Engineering controls
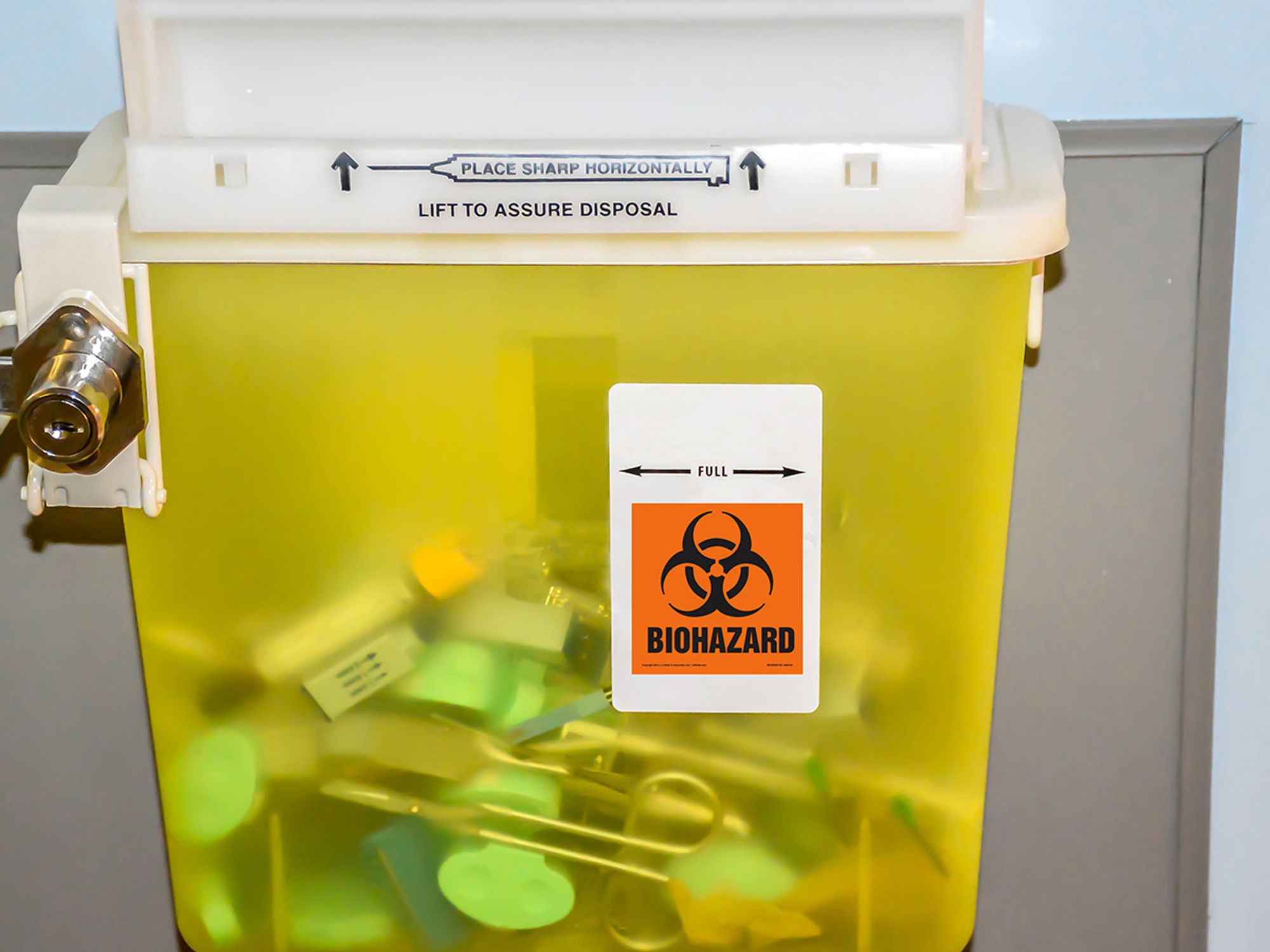
- Engineering controls eliminate or reduce bloodborne pathogen exposure by either removing the hazard or isolating the worker from exposure.
- Examples of engineering controls include safer medical devices, puncture-proof sharps disposal containers, and handwashing facilities.
- Engineering controls must be inspected and maintained or replaced on a regular basis to ensure they’re functioning as intended.
Engineering controls are devices that eliminate or reduce employee exposure to bloodborne pathogens in the workplace by either removing the hazard or isolating the worker from exposure.
Engineering controls should be used in combination with work practice controls to eliminate or minimize employee exposure. Where occupational exposure remains after institution of these controls, personal protective equipment (PPE) must also be used.
Types and locations of engineering controls
Examples of engineering controls include:
- Self-sheathing needles;
- Special containers for contaminated sharp instruments;
- Needleless systems; and
- Sharps with engineered sharps injury protection, meaning non-needle sharps or needle devices with built-in safety measures.
Engineering controls must be readily available in the area where they’re likely to be needed. Puncture-resistant sharps disposal containers must be easily accessible and located in areas where needles, syringes, or other sharp instruments are commonly used.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) does not require employers to provide personal sharps containers for employees who use lancets or insulin syringes for personal therapeutic reasons. However, to eliminate potential exposures to other employees, the employer may strongly insist that these employees bring their own sharps containers to the workplace.
Sharps used by employees for illegal drug use are covered under company-specific policies, which should be addressed when relevant during training.
According to OSHA, mouthpieces, resuscitation bags, pocket masks, or other ventilation devices are considered personal protective equipment; therefore, these would not fall under the engineering control category.
Maintenance of engineering controls
Engineering controls must be examined and maintained or replaced on a scheduled basis to ensure that each control is maintained and that it provides the protection intended. Regularly scheduled inspections are required to confirm, for instance:
- Protective shields have not been removed or broken; and
- Physical, mechanical, or replacement-dependent controls are functioning effectively.
Research labs and production facilities
Employers will want to note that human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and hepatitis B virus (HBV) research labs and production facilities may have more stringent engineering control requirements under 1910.1030(e).
