['CMV Parts and Maintenance']
['Tires']
04/07/2025
...
S1. Scope. This standard establishes performance requirements for automatic emergency braking (AEB) systems for light vehicles.
S2. Purpose. The purpose of this standard is to reduce the number of deaths and injuries that result from crashes in which drivers do not apply the brakes or fail to apply sufficient braking power to avoid or mitigate a crash.
S3. Application. This standard applies to passenger cars and to multipurpose passenger vehicles, trucks, and buses with a gross vehicle weight rating (GVWR) of 4,536 kilograms (10,000 pounds) or less.
S4. Definitions.
Adaptive cruise control system is an automatic speed control system that allows the equipped vehicle to follow a lead vehicle at a pre-selected gap by controlling the engine, power train, and service brakes.
Ambient illumination is the illumination as measured at the test surface, not including any illumination provided by the subject vehicle.
Automatic emergency braking (AEB) system is a system that detects an imminent collision with vehicles, objects, and road users in or near the path of a vehicle and automatically controls the vehicle's service brakes to avoid or mitigate the collision.
Brake pedal application onset is when 11 N of force has been applied to the brake pedal.
Forward collision warning is an auditory and visual warning provided to the vehicle operator by the AEB system that is designed to induce immediate forward crash avoidance response by the vehicle operator.
Forward collision warning onset is the first moment in time when a forward collision warning is provided.
Headway is the distance between the subject vehicle's frontmost plane normal to its centerline and as applicable: the vehicle test device's rearmost plane normal to its centerline; a parallel contact plane (to the subject vehicle's frontmost plane) on the pedestrian test mannequin; and the leading edge of the steel trench plate.
Lead vehicle is a vehicle test device facing the same direction and preceding a subject vehicle within the same travel lane.
Lead vehicle braking onset is the point at which the lead vehicle achieves a deceleration of 0.05 g due to brake application.
[Editor’s Note: The following definition is removed effective March 20, 2025.][Change Notice]
Masked threshold is the quietest level of a signal that can be perceived in the presence of noise.
Pedestrian test mannequin is a device used during AEB testing, when approaching pedestrians, meeting the specifications of subpart B of 49 CFR part 596.
Small-volume manufacturer means an original vehicle manufacturer that produces or assembles fewer than 5,000 vehicles annually for sale in the United States.
Steel trench plate is a rectangular steel plate often used in road construction to temporarily cover sections of pavement unsafe to drive over directly.
Subject vehicle is the vehicle under examination for compliance with this standard.
Travel path is the path projected onto the road surface of a point located at the intersection of the subject vehicle's frontmost vertical plane and longitudinal vertical center plane, as the subject vehicle travels forward.
Subject vehicle braking onset is the point at which the subject vehicle achieves a deceleration of 0.15 g due to the automatic control of the service brakes.
Vehicle test device is a device meeting the specifications set forth in subpart C of 49 CFR part 596.
S5. Requirements.
(a) Except as provided in S5(b), vehicles manufactured on or after September 1, 2029 must meet the requirements of this standard.
(b) The requirements of S5(a) do not apply to small-volume manufacturers, final-stage manufacturers, and alterers until one year after the dates specified in S5(a).
S5.1. Requirements when approaching a lead vehicle.
S5.1.1. Forward collision warning. A vehicle is required to have a forward collision warning system, as defined in S4 that provides an auditory and visual signal to the driver of an impending collision with a lead vehicle. The system must operate under the conditions specified in S6 when traveling at any forward speed that is greater than 10 km/h (6.2 mph) and less than 145 km/h (90.1 mph).
(a) Auditory signal.
(1) The auditory signal must have a high fundamental frequency of at least 800 Hz.
(2) The auditory signal must have a tempo in the range of 6-12 pulses per second and a duty cycle in the range of 0.25-0.95.
(3) The auditory signal as measured adjacent to a 50th percentile male driver's right ear (tragion) must have an intensity of 15-30 dB above the average noise level inside the vehicle when measured over a 5-second period under the range of test conditions specified in S6, at 100 km/h, with all vehicle openings closed, and all subject vehicle audio and sound-producing systems or functions that are not necessary for performing tests pursuant to the conditions in S6 and the procedures in S7, S8, S9 of this standard set to off. [Change Notice] [Previous Text]
(4) In-vehicle audio that is not related to a crash avoidance system warning must be muted, or reduced in volume during presentation of the FCW auditory signal to within 5 dB of the average noise level inside the vehicle (as measured in S5.1.1(a)(3)), for the duration of the first between-pulse period of the FCW auditory signal under the range of test conditions specified in S6, at 100 km/h, with all vehicle openings closed, and all subject vehicle audio and sound-producing systems or functions that are not necessary for performing tests pursuant to the conditions in S6 and the procedures in S7, S8, S9 of this standard set to off. [Change Notice] [Previous Text]
(b) Visual signal.
(1) The visual signal symbol must be located within an ellipse that extends ±18 degrees vertically and ±10 degrees horizontally of the driver forward line of sight based on the forward-looking eye midpoint (M f ) as described in S14 of 49 CFR §571.111. [Change Notice] [Previous Text]
(2) The visual signal must include the crash pictorial symbol in SAE J2400, 4.1.16, incorporated by reference (see §571.5).
(3) The visual signal symbol must be red in color and steady burning.
S5.1.2. Automatic emergency braking. A vehicle is required to have an automatic emergency braking system, as defined in S4, that applies the service brakes automatically when a collision with a lead vehicle is imminent. The system must operate under the conditions specified in S6 when the vehicle is traveling at any forward speed that is greater than 10 km/h (6.2 mph) and less than 145 km/h (90.1 mph).
S5.1.3. Performance test requirements. The vehicle must provide a forward collision warning and subsequently apply the service brakes automatically such that the subject vehicle does not collide with the lead vehicle when tested using the procedures in S7 under the conditions specified in S6. The forward collision warning is not required if adaptive cruise control is engaged. [Change Notice] [Previous Text]
S5.2. Requirements when approaching pedestrians.
