['Air Programs']
['Volatile Organic Compounds']
01/16/2025
...
§59.100 Applicability and designation of regulated entity.
(a) The provisions of this subpart apply to automobile refinish coatings and coating components manufactured on or after January 11, 1999 for sale or distribution in the United States.
(b) Regulated entities are manufacturers and importers of automobile refinish coatings or coating components that sell or distribute these coatings or coating components in the United States.
(c) The provisions of this subpart do not apply to automobile refinish coatings or coating components meeting the criteria in paragraphs (c)(1) through (c)(6) of this section.
(1) Coatings or coating components that are manufactured (in or outside the United States) exclusively for sale outside the United States.
(2) Coatings or coating components that are manufactured (in or outside the United States) before January 11, 1999.
(3) Coatings or coating components that are manufactured (in or outside the United States) for use by original equipment manufacturers.
(4) Coatings that are sold in nonrefillable aerosol containers.
(5) Lacquer topcoats or their components.
(6) Touch-up coatings.
§59.101 Definitions.
Adhesion promoter means a coating designed to facilitate the bonding of a primer or topcoat on surfaces such as trim moldings, door locks, and door sills, where sanding is impracticable, and on plastic parts and the edges of sanded areas.
Administrator means the Administrator of the United States Environmental Protection Agency (U.S. EPA) or an authorized representative.
Automobile means passenger cars, vans, motorcycles, trucks, and all other mobile equipment.
Automobile refinish coating component means any portion of a coating, such as a reducer or thinner, hardener, additive, etc., recommended (by its manufacturer or importer) to distributors or end-users for automobile refinishing. The raw materials used to produce the components that are mixed by the end-user to prepare a coating for application are not considered automobile refinish coating components. Any reference to automobile refinishing made by a manufacturer or importer on a container or in product literature constitutes a recommendation for automobile refinishing.
Automobile refinish coating or coating component importer, or importer, means any company, group, or individual that brings automobile refinish coatings or coating components from a location outside the United States into the United States for sale or distribution in the United States.
Automobile refinish coating or coating component manufacturer, or manufacturer, means any company, group, or individual that produces or packages automobile refinish coatings or coating components for sale or distribution in the United States, including an entity which produces or packages such coatings or coating components under a private label for another party.
Automobile refinishing means the process of coating automobiles or their parts, including partial body collision repairs, that is subsequent to the original coating applied at an automobile original equipment manufacturing plant.
Container means the individual receptacle that holds a coating or coating component for storage and distribution.
Cut-in, or jambing, clearcoat means a fast-drying, ready-to-spray clearcoat applied to surfaces such as door jambs and trunk and hood edges to allow for quick closure.
Elastomeric coating means a coating designed for application over flexible parts, such as elastomeric bumpers.
Exempt compounds means specific organic compounds that are not considered volatile organic compounds due to negligible photochemical reactivity. The exempt compounds are specified in §51.100(s) of this chapter.
Hardener means a coating component specifically designed to promote a faster cure of an enamel finish.
Impact-resistant coating means a coating designed to resist chipping caused by road debris.
Label means any written, printed, or graphic matter affixed to or appearing upon any automobile refinish coating or coating component container or package for purposes of identifying or giving information on the product, use of the product, or contents of the container or package.
Lacquer means a thermoplastic coating which dries primarily by solvent evaporation, and which is resoluble in its original solvent.
Low-gloss coating means a coating which exhibits a gloss reading less than or equal to 25 on a 60° glossmeter.
Mixing instructions means the coating or coating component manufacturer's or importer's specification of the quantities of coating components for mixing a coating.
Mobile equipment means any equipment that is physically capable of being driven or drawn upon a highway including, but not limited to, the following types of equipment: construction vehicles (such as mobile cranes, bulldozers, concrete mixers); farming equipment (wheel tractor, plow, pesticide sprayer); hauling equipment (truck trailers, utility bodies, camper shells); and miscellaneous equipment (street cleaners, golf carts).
Multi-colored topcoat means a topcoat that exhibits more than one color, is packaged in a single container, and camouflages surface defects on areas of heavy use, such as cargo beds and other surfaces of trucks and other utility vehicles.
Pretreatment wash primer means a primer that contains a minimum of 0.5 percent acid, by weight, that is applied directly to bare metal surfaces to provide corrosion resistance and to promote adhesion of subsequent coatings.
Primer means any coating applied prior to the application of a topcoat for the purpose of corrosion resistance and/or adhesion.
