...
Authority: 7 U.S.C. 136-136y; 21 U.S.C. 346a.
Subpart A - General Provisions
§158.1 Purpose and scope.
(a) Purpose. The purpose of this part is to specify the kinds of data and information EPA requires in order to make regulatory judgments under FIFRA secs. 3, 4, and 5 about the risks and benefits of pesticide products. Further, this part specifies the data and information needed to determine the safety of pesticide chemical residues under FFDCA sec. 408.
(b) Scope.(1) This part describes the minimum data and information EPA typically requires to support an application for pesticide registration or amendment; support the reregistration of a pesticide product; support the maintenance of a pesticide registration by means of the data call-in process, e.g., as used in the registration review program; or establish or maintain a tolerance or exemption from the requirements of a tolerance for a pesticide chemical residue.
(2) This part establishes general policies and procedures associated with the submission of data in support of a pesticide regulatory action.
(3) This part does not include study protocols, methodology, or standards for conducting or reporting test results; nor does this part describe how the Agency uses or evaluates the data and information in its risk assessment and risk management decisions, or the regulatory determinations that may be based upon the data.
(c) Scope of individual subparts.(1) Conventional pesticides.Subparts A, B, C, D, E, F, G, K, L, N, O, and R apply to conventional pesticides.
(2) Biochemical pesticides.Subparts A, B, E, R, and U apply to biochemical pesticides.
(3) Microbial pesticides.Subparts A, B, E, R, and V apply to microbial pesticides.
(4) Antimicrobial pesticides.Subparts A, B, C, D, E, R, and W of this part apply to antimicrobial pesticides.
[72 FR 60957, Oct. 26, 2007, as amended at 78 FR 26978, May 8, 2013; 87 FR 22474, Apr. 15, 2022]
§158.3 Definitions.
All terms defined in sec. 2 of the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act apply to this part and are used with the meaning given in the Act. Applicable terms from the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act also apply to this part. Individual subparts may contain definitions that pertain solely to that subpart. The following additional terms apply to this part:
Applicant means any person or entity, including for the purposes of this part a registrant, who submits, or is required to submit, to the Agency any application, petition, or submission intended to persuade EPA to grant, modify, or leave unmodified a registration or other approval required as a condition of sale or distribution of a pesticide. Such submissions may include, but are not limited to, the following:
(1) An application for registration or amended registration of a pesticide product under FIFRA sec. 3 or 24.
(2) A submission of data required in conjunction with reregistration of a currently registered product under FIFRA sec. 4.
(3) An application for an experimental use permit under FIFRA sec. 5.
(4) A submission of data in response to a notice issued by EPA under FIFRA sec. 3(c)(2)(B).
(5) A petition to establish or modify a tolerance or an exemption from the requirement of a tolerance for a pesticide chemical residue under FFDCA sec. 408.
Registration includes a new registration, amended registration and reregistration, unless stated otherwise.
§158.5 Applicability.
(a) The requirements of this part apply to the following submissions:
(1) An application for new or amended registration under FIFRA sec. 3 or 24.
(2) An application for experimental use permit under FIFRA sec. 5.
(3) A submission of data or information to support the continuation of a registration under FIFRA sec. 3, 4, or 24.
(4) A petition to establish, modify or revoke a tolerance or exemption from a tolerance under FFDCA sec. 408.
(b) The information specified in this part must be furnished with each submission described in paragraph (a) of this section if it has not been submitted previously, or if any previous submission is not accurate or complete.
§158.30 Flexibility.
(a) FIFRA provides EPA flexibility to require, or not require, data and information for the purposes of making regulatory judgments for pesticide products. EPA has the authority to establish or modify data needs for individual pesticide chemicals. The actual data required may be modified on an individual basis to fully characterize the use and properties, characteristics, or effects of specific pesticide products under review. The Agency encourages each applicant to consult with EPA to discuss the data requirements particular to its product prior to and during the registration process.
(b) The Agency cautions applicants that the data routinely required in this part may not be sufficient to permit EPA to evaluate the potential of the product to cause unreasonable adverse effects to man or the environment. EPA may require the submission of additional data or information beyond that specified in this part if such data or information are needed to appropriately evaluate a pesticide product.
(c) This part will be updated as needed to reflect evolving program needs and advances in science.
§158.32 Format of data submissions.
(a) General.(1) All data submitted under this part must be formatted in accordance with this section.
(2) The requirements of this section do not apply to administrative materials accompanying a data submission, including forms, labeling, and correspondence.
(b) Transmittal document. Each submission in support of a regulatory action must be accompanied by a transmittal document, which includes:
(1) Identity of the submitter.
(2) The transmittal date.
(3) Identification of the regulatory action with which the submission is associated, e.g., the registration or petition number.
(4) A list of the individual documents included in the submission.
(c) Individual documents. Unless otherwise specified by the Agency, each submission must be in the form of individual documents or studies. Previously submitted documents should not be resubmitted unless specifically requested by the Agency, but should be cited with adequate information to identify the previously submitted document. Each study or document should include the following:
(1) A title page including the following information:
(i) The title of the study, including identification of the substance(s) tested and the test name or data requirement addressed.
(ii) The author(s) of the study.
(iii) The date the study was completed.
(iv) If the study was performed in a laboratory, the name and address of the laboratory, project numbers or other identifying codes.
(v) If the study is a commentary on or supplement to another previously submitted study, full identification of the other study with which it should be associated in review.
(vi) If the study is a reprint of a published document, all relevant facts of publication, such as the journal title, volume, issue, inclusive page numbers, and date of publication.
(2) The appropriate statement(s) regarding any data confidentiality claims as described in §158.33.
(3) A statement of compliance or non-compliance with respect to Good Laboratory Practice Standards as required by 40 CFR 160.12, if applicable.
(4) A complete and accurate English translation must be included for any information that is not in English.
(5) A flagging statement as prescribed by §158.34, if applicable.
§158.33 Confidential data.
(a) Definitions. For the purposes of this section:
(1) Registered or previously registered pesticide means any pesticide containing an active ingredient contained in a product that is, or has ever been, an active ingredient in a product registered under sec. 3 of FIFRA. A registered pesticide that is the subject of an application for a new use falls within the category of “registered or previously registered pesticide.”
(2) Safety and efficacy information means information concerning the objectives, methodology, results, or significance of any test or experiment performed on or with a registered or previously registered pesticide or its separate ingredients, impurities, or degradation products, and any information concerning the effects of such pesticide on any organism or the behavior of such pesticide in the environment, including, but not limited to, data on safety to fish and wildlife, humans and other mammals, plants, animals, and soil, and studies on persistence, translocation and fate in the environment, and metabolism.
(b) Applicability.(1) This section applies to information submitted pursuant to this part. It supplements the general confidentiality procedures in 40 CFR part 2, subpart B, including FIFRA confidentiality procedures at 40 CFR 2.307. To the extent that provisions in this section conflict with those in 40 CFR part 2, subpart B, the provisions in this section take precedence. The provisions of 40 CFR 2.308 do not apply to information to which this section applies. In addition to complying with the requirements of this section, any confidentiality claims for information subject to 40 CFR part 174 (plant-incorporated protectants) must be substantiated at the time of submission as described in §174.9 of this chapter.
(2) FFDCA sec. 408(i) protects confidential information submitted in connection with an application for a tolerance or exemption to the same extent as FIFRA sec. 10. References in this section to FIFRA sec. 10 are deemed to apply equally to information submitted pursuant to FFDCA sec. 408, pursuant to the authority in sec. 408(i).
(c) Method of asserting business confidentiality claims(1) Claim required. Information to which this section applies (and which is submitted on or after the effective date of this regulation) will be deemed as not subject to a confidentiality claim unless a claim for that information is made in accordance with the procedures specified in this paragraph. Information not subject to a confidentiality claim may be made available to the public without further notice, subject to the requirements of FIFRA sec. 10(g).
(2) Statement required. Upon submission to EPA, each document must be accompanied by a signed and dated document containing either the statements in paragraph (c)(2)(i) or (ii) of this section. No claims or markings on the document or any attachments, other than these statements and attachments submitted in accordance with paragraph (c)(3) of this section, will be recognized as asserting a claim of confidentiality. The format of data submissions is set forth in §158.32.
(i) No claim of confidentiality.
No claim of confidentiality, on any basis whatsoever, is made for any information contained in this document. I acknowledge that information not designated as within the scope of FIFRA sec. 10(d)(1)(A), (B), or (C) and which pertains to a registered or previously registered pesticide is not entitled to confidential treatment and may be released to the public, subject to the provisions regarding disclosure to multinational entities under FIFRA sec. 10(g).
(ii) Claim of confidentiality.
Information claimed as confidential has been removed to a confidential attachment.
(3) Confidential attachment.(i) All information claimed as confidential must be submitted in a separate confidential attachment to the document and cross referenced to the specific location in the document from which it was removed. The confidential attachment must have its own title page and be paginated separately from the non-confidential document.
(ii) All information in the confidential attachment that consists of (or whose disclosure would in turn disclose) manufacturing or quality control processes must be individually identified in the confidential attachment as a claim for information within the scope of FIFRA sec. 10(d)(1)(A).
(iii) All information in the confidential attachment that consists of (or whose disclosure would in turn disclose) the details of any methods for testing, detecting, or measuring the quantity of any deliberately added inert ingredient of a pesticide, must be individually identified in the confidential attachment as a claim for information within the scope of FIFRA sec. 10(d)(1)(B).
(iv) All information in the confidential attachment that consists of (or whose disclosure would in turn disclose) the identity or percentage quantity of any deliberately added inert ingredient of a pesticide must be individually identified in the confidential attachment as a claim for information within the scope of FIFRA sec. 10(d)(1)(C).
(v) Information in the confidential attachment that is designated in accordance with paragraphs (c)(3)(ii) - (iv) of this section must be on a separate page from information that is not so designated.
(4) Voluntary release of information to States and foreign governments.(i) Submitters are encouraged to include with the statement required under paragraph (c)(2) of this section an additional statement to allow EPA to share information with State and foreign governments. EPA will not consider such a statement to be a waiver of confidentiality or proprietary claims for the information. The statement is as follows:
I authorize the Environmental Protection Agency to release any information contained in this document to State or foreign governments, without relinquishing proprietary rights or any confidentiality claims asserted above.
(ii) Information designated as releasable to state or foreign governments in accordance with this section may be released to such a government without further notice to the submitter. EPA will inform the State or foreign government of any of the confidentiality claims associated with the information.
(d) Release of information.(1) Safety and efficacy information that was submitted to EPA on or after May 4, 1988 and that has not been designated by the submitter as FIFRA sec. 10(d)(1)(A), (B), or (C) information in accordance with the applicable requirements of this section is not entitled to confidential treatment and may be disclosed to the public without further notice to the submitter, in accordance with paragraph (d)(2) of this section. Safety and efficacy information which has been designated by the submitter as FIFRA sec. 10(d)(1) (A), (B), or (C) information is entitled to confidential treatment only to the extent provided by FIFRA sec. 10(b), this section, and 40 CFR 2.208.
(2) Information that is not entitled to be protected as confidential in accordance with FIFRA sec. 10(b), this section and with EPA confidentiality regulations at 40 CFR part 2, subpart B, may be released to the public without the affirmation of non-multinational status provided under FIFRA sec. 10(g), provided that the information does not contain or consist of any complete unpublished report submitted to EPA, or excerpts or restatements of any such report which reveal the full methodology and complete results of the study, test, or experiment, and all explanatory information necessary to understand the methodology or interpret the results.
§158.34 Flagging of studies for potential adverse effects.
(a) Any applicant who submits a study of a type listed in paragraph (b) of this section must submit with the study a statement in accordance with paragraph (c) of this section.
(b) The following table indicates the study types and the criteria to be applied to each. Column 1 lists the study types by name. Column 2 lists the associated Pesticide Assessment Guideline number. Column 3 lists the criteria applicable to each type of study. Column 4 lists the reporting code to be included in the statement specified in paragraph (c) of this section when any criterion is met or exceeded.
| Study Type(s) | Guideline No. | Criteria: Treated animals show any of the following: | Criteria No. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carcinogenicity or combined carcinogenicity/chronic feeding study | 870.4200
870.4300 | An incidence of neoplasms in males or females which increases with dose (positive trend p≤0.05); or | 1 |
| A statistically significant (pairwise p≤0.05) increase of any type of neoplasm in any test group, males or females at any dose level, compared to concurrent control animals of the same sex; or | 2 | ||
| An increase in any type of uncommon or rare neoplasms in any test group, males or females animals at any dose level, compared to concurrent controls of the same sex; or | 3 | ||
| A decrease in the time to development of any type of neoplasms in any test group, males or females at any dose level, compared to concurrent controls of the same sex. | 4 | ||
| Prenatal developmental toxicity
Reproduction and fertility Developmental neurotoxicity | 870.3700
870.3800 870.6300 | When compared to concurrent controls, treated offspring show a dose-related increase in malformations, pre- or post-natal deaths, or persistent functional or behavioral changes on a litter basis in the absence of significant maternal toxicity at the same dose level. | 5 |
| Neurotoxicity | 870.6100
870.6200 | When compared to concurrent controls, treated animals show a statistically or biologically significant increase in neuropathological lesions or persistent functional or behavioral changes. | 6 |
| Chronic feeding
Carcinogenicity Reproduction and fertility Prenatal developmental toxicity Developmental neurotoxicity Acute or 90-day neurotoxicity | 870.4100
870.4200 870.3800 870.3700 870.6300 870.6200 | The no observed adverse effect level (NOAEL) from one of these studies is less than the NOAEL currently used by the Agency as the basis for either the acute or chronic reference dose. | 7 |
(c) Identification of studies. For each study of a type identified in paragraph (b) of this section, the applicant shall include the appropriate one of the following two statements, together with the signature of the authorized representative of the company, and the date of signature:
(1) Study does not meet or exceed criteria.
I have applied the criteria of 40 CFR 158.34 for flagging studies for potential adverse effects to the results of the attached study. This study neither meets nor exceeds any of the applicable criteria.
(2) Study meets or exceeds criteria.
I have applied the criteria of 40 CFR 158.34 for flagging studies for potential adverse effects to the results of the attached study. This study meets or exceeds the criteria numbered [insert all applicable reporting codes].
§158.45 Waivers.
(a) The data requirements specified in this part as applicable to a category of products will not always be appropriate for every product in that category. Some products may have unusual physical, chemical, or biological properties or atypical use patterns which would make particular data requirements inappropriate, either because it would not be possible to generate the required data or because the data would not be useful in the Agency's evaluation of the risks or benefits of the product. The Agency will waive data requirements it finds are inappropriate, but will ensure that sufficient data are available to make the determinations required by the applicable statutory standards.
(b)(1) Applicants are encouraged to discuss a data waiver request with the Agency before developing and submitting supporting data, information, or other materials.
(2) All waiver requests must be submitted to the Agency in writing. The request must clearly identify the data requirement(s) for which a waiver is sought along with an explanation and supporting rationale why the applicant believes the data requirement should be waived. In addition, the applicant must describe any unsuccessful attempts to generate the required data, furnish any other information which the applicant(s) believe(s) would support the request, and when appropriate, suggest alternative means of obtaining data to address the concern which underlies the data requirement.
(c) The Agency will review each waiver request and subsequently inform the applicant in writing of its decision. If the decision could apply to more than the requested product, the Agency, in its discretion, may choose to send a notice to all registrants or publish a notice in the Federal Register announcing the decision. An Agency decision denying a written request to waive a data requirement is a final Agency action.
§158.60 Minor use data policies.
FIFRA sec. 2(ll) defines the term “minor use”and FIFRA provides a number of statutory provisions concerning minor uses. In addition, EPA has established policies with respect to minor uses of pesticides, including, but not limited to, the following:
(a) A new data requirement pertinent to both an unregistered minor use and a registered major use will not be applied to a minor use applicant until it is applied to the major use registration.
(b) EPA will accept appropriate and adequate extrapolations and regional data to support establishment of individual minor use tolerances.
§158.70 Satisfying data requirements.
(a) General policy. The Agency will determine whether the data submitted or cited to fulfill the data requirements specified in this part are acceptable. This determination will be based on the design and conduct of the experiment from which the data were derived, and an evaluation of whether the data fulfill the purpose(s) of the data requirement. In evaluating experimental design, the Agency will consider whether generally accepted methods were used, sufficient numbers of measurements were made to achieve statistical reliability, and sufficient controls were built into all phases of the experiment. The Agency will evaluate the conduct of each experiment in terms of whether the study was conducted in conformance with the design, good laboratory practices were observed, and results were reproducible. The Agency will not reject data merely because they were derived from studies which, when initiated, were in accordance with an Agency-recommended protocol, even if the Agency subsequently recommends a different protocol, as long as the data fulfill the purposes of the requirements as described in this paragraph.
(1) The provisions in this part 158 should be read in conjunction with the provisions in §152.85 to claim eligibility for the formulators' exemption.
(2) [Reserved]
(b) Good laboratory practices. Applicants must adhere to the good laboratory practice (GLP) standards described in 40 CFR part 160 when conducting studies. Applicants must also adhere to GLP standards when conducting a study in support of a waiver request of any data requirement which is within the scope of the GLP requirements.
(c) Agency guidelines. EPA has published Test Guidelines that contain standards for conducting acceptable tests, guidance on the evaluation and reporting of data, definition of terms, and suggested study protocols. Copies of the Test Guidelines may be obtained by visiting the agency's website at www.epa.gov/pesticides.
(d) Study protocols(1) General. Any appropriate protocol may be used to generate the data required by this part, provided that it meets the purpose of the test standards specified in the pesticide assessment guidelines, and provides data of suitable quality and completeness as typified by the protocols cited in the guidelines. Applicants should use the test procedure which is most suitable for evaluation of the particular ingredient, mixture, or product. Accordingly, failure to follow a suggested protocol will not invalidate a test if another appropriate methodology is used.
(2) Organization for Economic Co-Operation and Development (OECD) protocols. Tests conducted in accordance with the requirements and recommendations of the applicable OECD protocols can be used to develop data necessary to meet the requirements specified in this part. Applicants should note, however, that certain of the OECD recommended test standards, such as test duration and selection of test species, are less restrictive than those recommended by EPA. Therefore, when using OECD protocols, care should be taken to observe the test standards in a manner such that the data generated by the study will satisfy the requirements of this part.
(e) Combining studies. Certain toxicology studies may be combined to satisfy data requirements. For example, carcinogenicity studies in rats may be combined with the rat chronic toxicity study. Combining appropriate studies may be expected to reduce usage of test animals as well as reduce the cost of studies. EPA encourages this practice by including standards for acceptable combined tests in the Pesticide Assessment Guidelines. Registrants and applicants are encouraged to consider combining other tests when practical and likely to produce scientifically acceptable results. Registrants and applicants, however, must consult with the EPA before initiating combined studies.
§158.75 Requirements for additional data.
The data routinely required by this part may not be sufficient to permit EPA to evaluate every pesticide product. If the information required under this part is not sufficient to evaluate the potential of the product to cause unreasonable adverse effects on man or the environment, additional data requirements will be imposed. However, EPA expects that the information required by this part will be adequate in most cases for an assessment of the properties and effects of the pesticide.
§158.80 Use of other data.
(a) Data developed in foreign countries. With certain exceptions, laboratory and field study data developed outside the United States may be submitted in support of a pesticide registration. Data generated in a foreign country which the Agency will not consider include, but are not limited to, data from tests which involved field test sites or a test material, such as a native soil, plant, or animal, that is not characteristic of the United States. Applicants submitting foreign data must take steps to ensure that U.S. materials are used, or be prepared to supply data or information to demonstrate the lack of substantial or relevant differences between the selected material or test site and the U.S. material or test site. Once submitted, the Agency will determine whether or not the data meet the data requirements.
(b) Data generated for other purposes. Data developed for purposes other than satisfaction of FIFRA data requirements, such as monitoring studies, may also satisfy data requirements in this part. Consultation with the Agency should be arranged if applicants are unsure about suitability of such data.
Subpart B - How To Use Data Tables
§158.100 Pesticide use patterns.
(a) General use patterns for conventional, biochemical, and microbial pesticides. There are six broad use categories used in the data tables. The six broad categories include terrestrial outdoor uses, aquatic outdoor uses, greenhouse uses, forestry uses, residential outdoor uses, and indoor uses of all types. The 6 broad use categories are further subdivided into 12 general use patterns which are the bases for data requirements established by use pattern. Within the data tables, general use patterns have been combined into single columns when the data requirements are the same for the combined uses. If there are no data requirements for a specific use, the column for that use is not included in the table. The 12 general use pattern groups used in the data table in this part are:
(1) Terrestrial food crop use.
(2) Terrestrial feed crop use.
(3) Terrestrial nonfood crop use.
(4) Aquatic food crop use.
(5) Aquatic nonfood use.
(6) Greenhouse food crop use.
(7) Greenhouse nonfood crop use.
(8) Forestry use.
(9) Residential outdoor use.
(10) Residential indoor use.
(11) Indoor food use.
(12) Indoor nonfood use.
(b) Pesticide use site index for conventional, biochemical, and microbial pesticides. The Pesticide Use Site Index for Conventional, Biochemical, and Microbial Pesticides is a comprehensive list of specific pesticide use sites. The index is alphabetized separately by site for all agricultural and all nonagricultural uses. The Pesticide Use Site Index associates each pesticide use site with one or more of the 12 general use patterns. It may be used in conjunction with the data tables to determine the applicability of data requirements to specific uses. The Pesticide Use Site Index for Conventional, Biochemical, and Microbial Pesticides will be updated periodically, and is available from the Agency or may be obtained from the Agency's Web site at http://www.epa.gov/pesticides.
(c) Antimicrobial pesticide use patterns. The general use patterns for antimicrobial pesticides are described in §158.2201.
(d) Pesticide use site index for antimicrobial pesticides. The Pesticide Use Site Index for Antimicrobial Pesticides is a comprehensive list of specific antimicrobial use sites. The index is alphabetized by antimicrobial use sites, and associates each antimicrobial use site with one or more of the antimicrobial use patterns. It may be used in conjunction with the data tables to determine the applicability of data requirements to specific uses. The Pesticide Use Site Index for Antimicrobial Pesticides will be updated periodically, and is available from the Agency or may be obtained from the Agency's Web site at http://www.epa.gov/pesticides.
(e) Determination of use pattern. Applicants unsure of the correct use pattern for their particular product should consult the Agency.
[72 FR 60957, Oct. 26, 2007, as amended at 78 FR 26978, May 8, 2013]
§158.110 Required and conditionally required data.
The tables in this part use the descriptors R (required), CR (conditionally required), and NR (not required) as a general indication of the applicability of a data requirement. In all cases, the test notes referred to in the table must be consulted to determine the actual applicability of the data requirement.
(a) EPA requires data designated as “required”(R) for products with a given use pattern in order to evaluate the risks or benefits of a product having that use pattern under any conditions established by the test notes.
(b) Data designated as “conditionally required” (CR) for products with a given use pattern are required by EPA to evaluate the risks or benefits of a product having that use pattern if the product meets the conditions specified in the notes accompanying the requirement. The determination of whether the data must be submitted is based on the product's use pattern, physical or chemical properties, expected exposure of nontarget organisms, and/or results of previous testing (for example, tier testing). Applicants must evaluate each applicable test note for the conditions and criteria to be considered in determining whether conditionally required data must be submitted.
(c) Data not required for the Agency's assessment of the risks and benefits of a particular use pattern are designated “not required” (NR) in data tables.
§158.120 Determining data requirements.
As with current practice, the actual data and studies required may be modified on an individual basis to fully characterize the use and properties of specific pesticide products under review. While EPA is attempting to assist the applicant in this subpart, it is important to emphasize that it is the applicant's obligation under FIFRA to demonstrate that an individual product meets the standard under FIFRA and/or FFDCA. Accordingly, applicants are encouraged to consult with the Agency on the appropriate data requirements as set forth here as they relate to their specific product prior to and during the registration process.
(a) Finding the appropriate data table.(1) Pesticide data requirements for conventional chemical active ingredients and related substances are presented in subparts D, E, F, G, K, L, N, and O of this part in the form of a series of data tables, each addressing a particular scientific discipline or data topic. Data requirements for biochemical and microbial pest control agents are contained and are described separately within subparts U and V of this part, respectively.
(2) Key to table notations. R = required data; CR = conditionally required data; NR = Not required; MP = manufacturing-use product; EP = end-use product; TEP = typical end-use product; TGAI = technical grade of the active ingredient; PAI = pure active ingredient; PAIRA = pure active ingredient, radiolabeled; Choice = choice of several test substances depending on studies required.
(b) Identifying required studies. To determine the specific kinds of data needed to support the registration use of each pesticide product, the applicant may:
(1) Refer to the applicable subpart(s) of this part. These subparts describe the data requirements including data tables for each subject area.
(2) Select the general use pattern(s) that best cover the use pattern(s) specified on the pesticide product label as explained in §158.100. All applicable use patterns must be included.
(3) Proceed down the appropriate general use pattern column in the table and note which tests are required (R), conditionally required (CR), or not required (NR). Required and conditionally required studies are described in §158.110.
(4) Review the notes for each requirement to determine its applicability to the specific product proposed for registration.
(5)(i) Proceed down the Test substance columns and determine the appropriate test substance needed for that study. If the data are intended to support a manufacturing-use product, use the MP column. If the data are intended to support an end-use product, use the EP column.
(ii) The test substances columns specify which substance is to be used for testing. Applicants should note that the substance that must be used when performing the study may or may not be the product itself. For example, the data from a certain study may be required to support the registration of an end-use product, but the test substance column may state that the particular test shall be performed using the technical grade of the active ingredient(s) in the end-use product.
(iii) Manufacturing-use products (MP) and end-use products (EP) containing a single active ingredient and no intentionally added inert ingredients are considered identical in composition to each other, and to the technical grade of the active ingredient (TGAI) from which they were derived. Therefore, the data from a test conducted using any one of these as the test substance is also suitable to meet the requirement (if any) for the same test to be conducted using either of the other substances.
(6) Refer to the Pesticide Assessment Guideline reference number for each study located in the first column. See §158.70(c) for information pertaining to the guidelines and how to obtain copies.
§158.130 Purposes of the registration data requirements.
(a) General. The data requirements for registration are intended to generate data and information necessary to address concerns pertaining to the identity, composition, potential adverse effects and environmental fate of each pesticide.
(b) Product chemistry(1) Product composition. Data on product composition are needed:
(i) To support the conclusions expressed in the statement of formula;
(ii) To compare to the composition of materials used in required testing under this part; and
(iii) To determine whether a product is “identical or substantially similar”to another product, a determination that involves the comparison of product composition.
(2) Nominal concentration and certified limits. The nominal concentration of a product, defined as that concentration that is expected to be present in a product as a result of the production or formulation process, is used to gauge the acceptability of the certified limits, which define the outer limits of the range of the product's ingredients. The certified limits are used to enforce the composition of the product and to ensure the accuracy of hazard assessments.
(3) Physical and chemical characteristics. The physical and chemical characteristics of an active ingredient or product are used:
(i) To confirm or provide supportive information on the identity and composition of the product;
(ii) To assess the hazards of the ingredient or product; and
(iii) To trigger or evaluate certain other studies required by this part.
(c) Product performance. Requirements to develop data on product performance provide a mechanism to ensure that pesticide products will perform as intended and that unnecessary pesticide exposure to the environment will not occur as a result of the use of ineffective products. Specific performance standards are used to validate the efficacy data in the public health areas, including disinfectants used to control microorganisms infectious to man in any area of the inanimate environment and those pesticides used to control vertebrates (such as rodents, birds, bats and skunks) that may directly or indirectly transmit diseases to humans.
(d) Toxicology-humans and domestic animals. Data required to assess hazards to humans and domestic animals are derived from a variety of acute, subchronic and chronic toxicity tests, and tests to assess mutagenicity and pesticide metabolism.
(1) Acute studies. Determination of acute oral, dermal and inhalation toxicity is usually the initial step in the assessment and evaluation of the toxic characteristics of a pesticide. These data provide information on health hazards likely to arise soon after, and as a result of, short-term exposure. Data from acute studies serve as a basis for classification and precautionary labeling. For example, acute toxicity data are used to calculate farmworker reentry intervals and to develop precautionary label statements pertaining to protective clothing requirements for applicators. They also provide information used in establishing the appropriate dose levels in subchronic and other studies; provide initial information on the mode of toxic action(s) of a substance; and determine the need for child resistant packaging. Information derived from primary eye and primary dermal irritation studies serves to identify possible hazards from exposure of the eyes, associated mucous membranes and skin.
(2) Subchronic studies. Subchronic tests provide information on health hazards that may arise from repeated exposures over a limited period of time. They provide information on target organs and accumulation potential. The resulting data are also useful in selecting dose levels for chronic studies and for establishing safety criteria for human exposure. These tests are not capable of detecting those effects that have a long latency period for expression (e.g., carcinogenicity).
(3) Chronic studies. Chronic toxicity studies (usually conducted by feeding the test substance to the test species) are intended to determine the effects of a substance in a mammalian species following prolonged and repeated exposure. Under the conditions of this test, effects which have a long latency period or are cumulative should be detected. The purpose of long-term carcinogenicity studies is to observe test animals over most of their life span for the development of neoplastic lesions during or after exposure to various doses of a test substance by an appropriate route of administration.
(4) Developmental toxicity and reproduction studies. The developmental toxicity study is designed to determine the potential of the test substance to induce structural and/or other abnormalities to the fetus as the result of exposure of the mother during pregnancy. Two-generation reproduction testing is designed to provide information concerning the general effects of a test substance on gonadal function, estrus cycles, mating behavior, conception, parturition, lactation, weaning, and the growth and development of the offspring. The study may also provide information about the effects of the test substance on neonatal morbidity, mortality, and preliminary data on prenatal developmental toxicity and serve as a guide for subsequent tests.
(5) Mutagenicity studies. For each test substance a battery of tests is required to assess the potential to affect the mammalian cell's genetic components. The objectives underlying the selection of a battery of tests for mutagenicity assessment are:
(i) To detect, with sensitive assay methods, the capacity of a chemical to alter genetic material in cells.
(ii) To determine the relevance of these mutagenic changes to mammals.
(iii) When mutagenic potential is demonstrated, to incorporate these findings in the assessment of heritable effects, carcinogenicity, and, possibly, other health effects.
(6) Metabolism studies. Data from studies on the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of a pesticide aid in the valuation of test results from other toxicity studies and in the extrapolation of data from animals to man. The main purpose of metabolism studies is to produce data which increases the Agency's understanding of the behavior of the chemical when considering the human exposure anticipated from intended uses of the pesticide.
(e) Hazards to nontarget organisms(1) General. The information required to assess hazards to nontarget organisms is derived from tests to determine pesticidal effects on birds, mammals, fish, terrestrial and aquatic invertebrates and plants. These tests include short-term acute, subacute, reproduction, simulated field, and full field studies arranged in a hierarchical or tier system which progresses from the basic laboratory tests to the applied field tests. The results of each tier of testing must be evaluated to determine the potential of the pesticide to cause adverse effects, and to determine whether further testing is required. A purpose common to all data requirements is to provide data which determine the need for (and appropriate wording for) precautionary label statements to minimize the potential adverse effects to nontarget organisms.
(2) Short-term studies. The short-term acute and subchronic laboratory studies provide basic toxicity information which serves as a starting point for the hazard assessment. These data are used: To establish acute toxicity levels of the active ingredient to the test organisms; to compare toxicity information with measured or estimated pesticide residues in the environment in order to assess potential impacts on fish, wildlife and other nontarget organisms; and to indicate whether further laboratory and/or field studies are needed.
(3) Long-term and field studies. Additional studies (i.e., avian, fish, and invertebrate reproduction, life cycle studies and plant field studies) may be required when basic data and environmental conditions suggest possible problems. Data from these studies are used to: Estimate the potential for chronic effects, taking into account the measured or estimated residues in the environment; and to determine if additional field or laboratory data are necessary to further evaluate hazards. Simulated field and/or field data are used to examine acute and chronic adverse effects on captive or monitored fish and wildlife populations under natural or near-natural environments. Such studies are required only when predictions as to possible adverse effects in less extensive studies cannot be made, or when the potential for adverse effects is high.
(f) Applicator and post-application exposure. Data are used to evaluate exposures to persons in occupational and non-occupational settings, including agricultural, residential, commercial, institutional and recreational sites. Data include oral, dermal and inhalation exposure data, post-application residue data, post-application monitoring data, use information, and human activity information. These data, together with toxicology data, are used to determine whether application or post-application risks are of concern, and, where appropriate, to develop post-application restrictions such as reentry restrictions.
(g) Pesticide spray drift evaluation. Data required to evaluate pesticide spray drift are derived from studies of droplet size spectrum and spray drift field evaluations. These data contribute to the development of the overall exposure estimate and, along with data on toxicity for humans, fish and wildlife, or plants, are used to assess the potential hazard of pesticides to these organisms. A purpose common to all these tests is to provide data which will be used to determine the need for (and appropriate wording for) precautionary labeling to minimize the potential adverse effect to nontarget organisms.
(h) Environmental fate(1) General. The data generated by environmental fate studies are used to: Assess the toxicity to man through exposure of humans to pesticide residues remaining after application, either upon reentering treated areas or from consuming inadvertantly-contaminated food; assess the presence of widely distributed and persistent pesticides in the environment which may result in loss of usable land, surface water, ground water, and wildlife resources; and, assess the potential environmental exposure of other nontarget organisms, such as fish and wildlife, to pesticides. Another specific purpose of the environmental fate data requirements is to help applicants and the Agency estimate expected environmental concentrations of pesticides in specific habitats where threatened or endangered species or other wildlife populations at risk are found.
(2) Degradation studies. The data from hydrolysis and photolysis studies are used to determine the rate of pesticide degradation and to identify pesticides that may adversely affect nontarget organisms.
(3) Metabolism studies. Data generated from aerobic and anaerobic metabolism studies are used to determine the nature and availability of pesticides to rotational crops and to aid in the evaluation of the persistence of a pesticide.
(4) Mobility studies. These data requirements pertain to leaching, adsorption/desorption, and volatility of pesticides. They provide information on the mode of transport and eventual destination of the pesticide in the environment. This information is used to assess potential environmental hazards related to: Contamination of human and animal food; loss of usable land and water resources to man through contamination of water (including ground water); and habitat loss of wildlife resulting from pesticide residue movement or transport in the environment.
(5) Dissipation studies. The data generated from dissipation studies are used to assess potential environmental hazards (under actual field use conditions) related to: Reentry into treated areas; hazards from residues in rotational crops and other food sources; and the loss of land as well as surface and ground water resources.
(i) Residue chemistry.(1) Residue chemistry data are used by the Agency to estimate the exposure of the general population to pesticide residues in food and for setting and enforcing tolerances for pesticide residues in food or feed.
(2) Information on the chemical identity and composition of the pesticide product, the amounts, frequency and time of the pesticide application, and results of tests on the amount of residues remaining on or in the treated food or feed, are needed to support a finding as to the magnitude and identity of residues which result in food or animal feed as a consequence of a proposed pesticide usage.
(3) Residue chemistry data are also needed to support the adequacy of one or more methods for the enforcement of the tolerance, and to support practicable methods for removing residues that exceed any proposed tolerance.
(4) Accumulation studies. Accumulation studies indicate pesticide residue levels in food supplies that originate from wild sources or from rotational crops. Rotational crop studies are necessary to establish realistic crop rotation restrictions and to determine if tolerances may be needed for residues on rotational crops. Data from irrigated crop studies are used to determine the amount of pesticide residues that could be taken up by representative crops irrigated with water containing pesticide residues. These studies allow the Agency to establish label restrictions regarding application of pesticides on sites where the residues can be taken up by irrigated crops. These data also provide information that aids the Agency in establishing any corresponding tolerances that would be needed for residues on such crops. Data from pesticide accumulation studies in fish are used to establish label restrictions to prevent applications in certain sites so that there will be minimal residues entering edible fish or shellfish. These residue data are also used to determine if a tolerance or action level is needed for residues in aquatic animals eaten by humans.
Subpart C - Experimental Use Permits
§158.200 Experimental use permit data requirements tables.
Sections 158.200 through 158.270 describe how to use these tables to determine the experimental use permit data requirements for a particular pesticide product. Notes that apply to an individual test and include specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions to the designated test are listed at the end of each table. Refer to 40 CFR part 172 for further information on experimental use permits.
§158.210 Experimental use permit data requirements for product chemistry.
All product chemistry data, as described in §158.310, must be submitted to support a request for an experimental use permit.
§158.220 Experimental use permit data requirements for product performance.
All product performance data, as described in paragraph (c) of this section, must be submitted to support a request for an experimental use permit.
(a) Use patterns.(1) The terrestrial use pattern includes products classified under the general use patterns of terrestrial food crop and terrestrial nonfood crop. The aquatic use pattern includes products classified under the general use patterns of aquatic food crop and aquatic nonfood crop. The greenhouse use pattern includes products classified under the general use patterns of greenhouse food crop and greenhouse nonfood crop. The indoor use pattern includes products classified under the general use patterns of indoor food and indoor nonfood use.