S5.2.1. Forward collision warning. A vehicle is required to have a forward collision warning system, as defined in S4, that provides an auditory and visual signal to the driver of an impending collision with a pedestrian. The system must operate under the conditions specified in S6 when the vehicle is traveling at any forward speed that is greater than 10 km/h (6.2 mph) and less than 73 km/h (45.3 mph). The forward collision warning system must meet the auditory signal and visual signal requirements specified in S5.1.1.
S5.2.2. Automatic emergency braking. A vehicle is required to have an automatic emergency braking system, as defined in S4, that applies the service brakes automatically when a collision with a pedestrian is imminent when the vehicle is under the conditions specified in S6 and is traveling at any forward speed that is greater than 10 km/h (6.2 mph) and less than 73 km/h (45.3 mph).
S5.2.3. Performance test requirements. The vehicle must provide a forward collision warning and apply the brakes automatically such that the subject vehicle does not collide with the pedestrian test mannequin when tested using the procedures in S8 under the conditions specified in S6.
S5.3. False activation. The vehicle must not automatically apply braking that results in peak additional deceleration that exceeds what manual braking would produce by 0.25 g or greater, when tested using the procedures in S9 under the conditions specified in S6.
S5.4. Malfunction detection and controls.
S5.4.1 The system must continuously detect system malfunctions, including performance degradation caused solely by sensor obstructions. If the system detects a malfunction, or if the system adjusts its performance such that it will not meet the requirements specified in S5.1, S5.2, or S5.3, the system must provide the vehicle operator with a telltale notification.
S5.4.2 Except as provided in S5.4.2.1 and S5.4.2.2, the manufacturer must not provide a control that will place the AEB system in a mode or modes in which it will no longer satisfy the performance requirements of S5.1, S5.2, and S5.3.
S5.4.2.1 The manufacturer may provide a control to allow AEB deactivation that is securely activated, provided the manufacturer enables such activation exclusively in a vehicle owned by a law enforcement agency.
S5.4.2.2 The manufacturer may allow AEB deactivation to occur during low-range four-wheel drive configurations, when the driver selects “tow mode,” or when another vehicle system is activated that will have a negative ancillary impact on AEB operation.
S5.4.3 The vehicle's AEB system must always return to the manufacturer's original default AEB mode that satisfies the requirements of S5.1, S5.2, and S5.3 at the initiation of each new ignition cycle, unless the vehicle is in a low-range four-wheel drive configuration selected by the driver on the previous ignition cycle designed for low-speed, off-road driving.
S6. Test conditions.
S6.1. Environmental conditions.
S6.1.1. Temperature. The ambient temperature is any temperature between 0 °C and 40 °C.
S6.1.2. Wind. The maximum wind speed is no greater than 10 m/s (22 mph) during lead vehicle avoidance tests and 6.7 m/s (15 mph) during pedestrian avoidance tests.
S6.1.3. Ambient lighting.
(a) Daylight testing.
(1) The ambient illumination on the test surface is any level at or above 2,000 lux.
(2) Testing is not performed while driving toward or away from the sun such that the horizontal angle between the sun and a vertical plane containing the centerline of the subject vehicle is less than 25 degrees and the solar elevation angle is less than 15 degrees.
(b) Dark testing.
(1) The ambient illumination on the test surface is any level at or below 0.2 lux.
(2) Testing is performed under any lunar phase.
(3) Testing is not performed while driving toward the moon such that the horizontal angle between the moon and a vertical plane containing the centerline of the subject vehicle is less than 25 degrees and the lunar elevation angle is less than 15 degrees.
S6.1.4. Precipitation. Testing is not conducted during periods of precipitation or when visibility is affected by fog, smoke, ash, or other particulate.
S6.2. Road conditions.
S6.2.1. Test Track surface and construction. The tests are conducted on a dry, uniform, solid-paved surface. Surfaces with debris, irregularities, or undulations, such as loose pavement, large cracks, or dips may not be used.
S6.2.2. Surface friction. The road test surface produces a peak friction coefficient (PFC) of 1.02 when measured using an ASTM F2493 standard reference test tire, in accordance with ASTM E1337-19 (incorporated by reference, see §571.5), at a speed of 64 km/h (40 mph), without water delivery.
S6.2.3. Slope. The test surface has any consistent slope between 0 percent and 1 percent.
S6.2.4. Markings. The road surface within 2 m of the intended travel path is marked with zero, one, or two lines of any configuration or color. If one line is used, it is straight. If two lines are used, they are straight, parallel to each other, and at any distance from 2.7 m to 4.5 m apart.
S6.2.5. Obstructions. Testing is conducted such that the vehicle does not travel beneath any overhead structures, including but not limited to overhead signs, bridges, or gantries. No vehicles, obstructions, or stationary objects are within 7.4 m of either side of the intended travel path except as specified.
S6.3. Subject vehicle conditions.
S6.3.1. Malfunction notification. Testing is not conducted while the AEB malfunction telltale specified in S5.4 is illuminated.
S6.3.2. Sensor obstruction. All sensors used by the system and any part of the vehicle immediately ahead of the sensors, such as plastic trim, the windshield, etc., are free of debris or obstructions.
S6.3.3. Tires. The vehicle is equipped with the original tires present at the time of initial sale. The tires are inflated to the vehicle manufacturer's recommended cold tire inflation pressure(s) specified on the vehicle's placard or the tire inflation pressure label.
S6.3.4. Brake burnish.
(a) Vehicles subject to §571.105 are burnished in accordance with S7.4 of §571.105.
(b) Vehicles subject to §571.135 are burnished in accordance with S7.1 of §571.135.