Primer-sealer means any coating applied prior to the application of a topcoat for the purpose of corrosion resistance, adhesion of the topcoat, and/or color uniformity and to promote the ability of an undercoat to resist penetration by the topcoat.
Primer-surfacer means any coating applied prior to the application of a topcoat for the purpose of filling surface imperfections in the substrate, corrosion resistance, and/or adhesion of the topcoat.
Reducer means any solvent used to thin enamels.
Underbody coating means a coating designed for protection and sound deadening that is typically applied to the wheel wells and underbody of an automobile.
Single-stage topcoat means a topcoat consisting of only one coating.
Specialty coatings means adhesion promoters, low-gloss coatings, bright metal trim repair coatings, jambing (cut-in) clearcoats, elastomeric coatings, impact resistant coatings, underbody coatings, uniform finish blenders, and weld-through primers.
Thinner means any solvent used to reduce the viscosity or solids content of a coating.
Three-stage topcoat means a topcoat composed of a pigmented basecoat, a midcoat, and a transparent clearcoat.
Topcoat means any coating or series of coatings applied over a primer or an existing finish for the purpose of protection or beautification.
Touch-up coating means a coating applied by brush, air-brush, or nonrefillable aerosol can to cover minor surface damage.
Two-stage topcoat means a topcoat consisting of a pigmented basecoat and a transparent clearcoat.
Uniform finish blender means a coating designed to blend a repaired topcoat into an existing topcoat.
United States means the United States of America, including the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, the Virgin Islands, Guam, American Samoa, and Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands.
Volatile organic compounds or VOC means any compound of carbon, other than those organic compounds that the Administrator has excluded in 40 CFR part 51, §51.100 from this definition.
VOC content means the weight of VOC per volume of coating, calculated according to the procedures in §59.104(a) of this subpart.
Water hold-out coating means a coating applied to the interior cavity areas of doors, quarter panels and rocker panels for the purpose of corrosion resistance to prolonged water exposure.
Weld-through primer means a primer that is applied to an area before welding is performed, and that provides corrosion resistance to the surface after welding has been performed.
§59.102 Standards.
(a) Except as provided in §59.106 of this subpart, any coating resulting from the mixing instructions of a regulated entity must meet the VOC content limit given in table 1 of this subpart. VOC content is determined according to §59.104(a).
(b) Different combinations or mixing ratios of coating components constitute different coatings. For example, coating components may be mixed one way to make a primer, and mixed another way to make a primer sealer. Each of these coatings must meet its corresponding VOC content limit in table 1 of this subpart. If the same combination and mixing ratio of coating components is recommended by a regulated entity for use in more than one category in table 1 of this subpart, then the most restrictive VOC content limit shall apply.
§59.103 Container labeling requirements.
Each regulated entity subject to this subpart must clearly display on each automobile refinish coating or coating component container or package, the day, month, and year on which the product was manufactured, or a code indicating such date.
§59.104 Compliance provisions.
(a) For the purpose of determining compliance with the VOC content limits in §59.102(a) of this subpart, each regulated entity shall determine the VOC content of a coating using the procedures described in paragraph (a)(1) or (a)(2) of this section, as appropriate.
(1) Determine the VOC content in grams of VOC per liter of coating prepared for application according to its mixing instructions, excluding the volume of any water or exempt compounds. VOC content shall be calculated using the following equation:
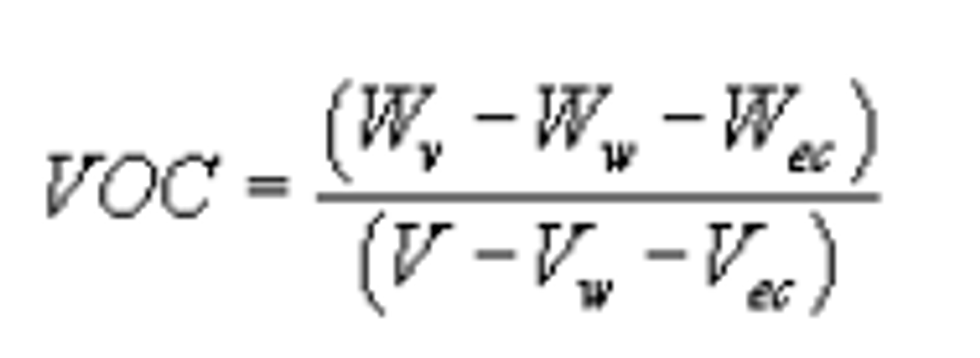
Where:
VOC content = grams of VOC per liter of coating;
Wv = mass of total volatiles, in grams;
Ww = mass of water, in grams;
Wec = mass of exempt compounds, in grams;
V = volume of coating, in liters;
Vw = volume of water, in liters; and
Vec = volume of exempt compounds, in liters.