(2) Data are also required for forestry and residential outdoor uses.
(b) Key. CR = Conditionally required; NR = Not required; R = Required; MP = Manufacturing-use product; EP = End-use product; TEP = Typical end-use product.
(c) Table. The following table shows the experimental use data requirements for product performance. The test notes are shown in paragraph (d) of this section.
Table - Experimental Use Permit Data Requirements for Product Performance
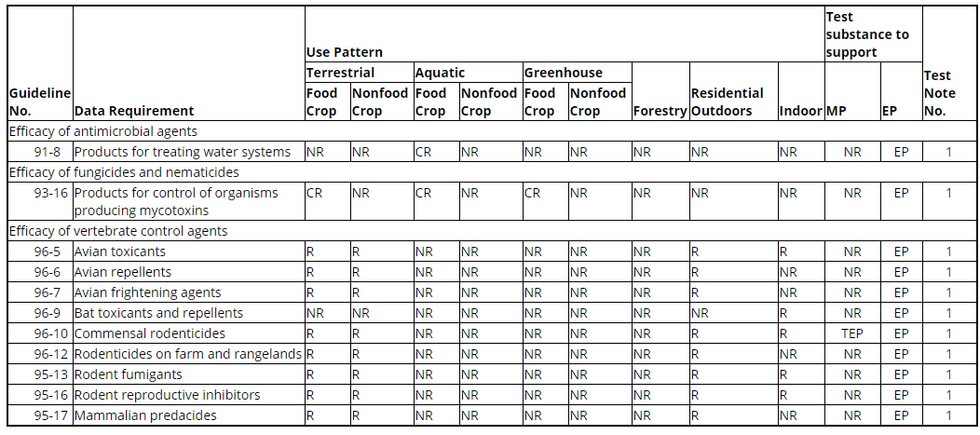
(d) Test notes. The following test notes apply to the data requirements in the table to paragraph (c) of this section.
1. The Agency has waived the requirement to submit efficacy data unless the pesticide product bears a claim to control pest microorganisms that pose a threat to human health and whose presence cannot readily be observed by the user including, but not limited to, microorganisms infectious to man in any area of the inanimate environment, or a claim to control vertebrates (such as rodents, birds, bats, canids, and skunks) that may directly or indirectly transmit diseases to humans. However each registrant must ensure through testing that his product is efficacious when used in accordance with label directions and commonly accepted pest control practices. The Agency reserves the right to require, on a case-by-case basis, submission of efficacy data for any pesticide product registered or proposed for registration.
2. [Reserved]
[72 FR 60957, Oct. 26, 2007, as amended at 73 FR 75596, Dec. 12, 2008]
§158.230 Experimental use permit data requirements for toxicology.
All toxicology data, as described in paragraph (c) of this section, must be submitted to support a request for an experimental use permit.
(a) Use patterns.(1) Food use patterns include products classified under the general use patterns of terrestrial food crop use, terrestrial feed crop use, aquatic food crop use, greenhouse food crop use, and indoor food use.
(2) Nonfood use patterns include products classified under the general use patterns of terrestrial nonfood crop use, aquatic nonfood crop use, aquatic nonfood outdoor use, greenhouse nonfood crop use, forestry use, residential outdoor use, indoor nonfood use, and indoor residential use.
(b) Key. CR = Conditionally required; NR = Not required; R = Required; EP = End-use product; MP = Manufacturing-use product; PAIRA = Pure active ingredient radio-labeled; TGAI = Technical grade of the active ingredient.
(c) Table. The following table shows the experimental use data requirements for toxicology. The test notes are shown in paragraph (d) of this section.
Table - Experimental Use Permit Toxicity Data Requirements
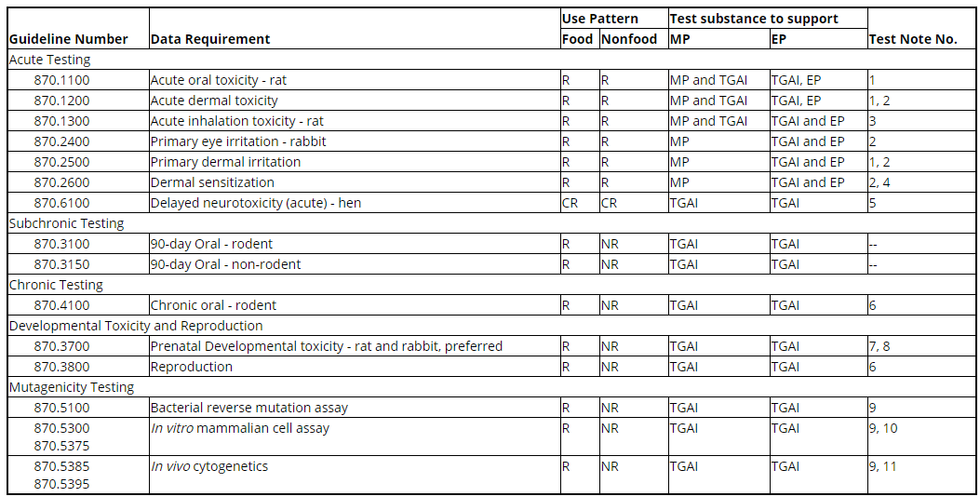
(d) Test notes. The following test notes apply to the data requirements in the table to paragraph (c) of this section.
1. Not required if test material is a gas or a highly volatile liquid.
2. Not required if test material is corrosive to skin or has a pH of less than 2 or greater than 11.5.
3. Required if the product consists of, or under conditions of use will result in, a respirable material (e.g., gas, vapor, aerosol, or particulate).
4. Required if repeated dermal exposure is likely to occur under conditions of use.
5. Required if the test material is an organophosphorus substance, which includes uncharged organophosphorus esters, thioesters, or anhydrides of organophosphoric, organophosphonic, or organophosphoramidic acids, or of related phosphorothioic, phosponothioic, or phosphorothioamidic acids, or is structurally related to other substances that may cause the delayed neurotoxicity sometimes seen in this class of chemicals.
6. These studies are seldom required to support EUPs. They may be required if the dietary exposure for these EUPs occupies a large part, e.g., greater than 50%, of the reference dose.
7. The oral route, by oral intubation, is preferred unless the chemical or physical properties of the test substance or the pattern of exposure suggests a more appropriate route of exposure.
8. May be combined with the 2-generation reproduction study in rodents by utilizing a second mating of the parental animals in either generation.
9. At a minimum, an initial battery of mutagenicity tests with possible confirmatory testing is required. Other relevant mutagenicity tests that may have been performed, plus a complete reference list must also be submitted.
10. Choice of assay using either:
i. Mouse lymphoma L5178Y cells, thymidine kinase (tk) gene locus, maximizing assay conditions for small colony expression or detection;
ii. Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) or Chinese hamster lung fibroblast (V79) cells, hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (hgprt) gene locus, accompanied by an appropriate in vitro test for clastogenicity; or
iii. CHO cells strains AS52, xanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (xprt) gene locus.
11. The micronucleus rodent bone marrow assay is preferred; however, rodent bone marrow assays using metaphase analysis (aberrations) are acceptable.
[72 FR 60957, Oct. 26, 2007, as amended at 73 FR 75596, Dec. 12, 2008]
§158.240 Experimental use permit data requirements for ecological effects.
All data for terrestrial nontarget organisms and aquatic nontarget organisms as described in §158.243 must be submitted to support a request for an experimental use permit. No data for nontarget plant protection must be submitted to support a request for an experimental use permit.
§158.243 Experimental use permit data requirements for terrestrial and aquatic nontarget organisms.
All terrestrial and aquatic nontarget organism data, as described in paragraph (c) of this section, must be submitted to support a request for an experimental use permit.
(a) Use patterns.(1) The terrestrial use pattern includes products classified under the general use patterns of terrestrial food crop, terrestrial feed crop, and terrestrial nonfood crop. The aquatic use pattern includes products classified under the general use patterns of aquatic food crop and aquatic nonfood. The greenhouse use pattern includes products classified under the general use patterns of greenhouse food crop and greenhouse nonfood crop. The indoor use pattern includes products classified under the general use patterns of indoor food and indoor nonfood use.
(2) Data are also required for the general use patterns of forestry and residential outdoor use.
(b) Key. CR = Conditionally required; NR = Not required; R = Required; TEP = Typical end-use product; TGAI = Technical grade of the active ingredient; commas between the test substances (e.g. TGAI, TEP) indicate that data may be required on the TGAI or TEP depending on the conditions set forth in the test note.
(c) Table. The following table shows the experimental use data requirements for terrestrial and aquatic nontarget organisms. The test notes are shown in paragraph (d) of this section.
| Guideline No. | Data Requirement | Use Pattern | Test substance | Test Note No. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Terrestrial | Aquatic | Forestry | Residential Outdoor | Greenhouse | Indoor | ||||
| Avian and Mammalian Testing | |||||||||
| 850.2100 | Avian oral toxicity | R | R | R | R | CR | CR | TGAI | 1, 2, 3 |
| 850.2200 | Avian dietary toxicity | R | R | R | R | NR | NR | TGAI | 1, 4 |
| Aquatic Organisms Testing | |||||||||
| 850.1075 | Freshwater fish toxicity | R | R | R | NR | NR | NR | TGAI, TEP | 1, 2, 5, 6, 11 |
| 850.1010 | Acute toxicity freshwater invertebrates | R | R | R | NR | NR | NR | TGAI, TEP | 1, 2, 6, 7, 11 |
| 850.1300 | Aquatic invertebrate life cycle (freshwater) | NR | R | R | NR | NR | NR | TGAI | 1, 7, 8 |
| 850.1400 | Fish early-life stage (freshwater) | NR | R | R | NR | NR | NR | TGAI | 1, 8, 9 |
| Accumulation Study | |||||||||
| 850.1730 | Fish | CR | CR | CR | NR | NR | NR | TGAI or PAIRA | 10 |
| Insect Pollinator Testing | |||||||||
| 850.3020 | Honeybee acute contact toxicity | R | R | R | NR | NR | NR | TGAI | 1 |
(d) Test notes. The following test notes apply to the data requirements in the table to paragraph (c) of this section.
1. Data using the TGAI are required to support all outdoor end-use product uses including, but not limited to, turf. Data are generally not required to support end-use products in the form of a gas, a highly volatile liquid, a highly reactive solid, or a highly corrosive material.
2. For greenhouse and indoor end-use products, data using the TGAI are required to support manufacturing-use products to be reformulated into these same end-use products or to support end-use products when there is no registered manufacturing-use product. Avian acute oral data are not required for liquid formulations for greenhouse and indoor uses. The study is not required if there is no potential for environmental exposure.
3. Data are required on one passerine species and either one waterfowl species or one upland game bird species for terrestrial, aquatic, forestry, and residential outdoor uses. Data are preferred on waterfowl or upland game bird species for indoor and greenhouse uses.
4. Data are required on waterfowl and upland game bird species.
5. Data are required on one coldwater fish and one warmwater fish for terrestrial, aquatic, forestry, and residential outdoor uses. For indoor and greenhouse uses, testing with only one of either fish species is required.
6. EP or TEP testing is required for any product which meets any of the following conditions:
i. The end-use pesticide will be introduced directly into an aquatic environment (e.g., aquatic herbicides and mosquito larvicides) when used as directed.
ii. The maximum expected environmental concentration (MEEC) or the estimated environmental concentration (EEC) in the aquatic environment is ≥one-half the LC50 or EC50 of the TGAI when the EP is used as directed.
iii. An ingredient in the end-use formulation other than the active ingredient is expected to enhance the toxicity of the active ingredient or to cause toxicity to aquatic organisms.
7. Data are required on one freshwater aquatic invertebrate species.
8. Data are generally not required for outdoor residential uses, other than turf, unless data indicate that pesticide residues from the proposed use(s) can potentially enter waterways.
9. Data are required on one freshwater fish species. If the test species is different from the two species used for the freshwater fish acute toxicity tests, a 96 hour LC50 on that species must also be provided.
10. Not required when:
i. The octanol/water partition coefficients of the pesticide and its major degradates are <1,000; or
ii. There are no potential exposures to fish and other nontarget aquatic organisms; or
iii. The hydrolytic half-life is <5 days at pH 5, 7 and 9.
11. The freshwater fish test species for the TEP testing is the most sensitive of the species tested with the TGAI. A freshwater invertebrate must also be tested with the EP or TEP using the same species tested with the TGAI.
[72 FR 60957, Oct. 26, 2007, as amended at 73 FR 75596, Dec. 12, 2008]
§158.250 Experimental use permit data requirements for human exposure.
No data for applicator exposure and post-application exposure must be submitted to support a request for an experimental use permit.
§158.260 Experimental use permit data requirements for environmental fate.
All environmental fate data, as described in paragraph (c) of this section, must be submitted to support a request for an experimental use permit.
(a) Use patterns.(1) The terrestrial use pattern includes products classified under the general use patterns of terrestrial food crop, terrestrial feed crop, and terrestrial nonfood. The aquatic use pattern includes the general use patterns of aquatic food crop, aquatic nonfood residential, and aquatic nonfood outdoors. The greenhouse use pattern includes both food and nonfood uses. The indoor use pattern includes food, nonfood, and residential indoor uses.
(2) Data are also required for the general use patterns of forestry use and residential outdoor use.
(b) Key. CR = Conditionally required; NR = Not required; R = Required; PAIRA = Pure active ingredient radio-labeled; TGAI = Technical grade of the active ingredient.
(c) Table. The following table shows the experimental use data requirements for environmental fate. The test notes are shown in paragraph (d) of this section.
| Guideline No. | Data Requirement | Use Pattern | Test substance | Test Note No. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Terrestrial | Aquatic | Greenhouse | Indoors | Forestry | Residential Outdoors | ||||
| Degradation Study - Laboratory | |||||||||
| 835.2120 | Hydrolysis | R | R | R | NR | R | R | TGAI or PAIRA | 1 |
| Metabolism Studies - Laboratory | |||||||||
| 835.4100 | Aerobic soil | R | CR | NR | NR | R | NR | TGAI or PAIRA | 2 |
| 835.4300 | Aerobic aquatic | NR | R | NR | NR | NR | NR | TGAI or PAIRA | -- |
| Mobility Study | |||||||||
| 835.1230
835.1240 | Leaching and adsorption/desorption | R | NR | NR | NR | R | NR | TGAI or PAIRA | 3 |
(d) Test notes. The following test notes apply to the data requirements in the table to paragraph (c) of this section.
1. Study is required for indoor uses in cases where environmental exposure is likely to occur. Such sites include, but are not limited to, agricultural premises, in or around farm buildings, barnyards, and beehives.
2. Required for aquatic uses for aquatic sites that are intermittently dry. Such sites include, but are not limited to cranberry bogs and rice paddies.
3. Adsorption and desorption using a batch equilibrium method is preferred. However, in some cases, for example, where the pesticide degrades rapidly, soil column leaching with unaged or aged columns may be more appropriate to fully characterize the potential mobility of the parent compound and major transformation products.
[72 FR 60957, Oct. 26, 2007, as amended at 73 FR 75596, Dec. 12, 2008]
§158.270 Experimental use permit data requirements for residue chemistry.
All residue chemistry data, as described in §158.1410, are required for an experimental use permit for which a temporary tolerance under FFDCA section 408(r) is sought. Residue chemistry data are not required for an experimental use permit issued on a crop-destruct basis.
§§ 158.280-158.290 [Reserved]
Subpart D - Product Chemistry
§158.300 Definitions.
The following terms are defined for the purposes of this subpart:
Active ingredient means any substance (or group of structurally similar substances, if specified by the Agency) that will prevent, destroy, repel or mitigate any pest, or that functions as a plant regulator, desiccant, defoliant, or nitrogen stabilizer, within the meaning of FIFRA sec. 2(b).
End-use product means a pesticide product whose labeling:
(1) Includes directions for use of the product (as distributed or sold, or after combination by the user with other substances) for controlling pests or defoliating, desiccating or regulating growth of plants, or as a nitrogen stabilizer, and
(2) does not state that the product may be used to manufacture or formulate other pesticide products.
Formulation means:
(1) The process of mixing, blending, or dilution of one or more active ingredients with one or more other active or inert ingredients, without an intended chemical reaction, to obtain a manufacturing-use product or an end-use product, or
(2) The repackaging of any registered product.
Impurity means any substance (or group of structurally similar substances if specified by the Agency), in a pesticide product other than an active ingredient or an inert ingredient, including unreacted starting materials, side reaction products, contaminants, and degradation products.
Impurity associated with an active ingredient means:
(1) Any impurity present in the technical grade of active ingredient; and
(2) Any impurity which forms in the pesticide product through reactions between the active ingredient and any other component of the product or packaging of the product.
Inert ingredient means any substance (or group of structurally similar substances if designated by the Agency), other than the active ingredient, which is intentionally included in a pesticide product.
Integrated system means a process for producing a pesticide product that:
(1) Contains any active ingredient derived from a source that is not an EPA-registered product; or
(2) Contains any active ingredient that was produced or acquired in a manner that does not permit its inspection by the Agency under FIFRA sec. 9(a) prior to its use in the process.
Manufacturing-use product means any pesticide product other than an end-use product. A product may consist of the technical grade of active ingredient only, or may contain inert ingredients, such as stabilizers or solvents.
Nominal concentration means the amount of an ingredient which is expected to be present in a typical sample of a pesticide product at the time the product is produced, expressed as a percentage by weight.
Starting material means a substance used to synthesize or purify a technical grade of active ingredient (or the practical equivalent of the technical grade ingredient if the technical grade cannot be isolated) by chemical reaction.
Technical grade of active ingredient means a material containing an active ingredient:
(1) Which contains no inert ingredient, other than one used for purification of the active ingredient; and
(2) Which is produced on a commercial or pilot plant production scale (whether or not it is ever held for sale).
§158.310 Product chemistry data requirements table.
(a) General. Sections 158.100 through 158.130 describe how to use this table to determine the product chemistry data requirements for a particular pesticide product. Notes that apply to an individual test and include specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions to the designated test are listed in paragraph (f) of the section.
(b) Use patterns. Product chemistry data are required for all pesticide products and are not use-specific.
(c) Test substance. Data requirements that list only the manufacturing-use product as the test substance apply to products containing solely the technical grade of the active ingredient and manufacturing-use products to which other ingredients have been intentionally added.
(d) Key. R = Required; CR = Conditionally required; MP = Manufacturing-use product; NR = Not required; EP = End-use product; TGAI = Technical grade of the active ingredient; PAI = Pure active ingredient.
(e) Table. The following table shows the data requirements for product chemistry. The table notes are shown in paragraph (f) of this section.
| Guideline Number | Data Requirement | Use Pattern | Test substance to support | Test Note No. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | MP | EP | |||
| Product Identity and Composition | |||||
| 830.1550 | Product identity and composition | R | MP | EP | 1 |
| 830.1600 | Description of materials used to produce the product | R | MP | EP | 2 |
| 830.1620 | Description of production process | R | MP | EP | 3 |
| 830.1650 | Description of formulation process | R | MP | EP | 4 |
| 830.1670 | Discussion of formulation of impurities | R | MP, and possibly TGAI | EP, and possibly TGAI | 5 |
| 830.1700 | Preliminary analysis | CR | MP, and possibly TGAI | EP, and possibly TGAI | 6, 9, 10 |
| 830.1750 | Certified limits | R | MP | EP | 7 |
| 830.1800 | Enforcement analytical method | R | MP | EP | 8 |
| 830.1900 | Submittal of samples | CR | MP, PAI and TGAI | EP, PAI, TGAI | 9, 11 |
| Physical and Chemical Properties | |||||
| 830.6302 | Color | R | MP and TGAI | EP | 9 |
| 830.6303 | Physical state | R | MP and TGAI | EP and TGAI | 9 |
| 830.6304 | Odor | R | MP and TGAI | EP | 9 |
| 830.6313 | Stability to normal and elevated temperatures, metals, and metal ions | R | MP and TGAI | EP | 9, 12, 26 |
| 830.6314 | Oxidation/reduction: chemical incompatibility | CR | MP | EP | 13 |
| 830.6315 | Flammability | CR | MP | EP | 14 |
| 830.6316 | Explodability | CR | MP | EP | 15 |
| 830.6317 | Storage stability | R | MP | EP | |
| 830.6319 | Miscibility | CR | MP | EP | 16 |
| 830.6320 | Corrosion characteristics | R | MP | EP | |
| 830.6321 | Dielectric breakdown voltage | CR | NR | EP | 17 |
| 830.7000 | pH | CR | MP and TGAI | EP and TGAI | 9, 18 |
| 830.7050 | UV/visible light absorption | R | TGAI or PAI | NR | -- |
| 830.7100 | Viscosity | CR | MP | EP | 19 |
| 830.7200 | Melting point/melting range | R | TGAI or PAI | TGAI or PAI | 9, 20 |
| 830.7220 | Boiling point/boiling range | R | TGAI or PAI | TGAI or PA | 9, 21 |
| 830.7300 | Density/relative density/bulk density | R | MP and TGAI | EP and TGAI | 9 |
| 830.7370 | Dissociation constants in water | R | TGAI or PAI | TGAI or PAI | 9, 22 |
| 830.7520 | Particle size, fiber length, and diameter distribution | CR | TGAI or PAI | EP | 23 |
| 830.7550
830.7560 830.7570 | Partition coefficient (n-octanol/water) | R | TGAI or PAI | TGAI or PAI | 24 |
| 830.7840
830.7860 | Water solubility | R | TGAI or PAI | TGAI or PAI | 9 |
| 830.7950 | Vapor pressure | R | TGAI or PAI | TGAI or PAI | 9, 25 |
(f) Test notes. The following test notes are applicable to the product chemistry data requirements in the table to paragraph (e) of this section:
1. Data must be provided in accordance with §158.320.
2. Data must be provided in accordance with §158.325.
3. Data must be provided in accordance with §158.330.
4. Data must be provided in accordance with §158.335.
5. Data must be provided in accordance with §158.340.
6. Data must be provided in accordance with §158.345.
7. Data must be provided in accordance with §158.350.
8. Data must be provided in accordance with §158.355.
9. If the TGAI cannot be isolated, data are required on the practical equivalent of the TGAI.
10. Data are required if the product is produced by an integrated system.
11. Basic manufacturers are required to provide the Agency with a sample of each TGAI used to formulate a product produced by an integrated system when the new TGAI is first used as a formulating ingredient in products registered under FIFRA. A sample of the active ingredient (PAI) suitable for use as an analytical standard is also required at this time. Samples of end-use products produced by an integrated system must be submitted on a case-by-case basis.
12. Data on the stability to metals and metal ions are required only if the TGAI is expected to come into contact with either material.
13. Required when the product contains an oxidizing or reducing agent.
14. Required when the product contains combustible liquids.
15. Required when the product is potentially explosive.
16. Required when the product is an emulsifiable liquid and is to be diluted with petroleum solvent.
17. Required when the EP is a liquid and is to be used around electrical equipment.
18. Required when the test substance is soluble or dispersible in water.
19. Required when the product is a liquid.
20. Required when the TGAI is solid at room temperature.
21. Required when the TGAI is liquid at room temperature.
22. Required when the test substance contains an acid or base functionality (organic or inorganic) or an alcoholic functionality (organic).
23. Required for water insoluble test substances (>10−6 g/l) and fibrous test substances with diameter of ≥0.1 µm.
24. Required if technical chemical is organic and non-polar.
25. Not required for salts.
26. Data on stability of the MP and TGAI to storage at normal temperatures are required. Data on the stability of the TGAI to high temperatures are required if the TGAI is expected to be subjected to temperatures >50°C (122°F) during production or storage.
§158.320 Product identity and composition.
Information on the composition of the pesticide product must be furnished. The information required by paragraphs (a), (b), and (f) of this section must be provided for each product. In addition, if the product is produced by an integrated system, the information on impurities required by paragraphs (c) and (d) of this section must be provided.
(a) Active ingredient. The following information is required for each active ingredient in the product:
(1) If the source of any active ingredient in the product is an EPA-registered product:
(i) The chemical and common name (if any) of the active ingredient, as listed on the source product.
(ii) The nominal concentration of the active ingredient in the product, based upon the nominal concentration of active ingredient in the source product.
(iii) Upper and lower certified limits of the active ingredient in the product, in accordance with §158.350.
(2) If the source of any active ingredient in the product is not an EPA-registered product:
(i) The chemical name according to Chemical Abstracts Society (CAS) nomenclature, the CAS Registry Number, and any common names.
(ii) The molecular, structural, and empirical formulae and the molecular weight or weight range.
(iii) The nominal concentration.
(iv) Upper and lower certified limits of the active ingredient in accordance with §158.350.
(v) The purpose of the ingredient in the formulation.
(b) Inert ingredients. The following information is required for each inert ingredient (if any) in the product:
(1) The chemical name of the ingredient according to Chemical Abstracts Society nomenclature, the CAS Registry Number, and any common names (if known). If the chemical identity or chemical composition of an ingredient is not known to the applicant because it is proprietary or trade secret information, the applicant must ensure that the supplier or producer of the ingredient submits to the Agency (or has on file with the Agency) information on the identity or chemical composition of the ingredient. Generally, it is not required that an applicant know the identity of each ingredient in a mixture that he uses in his product. However, in certain circumstances, the Agency may require that the applicant know the identity of a specific ingredient in such a mixture. If the Agency requires specific knowledge of an ingredient, it will notify the applicant in writing.
(2) The nominal concentration.
(3) Upper and lower certified limits in accordance with §158.350.
(4) The purpose of the ingredient in the formulation.
(c) Impurities of toxicological significance associated with the active ingredient. For each impurity associated with the active ingredient that is determined by EPA to be toxicologically significant, the following information is required:
(1) Identification of the ingredient as an impurity.
(2) The chemical name of the impurity.
(3) The nominal concentration of the impurity in the product.
(4) A certified upper limit, in accordance with §158.350.
(d) Other impurities associated with the active ingredient. For each other impurity associated with an active ingredient that was found to be present in any sample at a level ≥0.1 percent by weight of the technical grade active ingredient the following information is required:
(1) Identification of the ingredient as an impurity.
(2) The chemical name of the impurity.
(3) The nominal concentration of the impurity in the final product.
(e) Impurities associated with an inert ingredient. [Reserved]
(f) Ingredients that cannot be characterized. If the identity of any ingredient or impurity cannot be specified as a discrete chemical substance (such as mixtures that cannot be characterized or isomer mixtures), the applicant must provide sufficient information to enable EPA to identify its source and qualitative composition.
§158.325 Description of materials used to produce the product.
The following information must be submitted on the materials used to produce the product:
(a) Products not produced by an integrated system.(1) For each active ingredient that is derived from an EPA-registered product:
(i) The name of the EPA-registered product.
(ii) The EPA registration number of that product.
(2) For each inert ingredient:
(i) Each brand name, trade name, common name, or other commercial designation of the ingredient.
(ii) All information that the applicant knows (or that is reasonably available to him) concerning the composition (and, if requested by the Agency, chemical and physical properties) of the ingredient, including a copy of technical specifications, data sheets, or other documents describing the ingredient.
(iii) If requested by the Agency, the name and address of the producer of the ingredient or, if that information is not known to the applicant, the name and address of the supplier of the ingredient.
(b) Products produced by an integrated system.(1) The information required by paragraph (a)(1) of this section concerning each active ingredient that is derived from an EPA-registered product (if any).
(2) The following information concerning each active ingredient that is not derived from an EPA-registered product:
(i) The name and address of the producer of the ingredient (if different from the applicant).
(ii) Information about each starting material used to produce the active ingredient, as follows:
(A) Each brand name, trade name, or other commercial designation of the starting material.
(B) The name and address of the person who produces the starting material or, if that information is not known to the applicant, the name and address of each person who supplies the starting material.
(C) All information that the applicant knows (or that is reasonably available to him), concerning the composition (and if requested by the Agency, chemical or physical properties) of the starting material, including a copy of all technical specifications, data sheets, or other documents describing it.
(3) The information required by paragraph (a)(2) of this section concerning each inert ingredient.
(c) Additional information. On a case-by-case basis, the Agency may require additional information on substances used in the production of the product.
§158.330 Description of production process.
If the product is produced by an integrated system, the applicant must submit information on the production (reaction) processes used to produce the active ingredients in the product. The applicant must also submit information about the formulation process, in accordance with §158.335.
(a) Information must be submitted for the current production process for each active ingredient that is not derived from an EPA-registered product. If the production process is not continuous (a single reaction process from starting materials to active ingredient), but is accomplished in stages or by different producers, the information must be provided for each such production process.
(b) The following information must be provided for each process resulting in a separately isolated substance:
(1) The name and address of the producer who uses the process, if not the same as the applicant.
(2) A general characterization of the process (e.g., whether it is a batch or continuous process).
(3) A flow chart of the chemical equations of each intended reaction occurring at each step of the process, and of the duration of each step and of the entire process.
(4) The identity of the materials used to produce the product, their relative amounts, and the order in which they are added.
(5) A description of the equipment used that may influence the composition of the substance produced.
(6) A description of the conditions (e.g., temperature, pressure, pH, humidity) that are controlled during each step of the process to affect the composition of the substance produced, and the limits that are maintained.
(7) A description of any purification procedures (including procedures to recover or recycle starting materials, intermediates or the substance produced).
(8) A description of the procedures used to assure consistent composition of the substance produced, e.g., calibration of equipment, sampling regimens, analytical methods, and other quality control methods.
§158.335 Description of formulation process.
The applicant must provide information on the formulation process of the product (unless the product consists solely of a technical grade of active ingredient) as required by the following sections:
(a) Section 158.330(b)(2), pertaining to characterization of the process.
(b) Section 158.330(b)(4), pertaining to ingredients used in the process.
(c) Section 158.330(b)(5), pertaining to process equipment.
(d) Section 158.330(b)(6), pertaining to the conditions of the process.
(e) Section 158.330(b)(8), pertaining to quality control measures.
§158.340 Discussion of formation of impurities.
The applicant must provide a discussion of the impurities that may be present in the product, and why they may be present. The discussion should be based on established chemical theory and on what the applicant knows about the starting materials, technical grade of active ingredient, inert ingredients, and production or formulation process. If the applicant has reason to believe that an impurity that EPA would consider toxicologically significant may be present, the discussion must include an expanded discussion of the possible formation of the impurity and the amounts at which it might be present. The impurities which must also be discussed are the following, as applicable:
(a) Technical grade active ingredients and products produced by an integrated system.(1) Each impurity associated with the active ingredient which was found to be present in any analysis of the product conducted by or for the applicant.
(2) Each other impurity which the registrant or applicant has reason to believe may be present in his product at any time before use at a level ≥0.1 percent (1,000 ppm) by weight of the technical grade of the active ingredient, based on what he knows about the following:
(i) The composition (or composition range) of each starting material used to produce his product.
(ii) The impurities which the applicant knows are present (or believes are likely to be present) in the starting materials, and the known or presumed level (or range of levels) of these impurities.
(iii) The intended reactions and side reactions which may occur in the production of the product, and the relative amounts of byproduct impurities produced by such reactions.
(iv) The possible degradation of the ingredients in the product after its production but prior to its use.
(v) Post-production reactions between the ingredients in the product.
(vi) The possible migration of components of packaging materials into the pesticide.
(vii) The possible carryover of contaminants from use of production equipment previously used to produce other products or substances.
(viii) The process control, purification and quality control measures used to produce the product.
(b) Products not produced by an integrated system. Each impurity associated with the active ingredient which the applicant has reason to believe may be present in the product at any time before use at a level ≥0.1 percent (1,000 ppm) by weight of the product based on what he knows about the following:
(1) The possible carryover of impurities present in any registered product which serves as the source of any of the product's active ingredients. The identity and level of impurities in the registered source need not be discussed or quantified unless known to the formulator.
(2) The possible carryover of impurities present in the inert ingredients in the product.
(3) Possible reactions occurring during the formulation of the product between any of its active ingredients, between the active ingredients and inert ingredients, or between the active ingredient and the production equipment.
(4) Post-production reactions between any of the product's active ingredients and any other component of the product or its packaging.
(5) Possible migration of packaging materials into the product.
(6) Possible contaminants resulting from earlier use of equipment to produce other products.
(c) Expanded discussion. On a case-by-case basis, the Agency may require an expanded discussion of information on impurities:
(1) From other possible chemical reactions.
(2) Involving other ingredients.
(3) At additional points in the production or formulation process.
§158.345 Preliminary analysis.
(a) If the product is produced by an integrated system, the applicant must provide a preliminary analysis of each technical grade of active ingredient contained in the product to identify all impurities present at 0. 1 percent or greater of the technical grade of the active ingredient. The preliminary analysis should be conducted at the point in the production process after which no further chemical reactions designed to produce or purify the substances are intended.
(b) Based on the preliminary analysis, a statement of the composition of the technical grade of the active ingredient must be provided. If the technical grade of the active ingredient cannot be isolated, a statement of the composition of the practical equivalent of the technical grade of the active ingredient must be submitted.
§158.350 Certified limits.
The applicant must propose certified limits for the ingredients in the product. Certified limits become legally binding limits upon approval of the application. Certified limits will apply to the product from the date of production to date of use. If the product label bears a statement prohibiting use after a certain date, the certified limits will apply only until that date.
(a) Ingredients for which certified limits are required. Certified limits are required on the following ingredients of a pesticide product:
(1) An upper and lower limit for each active ingredient.
(2) An upper and lower limit for each inert ingredient.
(3) If the product is a technical grade of active ingredient or is produced by an integrated system, an upper limit for each impurity of toxicological significance associated with the active ingredient and found to be present in any sample of the product.
(4) On a case-by-case basis, certified limits for other ingredients or impurities as specified by EPA.
(b) EPA determination of standard certified limits for active and inert ingredients.(1) Unless the applicant proposes different limits as provided in paragraph (c) of this section, the upper and lower certified limits for active and inert ingredients will be determined by EPA. EPA will calculate the certified limits on the basis of the nominal concentration of the ingredient in the product, according to the table in paragraph (b)(2) of this section.
(2) Table of standard certified limits.
| If the nominal concentration (N) for the ingredient and percentage by weight for the ingredient is: | The certified limits for that ingredient will be as follows: | |
|---|---|---|
| Upper Limit | Lower Limit | |
| N ≤1.0% | N + 10%N | N - 10%N |
| 1.0% ≤N ≤20.0% | N + 5%N | N - 5%N |
| 20.0% ≤N ≤100.0% | N + 3%N | N - 3%N |
(c) Applicant proposed limits.(1) The applicant may propose a certified limit for an active or inert ingredient that differs from the standard certified limit calculated according to paragraph (b)(2) of this section.
(2) If certified limits are required for impurities, the applicants must propose a certified limit. The standard certified limits may not be used for such substances.
(3) Certified limits should:
(i) Be based on a consideration of the variability of the concentration of the ingredient in the product when good manufacturing practices and normal quality control procedures are used.
(ii) Allow for all sources of variability likely to be encountered in the production process.
(iii) Take into account the stability of the ingredient in the product and the possible formation of impurities between production and sale or distribution.
(4) The applicant may include an explanation of the basis of his proposed certified limits, including how the certified limits were arrived at (e.g., sample analysis, quantitative estimate based on production process), and its accuracy and precision. This will be particularly useful if the range of the certified limit for an active or inert ingredient is greater than the standard certified limits.
(d) Special cases. If the Agency finds unacceptable any certified limit (either standard, or applicant proposed), the Agency will inform the registrant or applicant of its determination and will provide supporting reasons. The Agency may also recommend alternative limits to the applicant. The Agency may require, on a case-by-case basis, any or all of the following:
(1) More precise limits.
(2) More thorough explanation of how the certified limits were determined.
(3) A narrower range between the upper and lower certified limits than that proposed.
(e) Certification statement. The applicant must certify the accuracy of the information presented, and that the certified limits of the ingredients will be maintained. The following statement, signed by the authorized representative of the company, is acceptable:
I hereby certify that, for purposes of FIFRA sec. 12(a)(1)(C), the description of the composition of [insert product name], EPA Reg. No. [insert registration number], refers to the composition set forth on the Statement of Formula and supporting materials. This description includes the representations that: (1) no ingredient will be present in the product in an amount greater than the upper certified limit or in an amount less than the lower certified limit (if required) specified for that ingredient in a currently approved Statement of Formula (or as calculated by the Agency); and (2) if the Agency requires that the source of supply of an ingredient be specified, that all quantities of such ingredient will be obtained from the source specified in the Statement of Formula.
§158.355 Enforcement analytical method.
An analytical method suitable for enforcement purposes must be provided for each active ingredient in the product and for each other ingredient or impurity that the Agency determines to be toxicologically significant.
Subpart E—Product Performance for Products Claiming Effectiveness Against Vertebrate Pests, Products With Prion-Related Claims, and Products for Control of Organisms Producing Mycotoxins
§158.400 Product performance data requirements table.
(a) General. Sections 158.100 through 158.130 describe how to use this table to determine the product performance data requirements for a particular pesticide product. Notes that apply to an individual test, including specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions to the designated test are listed in paragraph (e) of this section.