S6.3.5. Brake temperature. The average temperature of the service brakes on the hottest axle of the vehicle during testing, measured according to S6.4.1 of §571.135, is between 65°C and 100°C prior to braking.
S6.3.6. Fluids. All non-consumable fluids for the vehicle are at 100 percent capacity. All consumable fluids are at any level from 5 to 100 percent capacity.
S6.3.7. Propulsion battery charge. The propulsion batteries are charged at any level from 5 to 100 percent capacity.
S6.3.8. Cruise control. Cruise control, including adaptive cruise control, is configured under any available setting.
S6.3.9. Adjustable forward collision warning. Forward collision warning is configured in any operator-configurable setting.
S6.3.10. Engine braking. A vehicle equipped with an engine braking system that is engaged and disengaged by the operator is tested with the system in any selectable configuration.
S6.3.11. Regenerative braking. Regenerative braking is configured under any available setting.
S6.3.12. Headlamps.
(a) Daylight testing is conducted with the headlamp control in any selectable position.
(b) Darkness testing is conducted with the vehicle's lower beams active and separately with the vehicle's upper beams active.
(c) Prior to performing darkness testing, headlamps are aimed according to the vehicle manufacturer's instructions. The weight of the loaded vehicle at the time of headlamp aiming is within 10 kg of the weight of the loaded vehicle during testing.
S6.3.13. Subject vehicle loading. The vehicle load, which is the sum of any vehicle occupants and any test equipment and instrumentation, does not exceed 277 kg. The load does not cause the vehicle to exceed its GVWR or any axle to exceed its GAWR.
S6.3.14. AEB system initialization. The vehicle is driven at a speed of 10 km/h or higher for at least one minute prior to testing, and subsequently the starting system is not cycled off prior to testing.
S6.4. Equipment and test devices.
S6.4.1. The vehicle test device is specified in 49 CFR part 596, subpart C. Local fluttering of the lead vehicle's external surfaces does not exceed 10 mm perpendicularly from the reference surface, and distortion of the lead vehicle's overall shape does not exceed 25 mm in any direction.
S6.4.2. Adult pedestrian test mannequin is specified in 49 CFR part 596, subpart B.
S6.4.3. Child pedestrian test mannequin is specified in 49 CFR part 596, subpart B.
S6.4.4. The steel trench plate used for the false activation test has the dimensions 2.4 m x 3.7 m x 25 mm and is made of ASTM A36 steel. Any metallic fasteners used to secure the steel trench plate are flush with the top surface of the steel trench plate.
S7. Testing when approaching a lead vehicle.
S7.1. Setup.
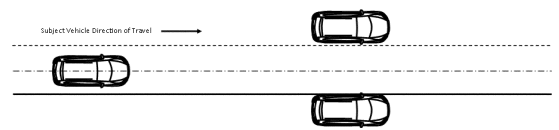
(a) The testing area is set up in accordance with figure 2 to this section.
(b) Testing is conducted during daylight.
(c) For reference, table 1 to S7.1 specifies the subject vehicle speed (V SV), lead vehicle speed (V LV), headway, and lead vehicle deceleration for each test that may be conducted.
(d) The intended travel path of the vehicle is a straight line toward the lead vehicle from the location corresponding to a headway of L 0.
(e) If the road surface is marked with a single or double lane line, the intended travel path is parallel to and 1.8 m from the inside of the closest line. If the road surface is marked with two lane lines bordering the lane, the intended travel path is centered between the two lines.
(f) For each test run conducted, the subject vehicle speed (V SV), lead vehicle speed (V LV), headway, and lead vehicle deceleration will be selected from the ranges specified in table 1 to S7.1.
| Speed (km/h) | Headway (m) | Lead vehicle decel (g) | Manual brake application | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V SV | V LV | ||||
| Stopped Lead Vehicle | Any 10-80 | 0 | — | — | No. |
| Any 70-100 | 0 | — | — | Yes. | |
| Slower-Moving Lead Vehicle | Any 40-80 | 20 | — | — | No. |
| Any 70-100 | 20 | — | — | Yes. | |
| Decelerating Lead Vehicle | 50 | 50 | Any 12-40 | Any 0.3-0.5 | No. |
| 50 | 50 | Any 12-40 | Any 0.3-0.5 | Yes. | |
| 80 | 80 | Any 12-40 | Any 0.3-0.5 | No. | |
| 80 | 80 | Any 12-40 | Any 0.3-0.5 | Yes. | |
S7.2. Headway calculation. For each test run conducted under S7.3 and S7.4, the headway (L), in meters, providing 5.0 seconds time to collision (TTC) is calculated. L is determined with the following equation where V is the speed of the subject vehicle in m/s and V is the speed of the lead vehicle in m/s:
Equation 1 to S7.2
L = TTC 0 × (V −V)
TTC 0 = 5.0
S7.3. Stopped lead vehicle.
S7.3.1. Test parameters.
(a) For testing with no subject vehicle manual brake application, the subject vehicle test speed is any speed between 10 km/h and 80 km/h, and the lead vehicle speed is 0 km/h.
(b) For testing with manual brake application of the subject vehicle, the subject vehicle test speed is any speed between 70 km/h and 100 km/h, and the lead vehicle speed is 0 km/h.
S7.3.2. Test conduct prior to forward collision warning onset.
(a) The lead vehicle is placed stationary with its longitudinal centerline coincident to the intended travel path.
(b) Before the headway corresponds to L 0, the subject vehicle is driven at any speed, in any direction, on any road surface, for any amount of time.
(c) The subject vehicle approaches the rear of the lead vehicle.
(d) Beginning when the headway corresponds to L 0, the subject vehicle speed is maintained within 1.6 km/h of the test speed with minimal and smooth accelerator pedal inputs.
(e) Beginning when the headway corresponds to L 0, the subject vehicle heading is maintained with minimal steering input such that the travel path does not deviate more than 0.3 m laterally from the intended travel path and the subject vehicle's yaw rate does not exceed ±1.0 deg/s.
