...
(a) Combustion turbines qualifying under §60.5520(d)(1) are not subject to any requirements in this section other than the requirement to maintain fuel purchase records for permitted fuel(s). If your combustion turbine uses non-uniform fuels as specified under §60.5520(d)(2), you must monitor heat input in accordance with paragraph (c)(1) of this section, and you must monitor CO 2 emissions in accordance with either paragraph (b), (c)(2), or (c)(5) of this section. For all other affected sources, you must prepare a monitoring plan to quantify the hourly CO 2 mass emission rate (tons/h), in accordance with the applicable provisions in 40 CFR 75.53(g) and (h). The electronic portion of the monitoring plan must be submitted using the ECMPS Client Tool and must be in place prior to reporting emissions data and/or the results of monitoring system certification tests under this subpart. The monitoring plan must be updated as necessary. Monitoring plan submittals must be made by the Designated Representative (DR), the Alternate DR, or a delegated agent of the DR (see §60.5555(d) and (e)).
(b) You must determine the hourly CO 2 mass emissions in kg from your affected EGU(s) according to paragraphs (b)(1) through (5) of this section, or, if applicable, as provided in paragraph (c) of this section.
(1) For an affected EGU that combusts coal you must, and for all other affected EGUs you may, install, certify, operate, maintain, and calibrate a CO 2 continuous emission monitoring system (CEMS) to directly measure and record hourly average CO 2 concentrations in the affected EGU exhaust gases emitted to the atmosphere, and a flow monitoring system to measure hourly average stack gas flow rates, according to 40 CFR 75.10(a)(3)(i). As an alternative to direct measurement of CO 2 concentration, provided that your EGU does not use carbon separation (e.g., carbon capture and storage), you may use data from a certified oxygen (O 2) monitor to calculate hourly average CO 2 concentrations, in accordance with 40 CFR 75.10(a)(3)(iii). If you measure CO 2 concentration on a dry basis, you must also install, certify, operate, maintain, and calibrate a continuous moisture monitoring system, according to 40 CFR 75.11(b). Alternatively, you may either use an appropriate fuel-specific default moisture value from 40 CFR 75.11(b) or submit a petition to the Administrator under 40 CFR 75.66 for a site-specific default moisture value.
(2) For each continuous monitoring system that you use to determine the CO 2 mass emissions, you must meet the applicable certification and quality assurance procedures in 40 CFR 75.20 and appendices A and B to 40 CFR part 75.
(3) You must use only unadjusted exhaust gas volumetric flow rates to determine the hourly CO 2 mass emissions rate from the affected EGU; you must not apply the bias adjustment factors described in Section 7.6.5 of appendix A to 40 CFR part 75 to the exhaust gas flow rate data.
(4) You must select an appropriate reference method to setup (characterize) the flow monitor and to perform the on-going RATAs, in accordance with 40 CFR part 75. If you use a Type-S pitot tube or a pitot tube assembly for the flow RATAs, you must calibrate the pitot tube or pitot tube assembly; you may not use the 0.84 default Type-S pitot tube coefficient specified in Method 2.
(5) Calculate the hourly CO 2 mass emissions (kg) as described in paragraphs (b)(5)(i) through (iv) of this section. Perform this calculation only for “valid operating hours”, as defined in §60.5540(a)(1).
(i) Begin with the hourly CO 2 mass emission rate (tons/h), obtained either from equation F-11 in appendix F to 40 CFR part 75 (if CO 2 concentration is measured on a wet basis), or by following the procedure in section 4.2 of appendix F to part 75 (if CO 2 concentration is measured on a dry basis).
(ii) Next, multiply each hourly CO 2 mass emission rate by the EGU or stack operating time in hours (as defined in 40 CFR 72.2), to convert it to tons of CO 2.
(iii) Finally, multiply the result from paragraph (b)(5)(ii) of this section by 907.2 to convert it from tons of CO 2 to kg. Round off to the nearest kg.