(b) Use patterns. The terrestrial use pattern includes products classified under the general use patterns of terrestrial food crop and terrestrial nonfood crop. The aquatic use pattern includes products classified under the general use patterns of aquatic food crop and aquatic nonfood. The greenhouse use pattern includes products classified under the general use patterns of greenhouse food crop and greenhouse nonfood crop. Data are also required for the general use patterns of forestry use, residential outdoor use, and indoor use, which includes both food and nonfood uses.
(c) Key. CR = Conditionally required; NR = Not required; R = Required; EP = End-use product; MP = Manufacturing-use product; TEP = Typical end-use product.
(d) Table. The following table lists the data requirements that pertain to product performance. The table notes are shown in paragraph (e) of this section.
Table - Product Performance Data Requirements

(e) Test notes. The following notes appy to the data requirements table in paragraph (d) of this section.
1. The Agency has waived the requirement to submit product performance data unless the pesticide product bears a claim to control pest microorganisms that pose a threat to human health and whose presence cannot readily be observed by the user including, but not limited to, microorganisms infectious to man in any area of the inanimate environment, or a claim to control vertebrates (such as rodents, birds, bats, canids, and skunks) that may directly or indirectly transmit diseases to humans. However each registrant must ensure through testing that his product is efficacious when used in accordance with label directions and commonly accepted pest control practices. The Agency reserves the right to require, on a case-by-case basis, submission of product performance data for any pesticide product registered or proposed for registration.
2. [Reserved]
[72 FR 60957, Oct. 26, 2007, as amended at 78 FR 13507, Feb. 28, 2013; 78 FR 26978, May 8, 2013]
Subpart F - Toxicology
§158.500 Toxicology data requirements table.
(a) General. Sections 158.100 through 158.130 describe how to use the data table in paragraph (d) of this section to determine the toxicology data requirements for a particular pesticide product. Notes that apply to an individual test and include specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions to the designated test in the table are listed in paragraph (e) of this section.
(b) Use patterns.(1) Food use patterns include products classified under the general use patterns of terrestrial food crop use, terrestrial feed crop use, aquatic food crop use, greenhouse food crop use, and indoor food use.
(2) Nonfood use patterns include products classified under the general use patterns of terrestrial nonfood crop use, aquatic nonfood use, greenhouse nonfood crop use, forestry use, residential outdoor use, and indoor nonfood use.
(c) Key. R = Required; CR = Conditionally required; NR = Not required; MP = Manufacturing-use product; EP = End-use product; TGAI = Technical grade of the active ingredient; PAI = Pure active ingredient; PAIRA = Pure active ingredient radio-labeled; Choice = Choice of several test substances depending on study required.
(d) Table. The following table lists the toxicology data requirements. The table notes are shown in paragraph (e) of this section.
Table - Toxicology Data Requirements

(e) Test notes. The following test notes apply to the requirements in the table to paragraph (d) of this section:
1. Not required if test material is a gas or a highly volatile liquid.
2. Diluted EP testing is required to support the end product registration if results using the EP meet the criteria for restricted use classification under §152.170(b) or special review consideration under §154.7(a)(1).
2.. Not required if the test material is corrosive to skin or has a pH of less than 2 or greater than 11.5.
4. Required if the product consists of, or under conditions of use will result in, a respirable material (e.g., gas, vapor, aerosol, or particulate).
5. Required if repeated dermal exposure is likely to occur under conditions of use.
6. Required if the test material is an organophosphorus substance, which includes uncharged organophosphorus esters; thioesters or anhydrides of organophosphoric, organophosphonic, or organophosphoramidic acids; or of related phosphorothioic, phosponothioic, or phosphorothioamidic acids; or is structurally related to other substances that may cause the delayed neurotoxicity sometimes seen in this class of chemicals.
7. As determined by the Agency, additional measurements may also be required, such as cholinesterase activity for certain pesticides, e.g., organophosphates and some carbamates. The route of exposure must correspond with the primary route of exposure.
8. Required for nonfood use pesticides if oral exposure could occur.
9. The 90-day study is required in the rat for hazard characterization (possibly endpoint selection) and dose-setting for the chronic/carcinogenicity study. It is not required in the mouse, but the Agency would strongly encourage the registrant to conduct a 90-day range finding for the purposes of dose selection for the mouse carcinogenicity study to achieve adequate dosing and an acceptable study. The registrant is also encouraged to consult with the Agency on the results of the 90-day mouse study prior to conducting the carcinogenicity study.
10. Required for agricultural uses or if repeated human dermal exposure may occur. Not required if an acceptable 90-day dermal toxicity study is performed and submitted.
11. EP testing is required if the product, or any component of it, may increase dermal absorption of the active ingredient(s) as determined by testing using the TGAI, or increase toxic or pharmacologic effects.
12. Required for food uses if either of the following criteria is met:
(i) The use pattern is such that the dermal route would be the primary route of exposure; or
(ii) The active ingredient is known or expected to be metabolized differently by the dermal route of exposure than by the oral route, and a metabolite is the toxic moiety.
13. Required if there is the likelihood of significant repeated inhalation exposure to the pesticide as a gas, vapor, or aerosol.
14. Based on estimates of the magnitude and duration of human exposure, studies of shorter duration, e.g., 21- or 28-days, may be sufficient to satisfy this requirement. Registrants should consult with the Agency to determine whether studies of shorter duration would meet this requirement.
15. Required if results of acute neurotoxicity study indicate significant statistical or biological effects, or if other available data indicate the potential for this type of delayed neurotoxicity, as determined by the Agency.
16. All 90-day subchronic studies in rats can be designed to simultaneously fulfill the requirements of the 90-day neurotoxicity study using separate groups of animals for testing. Although the subchronic guidelines include the measurement of neurological endpoints, they do not meet the requirement of the 90-day neurotoxicity study.
17. Required if either of the following are met:
(i) The use of the pesticide is likely to result in repeated human exposure over a considerable portion of the human lifespan, as determined by the Agency;
(ii) The use requires a tolerance or an exemption from the requirement of a tolerance.
18. Based on the results of the acute and subchronic neurotoxicity studies, or other available data, a combined chronic toxicity and neurotoxicity study may be required.
19. Studies which are designed to simultaneously fulfill the requirements of both the chronic oral and carcinogenicity studies (i.e., a combined study) may be conducted. Minimum acceptable study durations are:
(i) Chronic rodent feeding study (food use) - 24 months.
(ii) Chronic rodent feeding study (nonfood use) - 12 months.
(iii) Mouse carcinogenicity study - 18 months.
(iv) Rat carcinogenicity study - 24 months.
20. Required if any of the following, as determined by the Agency, are met:
(i) The use of the pesticide is likely to result in significant human exposure over a considerable portion of the human life span which is significant in terms of either frequency, duration, or magnitude of exposure;
(ii) The use requires a tolerance or an exemption from the requirement of a tolerance; or
(iii) The active ingredient, metabolite, degradate, or impurity (a) is structurally related to a recognized carcinogen, (b) causes mutagenic effects as demonstrated by in vitro or in vivo testing, or (c) produces a morphologic effect in any organ (e.g., hyperplasia, metaplasia) in subchronic studies that may lead to a neoplastic change.
21. If this study is modified or waived, a subchronic 90-day oral study conducted in the same species may be required.
22. Testing in two species is required for all uses.
23. The oral route, by oral intubation, is preferred unless the chemical or physical properties of the test substance or the pattern of exposure suggests a more appropriate route of exposure.
24. Additional testing by other routes may be required if the pesticide is determined to be a prenatal developmental toxicant after oral dosing.
25. May be combined with the 2-generation reproduction study in rodents by utilizing a second mating of the parental animals in either generation.
26. Required to support products intended for food uses and to support products intended for nonfood uses if use of the product is likely to result in significant human exposure over a portion of the human life span in terms of frequency, magnitude or duration of exposure.
27. An information-based approach to testing is preferred, which utilizes the best available knowledge on the chemical (hazard, pharmacokinetic, or mechanistic data) to determine whether a standard guideline study, an enhanced guideline study, or an alternative study should be conducted to assess potential hazard to the developing animal, or in some cases to support a waiver for such testing. Registrants should submit any alternative proposed testing protocols and supporting scientific rationale to the Agency prior to study initiation.
28. Study required using a weight-of-evidence approach considering:
(i) The pesticide causes treatment-related neurological effects in adult animal studies (i.e., clinical signs of neurotoxicity, neuropathology, functional or behavioral effects).
(ii) The pesticide causes treatment-related neurological effects in developing animals, following pre- and postnatal exposure (i.e., nervous system malformations or neuropathy, brain weight changes in offspring, functional or behavioral changes in the offspring).
(iii) The pesticide elicits a causative association between exposures and adverse neurological effects in human epidemiological studies.
(iv) The pesticide evokes a mechanism that is associated with adverse effects on the development of the nervous system (e.g., SAR relationship to known neurotoxicants, altered neuroreceptor or neurotransmitter responses).
29. The use of a combined study that utilizes the 2-generation reproduction study in rodents as a basic protocol for the addition of other endpoints or functional assessments in the immature animal is encouraged.
30. At a minimum, an initial battery of mutagenicity tests with possible confirmatory testing is required. Other relevant mutagenicity tests that may have been performed, plus a complete reference list must also be submitted.
31. Choice of assay using either:
(i) Mouse lymphoma L5178Y cells, thymidine kinase (tk) gene locus, maximizing assay conditions for small colony expression or detection;
(ii) Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) or Chinese hamster lung fibroblast (V79) cells, hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (hgprt) gene locus, accompanied by an appropriate in vitro test for clastogenicity; or
(iii) CHO cells strains AS52, xanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (xprt) gene locus.
32. The micronucleus rodent bone marrow assay is preferred; however, rodent bone marrow assays using metaphase analysis (aberrations) are acceptable.
33. Required when chronic or carcinogenicity studies are required. May be required if significant adverse effects are seen in available toxicology studies and these effects can be further elucidated by metabolism studies.
34. May be required if the product's use will result in exposure to domestic animals through, but not limited to, direct application.
35. A risk assessment assuming that dermal absorption is equal to oral absorption must be performed to determine if the study is required, and to identify the doses and duration of exposure for which dermal absorption is to be quantified.
36. A 1-year non-rodent study (i.e., 1-year dog study) would be required if the Agency finds that a pesticide chemical is highly bioaccumulating and is eliminated so slowly that it does not achieve steady state or sufficient tissue concentrations to elicit an effect during a 90-day study. EPA would require the appropriate tier II metabolism and pharmacokinetic studies to evaluate more precisely bioavailability, half-life, and steady state to determine if a longer duration dog toxicity study is needed.
§158.510 Tiered testing options for nonfood pesticides.
For nonfood use pesticides only, applicants have two options for generating and submitting required toxicology (§158.500) and human exposure (§158.1020, §158.1070, and §158.1410) studies. Applicants are to select one of the following:
(a) Acute, subchronic, chronic, and other toxicological studies on the active ingredient must be submitted together. The specific makeup of the set of toxicology study requirements is based on the anticipated exposure to the pesticide as determined by the Agency. If hazards are identified based upon review of these studies, specific exposure data will be required to evaluate risk.
(b) Certain toxicological and exposure studies must be submitted simultaneously with the toxicology data submitted in a tiered system. Exposure data must be submitted along with first tier toxicology data. The requirement for additional second and third level toxicology testing will be determined by the Agency based on the results of the first tiered studies.
(1) The required first-tier toxicology studies consist of:
(i) Battery of acute studies.
(ii) A subchronic 90-day dermal study or a subchronic 90-day inhalation study.
(iii) An acute and subchronic neurotoxicity screening battery in the rat.
(iv) Prenatal developmental toxicity studies in both the rat and rabbit.
(v) Reproduction and fertility studies in rats.
(vi) Battery of mutagenicity studies.
(vii) Immunotoxicity study.
(2) The conditionally required second-tier studies include:
(i) Subchronic 90-day feeding studies in both the rodent and nonrodent.
(ii) Dermal penetration study.
(3) The conditionally required third-tier studies include:
(i) Chronic feeding studies in the rodent.
(ii) Carcinogenicity.
(iii) Metabolism study.
(iv) Additional mutagenicity testing.
Subpart G - Ecological Effects
§158.630 Terrestrial and aquatic nontarget organisms data requirements table.
(a) General. Sections 158.100 through 158.130 describe how to use this table to determine the terrestrial and aquatic nontarget data requirements for a particular pesticide product. Notes that apply to an individual test including specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions to the designated test are listed in paragraph (e) of this section.
(b) Use patterns.(1) The terrestrial use pattern includes products classified under the general use patterns of terrestrial food crop, terrestrial feed crop, and terrestrial nonfood crop. The aquatic use pattern includes products classified under the general use patterns of aquatic food crop and aquatic nonfood use patterns. The greenhouse use pattern includes products classified under the general use patterns of greenhouse food crop and greenhouse nonfood crop. The indoor use pattern includes products classified under the general use patterns of indoor food and indoor nonfood use.
(2) Data are also required for the general use patterns of forestry and residential outdoor use.
(3) In general, for all outdoor end-uses, including turf, the following studies are required: Two avian oral LD50, two avian dietary LC50, two avian reproduction studies, two freshwater fish LC50, one freshwater invertebrate EC50, one honeybee acute contact LD50, one freshwater fish early-life stage, one freshwater invertebrate life cycle, and three estuarine acute LC50/EC50 studies -- fish, mollusk and invertebrate. All other outdoor residential uses, i.e., gardens and ornamental will not usually require the freshwater fish early-life stage, the freshwater invertebrate life-cycle, and the acute estuarine tests.
(c) Key. R = Required; CR = Conditionally required; NR = Not required; TGAI = Technical grade of the active ingredient; TEP = Typical end-use product; PAI = Pure active ingredient; EP = end-use product. Commas between the test substances (i.e., TGAI, TEP) indicate that data may be required on the TGAI or the TEP depending on the conditions set forth in the test note.
(d) Table. The following table shows the data requirements for nontarget terrestrial and aquatic organism. The table notes are shown in paragraph (e) of this section.
| Guideline Number | Data Requirement | Use Pattern | Test substance | Test Note No. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Terrestrial | Aquatic | Forestry | Residential Outdoor | Greenhouse | Indoor | ||||
| Avian and Mammalian Testing | |||||||||
| 850.2100 | Avian oral toxicity | R | R | R | R | CR | CR | TGAI | 1, 2, 3 |
| 850.2200 | Avian dietary toxicity | R | R | R | R | NR | NR | TGAI | 1, 4 |
| 850.2400 | Wild mammal toxicity | CR | CR | CR | CR | NR | NR | TGAI | 5 |
| 850.2300 | Avian reproduction | R | R | R | R | NR | NR | TGAI | 1, 4 |
| 850.2500 | Simulated or actual field testing | CR | CR | CR | CR | NR | NR | TEP | 6, 7 |
| Aquatic Organisms Testing | |||||||||
| 850.1075 | Freshwater fish toxicity | R | R | R | R | CR | CR | TGAI, TEP | 1, 2, 8, 9, 26 |
| 850.1010 | Acute toxicity freshwater invertebrates | R | R | R | R | CR | CR | TGAI, TEP | 1, 2, 9, 10, 26 |
| 850.1025
850.1035 850.1045 850.1055 850.1075 | Acute toxicity estuarine and marine organisms | R | R | R | R | NR | NR | TGAI, TEP | 1, 9, 11, 12, 26 |
| 850.1300 | Aquatic invertebrate life cycle (freshwater) | R | R | R | R | NR | NR | TGAI | 1, 10, 12 |
| 850.1350 | Aquatic invertebrate life cycle (saltwater) | CR | CR | CR | CR | NR | NR | TGAI | 12, 14, 15 |
| 850.1400 | Fish early-life stage (freshwater) | R | R | R | R | NR | NR | TGAI | 1, 12, 13 |
| 850.1400 | Fish early-life stage (saltwater) | CR | CR | CR | CR | NR | NR | TGAI | 12, 15, 16 |
| 850.1500 | Fish life cycle | CR | CR | CR | CR | NR | NR | TGAI | 17, 18 |
| 850.1710
850.1730 850.1850 | Aquatic organisms bioavailability, biomagnification, toxicity | CR | CR | CR | CR | NR | NR | TGAI, PAI, degradate | 19 |
| 850.1950 | Simulated or actual field testing for aquatic organisms | CR | CR | CR | CR | NR | NR | TEP | 7, 20 |
| Sediment Testing | |||||||||
| 850.1735 | Whole sediment: acute freshwater invertebrates | CR | CR | CR | CR | NR | NR | TGAI | 21 |
| 850.1740 | Whole sediment: acute marine invertebrates | CR | CR | CR | CR | NR | NR | TGAI | 21, 23 |
| Whole sediment: chronic invertebrates freshwater and marine | CR | CR | CR | CR | NR | NR | TGAI | 22, 23 | |
| Insect Pollinator Testing | |||||||||
| 850.3020 | Honeybee acute contact toxicity | R | CR | R | R | NR | NR | TGAI | 1 |
| 850.3030 | Honey bee toxicity of residues on foliage | CR | CR | CR | CR | NR | NR | TEP | 24 |
| 850.3040 | Field testing for pollinators | CR | CR | CR | CR | NR | NR | TEP | 25 |
(e) Test notes. The following test notes apply to terrestrial and aquatic nontarget organisms data requirements in the table to paragraph (d) of this section:
1. Data using the TGAI are required to support all outdoor end-use product uses including, but not limited to turf. Data are generally not required to support end-use products in the form of a gas, a highly volatile liquid, a highly reactive solid, or a highly corrosive material.
2. For greenhouse and indoor end-use products, data using the TGAI are required to support manufacturing-use products to be reformulated into these same end-use products or to support end-use products when there is no registered manufacturing-use product. Avian acute oral data are not required for liquid formulations for greenhouse and indoor uses. The study is not required if there is no potential for environmental exposure.
3. Data are required on one passerine species and either one waterfowl species or one upland game bird species for terrestrial, aquatic, forestry, and residential outdoor uses. Data are preferred on waterfowl or upland game bird species for indoor and greenhouse uses.
4. Data are required on waterfowl and upland game bird species.
5. Tests are required based on the results of lower tier toxicology studies, such as the acute and subacute testing, intended use pattern, and environmental fate characteristics that indicate potential exposure.
6. Higher tier testing may be required for a specific use pattern when a refined risk assessment indicates a concern based on laboratory toxicity endpoints and refined exposure assessments.
7. Environmental chemistry methods used to generate data associated with this study must include results of a successful confirmatory method trial by an independent laboratory. Test standards and procedures for independent laboratory validation are available as addenda to the guideline for this test requirement.
8. Data are required on one coldwater fish and one warmwater fish for terrestrial, aquatic, forestry, and residential outdoor uses. For indoor and greenhouse uses, testing with only one of either fish species is required.
9. EP or TEP testing is required for any product which meets any of the following conditions:
i. The end-use pesticide will be introduced directly into an aquatic environment (e.g., aquatic herbicides and mosquito larvicides) when used as directed.
ii. The maximum expected environmental concentration (MEEC) or the estimated environmental concentration (EEC) in the aquatic environment is ≥one-half the LC50 or EC50 of the TGAI when the EP is used as directed.
iii. An ingredient in the end-use formulation other than the active ingredient is expected to enhance the toxicity of the active ingredient or to cause toxicity to aquatic organisms.
10. Data are required on one freshwater aquatic invertebrate species.
11. Data are required on one estuarine/marine mollusk, one estuarine/marine invertebrate and one estuarine/marine fish species.
12. Data are generally not required for outdoor residential uses, other than turf, unless data indicate that pesticide residues from the proposed use(s) can potentially enter waterways.
13. Data are required on one freshwater fish species. If the test species is different from the two species used for the freshwater fish acute toxicity tests, a 96-hour LC50 on that species must also be provided.
14. Data are required on one estuarine/marine invertebrate species.
15. Data are required on estuarine/marine species if the product meets any of the following conditions:
i. Intended for direct application to the estuarine or marine environment.
ii. Expected to enter this environment in significant concentrations because of its expected use or mobility patterns.
iii. If the acute LC50 or EC50 <1 milligram/liter (mg/l).
iv. If the estimated environmental concentration (EEC) in water is ≥0.01 of the acute EC50 or LC50 or if any of the following conditions exist:
A. Studies of other organisms indicate the reproductive physiology of fish and/or invertebrates may be affected.
B. Physicochemical properties indicate bioaccumulation of the pesticide.
C. The pesticide is persistent in water (e.g., half-life in water >4 days).
16. Data are required on one estuarine/marine fish species.
17. Data are required on estuarine/marine species if the product is intended for direct application to the estuarine or marine environment, or the product is expected to enter this environment in significant concentrations because of its expected use or mobility patterns.
18. Data are required on freshwater species if the end-use product is intended to be applied directly to water, or is expected to be transported to water from the intended use site, and when any of the following conditions apply:
i. If the estimated environmental concentration (EEC) is ≥0.1 of the no-observed-effect level in the fish early-life stage or invertebrate life cycle test;
ii. If studies of other organisms indicate that the reproductive physiology of fish may be affected.
19. Not required when:
i. The octanol/water partition coefficients of the pesticide and its major degradates are <1,000; or
ii. There are no potential exposures to fish and other nontarget aquatic organisms; or
iii. The hydrolytic half-life is <5 days at pH 5, 7 and 9.
20. Data are required based on the results of lower tier studies such as acute and chronic aquatic organism testing, intended use pattern, and environmental fate characteristics that indicate significant potential exposure.
21. Data are required if:
i. The half-life of the pesticide in the sediment is ≤10 days in either the aerobic soil or aquatic metabolism studies and if any of the following conditions exist:
A. The soil partition coefficient (Kd) is ≥50.
B. The log Kow is ≥3.
C. The Koc ≥1,000.
ii. Registrants must consult with the Agency on appropriate test protocols prior to designing the study.
22. Data are required if:
i. The estimated environmental concentration (EEC) in sediment is >0.1 of the acute LC50/EC50 values and
ii. The half-life of the pesticide in the sediment is >10 days in either the aerobic soil or aquatic metabolism studies and if any of the following conditions exist:
A. The soil partition coefficient (Kd) is ≥50.
B. The log Kow is ≥3.
C. The Koc ≥1,000.
iii. Registrants must consult with the Agency on appropriate test protocols prior to designing the study.
23. Sediment testing with estuarine/marine test species is required if the product is intended for direct application to the estuarine or marine environment or the product is expected to enter this environment in concentrations which the Agency believes to be significant, either by runoff or erosion, because of its expected use or mobility pattern.
24. Data are required only when the formulation contains one or more active ingredients having an acute LD50 of <11 micrograms per bee as determined in the honey bee acute contact study and the use pattern(s) indicate(s) that honey bees may be exposed to the pesticide.
25. Required if any of the following conditions are met:
i. Data from other sources (Experimental Use Permit program, university research, registrant submittals, etc.) indicate potential adverse effects on colonies, especially effects other than acute mortality (reproductive, behavioral, etc.);
ii. Data from residual toxicity studies indicate extended residual toxicity.
iii. Data derived from studies with terrestrial arthropods other than bees indicate potential chronic, reproductive or behavioral effects.
26. The freshwater fish test species for the TEP testing is the most sensitive of the species tested with the TGAI. Freshwater invertebrate and acute estuarine and marine organisms must also be tested with the EP or TEP using the same species tested with the TGAI.
§158.660 Nontarget plant protection data requirements table.
(a) General. Sections 158.100 through158.130 describe how to use this table to determine the nontarget plant data requirements for a particular pesticide product. Notes that apply to an individual test and include specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions to the designated test are listed in paragraph (e) of this section.
(b) Use patterns.(1) The terrestrial use pattern includes products classified under the general use patterns of terrestrial food crop, terrestrial feed crop, and terrestrial nonfood. The aquatic use pattern includes only the general use patterns of aquatic food crops and aquatic nonfood.
(2) Data are also required for the general use patterns of forestry use and residential outdoor use.
(c) Key. R = Required; CR = Conditionally required; NR = Not required; TGAI = Technical grade of the active ingredient; TEP = Typical end-use product.
(d) Table. The following table shows the nontarget plant protection data requirements. The table notes are shown in paragraph (e) of this section.
| Guideline Number | Data Requirement | Use Pattern | Test substance | Test Note No. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Terrestrial | Aquatic | Forestry and Residential Outdoor | ||||
| Nontarget Area Phytotoxicity - Tier I | ||||||
| 850.4100 | Seedling emergence | R | R | R | TEP | 1, 2, 7 |
| 850.4150 | Vegetative vigor | R | R | R | TEP | 1, 2, 3, 7 |
| 850.4400
850.5400 | Aquatic plant growth (algal and aquatic vascular plant toxicity) | R | R | R | TEP or TGAI | 1, 2, 7 |
| Nontarget Area Phytotoxicity - Tier II | ||||||
| 850.4100 | Seedling emergence | CR | CR | CR | TEP | 1, 4, 5, 7 |
| 850.4150 | Vegetative vigor | CR | CR | CR | TEP | 1, 3, 4, 5, 7 |
| 850.4400
850.5400 | Aquatic plant growth (algal and aquatic vascular plant toxicity) | CR | CR | CR | TEP or TGAI | 1, 4, 6, 7 |
| Nontarget Area Phytotoxicity - Tier III | ||||||
| 850.4300 | Terrestrial field | CR | CR | CR | TEP | 1, 7, 8, 10 |
| 850.4450 | Aquatic field | CR | CR | CR | TEP | 1, 7, 8, 10 |
| Target Area Phytotoxicity | ||||||
| 850.4025 | Target area phytotoxicity | CR | CR | CR | TEP | 1, 7, 9, 10 |
(e) Test notes. The following test notes apply to the table in paragraph (d) of this section.
1. Not required for contained pesticide treatments such as bait boxes and pheromone traps unless adverse effects reports are received by the Agency.
2. Not required for known phytotoxicants.
3. Generally not required for granular formulations. May be requested on a case-by-case basis.
4. Required for known phytotoxicants such as herbicides, desiccants and defoliants.
5. Required if a tested terrestrial species exhibits a 25 percent or greater detrimental effect in the Tier I study. When Tier II testing is required, the test species should be the species that showed detrimental effects in the Tier I testing.
6. Required if the tested aquatic species exhibits a 50 percent or greater detrimental effect in the Tier I study. When Tier II testing is required, the test species should be the species that showed detrimental effects in the tier I testing.
7. Not required for aquatic residential uses.
8. Environmental chemistry methods used to generate data must include the results of a successful confirmatory method trial by an independent laboratory.
9. Tests are required on a case-by-case basis based on the results of lower tier phytotoxicity studies, adverse incident reports, intended use pattern, and environmental fate characteristics that indicate potential exposure.
10. Registrants must consult with the Agency on appropriate test protocols prior to designing the study.
Subparts H-J [Reserved]
§§ 158.700-158.900 [Reserved]
Subpart K - Human Exposure
§158.1000 Applicator exposure - general requirements.
(a) If EPA determines that industrial standards, such as the workplace standards set by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), provide adequate protection from risk under FIFRA for a particular pesticide use pattern, exposure data may not be required for that use pattern. Applicants should consult with the Agency on appropriate testing prior to the initiation of studies.
(b) The Agency may accept surrogate exposure data estimations from other sources to satisfy applicator exposure data requirements if the data meet the basic quality assurance, quality control, good laboratory practice, and other scientific requirements set by EPA. In order to be acceptable, the Agency must find that the surrogate exposure data estimations have adequate information to address applicator exposure data requirements and contain adequate replicates of acceptable quality data to reflect the specific use prescribed on the label and the applicator activity of concern, including formulation type, application methods and rates, type of activity, and other pertinent information. The Agency will consider using such surrogate data for evaluating human exposure on a case-by-case basis.
§158.1010 Applicator exposure - criteria for testing.
Applicator exposure data described in paragraph (d) of this section are required based on toxicity and exposure criteria. Data are required if a product meets, as determined by the Agency, at least one of the toxicity criteria in paragraph (a) of this section and either or both of the exposure criteria in paragraph (b) of this section.
(a) Toxicity criteria.(1) Evidence of potentially significant adverse effects have been observed in any applicable toxicity study.
(2) Scientifically sound epidemiological or poisoning incident data indicate that adverse health effects may have resulted from handling of the pesticide.
(b) Exposure criteria.(1) Dermal exposure may occur during the prescribed use.
(2) Respiratory exposure may occur during the prescribed use.
§158.1020 Applicator exposure data requirements table.
(a) General. Sections 158.100 through 158.130 describe how to use this table to determine the applicator exposure data requirements for a particular pesticide product. Notes that apply to an individual test and include specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions to the designated test are listed in paragraph (e) of this section.
(b) Use patterns.(1) Occupational use patterns include products classified under the general use patterns of terrestrial food crop, terrestrial feed crop, terrestrial nonfood crop, aquatic food, aquatic nonfood use, forestry, greenhouse food, greenhouse nonfood, indoor food use, and indoor nonfood use. Occupational use patterns also include commercial (“for hire”) applications to residential outdoor and indoor sites.
(2) Residential use patterns include residential outdoor use and residential indoor use. These use patterns are limited to nonoccupational, i.e., nonprofessional, pesticide applications.
(c) Key. R = Required; CR = Conditionally required; TEP = Typical end-use product.
(d) Table. The data requirements listed pertain to pesticide products that meet the testing criteria outlined in §158.1010. The table notes are shown in paragraph (e) of this section.
| Guideline Number | Data requirement | Use pattern | Test substance | Test Note No. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Occupational | Residential | ||||
| 875.1100 | Dermal outdoor exposure | R | R | TEP | 1, 2, 3 |
| 875.1200 | Dermal indoor exposure | R | R | TEP | 1, 2, 4 |
| 875.1300 | Inhalation outdoor exposure | R | R | TEP | 1, 2, 3 |
| 875.1400 | Inhalation indoor exposure | R | R | TEP | 1, 2, 4 |
| 875.1500 | Biological monitoring | CR | CR | TEP | 1, 2 |
| 875.1600 | Data reporting and calculations | R | R | TEP | 5 |
| 875.1700 | Product use information | R | R | TEP | -- |
(e) Test notes. The following notes apply to the data requirements in the table to paragraph (d) of this section:
1. Protocols must be submitted for approval prior to the initiation of the study. Details for developing protocols are available from the Agency.
2. Biological monitoring data may be submitted in addition to, or in lieu of, dermal and inhalation exposure data, provided the human pharmacokinetics of the pesticide and/or metabolite/analog compounds (i.e., whichever method is selected as an indicator of body burden or internal dose) allow for the back calculation to actual dose.
3. Data are required if the product is applied outdoors.
4. Data are required if the product is applied indoors.
5. Data reporting and calculations are required when handler exposure data are submitted.
§158.1050 Post-application exposure - general requirements.
(a) If EPA determines that industrial standards, such as the workplace standards set by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration, provide adequate protection for a particular pesticide use pattern, post-application exposure data may not be required for that use pattern. Applicants should consult with the Agency on appropriate testing before the initiation of studies.
(b) The Agency may accept surrogate exposure data from other sources to satisfy post-application exposure data requirements if the data meet the basic quality assurance, quality control, good laboratory practice, and other scientific needs of EPA. In order to be acceptable, among other things, the Agency must find that the surrogate exposure data have adequate information to address post-application exposure data requirements and contain adequate replicates of acceptable quality data to reflect the specific use prescribed on the label and the post-application activity of concern, including formulation type, application methods and rates, type of activity, and other pertinent information. The Agency will consider using such surrogate data for evaluating human exposure on a case-by-case basis.
§158.1060 Post-application exposure - criteria for testing.
Exposure data described in §158.1070(d) are required based upon toxicity and exposure criteria. Data are required if a product meets, as determined by the Agency, either or both of the toxicity criteria in paragraph (a) of this section and either or both of the exposure criteria in paragraph (b) of this section.
(a) Toxicity criteria.(1) Evidence of potentially significant adverse health effects have been observed in any applicable toxicity study.
(2) Scientifically sound epidemiological or poisoning incident data indicate that adverse health effects may have resulted from post-application exposure to the pesticide.
(b) Exposure criteria. The need for data from potential exposure resulting from situations not covered by this paragraph should be discussed with the Agency.
(1) For outdoor uses.(i) Occupational human post-application exposure to pesticide residues on plants or in soil could occur as the result of cultivation, pruning, harvesting, mowing or other work-related activity. Such uses include agricultural food, feed, and fiber commodities, forest trees, ornamental plants, and turf grass.
(ii) Residential human post-application exposure to pesticide residues on plants or in soil could occur. Such uses may include turf grass, fruits, vegetables, and ornamentals grown at sites, including, but not limited to, homes, parks, and recreation areas.
(2) For indoor uses.(i) Occupational human post-application exposure to pesticide residues could occur following the application of the pesticide to indoor spaces or surfaces at agricultural or commercial sites, such as, but not limited to, agricultural animal facilities and industrial or manufacturing facilities.
(ii) Residential human post-application exposure to pesticide residues could occur following the application of the pesticide to indoor spaces or surfaces at residential sites, such as, but not limited to homes, daycare centers, hospitals, schools, and other public buildings.
§158.1070 Post-application exposure data requirements table.
(a) General. Sections 158.100 through 158.130 describe how to use this table to determine the post-application data requirements for a particular pesticide product. Notes that apply to an individual test and include specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions to the designated test are listed in paragraph (e) of this section.
(b) Use patterns.(1) Occupational use patterns include products classified under the general use patterns of terrestrial food crop, terrestrial feed crop, terrestrial nonfood use, aquatic food, aquatic nonfood use, forestry, greenhouse food, greenhouse nonfood, indoor food, and indoor nonfood. Occupational use patterns also include commercial (“for hire”) applications to residential outdoor and indoor sites.
(2) Residential use patterns include residential outdoor use and indoor residential use. These use patterns are limited to nonoccupational, i.e., nonprofessional, pesticide applications.
(c) Key. R = Required; CR = Conditionally required; NR = Not required; TEP = Typical end-use product.
(d) Table. The data requirements listed in the following table pertain to pesticide products that meet the testing criteria outlined in §158.1060. The table notes are shown in paragraph (e) of this section.
| Guideline Number | Data Requirement | Use Pattern | Test Substance | Test Note No. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Occupational | Residential | ||||
| 875.2100 | Dislodgeable foliar residue and turf transferable residues | R | R | TEP | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 |
| 875.2200 | Soil residue dissipation | R | CR | TEP | 1, 2, 6, 7 |
| 875.2300 | Indoor surface residue dissipation | R | R | TEP | 1, 2, 8, 9 |
| 875.2400 | Dermal exposure | R | R | TEP | 1, 2, 10, 11, 12 |
| 875.2500 | Inhalation exposure | R | R | TEP | 1, 10, 11, 12 |
| 875.2600 | Biological monitoring | CR | CR | TEP | 1, 12, 13 |
| 875.2700 | Product use information | R | R | TEP | -- |
| 875.2800 | Description of human activity | R | R | TEP | -- |
| 875.2900 | Data reporting and calculations | R | R | TEP | 14 |
| 875.3000 | Nondietary ingestion exposure | NR | R | TEP | 1, 11, 15 |
(e) Test notes. The following test notes apply to the data requirements in the table to paragraph (d) of this section:
1. Protocols must be submitted for approval prior to the initiation of the study. Details for developing protocols are available from the Agency.
2. Bridging applicable residue dissipation data to dermal exposure data is required.
3. Turf grass transferable residue dissipation data are required when pesticides are applied to turf grass. Dislodgeable foliar residue dissipation data are required when pesticides are applied to the foliage of plants other than turf grass.
4. Data are required for occupational sites if (i) there are uses on turf grass or other plant foliage, and (ii) the human activity data indicate that workers are likely to have post-application dermal contact with treated foliage while participating in typical activities.
5. Data are required for residential sites if there are uses on turf grass or other plant foliage.
6. Data are required for occupational sites, if (i) there are outdoor or greenhouse uses to or around soil or other planting media, and (ii) the human activity data indicate that workers are likely to have post-application dermal contact with treated soil or planting media while participating in typical activities.
7. Data are required for residential sites if the pesticide is applied to or around soil or other planting media both outdoors and indoors, e.g., residential greenhouse or houseplant uses.
8. Data are required for occupational sites if the pesticide is applied to or around on non-plant surfaces, e.g., flooring or countertops, and if the human activity data indicate that workers are likely to have post-application dermal contact with treated indoor surfaces while participating in typical activities.
9. Data are required for residential sites if the pesticide is applied to or around non-plant surfaces, e.g., flooring and countertops.
10. Data are required for occupational sites if the human activity data indicate that workers are likely to have post-application exposures while participating in typical activities.
11. Data are required for residential sites if post-application exposures are likely.
12. Biological monitoring data may be submitted in addition to, or in lieu of, dermal and inhalation exposure data provided the human pharmocokinetics of the pesticide and/or metabolite/analog compounds (i.e., whichever method is selected as an indicator of body burden or internal dose) allow for a back-calculation to the total internal dose.
13. Data are required when passive dosimetry techniques are not applicable for a particular exposure scenario, such as a swimmer exposure to pesticides.