S7.3.3. Test conduct after forward collision warning onset.
(a) The accelerator pedal is released at any rate such that it is fully released within 500 ms. This action is omitted for vehicles tested with cruise control active.
(b) For testing conducted with manual brake application, the service brakes are applied as specified in S10. The onset of brake pedal application occurs 1.0 ± 0.1 second after forward collision warning onset.
(c) For testing conducted without manual brake application, no manual brake application is made until the test completion criteria of S7.3.4 are satisfied.
S7.3.4. Test completion criteria. The test run is complete when the subject vehicle comes to a complete stop without making contact with the lead vehicle or when the subject vehicle makes contact with the lead vehicle.
S7.4. Slower-moving lead vehicle.
S7.4.1. Test parameters.
(a) For testing with no subject vehicle manual brake application, the subject vehicle test speed is any speed between 40 km/h and 80 km/h, and the lead vehicle speed is 20 km/h.
(b) For testing with manual brake application of the subject vehicle, the subject vehicle test speed is any speed between 70 km/h and 100 km/h, and the lead vehicle speed is 20 km/h.
S7.4.2. Test conduct prior to forward collision warning onset.
(a) The lead vehicle is propelled forward in a manner such that the longitudinal center plane of the lead vehicle does not deviate laterally more than 0.3m from the intended travel path.
(b) The subject vehicle approaches the lead vehicle.
(c) Before the headway corresponds to L 0, the subject vehicle is driven at any speed, in any direction, on any road surface, for any amount of time.
(d) Beginning when the headway corresponds to L 0, the subject vehicle and lead vehicle speed is maintained within 1.6 km/h of the test speed with minimal and smooth accelerator pedal inputs.
(e) Beginning when the headway corresponds to L 0, the subject vehicle and lead vehicle headings are be maintained with minimal steering input such that the subject vehicle's travel path does not deviate more than 0.3 m laterally from the centerline of the lead vehicle, and the yaw rate of the subject vehicle does not exceed ±1.0 deg/s prior to the forward collision warning onset.
S7.4.3. Test conduct after forward collision warning onset.
(a) The subject vehicle's accelerator pedal is released at any rate such that it is fully released within 500 ms. This action is omitted for vehicles tested with cruise control active.
(b) For testing conducted with manual braking application, the service brakes are applied as specified in S10. The onset of brake pedal application is 1.0 ±0.1 second after the forward collision warning onset.
(c) For testing conducted without manual braking application, no manual brake application is made until the test completion criteria of S7.4.4 are satisfied.
S7.4.4. Test completion criteria. The test run is complete when the subject vehicle speed is less than or equal to the lead vehicle speed without making contact with the lead vehicle or when the subject vehicle makes contact with the lead vehicle.
S7.5. Decelerating lead vehicle.
S7.5.1. Test parameters.
(a) The subject vehicle test speed is 50 km/h or 80 km/h, and the lead vehicle speed is identical to the subject vehicle test speed.
(b) [Reserved]
S7.5.2. Test conduct prior to lead vehicle braking onset.
(a) Before the 3 seconds prior to lead vehicle braking onset, the subject vehicle is be driven at any speed, in any direction, on any road surface, for any amount of time.
(b) Between 3 seconds prior to lead vehicle braking onset and lead vehicle braking onset:
(1) The lead vehicle is propelled forward in a manner such that the longitudinal center plane of the vehicle does not deviate laterally more than 0.3 m from the intended travel path.
(2) The subject vehicle follows the lead vehicle at a headway of any distance between 12 m and 40 m.
(3) The subject vehicle's speed is maintained within 1.6 km/h of the test speed with minimal and smooth accelerator pedal inputs prior to forward collision warning onset.
(4) The lead vehicle's speed is maintained within 1.6 km/h.
(5) The subject vehicle and lead vehicle headings are maintained with minimal steering input such that their travel paths do not deviate more than 0.3 m laterally from the centerline of the lead vehicle, and the yaw rate of the subject vehicle does not exceed ±1.0 deg/s until onset of forward collision warning.
S7.5.3. Test conduct following lead vehicle braking onset.
(a) The lead vehicle is decelerated to a stop with a targeted average deceleration of any value between 0.3g and 0.5g. The targeted deceleration magnitude is achieved within 1.5 seconds of lead vehicle braking onset and is maintained until 250 ms prior to coming to a stop.
(b) After forward collision warning onset, the subject vehicle's accelerator pedal is released at any rate such that it is fully released within 500 ms. This action is omitted for vehicles with cruise control active.
(c) For testing conducted with manual braking application, the service brakes are applied as specified in S10. The brake pedal application onset occurs 1.0 ± 0.1 second after the forward collision warning onset.
(d) For testing conducted without manual braking application, no manual brake application is made until the test completion criteria of S7.5.4 are satisfied.
S7.5.4. Test completion criteria. The test run is complete when the subject vehicle comes to a complete stop without making contact with the lead vehicle or when the subject vehicle makes contact with the lead vehicle.
S8. Testing when approaching a pedestrian.
S8.1. Setup.
S8.1.1. General.
(a) For reference, table 2 to S8.1.1 specifies the pedestrian test mannequin direction of travel, overlap, obstruction condition and speed (V P), the subject vehicle speed (V SV), and the lighting condition for each test that may be conducted.
(b) The intended travel path of the vehicle is a straight line originating at the location corresponding to a headway of L 0.
(c) If the road surface is marked with a single or double lane line, the intended travel path is parallel to and 1.8 m from the inside of the closest line. If the road surface is marked with two lane lines bordering the lane, the intended travel path is centered between the two lines.