(2) The VOC content of a multi-stage topcoat shall be calculated using the following equation:
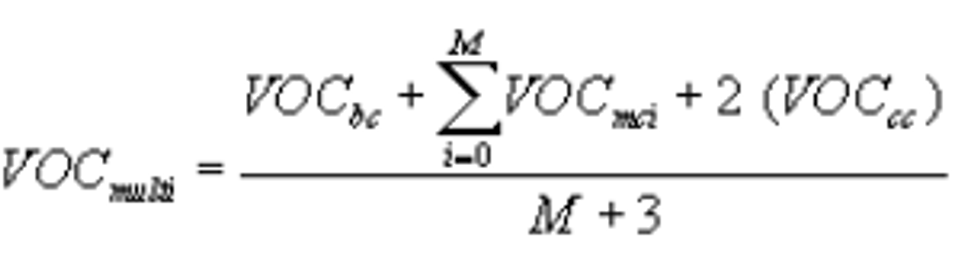
Where:
VOCmulti = VOC content of a multi-stage topcoat, in grams of VOC per liter of coating;
VOCbc = VOC content of the basecoat, as determined in paragraph (a)(1) or (f) of this section;
VOCmci = VOC content of midcoat i, as determined in paragraph (a)(1) or (f) of this section;
VOCcc = VOC content of the clearcoat, as determined in paragraph (a)(1) or (f) of this section; and
M = Number of midcoats.
(b) To determine the composition of a coating in order to perform the calculations in paragraph (a) of this section, the reference method for VOC content is Method 24 of appendix A of 40 CFR part 60, except as provided in paragraph (f) of this section. To determine the VOC content of a coating, the regulated entity may use Method 24 of appendix A of 40 CFR part 60, an alternative method as provided in paragraph (f) of this section, or any other reasonable means for predicting that the coating has been formulated as intended (e.g., quality assurance checks, recordkeeping). However, if there are any inconsistencies between the results of a Method 24 test and any other means for determining VOC content, the Method 24 test results will govern. The Administrator may require the regulated to conduct a Method 24 analysis.
(c) If a regulated entity recommends that its coating component(s) be combined with coating components of another regulated entity, and if the coating resulting from such a combination does not comply with the VOC content limit in §59.102 (a) of this subpart, then the former regulated entity is out of compliance, unless the entity submits Method 24 data to the Administrator demonstrating that its recommended combination of coating components meets the VOC content limit in §59.102(a). If the latter regulated entity does not make the recommendation of such use of the coating components, then that entity is not out of compliance for purposes of that resulting coating.
(d) Pretreatment wash primers: Except as provided in paragraph (f) of this section, the acid weight percent of pretreatment wash primers must be determined using the American Society for Testing and Materials Test Method D 1613-96 (incorporated by reference in §59.110). If the pigment in a pretreatment wash primer prevents the use of this test method for determining the acid weight percent of the coating, then the test method shall be used for the nonpigmented component of the coating, and the acid weight percent shall be calculated based on the acid content of the nonpigmented component and the mixing ratio of the nonpigmented component to the remaining components recommended by the regulated entity.
(e) Low-gloss coatings: Except as provided in paragraph (f) of this section, the gloss reading of low-gloss coatings must be determined using the American Society for Testing and Materials Test Method D 523-89 (incorporated by reference in §59.110).
(f) The Administrator may approve, on a case-by-case basis, a regulated entity's use of an alternative method in lieu of Method 24 for determining the VOC content of coatings if the alternative method is demonstrated to the Administrator's satisfaction to provide results that are acceptable for purposes of determining compliance with this subpart.
(g) The Administrator may determine a regulated entity's compliance with the provisions of this subpart based on information required by this subpart or any other information available to the Administrator.
[63 FR 48815, Sept. 11, 1998; 63 FR 64761, Nov. 23, 1998]
§59.105 Reporting requirements.
(a) Each regulated entity must submit an initial report no later than January 11, 1999 or within 180 days of the date that the regulated entity first manufactures or imports automobile refinish coatings or coating components, whichever is later. The initial report must include the information in paragraphs (a)(1) through (a)(4) of this section.
(1) The name and mailing address of the regulated entity.
(2) An explanation of each date code, if such codes are used to represent the date of manufacture, as provided in §59.103.
(3) The street address of each of the regulated entity's facilities in the United States that is producing, packaging, or importing automobile refinish coatings or coating components subject to the provisions of this subpart.