14. Data reporting and calculations are required when any post-application exposure monitoring data are submitted.
15. The selection of a sampling method will depend on the nondietary pathway(s) of interest. Data must be generated to consider all potential pathways of nondietary ingestion exposure that are applicable (e.g., soil ingestion, hand-to-mouth transfer, and object-to-mouth transfer of surface residues).
Subpart L - Spray Drift
§158.1100 Spray drift data requirements table.
(a) General. Sections 158.100 through 158.130 describe how to use this table to determine the spray drift data requirements for a particular pesticide product. Notes that apply to an individual test, including specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions to the designated test are listed in paragraph (e) of this section.
(b) Use patterns. The terrestrial use pattern includes products classified under the general use patterns of terrestrial food crop and terrestrial nonfood crop. The aquatic use pattern includes products classified under the general use patterns of aquatic food crop and aquatic nonfood. The greenhouse use pattern includes products classified under the general use patterns of greenhouse food crop and greenhouse nonfood crop. Data are also required for the general use patterns of forestry use, residential outdoor use, and indoor use.
(c) Key. CR = Conditionally required; NR = Not required; TEP = Typical end-use product; MP = Manufacturing use product; EP = End-use product.
(d) Table. The following table lists the data requirements that pertain to spray drift. The table notes are shown in paragraph (e) of this section.
Table - Spray Drift Data Requirements

(e) Test notes. The following notes apply to the requirements in the table to paragraph (d) of this section:
1. This study is required when aerial applications (rotary and fixed winged) and mist blower or other methods of ground application are proposed and it is estimated that the detrimental effect level of those nontarget organisms expected to be present would be exceeded. The nontarget organisms include humans, domestic animals, fish and wildlife, and nontarget plants.
2. [Reserved]
Subpart M [Reserved]
§§ 158.1200-158.1299 [Reserved]
Subpart N - Environmental Fate
§158.1300 Environmental fate data requirements table.
(a) General. All environmental fate data, as described in paragraph (c) of this section, must be submitted to support a request for registration.
(b) Use patterns.(1) The terrestrial use pattern includes products classified under the general use patterns of terrestrial food crop, terrestrial feed crop, and terrestrial nonfood. The aquatic use pattern includes the general use patterns of aquatic food crop, and aquatic nonfood. The greenhouse use pattern includes both food and nonfood uses. The indoor use pattern includes food, nonfood, and residential indoor uses.
(2) Data are also required for the general use patterns of forestry use and residential outdoor use.
(c) Key. CR = Conditionally required; NR = Not required; R = Required; PAIRA = Pure active ingredient radio-labeled; TGAI = Technical grade of the active ingredient; TEP = Typical end-use product.
(d) Table. The following table shows the data requirements for environmental fate. The test notes are shown in paragraph (e) of this section.
| Guideline Number | Data Requirement | Use Pattern | Test substance | Test Note No. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Terrestrial | Aquatic | Greenhouse | Indoor | Forestry | Residential Outdoor | ||||
| Degradation Studies - Laboratory | |||||||||
| 835.2120 | Hydrolysis | R | R | R | CR | R | R | TGAI or PAIRA | 1 |
| 835.2240 | Photodegradation in water | R | R | NR | NR | R | NR | TGAI or PAIRA | 2 |
| 835.2410 | Photodegradation on soil | R | NR | NR | NR | R | NR | TGAI or PAIRA | 3 |
| 835.2370 | Photodegradation in air | CR | NR | CR | NR | CR | CR | TGAI or PAIRA | 4 |
| Metabolism Studies - Laboratory | |||||||||
| 835.4100 | Aerobic soil | R | CR | R | NR | R | R | TGAI or PAIRA | 5 |
| 835.4200 | Anaerobic soil | R | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | TGAI or PAIRA | -- |
| 835.4300 | Aerobic aquatic | R | R | NR | NR | R | NR | TGAI or PAIRA | -- |
| 835.4400 | Anaerobic aquatic | R | R | NR | NR | R | NR | TGAI or PAIRA | -- |
| Mobility Studies | |||||||||
| 835.1230
835.1240 | Leaching and adsorption/desorption | R | R | R | NR | R | R | TGAI or PAIRA | 6 |
| 835.1410 | Volatility - laboratory | CR | NR | CR | NR | NR | NR | TEP | 4 |
| 835.8100 | Volatility - field | CR | NR | CR | NR | NR | NR | TEP | -- |
| Dissipation Studies - Field | |||||||||
| 835.6100 | Terrestrial | R | CR | NR | NR | CR | R | TEP | 5, 7, 12 |
| 835.6200 | Aquatic (sediment) | CR | R | NR | NR | NR | NR | TEP | 7, 8 |
| 835.6300 | Forestry | NR | NR | NR | NR | CR | NR | TEP | 7, 9, 12 |
| 835.6400 | Combination and tank mixes | CR | CR | NR | NR | NR | NR | TEP | 10 |
| Ground Water Monitoring | |||||||||
| 835.7100 | Ground water monitoring | CR | NR | NR | NR | CR | CR | TEP | 7, 9, 11 |
(e) Test notes. The following test notes apply to the requirements in the table to paragraph (d) of this section:
1. Study is required for indoor uses in cases where environmental exposure is likely to occur. Such sites include, but are not limited to, agricultural premises, in or around farm buildings, barnyards, and beehives.
2. Not required when the electronic absorption spectra, measured at pHs 5, 7, and 9, of the chemical and its hydrolytic products, if any, show no absorption or tailing between 290 and 800 nm.
3. Not required when the chemical is to be applied only by soil injection or is incorporated in the soil.
4. Requirement based on use patterns and other pertinent factors including, but not limited to, the Henry's Law Constant of the chemical. In view of methodological difficulties with the study of photodegradation in air, prior consultation with the Agency regarding the protocol is recommended before the test is performed.
5. Required for aquatic food and nonfood crop uses for aquatic sites that are intermittently dry. Such sites include, but are not limited to, cranberry bogs and rice paddies.
6. Adsorption and desorption using a batch equilibrium method is preferred. However in some cases, for example, where the pesticide degrades rapidly, soil column leaching with unaged or aged columns may be more appropriate to fully characterize the potential mobility of the parent compound and major transformation products.
7. Environmental chemistry methods used to generate data associated with this study must include results of a successful confirmatory method trial by an independent laboratory. Test standards and procedures for independent laboratory validation are available as addenda to the guideline for this test requirement.
8. Requirement for terrestrial uses is based on potential for aquatic exposure and if pesticide residues have the potential for persistence, mobility, nontarget aquatic toxicity or bioaccumulation. Not required for aquatic residential uses. Field testing under the terrestrial field dissipation requirement may be more appropriate for some aquatic food crops, such as rice and cranberry uses, that are managed to have a dry-land period for production. The registrant is encouraged to consult with the Agency on protocols.
9. Agency approval of a protocol is necessary prior to initiation of the study.
10. This study may be triggered if there is specific evidence that the presence of one pesticide can affect the dissipation characteristics of another pesticide when applied simultaneously or serially.
11. Required if the weight-of-evidence indicates that the pesticide and/or its degradates is likely to leach to ground water, taking into account other factors such as the toxicity of the chemicals(s), available monitoring data, and the vulnerability of ground water resources in the pesticide use area.
12. If the terrestrial dissipation study cannot assess all of the major routes of dissipation, the forestry study will be required.
Subpart O - Residue Chemistry
§158.1400 Definitions.
The following terms are defined for the purposes of this subpart:
Livestock, for the purposes of this section, includes all domestic animals that are bred for human consumption, including, but not limited to, cattle, swine, sheep, and poultry.
Plant or animal metabolite means a pesticide chemical residue that is the result of biological breakdown of the parent pesticide within the plant or animal.
Residue of concern means the parent pesticidal compound and its metabolites, degradates, and impurities of toxicological concern.
Tolerance, for the purposes of this section, includes the establishment of a new tolerance or tolerance exemption, or amended tolerance or tolerance exemption.
§158.1410 Residue chemistry data requirements table.
(a) General. Sections 158.100 through 158.130 describe how to use this table to determine the residue chemistry data requirements for a particular pesticide product. Notes that apply to an individual test and include specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions to the designated test are listed in paragraph (e) of this section.
(b) Use patterns.(1) Data are required or conditionally required for all pesticides used in or on food and for residential outdoor uses where food crops are grown. Food use patterns include products classified under the general use patterns of terrestrial food crop use, terrestrial feed crop use, aquatic food crop use, greenhouse food crop use, and indoor food use.
(2) Data may be required for nonfood uses if pesticide residues may occur in food or feed as a result of the use. Data requirements for these nonfood uses will be determined on a case-by-case basis. For example, most products used in or near kitchens require residue data for risk assessment purposes even though tolerances may not be necessary in all cases.
(c) Key. R = Required; CR = Conditionally required; NR = Not required; TGAI = Technical grade of the active ingredient; PAI = Pure active ingredient; PAIRA = Pure active ingredient radio-labeled; Residue of concern= the active ingredient and its metabolites, degradates, and impurities of toxicological concern; TEP = Typical end-use product.
(d) Table. The following table list the data requirements for residue chemistry related to food uses. The table notes are shown in paragraph (e) of this section.
| Guideline Number | Data Requirement | Use Pattern | Test substance | Test Note No. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Terrestrial Food or Feed | Aquatic Food | Greenhouse Food | Indoor Food | Residential Outdoor | ||||
| Supporting Information | ||||||||
| 860.1100 | Chemical identity | R | R | R | R | R | TGAI | -- |
| 860.1200 | Directions for use | R | R | R | R | R | -- | -- |
| 860.1550 | Proposed tolerance | R | R | R | CR | NR | -- | 1 |
| 860.1560 | Reasonable grounds in support of petition | R | R | R | CR | NR | -- | 1 |
| 860.1650 | Submittal of analytical reference standards | R | R | R | CR | NR | PAI and residue of concern | 1, 2, 25 |
| Nature of the residue | ||||||||
| 860.1300 | Nature of the residue in plants | R | R | R | CR | CR | PAIRA | 3, 4, 25 |
| 860.1300 | Nature of the residue in livestock | CR | CR | CR | CR | NR | PAIRA or radiolabeled plant metabolite | 1, 6, 25 |
| 860.1850 | Confined rotational crops | CR | CR | NR | NR | NR | PAIRA | 7 |
| Analytical methods | ||||||||
| 860.1340 | Residue analytical methods | R | R | R | CR | CR | Residue of concern | 1, 3, 8, 9, 10, 25 |
| 860.1360 | Multiresidue method | R | R | R | CR | NR | Residue of concern | 1, 11, 25 |
| Magnitude of the residue | ||||||||
| 860.1380 | Storage stability | R | R | R | CR | CR | TEP or residue of concern | 1, 3, 10, 12, 25 |
| 860.1500 | Crop field trials | R | R | R | CR | CR | TEP | 3, 10, 14, 24, 25 |
| 860.1520 | Processed food or feed | CR | CR | CR | CR | NR | TEP | 1, 15, 25 |
| 860.1480 | Meat/milk/poultry/eggs | CR | CR | CR | CR | NR | TGAI or plant metabolite | 1, 16, 17, 18, 25 |
| 860.1400 | Potable water | NR | R | NR | NR | NR | TEP | 19, 25 |
| 860.1400 | Fish | NR | R | NR | NR | NR | TEP | 5, 25 |
| 860.1400 | Irrigated crops | NR | CR | NR | NR | NR | TEP | 20, 25 |
| 860.1460 | Food handling | NR | NR | NR | CR | NR | TEP | 1, 21, 25 |
| 860.1540 | Anticipated residues | CR | CR | CR | CR | NR | Residue of concern | 1, 13, 22, 26 |
| 860.1900 | Field rotational crops | CR | CR | NR | NR | NR | TEP | 23, 25 |
(e) Test notes. The following test notes apply to the data requirements in the table to paragraph (d) of this section.
1. Required if indoor use could result in pesticide residues in or on food or feed.
2. Material safety data sheets must accompany standards as specified by OSHA in 29 CFR 1910.1200.
3. Required for residential outdoor uses on food crops if the corresponding agricultural use is not approved or the residential use is expected to produce higher residues based on the label directions.
4. Required for indoor uses where the pesticide is applied directly to food, in order to determine metabolites and/or degradates. Not required when only indirect contact with food would occur (e.g., crack and crevice treatments).
5. Data for fish are required for all pesticides applied directly to water inhabited, or which will be inhabited, by fish that may be caught or harvested for human consumption.
6. Required when a pesticide is to be applied directly to livestock, to livestock premises, to livestock drinking water, or to crops used for livestock feed. If results from the plant metabolism study show differing metabolites in plants from those found in animals, an additional livestock metabolism study involving dosing with the plant metabolite(s) may also be required.
7. Required when the Agency determines that it is reasonably foreseeable that a food or feed crop could be subsequently planted on the site of pesticide application after harvest or failure of the treated crop. Typically not required for pesticide uses in permanent food crops (e.g., various tree crops, vines) or semi-permanent crops (e.g., asparagus, pineapples).
8. A residue analytical method suitable for enforcement purposes is required whenever a numeric tolerance (including temporary and time-limited tolerances) is proposed.
9. New analytical methods to be used for enforcement purposes must include results from an independent laboratory validation.
10. A residue method, storage stability data, and crop field trials are required for the nonfood crop tobacco (green, freshly harvested). Depending on the level of residues found on the green tobacco, additional data may be required on cured/dried tobacco and pyrolysis products.
11. Data are required to determine whether FDA/USDA multiresidue methodology would detect and identify the pesticides and any metabolites.
12. Data are required for any magnitude of the residue study unless analytical samples are stored frozen for 30 days or less, and the active ingredient is not known to be volatile or labile.
13. Studies using single serving samples of a raw agricultural commodity may be needed for acutely toxic pesticides and/or their metabolites. These residue studies must be conducted using a statistical design accepted by the Agency.
14. Required for indoor uses which are direct postharvest treatments of raw agricultural commodities (e.g., fungicidal waxes or stored grain fumigants).
15. Data on the nature and level of residues in processed food/feed are required if residues could potentially concentrate on processing thus requiring the establishment of a separate tolerance higher than that of the raw agricultural commodity.
16. Required when the pesticide use is a direct application to livestock.
17. Data are required if pesticide residues are present in or on livestock feed items or intentionally added to drinking water. These studies, however, may not be required in cases where the livestock metabolism studies indicate negligible transfer of the pesticide's residues of concern to tissues, milk, and eggs at the maximum expected exposure level for the animals.
18. If results from the plant metabolism study show differing metabolites in plants from those found in animals, an additional livestock feeding study involving dosing with the plant metabolite(s) may also be required.
19. Data are required whenever a pesticide may be applied directly to water, unless it can be demonstrated that the treated water would not be available for human or livestock consumption.
20. Data are required when a pesticide is to be applied directly to water that could be used for irrigation or to irrigation facilities such as irrigation ditches.
21. Data are required whenever a pesticide may be used in a food handling or feed handling establishment.
22. Required when residues at the tolerance level may result in a risk of concern. These data may include washing, cooking, processing or degradation studies as well as market basket surveys for a more precise residue determination.
23. Typically required if pesticide residues of concern greater than 0.01 ppm are found in crops at the appropriate plant back intervals (taking into account plant back restrictions on product labels) in the confined rotational crop study. If residues of concern in the confined study are greater than 0.01 ppm but less than the limit of quantitation of the analytical method to be used on field trial samples, the Agency will consider not requiring, on a case-by-case basis, the limited field trials. If there are particular toxicological concerns with the parent pesticide or any metabolites, limited field studies may be needed if such residues are identified at levels below 0.01 ppm in the confined study.
24. Crop field trials are required to establish tolerances on rotational crops when quantifiable residues of concern are observed in the field rotational crops study.
25. Not required for an exemption from a tolerance provided that dietary exposure estimates are not needed due to low toxicity or that theoretical estimates of exposure are adequate to assess dietary risk.
26. Not required for an exemption from a tolerance.
Subparts P-Q [Reserved]
Subpart R—Product Performance for Products Claiming Effectiveness Against Invertebrate Pests
§158.1700 General requirements.
(a) General. Each applicant must ensure through testing that their product is efficacious when used in accordance with label directions and commonly accepted pest control practices. The Agency may require, as specified herein and on a case-by-case basis, submission of product performance data for any pesticide product registered or proposed for registration or amendment.
(1) Test substance. All product performance testing is performed using the end-use product.
(2) Test organism. All product performance testing must report the species tested.
(3) Testing. All products are to be tested to support the claim(s) made on the labeling of the pesticide product.
(4) Data requirements. To determine the specific product performance data required to support the registration of each pesticide product, the applicant must refer to the applicable sections of this subpart.
(b) Product performance data submission. Each product that bears a claim subject to this subpart, must be supported by submission of product performance data, as listed in this subpart. This product performance data must be submitted with any application for registration or amended registration. For the pest-specific claims listed in this subpart, data must be for the species specified to support the claim. For pests listed as part of a group or subgroup, pest-specific data would also need to be submitted to support a pest-specific claim.
[87 FR 22475, Apr. 15, 2022]
§158.1701 Definitions.
Definitions. The following terms are defined for purposes of this subpart.
Complete protection time (CPT) means the time from application of a skin-applied insect repellent until efficacy failure, which is described in Product Performance Test Guideline 810.3700.
Introduction means the intentional or unintentional escape, release, dissemination, or placement of a species into an ecosystem as a result of human activity.
Invasive species means with respect to a particular ecosystem, any species that is not native to that ecosystem, and whose introduction does or is likely to cause economic or environmental harm or harm to human health.
Performance standard means a benchmark or reference against which the efficacy of the pesticide is compared (including, but not limited to, the ability of the pesticide product to control, kill, or repel an invertebrate pest species).
Pest group labeling claim means a claim or statement on the labeling of the pesticide product that the product is effective against a group of related species or taxa demonstrating adequate similarity in basic biology and life history characteristics to permit identification of representative test species for the entire assemblage of taxa.
Pest-specific labeling claim means a claim or statement on the labeling of the pesticide product that the product is effective against a particular arthropod species, such as German cockroach or house fly.
Pest sub-group labeling claim means a claim or statement on the labeling of the pesticide product that the product is effective against a set of related species or taxa demonstrating adequate similarity in basic biology and life history characteristics to permit identification of representative test species and part of a larger identified taxonomic grouping (e.g., Biting flies) that includes other pest species, which may or may not have a specified pest group.
Skin-applied insect repellent means a product intended to disrupt the host-seeking behavior of insects or other arthropods, driving or keeping them away from treated human skin. The repellent product, such as a liquid, lotion, or spray, is intended to be applied directly to human skin. Efficacy of skin-applied insect repellents is expressed as complete protection time.
Species means a group of organisms all of which have a high degree of physical and genetic similarity, generally breed only among themselves, and show persistent differences from members of allied groups of organisms.
Wood-destroying applies to pests that feed on or nest in wood, and therefore are highly destructive to wood buildings or structures, and stored lumber.
Vector means any organism capable of transmitting the causative agent of human and/or animal disease, including but not limited to mosquitoes and ticks.
[87 FR 22475, Apr. 15, 2022]
§158.1703 Application categories.
The following terms are defined for purposes of this subpart.
Bait treatment means a pesticide product intended to be ingested by the target pest that kills or controls an invertebrate pest such as ants, cockroaches, or termites. This is normally through the insect feeding on the product directly, but may also include products which the target will contact and later ingest during grooming/cleaning. The attractiveness of these products is through the use of a palatable food base, however they may also incorporate an attractant (e.g., pheromone) which is intended to attract the target pests over a greater distance.
Soil-applied termiticides means pesticide products that are applied to the soil beneath and/or adjacent to the structure, pre- or post-construction, to kill or control termites. Treatments can be preventive (i.e., to provide structural protection before a termite infestation is present) or remedial (i.e., to kill and control a termite infestation when present).
Spatial repellents include treatments of both indoor and outdoor sites where the product is applied into the air rather than onto a surface or the skin in order to drive away insects or other arthropods from that space. They are intended to repel the target pest through the dispersal of pesticide into the atmosphere of a room or other open space.
Structural protection means the prevention of termite or other wood-destroying pest activity in an entire structure as the result of an application of a pesticide product.
Wood protectants and other non-structural protection means the prevention of termite or other wood-destroying pest activity only to the treated wood (or other treated material), whereas structural protectants, however applied, claim to prevent damage to the structure.
[87 FR 22475, Apr. 15, 2022]
§158.1704 Performance standards for data acceptability.
(a) General. The claim stated on the pesticide product labeling (such as knockdown, control, mortality, or repellency) determines the performance standard that must be met. In the absence of specific pest/labeling claims/performance standards specified in §§158.1708 through 158.1786, the performance standards of paragraphs (b) and (c) of this section apply.
(b) Skin-applied insect repellent labeling claims.(1) For skin-applied insect repellent labeling claims, the performance standard must be greater than or equal to 2-hours complete protection time.
(2) Any testing required under this part which involves any human subjects must comply with all applicable requirements under 40 CFR part 26. For example, 40 CFR part 26 requirements are pertinent to the part 158 testing requirement if the testing involves intentional exposure of human subjects. Protocols for such testing must be submitted to EPA for review prior to study initiation. Those protocols determined by EPA to involve intentional exposure of human subjects also require review by EPA's Human Studies Review Board (HSRB)) prior to study initiation. If you are uncertain about the applicability of the 40 CFR part 26 requirements to this 40 CFR part 158 testing requirement or uncertain about the nature of your planned testing (such as, for example, whether the testing would involve intentional exposure of human subjects or whether the testing would be an observational study), you should contact the Agency prior to initiating the testing.
(c) Labeling claims for products other than skin-applied insect repellents. Unless otherwise specified in §§158.1712 through 158.1786, a minimum performance standard of 90 percent is required, except skin-applied insect repellents as specified in paragraph (b) of this section, and non-wearable spatial repellents, where a minimum performance standard of 75 percent is required.
[87 FR 22475, Apr. 15, 2022]
§158.1705 Test guidelines.
EPA has published the Harmonized Test Guidelines, which set forth the recommended approach to generate the data required in this subpart. The Product Performance Guidelines (Series 810, Group C—Invertebrate Control Agent Test Guidelines) are available on the Agency's website. These guidelines cover some, but not all, of the tests that would be used to generate data under this subpart. In instances where there is a conflict between one of the Harmonized Test Guidelines and the provisions of this subpart, this subpart will control.
[87 FR 22475, Apr. 15, 2022]
§158.1707 Data requirement modifications.
The data requirements (including the performance standards associated with the data requirements) specified in this subpart as applicable to a category of products will not always be appropriate for every product in that category. Data requirements may, on a case-by-case basis, be modified by EPA in response to requests for novel technologies or products that have unusual physical, chemical, or biological properties or atypical use patterns which would make a particular data requirement, or data performance standard, inappropriate. Requests for such data requirement modifications must be submitted in the same manner as waiver requests submitted under 40 CFR 158.45. EPA will respond in writing to those requests. The Agency may grant the request if it finds such modifications are appropriate for the pesticide in question, and will ensure that sufficient data are available to make the determinations required by the applicable statutory standards.
[87 FR 22475, Apr. 15, 2022]
§158.1708 Invasive species claims.
(a) General. In addition to those species specified in paragraph (b) of this section, if an application for registration or amended registration requests a labeling claim for effectiveness against an invasive invertebrate species, then on a case-by-case basis, EPA may require submission of product performance data and establish performance standards for those data to support those claims for effectiveness.
(b) Specific. Applications for registration or amended registration requests for a labeling claim for the emerald ash borer, Agrilus planipennis, or Asian longhorned beetle, Anoplophora glabripennis, must be accompanied by product performance data to support those claims for effectiveness.
[87 FR 22475, Apr. 15, 2022]
§158.1709 Invertebrate disease vector claims.
If an application for registration or amended registration requests a labeling claim specific to a disease vector (such as repels mosquitoes that may carry West Nile virus), then submission of test data conducted with the species specific to the disease vector claim and meeting the specific performance standard for that species is required even if the disease vector species is not the test species required in §§158.1712 through 158.1786.
[87 FR 22475, Apr. 15, 2022]
§158.1710 Structural and wood-destroying pest claims.
If an application for registration or amended registration requests a labeling claim specific to a structural or wood-destroying pest not identified in §§158.1782 through 158.1786, EPA may require submission of product performance data, with testing on that specific pest and subject to specific performance standards, to support those claims for effectiveness.
[87 FR 22475, Apr. 15, 2022]
§158.1712 Mites (excluding chiggers).
(a) General. The tables and test notes in this section apply to dust, human itch or scabies, and dog follicle mites. The claim stated on the pesticide product labeling determines the required test species. The required test species for a specific type of mite claim appear in paragraph (b) of this section and the required performance standards appear in paragraph (c) of this section.
(b) Test species. For pesticide products making a claim against mites, the required test species appear in the following table.
| Labeling claim | Required test species |
|---|---|
| Dog Follicle Mite | Dog follicle mite (Demodex canis). |
| Dust Mite | Testing on one of the following species is required: American house dust mite (Dermatophagoides farinae) OR European house dust mite (Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus). |
| Human Itch or Scabies Mite | Human itch mite (Sarcoptes scabiei). |
(c) Performance standards.(1) For the dog follicle mite, the performance standard is 100 percent.
(2) For the human itch or scabies mite, the performance standard is 100 percent.
[87 FR 22475, Apr. 15, 2022]
§158.1714 Chiggers.
If the pesticide product labeling makes a claim against chiggers, then testing is required using the following test species: Chigger (Trombicula alfreddugesi).
[87 FR 22475, Apr. 15, 2022]
§158.1718 Ticks.
(a) General. The table and test notes in this section apply to hard ticks (including cattle ticks) and soft ticks. The claim stated on the pesticide product labeling determines the required test species. The required test species for a specific type of tick claim appear in paragraph (b) of this section. Specific parameters that apply to individual tests appear in paragraph (c) of this section. For a claim against any specific species of “ticks,” that individual species and all the listed representative species for “ticks” must be tested, but not the representative species for cattle ticks or soft ticks. Claims against ticks in association with tick borne diseases are also subject to the requirements in §158.1709.
(b) Test species. For pesticide products making a claim against ticks, the required test species appear in the following table.
| Labeling claim | Required test species |
|---|---|
| Ticks |
Testing on a total of three hard tick species is required:
Blacklegged tick (Ixodes scapularis) AND Lone star tick (Amblyomma americanum). AND One of the following three species: American dog tick (Dermacentor variabilis) OR Brown dog tick (Rhipicephalus sanguineus) OR Rocky Mountain wood tick (Dermacentor andersoni). |
| Cattle Ticks |
Testing on one of the following species is required:
Southern cattle tick (Rhipicephalus microplus) OR Cattle fever tick (Rhipicephalus annulatus). |
| Soft Ticks | Soft tick (Ornithodoros hermsi). |
(c) Specific parameters. The following parameters are required.
1. For products applied to dogs, testing is required on three species: Blacklegged tick (Ixodes scapularis), American dog tick (Dermacentor variabilis), and Brown dog tick (Rhipicephalus sanguineus).
2. For products applied to cats, testing is required on three species: Blacklegged tick (Ixodes scapularis), Lone star tick (Amblyomma americanum), and American dog tick (Dermacentor variabilis).
[87 FR 22475, Apr. 15, 2022]
§158.1722 Scorpions.
If the pesticide product labeling makes a claim against scorpions, then testing is required using one of the following test species: Striped bark scorpion (Centruroides vittatus) or Arizona bark scorpion (Centrurioides sculpturatus).
[87 FR 22475, Apr. 15, 2022]
§158.1726 Spiders.
(a) General. The table in this section applies to spiders. The product labeling claim determines the required test species. The required test species for spider labeling claims appear in paragraph (b) of this section.
(b) Test species. For products making a claim against spiders, the test species for labeling claims appear in the following table.
| Labeling claim | Required test species |
|---|---|
| Pest Group Claim | |
| Spiders |
Testing on two species is required:
Brown recluse spider (Loxosceles reclusa). AND One of the following species is required: Northern black widow spider (Latrodectus variolus) OR Southern black widow spider (Latrodectus mactans) OR Western black widow spider (Latrodectus hesperus). |
| Pest Sub-Group Claims | |
| Black Widow Spiders |
Testing on one of the following species is required: Northern black widow spider (Latrodectus variolus) OR Southern black widow spider (Latrodectus mactans) OR Western black widow spider (Latrodectus hesperus). |
| Pest-Specific Claims | |
| Brown recluse spider | Brown recluse spider (Loxosceles reclusa). |
| Brown widow spider | Brown widow spider (Latrodectus geometricus). |
| Northern black widow spider | Northern black widow spider (Latrodectus variolus). |
| Southern black widow spider | Southern black widow spider (Latrodectus mactans). |
| Western black widow spider | Western black widow spider (Latrodectus hesperus). |
[87 FR 22475, Apr. 15, 2022]
§158.1732 Centipedes.
(a) General. The table in this section applies to centipedes. The product labeling claim determines the required test species. The required test species for a labeling claim appears in paragraph (b) of the section.
(b) Test species. For products making a claim against centipedes, the required test species for a labeling claim is set forth in the following table.
| Labeling claim | Required test species |
|---|---|
| Centipedes |
Testing on one of the following species is required: House centipede (Scutigera coleoptrata) OR Florida blue centipede (Hemiscolopendra marginata) OR Scolopendra sp. |
[87 FR 22475, Apr. 15, 2022]
§158.1736 Lice.
(a) General. The table in this section applies to human lice. The product labeling claim determines the required test species. The required test species for a labeling claim appears in paragraph (b) of this section. The required performance standards appear in paragraph (c) of this section.
(b) Test species. For products making a claim against lice, the required test species for a labeling claim appear in the following table.
| Labeling claim | Required test species |
|---|---|
| Lice |
Testing on one of the following species is required: Head louse (Pediculus humanus capitis) OR Body louse (Pediculus humanus humanus). |
(c) Performance standards. For labeling claims against lice, a performance standard of 100 percent is required.
[87 FR 22475, Apr. 15, 2022]
§158.1740 Fleas.
(a) General. The table in this section applies to fleas. The product labeling claim determines the required test species. The required test species for a labeling claim appears in paragraph (b) of this section.
(b) Test species. For products making a claim against fleas, the required test species for a labeling claim is set forth in the following table.
| Labeling claim | Required test species |
|---|---|
| Pest Group Claim | |
| Fleas |
Testing on the following species is required:
Cat flea (Ctenocephalides felis). |
| Pest-Specific Claims | |
| Cat flea | Cat flea (Ctenocephalides felis). |
| Chigoe flea | Chigoe flea (Tunga penetrans). |
| Dog flea | Dog Flea (Ctenocephalides canis). |
| Hen flea | Hen flea (Ceratophyllus gallinae). |
| Human flea | Human flea (Pulex irritans). |
| Oriental rat flea | Oriental rat flea (Xenopsylla cheopis). |
[87 FR 22475, Apr. 15, 2022]
§158.1744 Cockroaches.
(a) General. The table in this section applies to cockroaches. The product labeling claim determines the required test species. The required test species for a labeling claim appears in paragraph (b) of this section.
(b) Test species. For products making a claim against cockroaches, the required test species for a labeling claim for cockroaches and the test species for pest-specific label claims appear in the following table.
| Labeling claim | Required test species |
|---|---|
| Pest Group Claims | |
| Cockroaches |
Testing on two species is required:
American cockroach (Periplaneta americana) AND German cockroach (Blattella germanica). |
| Pest-Specific Claims | |
| American cockroach | American cockroach (Periplaneta americana). |
| Australian cockroach | Australian cockroach (Periplaneta australasiae). |
| Brown cockroach | Brown cockroach (Periplaneta brunnea). |
| Brownbanded cockroach | Brownbanded cockroach (Supella longipalpa). |
| German cockroach | German cockroach (Blattella germanica). |
| Oriental cockroach | Oriental cockroach (Blatta orientalis). |
| Smokybrown cockroach | Smokybrown cockroach (Periplaneta fuliginosa). |
| Turkestan cockroach | Turkestan cockroach (Blatta lateralis). |
[87 FR 22475, Apr. 15, 2022]
§158.1748 Keds, screwworms, and bot flies.
(a) General. The table in this section applies to keds, screwworms, and bot flies. The product labeling claim determines the required test species. The required test species for labeling claims appear in paragraph (b) of this section.
(b) Test species. For products making a claim against keds, screwworms, and bot flies, the required test species for a labeling claim appear in the following table.
| Labeling claim | Required test species |
|---|---|
| Bot Flies (excluding Human bot fly) |
Testing is required on one of the following species:
Horse bot fly (Gasterophilus intestinalis) OR Throat bot fly (Gasterophilus nasalis) OR Nose bot fly (Gasterophilus haemorrhoidalis). |
| Human bot fly | Human bot fly (Dermatobia hominis). |
| Keds |
Testing is required on the following species:
Sheep ked (Melophagus ovinus). |
| Screwworms |
Testing is required on one of the following species:
Screwworm (Cochliomyia hominivorax) OR Secondary screwworm (Cochliomyia macellaria). |
[87 FR 22475, Apr. 15, 2022]
§158.1752 Flies.
(a) General. The table in this section applies to flies. The product labeling claim determines the required test species. The required test species for a labeling claim against flies appear in paragraph (b) of this section.
(b) Test species. For products making a claim against flies, the required test species for a labeling claim against flies appear in the following table.
| Labeling claim | Required test species |
|---|---|
| Pest Group Claim | |
| Flies |
Testing of five species is required:
House fly (Musca domestica) AND Flesh fly (Sarcophaga sp., Wohlfahrtia sp., and other genera of flesh flies) OR Blow fly (Phaenicia sp., Calliphora sp., and other genera of blow flies) AND Stable fly (Stomoxys calcitrans) AND Biting midge (punkie, granny nipper, no-see-um) (any Culicoides sp.) OR Black fly (any Simulium sp. or Prosimulium sp.) OR Black gnat (any Leptoconops sp.) AND Black horse fly (Tabanus atratus) OR Deer fly (Chrysops sp.) OR Striped horse fly (Tabanus lineola). |
| Pest Sub-Group Claims | |
| Filth Flies |
Testing on two species is required:
House fly (Musca domestica). AND One of the following species is required: Flesh fly (Sarcophaga sp., Wohlfahrtia sp., and other genera of flesh flies) OR Blow fly (Phaenicia sp., Calliphora sp., and other genera of blow flies). |
| Biting flies (excluding Sand flies) |
Testing is required on three species:
Stable fly (Stomoxys calcitrans) AND one of the large biting fly species: Black horse fly (Tabanus atratus) OR Deer fly (Chrysops sp.) OR Striped horse fly (Tabanus lineola). AND one of the small biting fly species: Biting midge (punkie, granny nipper, no-see-um) (any Culicoides sp.) OR Black fly (any Simulium sp. or Prosimulium sp.) OR Black gnat (any Leptoconops sp.). |
| Large Biting Flies |
Testing is required on two species:
Stable fly (Stomoxys calcitrans). AND one of the following species: Black horse fly (Tabanus atratus) OR Deer fly (Chrysops sp.) OR Striped horse fly (Tabanus lineola). |
| Small Biting Flies (excluding Sand flies) | Testing is required on one of the following species: Biting midge (punkie, granny nipper, no-see-um) (Culicoides sp.) OR Black fly (Simulium sp. OR Prosimulium sp.) OR Black gnat (Leptoconops sp.). |
| Pest-Specific Claims | |
| Blow fly | Blow fly (Phaenicia sp., Calliphora sp., and other genera of blow flies). |
| Cluster fly | Cluster fly (Pollenia rudis). |
| Face fly | Face fly (Musca autumnalis). |
| Flesh fly | Flesh fly (Sarcophaga sp., Wohlfahrtia sp., and other genera of flesh flies). |
| House fly | House fly (Musca domestica). |
| Little house fly | Little house fly (Fannia canicularis). |
| Biting midges (punkie, granny nipper, no-see-um) | Biting midge (punkie, granny nipper, no-see-um) (Culicoides sp.). |
| Black flies | Testing on one of the following species is required: Simulium sp. OR Prosimulium sp. |
| Black gnats | Black gnat (Leptoconops sp.). |
| Deer flies | Deer fly (Chrysops sp.). |
| Greenhead | Greenhead (Tabanus nigrovittatus). |
| Horn fly | Horn fly (Haematobia irritans). |
| Horse flies | Testing on one of the following species is required: Black horse fly (Tabanus atratus), OR Striped horse fly (Tabanus lineola). |
| Sand flies | Testing on one of the following species is required: Lutzomyia sp. OR Phlebotomus sp. |
| Stable fly | Stable fly (Stomoxys calcitrans). |
[87 FR 22475, Apr. 15, 2022]
§158.1756 Mosquitoes.
(a) General. The tables and test notes in this section apply to mosquitoes. The required test species for a labeling claim against mosquitoes appears in paragraph (b) of this section. For a claim against any specific species of mosquito, that individual species and all the required test genera must be tested. Claims against mosquitos in association with mosquito-borne diseases are also subject to the requirements in §158.1709.