(d) For each test run conducted, the subject vehicle speed (V SV) will be selected from the range specified in table 2 to S8.1.1.
| Direction | Overlap | Obstructed | Speed (km/h) | Lighting condition | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V SV | V P | |||||
| Pedestrian Crossing Road | Right | 25 | No | Any 10-60 | 5 | Daylight |
| Right | 50 | No | Any 10-60 | 5 | Daylight Lower Beams Upper Beams | |
| Left | 50 | No | Any 10-60 | 8 | Daylight | |
| Right | 50 | Yes | Any 10-50 | 5 | Daylight | |
| Stationary Pedestrian | Right | 25 | No | Any 10-55 | 0 | Daylight Lower Beams Upper Beams |
| Pedestrian Moving Along the Path | Right | 25 | No | Any 10-65 | 5 |
Daylight
Lower Beams Upper Beams |
S8.1.2. Overlap. As depicted in figure 1 to this section, overlap describes the location of the point on the front of the subject vehicle that would make contact with a pedestrian if no braking occurred. Overlap is the percentage of the subject vehicle's overall width that the pedestrian test mannequin traverses. It is measured from the right or the left, depending on the side of the subject vehicle where the pedestrian test mannequin originates. For each test run, the actual overlap will be within 0.15 m of the specified overlap.
S8.1.3. Pedestrian test mannequin.
(a) For testing where the pedestrian test mannequin is secured to a moving apparatus, the pedestrian test mannequin is secured so that it faces the direction of motion. The pedestrian test mannequin leg articulation starts on apparatus movement and stops when the apparatus stops.
(b) For testing where the pedestrian test mannequin is stationary, the pedestrian test mannequin faces away from the subject vehicle, and the pedestrian test mannequin legs remain still.
S8.2. Headway calculation. For each test run conducted under S8.3, S8.4, and S8.5, the headway (L0), in meters, providing 4.0 seconds time to collision (TTC) is calculated. L0 is determined with the following equation where VSV is the speed of the subject vehicle in m/s and VP-y is the component of speed of the pedestrian test mannequin in m/s in the direction of the intended travel path:
Equation 2 to S8.2
L = TTC 0 × (V − V)
TTC 0 = 4.0
S8.3. Pedestrian crossing road.
S8.3.1. Test parameters and setup (unobstructed from right).
(a) The testing area is set up in accordance with figure 3 to this section.
(b) Testing is conducted in the daylight or darkness conditions, except that testing with the pedestrian at the 25 percent overlap is only conducted in daylight conditions.
(c) Testing is conducted using the adult pedestrian test mannequin.
(d) The movement of the pedestrian test mannequin is perpendicular to the subject vehicle's intended travel path.
(e) The pedestrian test mannequin is set up 4.0 ± 0.1 m to the right of the intended travel path.
(f) The intended overlap is 25 percent from the right or 50 percent.
(g) The subject vehicle test speed is any speed between 10 km/h and 60 km/h.
(h) The pedestrian test mannequin speed is 5 km/h.
S8.3.2 Test parameters and setup (unobstructed from left).
(a) The testing area is set up in accordance with figure 4 to this section.
(b) Testing is conducted in the daylight condition.
(c) Testing is conducted using the adult pedestrian mannequin.
(d) The movement of the pedestrian test mannequin is perpendicular to the intended travel path.
(e) The pedestrian test mannequin is set up 6.0 ± 0.1 m to the left of the intended travel path.
(f) The intended overlap is 50 percent.
(g) The subject vehicle test speed is any speed between 10 km/h and 60 km/h.
(h) The pedestrian test mannequin speed is 8 km/h.
S8.3.3. Test parameters and setup (obstructed).
(a) The testing area is set up in accordance with figure 5 to this section.
(b) Testing is conducted in the daylight condition.
(c) Testing is conducted using the child pedestrian test mannequin.
(d) The movement of the pedestrian test mannequin is perpendicular to the intended travel path.
(e) The pedestrian test mannequin is set up 4.0 ± 0.1 m to the right of the intended travel path.
(f) The intended overlap is 50 percent.
(g) Two vehicle test devices are secured in stationary positions parallel to the intended travel path. The two vehicle test devices face the same direction as the intended travel path. One vehicle test device is directly behind the other separated by 1.0 ± 0.1 m. The frontmost plane of the vehicle test device furthermost from the subject vehicle is located 1.0 ± 0.1 m from the parallel contact plane (to the subject vehicle's frontmost plane) on the pedestrian test mannequin. The left side of each vehicle test device is no less than 2.2 m to the right of the vertical plane through the intended travel path. The left side of each vehicle test device is no less than 1.15 m to the right of the vertical plane parallel to the plane through the intended travel path tangent to the 0 percent overlap point. [Change Notice] [Previous Text]
(h) The subject vehicle test speed is any speed between 10 km/h and 50 km/h.
(i) The pedestrian test mannequin speed is 5 km/h.
S8.3.4. Test conduct prior to forward collision warning or subject vehicle braking onset.
(a) Before the headway corresponds to L 0, the subject vehicle is driven at any speed, in any direction, on any road surface, for any amount of time.
(b) The subject vehicle approaches the crossing path of the pedestrian test mannequin.
(c) Beginning when the headway corresponds to L 0, the subject vehicle speed is maintained within 1.6 km/h of the test speed with minimal and smooth accelerator pedal inputs.
(d) Beginning when the headway corresponds to L 0, the subject vehicle heading is maintained with minimal steering inputs such that the subject vehicle's travel path does not deviate more than 0.3 m laterally from the intended travel path, and the yaw rate of the subject vehicle does not exceed ±1.0 deg/s prior to any automated braking onset.
(e) The pedestrian test mannequin apparatus is triggered at a time such that the pedestrian test mannequin meets the intended overlap, subject to the criteria in S8.1.2. The pedestrian test mannequin achieves its intended speed within 1.5 m after the apparatus begins to move and maintains its intended speed within 0.4 km/h until the test completion criteria of S8.3.6 are satisfied.