(4) A list of the categories from table 1 of this subpart for which the regulated entity recommends the use of automobile refinish coatings or coating components.
(b) Each regulated entity must submit an explanation of any new date codes used by the regulated entity no later than 30 days after products bearing the new date code are first introduced into commerce.
§59.106 Variance.
(a) Any regulated entity that cannot comply with the requirements of this subpart because of circumstances beyond its reasonable control may apply in writing to the Administrator for a temporary variance. The variance application must include the information specified in paragraphs (a)(1) through (a)(3).
(1) The specific grounds upon which the variance is sought.
(2) The proposed date(s) by which the regulated entity will achieve compliance with the provisions of this subpart. This date must be no later than 5 years after the issuance of a variance.
(3) A compliance plan detailing the method(s) by which the regulated entity will achieve compliance with the provisions of this subpart.
(b) Upon receipt of a variance application containing the information required in paragraph (a) of this section, the Administrator will publish a notice of such application in the Federal Register and, if requested by any party, will hold a public hearing to determine whether, under what conditions, and to what extent, a variance from the requirements of this subpart is necessary and will be granted. If requested, a hearing will be held no later than 75 days after receipt of a variance application. Notice of the time and place of the hearing will be sent to the applicant by certified mail not less than 30 days prior to the hearing. At least 30 days prior to the hearing, the variance application will be made available to the public for inspection. Information submitted to the Administrator by a variance applicant may be claimed as confidential. The Administrator may consider such confidential information in reaching a decision on a variance application. Interested members of the public will be allowed a reasonable opportunity to testify at the hearing.
(c) The Administrator will issue a variance if the criteria specified in paragraphs (c)(1) and (c)(2) are met to the satisfaction of the Administrator.
(1) If complying with the provisions of this subpart would not be technologically or economically feasible, and
(2) The compliance plan proposed by the applicant can reasonably be implemented and will achieve compliance as expeditiously as possible.
(d) Any variance will specify dates by which the regulated entity will achieve increments of progress towards compliance, and will specify a final compliance date by which the regulated entity will achieve compliance with this subpart.
(e) A variance will cease to be effective upon failure of the party to whom the variance was issued to comply with any term or condition of the variance.
(f) Upon the application of any party, the Administrator may review and, for good cause, modify or revoke a variance after holding a public hearing in accordance with the provisions of paragraph (b) of this section.
§59.107 Addresses of EPA Regional Offices.
All requests, reports, submittals, and other communications to the Administrator pursuant to this regulation shall be submitted to the Regional Office of the EPA which serves the State or territory in which the corporate headquarters of the regulated entity resides. These areas are indicated in the following list of EPA Regional Offices.
EPA Region I (Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, Vermont) Director, Enforcement and Compliance Assurance Division, U.S. EPA Region I, 5 Post Office Square—Suite 100 (04-2), Boston, MA 02109-3912, Attn: Air Compliance Clerk.
EPA Region II (New Jersey, New York, Puerto Rico, Virgin Islands), Director, Division of Enforcement and Compliance Assistance, 290 Broadway, New York, NY 10007-1866.
EPA Region III (Delaware, District of Columbia, Maryland, Pennsylvania, Virginia, West Virginia), Air Protection Division, 1650 Arch Street, Philadelphia, PA 19103.
EPA Region IV (Alabama, Florida, Georgia, Kentucky, Mississippi, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee), Director, Air, Pesticides and Toxics, Management Division, 345 Courtland Street, NE., Atlanta, GA 30365.
EPA Region V (Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Minnesota, Ohio, Wisconsin), Director, Air and Radiation Division, 77 West Jackson Blvd., Chicago, IL 60604-3507.
EPA Region VI (Arkansas, Louisiana, New Mexico, Oklahoma, Texas), Director, Air, Pesticides and Toxics Division, 1445 Ross Avenue, Dallas, TX 75202-2733.
EPA Region VII (Iowa, Kansas, Missouri, Nebraska), Director, Air and Waste Management Division, 11201 Renner Boulevard, Lenexa, Kansas 66219.
EPA Region VIII (Colorado, Montana, North Dakota, South Dakota, Utah, Wyoming), Director, Air and Toxics Division, 999 18th Street, 1 Denver Place, Suite 500, Denver, Colorado 80202-2405.