(b) Test species. For products making a claim against mosquitoes, the required test species for a labeling claim is set forth in the following table.
| Labeling claim | Required test species |
|---|---|
| Mosquitoes | Testing in three genera (Culex, Aedes, and Anopheles) of mosquitoes is required. |
| One of the following Culex species: Culex pipiens OR Culex quinquefasciatus OR Culex tarsalis. | |
| AND one of the following Aedes species: Aedes aegypti OR Aedes albopictus. | |
| AND one of the following Anopheles species: Anopheles albimanus OR Anopheles freeborni OR Anopheles gambiae OR Anopheles hermsi OR Anopheles punctipennis OR Anopheles quadrimaculatus OR Anopheles stephensi. |
[87 FR 22475, Apr. 15, 2022]
§158.1768 Bed bugs.
(a) General. The table in this section applies to bed bugs. The product labeling claim determines the required test species. The required test species for a labeling claim appears in paragraph (b) of this section.
(b) Test species. For products making a claim against bed bugs, the required test species for a labeling claim appear in the following table.
| Labeling claim | Required test species |
|---|---|
| Pest Group Claim | |
| Bed bugs | Common bed bug (Cimex lectularius). |
| Pest-Specific Claims | |
| Common bed bug | Common bed bug (Cimex lectularius). |
| Tropical bed bug | Tropical bed bug (Cimex hemipterus). |
[87 FR 22475, Apr. 15, 2022]
§158.1772 Conenose bugs and kissing bugs.
(a) General. The table in this section applies to Conenose bugs and Kissing bugs. The product labeling claim determines the required test species. The required test species for a labeling claim appears in paragraph (b) of this section.
(b) Test species. For products making a claim against either the conenose and/or kissing bugs, the required test species for a labeling claim is set forth in the following table.
| Labeling claim | Required test species |
|---|---|
| Conenose bug | Conenose bug (Triatoma sanguisuga). |
| Kissing bug | Kissing bug (Triatoma protracta). |
[87 FR 22475, Apr. 15, 2022]
§158.1776 Ants (excluding carpenter ants).
(a) General. The table in this section applies to ants (excluding carpenter ants). The product labeling claim determines the required test species. The required test species for labeling claims appear in paragraph (b) of this section.
(b) Test species. For products making a claim against ants (excluding carpenter ants), the required test species for a labeling claim appear in the following table, unless otherwise specified in paragraphs (c) or (d) of this section. The group and sub-group claims in this paragraph are for direct kill and residual surface application claims against foraging ants only (excluding colony claims).
| Labeling claim | Required test species |
|---|---|
| Pest Group Claim | |
| Ants (excluding carpenter ants) |
Testing is required on the following two species: Pharaoh ant (Monomorium pharaonis) AND Red imported fire ant (Solenopsis invicta). |
| Pest Sub-Group Claim | |
| Fire and Harvester |
Testing is required on the following species: Red imported fire ant (Solenopsis invicta). |
| Fire ants |
Testing is required on the following species: Red imported fire ant (Solenopsis invicta). |
| Pest-Specific Claims | |
| European fire ant | European fire ant (Myrmica rubra). |
| Harvester ant | Harvester ant (Pogonomyrmex sp.). |
| Pharaoh ant | Pharaoh ant (Monomorium pharaonis). |
| Red imported fire ant | Red imported fire ant (Solenopsis invicta). |
| Southern fire ant | Southern fire ant (Solenopsis xyloni). |
| Tropical fire ant | Tropical fire ant (Solenopsis geminata). |
| Black imported fire ant | Black imported fire ant (Solenopsis richteri). |
(c) Colony Claims. For colony claims, testing must be done for each species listed or each representative species, in the case of a group. For colony claims against the red and/or black imported fire ants, testing may be done on, S. invicta, S. richteri, or their hybrid.
(d) Bait products or claims involving outdoor use. The group and sub-group claims in paragraph (b) of this section are for direct kill and residual surface application claims against foraging ants only (excluding colony claims). For bait products or claims involving outdoor use, testing must be specific to the species listed or each representative species, in the case of a group.
[87 FR 22475, Apr. 15, 2022]
§158.1780 Bees, wasps, yellowjackets, and hornets.
(a) General. The table in this section applies to bees, wasps, yellowjackets, and hornets. The labeling claim determines the required test species. The required test species for labeling claims appear in paragraph (b) of this section.
(b) Test species. For products making a claim against bees, wasps, yellowjackets, and hornets, the required test species for a labeling claim appear in the following table, unless otherwise specified in paragraph (c) of this section.
| Labeling claim | Required test species |
|---|---|
| Pest Group Claims | |
| Bees, Wasps, Yellowjackets, and Hornets |
Testing on three species is required:
Two Yellowjacket species (one Vespula sp. AND the Bald-faced hornet (Dolichovespula maculata)) AND one Paper wasp (Polistes sp.). |
| Pest-Specific Claims | |
| Bald-faced hornet | Bald-faced hornet (Dolichovespula maculata). |
| Mud dauber wasp | Mud dauber wasp (Sphecidae sp.). |
| Paper wasp | Paper wasp (Polistes sp.). |
| Yellowjackets | Yellowjacket (Vespula sp.). |
(c) Colony claims. For colony claims, except Vespula spp., testing must be specific to the species listed. Acceptable data for any Vespula species may support a yellowjacket colony claim for ground nesting Vespula species; however, species-specific claims need to be supported by data from testing of the specific species. Colony claims have a performance standard of 100%.
[87 FR 22475, Apr. 15, 2022]
§158.1782 Carpenter ants.
(a) General. The table in this section applies to carpenter ants. The product labeling claim determines the required test species. The required test species for labeling claims appear in paragraph (b) of this section. The required performance standards appear in paragraph (c) of this section.
(b) Test species. For products making a claim against carpenter ants, the required test species for a labeling claim appear in the following table. The group and sub-group claims in this paragraph are for direct kill and residual surface application claims against foraging ants only (excluding colony claims).
| Labeling claim | Required test species |
|---|---|
| Carpenter ants |
Testing on one of the following carpenter ant species is required:
Black carpenter ant (Camponotus pennsylvanicus) OR Florida carpenter ant (Camponotus floridanus) OR Western carpenter ant (Camponotus modoc). |
(c) Performance standards. The performance standards for pesticide products making certain claims against carpenter ants appear in the following table and in paragraphs (d) and (e)of this section. The performance standards for labeling claims not covered in this section appear in §158.1704.
| Claim category | Performance standard |
|---|---|
| Non-Structural Protection: Wood Preservative Treatment | 100% prevention of damage to wood for ≥2 years. |
| Structural Protection, except Baits | 95% prevention of damage to wood ≥5 years. |
| Structural Protection: Bait Treatment | 95% prevention of damage to wood ≥3 years. |
(d) Colony Claims. For colony claims, testing must be done for each species listed or each representative species, in the case of a group.
(e) Bait products or claims involving outdoor use. The group and sub-group claims in paragraph (b) of this section are for direct kill and residual surface application claims against foraging ants only (excluding colony claims). For bait products or claims involving outdoor use, testing must be specific to the species listed or each representative species, in the case of a group.
[87 FR 22475, Apr. 15, 2022]
§158.1784 Wood-destroying beetles.
(a) General. The tables and test notes in this section apply to wood-destroying beetles. The labeling claim determines the required test species. The required test species for a labeling claim appears in paragraph (b) of this section. The required performance standards appear in paragraph (c) of this section.
(b) Test species. For products making a claim against wood-destroying beetles, the required test species for a labeling claim is set forth in the following table.
| Labeling claim | Required test species |
|---|---|
| True powderpost beetles | Testing on one species from the Lyctinae subfamily is required. |
| Wood-destroying or wood-boring beetles | Testing on three species is required: Anobiid beetle (Anobiidae sp.) AND Bostrichid beetle (Bostrichidae sp.) AND Old house borer (Hylotrupes bajulus/8). |
(c) Performance standards. The performance standards for pesticide products making certain claims against wood-destroying beetles appear in the following table. The performance standards for labeling claims that are not specifically provided in the following table appear in §158.1704.
| Claim category | Performance standard |
|---|---|
| Non-Structural Protection: Wood Preservative Treatment | 100% prevention of damage to wood for ≥2 years. |
| Structural Protection, except Baits | 95% prevention of damage to wood ≥5 years. |
| Structural Protection: Bait Treatment | 95% prevention of damage to wood ≥3 years. |
[87 FR 22475, Apr. 15, 2022]
§158.1786 Termites.
(a) General. The tables and test notes in this section apply to the subterranean termite, desert subterranean termite, Formosan subterranean termite, drywood termite, and dampwood termite. The labeling claim determines the required test species. The required test species for labeling claims appear in paragraph (b) of this section. The required performance standards appear in paragraph (c) of this section.
(b) Test species. For products making a claim against termites, the required test species for a labeling claim appear in the following table. For the structural protection and wood preservative claim categories, a claim against any specific genus of subterranean termite must be supported by data on that individual genus and all the required test genera for a subterranean termite claim must be tested and submitted.
| Labeling claim | Required test species |
|---|---|
| Pest Group Claim | |
| Termites |
Testing on species from four genera of termites is required:
Testing is required on the following Coptotermes termite: Coptotermes formosanus AND one of the following Reticulitermes species: Reticulitermes flavipes OR Reticulitermes hesperus OR Reticulitermes virginicus AND one of the following arboreal termite species: Nasutitermes corniger AND one of the following drywood termite species: Cryptotermes brevis OR Cryptotermes cavifrons OR Incisitermes minor OR Incisitermes snyderi. |
| Pest Sub-Group Claim | |
| Arboreal Termites |
Testing of one arboreal termite species is required:
Nasutitermes corniger. |
| Dampwood Termites |
Testing of the following dampwood termite is required:
Zootermopsis sp. |
| Drywood Termites |
Testing of one of the following drywood termites is required:
Cryptotermes brevis OR Cryptotermes cavifrons OR Incisitermes minor OR Incisitermes snyderi. |
| Subterranean Termites, including Formosan Subterranean Termites | Testing in two genera of termites is required: Testing on the following Coptotermes species is required: Coptotermes formosanus AND one of the following Reticulitermes species: Reticulitermes flavipes OR Reticulitermes hesperus OR Reticulitermes virginicus. |
(c) Performance standards. The performance standards for pesticide products making certain claims against termites appear in the following table. The performance standards for labeling claims not provided in the following table appear in §158.1704.
| Claim category | Performance standard |
|---|---|
| Non-Structural Protection: Wood Preservative Treatment | 100% prevention of damage to wood for ≥2 years. |
| Structural Protection, except Baits | 95% prevention of damage to wood ≥5 years. |
| Structural Protection: Bait Treatment | 95% prevention of damage to wood ≥3 years. |
[87 FR 22475, Apr. 15, 2022]
Subparts S-T [Reserved]
§§ 158.1500-158.1900 [Reserved]
Subpart U - Biochemical Pesticides
§158.2000 Biochemical pesticides definition and applicability.
This subpart applies to all biochemical pesticides as defined in paragraphs (a), (b), and (c) of this section.
(a) Definitions. The following terms are defined for the purposes of subpart U of this part.
(1) A biochemical pesticide is a pesticide that:
(i) Is a naturally-occurring substance or structurally-similar and functionally identical to a naturally-occurring substance;
(ii) Has a history of exposure to humans and the environment demonstrating minimal toxicity, or in the case of a synthetically-derived biochemical pesticides, is equivalent to a naturally-occurring substance that has such a history; and
(iii) Has a non-toxic mode of action to the target pest(s).
(2) A Pheromone is a compound produced by a living organism or is a synthetically derived substance that is structurally similar and functionally identical to a naturally-occurring pheromone, which, alone or in combination with other such compounds, modifies the behavior of other individuals of the same species.
(i) An Arthropod Pheromone is a pheromone produced by a member of the taxonomic phylum Arthropoda.
(ii) A Lepidopteran Pheromone is an arthropod pheromone produced by a member of the insect order Lepidoptera.
(iii) A Straight Chain Lepidopteran Pheromone is a lepidopteran pheromone consisting of an unbranched aliphatic chain (between 9 and 18 carbons) ending in an alcohol, aldehyde, or acetate functional group and containing up to three double bonds in the aliphatic backbone.
(b) Examples. Biochemical pesticides include, but are not limited to:
(1) Semiochemicals (insect pheromones and kairomones),
(2) Natural plant and insect regulators,
(3) Naturally-occurring repellents and attractants, and
(4) Enzymes.
(c) Applicability. The Agency may review, on a case-by-case basis, naturally-occurring pesticides that do not clearly meet the definition of a biochemical pesticide in an effort to ensure, to the greatest extent possible, that only the minimum testing sufficient to make scientifically sound regulatory decisions would be conducted. The Agency will review applications for registration of naturally-occurring pesticides to determine whether to review the pesticide under this subpart U.
§158.2010 Biochemical pesticides data requirements.
(a) Sections 158.2030 through 158.2070 identify the data requirements that are required to support registration of biochemical pesticides. Sections 158.2080 through 158.2084 identify the data requirements that are required to support Experimental Use Permits (EUPs). Variations in the test conditions are identified within the test notes. Definitions that apply to all biochemical data requirements can be found in §158.2000.
(b) Each data table includes “use patterns” under which the individual data are required, with variations including food and nonfood uses for terrestrial and aquatic applications, greenhouse, indoor, forestry, and residential outdoor applications under certain circumstances.
(c) The categories for each data requirement are “R”, which stands for required, and “CR” which stands for conditionally required. Generally, “R” indicates that the data are more likely required than for those data requirements with “CR.” However, in each case, the regulatory text preceding the data table and the test notes following the data table must be used to determine whether the data requirement must be satisfied.
(d) Each table identifies the test substance that is required to be tested to satisfy the data requirement. Test substances may include: technical grade active ingredient (TGAI), manufacturing-use product (MP), end-use product (EP), typical end-use product (TEP), residue of concern, and pure active ingredient (PAI) or all of the above (All). Commas between the test substances (i.e., TGAI, EP) indicate that data may be required on the TGAI or EP or both depending on the conditions set forth in the test note.
(e) The data requirements are organized into a tier-testing system with specified additional studies at higher tiers being required if warranted by adverse effects observed in lower tier studies. The lower tier studies are a subset of those required for conventional pesticides, and the studies overall are generally selected from those required for conventional pesticides.
(f) Two sets of guideline numbers are provided for some of the environmental fate data requirements. For ease of understanding, the current guidelines will be used as an interim measure until the new guidelines (in parentheses) are finalized.
§158.2030 Biochemical pesticides product chemistry data requirements table.
(a) General.(1) Sections 158.100 through 158.130 describe how to use this table to determine the product chemistry data requirements for a particular pesticide product. Notes that apply to an individual test and include specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions to the designated test are listed in paragraph (e) of the section.
(2) Definitions in §158.300 apply to data requirements in this section.
(b) Use patterns. Product chemistry data are required for all pesticide products and are not use specific.
(c) Key. R = Required; CR = Conditionally required; NR = Not required; MP = Manufacturing-use product; EP = End-use product; TEP = Typical end-use product; TGAI = Technical grade of the active ingredient; Residue of concern = the active ingredient and its metabolites, degradates, and impurities of toxicological concern; All = All of the above.
(d) Table. The following table shows the data requirements for biochemical pesticides product chemistry. The test notes are shown in paragraph (e) of this section.
| Guideline Number | Data Requirement | All Use Patterns | Test Substance | Test Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MP | EP | ||||
| Product Identity and Composition | |||||
| 880.1100 | Product identity and composition | R | TGAI, MP | TGAI, EP | 1, 2 |
| 880.1200 | Description of starting materials, production and formulation process | R | TGAI, MP | TGAI, EP | 2, 3 |
| 880.1400 | Discussion of formation of impurities | R | TGAI and MP | TGAI and EP | 4 |
| Analysis and Certified Limits | |||||
| 830.1700 | Preliminary analysis | CR | TGAI and MP | TGAI and EP | 5, 8 |
| 830.1750 | Certified limits | R | MP | EP | 6 |
| 830.1800 | Enforcement analytical method | R | MP | EP | 7 |
| Physical and Chemical Characteristics | |||||
| 830.6302 | Color | R | TGAI | TGAI | 8 |
| 830.6303 | Physical state | R | TGAI and MP | TGAI and EP | 8 |
| 830.6304 | Odor | R | TGAI | TGAI | 8 |
| 830.6313 | Stability to normal and elevated temperatures, metals and metal ions | R | TGAI | TGAI | 8, 17 |
| 830.6315 | Flammability | CR | MP | EP | 9 |
| 830.6317 | Storage stability | R | MP | EP | -- |
| 830.6319 | Miscibility | CR | MP | EP | 10 |
| 830.6320 | Corrosion characteristics | R | MP | EP | -- |
| 830.7000 | pH | CR | TGAI and MP | TGAI and EP | 8, 11 |
| 830.7050 | UV/Visible light absorption | R | TGAI | TGAI | -- |
| 830.7100 | Viscosity | CR | MP | EP | 12 |
| 830.7200 | Melting point/melting range | CR | TGAI | TGAI | 8, 13 |
| 830.7220 | Boiling point/boiling range | CR | TGAI | TGAI | 8, 14 |
| 830.7300 | Density/relative density/bulk density | R | TGAI and MP | TGAI and EP | 8, 18 |
| 830.7520 | Particle size, fiber length, and diameter distribution | CR | TGAI | TGAI | 8, 15 |
| 830.7550
830.7560 830.7570 | Partition coefficient (n-Octanol /Water) | CR | TGAI | TGAI | 16 |
| 830.7840 | Water solubility | R | TGAI | TGAI | 8 |
| 830.7950 | Vapor pressure | R | TGAI | TGAI | 8, 19 |
(e) Test notes. The following test notes are applicable to the data requirements for biochemical pesticides product chemistry and are referenced in the last column of the table in paragraph (d) of this section.
1. Data must be provided in accordance with §158.320.
2. If the MP and EP are produced by an integrated formulation system (non-registered source), these data are also required on TGAI.
3. Data must be provided in accordance with §§158.325, 158.330, and §158.335.
4. Data must be provided in accordance with §158.340.
5. Data must be provided in accordance with §158.345. Also, required to support the registration of each manufacturing-use product (including registered TGAIs) and end-use products produced by an integrated formulation system. Data on other end-use products would be required on a case-by-case basis.
6. Data must be provided in accordance with §158.350.
7. Data must be provided in accordance with §158.355.
8. If the TGAI cannot be isolated, data are required on the practical equivalent of the TGAI. EP testing may also be appropriate.
9. Required if the product contains combustible liquids.
10. Required if the product is an emulsifiable liquid and is to be diluted with petroleum solvents.
11. Required if the test substance is soluble or dispersible in water.
12. Required if the product is a liquid.
13. Required when the technical chemical is a solid at room temperature.
14. Required when the technical chemical is a liquid at room temperature.
15. Required for water insoluble test substances (>10−6g/l) and fibrous test substances with diameter ≥0.1 µm.
16. Required for organic chemicals unless they dissociate in water or are partially or completely soluble in water.
17. Data on the stability to metals and metal ions is required only if the active ingredient is expected to come in contact with either material during storage.
18. True density or specific density are required for all test substances. Data on bulk density is required for MPs or EPs that are solid at room temperature.
19. Not required for salts.
§158.2040 Biochemical pesticides residue data requirements table.
(a) General. Sections 158.100 through 158.130 describe how to use this table to determine the biochemical pesticides residue data requirements for a particular pesticide product and the substance that needs to be tested. These data requirements apply to all biochemical pesticides, i.e., naturally occurring insect repellents and attractants, semiochemicals (e.g., insect pheromones), natural and plant growth regulators. Notes that apply to an individual test and include specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions to the designated test are listed in paragraph (e) of this section.
(b) Use patterns.(1) Data are required or conditionally required for all pesticides used in or on food and for residential outdoor uses where food crops are grown. Food use patterns include products classified under the general use patterns of terrestrial food crop use, terrestrial feed crop use, aquatic food crop use, greenhouse food crop use, and indoor food use. Data are also conditionally required for aquatic nonfood use if there is direct application to water that could subsequently result in exposure to food.
(2) Data are conditionally required for nonfood uses if pesticide residues may occur in food or feed as a result of the use. Data requirements for these nonfood uses would be determined on a case-by-case basis. For example, most products used in or near kitchens require residue data for risk assessment purposes even though tolerances may not be necessary in all cases.
(c) Key. R = Required; CR = Conditionally required; NR = Not required; MP = Manufacturing end-use product; EP = End-use product; TEP = Typical end-use product; TGAI = Technical grade of the active ingredient; Residue of concern = the active ingredient and its metabolites, degradates, and impurities of toxicological concern; All = All of the above. Specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions to the designated test procedures appear in paragraph (e) of this section, and apply to the individual tests in the following table:
(d) Data requirements table. The following table shows the data requirements for biochemical pesticides residue. The test notes are shown in paragraph (e) of this section.
| Guideline Number | Data Requirement | Use Patterns | Test Substance | Test Notes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Terrestrial | Aquatic | Greenhouse Food | Indoor Food | ||||
| Food/Feed | Food | ||||||
| Supporting Information | |||||||
| 860.1100 | Chemical identity | CR | CR | CR | CR | TGAI | 1, 2, 4 |
| 860.1200 | Directions for use | CR | CR | CR | CR | -- | 1, 3, 4 |
| Nature of the Residue | |||||||
| 860.1300 | Nature of the residue in plants | CR | CR | CR | CR | TGAI | 1, 4, 5, 6 |
| 860.1300 | Nature of the residue in livestock | CR | CR | CR | CR | TGAI or plant metabolite | 1, 7, 8, 10, 13 |
| 860.1340 | Residue analytical method | CR | CR | R | CR | Residue of concern | 4, 9, 10 |
| 860.1360 | Multiresidue method | CR | CR | R | CR | Residue of concern | 10, 11 |
| Magnitude of the Residue | |||||||
| 860.1400 | Potable water | NR | CR | NR | NR | TGAI | 1, 12 |
| 860.1400 | Fish | NR | CR | NR | NR | TGAI | 1, 13 |
| 860.1400 | Irrigated crops | NR | CR | NR | NR | TGAI | 1, 14 |
| 860.1460 | Food handling | NR | NR | NR | CR | TGAI | 1, 15 |
| 860.1480 | Meat/milk/poultry/eggs | CR | CR | CR | CR | TGAI or plant metabolites | 1, 7, 8, 10 |
| 860.1500 | Crop field trials | CR | CR | CR | CR | TEP | 1, 3, 4 |
| 860.1520 | Processed food/feed | CR | CR | CR | CR | TEP | 1, 16 |
| 860.1540 | Anticipated residues | CR | CR | CR | CR | Residue of concern | 1, 10, 17 |
| 860.1550 | Proposed tolerances | CR | CR | CR | CR | -- | 1, 18 |
| 860.1560 | Reasonable grounds in support of the petition | CR | CR | CR | CR | -- | 1, 10 |
| 860.1650 | Submittal of analytical reference standards | CR | CR | CR | CR | TGAI and residue of concern | 10, 19 |
(e) Test notes. The following test notes are applicable to the data requirements for biochemical pesticides product chemistry and are in the last column of the table contained in paragraph (d) of this section.
1. Residue chemistry data requirements apply to biochemical pesticide products when Tier II or Tier III toxicology data are required, as specified for biochemical agents in the biochemical human health assessment data requirements, §158.2050.
2. The same chemical identity data are required for biochemical product chemistry data requirements, §158.2030, with an emphasis on impurities.
3. Required information includes crops to be treated, rate of application, number and timing of applications, preharvest intervals, and relevant restrictions.
4. Required for residential outdoor uses on food crops if the corresponding agricultural use is not approved or the residential use is expected to produce higher residues based on the label directions.
5. Required unless it is an arthropod pheromone applied at a rate less than or equal to 150 grams active ingredient per acre.
6. Required for indoor uses where the pesticide is applied directly to food, in order to determine metabolites and/or degradates. Not required when only indirect contact with food would occur (e.g., crack and crevice treatments).
7. Required when a pesticide is to be applied directly to livestock, to livestock premises, to livestock drinking water, or to crops used for livestock feed.
8. If results from the plant metabolism study show differing metabolites in plants from those found in animals, an additional livestock metabolism study involving dosing with the plant metabolite(s) may also be required.
9. A residue analytical method suitable for enforcement of tolerances is required whenever a numeric tolerance (including temporary and time-limited tolerances) is proposed.
10. Required if indoor use could result in pesticide residues in or on food or feed.
11. Data are required to determine whether FDA/USDA multiresidue methodology would detect and identify the pesticides and any metabolites.
12. Data are required whenever a pesticide may be applied directly to water, unless it can be demonstrated that the treated water would not be available for human or livestock consumption.
13. Data on fish are required for all pesticides applied directly to water inhabited, or which will be inhabited by fish that may be caught or harvested for human consumption.
14. Data are required when a pesticide is to be applied directly to water that could be used for irrigation or to irrigation facilities such as irrigation ditches.
15. Data are required whenever a pesticide may be used in food/feed handling establishments.
16. Data on the nature and level of residue in processed food/feed are required when detectible residues could potentially concentrate on processing thus requiring the establishment of a separate tolerance higher than that of the raw agricultural commodity.
17. Required when residues at the tolerance level may result in risk of concern. These data may include washing, cooking, processing, or degradation studies as well as market basket surveys for a more precise residue determination.
18. The proposed tolerance must reflect the maximum residue likely to occur in crops, in meat, milk, poultry, or eggs.
19. Required when a residue analytical method is required.
§158.2050 Biochemical pesticides human health assessment data requirements table.
(a) General.(1) Sections 158.100 through 158.130 describe how to use this table to determine the biochemical human health assessment data requirements for a particular biochemical pesticide product.
(2) The data in this section are not required for straight chain lepidopteran pheromones when applied up to a maximum use rate of 150 grams active ingredient/acre/year.
(b) Use patterns.(1) Food use patterns, in general, include products classified under the following general uses: terrestrial food crop use; terrestrial feed crop use; aquatic food crop use; greenhouse food crop use.
(2) Nonfood use patterns include products classified under the general use patterns of terrestrial nonfood crop use; aquatic nonfood residential use; aquatic nonfood outdoor use; aquatic nonfood industrial use; greenhouse nonfood crop use; forestry use; residential outdoor use; residential indoor use; indoor food use; indoor nonfood use; indoor medical use.
(c) Key. R = Required; CR = Conditionally required; NR = Not required; MP = Manufacturing-use product; EP = End-use product; TEP = Typical end-use product; TGAI = Technical grade of the active ingredient; Residue of concern = the active ingredient and its metabolites, degradates, and impurities of toxicological concern; All = All of the above. Specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions to the designated test procedures appear in paragraph (e) of this section, and apply to the individual tests in the following table:
(d) Table. The following table shows the data requirements for biochemical pesticides human health assessment. The test notes are shown in paragraph (e) of this section.
| Guideline Number | Data Requirement | Use Patterns | Test Substance | Test Notes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Food | Nonfood | MP | EP | |||
| Tier I | ||||||
| Acute Testing | ||||||
| 870.1100 | Acute oral toxicity - rat | R | R | TGAI and MP | TGAI and EP | 1 |
| 870.1200 | Acute dermal toxicity | R | R | TGAI and MP | TGAI and EP | 1, 2 |
| 870.1300 | Acute inhalation toxicity - rat | R | R | TGAI and MP | TGAI and EP | 3 |
| 870.2400 | Primary eye irritation - rabbit | R | R | TGAI and MP | TGAI and EP | 2 |
| 870.2500 | Primary dermal irritation | R | R | TGAI and MP | TGAI and EP | 1, 2 |
| 870.2600 | Dermal sensitization | R | R | TGAI and MP | TGAI and EP | 2, 4 |
| none | Hypersensitivity incidents | R | R | All | All | 5 |
| Subchronic Testing | ||||||
| 870.3100 | 90-day oral (one species) | R | CR | TGAI | TGAI | 6 |
| 870.3250 | 90-day dermal - rat | CR | CR | TGAI | TGAI | 7 |
| 870.3465 | 90-day inhalation - rat | CR | CR | TGAI | TGAI | 8 |
| Developmental Toxicity | ||||||
| 870.3700 | Prenatal developmental - rat preferably | R | CR | TGAI | TGAI | 9 |
| Mutagenicity Testing | ||||||
| 870.5100 | Bacterial reverse mutation test | R | CR | TGAI | TGAI | 10 |
| 870.5300
870.5375 | In vitro mammalian cell assay | R | CR | TGAI | TGAI | 10, 11 |
| Tier II | ||||||
| Mutagenicity Testing (In vivo cytogenetics) | ||||||
| 870.5385
870.5895 | In vivo Mammalian Cytogenetics | CR | CR | TGAI | TGAI | 13 |
| Developmental Toxicity | ||||||
| 870.3700 | Prenatal developmental | CR | CR | TGAI | TGAI | 9 |
| Special Tests | ||||||
| 880.3550 | Immunotoxicity | CR | CR | TGAI | TGAI | 12, 13 |
| Applicator/User Exposure | ||||||
| 875.1100 | Dermal outdoor exposure | CR | CR | TGAI | TGAI | 15 |
| 875.1200 | Dermal indoor exposure | CR | CR | TGAI | TGAI | 15 |
| 875.1300 | Inhalation outdoor exposure | CR | CR | TGAI | TGAI | 15 |
| 875.1400 | Inhalation indoor exposure | CR | CR | TGAI | TGAI | 15 |
| 875.1500 | Biological monitoring | CR | CR | TGAI | TGAI | 15 |
| Tier III | ||||||
| Chronic Testing/Special Testing | ||||||
| 880.3800 | Immune response | CR | CR | TGAI | TGAI | 14 |
| 870.3800 | Reproduction and fertility effects | CR | CR | TGAI | TGAI | 16 |
| 870.4100 | Chronic oral - rodent and nonrodent | CR | CR | TGAI | TGAI | 17 |
| 870.4200 | Carcinogenicity - two species - rat and mouse preferred | CR | CR | TGAI | TGAI | 18 |
| 870.5380 | Mammalian spermatogonial chromosome aberration test | CR | CR | TGAI | TGAI | 19 |
| Special Testing | ||||||
| 870.7200 | Companion animal safety | CR | CR | NR | TGAI or EP | 20 |
(e) Test notes. The following test notes are applicable to the data requirements for biochemical pesticides human health assessment as referenced in the last column of the table in paragraph (d) of this section.
1. Required unless the test material is a gas or highly volatile (vapor pressure >10−4torr (mm/Hg)).
2. Required unless the test material is corrosive to skin or has pH <2 or >11.5.
3. Required when the pesticide, under conditions of use, would result in respirable material (e.g., gas, volatile substance or aerosol/particulate), unless it is a straight chain lepidopteran pheromone.
4. Required if repeated contact with human skin is likely to occur under conditions of use.
5. Hypersensitivity incidents must be reported as adverse effects data.
6. Required for non-food uses that are likely to result in repeated oral exposure to humans.
7. Required to support uses involving purposeful application to the human skin or which would result in comparable prolonged human exposure to the product (e.g., insect repellents) and if any of the following criteria are met:
i. Data from a 90-day oral study are not required.
ii. The active ingredient is known or expected to be metabolized differently by the dermal route of exposure than by the oral route and the metabolite is of toxicological concern.
iii. The use pattern is such that the dermal route would be the primary route of exposure.
8. Required if there is a likelihood of significant levels of repeated inhalation exposure to the pesticide as a gas, vapor, or aerosol.
9. Required if the use of the product under widespread and commonly recognized practice may reasonably be expected to result in significant exposure to female humans (e.g., occupational exposure or repeated application of insect repellents directly to the skin). Tier II data is required on a different test species from Tier I data when developmental effects are observed in the first study and information on species-to-species extrapolation is needed.
10. Required to support nonfood uses if either:
i. The use is likely to result in significant human exposure; or
ii. The active ingredient (or its metabolites) is structurally related to a known mutagen or belongs to any chemical class of compounds containing a known mutagen. Additional mutagenicity tests that may have been performed plus a complete reference list must also be submitted. Subsequent testing may be required based on the available evidence.
11. Choice of assay using either:
i. Mouse lymphoma L5178Y cells, thymidine kinase (tk) gene locus, maximizing assay conditions for small colony expression or detection;
ii. Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) or Chinese hamster lung fibroblast (V79) cells, hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (hgprt) gene locus, accompanied by an appropriate in vitro test for clastogenicity; or
iii. CHO cells strains AS52, xanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (xprt) gene locus.
12. Required if there are effects on hematology, clinical chemistry, lymphoid organ weights, and histopathology are observed in the 90-day studies.
13. The micronucleus rodent bone marrow assay is preferred; however, rodent bone marrow assays using metaphase analysis (aberrations) are acceptable.
14. Required if adverse effects are observed in the Tier II immunotoxicity study. The protocol for evaluating adverse effects to the immune response should be developed after evaluating the effects noted in the immunotoxicity study.
15. These data are required when the data used for the human health assessment indicates that the biochemical may pose a potential hazard to the applicator/user.
16. Required if there is evidence of:
i. Endocrinological effects from the subchronic toxicity studies.
ii. Developmental effects in the prenatal developmental toxicity study(s), or
iii. Genotoxicity to mammals based on results from the mutagenicity tests.
The use of a combined study that utilizes the two-generation reproduction study in rodents (guideline 870.3800) as a basic protocol for the addition of other endpoints or functional assessments in the immature animal is encouraged.
17. Required if the potential for adverse chronic effects is indicated based on any of the following:
i. The subchronic effect level established in the following Tier I studies: 90-day oral toxicity study, 90-day dermal toxicity study, or 90-day inhalation toxicity study.
ii. The pesticide use pattern (e.g., rate, frequency, and site of application).
iii. The frequency and level of repeated human exposure that is expected.
18. Required if the product meets either of the following criteria:
i. The active ingredient (or any of its metabolites, degradation products, or impurities) produce(s) in Tier I subchronic studies a morphologic effect (e.g., hyperplasia or metaplasia) in any organ that potentially could lead to neoplastic change.
ii. Adverse cellular effects suggesting carcinogenic potential are observed in Tier II immunotoxicity and Tier III immune response study or in Tier II mammalian mutagenicity assays.
In addition, a 90-day range finding study in both rats and mice is required to determine the dose levels if carcinogenicity studies are required. If the mouse carcinogenicity study is not required, the 90-day mouse subchronic study is likewise not required.
19. Required if results from lower tiered mutation or reproductive studies indicate there is potential for chromosomal aberration to occur.
20. May be required if the product's use will result in exposure to domestic animals through, but not limited to, direct application or consumption of treated feed.
§158.2060 Biochemical pesticides nontarget organisms and environmental fate data requirements table.
(a) General.(1) Sections 158.100 through 158.130 describe how to use this table to determine the terrestrial and aquatic nontarget organisms and fate data requirements for a particular biochemical pesticide product. Notes that apply to an individual test including specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions to the designated test are listed in paragraph (e) of this section. In general, for all outdoor end-use products including turf, the following studies are required: one avian acute oral, one avian dietary, one acute freshwater fish, one acute freshwater invertebrate study, plant toxicity testing, and a honeybee acute contact study.
(2) The data in this section are not required for arthropod pheromones when applied at up to a maximum use rate of 150 grams active ingredient/acre/year except when the product is expected to be available to avian species (i.e., granular formulation).
(b) Use patterns. The terrestrial use pattern includes products classified under the general use patterns of terrestrial food crop, terrestrial feed crop, and terrestrial nonfood/nonfeed crop. The greenhouse use pattern includes products classified under the general use patterns of greenhouse food crop and greenhouse nonfood crop. The indoor use pattern includes products classified under the general use patterns of indoor food and nonfood use. The remaining terrestrial uses include: forestry and residential outdoor use. Data are also required for the general use patterns of aquatic food and nonfood crop use.
