Who is subject to RMP?

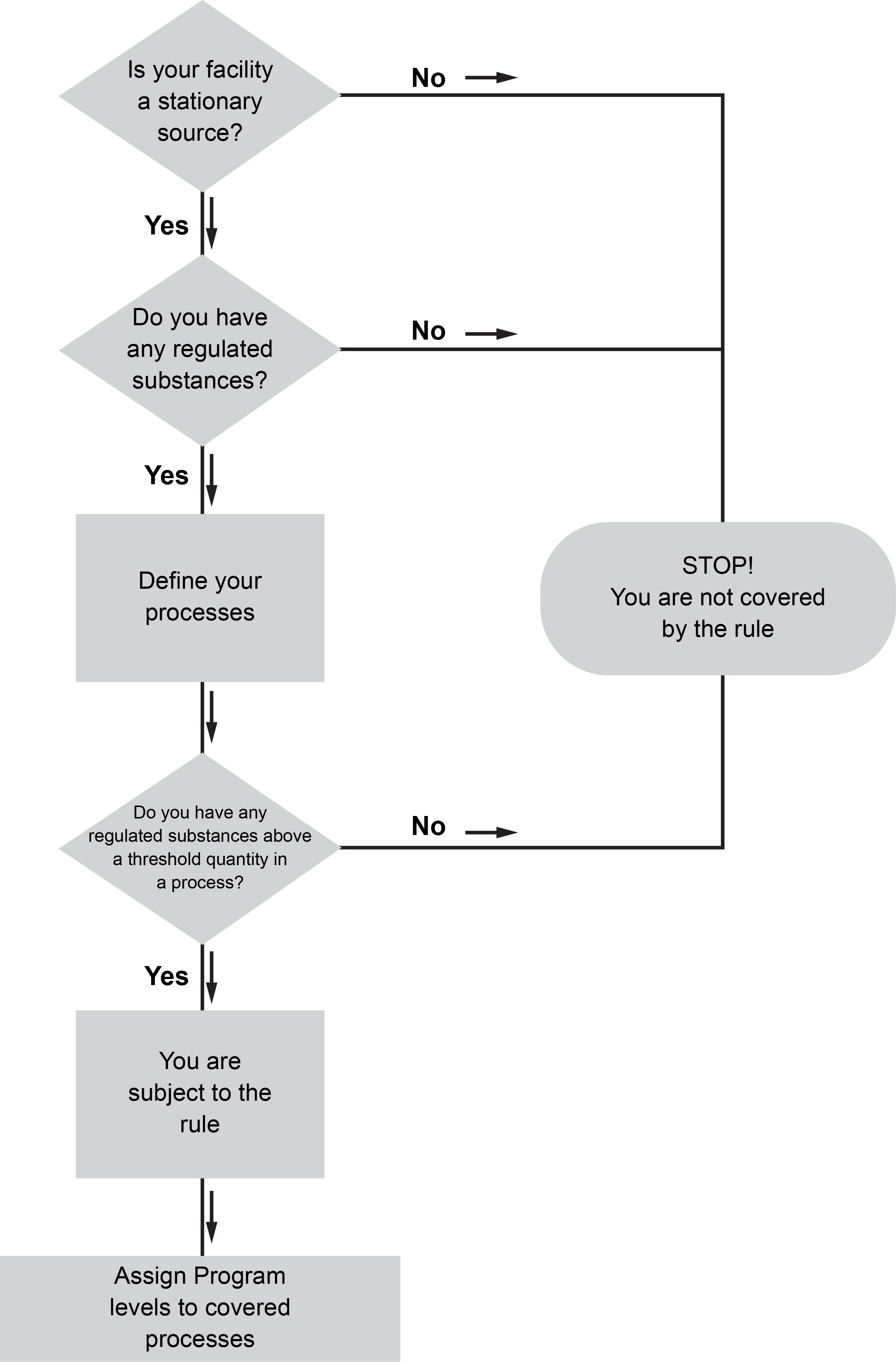
- Stationary sources that have more than a threshold quantity of a regulated substance in a process can use the included decision tree to determine if the company is subject to the Risk Management Plan (RMP) rule.
The requirements of 40 Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) 68 apply to stationary sources that have more than a threshold quantity of a regulated substance in a process, as determined under 68.115. A quick glance at this flow chart can help determine if the company’s facility is subject to the Risk Management Plan (RMP) rule.
Chemical lists
The RMP rule includes a List of Regulated Substances under 112(r) of the Clean Air Act (including common synonyms) to help assess if a particular chemical is subject to the rule. Where the Clean Air Act 112(r) program has been delegated to a state, that state may have additional requirements for the federally listed chemicals, and/or additional listed chemicals.
Thresholds
Threshold quantities of chemicals regulated under the RMP rule are included (in units of pounds) on the List of Regulated Substances under 112(r) of the Clean Air Act.
Process
The Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA’s) definition of process is identical to the definition of process under the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) Process Safety Management (PSM) standard. Under the RMP rule, a process is defined as “Any activity involving a regulated substance, including any use, storage, manufacturing, handling, or on-site movement of such substances, or combination of these activities.” For the purposes of this definition, any group of vessels that are interconnected, or separate vessels that are located such that a regulated substance could be involved in a potential release, shall be considered a single process.
Examples of “vessels” include:
- Reactors
- Tanks
- Drums
- Barrels
- Cylinders
- Vats
- Kettles
- Boilers
- Pipes
- Hoses
- Other containers
