['Air Programs']
['Mobile Emission Sources']
08/01/2024
...
This section applies to new 2007 and later model year diesel heavy-duty engines and vehicles. Starting in model year 2021, this section also applies to all heavy HDE, regardless of fuel or combustion cycle (see 40 CFR 1036.140(a) and 1036.150(c)). Section 86.007-11 includes text that specifies requirements that differ from §86.004-11. Where a paragraph in §86.004-11 is identical and applicable to §86.007-11, this may be indicated by specifying the corresponding paragraph and the statement “[Reserved]. For guidance see §86.004-11.”
(a)(1) Exhaust emissions from new 2007 and later model year diesel HDEs shall not exceed the following:
(i) Oxides of Nitrogen (NOX). (A) 0.20 grams per brake horsepower-hour (0.075 grams per megajoule).
(B) A manufacturer may elect to include any or all of its diesel HDE families in any or all of the NOX and NOX plus NMHC emissions ABT programs for HDEs, within the restrictions described in §86.007-15 or §86.004-15. If the manufacturer elects to include engine families in any of these programs, the NOX FELs may not exceed the following FEL caps: 2.00 grams per brake horsepower-hour (0.75 grams per megajoule) for model years before 2010; 0.50 grams per brake horsepower-hour (0.19 grams per megajoule) for model years 2010 and later. This ceiling value applies whether credits for the family are derived from averaging, banking, or trading programs.
(ii)(A) Nonmethane hydrocarbon (NMHC) for engines fueled with diesel fuel. 0.14 grams per brake horsepower-hour (0.052 grams per megajoule).
(B) Nonmethane-nonethane hydrocarbon (NMNEHC) for engines fueled with natural gas or liquefied petroleum gas. 0.14 grams per brake horsepower-hour (0.052 grams per megajoule).
(C) Nonmethane hydrocarbon equivalent (NMHCE) for engines fueled with methanol. 0.14 grams per brake horsepower-hour (0.052 grams per megajoule).
(iii) Carbon monoxide. 15.5 grams per brake horsepower-hour (5.77 grams per megajoule).
(iv) Particulate. (A) 0.01 grams per brake horsepower-hour (0.0037 grams per megajoule).
(B) A manufacturer may elect to include any or all of its diesel HDE families in any or all of the particulate ABT programs for HDEs, within the restrictions described in §86.007-15 or other applicable sections. If the manufacturer elects to include engine families in any of these programs, the particulate FEL may not exceed 0.02 grams per brake horsepower-hour (0.0075 grams per megajoule).
(2) The standards set forth in paragraph (a)(1) of this section refer to the exhaust emitted over the duty cycle specified in paragraphs (a)(2)(i) through (iii) of this section, where exhaust emissions are measured and calculated as specified in paragraphs (a)(2)(iv) and (v) of this section in accordance with the procedures set forth in subpart N of this part, except as noted in §86.007-23(c)(4):
(i) Perform the test interval set forth in paragraph (f)(2) of appendix I of this part with a cold-start according to 40 CFR part 1065, subpart F. This is the cold-start test interval.
(ii) Shut down the engine after completing the test interval and allow 20±1 minutes to elapse. This is the hot soak.
(iii) Repeat the test interval. This is the hot-start test interval.
(iv) Calculate the total emission mass of each constituent, m, and the total work, W, over each test interval according to 40 CFR 1065.650.
(v) Determine your engine's brake-specific emissions using the following calculation, which weights the emissions from the cold-start and hot-start test intervals:
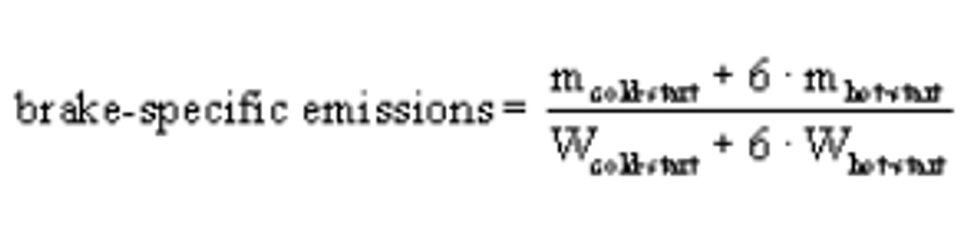
(3) SET (i) Exhaust emissions, as determined under §86.1360-2007(b) pertaining to the supplemental emission test cycle, for each regulated pollutant shall not exceed 1.0 times the applicable emission standards or FELs specified in paragraph (a)(1) of this section.