(iv) The hourly CO 2 tons/h values and EGU (or stack) operating times used to calculate CO 2 mass emissions are required to be recorded under 40 CFR 75.57(e) and must be reported electronically under 40 CFR 75.64(a)(6). You must use these data to calculate the hourly CO 2 mass emissions.
(c) If your affected EGU exclusively combusts liquid fuel and/or gaseous fuel, as an alternative to complying with paragraph (b) of this section, you may determine the hourly CO2 mass emissions according to paragraphs (c)(1) through (4) of this section. If you use non-uniform fuels as specified in §60.5520(d)(2), you may determine CO2 mass emissions during the compliance period according to paragraph (c)(5) of this section.
(1) If you are subject to an output-based standard and you do not install CEMS in accordance with paragraph (b) of this section, you must implement the applicable procedures in appendix D to part 75 of this chapter to determine hourly EGU heat input rates (MMBtu/h), based on hourly measurements of fuel flow rate and periodic determinations of the gross calorific value (GCV) of each fuel combusted.
(2) For each measured hourly heat input rate, use Equation G-4 in appendix G to part 75 of this chapter to calculate the hourly CO2 mass emission rate (tons/h). You may determine site-specific carbon-based F-factors (Fc) using Equation F-7b in section 3.3.6 of appendix F to part 75 of this chapter, and you may use these Fc values in the emissions calculations instead of using the default Fc values in the Equation G-4 nomenclature.
(3) For each “valid operating hour” (as defined in §60.5540(a)(1), multiply the hourly tons/h CO 2 mass emission rate from paragraph (c)(2) of this section by the EGU or stack operating time in hours (as defined in 40 CFR 72.2), to convert it to tons of CO 2 . Then, multiply the result by 907.2 to convert from tons of CO 2 to kg. Round off to the nearest two significant figures.
(4) The hourly CO2 tons/h values and EGU (or stack) operating times used to calculate CO2 mass emissions are required to be recorded under §75.57(e) of this chapter and must be reported electronically under §75.64(a)(6) of this chapter. You must use these data to calculate the hourly CO2 mass emissions.
(5) If you operate a combustion turbine firing non-uniform fuels, as an alternative to following paragraphs (c)(1) through (4) of this section, you may determine CO2 emissions during the compliance period using one of the following methods:
(i) Units firing fuel gas may determine the heat input during the compliance period following the procedure under §60.107a(d) and convert this heat input to CO2 emissions using Equation G-4 in appendix G to part 75 of this chapter.
(ii) You may use the procedure for determining CO2 emissions during the compliance period based on the use of the Tier 3 methodology under §98.33(a)(3) of this chapter.
(d) Consistent with §60.5520, you must determine the basis of the emissions standard that applies to your affected source in accordance with either paragraph (d)(1) or (2) of this section, as applicable:
(1) If you operate a source subject to an emissions standard established on an output basis (e.g., lb of CO 2 per gross or net MWh of energy output), you must install, calibrate, maintain, and operate a sufficient number of watt meters to continuously measure and record the hourly gross electric output or net electric output, as applicable, from the affected EGU(s). These measurements must be performed using 0.2 class electricity metering instrumentation and calibration procedures as specified under ANSI No. C12.20-2010 (incorporated by reference, see §60.17). For a combined heat and power (CHP) EGU, as defined in §60.5580, you must also install, calibrate, maintain, and operate meters to continuously (i.e., hour-by-hour) determine and record the total useful thermal output. For process steam applications, you will need to install, calibrate, maintain, and operate meters to continuously determine and record the hourly steam flow rate, temperature, and pressure. Your plan shall ensure that you install, calibrate, maintain, and operate meters to record each component of the determination, hour-by-hour.