(c) Key. R = Required; CR = Conditionally required; NR = Not required; MP = Manufacturing-use product; EP = End-use product; TEP = Typical end-use product; TGAI = Technical grade of the active ingredient; Residue of concern = the active ingredient and its metabolites, degradates, and impurities of toxicological concern; All = All of the above. Specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions to the designated test procedures appear in paragraph (e) of this section, and apply to the individual tests in the following table:
(d) Table. The following table shows the data requirements for biochemical pesticides nontarget organisms and environmental fate. The test notes are shown in paragraph (e) of this section.
| Guideline Number | Data Requirement | Use Patterns | Test Substance | Test Notes | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Terrestrial | Aquatic | Greenhouse | Forestry, Residential Outdoor | Indoor | ||||
| Food/Feed/Nonfood | Food/Nonfood | Food/Nonfood | Food/Nonfood | |||||
| Tier I | ||||||||
| Avian Testing | ||||||||
| 850.2100 | Avian acute oral toxicity | R | R | CR | R | CR | TGAI, EP | 1, 2, 3, 4 |
| 850.2200 | Avian dietary toxicity | R | R | CR | R | CR | TGAI, EP | 1, 2, 3, 4 |
| Aquatic Organism Testing | ||||||||
| 850.1075 | Fish acute toxicity, freshwater | R | R | CR | R | CR | TGAI, EP | 2, 3, 4, 5 |
| 850.1010 | Aquatic invertebrate acute toxicity, freshwater | R | R | CR | R | CR | TGAI, EP | 2, 3, 5 |
| Nontarget Plant Testing | ||||||||
| 850.4100 | Terrestrial Plant Toxicity, Seedling emergence | R | R | NR | R | NR | TGAI, EP | 5 |
| 850.4150 | Terrestrial Plant Toxicity, Vegetative vigor | R | R | NR | R | NR | TGAI, EP | 5 |
| Insect Testing | ||||||||
| 880.4350 | Nontarget Insect Testing | R | R | R | R | NR | TGAI | 14 |
| Tier II | ||||||||
| Environmental Fate Testing | ||||||||
| 163-1 (835.1230) | Sediment and soil adsorption/desorption for parent and degradates | CR | CR | CR | CR | NR | TGAI | 6 |
| 163-1 (835.1240) | Soil column leaching | CR | CR | CR | CR | NR | TGAI | 6 |
| 163-2 (835.1410) | Laboratory volatilization from soil | CR | NR | CR | CR | NR | TEP | 7 |
| 161-1 (835.2120) | Hydrolysis | CR | CR | CR | CR | NR | TGAI | 6 |
| 161-1 (835.4100) | Aerobic soil metabolism | CR | NR | CR | CR | NR | TGAI | 6 |
| 161-2 (835.2240) | Photodegradation in water | CR | CR | CR | CR | NR | TGAI | 6 |
| 161-3 (835.2410) | Photodegradation on soil | CR | NR | CR | CR | NR | TGAI | 6 |
| 162-2 (835.4200) | Anaerobic soil metabolism | CR | NR | NR | NR | NR | TGAI | 6 |
| 162-4 (835.4300) | Aerobic aquatic metabolism | CR | CR | CR | CR | NR | TGAI | 6 |
| 162-3 (835.4400) | Anaerobic aquatic metabolism | CR | CR | NR | NR | NR | TGAI | 6 |
| 880.4425 | Dispenser - water leaching | CR | NR | CR | CR | NR | EP | 8 |
| Nontarget Plant | ||||||||
| 850.4225 | Seedling emergence | R | R | NR | R | NR | TGAI | 9 |
| 850.4250 | Vegetative vigor | R | R | NR | R | NR | TGAI | 9 |
| Tier III | ||||||||
| Aquatic Fauna Chronic, Life Cycle, and Field Studies | ||||||||
| 850.1300
850.1400 850.1500 | Freshwater fish/invertebrate testing | CR | CR | NR | CR | NR | TGAI | 10 |
| 850.1025
850.1035 850.1045 850.1055 850.1350 850.1400 850.1500 | Marine/Estuarine fish/invertebrate animal testing | CR | CR | NR | CR | NR | TGAI | 10 |
| 850.1950 | Aquatic field fish/invertebrate testing | CR | CR | NR | CR | NR | EP | 10 |
| Terrestrial Wildlife | ||||||||
| 850.2300 | Avian Reproduction | CR | CR | NR | CR | NR | TGAI | 11 |
| 850.2400 | Wild mammal acute toxicity | CR | CR | NR | CR | NR | TGAI | 11 |
| 850.2500 | Terrestrial field testing | CR | CR | NR | CR | NR | EP | 11 |
| Beneficial Insects | ||||||||
| 850.3040 | Field testing for Pollinators | CR | CR | NR | CR | NR | TEP | 12 |
| Nontarget Plants | ||||||||
| 850.4225
850.4250 850.4300 850.4450 | Nontarget plant | CR | CR | NR | CR | NR | TGAI | 13 |
(e) Test notes. The following test notes are applicable to the data requirements for biochemical pesticides nontarget organisms and environmental fate as referenced in the last column of the table contained in paragraph (d) of this section.
1. Required for the EP when any end-use formulation may contain other ingredients that may be toxic to nontarget organisms or to support arthropod pheromones that would be available to avian wildlife, (e.g., a granular product).
2. Tests for pesticides intended solely for indoor application would be required on a case-by-case basis, depending on use pattern, physical/chemical properties, production volume, and other pertinent factors.
3. Not required for any use groups if the pesticide is highly volatile (estimated volatility >5 × 10−5atm m 3/mol).
4. Preferred test species are Upland game, waterfowl, or passerine for avian acute oral toxicity studies; Upland game and waterfowl for avian dietary studies; and coldwater fish species for acute freshwater fish studies.
5. Required for the EP when the end-use formulation may contain other ingredients that may be toxic to nontarget organisms.
6. Required on a case-by-case basis when results from Tier I studies indicate adverse effects.
7. Required when results of any one or more of the nontarget organism studies in Tier I indicate potential adverse effects on nontarget organisms and the pesticide is to be applied on land. In view of methdological difficulties with the study of photodegradation in air, prior consultation with the Agency regarding the protocol is recommended before the test is performed.
8. Required when results of any one or more of the nontarget organism studies in Tier I indicate potential adverse effects on nontarget organisms and the pesticide is to be applied in a passive dispenser.
9. Required to support registration of known phytotoxicants, i.e., herbicides, desiccants, defoliants, and plant growth regulators.
10. Required if environmental fate characteristics indicate that the estimated environmental concentration of the pesticide in the aquatic environment is >0.01 of any EC50 or LC50 determined in the aquatic nontarget organism testing.
11. Required if either of the following criteria are met:
i. Environmental fate characteristics indicate that the estimated concentration of the pesticide in the terrestrial environment is >0.20 the avian dietary LC50 or equal to >0.20 the avian oral single dose LD50 (converted to ppm).
ii. The pesticide or any of its metabolites or degradation products are stable in the environment to the extent that potentially toxic amounts may persist in the avian or mammalian feed.
12. Required when results of Tier I nontarget organism studies indicate potential adverse effects on nontarget insects and results of Tier II tests indicate exposure of nontarget insects. Additional insect species may have to be tested if necessary to address issues raised by use patterns and potential exposure of important nontarget insect species, (e.g., threatened or endangered species).
13. Required if the product is expected to be transported from the site of application by air, soil, or water. The extent of movement would be determined by the results of the Tier II environmental fate studies.
14. Required depending on pesticide mode of action, method and timing of application, and results of any available efficacy data. Typically the honeybee acute toxicity guideline (guideline 850.3020) satisfies this requirement, however, additional nontarget insect species may have to be tested if necessary to address issues raised by use patterns and potential exposure of important nontarget insect species, (e.g., endangered species.)
§158.2070 Biochemical pesticides product performance data requirements.
(a) General. Product performance data must be developed for all biochemical pesticides. Each applicant must ensure through testing that the product is efficacious when used in accordance with label directions and commonly accepted pest control practices. The Agency may require, on a case-by-case basis, submission of product performance data for any pesticide product registered or proposed for registration or amendment.
(b) Product performance data for each product that bears a claim against an invertebrate pest that is covered by subpart R of this part. The product performance data requirements and performance standards of subpart R of this part apply to biochemical products covered by this subpart. Product performance data must be submitted with any application for registration or amended registration. However, data requirements and the performance standards that determine the acceptability of data may be waived or modified on a case-by-case basis pursuant to the waiver provisions in §158.45 and modification provisions in §158.1707.
(c) Product performance data for each product that bears a public health pest claim, excluding those covered under paragraph (b). Product performance data must be submitted with any application for registration or amended registration, if the product bears a claim to control public health pests, such as pest microorganisms infectious to humans in any area of the inanimate environment, or a claim to control vertebrates, including but not limited to, rodents, birds, bats, canids, and skunks.
[87 FR 22484, Apr. 15, 2022]
§158.2080 Experimental use permit data requirements - biochemical pesticides.
(a) Sections 158.2081 through 158.2084 describe the experimental use permit (EUP) data requirements for biochemical pesticides. Variations in the test conditions are identified within the test notes. Definitions that apply to all biochemical data requirements can be found in §158.2000.
(b) For general information on the data requirement tables, see §158.2010(b)-(f).
§158.2081 Experimental use permit biochemical pesticides product chemistry data requirements table.
(a) General.(1) Sections 158.100 through 158.130 describe how to use this table to determine the product chemistry data requirements for a particular biochemical pesticide product. Notes that apply to an individual test and include specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions to the designated test are listed in paragraph (e) of the section.
(2) Depending on the results of the required product chemistry studies, appropriate use restrictions, labeling requirements, or special packaging requirements may be imposed.
(b) Use patterns. Product chemistry data are required for all pesticide products and are not use specific.
(c) Key. R = Required; CR = Conditionally required; NR = Not required; MP = Manufacturing-use product; EP = End-use product; TEP = Typical end-use product; TGAI = Technical grade of the active ingredient; Residue of concern = the active ingredient and its metabolites, degradates, and impurities of toxicological concern; All = All of the above. Specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions to the designated test procedures appear in paragraph (e) of this section, and apply to the individual tests in the following table:
(d) Table. The following table shows the data requirements for experimental use permit biochemical pesticides product chemistry. The test notes are shown in paragraph (e) of this section.
| Guideline Number | Data Requirement | All Use Patterns | Test Substance | Test Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MP | EP | ||||
| Product Identity and Composition | |||||
| 880.1100 | Product identity and composition | R | TGAI, MP | TGAI, EP | 1, 2 |
| 880.1200 | Description of starting materials, production and formulation process | R | TGAI, MP | TGAI, EP | 2, 3 |
| 880.1400 | Discussion of formation of impurities | R | TGAI and MP | TGAI and EP | 4 |
| Analysis and Certified Limits | |||||
| 830.1700 | Preliminary analysis | CR | TGAI and MP | TGAI and EP | 5, 8 |
| 830.1750 | Certified limits | R | MP | EP | 6 |
| 830.1800 | Enforcement analytical method | R | MP | EP | 7 |
| Physical and Chemical Characteristics | |||||
| 830.6302 | Color | R | TGAI | TGAI | 8 |
| 830.6303 | Physical state | R | TGAI and MP | TGAI and EP | 8 |
| 830.6304 | Odor | R | TGAI | TGAI | 8 |
| 830.6313 | Stability to normal and elevated temperatures, metals and metal ions | R | TGAI | TGAI | 8, 17 |
| 830.6315 | Flammability | CR | MP | EP | 9 |
| 830.6317 | Storage stability | R | MP | EP | -- |
| 830.6319 | Miscibility | CR | MP | EP | 10 |
| 830.6320 | Corrosion characteristics | R | MP | EP | -- |
| 830.7000 | pH | CR | TGAI and MP | TGAI and EP | 8, 11 |
| 830.7050 | UV/Visible light absorption | R | TGAI | TGAI | -- |
| 830.7100 | Viscosity | CR | MP | EP | 12 |
| 830.7200 | Melting point/melting range | CR | TGAI | TGAI | 8, 13 |
| 830.7220 | Boiling point/boiling range | CR | TGAI | TGAI | 8, 14 |
| 830.7300 | Density/relative density/bulk density | R | TGAI and MP | TGAI and EP | 8, 18 |
| 830.7520 | Particle size, fiber length, and diameter distribution | CR | TGAI | TGAI | 8, 15 |
| 830.7550
830.7560 830.7570 | Partition coefficient (n-Octanol /Water) | CR | TGAI | TGAI | 16 |
| 830.7840 | Water solubility | R | TGAI | TGAI | 8 |
| 830.7950 | Vapor pressure | R | TGAI | TGAI | 8, 19 |
(e) Test notes. The following test notes are applicable to the data requirements for experimental use permit biochemical pesticides product chemistry and are referenced in the last column of the table in paragraph (d) of this section.
1. Data must be provided in accordance with §158.320.
2. If the MP and EP are produced by an integrated formulation system (non-registered source), these data are also required on TGAI.
3. Data must be provided in accordance with §158.325, §158.330, and §158.335.
4. Data must be provided in accordance with §158.340.
5. Data must be provided in accordance with §158.345. Also, required to support the registration of each manufacturing-use product (including registered TGAIs) and end-use products produced by an integrated formulation system. Data on other end-use products would be required on a case-by-case basis. For pesticides in the production stage, a preliminary product analytical method and data would suffice to support an experimental use permit.
6. Data must be provided in accordance with §158.350.
7. Data must be provided in accordance with §158.355.
8. If the TGAI cannot be isolated, data are required on the practical equivalent of the TGAI. EP testing may also be appropriate.
9. Required if the product contains combustible liquids.
10. Required if the product is an emulsifiable liquid and is to be diluted with petroleum solvents.
11. Required if the test substance is soluble or dispersible in water.
12. Required if the product is a liquid.
13. Required when the technical chemical is a solid at room temperature.
14. Required when the technical chemical is a liquid at room temperature.
15. Required for water insoluble test substances (>10−6g/l) and fibrous test substances with diameter ≥0.1 µm.
16. Required for organic chemicals unless they dissociate in water or are partially or completely soluble in water.
17. Data on the stability to metals and metal ions is required only if the active ingredient is expected to come in contact with either material during storage.
18. True density or specific density are required for all test substances. Data on bulk density is required for MPs or EPs that are solid at room temperature.
19. Not required for salts.
§158.2082 Experimental use permit biochemical pesticides residue data requirements table.
(a) General. Sections 158.100 through 158.130 describe how to use this table to determine the biochemical pesticides residue data requirements for a particular pesticide product and the substance that needs to be tested. These data requirements apply to all biochemical pesticides, i.e., naturally occurring insect repellents and attractants, semiochemicals (e.g., insect pheromones), natural and plant growth regulators. Notes that apply to an individual test and include specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions to the designated test are listed in paragraph (e) of this section.
(b) Use patterns.(1) Data are required or conditionally required for all pesticides used in or on food and for residential outdoor uses where food crops are grown. Food use patterns include products classified under the general use patterns of terrestrial food crop use, terrestrial feed crop use, aquatic food crop use, greenhouse food crop use, and indoor food use. Data are also conditionally required for aquatic nonfood use if there is direct application to water that could subsequently result in exposure to food.
(2) Data are conditionally required for nonfood uses if pesticide residues may occur in food or feed as a result of the use. Data requirements for these nonfood uses would be determined on a case-by-case basis. For example, most products used in or near kitchens require residue data for risk assessment purposes even though tolerances may not be necessary in all cases.
(c) Key. R = Required; CR = Conditionally required; NR = Not required; MP = Manufacturing end-use product; EP = End-use product; TEP = Typical end-use product; TGAI = Technical grade of the active ingredient; Residue of concern = the active ingredient and its metabolites, degradates,and impurities of toxicological concern. All = All of the above. Specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions to the designated test procedures appear in paragraph (e) of this section, and apply to the individual tests in the following table:
(d) Data table. The following table shows the data requirements for biochemical pesticides residue. The test notes are shown in paragraph (e) of this section.
| Guideline Number | Data Requirement | Use Patterns | Test Substance | Test Notes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Terrestrial | Aquatic | Greenhouse Food | Indoor Food | ||||
| Food/Feed | Food | ||||||
| Supporting Information | |||||||
| 860.1100 | Chemical identity | CR | CR | CR | CR | TGAI | 1, 2, 4 |
| 860.1200 | Directions for use | CR | CR | CR | CR | -- | 1, 3, 4 |
| Nature of Residue | |||||||
| 860.1300 | Nature of the residue in plants | CR | CR | CR | CR | TGAI | 1, 4, 5, 6 |
| 860.1300 | Nature of the residue in livestock | CR | CR | CR | CR | TGAI or plant metabolite | 1, 7, 8, 9, 13 |
| Magnitude of the Residue | |||||||
| 860.1400 | Potable water | NR | CR | NR | NR | TGAI | 1, 11 |
| 860.1400 | Fish | NR | CR | NR | NR | TGAI | 1, 12 |
| 860.1400 | Irrigated crops | NR | CR | NR | NR | TGAI | 1, 13 |
| 860.1460 | Food handling | NR | NR | NR | CR | TGAI | 1, 14 |
| 860.1480 | Meat/milk/poultry/eggs | CR | CR | CR | CR | TGAI or plant metabolites | 1, 7, 8, 9 |
| 860.1500 | Crop field trials | CR | CR | CR | CR | TEP | 1, 3, 4 |
| 860.1520 | Processed food/feed | CR | CR | CR | CR | TEP | 1, 15 |
| 860.1540 | Anticipated residues | CR | CR | CR | CR | Residue of concern | 1, 9, 16 |
| 860.1550 | Proposed tolerances | CR | CR | CR | CR | -- | 1, 17 |
| 860.1560 | Reasonable grounds in support of the petition | CR | CR | CR | CR | -- | 1, 9 |
| 860.1650 | Submittal of analytical reference standards | CR | CR | CR | CR | TGAI and residue of concern | 9, 18 |
(e) Test notes. The following test notes are applicable to the data requirements for biochemical pesticides product chemistry and are referenced referenced in the last column of the table contained in paragraph (d) of this section.
1. Residue chemistry data requirements apply to biochemical pesticide products when Tier II or Tier III toxicology data are required, as specified for biochemical agents in the biochemical human health assessment data requirements, §158.2050.
2. The same chemical identity data are required for biochemical product chemistry data requirements,§158.2030 with an emphasis on impurities.
3. Required information includes crops to be treated, rate of application, number and timing of applications, preharvest intervals, and relevant restrictions.
4. Required for residential outdoor uses on food crops if the corresponding agricultural use is not approved or the residential use is expected to produce higher residues based on the label directions.
5. Required unless it is an arthropod pheromone applied at a rate less than or equal to 150 grams active ingredient per acre.
6. Required for indoor uses where the pesticide is applied directly to food, in order to determine metabolites and/or degradates. Not required when only indirect contact with food would occur (e.g., crack and crevice treatments).
7. Required when a pesticide is to be applied directly to livestock, to livestock premises, to livestock drinking water, or to crops used for livestock feed. If results from the plant metabolism study show differing metabolites in plants form those found in animals, an additional livestock metabolism study involving dosing with the plant metabolite(s) may also be required.
8. Livestock feeding studies are required whenever a pesticide residue is present in livestock feed or when direct application to livestock uses occurs.
9. Required if indoor use could result in pesticide residues in or on food or feed.
10. Data are required to determine whether FDA/USDA multiresidue methodology would detect and identify the pesticides and any metabolites.
11. Data are required whenever a pesticide may be applied directly to water, unless it can be demonstrated that the treated water would not be available for human or livestock consumption.
12. Data on fish are required for all pesticides applied directly to water inhabited, or which will be inhabited, by fish that may be caught or harvested for human consumption.
13. Data are required when a pesticide is to be applied directly to water that could be used for irrigation or to irrigation facilities such as irrigation ditches.
14. Data are required whenever a pesticide may be used in food/feed handling establishments.
15. Data on the nature and level of residue in processed food/feed are required when detectible residues could potentially concentrate on processing thus requiring the establishment of a separate tolerance higher than that of the raw agricultural commodity.
16 Anticipated residue data are required when the assumption of tolerance level residues would result in predicted exposure at an unsafe level of exposure. Data, using single serving samples of a raw agricultural commodity, on the level or residue in food as consumed would be used to obtain a more precise estimate of potential dietary exposure. These data may also include washing, cooking, processing or degradation studies as well as market basket surveys for a more precise residue determination.
17. The proposed tolerance must reflect the maximum residue likely to occur in crops, in meat, milk, poultry, or eggs.
18. Required when a residue analytical method is required.
§158.2083 Experimental use permit biochemical pesticides human health assessment data requirements table.
(a) General.(1) Sections 158.100 through 158.130 describe how to use this table to determine the human health assessment data requirements for a particular biochemical pesticide product.
(2) The data in this section are not required for straight chain lepidopteran pheromones when applied up to a maximum use rate of 150 grams active ingredient/acre/year.
(b) Use patterns.(1) Food use patterns, in general, include products classified under the following general uses: terrestrial food crop use; terrestrial feed crop use; aquatic food crop use; greenhouse food crop use.
(2) Nonfood use patterns include products classified under the general use patterns of terrestrial nonfood crop use; aquatic nonfood residential use; aquatic nonfood outdoor use; aquatic nonfood industrial use; greenhouse nonfood crop use; forestry use; residential outdoor use; residential indoor use; indoor food use; indoor nonfood use; indoor medical use.
(c) Key. R = Required; CR = Conditionally required; NR = Not required; MP = Manufacturing-use product; EP = End-use product; TEP = Typical end-use product; TGAI = Technical grade of the active ingredient; Residue of concern = the active ingredient and its metabolites, degradates, and impurities of toxicological concern; All = All of the above. Specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions to the designated test procedures appear in paragraph (e) of this section, and apply to the individual tests in the following table:
(d) Table. The following table shows the data requirements for experimental use permit biochemical pesticides human health assessment. The test notes are shown in paragraph (e) of this section.
Table - EUP Biochemical Pesticides Human Health Assessment Data Requirements

(e) Test notes. The following test notes are applicable to the data requirements for experimental use permit biochemical pesticides human health assessment as referenced in the last column of the table in paragraph (d) of this section.
1. Required unless the test material is a gas or highly volatile (vapor pressure >10−4torr (mm/Hg)).
2. Required unless the test material is corrosive to skin or has pH <2 or >11.5.
3. Required when the pesticide, under conditions of use, would result in respirable material (e.g., gas, volatile substance or aerosol/particulate), unless it is a straight chain lepidopteran pheromone.
4. Hypersensitivity incidents must be reported as adverse effects data.
5. Required if the use of the product under widespread and commonly recognized practice may reasonably be expected to result in significant exposure to female humans (e.g., occupational exposure or repeated application of insect repellents directly to the skin). Tier II data is required on a different test species from Tier I data when developmental effects are observed in the first study and information on species-to-species extrapolation is needed.
6. Required to support nonfood uses if either:
i. The use is likely to result in significant human exposure; or
ii. The active ingredient (or its metabolites) is structurally related to a known mutagen or belongs to any chemical class of compounds containing a known mutagen.
Additional mutagenicity tests that may have been performed plus a complete reference list must also be submitted. Subsequent testing may be required based on the available evidence.
7. Choice of assay using either:
i. Mouse lymphoma L5178Y cells, thymidine kinase (tk) gene locus, maximizing assay conditions for small colony expression or detection;
ii. Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) or Chinese hamster lung fibroblast (V79) cells, hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (hgprt) gene locus, accompanied by an appropriate in vivo test for clastogenicity; or
iii. CHO cells strains AS52, xanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (xprt) gene locus.
§158.2084 Experimental use permit biochemical pesticides nontarget organisms and environmental fate data requirements table.
(a) General.(1) Sections 158.100 through 158.130 describe how to use this table to determine the terrestrial and aquatic nontarget organisms and fate data requirements for a particular biochemical pesticide product. Notes that apply to an individual test including specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions to the designated test are listed in paragraph (e) of this section. In general, for all outdoor end-use products including turf, the following studies are required: one avian acute oral, one avian dietary, one acute freshwater fish, and one acute freshwater invertebrate study.
(2) The data in this section are not required for arthropod pheromones when applied at up to a maximum use rate of 150 grams active ingredient/acre/year except when the product is expected to be available to avian species (i.e., granular formulation).
(b) Use patterns. The terrestrial use pattern includes products classified under the general use patterns of terrestrial food crop, terrestrial feed crop, and terrestrial nonfood/nonfeed crop. The greenhouse use pattern includes products classified under the general use patterns of greenhouse food crop and greenhouse nonfood crop. The indoor use pattern includes products classified under the general use patterns of indoor food and nonfood use. The remaining terrestrial uses include forestry and residential outdoor use. Data are also required for the general use patterns of aquatic food and nonfood crop use.
(c) Key. R = Required; CR = Conditionally required; NR = Not required; MP = Manufacturing-use product; EP = End-use product; TEP = Typical end-use product; TGAI = Technical grade of the active ingredient; Residue of concern = the active ingredient and its metabolites, degradates, and impurities of toxicological concern; All = All of the above. Specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions to the designated test procedures appear in paragraph (e) of this section, and apply to the individual tests in the following table:
(d) Table. The following table shows the data requirements for experimental use permit biochemical pesticides nontarget organisms and environmental fate. The test notes are shown in paragraph (e) of this section.
Table - EUP Biochemical Pesticides Nontarget Organisms and Environmental Fate Data Requirements

(e) Test notes. The following test notes are applicable to the data requirements for experimental use permit biochemical pesticides nontarget organisms and environmental fate as referenced in the last column of the table contained in paragraph (d) of this section.
1. Required for the EP when any end-use formulation may contain other ingredients that may be toxic to nontarget organisms or to support arthropod pheromones that would be available to avian wildlife, (e.g., a granular product).
2. Not required for any use groups if the pesticide is highly volatile (estimated volatility >5 × 10−5atm m 3/mol).
3. Preferred test species are: upland game, waterfowl, or passerine for avian acute oral toxicity studies; upland game or waterfowl for avian dietary studies; and coldwater fish for acute freshwater fish studies.
4. Required for the EP when the end-use formulation may contain other ingredients that may be toxic to nontarget organisms.
Subpart V - Microbial Pesticides
§158.2100 Microbial pesticides definition and applicability.
(a) This subpart applies to all living or dead microbial pesticides as described in paragraphs (b) and (c) of this section.
(b) Definition.Microbial pesticide is a microbial agent intended for preventing, destroying, repelling, or mitigating any pest, or intended for use as a plant regulator, defoliant, or desiccant, that:
(1) Is a eucaryotic microorganism including, but not limited to, protozoa, algae, and fungi;
(2) Is a procaryotic microorganism, including, but not limited to, Eubacteria and Archaebacteria; or
(3) Is a parasitically replicating microscopic element, including, but not limited to, viruses.
(c) Applicability. (1) This subpart applies to microbial pesticides as specified in paragraphs (c)(2), (c)(3), and (c)(4) of this section.
(2) Each new isolate of a microbial pesticide is a new active ingredient and must be registered independently of any similarly designated and already registered microbial pesticide active ingredient. Each new isolate for which registration is sought must have a unique identifier following the taxonomic name of the microorganism, and the registration application must be supported by data required in this subpart. This does not preclude the possibility of using data from another isolate, provided sufficient similarity is established, to support registration.
(3) Genetically modified microbial pesticides may be subject to additional data or information requirements on a case-by-case basis depending on the particular microbial agent and/or its parental strains, the proposed pesticide use pattern, and the manner and extent to which the organism has been genetically modified.
(4) Pest control organisms such as insect predators, nematodes, and macroscopic parasites are exempt from the requirements of FIFRA as authorized by section 25(b) of FIFRA and specified in §152.20 (a) of this chapter.
[72 FR 61002, Oct. 26, 2007, as amended at 77 FR 52612, Aug. 30, 2012]
§158.2110 Microbial pesticides data requirements.
(a) For all microbial pesticides.(1) The following §158.2120 through §158.2150 identify the data requirements that are required to support registration of microbial pesticides. The variations in the test conditions are identified within the test notes.
(2) Each data table includes “use patterns” under which the individual data are required, with variations including all use patterns, food and nonfood uses for terrestrial and aquatic applications, greenhouse, indoor, forestry, and residential outdoor applications under certain circumstances.
(3) The categories for each data requirement are “R,” which stands for required, and “CR” which stands for conditionally required. If a bracket appears around the “R” or “CR,” the data are required for both the registration and experimental use permit requests. Generally, “R” indicates that the data are more likely required than for those data requirements with “CR.” However, in each case, the regulatory text preceding the data table and the test notes following the data table must be used to determine whether the data requirement must be satisfied.
(4) Each table identifies the test substance that is required to be tested to satisfy the data requirement. Test substances may include: technical grade active ingredient (TGAI), manufacturing-use product (MP), end-use product (EP), typical end-use product (TEP), residue of concern, and pure active ingredient (PAI) or all of the above (All). Commas between the test substances (i.e., TGAI, EP) indicate that data may be required on the TGAI or EP or both depending on the conditions set forth in the test note. Data requirements which list two test substances (i.e., TGAI and EP) indicate that both are required to be tested. Data requirements that list only MP as the test substance apply to products containing solely the technical grade of the active ingredient and manufacturing-use products to which other ingredients have been intentionally added. Data requirements listing the EP as the test substance apply to any EP with an ingredient in the end-use formulation other than the active ingredient that is expected to enhance the toxicity of the product.
(b) Additional data requirements for genetically modified microbial pesticides. Additional requirements for genetically modified microbial pesticides may include but are not limited to: genetic engineering techniques used; the identity of the inserted or deleted gene segment (base sequence data or enzyme restriction map of the gene); information on the control region of the gene in question; a description of the “new” traits or characteristics that are intended to be expressed; tests to evaluate genetic stability and exchange; and selected Tier II environmental expression and toxicology tests.
§158.2120 Microbial pesticides product analysis data requirements table.
(a) General. Sections 158.100 through 158.130 describe how to use this table to determine the product analysis data requirements and the substance to be tested for a particular microbial pesticide. Notes that apply to an individual test and include specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions to the designated test are identified in paragraph (d) of this section.
(b) Key. R = Required; CR = Conditionally required; NR = Not required; MP = Manufacturing-use product; EP = End-use product; TEP = Typical end-use product; TGAI = Technical grade of the active ingredient; All = All of the above.
(c) Table. The table in this paragraph shows the data requirements for microbial pesticides product analysis. The test notes are shown in paragraph (d) of this section.
| Test guideline No. | Data requirement | All use
patterns | Test substance | Test notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MP | EP | ||||
| Product Chemistry and Composition | |||||
| 885.1100 | Product identity | R | MP | EP | |
| 885.1200 | Manufacturing process | R | TGAI and MP | TGAI and EP | |
| 885.1250 | Deposition of a sample in a nationally recognized culture collection | R | TGAI | TGAI | 1 |
| 885.1300 | Discussion of formation of unintentional ingredients | R | TGAI and MP | TGAI and EP | |
| Analysis and Certified Limits | |||||
| 885.1400 | Analysis of samples | R | TGAI and MP | TGAI and EP | 2 |
| 885.1500 | Certification of limits | R | MP | EP | |
| Physical and Chemical Characteristics | |||||
| 830.6302 | Color | R | TGAI | TGAI | |
| 830.6303 | Physical state | R | TGAI | TGAI | |
| 830.6304 | Odor | R | TGAI | TGAI | |
| 830.6313 | Stability to normal and elevated temperatures, metals, and metal ions | R | TGAI | TGAI | |
| 830.6317 | Storage stability | R | TGAI and MP | TGAI and EP | |
| 830.6319 | Miscibility | R | MP | EP | 3 |
| 830.6320 | Corrosion characteristics | R | MP | EP | 4 |
| 830.7000 | pH | R | TGAI | TGAI | |
| 830.7100 | Viscosity | R | MP | EP | 5 |
| 830.7300 | Density/relative density/bulk density (specific gravity) | R | TGAI | TGAI | |
(d) Test notes. The following test notes are applicable to the data requirements for microbial pesticides product analysis as referenced in the last column of the table contained in paragraph (c) of this section.
1. Required for each isolate of a microbial pesticide. Isolates must be deposited with an agreement to ensure that the sample will be maintained and will not be discarded for the duration of the associated registration(s).
2. Required to support registration of each manufacturing-use product and end-use product. This analysis must be conducted at the point in the production process after which there would be no potential for microbial contamination or microbial regrowth. For full registration, generally an analysis of samples is a compilation of batches, over a period of time, depending on the frequency of manufacturing.
3. Only required for emulsifiable liquid forms of microbial pesticides.
4. Required when microbial pesticides are packaged in metal, plastic, or paper containers.
5. Only required for liquid forms of microbial pesticides.
[72 FR 61002, Oct. 26, 2007, as amended at 77 FR 52612, Aug. 30, 2012]
§158.2130 Microbial pesticides residue data requirements table.
(a) General. Sections 158.100 through 158.130 describe how to use this table to determine the residue chemistry data requirements and the substance to be tested for a particular microbial pesticide. Specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions to the designated test appear in paragraph (d) of this section, and the procedures appear in paragraph (e) of this section.
(b) Key. R = required; CR = Conditionally required; NR = Not required; MP = Manufacturing-use product; EP = End-use product; TEP = Typical end-use product; TGAI = Technical grade of the active ingredient; All = All of the above. Specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions to the designated test procedures appear in paragraph (d) of this section, and apply to the individual tests in the following table:
(c) Table. The following table shows the data requirements for microbial pesticides residue. The test notes are shown in paragraph (d) of this section.
| Guideline Number | Data Requirement | All Use Patterns | Test Substance Data to Support MP or EP | Test Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 885.2100 | Chemical Identity | CR | EP | 1 |
| 885.2200 | Nature of the Residue in plants | CR | EP | 1 |
| 885.2250 | Nature of the Residue in animals | CR | EP | 1 |
| 885.2300 | Analytical methods - plants | CR | TGAI | 1 |
| 885.2350 | Analytical methods - animals | CR | TGAI | 1 |
| 885.2400 | Storage Stability | CR | EP | 1 |
| 885.2500 | Magnitude of residue in plants | CR | EP | 1 |
| 885.2550 | Magnitude of residues in meat, milk, poultry, eggs | CR | EP | 1 |
| 885.2600 | Magnitude of residues in potable water, fish, and irrigated crops | CR | EP | 1 |
(d) Test notes. The following test note is applicable to the data requirements for microbial pesticides residue as referenced in the last column of the table contained in paragraph (c) of this section.
1. Required when the results of testing:
i. Indicate the potential to cause adverse human health effects or the product characterization indicates the microbial pesticide has a significant potential to produce a mammalian toxin; and
ii. The use pattern is such that residues may be present in or on food or feed crops.
§158.2140 Microbial pesticides toxicology data requirements table.
(a) General. Sections 158.100 through 158.130 describe how to use this table to determine the toxicology data requirements for a particular pesticide product. Notes that apply to an individual test and include specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions to the designated test are listed in paragraph (d) of this section.
(b) Key. R = Required; CR = Conditionally required; NR = Not required; MP = Manufacturing-use product; EP = End-use product; TEP = Typical end-use product; TGAI = Technical grade of the active ingredient; All = All of the above. Specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions to the designated test procedures appear in paragraph (d) of this section, and apply to the individual tests in the following table:
(c) Table. The following table shows the data requirements for microbial pesticides toxicology. The test notes are shown in paragraph (d) of this section.
| Guideline Number | Data Requirement | All Use Patterns | Test Substance | Test Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tier I | ||||
| 885.3050 | Acute oral toxicity/pathogenicity | R | TGAI | 1 |
| 885.3150 | Acute pulmonary toxicity/pathogenicity | R | TGAI | -- |
| 885.3200 | Acute injection toxicity/pathogenicity/(intravenous)
Acute injection toxicity/pathogenicity/(intraperitoneal) | R | TGAI | 2 |
| 885.3400 | Hypersensitivity incidents | R | All | 3 |
| 885.3500 | Cell culture | R | TGAI | 4 |
| 870.1100 | Acute oral toxicity | R | MP , EP | 1, 5 |
| 870.1200 | Acute dermal toxicity | R | MP , EP | 5 |
| 870.1300 | Acute inhalation toxicity | R | MP , EP | 5, 6 |
| 870.2400 | Acute eye irritation | R | MP , EP | 5 |
| 870.2500 | Primary dermal irritation | R | MP , EP | 5 |
| Tier II | ||||
| 885.3550 | Acute toxicology | CR | TGAI | 7 |
| 885.3600 | Subchronic toxicity/pathogenicity | CR | TGAI | 8 |
| Tier III | ||||
| 885.3650 | Reproductive fertility effects | CR | TGAI | 9, 13 |
| 870.4200 | Carcinogenicity | CR | TGAI | 10, 13 |
| 870.7800 | Immunotoxicity | CR | TGAI | 11, 13 |
| 885.3000 | Infectivity/pathogenicity analysis | CR | TGAI | 12, 13 |
(d) Test notes. The following test notes are applicable to the data requirements for microbial pesticides toxicology as referenced in the last column of the table contained in paragraph (c) of this section:
1. The acute oral toxicity/pathogenicity study is required to support the TGAI. However, it can be combined with the unit dose portion of the acute oral toxicity study, with an EP or MP test material to fulfill the requirement for the TGAI and the MP or EP in a single study, if the new protocol is designed to address the endpoints of concern.
2. Data not required for products whose active ingredient is a virus. For test materials whose size or consistency may prevent use of an intravenous injection, the intraperitoneal injection procedure may be employed.
3. Hypersensitivity incidents, including immediate type and delayed-type reactions of humans or domestic animals, occur during the testing or production of the TGAI, MP, or EP, or are otherwise known to the applicant must be reported if they occur.
4. Data must be submitted only for products whose active ingredient is a virus.
5. The 870 series studies for the MP and EP are intended to provide data on the acute toxicity of the product. Waivers for any or all of these studies may be granted when the applicant can demonstrate that the combination of inert ingredients is not likely to pose any significant human health risks. Where appropriate, the limit dose approach to testing is recommended.
6. Required when the product consists of, or under conditions of use would result in, an inhalable material (e.g., gas, volatile substances, or aerosol particulate).
7. Data required when significant toxicity, in the absence of pathogenicity and significant infectivity, is observed in acute oral, injection, or pulmonary studies (Tier I). Route(s) of exposure correspond to route(s) where toxicity was observed in Tier I studies. The toxic component of the TGAI is to be tested.
8. Data required when significant infectivity and/or unusual persistence is observed in the absence of pathogenicity or toxicity in Tier I studies. Routes of exposure (oral and/or pulmonary) correspond to routes in Tier I studies where adverse effects were noted. Data may also be required to evaluate adverse effects due to microbial contaminants or to toxic byproducts.