EPA Region IX (Arizona, California, Hawaii and Nevada; the territories of American Samoa and Guam; the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands; the territories of Baker Island, Howland Island, Jarvis Island, Johnston Atoll, Kingman Reef, Midway Atoll, Palmyra Atoll, and Wake Islands; and certain U.S. Government activities in the freely associated states of the Republic of the Marshall Islands, the Federated States of Micronesia, and the Republic of Palau), Director, Air Division, 75 Hawthorne Street, San Francisco, CA 94105.
EPA Region X (Alaska, Oregon, Idaho, Washington), Director, Air and Toxics Division, 1200 Sixth Avenue, Seattle, WA 98101.
[64 FR 48815, Sept. 11, 1998, as amended at 75 FR 69349, Nov. 12, 2010; 76 FR 49672, Aug. 11, 2011; 78 FR 37976, June 25, 2013; 84 FR 34068, July 17, 2019]
§59.108 State Authority.
The provisions in this regulation shall not be construed in any manner to preclude any State or political subdivision thereof from:
(a) Adopting and enforcing any emission standard or limitation applicable to a manufacturer or importer of automobile refinish coatings or components in addition to the requirements of this subpart.
(b) Requiring the manufacturer or importer of automobile refinish coatings or components to obtain permits, licenses, or approvals prior to initiating construction, modification, or operation of a facility for manufacturing an automobile refinish coating component.
§59.109 Circumvention.
Each manufacturer and importer of any automobile refinish coating or component subject to the provisions of this subpart must not alter, destroy, or falsify any record or report, to conceal what would otherwise be noncompliance with this subpart. Such concealment includes, but is not limited to, refusing to provide the Administrator access to all required records and date-coding information, altering the VOC content of a coating or component batch, or altering the results of any required tests to determine VOC content.
§59.110 Incorporations by Reference.
(a) The following material is incorporated by reference in the paragraphs noted in §59.104. These incorporations by reference were approved by the Director of the Federal Register in accordance with 5 U.S.C. 552(a) and 1 CFR part 51. These materials are incorporated as they exist on the date of the approval, and notice of any changes in these materials will be published in the Federal Register.
(1) ASTM D 1613-96, Standard Test Method for Acidity in Volatile Solvents and Chemical Intermediates Used in Paint, Varnish, Lacquer, and Related Products, IBR approved for §59.104(d).
(2) ASTM D 523-89, Standard Test Method for Specular Gloss, IBR approved for §59.104(e).
(b) The materials are available for inspection at the Air and Radiation Docket and Information Center, U.S. EPA, 401 M St., SW., Washington, DC; and at the EPA Library (MD-35), U.S. EPA, Research Triangle Park, North Carolina, or at the National Archives and Records Administration (NARA). For information on the availability of this material at NARA, call 202-741-6030, or go to: http://www.archives.gov/federal_register/code_of_federal_regulations/ibr_locations.html. The materials are available for purchase from the following address: American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM), 100 Barr Harbor Drive, West Conshohocken, PA, 19428, telephone number (610) 832-9500.
[64 FR 48815, Sept. 11, 1998, as amended at 69 FR 18803, Apr. 9, 2004]
§59.111 Availability of information and confidentiality.
(a) Availability of information. The availability to the public of information provided to or otherwise obtained by the Administrator under this part shall be governed by part 2 of this chapter.
(b) Confidentiality. All confidential business information entitled to protection under section 114(c) of the Act that must be submitted or maintained by each regulated entity pursuant to this section shall be treated in accordance with 40 CFR part 2, subpart B.
Table 1 to Subpart B of Part 59 - Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) Content Limits for Automobile Refinish Coatings
| Coating category | Grams VOC per liter | Pounds VOC per gallon a |
|---|---|---|
| a English units are provided for information only. Compliance will be determined based on the VOC content limit, as expressed in metric units. | ||
| Pretreatment wash primers | 780 | 6.5 |
| Primers/primer surfacers | 580 | 4.8 |
| Primer sealers | 550 | 4.6 |
| Single/two-stage topcoats | 600 | 5.0 |
| Topcoats of more than two stages | 630 | 5.2 |
| Multi-colored topcoats | 680 | 5.7 |
| Specialty coatings | 840 | 7.0 |
['Air Programs']
['Volatile Organic Compounds']
UPGRADE TO CONTINUE READING
Load More
J. J. Keller is the trusted source for DOT / Transportation, OSHA / Workplace Safety, Human Resources, Construction Safety and Hazmat / Hazardous Materials regulation compliance products and services. J. J. Keller helps you increase safety awareness, reduce risk, follow best practices, improve safety training, and stay current with changing regulations.
Copyright 2025 J. J. Keller & Associate, Inc. For re-use options please contact copyright@jjkeller.com or call 800-558-5011.
