Is your mobile equipment exempt from HVUT?
With only a few exceptions, highway motor vehicles weighing in at 55,000 pounds or more are taxable under the Heavy Vehicle Use Tax (HVUT) program. But if your mobile machinery falls under one of those exceptions, you won’t need to report it on your Form 2290 or pay the tax.
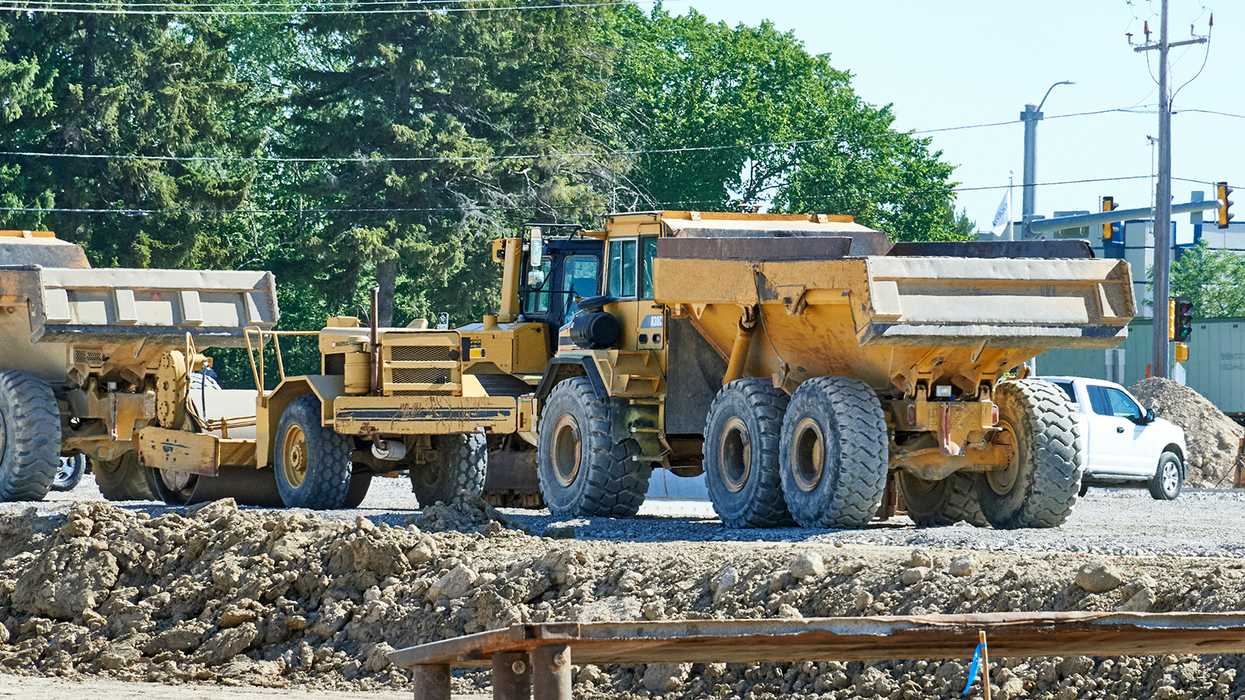
Vehicles specifically designed for non-transportation purposes fall under the “mobile machinery” exemption. The key to the exemption lies in the definition of a “highway vehicle.”
A highway motor vehicle includes any self-propelled vehicle designed to carry a load over public highways, whether or not it is also designed to perform other functions. Examples of vehicles that are designed to carry a load over public highways include trucks, truck tractors, and buses. Now let's look at what's not a highway vehicle.
Specially designed for non-transportation functions
With regard to mobile machinery, a self-propelled vehicle is not a highway vehicle if all the following apply:
- The chassis:
- Has permanently mounted machinery or equipment used to perform certain operations (construction, manufacturing, drilling, mining, timbering, processing, farming, or similar operations); and
- The operation of the machinery or equipment is unrelated to transportation on or off the public highways;
- The chassis is specially designed to serve only as a mobile carriage and mount (and the power source in some cases) for the machinery or equipment; and
- The chassis couldn’t, because of its special design and without substantial structural modification, be used as part of a vehicle designed to carry any other load.
Common examples of vehicles that may fall into this category include mobile cranes, bulldozers, backhoes, agricultural machinery, and drilling rigs.
Specially designed for off-highway transportation
A vehicle isn’t treated as a highway vehicle under HVUT if:
- It is specially designed for the primary function of transporting a particular type of load other than over the public highway, and
- Because of this special design, the vehicle’s capability to transport a load over a public highway is substantially limited or impaired.
To make this determination, consider:
- The vehicle’s size;
- Whether the vehicle is subject to licensing, safety, or other requirements; and
- Whether the vehicle can transport a load at a sustained speed of at least 25 miles per hour.
Common examples of vehicles that may fall into this category include mobile cranes, mining equipment, and agricultural machinery (such as certain tractors and combines).
Key to remember: If your mobile machinery qualifies for the exemption under HVUT, you won’t need to report it on your Form 2290 or pay the tax.