9. Data are required when one or more of the following criteria are met:
i. Significant infectivity of the microbial pest control agent (MPCA) was observed in test animals in the Tier II subchronic study and in which no significant signs of toxicity or pathogenicity were observed.
ii. The microbial pesticide is a virus which can persist or replicate in mammalian cell culture lines.
iii. The microbial pesticide is not amenable to thorough taxonomic classification, and is related to organisms known to be parasitic for mammalian cells.
iv. The microbial pesticide preparation is not well purified, and may contain contaminants which are parasitic for mammals.
10. Data may be required for products known to contain or suspected to contain carcinogenic viruses or for microbial components that are identified as having significant toxicity in Tier II testing.
11. Data may be required for products known to contain or suspected to contain viruses that can interact in an adverse manner with components of the mammalian immune system.
12. An analysis of human infectivity/pathogenicity potential using scientific literature, genomic analysis, and/or actual specific cell culture/animal data may be required for products known to contain or suspected of containing intracellular parasites of mammalian cells for products that exhibit pathogenic characteristics in Tier I and/or Tier II, for products which are closely related to known human pathogens based on the product analysis data, or for known human pathogens that have been “disarmed” or rendered non-pathogenic for humans.
13. Test standards may have to be modified depending on the characteristics of the microorganism. Requirements may vary for these studies depending on the active ingredient being tested. Consultation with the Agency is advised before performing these Tier III studies.
§158.2150 Microbial pesticides nontarget organisms and environmental fate data requirements table.
(a) General. Sections 158.100 through 158.130 describe how to use this table to determine the terrestrial and aquatic nontarget organisms data requirements for a particular microbial pesticide product. Notes that apply to an individual test including specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions to the designated test are listed in paragraph (e) of this section.
(b) Use patterns. Aquatic uses include: food and feed, nonfood uses (e.g., outdoor, residential, and industrial). Terrestrial uses include: Food, Feed, Non-Food, Forestry, Residential outdoor, greenhouse (food and food), Indoor (food and nonfood), and Industrial.
(c) Key. R = Required; CR = Conditionally required; NR = Not required; MP = Manufacturing-use product; EP = End-use product; TEP = Typical end-use product; TGAI = Technical grade of the active ingredient; All = All of the above. Specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions to the designated test procedures appear in paragraph (e) of this section, and apply to the individual tests in the following table:
(d) Table. The following table shows the data requirements for microbial pesticides nontarget organisms and environmental fate. The test notes are shown in paragraph (e) of this section.
Table - Microbial Pesticides Nontarget Organisms and Environmental Fate Data Requirements


(e) Test notes. The following test notes are applicable to the data requirements for microbial pesticides nontarget organism and environmental fate as referenced in the last column of the table contained in paragraph (d) of this section.
1. Tests for pesticides intended solely for indoor application would be required on a case-by-case basis, depending on use pattern, production volume, and other pertinent factors.
2. The preferred species for the avian oral study is either the upland game or waterfowl. The preferred species for the avian inhalation toxicity/pathogenicity study and the avian chronic toxicity/pathogenicity study is the upland game. There is also the option to test the passerine if there is a concern. The coldwater fish is preferred for freshwater fish testing. However, two species (coldwater and warmwater fish species are the preferred species) must be tested for uses involving direct freshwater exposure. Freshwater invertebrate testing is also required.
3. Data required when the nature of the microbial pesticide and/or its toxins indicates potential pathogenicity to birds.
4. Required on a case-by-case basis if results of tests required by §158.2140 are inadequate or inappropriate for assessment of hazards to wild mammals.
5. Required when there will be significant exposure to aquatic organisms (fish and invertebrates).
6. Required if the product is intended for direct application into the estuarine or marine environment or expected to enter this environment in significant concentrations because of expected use or mobility pattern.
7. Required if the microbial pesticide is taxonomically related to a known plant pathogen.
8. Data are not required unless an active microbial ingredient controls the target insect pest by a mechanism of infectivity; i.e., may create an epizootic condition in nontarget insects.
9. Required if toxic or pathogenic effects are observed in one or more of the following tests for microbial pesticides:
i. Avian acute oral or avian inhalation studies.
ii. Wild mammal studies.
iii. Nontarget plant studies (terrestrial).
iv. Honey bee studies.
v. Nontarget insect studies.
10. Required when toxic or pathogenic effects are observed in any of the following Tier I tests for microbial pest control agents:
i. Freshwater fish studies.
ii. Freshwater invertebrate studies.
iii. Nontarget plant studies (aquatic).
11. Required if product is applied on land or in fresh water or marine/estuarine environments and toxic or pathogenic effects are observed in any of the following Tier I tests for microbial pesticides:
i. Estuarine and marine animal toxicity and pathogenicity.
ii. Plant studies - estuarine or marine species.
12. An appropriate dose-response toxicity test is required when toxic effects on nontarget terrestrial wildlife or aquatic organisms (including plants) are reported in one or more Tier I tests and results of Tier II tests indicate exposure of the microbial agent to the affected nontarget terrestrial wildlife or aquatic organisms. The protocols for these tests may have to be modified in accordance with results from the nontarget organism and environmental expression studies.
13. Required when one or more of the following are present:
i. Pathogenic effects are observed in Tier I avian studies.
ii. Tier II environmental expression testing indicate that long-term exposure of terrestrial animals is likely.
14. Required when product is intended for use in water or expected to be transported to water from the intended use site, and when pathogenicity or infectivity was observed in Tier I aquatic studies.
15. Required if, after an analysis of the microbial pesticide's ability to survive and multiply in the environment and what ecological habitat it would occupy, the intended use patterns, and the results of previous nontarget organisms and environmental expression tests, it is determined that use of the microbial agent may result in adverse effects on the nontarget organisms in aquatic environments. Testing is to determine if applications of the microbial pest control would be expected to disrupt the balance of populations in the target ecosystem.
16. Tier IV studies may be conducted as a condition of registration as post-registration monitoring if the potential for unreasonable adverse effects appears to be minimal during that period of use due to implementation of mitigation measures.
17. Required when both of the following conditions occur:
i. Pathogenic effects observed at actual or expected field residue exposure levels are reported in Tier III; and
ii. The Agency determines that quarantine methods would not prevent the microbial pesticide from contaminating areas adjacent to the test area.
18. Short term simulated or actual field studies are required when it is determined that the product is likely to cause adverse short-term or acute effects, based on consideration of available laboratory data, use patterns, and exposure rates.
19. Data from a long-term simulated field test (e.g., where reproduction and growth of confined populations are observed) and/or an actual field test (e.g., where reproduction and growth of natural populations are observed) are required if laboratory data indicate that adverse long-term, cumulative, or life-cycle effects may result from intended use.
20. Since test standards would be developed on a case-by-case basis, consultation with the Agency and development of a protocol is advised before performing these Tier IV studies.
§158.2160 Microbial pesticides product performance data requirements.
(a) General. Product performance data must be developed for all microbial pesticides. Each applicant must ensure through testing that the product is efficacious when used in accordance with label directions and commonly accepted pest control practices. The Agency may require, on a case-by-case basis, submission of product performance data for any pesticide product registered or proposed for registration or amendment.
(b) Product performance data for each product that bears a claim against an invertebrate pest that is covered by subpart R of this part. The product performance data requirements and the performance standards of subpart R of this part apply to microbial products covered by this subpart. Product performance data must be submitted with any application for registration or amended registration. However, data requirements and the performance standards that determine the acceptability of data may be modified on a case-by-case basis pursuant to the waiver provisions in §158.45 and the provisions in §158.1707.
(c) Product performance data for each product that bears a public health pest claim, excluding those covered under paragraph (b). Product performance data must be submitted with any application for registration or amended registration, if the product bears a claim to control public health pests, such as pest microorganisms infectious to humans in any area of the inanimate environment, or a claim to control vertebrates, including but not limited to, rodents, birds, bats, canids, and skunks.
[87 FR 22484, Apr. 15, 2022]
§158.2170 Experimental use permit data requirements - microbial pesticides.
(a) For all microbial pesticides.(1) The following §158.2171 through §158.2174 identify the data requirements that are required to support experimental use permits for microbial pesticides. The variations in the test conditions are identified within the test notes.
(2) For general information on the data requirement tables, see §158.2110(a)(2)-(4).
(b) Additional data requirements for genetically modified microbial pesticides. Additional requirements for genetically modified microbial pesticides may include but are not limited to: genetic engineering techniques used; the identity of the inserted or deleted gene segment (base sequence data or enzyme restriction map of the gene); information on the control region of the gene in question; a description of the “new” traits or characteristics that are intended to be expressed; tests to evaluate genetic stability and exchange; and selected Tier II environmental expression and toxicology tests.
§158.2171 Experimental use permit microbial pesticides product analysis data requirements table.
(a) General. Sections 158.100 through 158.130 describe how to use this table to determine the product analysis data requirements and the substance to be tested for a particular microbial pesticide. Notes that apply to an individual test and include specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions to the designated test are identified in paragraph (d) of this section.
(b) Key. R = Required; CR = Conditionally required; NR = Not required; MP = Manufacturing-use product; EP = End-use product; TEP = Typical end-use product; TGAI = Technical grade of the active ingredient; All = All of the above.
(c) Table. The table in this paragraph shows the data requirements for experimental use permit microbial pesticides product analysis. The test notes are shown in paragraph (d) of this section.
| Test guideline No. | Data requirement | All use patterns | Test substance | Test notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MP | EP | ||||
| Product Chemistry and Composition | |||||
| 885.1100 | Product identity | R | MP | EP | |
| 885.1200 | Manufacturing process | R | TGAI and MP | TGAI and EP | 1, 2 |
| 885.1250 | Deposition of a sample in a nationally recognized culture collection | R | TGAI | TGAI | 3 |
| 885.1300 | Discussion of formation of unintentional ingredients | R | TGAI and MP | TGAI and EP | 2 |
| Analysis and Certified Limits | |||||
| 885.1400 | Analysis of samples | R | TGAI and MP | TGAI and EP | 2, 4 |
| 885.1500 | Certification of limits | R | MP | EP | |
| Physical and Chemical Characteristics | |||||
| 830.6302 | Color | R | TGAI | TGAI | |
| 830.6303 | Physical state | R | TGAI | TGAI | |
| 830.6304 | Odor | R | TGAI | TGAI | |
| 830.6313 | Stability to normal and elevated temperatures, metals, and metal ions | R | TGAI | TGAI | |
| 830.6317 | Storage stability | R | TGAI and MP | TGAI and EP | |
| 830.6319 | Miscibility | R | MP | EP | 5 |
| 830.6320 | Corrosion characteristics | R | MP | EP | 6 |
| 830.7000 | pH | R | TGAI | TGAI | |
| 830.7100 | Viscosity | R | MP | EP | 7 |
| 830.7300 | Density/relative density/bulk density (specific gravity) | R | TGAI | TGAI | |
(d) Test notes. The following test notes are applicable to the data requirements for experimental use permit microbial pesticides product analysis as referenced in the last column of the table contained in paragraph (c) of this section.
1. If an experimental use permit is being sought, and if the pesticide is not already under full-scale production, a schematic diagram and/or description of the manufacturing process suffices.
2. If an experimental use permit is being sought, and if the product is not already under full-scale production, a discussion of unintentional ingredients is required to be submitted to the extent this information is available.
3. Required for each isolate of a microbial pesticide. Isolates must be deposited with an agreement to ensure that the sample will be maintained and will not be discarded for the duration of the associated experimental use permit(s).
4. Required to support registration of each manufacturing-use product and end-use product. This analysis must be conducted at the point in the production process after which there would be no potential for microbial contamination or microbial regrowth. For pesticides in the production stage, a preliminary product analytical method and data would suffice to support an experimental use permit. For full registration, generally an analysis of samples is a compilation of batches, over a period of time, depending on the frequency of manufacturing.
5. Only required for emulsifiable liquid forms of microbial pesticides.
6. Required when microbial pesticides are packaged in metal, plastic, or paper containers.
7. Only required for liquid forms of microbial pesticides.
[72 FR 61002, Oct. 26, 2007, as amended at 77 FR 52613, Aug. 30, 2012]
§158.2172 Experimental use permit microbial pesticides residue data requirements table.
(a) General. Sections 158.100 through 158.130 describe how to use this table to determine the residue chemistry data requirements and the substance to be tested for a particular microbial pesticide. Specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions to the designated test appear in (d) of this section, and the procedures appear in paragraph (e) of this section.
(b) Key. R = Required; CR = Conditionally required; NR = Not required; MP = Manufacturing-use product; EP = End-use product; TEP = Typical end-use product; TGAI = Technical grade of the active ingredient; All = All of the above. Specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions to the designated test procedures appear in paragraph (d) of this section, and apply to the individual tests in the following table:
(c) Table. The following table shows the data requirements for experimental use permit microbial pesticides residue. The test notes are shown in paragraph (d) of this section.
| Guideline Number | Data Requirement | All Use Patterns | Test Substance Data to Support MP or EP | Test Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 885.2100 | Chemical Identity | CR | EP | 1 |
| 885.2200 | Nature of the Residue in plants | CR | EP | 1 |
| 885.2250 | Nature of the Residue in animals | CR | EP | 1 |
| 885.2300 | Analytical methods - plants | CR | TGAI | 1 |
| 885.2350 | Analytical methods-animals | CR | TGAI | 1 |
| 885.2400 | Storage Stability | CR | EP | 1 |
| 885.2500 | Magnitude of residue in plants | CR | EP | 1 |
| 885.2550 | Magnitude of residues in meat, milk, poultry, eggs | CR | EP | 1 |
| 885.2600 | Magnitude of residues in potable water, fish, and irrigated crops | CR | EP | 1 |
(d) Test notes. The following test note is applicable to the data requirements for experimental use permit microbial pesticides residue as referenced in the last column of the table contained in paragraph (c) of this section.
1. Required when the results of testing:
i. Indicate the potential to cause adverse human health effects or the product characterization indicates the microbial pesticide has a significant potential to produce a mammalian toxin; and
ii. The use pattern is such that residues may be present in or on food or feed crops.
§158.2173 Experimental use permit microbial pesticides toxicology data requirements table.
(a) General. Sections 158.100 through 158.130 describe how to use this table to determine the toxicology data requirements for a particular microbial pesticide product. Notes that apply to an individual test and include specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions to the designated test are listed in paragraph (d) of this section.
(b) Key. R = Required; CR = Conditionally required; NR = Not required; MP = Manufacturing-use product; EP = End-use product; TEP = Typical end-use product; TGAI = Technical grade of the active ingredient; All = All of the above. Specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions to the designated test procedures appear in paragraph (d) of this section, and apply to the individual tests in the following table:
(c) Table. The following table shows the data requirements for microbial pesticide toxicology. The test notes are shown in paragraph (d) of this section.
| Guideline Number | Data Requirement | All Use Patterns | Test Substance | Test Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 885.3050 | Acute oral toxicity/pathogenicity | R | TGAI | 1 |
| 885.3150 | Acute pulmonary toxicity/pathogenicity | R | TGAI | -- |
| 885.3200 | Acute injection toxicity/pathogenicity/(intravenous)
Acute injection toxicity/pathogenicity/(intraperitoneal) | R | TGAI | 2 |
| 885.3400 | Hypersensitivity incidents | R | All | 3 |
| 885.3500 | Cell culture | R | TGAI | 4 |
| 870.1100 | Acute oral toxicity | R | MP, EP | 1, 5 |
| 870.1200 | Acute dermal toxicity | R | MP, EP | 5 |
| 870.1300 | Acute inhalation toxicity | R | MP, EP | 5, 6 |
| 870.2400 | Acute eye irritation | R | MP, EP | 5 |
| 870.2500 | Primary dermal irritation | CR | MP, EP | 5 |
(d) Test notes. The following test notes are applicable to the data requirements for experimental use permit microbial pesticides toxicology as referenced in the last column of the table contained in paragraph (c) of this section:
1. The acute oral toxicity/pathogenicity study is required to support the TGAI. However, it can be combined with the unit dose portion of the acute oral toxicity study, with an EP or MP test material to fulfill the requirement for the TGAI and the MP or EP in a single study, if the new protocol is designed to address the endpoints of concern.
2. Data not required for products whose active ingredient is a virus. For test materials whose size or consistency may prevent use of an intravenous injection, the intraperitoneal injection procedure may be employed.
3. Hypersensitivity incidents, including immediate type and delayed type reactions of humans or domestic animals occur during the testing or production of the TGAI, MP, or EP, or are otherwise known to the applicant must be reported if they occur.
4. Data must be submitted only for products whose active ingredient is a virus.
5. The 870 series studies for the MP and EP are intended to provide data on the acute toxicity of the product. Waivers for any or all of these studies may be granted when the applicant can demonstrate that the combination of inert ingredients is not likely to pose any significant human health risks. Where appropriate, the limit dose approach to testing is recommended.
6. Required when the product consists of, or under conditions of use that would result in an inhalable material (e.g., gas, volatile substances, or aerosol particulate).
§158.2174 Experimental use permit microbial pesticides nontarget organisms and environmental fate data requirements table.
(a) General. Sections 158.100 through 158.130 describe how to use this table to determine the terrestrial and aquatic nontarget organisms data requirements for a particular microbial pesticide product. Notes that apply to an individual test including specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions to the designated test are listed in paragraph (e) of this section.
(b) Use patterns. Aquatic uses include: food and feed, nonfood uses (e.g., outdoor, residential, and industrial). Terrestrial uses include: Food, Feed, Non-Food, Forestry, Residential outdoor, greenhouse (food and food), Indoor (food and nonfood), and Industrial.
(c) Key. R = Required; CR = Conditionally required; NR = Not required; MP = Manufacturing-use product; EP = End-use product; TEP = Typical end-use product; TGAI = Technical grade of the active ingredient; All = All of the above. Specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions to the designated test procedures appear in paragraph (e) of this section, and apply to the individual tests in the following table:
(d) Table. The following table shows the data requirements for experimental use permit microbial pesticides nontarget organisms and environmental fate. The test notes are shown in paragraph (e) of this section.
Table - EUP Microbial Pesticides Nontarget Organisms and Environmental Fate Data Requirements

(e) Test notes. The following test notes are applicable to the data requirements for microbial pesticides nontarget organism and environmental fate as referenced in the last column of the table contained in paragraph (d) of this section.
1. Tests for pesticides intended solely for indoor application would be required on a case-by-case basis, depending on use pattern, production volume, and other pertinent factors. Tests to support EUP's are based on the application timing and acreage.
2. The preferred species for the avian oral study is either the upland game or waterfowl. The preferred species for the avian inhalation toxicity/pathogenicity study and the avian chronic toxicity/pathogenicity study is the upland game. There is also the option to test a passerine species if there is a concern. The coldwater fish is preferred for freshwater fish testing. However, two species (coldwater and warmwater fish are the preferred species) must be tested for uses involving direct freshwater exposure. Freshwater invertebrates are preferred for invertebrate testing.
3. Required when there will be significant exposure to aquatic organisms (fish and invertebrates).
4. Required if the microbial pesticide is taxonomically related to a known plant pathogen.
5. Data are not required unless an active microbial ingredient controls the target insect pest by a mechanism of infectivity; i.e., may create an epizootic condition in nontarget insects.
Subpart W - Antimicrobial Pesticide Data Requirements
§158.2200 Applicability.
Part 158, subpart W establishes data requirements for any pesticide product that is:
(a) A pesticide that is intended for use as an “antimicrobial pesticide” within the meaning of FIFRA sec. 2(mm)(1)(A), regardless of whether it also meets the criterion of FIFRA sec. 2(mm)(1)(B). That criterion excludes from the definition any antimicrobial product that is intended for a food-use requiring a tolerance or exemption under FFDCA sec. 408 or a food additive regulation or clearance under FFDCA sec. 409. EPA will apply this subpart to all products intended for an antimicrobial use, purpose or function; the exclusion in FIFRA sec. 2(mm)(1)(B) does not exclude products from the data requirements of this subpart.
(b) A product that bears both antimicrobial and non-antimicrobial uses or claims is subject to the data requirements for pesticides in subparts C through O, R, and U or V of this part with respect to its non-antimicrobial uses and claims, and to the requirements of this subpart with respect to its antimicrobial uses and claims.
(c) A wood preservative, including a product that is intended to prevent wood degradation problems due to fungal rot or decay, sapstain, or molds.
(d) An antifoulant, including a product that is intended to kill or repel organisms that can attach to underwater surfaces, such as boat bottoms.
[87 FR 22484, Apr. 15, 2022]
§158.2201 Antimicrobial use patterns.
(a) Antimicrobial use patterns. The 12 general use patterns used in the data tables in this subpart are:
(1) Agricultural premises and equipment.
(2) Food-handling/storage establishments, premises and equipment.
(3) Commercial, institutional and industrial premises and equipment.
(4) Residential and public access premises.
(5) Medical premises and equipment.
(6) Human drinking water systems.
(7) Materials preservatives.
(8) Industrial processes and water systems.
(9) Antifoulant paints and coatings.
(10) Wood preservatives.
(11) Swimming pools.
(12) Aquatic areas.
(b) Use site index. The Pesticide Use Site Index for Antimicrobial Pesticides is a comprehensive list of specific antimicrobial use sites. The Index associates antimicrobial use sites with one or more of the 12 antimicrobial use patterns. It is to be used in conjunction with the data tables in this subpart to determine the applicability of data requirements to specific uses. The Antimicrobial Pesticide Use Site Index, which will be updated periodically, is available from the Agency or may be obtained from the Agency's Web site at http://www.epa.gov/pesticides.
§158.2203 Definitions.
The following terms are defined for the purposes of this subpart:
Disinfectant means a substance, or mixture of substances, that destroys or irreversibly inactivates bacteria, fungi and viruses, but not necessarily bacterial spores, in the inanimate environment.
Fungicide means a substance, or mixture of substances, that destroys fungi (including yeasts) and fungal spores pathogenic to man or other animals in the inanimate environment.
Microbiological water purifier means any unit, water treatment product or system that removes, kills or inactivates all types of disease-causing microorganisms from the water, including bacteria, viruses and protozoan cysts, so as to render the treated water safe for drinking.
Sanitizer means a substance, or mixture of substances, that reduces the bacteria population in the inanimate environment by significant numbers, but does not destroy or eliminate all bacteria. Sanitizers meeting Public Health Ordinances are generally used on food contact surfaces and are termed sanitizing rinses.
Sterilant means a substance, or mixture of substances, that destroys or eliminates all forms of microbial life in the inanimate environment, including all forms of vegetative bacteria, bacterial spores, fungi, fungal spores, and viruses.
Tuberculocide means a substance, or mixture of substances, that destroys or irreversibly inactivates tubercle bacilli in the inanimate environment.
Virucide means a substance, or mixture of substances, that destroys or irreversibly inactivates viruses in the inanimate environment.
§158.2204 Public health and nonpublic health claims.
(a) Public health claim. An antimicrobial pesticide is considered to make a public health claim if the pesticide product bears a claim to control pest microorganisms that pose a threat to human health, and whose presence cannot readily be observed by the user, including but not limited to, microorganisms infectious to man in any area of the inanimate environment. A product makes a public health claim if one or more of the following apply:
(1) A claim is made for control of specific microorganisms that are directly or indirectly infectious or pathogenic to man (or both man and animals). Examples of specific microorganisms include, but are not limited to: Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli (E. coli), human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), Streptococcus, and Staphylococcus aureus. Claims for control of microorganisms infectious or pathogenic only to animals (such as canine distemper virus or hog cholera virus) are not considered public health claims.
(2) A claim is made for the pesticide product as a sterilant, disinfectant, virucide, sanitizer, or tuberculocide against microorganisms that are infectious or pathogenic to man.
(3) A claim is made for the pesticide product as a fungicide against fungi infectious or pathogenic to man, or the product does not clearly state that it is intended for use only against nonpublic health fungi.
(4) A claim is made for the pesticide product as a microbiological water purifier or microbial purification system.
(5) A non-specific claim is made that the pesticide product will beneficially impact or affect public health at the site of use or in the environment in which it is applied, and:
(i) The pesticide product contains one or more ingredients that, under the criteria in 40 CFR 153.125(a), is an active ingredient with respect to a public health microorganism and there is no other functional purpose for the ingredient in the product; or
(ii) The pesticide product is similar in composition to a registered pesticide product that makes antimicrobial public health claims.
(b) Nonpublic health claim. An antimicrobial pesticide is considered to make a nonpublic health claim if the pesticide product bears a claim to control microorganisms of economic or aesthetic significance, where the presence of the microorganism would not normally lead to infection or disease in humans. Examples of nonpublic health claims include, but are not limited to: Algaecides, slimicides, preservatives and products for which a pesticidal claim with respect to odor sources is made.
§158.2210 Product chemistry.
The product chemistry data requirements of subpart D of this part apply to antimicrobial products covered by this subpart.
§158.2220 Product performance.
(a) General(1) Product performance requirement for all antimicrobial pesticides. Each applicant must ensure through testing that his product is efficacious when used in accordance with label directions and commonly accepted pest control practices. The Agency may require, on a case-by-case basis, submission of product performance data for any pesticide product registered or proposed for registration or amendment.
(2) Product performance data for each product that bears a public health claim. Each product that bears a public health claim, as described in §158.2204(a), must be supported by product performance data, as listed in the table in paragraph (c) of this section. Product performance data must be submitted with any application for registration or amended registration.
(3) Product performance data for each product that bears a nonpublic health claim. Each product that bears a nonpublic health claim, as described in §158.2204(b), must be supported by product performance data. Each registrant must ensure through testing that his product is efficacious when used in accordance with label directions and commonly accepted practices. The Agency reserves the right to require, on a case-by-case basis, submission of product performance data for any pesticide product registered or proposed for registration or amendment.
(4) Determination of data requirements. Subpart B of this part and §158.2201 describe how to use the table in paragraph (c) of this section to determine the product performance data requirements for antimicrobial pesticide products.
(b) Key. R = Required; EP = End-use product.
(c) Antimicrobial product performance data requirements table. The following table shows the data requirements for antimicrobial product performance.
| Guideline No. | Data requirement | All use patterns | Test substance |
|---|---|---|---|
| 810.2100 | Sterilants - Efficacy Data Recommendations | R | EP |
| 810.2200 | Disinfectants for Use on Hard Surfaces - Efficacy Data Recommendations | R | EP |
| 810.2300 | Sanitizers for Use on Hard Surfaces - Efficacy Data Recommendations | R | EP |
| 810.2400 | Disinfectants and Sanitizers for Use on Fabrics and Textiles - Efficacy Data Recommendations | R | EP |
| 810.2500 | Air Sanitizers - Efficacy Data Recommendations | R | EP |
| 810.2600 | Disinfectants for Use in Water - Efficacy Data Recommendations | R | EP |
§158.2230 Toxicology.
(a) General. Subpart B of this part and §158.2201 describe how to use the table in paragraph (g) of this section to determine the toxicology data requirements for an antimicrobial pesticide product. Notes that apply to an individual test, including specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions are listed in paragraph (h) of this section.
(b) Uses. The applicant for registration must first determine whether the use is likely to result in pesticide residues in food or water and therefore consult the “Food Use” columns of the table in paragraph (g) of this section. Generally, if the residues of the antimicrobial result from an application to a surface or if incorporated into a material that may come into contact with food or feed, and residues may be expected to transfer to such food or feed, then the “Indirect Food Uses” columns is to be consulted.
(c) Tiering of data requirements. Applicants for registration of antimicrobials may perform tests in a tiered fashion. After the initially required tests are conducted, additional testing may be required if results of the initial tests trigger the need for additional data. Conditions that trigger the need for additional data are given in the test notes in paragraph (h) of this section.
(d) 200 parts per billion (ppb). The 200 ppb level was originally used by the Food and Drug Administration with respect to the concentration of residues in or on food for tiering of data requirements for indirect food use biocides. The Agency has also adopted this same residue level for determining toxicology data requirements for indirect food uses of antimicrobial pesticides. The 200 ppb level is the concentration of antimicrobial residues in or on the food item.
(e) Use of OSHA standards. If EPA determines that industrial standards, such as the workplace standards set by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA standards), provide adequate protection for a particular pesticide or a particular use pattern, additional toxicity data may not be required for that pesticide or the use pattern.
(f) Key. R = Required; CR = Conditionally required; NR = Not required; MP = Manufacturing-use product; EP = End-use product; TGAI = Technical grade of the active ingredient; TEP = Typical end-use product; PAI = Pure active ingredient; PAIRA = Pure active ingredient, radiolabeled; Choice = choice of several test substances depending on studies required.
(g) Antimicrobial toxicology data requirements table. The following table shows the data requirements for toxicology. The test notes applicable to the data requirements in this table appear in paragraph (h) of this section.
Table - Antimicrobial Toxicology Data Requirements


(h) Test notes. The following test notes apply to the data requirements in the table to paragraph (g) of this section:
1. Not required if test material is a gas or highly volatile liquid.
2. The six end-use product (EP) acute toxicity studies are required using the product as formulated for sale and distribution. In addition, if the EP label has directions for diluting the product, then, the applicant may also need to conduct certain of the acute toxicity studies using the highest concentration labeled for dilution (i.e., the least diluted product). The end-use dilution testing is in addition to the testing conducted on the EP.
3. Not required if test material is corrosive to skin or has pH less than 2 or greater than 11.5.
4. Data are required when the product consists of, or under conditions of use will result in, a respirable material (e.g., gas, vapor, aerosol or particulates).
5. Data are required if repeated dermal exposure is likely to occur under conditions of use.
6. For indirect food uses ≤200 ppb, and all other nonfood uses, data are required if the neurotoxicity screen in the 90-day oral rodent study or other data indicate neurotoxicity.
7. The 90-day dermal toxicity study and/or 90-day inhalation toxicity study are required if the Agency determines that dermal and/or inhalation exposure is the primary route of exposure.
8. All 90-day subchronic studies in the rodent can be designed to simultaneously fulfill the requirements of the 90-day neurotoxicity and/or immunotoxicity studies by adding separate groups of animals for testing of neurotoxicity and/or immunotoxicity parameters.
9. The 90-day study is required in the rodent for hazard characterization (possibly endpoint selection) and dose-setting for the chronic/carcinogenicity study. It is not required in the mouse, but the Agency would encourage the applicant to conduct a 90-day range finding study for the purposes of dose selection for the mouse carcinogenicity study to achieve adequate dosing and an acceptable study.
10. A 1-year non-rodent study (i.e., 1-year dog study) may be required if the Agency finds that a pesticide chemical is highly bioaccumulative and slowly eliminated. EPA may also require the appropriate metabolism and pharmacokinetic studies to evaluate more precisely bioavailability, half life, and steady state to determine if a longer duration dog toxicity study is needed.
11. Although the subchronic toxicity testing guidelines include measurement of neurological endpoints, such screens do not meet the requirement of the 90-day neurotoxicity study. For nonfood uses, if the 90-day study does not include a neurotoxicity screen, then the acute neurotoxicity study will be required.
12. Data are required if all of the following criteria are met:
i. The intended use of the antimicrobial pesticide product is expected to result in repeated dermal human exposure to the product.
ii. Data from a 90-day dermal toxicity study are not available.
iii. The 90-day dermal toxicity study has not been triggered.
13. EP testing is required if the product or any component of the product may increase dermal absorption of the active ingredient(s) or increases its toxic or pharmacologic effects, as determined by testing using the TGAI or based on available information about the toxic effects of the product or its components.
14. Data are required if the active ingredient in the product is known or expected to be metabolized differently by the dermal route of exposure than by the oral route, and a metabolite of the active ingredient is the toxic moiety.
15. A 90-day oral toxicity test is not required for heating, ventilation, air conditioning, and refrigeration systems (collectively referred to as HVAC&R). Instead, two 90-day toxicity tests, one by the dermal route and one by the inhalation route are required.
16. Data are required if there is the likelihood of significant repeated inhalation exposure to the pesticide as a gas, vapor, or aerosol.
17. Based on estimates of the magnitude and duration of human exposure, studies of shorter duration, e.g., 21- or 28-days, may be sufficient to satisfy this requirement. The prime consideration in determining the appropriateness of a shorter duration study is the likely period of time for which humans will be exposed.
18. Based on the positive results of the acute or 90-day neurotoxicity studies, or on other data indicating neurotoxicity, a chronic neurotoxicity study (i.e., a chronic study with additional neurotoxicity evaluations) may be required to provide information about potential neurotoxic effects from long-term exposures.
19. Studies which are designed to simultaneously fulfill the requirements of both the chronic oral and carcinogenicity studies (i.e., a combined study) may be conducted.
20. For indirect food uses ≤200 ppb, and all other nonfood uses, data are required if either of the following criteria are met:
i. The use of the pesticide is likely to result in repeated human exposure over a considerable portion of the human lifespan; or
ii. The use requires that a tolerance, tolerance exemption, or food additive regulation or clearance be established.
21. For indirect food uses ≤200 ppb, and all other nonfood uses, data are required if any of the following criteria, are met:
i. The use of the pesticide is likely to result in significant human exposure over a considerable portion of the human life span which is significant in terms of frequency, time, duration, and/or magnitude of exposure.
ii. The use requires that a tolerance, tolerance exemption, or food additive regulation or clearance be established.
iii. The active ingredient, metabolite, degradate, or impurity:
A. Is structurally related to a recognized carcinogen;
B. Causes mutagenic effects as demonstrated by in vitro or in vivo testing; or
C. Produces a morphologic effect in any organ (e.g., hyperplasia, metaplasia) in subchronic studies that may lead to a neoplastic change.
22. If the requirement for a carcinogenicity study in any species is modified or waived for any reason, then a subchronic 90-day oral study in the same species may be required.
23. Testing in two species is required for all uses.
24. The oral route, by oral intubation, is preferred, unless the chemical or physical properties of the test substance, or the pattern of human exposure, suggest a more appropriate route of exposure.
25. Additional testing by other routes of exposure may be required if the pesticide is determined to be a prenatal developmental toxicant after oral dosing.
26. The developmental toxicity study in rodents may be combined with the two-generation reproduction study in rodents by using a second mating of the parental animals in either generation. Protocols must be approved by the Agency prior to the initiation of the study.
27. A two-generation reproduction study is required.
28. An information-based approach to testing is preferred, which utilizes the best available knowledge on the chemical (hazard, pharmacokinetic, or mechanistic data) to determine whether a standard guideline study, an enhanced guideline study, or an alternative study should be conducted to assess potential hazard to the developing animal. Applicants must submit any alternative proposed testing protocols and supporting scientific rationale to the Agency. Protocols must be approved by the Agency prior to the initiation of the study.
29. The use of a combined two-generation reproduction/developmental neurotoxicity study that utilizes the two-generation reproduction study in rodents as a basic protocol for the addition of other endpoints or functional assessments in the immature animal is encouraged.
30. A DNT study is required using a weight-of-evidence approach when:
i. The pesticide causes treatment-related neurological effects in adult animal studies (i.e., clinical signs of neurotoxicity, neuropathology, functional or behavioral effects).
ii. The pesticide causes treatment-related neurological effects in developing animals, following pre- or post-natal exposure (i.e., nervous system malformations or neuropathy, brain weight changes in offspring, functional or behavioral changes in the offspring).
iii. The pesticide elicits a causative association between exposures and adverse neurological effects in human epidemiological studies.
iv. The pesticide evokes a mechanism that is associated with adverse effects on the development of the nervous system (i.e., structure-activity-relationship (SAR) to known neurotoxicants, altered neuroreceptor or neurotransmitter responses).
31. To facilitate the weight-of-evidence determination for the pesticide's mutagenicity, in addition to those specifically listed in this table, the Agency requires submission of other mutagenicity test results that may have been performed. A reference list of all studies and papers known to the applicant concerning the mutagenicity of the test chemical must be submitted with the required studies.
32. Due to the nature of antimicrobials, if testing with bacterial strains has not been conducted, then testing using a mammalian cell assay such as the mouse lymphoma TK ±assay is preferred. If reverse mutation assay testing with bacterial strains has already been conducted, and the testing was conducted at levels that did not cause toxicity to the bacterial strains tested, then the applicant may submit the study to fulfill this data requirement.
33. For the in vitro mammalian gene mutation study, there is a choice of assays using either mouse lymphoma L5178Y cell thymidine kinase (tk) gene locus, maximizing assay conditions for small colony expression and detection; Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) or Chinese hamster lung fibroblast (v79) cells, hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (hgprt) gene locus, accompanied by an appropriate in vitro test for clastogenicity; or CHO cells strains AS52, xanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (xprt) gene locus.
34. There is a choice of assays, but the micronucleus rodent bone marrow assay is preferred; the rodent bone marrow assays using metaphase analysis (aberrations) are acceptable.
35. Data are required when chronic toxicity or carcinogenicity studies are also required.
36. Data is required if the product label directs that it be applied to domestic animals, such as cats, dogs, cattle, pigs, and horses.
