short circuit) or human error (such as holding a metal object too close to energized equipment).
One-second duration
Unlike a flash fire, an electric arc can begin and end in less than a second. Bystanders see a flash and hear a loud boom, and it is over.
Electric arc
A person can be severely injured or killed by this arc’s huge amount of heat. The temperature of the arc can range from 15,000 to 35,000 degrees Fahrenheit (F). (Heat above 122 degrees (F) can cause third-degree burns, which do not heal.) You can imagine what this heat can do to the human body.
Flying molten metal
The arc also immediately turns the electrical conductors into molten metal droplets that fly away from the source near the sound speed. These projectiles can travel quite a distance, starting clothing and other materials on fire.
Arc blast
Not only does the electric arc generate excessive heat, but this heat also causes an intense pressure wave that usually throws the employees working nearby away from the arc. This wave is so strong it can break eardrums and cause concussions and broken bones.
Explosions and/or fire
The heat from electric arcs can ignite combustible or flammable vapors in the air, causing an explosion. Materials stored nearby can also start on fire.
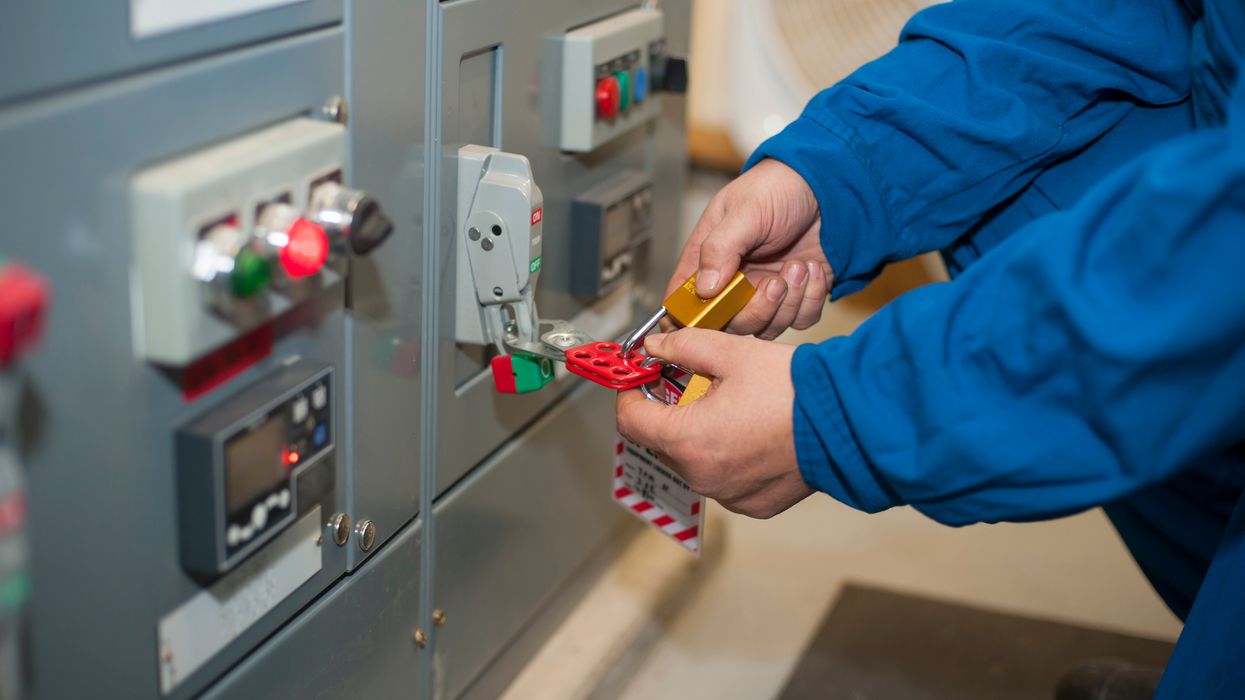
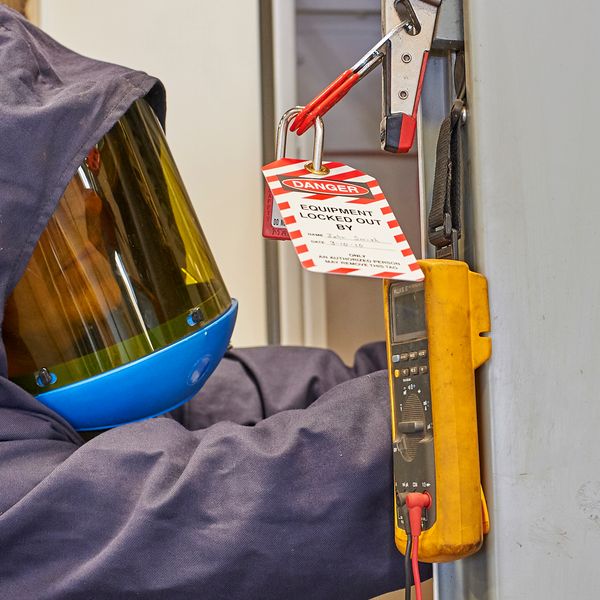
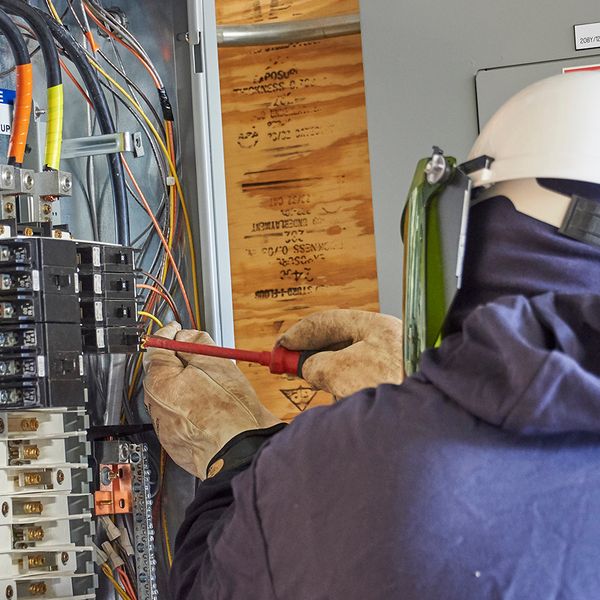
Personal protective equipment (PPE)
Whenever electrical workers have the chance of exposure to an electric arc, they must wear clothing and eye protection resistant to the flash. Make sure your employer provides you with the necessary PPE.
Cost of an electric arc accident
The monetary cost of an electric arc accident can run into hundreds of thousands of dollars. Damage to equipment and facility, lost production time, increased insurance expenses, medical bills, worker’s compensation, and legal costs can all result from one electric arc accident.
Key to remember
Electricity has long been recognized as a serious workplace hazard, exposing workers to electric shock, burns, fires, and arc-flash explosions. OSHA’s electrical standard minimizes these potential hazards by specifying safety requirements in the design and use of electrical equipment and systems.