S8.3.5. Test conduct after either forward collision warning or subject vehicle braking onset.
(a) After forward collision warning or subject vehicle braking onset, the subject vehicle's accelerator pedal is released at any rate such that it is fully released within 500 ms. This action is omitted for vehicles with cruise control active.
(b) No manual brake application is made until the test completion criteria of S8.3.6 are satisfied.
(c) The pedestrian mannequin continues to move until the completion criteria of S8.3.6 are satisfied.
S8.3.6. Test completion criteria. The test run is complete when the subject vehicle comes to a complete stop without making contact with the pedestrian test mannequin, when the pedestrian test mannequin is no longer in the path of the subject vehicle, or when the subject vehicle makes contact with the pedestrian test mannequin.
S8.4. Stationary pedestrian.
S8.4.1. Test parameters and setup.
(a) The testing area is set up in accordance with figure 6 to this section.
(b) Testing is conducted in the daylight or darkness conditions.
(c) Testing is conducted using the adult pedestrian test mannequin.
(d) The pedestrian mannequin is set up at the 25 percent right overlap position facing away from the approaching vehicle.
(e) The subject vehicle test speed is any speed between 10 km/h and 55 km/h.
(f) The pedestrian mannequin is stationary.
S8.4.2. Test conduct prior to forward collision warning or subject vehicle braking onset.
(a) Before the headway corresponds to L 0, the subject vehicle is driven at any speed, in any direction, on any road surface, for any amount of time.
(b) The subject vehicle approaches the pedestrian test mannequin.
(c) Beginning when the headway corresponds to L 0, the subject vehicle speed is maintained within 1.6 km/h of the test speed with minimal and smooth accelerator pedal inputs.
(d) Beginning when the headway corresponds to L 0, the subject vehicle heading is maintained with minimal steering inputs such that the subject vehicle's travel path does not deviate more than 0.3 m laterally from the intended travel path, and the yaw rate of the subject vehicle does not exceed ±1.0 deg/s prior to any automated braking onset.
S8.4.3. Test conduct after either forward collision warning or subject vehicle braking onset.
(a) After forward collision warning or subject vehicle braking onset, the subject vehicle's accelerator pedal is released at any rate such that it is fully released within 500 ms. This action is omitted with vehicles with cruise control active.
(b) No manual brake application is made until the test completion criteria of S8.4.4 are satisfied.
S8.4.4. Test completion criteria. The test run is complete when the subject vehicle comes to a complete stop without making contact with the pedestrian test mannequin, or when the subject vehicle makes contact with the pedestrian test mannequin.
S8.5. Pedestrian moving along the path.
S8.5.1. Test parameters and setup.
(a) The testing area is set up in accordance with figure 7 to this section.
(b) Testing is conducted in the daylight or darkness conditions.
(c) Testing is conducted using the adult pedestrian test mannequin.
(d) The movement of the pedestrian test mannequin is parallel to and in the same direction as the subject vehicle.
(e) The pedestrian test mannequin is set up in the 25 percent right offset position.
(f) The subject vehicle test speed is any speed between 10 km/h and 65 km/h.
(g) The pedestrian test mannequin speed is 5 km/h.
S8.5.2. Test conduct prior to forward collision warning or subject vehicle braking onset.
(a) Before the headway corresponds to L 0, the subject vehicle is driven at any speed, in any direction, on any road surface, for any amount of time.
(b) The subject vehicle approaches the pedestrian test mannequin.
(c) Beginning when the headway corresponds to L 0, the subject vehicle speed is maintained within 1.6 km/h of the test speed with minimal and smooth accelerator pedal inputs.
(d) Beginning when the headway corresponds to L 0, the subject vehicle heading is maintained with minimal steering inputs such that the travel path does not deviate more than 0.3 m laterally from the intended travel path, and the yaw rate of the subject vehicle does not exceed ±1.0 deg/s prior to any automated braking onset.
(e) The pedestrian test mannequin apparatus is triggered any time after the distance between the front plane of the subject vehicle and a parallel contact plane on the pedestrian test mannequin corresponds to L 0. The pedestrian test mannequin achieves its intended speed within 1.5 m after the apparatus begins to move and maintains its intended speed within 0.4 km/h until the test completion criteria of S8.5.4 are satisfied.
S8.5.3. Test conduct after either forward collision warning or subject vehicle braking onset.
(a) After forward collision warning or subject vehicle braking onset, the subject vehicle's accelerator pedal is released at any rate such that it is fully released within 500 ms. This action is omitted for vehicles with cruise control active.
(b) No manual brake application is made until the test completion criteria of S8.5.4 are satisfied.
S8.5.4. Test completion criteria. The test run is complete when the subject vehicle slows to speed below the pedestrian test mannequin travel speed without making contact with the pedestrian test mannequin or when the subject vehicle makes contact with the pedestrian test mannequin.
S9. False AEB activation.
S9.1. Headway calculation. For each test run to be conducted under S9.2 and S9.3, the headway (L L L), in meters, providing 5.0 seconds, 2.1 seconds, and 1.1 seconds time to collision (TTC) is calculated. L0, L , and L are determined with the following equation where VSV is the speed of the subject vehicle in m/s:
Equation 3 to S9.1
Lx = TTC x × (VSV)
TTC0 = 5.0
TTC2.1 = 2.1
TTC1.1 = 1.1
S9.2. Steel trench plate.
S9.2.1. Test parameters and setup.
(a) The testing area is set up in accordance with figure 8 to this section.
(b) The steel trench plate is secured flat on the test surface so that its longest side is parallel to the vehicle's intended travel path and horizontally centered on the vehicle's intended travel path.
(c) The subject vehicle test speed is 80 km/h.
(d) Testing is conducted with manual brake application and without manual brake application.
(e) Testing is conducted during daylight.
S9.2.2. Test conduct.