(2) If you operate a source subject to an emissions standard established on a heat-input basis (e.g., lb CO2/MMBtu) and your affected source uses non-uniform heating value fuels as delineated under §60.5520(d), you must determine the total heat input for each fuel fired during the compliance period in accordance with one of the following procedures:
(i) Appendix D to part 75 of this chapter;
(ii) The procedures for monitoring heat input under §60.107a(d);
(iii) If you monitor CO2 emissions in accordance with the Tier 3 methodology under §98.33(a)(3) of this chapter, you may convert your CO2 emissions to heat input using the appropriate emission factor in table C-1 of part 98 of this chapter. If your fuel is not listed in table C-1, you must determine a fuel-specific carbon-based F-factor (Fc) in accordance with section 12.3.2 of EPA Method 19 of appendix A-7 to this part, and you must convert your CO2 emissions to heat input using Equation G-4 in appendix G to part 75 of this chapter.
(e) Consistent with §60.5520, if two or more affected EGUs serve a common electric generator, you must apportion the combined hourly gross or net energy output to the individual affected EGUs according to the fraction of the total steam load and/or direct mechanical energy contributed by each EGU to the electric generator. Alternatively, if the EGUs are identical, you may apportion the combined hourly gross or net electrical load to the individual EGUs according to the fraction of the total heat input contributed by each EGU. You may also elect to develop, demonstrate, and provide information satisfactory to the Administrator on alternate methods to apportion the gross energy output. The Administrator may approve such alternate methods for apportioning the gross energy output whenever the demonstration ensures accurate estimation of emissions regulated under this part.
(f) In accordance with §§60.13(g) and 60.5520, if two or more affected EGUs that implement the continuous emission monitoring provisions in paragraph (b) of this section share a common exhaust gas stack you must monitor hourly CO 2 mass emissions in accordance with one of the following procedures:
(1) If the EGUs are subject to the same emissions standard in table 1 or 2 to this subpart, you may monitor the hourly CO 2 mass emissions at the common stack in lieu of monitoring each EGU separately. If you choose this option, the hourly gross or net energy output (electric, thermal, and/or mechanical, as applicable) must be the sum of the hourly loads for the individual affected EGUs and you must express the operating time as “stack operating hours” (as defined in 40 CFR 72.2). If you attain compliance with the applicable emissions standard in §60.5520 at the common stack, each affected EGU sharing the stack is in compliance.
(2) As an alternative, or if the EGUs are subject to different emission standards in table 1 or 2 to this subpart, you must either:
(i) Monitor each EGU separately by measuring the hourly CO 2 mass emissions prior to mixing in the common stack or
(ii) Apportion the CO 2 mass emissions based on the unit's load contribution to the total load associated with the common stack and the appropriate F-factors. You may also elect to develop, demonstrate, and provide information satisfactory to the Administrator on alternate methods to apportion the CO 2 emissions. The Administrator may approve such alternate methods for apportioning the CO 2 emissions whenever the demonstration ensures accurate estimation of emissions regulated under this part.
(g) In accordance with §§60.13(g) and 60.5520 if the exhaust gases from an affected EGU that implements the continuous emission monitoring provisions in paragraph (b) of this section are emitted to the atmosphere through multiple stacks (or if the exhaust gases are routed to a common stack through multiple ducts and you elect to monitor in the ducts), you must monitor the hourly CO2 mass emissions and the “stack operating time” (as defined in §72.2 of this chapter) at each stack or duct separately. In this case, you must determine compliance with the applicable emissions standard in Table 1 or 2 of this subpart by summing the CO2 mass emissions measured at the individual stacks or ducts and dividing by the total gross or net energy output for the affected EGU.
[89 FR 40030, May 9, 2024]
(a) In accordance with §60.5520, if you are subject to an output-based emission standard or you burn non-uniform fuels as specified in §60.5520(d)(2), you must demonstrate compliance with the applicable CO 2 emission standard in table 1 or 2 to this subpart as required in this section. For the initial and each subsequent 12-operating-month rolling average compliance period, you must follow the procedures in paragraphs (a)(1) through (8) of this section to calculate the CO 2 mass emissions rate for your affected EGU(s) in units of the applicable emissions standard (e.g., either kg/MWh or kg/GJ). You must use the hourly CO 2 mass emissions calculated under §60.5535(b) or (c), as applicable, and either the generating load data from §60.5535(d)(1) for output-based calculations or the heat input data from §60.5535(d)(2) for heat-input-based calculations. Combustion turbines firing non-uniform fuels that contain CO 2 prior to combustion (e.g., blast furnace gas or landfill gas) may sample the fuel stream to determine the quantity of CO 2 present in the fuel prior to combustion and exclude this portion of the CO 2 mass emissions from compliance determinations.
