Want to provide forklift training in-house? No problem, here’s how!
Training forklift operators is an OSHA requirement per 1910.178(l). Do you want to do it in house? If you said yes, follow this step-by-step guide.
It all starts with a competent trainer. OSHA’s view is that all operator training and evaluation must be conducted by persons who have the “knowledge, training, and experience” to train operators and evaluate their competence. The standard doesn’t go into any more detail. It’s up to the employer to ensure trainers meet these general qualifications, but OSHA has no requirements for trainers to take certain classes, hold any sort of certifications, or be re-certified as trainers at specified intervals.
| Need more information on OSHA’s Forklift Standard? See our ezExplanation on Powered Industrial Trucks. |
The only aspect that OSHA has clarified is that the trainer does need to have experience operating the equipment and attachments. However, the standard doesn’t require that the trainers operate a forklift regularly (that is, outside of their operator training duties) as part of their job function or responsibility.
#1 Start here
First, OSHA requires that all operators must be trained prior to being allowed to operate forklifts. And the same thing goes for pallet trucks, order pickers, and stand-up units…. Any powered type of material handling equipment requires training.
But what does training entail? Well, the OSHA regulations are very specific. All operators must receive a combination of training. Training must consist of formal training, which is a lecture, discussion, interactive computer learning, video tape, written material, and so on.
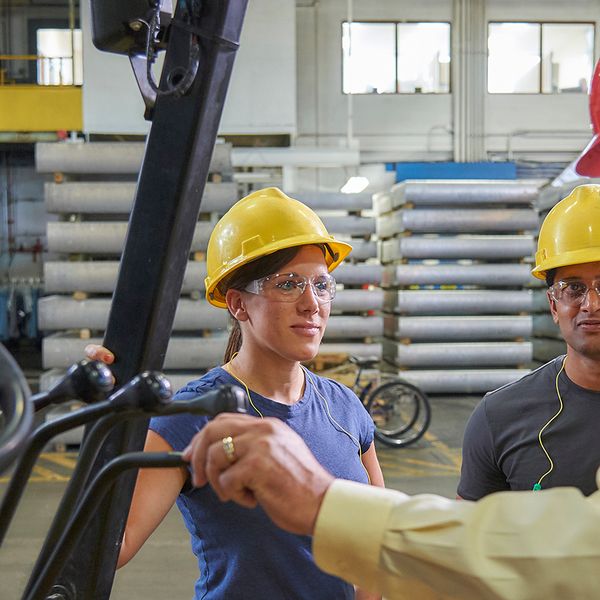
They must also receive practical training, which means demonstrations performed by the trainer and practical exercises performed by the trainee.
And the third component is that operators must receive a performance evaluation. So, they must operate the equipment and be observed and evaluated before being considered trained per the OSHA standard.
Usually, you’ll introduce the concepts during the classroom portion of training, the more informational aspects, such as the OSHA requirements. Then you’ll use the practical part of training to familiarize trainees with controls, talk about load handling, and so on. With the practical part, it’s usually best to ramp up the training, meaning start with simple skills and then build on those.
#2 Train on these topics
Aside from requirements for how to do the training, OSHA gives us a detailed list of topics to cover during the training.
The main categories are truck-related and workplace-related topics. And remember that OSHA does require you to include information on OSHA’s forklift standard as part of the training program. This requirement can be easy to overlook, but a good way to approach it is in the classroom portion of the program.
Keep in mind that if a topic doesn’t apply to your trucks or workplace, you don’t have to train on it. For example, if you don’t have any ramps or hazardous (classified) locations in your facility, your forklift operators don’t need training on these topics.
Truck-related topics include the following:
- Operation instruction, warnings
- Differences between forklift and automobile
- Controls, instrumentation
- Engine, motor operation
- Steering
- Visibility, restrictions
- Fork, attachment operation
- Capacity
- Stability
- Inspection, maintenance
- Refueling, recharging
- Operating limitations
- Operator’s manual instructions, precautions
Workplace-related topics are examples like these:
- Surfaces
- Load composition
- Load handling
- Pedestrians
- Narrow, restricted areas
- Hazardous (classified) locations
- Ramps
- Poor ventilation
- Other hazards
#3 Determine success
The trainees must successfully complete the formal and practical instruction, but how you determine success is up to you. For the classroom portion, you could give a written or oral test or otherwise evaluate the trainees’ knowledge. For the practical training, the trainee must be able to safely perform all the operations used on the job.
#4 End here
An evaluation of the operator’s performance in the workplace must be conducted at the time of initial training. And an evaluation is required to determine the effectiveness of any refresher training.
Also, you must conduct an evaluation at least every three years. This means that at least once every three years every operator must be observed while they operate in the workplace under actual workplace conditions. During the evaluation, the operator must also be able to answer pertinent questions to demonstrate they have the knowledge to operate the forklift safely.
A key point to note here, this evaluation must be more than just a written or verbal test. The employer must observe the operator in action performing all typical tasks related to running the forklift. And, going back to where we started, the evaluation must be conducted by someone who has the knowledge, training, and experience to evaluate the truck operator’s competence.
Document the evaluation — this means placing a record in your training file that includes the name of the operator, the date of the training, the date of the evaluation, and the identity of the person(s) performing the training or evaluation.
Action item
This may be a good time for you to review your options for training forklift operators to ensure they’re meeting these guidelines. And, it’s always a great idea to have all your training procedures in written format for consistency.
Key to remember
Training forklift operators is an OSHA requirement. Follow this step-by-step guide and you can do it in-house.