(ii) For engines not having a NOX FEL less than1.5 g/bhp-hr, gaseous exhaust emissions shall not exceed the steady-state interpolated values determined by the Maximum Allowable Emission Limits (for the corresponding speed and load), as determined under §86.1360-2007(f), when the engine is operated in the steady-state control area defined under §86.1360-2007(d).
(4) NTE (i)(A) The brake-specific exhaust NMHC or NOX emissions in g/bhp-hr, as determined under §86.1370-2007 pertaining to the not-to-exceed test procedures, shall not exceed 1.5 times the applicable NMHC or NOX emission standards or FELs specified in paragraph (a)(1) of this section, during engine and vehicle operation specified in paragraph (a)(4)(ii) of this section except as noted in paragraph (a)(4)(iii) of this section.
(B) For engines not having a NOX FEL less than1.50 g/bhp-hr, the brake-specific NOX and NMHC exhaust emissions in g/bhp-hr, as determined under §86.1370-2007 pertaining to the not-to-exceed test procedures, shall not exceed 1.25 times the applicable emission standards or FELs specified in paragraph (a)(1) of this section (or of §86.004-11, as allowed by paragraph (g) of this section), during engine and vehicle operation specified in paragraph (a)(4)(ii) of this section except as noted in paragraph (a)(4)(iii) of this section.
(C) The brake-specific exhaust PM emissions in g/bhp-hr, as determined under §86.1370-2007 pertaining to the not-to-exceed test procedures, shall not exceed 1.5 times the applicable PM emission standards or FEL (for FELs above the standard only) specified in paragraph (a)(1) of this section, during engine and vehicle operation specified in paragraph (a)(4)(ii) of this section except as noted in paragraph (a)(4)(iii) of this section.
(D) The brake-specific exhaust CO emissions in g/bhp-hr, as determined under §86.1370-2007 pertaining to the not-to-exceed test procedures, shall not exceed 1.25 times the applicable CO emission standards or FEL specified in paragraph (a)(1) of this section, during engine and vehicle operation specified in paragraph (a)(4)(ii) of this section except as noted in paragraph (a)(4)(iii) of this section.
(ii) For each engine family, the not-to-exceed emission limits must apply during one of the following two ambient operating regions:
(A) The not-to-exceed limits apply for all altitudes less than or equal to 5,500 feet above sea-level, during all ambient conditions (temperature and humidity). Temperature and humidity ranges for which correction factors are allowed are specified in §86.1370-2007(e); or
(B)(1) The not-to-exceed emission limits apply at all altitudes less than or equal to 5,500 feet above sea-level, for temperatures less than or equal to the temperature determined by the following equation at the specified altitude:
T = −0.00254 × A + 100
Where:
T = ambient air temperature in degrees Fahrenheit.
A = altitude in feet above sea-level (A is negative for altitudes below sea-level).
(2) Temperature and humidity ranges for which correction factors are allowed are specified in §86.1370-2007(e);
(iii) For engines equipped with exhaust gas recirculation, the not-to-exceed emission limits specified in paragraph (a)(4)(i) of this section do not apply to engine or vehicle operation during cold operating conditions as specified in §86.1370-2007(f).
(iv) Deficiencies for NTE emission standards. (A) For model years 2007 through 2009, upon application by the manufacturer, the Administrator may accept a HDDE as compliant with the NTE standards even though specific requirements are not fully met. Such compliances without meeting specific requirements, or deficiencies, will be granted only if compliance would be infeasible or unreasonable considering such factors as, but not limited to: Technical feasibility of the given hardware and lead time and production cycles including phase-in or phase-out of engines or vehicle designs and programmed upgrades of computers. Deficiencies will be approved on an engine model and/or horsepower rating basis within an engine family, and each approval is applicable for a single model year. A manufacturer's application must include a description of the auxiliary emission control device(s) which will be used to maintain emissions to the lowest practical level, considering the deficiency being requested, if applicable. An application for a deficiency must be made during the certification process; no deficiency will be granted to retroactively cover engines already certified.