(a) Before the headway corresponds to L 0, the subject vehicle is driven at any speed, in any direction, on any road surface, for any amount of time.
(b) The subject vehicle approaches the steel trench plate.
(c) Beginning when the headway corresponds to L 0, the subject vehicle speed is maintained within 1.6 km/h of the test speed with minimal and smooth accelerator pedal inputs.
(d) Beginning when the headway corresponds to L 0, the subject vehicle heading is maintained with minimal steering input such that the travel path does not deviate more than 0.3 m laterally from the intended travel path, and the yaw rate of the subject vehicle does not exceed ±1.0 deg/s.
(e) If forward collision warning occurs, the subject vehicle's accelerator pedal is released at any rate such that it is fully released within 500 ms. This action is omitted for vehicles with cruise control active.
(f) For tests where no manual brake application occurs, manual braking is not applied until the test completion criteria of S9.2.3 are satisfied.
(g) For tests where manual brake application occurs, the subject vehicle's accelerator pedal, if not already released, is released when the headway corresponds to L 2.1 at any rate such that it is fully released within 500 ms.
(h) For tests where manual brake application occurs, the service brakes are applied as specified in S10. The brake application pedal onset occurs at headway L 1.1.
S9.2.3. Test completion criteria. The test run is complete when the subject vehicle comes to a stop prior to crossing over the leading edge of the steel trench plate or when the subject vehicle crosses over the leading edge of the steel trench plate.
S9.3. Pass-through.
S9.3.1. Test parameters and setup.
(a) The testing area is set up in accordance with figure 9 to this section.
(b) Two vehicle test devices are secured in a stationary position parallel to one another with a lateral distance of 4.5 m ±0.1 m between the vehicles' closest front wheels. The centerline between the two vehicles is parallel to the intended travel path.
(c) The subject vehicle test speed is 80 km/h.
(d) Testing is conducted with manual brake application and without manual brake application.
(e) Testing is conducted during daylight.
S9.3.2. Test conduct.
(a) Before the headway corresponds to L 0, the subject vehicle is driven at any speed, in any direction, on any road surface, for any amount of time.
(b) The subject vehicle approaches the gap between the two vehicle test devices.
(c) Beginning when the headway corresponds to L 0, the subject vehicle speed is maintained within 1.6 km/h with minimal and smooth accelerator pedal inputs.
(d) Beginning when the headway corresponds to L 0, the subject vehicle heading is maintained with minimal steering input such that the travel path does not deviate more than 0.3 m laterally from the intended travel path, and the yaw rate of the subject vehicle does not exceed ±1.0 deg/s.
(e) If forward collision warning occurs, the subject vehicle's accelerator pedal is released at any rate such that it is fully released within 500 ms.
(f) For tests where no manual brake application occurs, manual braking is not applied until the test completion criteria of S9.3.3 are satisfied.
(g) For tests where manual brake application occurs, the subject vehicle's accelerator pedal, if not already released, is released when the headway corresponds to L 2.1 at any rate such that it is fully released within 500 ms.
(h) For tests where manual brake application occurs, the service brakes are applied as specified in S10. The brake application onset occurs when the headway corresponds to L 1.1.
S9.3.3. Test completion criteria. The test run is complete when the subject vehicle comes to a stop prior to its rearmost point passing the vertical plane connecting the forwardmost point of the vehicle test devices or when the rearmost point of the subject vehicle passes the vertical plane connecting the forwardmost point of the vehicle test devices.
S10. Subject vehicle brake application procedure.
S10.1. The procedure begins with the subject vehicle brake pedal in its natural resting position with no preload or position offset.
S10.2. At the option of the manufacturer, either displacement feedback, hybrid feedback, or force feedback control is used.
S10.3. Displacement feedback procedure. For displacement feedback, the commanded brake pedal position is the brake pedal position that results in a mean deceleration of 0.4 g in the absence of AEB system activation.
(a) The mean deceleration is the deceleration over the time from the brake pedal achieving the commanded position to 250 ms before the vehicle comes to a stop.
(b) The pedal displacement controller displaces the brake pedal at a rate of 254 mm/s ±25.4 mm/s to the commanded brake pedal position.
(c) The pedal displacement controller may overshoot the commanded position by any amount up to 20 percent. If such an overshoot occurs, it is corrected within 250 ms from when the commanded position is first achieved.
(d) The achieved brake pedal position is any position within 10 percent of the commanded position from 250 ms after the commanded brake pedal position is first achieved to the end of the test.
S10.4. Hybrid brake pedal feedback procedure. For hybrid brake pedal feedback, the commanded brake pedal application is the brake pedal position and a subsequent commanded brake pedal force that results in a mean deceleration of 0.4 g in the absence of AEB system activation.
(a) The mean deceleration is the deceleration over the time from the brake pedal achieving the commanded position to 250 ms before the vehicle comes to a stop.
(b) The hybrid controller displaces the brake pedal at a rate of 254 mm/s ±25.4 mm/s to the commanded pedal position.
(c) The hybrid controller may overshoot the commanded position by any amount up to 20 percent. If such an overshoot occurs, it is corrected within 250 ms from then the commanded position is first achieved.
(d) The hybrid controller begins to control the force applied to the brake pedal and stops controlling pedal displacement within 100 ms after the commanded brake pedal displacement occurs.
(e) The hybrid controller applies a pedal force of at least 11.1 N from the onset of the brake application until the end of the test.
(f) The average pedal force is maintained within 10 percent of the commanded brake pedal force from 350 ms after commended pedal displacement occurs until test completion.
S10.5. Force feedback procedure. For force feedback, the commanded brake pedal application is the brake pedal force that results in a mean deceleration of 0.4 g in the absence of AEB system activation.
(a) The mean deceleration is the deceleration over the time from when the commanded brake pedal force is first achieved to 250 ms before the vehicle comes to a stop.