(1) Each compliance period shall include only “valid operating hours” in the compliance period, i.e., operating hours for which:
(i) “Valid data” (as defined in §60.5580) are obtained for all of the parameters used to determine the hourly CO 2 mass emissions (kg) and, if a heat input-based standard applies, all the parameters used to determine total heat input for the hour are also obtained; and
(ii) The corresponding hourly gross or net energy output value is also valid data (Note: For hours with no useful output, zero is considered to be a valid value).
(2) You must exclude operating hours in which:
(i) The substitute data provisions of 40 CFR 75 are applied for any of the parameters used to determine the hourly CO 2 mass emissions or, if a heat input-based standard applies, for any parameters used to determine the hourly heat input;
(ii) An exceedance of the full-scale range of a continuous emission monitoring system occurs for any of the parameters used to determine the hourly CO 2 mass emissions or, if applicable, to determine the hourly heat input; or
(iii) The total gross or net energy output (P gross/net) or, if applicable, the total heat input is unavailable.
(3) For each compliance period, at least 95 percent of the operating hours in the compliance period must be valid operating hours, as defined in paragraph (a)(1) of this section.
(4) You must calculate the total CO 2 mass emissions by summing the valid hourly CO 2 mass emissions values from §60.5535 for all of the valid operating hours in the compliance period.
(5) For each valid operating hour of the compliance period that was used in paragraph (a)(4) of this section to calculate the total CO 2 mass emissions, you must determine P gross/net (the corresponding hourly gross or net energy output in MWh) according to the procedures in paragraphs (a)(5)(i) and (ii) of this section, as appropriate for the type of affected EGU(s). For an operating hour in which a valid CO 2 mass emissions value is determined according to paragraph (a)(1)(i) of this section, if there is no gross or net electrical output, but there is mechanical or useful thermal output, you must still determine the gross or net energy output for that hour. In addition, for an operating hour in which a valid CO 2 mass emissions value is determined according to paragraph (a)(1)(i) of this section, but there is no (i.e., zero) gross electrical, mechanical, or useful thermal output, you must use that hour in the compliance determination. For hours or partial hours where the gross electric output is equal to or less than the auxiliary loads, net electric output shall be counted as zero for this calculation.
(i) Calculate P gross/net for your affected EGU using the following equation. All terms in the equation must be expressed in units of MWh. To convert each hourly gross or net energy output (consistent with §60.5520) value reported under 40 CFR part 75 to MWh, multiply by the corresponding EGU or stack operating time.
Equation 1 to paragraph (a)(5)(i)
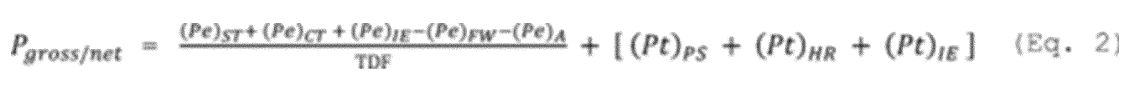
Where:
P gross/net = In accordance with §60.5520, gross or net energy output of your affected EGU for each valid operating hour (as defined in §60.5540(a)(1)) in MWh.
(Pe) ST = Electric energy output plus mechanical energy output (if any) of steam turbines in MWh.
(Pe) CT = Electric energy output plus mechanical energy output (if any) of stationary combustion turbine(s) in MWh.
(Pe) IE = Electric energy output plus mechanical energy output (if any) of your affected EGU's integrated equipment that provides electricity or mechanical energy to the affected EGU or auxiliary equipment in MWh.
(Pe) FW = Electric energy used to power boiler feedwater pumps at steam generating units in MWh. Not applicable to stationary combustion turbines, IGCC EGUs, or EGUs complying with a net energy output based standard.