(B) Unmet requirements should not be carried over from the previous model year except where unreasonable hardware or software modifications would be necessary to correct the deficiency, and the manufacturer has demonstrated an acceptable level of effort toward compliance as determined by the Administrator. The NTE deficiency should only be seen as an allowance for minor deviations from the NTE requirements. The NTE deficiency provisions allow a manufacturer to apply for relief from the NTE emission requirements under limited conditions. EPA expects that manufacturers should have the necessary functioning emission control hardware in place to comply with the NTE.
(C) For model years 2010 through 2013, the Administrator may allow up to three deficiencies per engine family. The provisions of paragraphs (a)(4)(iv)(A) and (B) of this section apply for deficiencies allowed by this paragraph (a)(4)(iv)(C). In determining whether to allow the additional deficiencies, the Administrator may consider any relevant factors, including the factors identified in paragraph (a)(4)(iv)(A) of this section. If additional deficiencies are approved, the Administrator may set any additional conditions that he/she determines to be appropriate.
(v) The emission limits specified in paragraphs (a)(3) and (a)(4) of this section shall be rounded to the same number of significant figures as the applicable standards in paragraph (a)(1) of this section using ASTM E29-93a (Incorporated by reference at §86.1).
(vi) Manufacturers are not required to provide engine information exclusively related to in-use testing as part of initial certification. However, upon request from EPA the manufacturers must provide the information which clearly identifies parameters defining all NTE deficiencies described under paragraph (a)(4)(iv) of this section and parameters defining all NTE limited testing regions described under §86.1370-2007(b)(6) and (7) that are requested. When requested, deficiencies and limited testing regions must be reported for all engine families and power ratings in English with sufficient detail for us to determine if a particular deficiency or limited testing region will be encountered in the emission test data from the portable emission-sampling equipment and field-testing procedures referenced in §86.1375. Such information is to be provided within 60 days of the request from EPA.
(b)(1) introductory text through (b)(1)(iii) [Reserved]. For guidance see §86.004-11.
(b)(1)(iv) Operation within the NTE zone (defined in §86.1370-2007) must comply with a filter smoke number of 1.0 under steady-state operation, or the following alternate opacity limits:
(A) A 30 second transient test average opacity limit of 4% for a 5 inch path; and
(B) A 10 second steady state test average opacity limit of 4% for a 5 inch path.
(2)(i) The standards set forth in §86.004-11 (b)(1)(i)-(iii) refer to exhaust smoke emissions generated under the conditions set forth in subpart I of this part and measured and calculated in accordance with those procedures.
(ii) The standards set forth in paragraph (b)(1)(iv) of this section refer to exhaust smoke emissions generated under the conditions set forth in §86.1370-2007 and calculated in accordance with the procedures set forth in §86.1372-2007.
(b)(3) and (b)(4) [Reserved]. For guidance see §86.004-11.
(c) No crankcase emissions shall be discharged directly into the ambient atmosphere from any new 2007 or later model year diesel HDE, with the following exception: HDEs equipped with turbochargers, pumps, blowers, or superchargers for air induction may discharge crankcase emissions to the ambient atmosphere if the emissions are added to the exhaust emissions (either physically or mathematically) during all emission testing. Manufacturers taking advantage of this exception must manufacture the engines so that all crankcase emission can be routed into a dilution tunnel (or other sampling system approved in advance by the Administrator), and must account for deterioration in crankcase emissions when determining exhaust deterioration factors. For the purpose of this paragraph (c), crankcase emissions that are routed to the exhaust upstream of exhaust aftertreatment during all operation are not considered to be “discharged directly into the ambient atmosphere.”
(d) Every manufacturer of new motor vehicle engines subject to the standards prescribed in this section shall, prior to taking any of the actions specified in section 203(a)(1) of the Act, test or cause to be tested motor vehicle engines in accordance with applicable procedures in subpart I or N of this part to ascertain that such test engines meet the requirements of paragraphs (a), (b), (c), and (d) of this section.
(e) [Reserved]. For guidance see §86.004-11.
