Which employees are protected?
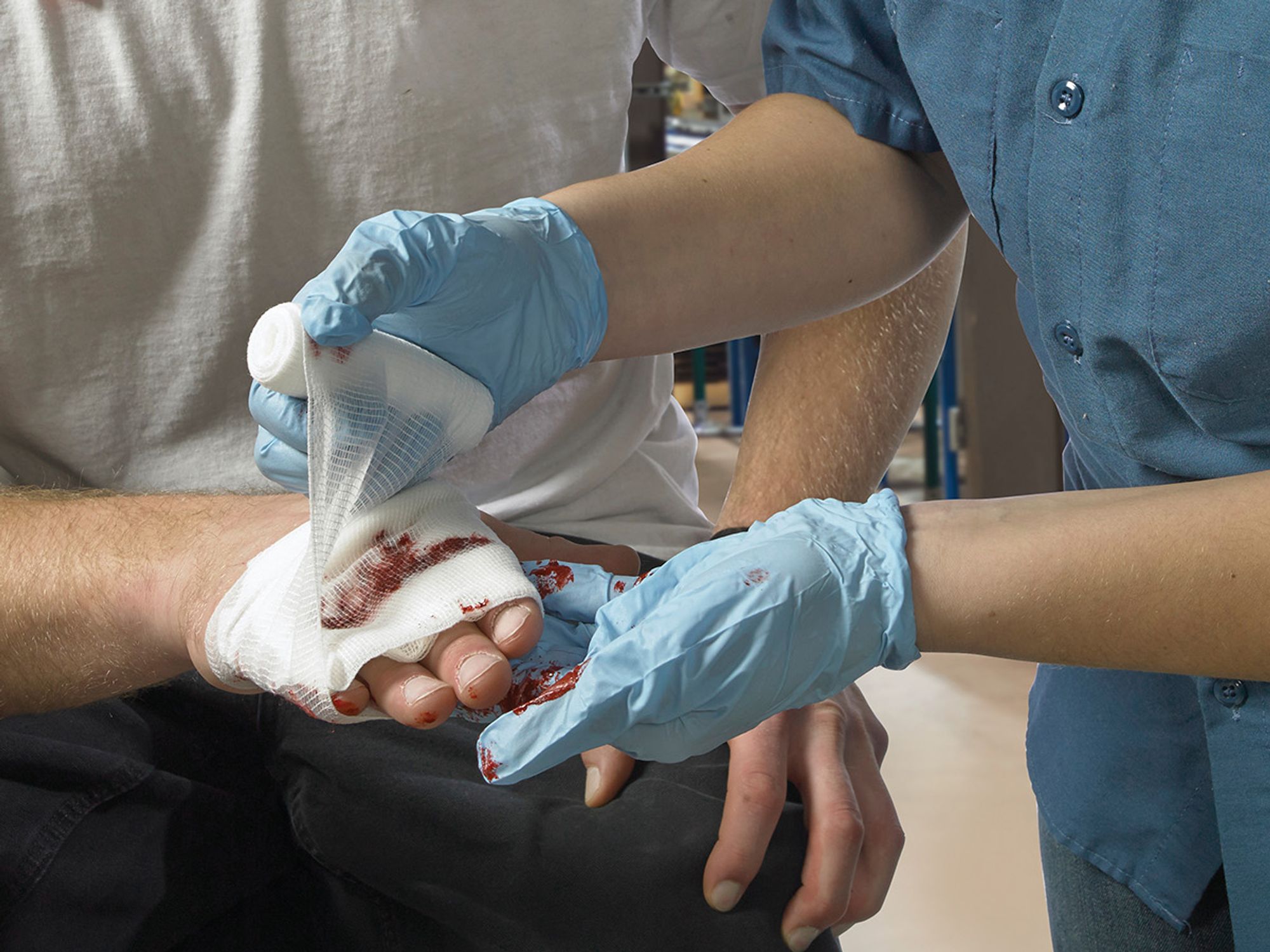
- Not all employees are protected by the Bloodborne Pathogens Standard, and it can be hard to tell who is and who isn’t.
- The standard covers all employees who have occupational exposure.
- It does not cover non-employees and Good Samaritans.
Probably the most confusing part of the Bloodborne Pathogens Standard is figuring out who’s protected by 1910.1030.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) estimates that more than 8.4 million employees in the U.S. require bloodborne pathogens training under 1910.1030.
Employers are required to train all employees with occupational exposure, whether their employment is full-time, part-time, contract, or temporary. However, OSHA jurisdiction extends only to employees, not to other people in the workplace such as unpaid students.
OSHA does not list jobs or tasks with occupational exposure, so employers must determine which jobs are covered at their workplace. If only some employees in a job class have occupational exposure, the employer must identify which tasks in those jobs present occupational exposure.