(Pe) A = Electric energy used for any auxiliary loads in MWh. Not applicable for determining P gross .
(Pt) PS = Useful thermal output of steam (measured relative to standard ambient temperature and pressure (SATP) conditions, as applicable) that is used for applications that do not generate additional electricity, produce mechanical energy output, or enhance the performance of the affected EGU. This is calculated using the equation specified in paragraph (a)(5)(ii) of this section in MWh.
(Pt) HR = Non steam useful thermal output (measured relative to SATP conditions, as applicable) from heat recovery that is used for applications other than steam generation or performance enhancement of the affected EGU in MWh.
(Pt) IE = Useful thermal output (relative to SATP conditions, as applicable) from any integrated equipment is used for applications that do not generate additional steam, electricity, produce mechanical energy output, or enhance the performance of the affected EGU in MWh.
TDF = Electric Transmission and Distribution Factor of 0.95 for a combined heat and power affected EGU where at least 20.0 percent of the total gross or net energy output consists of electric or direct mechanical output and 20.0 percent of the total gross or net energy output consists of useful thermal output on a 12-operating-month rolling average basis, or 1.0 for all other affected EGUs.
(ii) If applicable to your affected EGU (for example, for combined heat and power), you must calculate (Pt) PS using the following equation:
Equation 2 to Paragraph (a)(5)(ii)
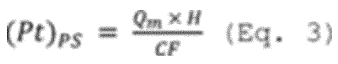
Where:
Q m = Measured useful thermal output flow in kg (lb) for the operating hour.
H = Enthalpy of the useful thermal output at measured temperature and pressure (relative to SATP conditions or the energy in the condensate return line, as applicable) in Joules per kilogram (J/kg) (or Btu/lb).
CF = Conversion factor of 3.6 × 10 9 J/MWh or 3.413 × 10 6 Btu/MWh.
(6) Sources complying with energy output-based standards must calculate the basis (i.e., denominator) of their actual 12-operating month emission rate in accordance with paragraph (a)(6)(i) of this section. Sources complying with heat input based standards must calculate the basis of their actual 12-operating month emission rate in accordance with paragraph (a)(6)(ii) of this section.
(i) In accordance with §60.5520 if you are subject to an output-based standard, you must calculate the total gross or net energy output for the affected EGU's compliance period by summing the hourly gross or net energy output values for the affected EGU that you determined under paragraph (a)(5) of this section for all of the valid operating hours in the applicable compliance period.
(ii) If you are subject to a heat input-based standard, you must calculate the total heat input for each fuel fired during the compliance period. The calculation of total heat input for each individual fuel must include all valid operating hours and must also be consistent with any fuel-specific procedures specified within your selected monitoring option under §60.5535(d)(2).
(7) If you are subject to an output-based standard, you must calculate the CO 2 mass emissions rate for the affected EGU(s) (kg/MWh) by dividing the total CO 2 mass emissions value calculated according to the procedures in paragraph (a)(4) of this section by the total gross or net energy output value calculated according to the procedures in paragraph (a)(6)(i) of this section. Round off the result to two significant figures if the calculated value is less than 1,000; round the result to three significant figures if the calculated value is greater than 1,000. If you are subject to a heat input-based standard, you must calculate the CO 2 mass emissions rate for the affected EGU(s) (kg/GJ or lb/MMBtu) by dividing the total CO 2 mass emissions value calculated according to the procedures in paragraph (a)(4) of this section by the total heat input calculated according to the procedures in paragraph (a)(6)(ii) of this section. Round off the result to two significant figures.
(b) In accordance with §60.5520, to demonstrate compliance with the applicable CO 2 emission standard, for the initial and each subsequent 12-operating-month compliance period, the CO 2 mass emissions rate for your affected EGU must be determined according to the procedures specified in paragraph (a)(1) through (8) of this section and must be less than or equal to the applicable CO 2 emissions standard in table 1 or 2 to this subpart, or the emissions standard calculated in accordance with §60.5525(a)(2).
[89 FR 40031, May 9, 2024]