(f) Model year 2007 and later diesel-fueled heavy-duty engines and vehicles for sale in Guam, American Samoa, or the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands may be subject to alternative standards under 40 CFR 1036.655.
(g) Model years 2018 through 2026 engines at or above 56 kW that will be installed in specialty vehicles as allowed by 40 CFR 1037.605 may meet alternate emission standards as follows:
(1) The engines must be of a configuration that is identical to one that is certified under 40 CFR part 1039, and meet the following additional standards using the same duty cycles that apply under 40 CFR part 1039:
(i) The engines must be certified with a Family Emission Limit for PM of 0.020 g/kW-hr.
(ii) Diesel-fueled engines using selective catalytic reduction must meet an emission standard of 0.1 g/kW-hr for N2O.
(2) Except as specified in this paragraph (g), engines certified under this paragraph (g) must meet all the requirements that apply under 40 CFR part 1039 instead of the comparable provisions in this subpart A. Before shipping engines under this section, you must have written assurance from the vehicle manufacturers that they need a certain number of exempted engines under this section. In your annual production report under 40 CFR 1039.250, count these engines separately and identify the vehicle manufacturers that will be installing them. Treat these engines as part of the corresponding engine family under 40 CFR part 1039 for compliance purposes such as selective enforcement audits, in-use testing, defect reporting, and recall.
(3) The engines must be labeled as described in §86.095-35, with the following statement instead of the one specified in §86.095-35(a)(3)(iii)(H): “This engine conforms to alternate standards for specialty vehicles under 40 CFR 86.007-11(g)”. Engines certified under this paragraph (g) may not have the label specified for nonroad engines in 40 CFR part 1039 or any other label identifying them as nonroad engines.
(4) In a separate application for a certificate of conformity, identify the corresponding nonroad engine family, describe the label required under this paragraph (g), state that you meet applicable diagnostic requirements under 40 CFR part 1039, and identify your projected U.S.-directed production volume.
(5) No additional certification fee applies for engines certified under this paragraph (g).
(6) Engines certified under this paragraph (g) may not generate or use emission credits under this part or under 40 CFR part 1039. The vehicles in which these engines are installed may generate or use emission credits as described in 40 CFR part 1037.
(7) Engines may instead meet standards for heavy-duty highway engines in California, as demonstrated by an Executive Order issued by the California Air Resources Board.
(h)(1) For model years prior to 2012, for purposes of determining compliance after title or custody has transferred to the ultimate purchaser, for engines having a NOX FEL no higher than 1.30 g/bhp-hr, the applicable compliance limit shall be determined by adding the applicable adjustment from paragraph (h)(2) of this section to the otherwise applicable standard or FEL for NOX.
(2)(i) For engines with 110,000 or fewer miles, the adjustment is 0.10 g/bhp-hr.
(ii) For engines with 110,001 to 185,000 miles, the adjustment is 0.15 g/bhp-hr.
(iii) For engines with 185,001 or more miles, the adjustment is 0.20 g/bhp-hr.
(3) For model years prior to 2012, for purposes of determining compliance after title or custody has transferred to the ultimate purchaser, the applicable compliance limit shall be determined by adding 0.01 g/bhp-hr to the otherwise applicable standard or FEL for PM.
(i) [Reserved]
(j) Engines installed in new glider vehicles are subject to the standards of this section as specified in 40 CFR part 1037.
[65 FR 59954, Oct. 6, 2000, as amended at 66 FR 5161, Jan. 18, 2001; 70 FR 34619, June 14, 2005; 70 FR 40432, July 13, 2005; 71 FR 51486, Aug. 30, 2006; 73 FR 37192, June 30, 2008; 81 FR 73974, Oct. 25, 2016; 88 FR 4473, Jan. 24, 2023]
READ MORESHOW LESS
['Air Programs']
['Mobile Emission Sources']
Load More
J. J. Keller is the trusted source for DOT / Transportation, OSHA / Workplace Safety, Human Resources, Construction Safety and Hazmat / Hazardous Materials regulation compliance products and services. J. J. Keller helps you increase safety awareness, reduce risk, follow best practices, improve safety training, and stay current with changing regulations.
Copyright 2024 J. J. Keller & Associate, Inc. For re-use options please contact copyright@jjkeller.com or call 800-558-5011.