(b) The force controller achieves the commanded brake pedal force within 250 ms. The application rate is unrestricted.
(c) The force controller may overshoot the commanded force by any amount up to 20 percent. If such an overshoot occurs, it is corrected within 250 ms from when the commanded force is first achieved.
(d) The force controller applies a pedal force of at least 11.1 N from the onset of the brake application until the end of the test.
(e) The average pedal force is maintained within 10 percent of the commanded brake pedal force from 250 ms after commended pedal force occurs until test completion.
Figure 1 to §571.127—Percentage Overlap Nomenclature
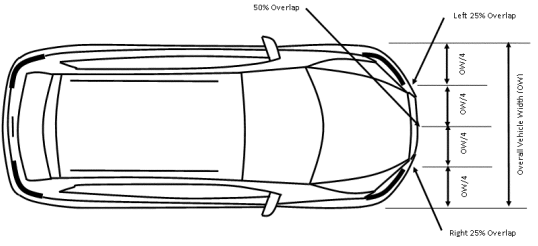
Figure 2 to §571.127—Setup for Lead Vehicle Automatic Emergency Braking
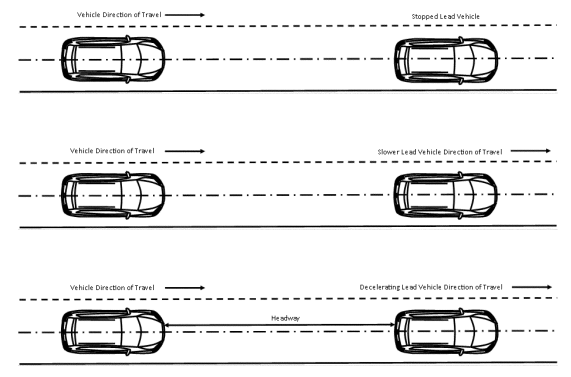
Figure 3 to §571.127—Setup for Pedestrian, Crossing Path, Right
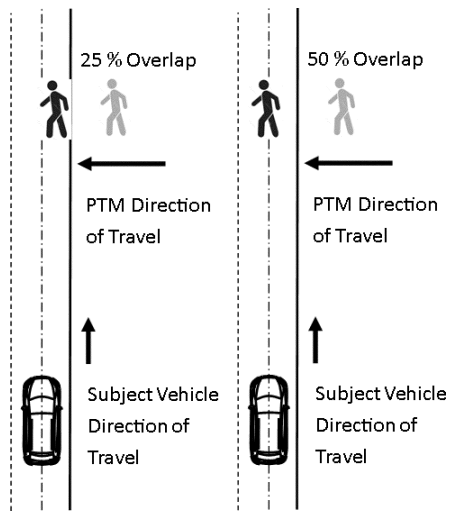
Figure 4 to §571.127—Setup for Pedestrian, Crossing Path, Left
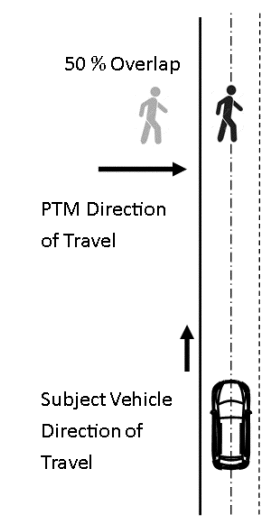
Figure 5 to §571.127—Setup for Pedestrian, Obstructed
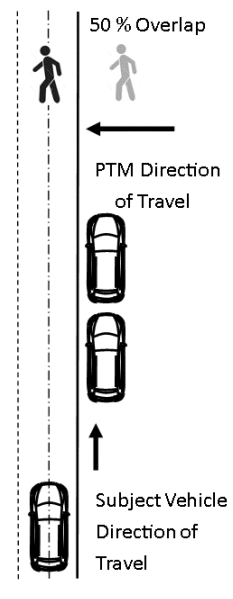
Figure 6 to §571.127—Setup for Pedestrian Along-Path Stationary
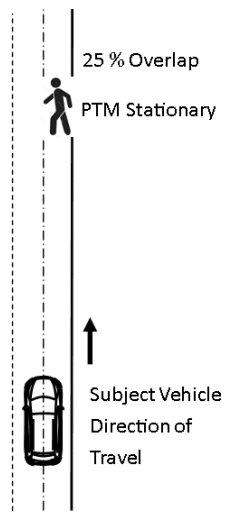
Figure 7 to §571.127—Setup for Pedestrian Along-Path Moving
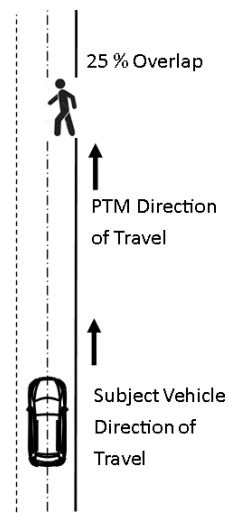
Figure 8 to §571.127—Steel Trench Plate
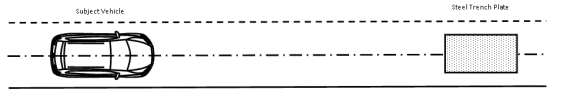
Figure 9 to §571.127—Pass-through
[89 FR 39779, May 9, 2024; 89 FR 93220, Nov. 26, 2024]
['CMV Parts and Maintenance']
['Tires']
UPGRADE TO CONTINUE READING
Load More
J. J. Keller is the trusted source for DOT / Transportation, OSHA / Workplace Safety, Human Resources, Construction Safety and Hazmat / Hazardous Materials regulation compliance products and services. J. J. Keller helps you increase safety awareness, reduce risk, follow best practices, improve safety training, and stay current with changing regulations.
Copyright 2025 J. J. Keller & Associate, Inc. For re-use options please contact copyright@jjkeller.com or call 800-558-5011.