37. In the absence of dermal absorption data or a repeated dose dermal toxicity study, the assumption of 100 percent dermal absorption would be used in a risk assessment to determine if a dermal penetration study is required, and to identify the doses and duration of exposure for which dermal absorption is to be quantified.
38. Required for nonfood uses, if oral exposure could occur.
39. Data may be required if significant adverse effects are seen in available toxicology studies and these effects can be further elucidated by metabolism and pharmacokinetics studies.
§158.2240 Nontarget organisms.
(a) General. Subpart B of this part and §158.2201 describe how to use the table in paragraph (c) of this section to determine the terrestrial and aquatic nontarget organisms data requirements for a particular antimicrobial pesticide product. Notes that apply to an individual test, including specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions are listed in paragraph (d) of this section.
(1) Terrestrial and aquatic nontarget organism data are required to support the registration of most end-use and manufacturing-use antimicrobial products.
(2) Data are generally not required to support end-use products of a gas, highly volatile liquid, highly reactive solid, or a highly corrosive material.
(3) Data on transformation/degradation products or leachate residues of the parent compound are also required to support registration, if the transformation/degradation/degradation products or leachate residues meet one of the following criteria:
(i) More toxic, persistent, or bioaccumulative than the parent;
(ii) Have been shown to cause adverse effects in mammalian or aquatic reproductive studies; or
(iii) The moiety of concern (i.e., functional group in the parent chemical molecule that imparts adverse effects) remains intact.
(4) If an antimicrobial may be applied to a field crop, horticultural crop, or turf, then the data requirements in §158.630 apply.
(5) For the purpose of determining data requirements, the all other use patterns category includes the following use patterns:
(i) Agricultural premises and equipment.
(ii) Food-handling/storage establishments, premises, and equipment.
(iii) Commercial, institutional and industrial premises and equipment.
(iv) Residential and public access premises.
(v) Medical premises and equipment.
(vi) Human drinking water systems.
(vii) Materials preservatives.
(viii) Swimming pools.
(b) Key. MP = Manufacturing use product; EP = End-use product; R = Required; CR = Conditionally required; NR = Not required; TGAI = Technical grade of the active ingredient; TEP = Typical end-use product; PAIRA = Pure active ingredient radiolabeled; a.i. = active ingredient.
(c) Antimicrobial nontarget organism data requirements table. The following table shows the data requirements for nontarget organisms. The test notes appear in paragraph (d) of this section.
Table - Antimicrobial Nontarget Organism Data Requirements
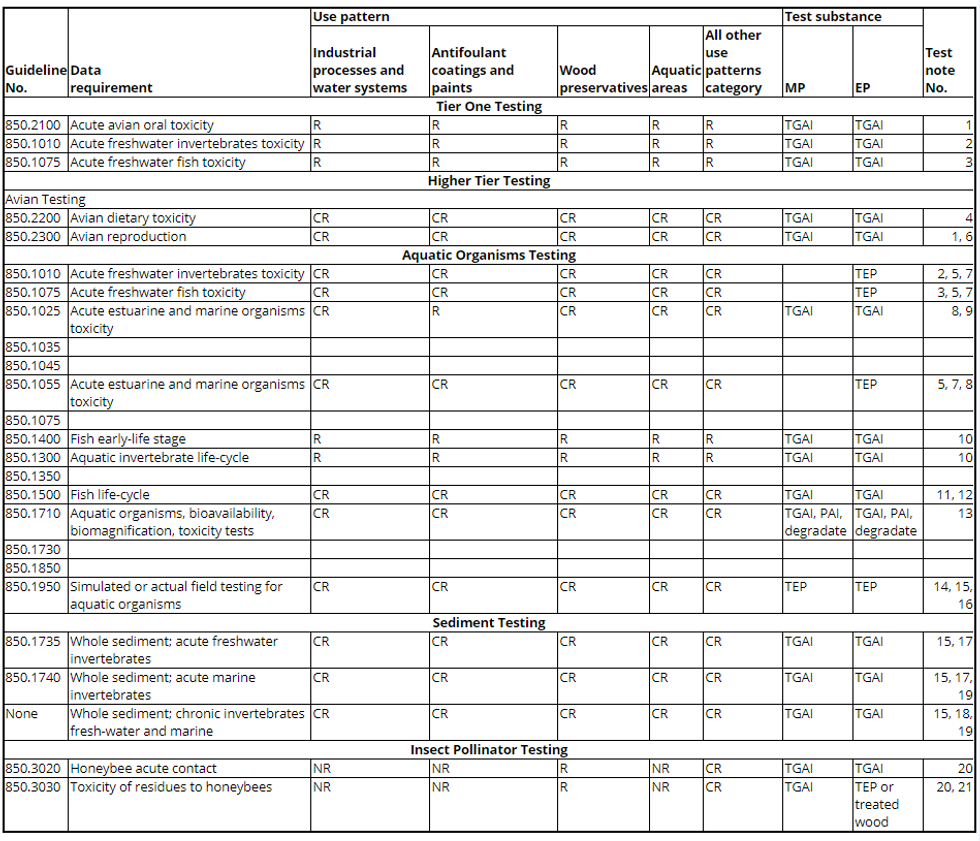
(d) Test notes. The following test notes apply to the data requirements in the table to paragraph (c) of this section:
1. For industrial processes and water systems, antifoulant paints and coatings, wood preservatives, and aquatic areas, data are required for two avian species: one waterfowl species and one upland game bird species. For the all other use patterns category (as specified in §158.2240(a)(5)), data are required for one avian species.
2. Data are required on one freshwater aquatic invertebrate species.
3. For the industrial processes and water systems, antifoulant paints and coatings, wood preservatives, and aquatic use pattern areas, data are required on two species of fish, one cold water species and one warm water species. For the all other use patterns category (as specified in §158.2240(a)(5)), data are required on one species of fish, either one cold water species or one warm water species. Testing on a second species is required if the active ingredient or principal transformation products are stable in the environment and the LC50 in the first species is less than or equal to 1 ppm or 1 mg/L.
4. Data are required on one avian species, either one waterfowl species or one upland game bird species, if the avian acute oral LD50 (TGAI testing) is less than or equal to 100 mg/a.i./kg and a.i. residues or its principal transformation products are likely to occur in avian feed items. Data on the second species are required if the avian dietary LC50 in the first species tested is less than or equal to 500 ppm a.i. in the diet.
5. If TEP testing cannot be conducted due to the physical characteristics of the test substance (for example, a paint), then the applicant should request a waiver.
6. Data are required if one or more of the following criteria are met:
i. Birds may be subjected to repeated or continued exposure to the pesticide or any of its transformation products, especially preceding or during the breeding season.
ii. The pesticide or any of its major metabolites or degradation products are stable in the environment to the extent that a potentially toxic amount may persist in avian feed.
iii. The pesticide or any of its major metabolites or degradation products are stored or accumulated in plant or animal tissues, as indicated by the octanol/water partition coefficient (Kow is greater than or equal to 1,000), accumulation studies, metabolic release and retention studies, or as indicated by structural similarity to known bioaccumulative chemicals.
iv. Any other information, such as that derived from mammalian reproduction studies, indicates that reproduction in terrestrial vertebrates may be adversely affected by the anticipated use of the pesticide product.
7. TEP testing is required for any product which meets one or more of the following conditions:
i. When based on deterministic modeling results: If the Estimated Environmental Concentration (EEC) in the aquatic environment is equal to or greater than one-half the LC50/EC50 of the TGAI.
ii. When based on probabilistic modeling results: If the estimated 10th percentile 7Q10 Surface Water Concentration exceeds the acute concentration of concern (i.e., one-half the LC50/EC50).
iii. If an ingredient in the end-use product other than the active ingredient is expected to enhance the toxicity of the active ingredient or to cause toxicity to aquatic organisms.
iv. The end-use antimicrobial product will be applied directly into an aquatic environment.
8. Data are required on one estuarine/marine mollusk, one other estuarine/marine invertebrate, and one estuarine/marine fish species.
9. For the all other use patterns category (as specified in §158.2240(a)(5)), industrial processes and water systems, wood preservatives, and aquatic areas, data are required if the pesticide residues from the parent compound and/or transformation products are likely to enter the estuarine/marine environment.
10. Testing must be conducted with the most sensitive organism (either freshwater or estuarine/marine vertebrates, or freshwater or estuarine/marine invertebrates), as determined from the results of the acute toxicity tests (acute EC50 freshwater invertebrates; acute LC50/EC50 estuarine and marine organisms; acute freshwater fish LC50).
11. Data are required on estuarine/marine species if the product is intended for direct application to the estuarine or marine environment, or the product is expected to enter this environment in significant concentrations because of its expected use or mobility patterns.
12. Data are required on freshwater species if the end-use product is intended to be applied directly to water, or is expected to be transported to water from the intended use site, and when one or more of the following conditions apply:
i. When based on deterministic modeling results: If the Estimated Environmental Concentration (EEC) in water is equal to or greater than 0.1 of the no-observed-adverse-effect concentration or no-observed-adverse-effect level (NOAEC/NOAEL) in the fish early-life stage or invertebrate life cycle tests.
ii. When based on probabilistic modeling results: If the estimated 10th percentile 7Q10 Surface Water Concentration based on probabilistic modeling exceeds for 20 days or more the chronic concentration of concern (i.e., one-tenth the NOAEC or NOAEL) determined in the fish early-life stage or invertebrate life cycle tests.
iii. If studies of other organisms indicate that the reproductive physiology of fish may be affected.
13. Not required when:
i. The octanol/water partition coefficients of the pesticide and its major degradates are less than 1,000;
ii. There are no potential exposures to fish and other nontarget aquatic organisms; or
iii. The hydrolytic half-life is less than 5 days at pH 5, 7, and 9.
14. Environmental chemistry methods used to generate data associated with this study must include results of a successful confirmatory method trial by an independent laboratory. Test standards and procedures for independent laboratory validation are available as addenda to the guideline for this test requirement.
15. Protocols must be approved by the Agency prior to the initiation of the study.
16. Data are required if the intended use pattern, and the physical/chemical properties and environmental fate characteristics of the antimicrobial indicate significant potential exposure, and, based on the results of the acute and chronic aquatic organism testing, significant impairment of nontarget aquatic organisms could result.
17. Data are required if the half-life of the pesticide in the sediment is equal to or less than 10 days in either the aerobic soil or aquatic metabolism studies, and if one or more of the following conditions are met:
i. The soil partition coefficient (Kd) is equal to or greater than 50 L/kg.
ii. The log Kow is equal to or greater than 3.
iii. The Koc is equal to or greater than 1,000.
18. Data are required if the EEC in sediment is greater than 0.1 of the acute LC50/EC50 values and if one or more of the following conditions are met:
i. The soil partition coefficient (Kd) is equal to or greater than 50 L/kg.
ii. The log Kow is equal to or greater than 3.
iii. The Koc is equal to or greater than 1,000.
19. Sediment testing with estuarine/marine test species is required if the product is intended for direct application to the estuarine or marine environment or the product is expected to enter this environment in significant concentrations either by runoff or erosion, because of its expected use or mobility pattern.
20. For the all other use patterns category (as specified in §158.2240(a)(5)), data are required only for beehive applications when the beehive (empty or occupied) may be treated.
21. A study similar to “Honey Bee Toxicity of Residues on Foliage” is required using treated wood instead of the foliage. Protocols must be approved by the Agency prior to the initiation of the study.
§158.2250 Nontarget plant protection.
(a) Subpart B of this part and §158.2201 describe how to use the table in paragraph (f) of this section to determine the nontarget plant protection data requirements for a particular antimicrobial pesticide product. Notes that apply to an individual test including specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions are listed in paragraph (g) of this section.
(b) Data on transformation/degradation products or leachate residues of the parent compound are also required to support registration, if the transformation/degradation products or leachate residues meet one of the following criteria:
(1) More toxic, persistent, or bioaccumulative than the parent;
(2) Have been shown to cause adverse effects in mammalian or aquatic reproductive studies; or
(3) The moiety of concern (i.e., functional group in the parent chemical molecule that imparts adverse effects) remains intact.
(c) For the purpose of determining data requirements, the all other use patterns category includes the following use patterns:
(1) Agricultural premises and equipment.
(2) Food-handling/storage establishments, premises, and equipment.
(3) Commercial, institutional and industrial premises and equipment.
(4) Residential and public access premises.
(5) Medical premises and equipment.
(6) Human drinking water systems.
(7) Materials preservatives.
(8) Swimming pools.
(d) If an antimicrobial may be applied to a field crop, horticultural crop, or turf, then the data requirements in §158.660 apply.
(e) Key. MP = Manufacturing use product; EP = End-use product; R = Required; CR = Conditionally required; NR = Not required; TGAI = Technical grade of the active ingredient; TEP = Typical end-use product.
(f) Nontarget plant protection data requirements table. The following table shows the data requirements for nontarget plant protection. The test notes appear in paragraph (g) of this section.
Table - Nontarget Plant Protection Data Requirements

(g) Test notes. The following test notes apply to the data requirements in the table to paragraph (f) of this section:
1. Data on only one plant species (rice, Oryza sativa) are required.
2. Data are required if the risk quotient from any aquatic plant growth Tier II study exceeds a level of concern for aquatic plants.
3. Not required when:
i. There are no potential exposures to plants;
ii. The hydrolytic half-life is less than 5 days at pH 5, 7, and 9; or
iii. The results of a biodegradation study indicate that the active ingredient or principal degradation products are not biodegradable in 28 days, i.e., the biodegradation curve has not reached a plateau for at least three determinations within the 28 days.
4. For TEP testing, data are required for the applicant's end-use product if an ingredient in the end-use product, other than the active ingredient, is expected to enhance the toxicity of the active ingredient.
5. One Tier II (dose response) study, conducted with Selenastrum capricornutum, is required for the all other use patterns category (as specified in §158.2250(c)). If the results of this study exhibit detrimental effects (EC50 less than 1.0 ppm or mg/L), then additional Tier II (dose response) studies are required on three species (Anabaena flos-aquae, Navicula pelliculosa, and Skeletonema costatum).
6. For industrial processes and water systems, antifoulant coatings and paints, wood preservatives, and aquatic areas, Tier II (dose response) studies are required on four species (Anabaena flos-aquae, Navicula pelliculosa, Skeletonema costatum, and Selenastrum capricornutum).
7. Environmental chemistry methods used to generate data must include the results of a successful confirmatory method trial by an independent laboratory.
8. Tests are required on a case-by-case basis based on the results of lower tier plant protection studies, adverse incident reports, intended use pattern, and environmental fate characteristics that indicate potential exposure.
9. Protocols must be approved by the Agency prior to the initiation of the study.
10. For the all other use patterns category (as specified in §158.2250(c)), data are required if the aquatic (algal) plant growth Tier II study demonstrates detrimental effects at less than 1.0 ppm or mg/L.
§158.2260 Applicator exposure.
(a) General. Subpart B of this part and §158.2201 describe how to use the table in paragraph (d) of this section to determine the applicator exposure data requirements for antimicrobial pesticide products. Notes that apply to an individual test including specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions are listed in paragraph (e) of this section.
(1) The Agency may accept surrogate exposure data estimations and/or modeling estimations from other sources to satisfy exposure data requirements. The surrogate data must meet the basic quality assurance, quality control, good laboratory practice, and other scientific requirements set by EPA. To be acceptable, the Agency must find that the surrogate exposure data estimations have adequate information to address the applicable exposure data requirements and contain adequate monitoring events of acceptable quality. The data must reflect the specific use prescribed on the label and the activity of concern, including formulation type, application methods and rates, type of activity, and other pertinent information.
(2) Occupational uses include not only handlers, mixers, loaders, and applicators, but also commercial applications to residential sites. Residential uses are limited to non-occupational, i.e., non-professional, antimicrobial applications. Both occupational and residential applicator data may be required for the same product.
(b) Criteria for testing. Applicator exposure data described in the table to paragraph (d) of this section are required based on toxicity and exposure criteria. Data are required if at least one of the toxicity criteria in paragraph (b)(1) of this section, and at least one of the exposure criteria in paragraph (b)(2) of this section are met.
(1) Toxicity criteria.(i) Evidence of potentially significant adverse effects have been observed in any applicable toxicity studies.
(ii) Scientifically sound epidemiological or poisoning incident data with a clear cause-effect relationship indicating that adverse health effects may have resulted from exposure to the pesticide.
(2) Exposure criteria.(i) Dermal exposure may occur during product use.
(ii) Respiratory exposure may occur during product use.
(c) Key. R = Required; CR = Conditionally required; TEP = Typical end-use product.
(d) Antimicrobial applicator exposure data requirements table. The following table shows the data requirements for applicator exposure. The test notes appear in paragraph (e) of this section.
| Guideline No. | Data requirements | Use sites | Test substance | Test note No. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Occupational | Residential | ||||
| 875.1100 | Dermal exposure | R | R | TEP | 1, 2, 3, 4 |
| 875.1200 | |||||
| 875.1300 | Inhalation exposure | R | R | TEP | 1, 2, 3, 4 |
| 875.1400 | |||||
| 875.1500 | Biological monitoring | CR | CR | TEP | 1, 2, 3 |
| 875.1600 | Data reporting and calculations | R | R | TEP | 5 |
| 875.1700 | Product use information | R | R | TEP | |
(e) Test notes. The following test notes apply to the data requirements in the table to paragraph (d) of this section:
1. Prior to initiation of the study, protocols involving intentional exposure of human subjects must be submitted for review by EPA and then the Human Studies Review Board (HSRB) according to 40 CFR 26.1125. Examples of proposed human study research can be found in various reviews provided by the Human Studies Review Board (http://www.epa.gov/osa/hsrb/index.htm).
2. Biological monitoring data may be submitted in addition to, or in lieu of, dermal and inhalation passive dosimetry exposure data, provided the human pharmacokinetics of the pesticide or metabolite/analog compounds (i.e., whichever method is selected as an indicator of body burden or internal dose) allow for the back calculation to the total internal dose.
3. For products with both indoor and outdoor uses, and similar conditions of use, data are generally required for the indoor applications only. However, data for outdoor uses are required if the Agency expects outdoor uses to result in greater exposure than indoor uses (e.g., higher use rates and application frequency, or longer exposure duration, or application methods/equipment create potential for increased dermal or inhalation exposure in outdoor versus indoor use sites). In certain cases, when a pesticide may be used both indoors and outdoors under dissimilar conditions of use, the Agency may require submission of applicator exposure data for both use patterns.
4. EPA will consider waiving this data requirement for antimicrobials applied via closed loading systems if the antimicrobial has a low vapor pressure.
5. Data reporting and calculations are required only if handler exposure data are required.
§158.2270 Post-application exposure.
(a) General. Subpart B of this part and §158.2201 describe how to use the table in paragraph (d) of this section to determine the post-application exposure data requirements for antimicrobial pesticide products. The data generated during these studies are used to determine the quantity of pesticide to which people may be exposed after application. Notes that apply to an individual test, including specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions to the designated test, are listed in paragraph (e) of this section.
(1) Post-application exposure data are required when certain toxicity criteria are met and the human activities associated with the pesticide's use pattern can lead to potential adverse exposures.
(2) The Agency may accept surrogate exposure data estimations and/or modeling estimations from other sources to satisfy exposure data requirements. The surrogate data must meet the basic quality assurance, quality control, good laboratory practice, and other scientific requirements set by EPA. To be acceptable, the Agency must find that the surrogate exposure data estimations have adequate information to address the applicable exposure data requirements and contain adequate monitoring events of acceptable quality. The data must reflect the specific use prescribed on the label and the activity of concern, including formulation type, application methods and rates, type of activity, and other pertinent information.
(b) Criteria for testing. Post-application exposure data described in the table to paragraph (d) of this section are required based on toxicity and exposure criteria. Data are required if at least one of the toxicity criteria in paragraph (b)(1) of this section, and at least one of the exposure criteria in paragraph (b)(2) of this section are met.
(1) Toxicity criteria.(i) Evidence of potentially significant adverse effects have been observed in any applicable toxicity studies.
(ii) Scientifically sound epidemiological or poisoning incident data with a clear cause-effect relationship indicating that adverse health effects may have resulted from exposure to the pesticide.
(2) Exposure criteria(i) Outdoor uses.(A) Occupational human post-application or bystander exposure to residues of antimicrobial pesticides could occur as the result of, but is not limited to, worker reentry into treatment sites, clean-up and equipment maintenance tasks, handling wood preservative-treated wood, or other work-related activity.
(B) Residential human post-application or bystander exposure to residues of antimicrobial pesticides could occur following the application of antimicrobial pesticides to outdoor areas and spaces at residential sites, such as, but not limited to homes, daycare centers, and other public buildings.
(ii) Indoor uses.(A) Occupational human post-application or bystander exposure to pesticide residues could occur following the application of the antimicrobial pesticide to indoor spaces or surfaces.
(B) Residential human post-application or bystander exposure to pesticide residues could occur following the application of the antimicrobial pesticide to indoor spaces or surfaces at residential sites, such as, but not limited to homes, daycare centers, hospitals, schools, and other public buildings.
(c) Key. R = Required; CR = Conditionally required; NR = Not required; TEP = Typical end-use product.
(d) Antimicrobial post-application exposure data requirements table. The following table shows the data requirements for post-application exposure. The test notes appear in paragraph (e) of this section.
| Guideline No. | Data requirement | Use sites | Test substance | Test note No. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Occupational | Residential | ||||
| 875.2200 | Soil residue dissipation | CR | CR | TEP | 2, 3 |
| 875.2300 | Indoor surface residue dissipation | CR | R | TEP | 3, 4, 5, 6 |
| 875.2400 | Dermal exposure | CR | CR | TEP | 1, 7, 8 |
| 875.2500 | Inhalation exposure | CR | CR | TEP | 1,7, 8, 9 |
| 875.2600 | Biological monitoring | CR | CR | TEP | 1, 8 |
| 875.2700 | Product use information | R | R | TEP | |
| 875.2800 | Description of human activity | R | R | TEP | |
| 875.2900 | Data reporting and calculations | R | R | TEP | 10 |
(e) Test notes. The following test notes apply to the data requirements in the table to paragraph (d) of this section:
1. Prior to initiation of the study, protocols involving intentional exposure of human subjects must be submitted for review by EPA and then the Human Studies Review Board (HSRB) according to 40 CFR 26.1125. Examples of proposed human study research can be found in various reviews provided by the Human Studies Review Board (HSRB) (http://www.epa.gov/osa/hsrb/index.htm).
2. For residential wood preservative uses, data may be required if soil has the potential to be an important exposure pathway, and soil is in contact with or adjacent to treated wood, including but not limited to decks, play sets, and gazebos,
3. Protocols must be approved by the Agency prior to the initiation of the study.
4. For wood preservatives, data are required for treated wood surfaces where post-application contact with treated wood is anticipated.
5. For occupational uses, data are required if the pesticide may be applied to or around surfaces, and if the human activity data indicate that workers are likely to have post-application dermal contact with treated surfaces while participating in typical activities.
6. Data are required for residential use sites, schools, and daycare institutions. This includes but is not limited to the following: Residential and public access premises; material preservatives (including those used in residential products, including but not limited to clothing and plastic toys) and wood preservatives (when contact with treated wood is likely to occur).
7. Data are required for occupational and residential uses if the human activity data indicate the potential for post-application dermal and/or inhalation exposures while participating in typical activities and no acceptable modeling options are available.
8. Biological monitoring data may be submitted in addition to, or in lieu of, dermal and inhalation passive dosimetry exposure data provided the human pharmacokinetics of the pesticide or metabolite/analog compounds (i.e., whichever method is selected as an indicator of body burden or internal dose) allow for a back-calculation to the total internal dose.
9. Data are required for occupational and residential uses if there is the potential for bystander exposure and the pesticide use could result in respirable and/or inhalable material (e.g., gas, vapor, aerosol, or particulates).
10. Data reporting and calculations are required only if post-application exposure data are required.
§158.2280 Environmental fate.
(a) General. Subpart B of this part and §158.2201 describe how to use the table in paragraph (c) of this section to determine the environmental fate data requirements for antimicrobial pesticide products. Notes that apply to an individual test including specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions are listed in paragraph (d) of this section.
(1) Environmental fate data are required to support the registrations of all end-use and manufacturing-use antimicrobial products.
(2) Data on transformation/degradation products or leachate residues of the parent compound are also required to support registration, if the transformation/degradation products or leachate residues meet one of the following criteria:
(i) More toxic, persistent, or bioaccumulative than the parent;
(ii) Have been shown to cause adverse effects in mammalian or aquatic reproductive studies; or
(iii) The moiety of concern (i.e., functional group in the parent chemical molecule that imparts adverse effects) remains intact.
(3) For the purpose of determining data requirements, the all other use patterns category includes the following use patterns:
(i) Agricultural premises and equipment.
(ii) Food-handling/storage establishments, premises, and equipment.
(iii) Commercial, institutional and industrial premises and equipment.
(iv) Residential and public access premises.
(v) Medical premises and equipment.
(vi) Human drinking water systems.
(vii) Materials preservatives.
(viii) Swimming pools.
(b) Key. MP = Manufacturing use product; EP = End-use product; R = Required; CR = Conditionally required; NR = Not required; TGAI = Technical grade of the active ingredient; TEP = Typical end-use product; PAIRA = Pure active ingredient radiolabeled; ROC = residue of concern.
(c) Antimicrobial environmental fate data requirements table. The following table shows the data requirements for environmental fate. The test notes appear in paragraph (d) of this section.
Table - Antimicrobial Environmental Fate Data Requirements
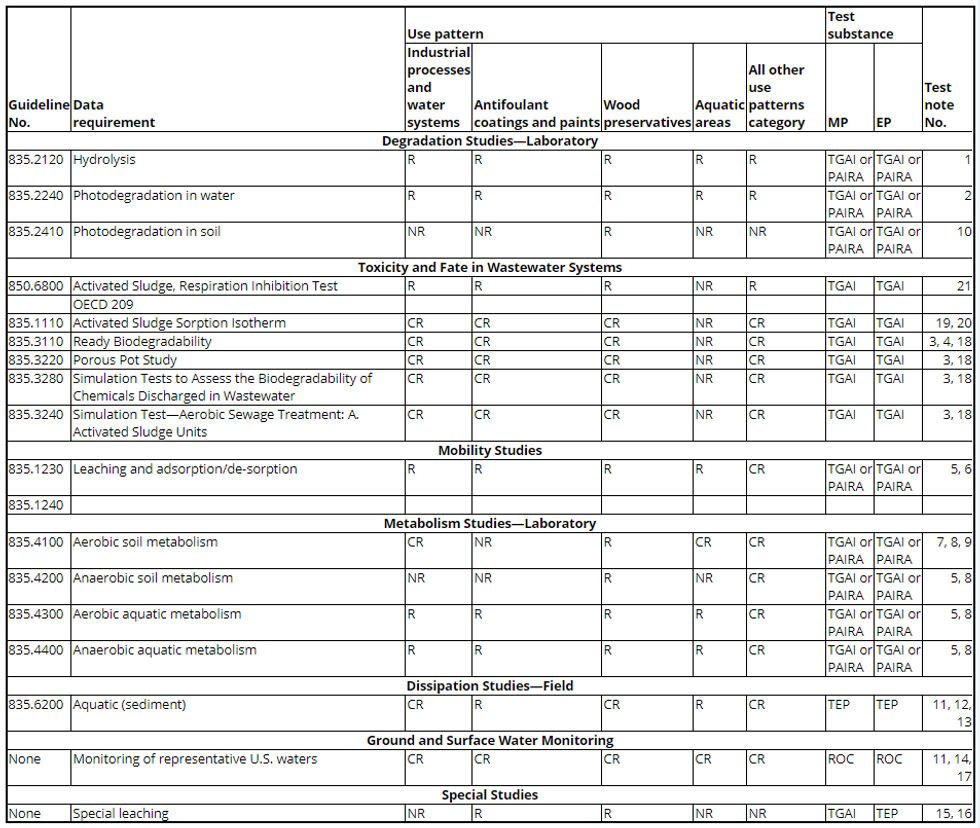
(d) Test notes. The following test notes apply to the data requirements in the table in paragraph (c) of this section:
1. For testing antifoulant paints and coatings, testing is to be performed separately with both sterile buffered distilled water and sterile synthetic seawater at pHs 5, 7, and 9.
2. Not required if:
i. The electronic absorption spectra, measured at pHs 5, 7 and 9, of the chemical and its hydrolytic products, if any, show no absorption or tailing between 290 and 800 nm, inclusive; or
ii. The results of the hydrolysis study at all three pHs (5, 7, and 9) demonstrates a half-life of less than 30 days.
3. The results of the activated sludge, respiration inhibition (ASRI) test determine which of the following tests are required: Ready biodegradability, porous pot, the biodegradation in activated sludge study as described in the “Simulation Tests to Assess the Biodegradability of Chemicals Discharged in Wastewater,” or simulation test - aerobic sewage treatment: A. activated sludge units.
i. If the ASRI test EC50 is equal to or less than 20 mg/L, then the applicant must choose either to:
A. Conduct the biodegradation in activated sludge study as described in the “Simulation Tests to Assess the Biodegradability of Chemicals Discharged in Wastewater”;
B. Conduct the porous pot test; or
C. Conduct the simulation test - aerobic sewage treatment: A. activated sludge units.
ii. If the ASRI test EC50 is greater than 20 mg/L, then the applicant must choose either to:
A. Conduct a ready biodegradability study; or
B. Conduct one of the following studies: The biodegradation in activated sludge study as described in the “Simulation Tests to Assess the Biodegradability of Chemicals Discharged in Wastewater,” the porous pot test, or the simulation test - aerobic sewage treatment: A. activated sludge units.
4. Pass criteria for the ready biodegradability study are: 70 percent removal of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) and 60 percent removal of theoretical oxygen demand (ThOD) or theoretical carbon dioxide (ThCO2) production for respirometric methods. These pass levels must be reached in a 10-day window within the 28-day period of the test. If the antimicrobial passes the ready biodegradability study, then no further testing is required. If the antimicrobial fails the ready biodegradability study, then the applicant must conduct one of the following studies: The biodegradation in activated sludge study as described in the “Simulation Tests to Assess the Biodegradability of Chemicals Discharged in Wastewater,” the porous pot test, or the simulation test - aerobic sewage treatment: A. activated sludge units.
5. For the all other use patterns category (as specified in §158.2280(a)(3)), data are required based on a weight-of-evidence evaluation of the results of the hydrolysis, photodegradation in water, activated sludge sorption isotherm, biodegradability, and activated sludge, respiration inhibition tests.
6. Adsorption and desorption using a batch equilibrium method is preferred. In some cases, as when the antimicrobial pesticide degrades rapidly, soil column leaching with unaged or aged columns may be more appropriate to fully characterize the potential mobility of the parent compound and major transformation products.
7. For industrial processes and water systems, aquatic areas, and the all other use patterns category (as specified in §158.2280(a)(3)), data are required based on a weight-of-evidence evaluation of the results of the hydrolysis, photodegradation in water, activated sludge sorption isotherm, biodegradability, and activated sludge, respiration inhibition tests.
8. The environmental media (soil, water, hydrosoil, and biota) to be utilized in these studies must be collected from areas representative of potential use sites.
9. For industrial processes and water systems, and aquatic areas, data are required for use sites that are intermittently dry.
10. Data are not required if the antimicrobial is an inorganic substance or a metal salt; or if the standardized soil profiles demonstrate that the antimicrobial is likely to readily degrade either microbially or via redox reactions (chemically) and no transformation/degradate/leachate products of concern (as described under §158.2280(a)(2)) are produced.
11. Analytical methods used to generate data associated with this study must include results of a successful confirmatory method trial by an independent laboratory.
12. Protocols must be approved by the Agency prior to the initiation of the study.
13. For industrial processes and water systems, wood preservatives, and the all other use patterns category (as specified in §158.2280(a)(3)), data are required based on the potential for aquatic exposure and if the weight-of-evidence indicates that the active ingredient or principal transformation products are likely to have the potential for persistence, mobility, nontarget aquatic toxicity, or bioaccumulation.
14. Data are required if the weight-of-evidence indicates that the active ingredient or principal transformation products are likely to occur in nontarget freshwater, estuarine, or marine waters such that human or environmental exposures are likely to occur. In making that determination, the Agency takes into account other factors such as the toxicity of the chemical(s), available monitoring data and the vulnerability of the freshwater, estuarine, or marine water resources in the antimicrobial use area.
15. For wood preservatives, an aquatic leaching study is required. A soil leaching study is required if human or environmental exposures are likely to occur from leachates that contain the active ingredient or principal transformation products from wood treated with a preservative product. Protocols must be approved by the Agency prior to the initiation of the study.
16. For antifoulant paints and coatings, a leaching study is required. Protocols must be approved by the Agency prior to the initiation of the study.
17. Protocols, which include the residues of concern (such as parent, degradate/transformation product, and/or leachate residues) that would be monitored, must be approved by the Agency prior to the initiation of the study.
18. A biodegradation study is not required if the antimicrobial meets one or more of the following criteria:
i. Classified as a metal,
ii. Relatively volatile, but not hydrophobic,
iii. Highly reactive,
iv. Both the parent and all transformation/degradate products (as described under §158.2280(a)(2)) have half-lives of less than 3 hours,
v. None of the registered or proposed product uses would result in transport of the parent and its transformation/degradate products (as described under §158.2280(a)(2)) to a wastewater treatment plant.
19. The activated sludge sorption isotherm test is not required if the antimicrobial is:
i. Relatively volatile, but not hydrophobic;
ii. Highly reactive; or
iii. The log Kow is less than 3.0.
20. If the criteria of test note 19 of this paragraph are not met, then the activated sludge sorption isotherm test is required if one or more of the following criteria are also met:
i. The antimicrobial is a metal,
ii. The log Kow is greater than or equal to 3.0,
iii. The antimicrobial is positively charged or polycationic,
iv. The EC50 in the activated sludge, respiration inhibition test is less than or equal to 20 mg/L,
v. The EC50 in the activated sludge, respiration inhibition test is greater than 20 mg/L, and the antimicrobial fails the ready biodegradability study.
21. The activated sludge respiration inhibition study is not required if none of the registered or proposed product uses would result in transport of the parent and its transformation/degradate products (as described under §158.2280(a)(2)) to a wastewater treatment plant.
§158.2290 Residue chemistry.
(a) General. Subpart B of this part and §158.2201 describe how to use the table in paragraph (h) of this section to determine the residue chemistry data requirements for antimicrobial pesticide products. Notes that apply to an individual test including specific conditions, qualifications, or exceptions are listed in paragraph (i) of this section.
(b) Residue chemistry data are required for:
(1) Antimicrobial end-use products with uses that may result in residues in or on food, including but not limited to:
(i) Products that require a tolerance, tolerance exemption, or food additive regulation or clearance.
(ii) Products that may be used to treat livestock or poultry drinking water, for food egg washing, or for fruit and vegetable rinses.
(iii) Products that may be applied to a surface or incorporated into a material that may contact food or feed. Data are required regardless of whether the antimicrobial is applied or impregnated for the purpose of imparting antimicrobial protection to external surfaces of the substance or article, or for the purpose of protecting the substance or article itself.
(iv) Products that may be applied to water that have the potential to result in residues in potable water, or in water used for livestock and poultry drinking water, irrigation of crops, or water containing fish that may be used for human food.
(v) Wood preservative or antifoulant products intended for treating submerged materials that may result in food contact (e.g., lobster pots, fish cages on fish farms).
(2) Each manufacturing-use product bearing directions for formulation into an end-use product bearing uses described in paragraph (b)(1) of this section.
(c) Residue chemistry data are not required under paragraph (b) of this section if no adverse effects (no toxicity endpoints) are associated with dietary exposure to the active ingredient or if theoretical (high-end) dietary exposure estimates combined with the applicable toxicity endpoint result in acute and chronic dietary risks that are below the Agency levels of concern.
(d) For purposes of this section, Magnitude of the Residue Studies include the following: Food-handling, migration studies, potable water, fish, irrigated crops, meat/milk/poultry/eggs, crop field trails, processed food or feed, and anticipated residues.
(e) If the antimicrobial chemical may be applied to a field crop, then the residue chemistry data requirements of §158.1410 apply.
(f) The following term is defined for the purposes of this section: Residue of concern means the parent pesticidal compound and its metabolites, degradates, and impurities of toxicological concern.
(g) Key. R = Required; CR = Conditionally required; NR = Not required; TGAI = Technical grade of the active ingredient; TEP = Typical end-use product; PAI = Pure active ingredient; PAIRA = Pure active ingredient radiolabeled; ROC = Residue of concern.
(h) Antimicrobial residue chemistry data requirements table. The following table shows the data requirements for residue chemistry. The test notes appear in paragraph (i) of this section.
| Guideline No. | Data requirement | Uses | Test
substance | Test note No. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agricultural
premise | Indirect food | Direct food | Aquatic | ||||
| Supporting Information | |||||||
| 860.1100 | Chemical identity | R | R | R | R | TGAI | |
| 860.1200 | Directions for use | R | R | R | R | ||
| 860.1550 | Proposed tolerance/tolerance exemption | R | R | R | R | 1 | |
| 860.1560 | Reasonable grounds in support of petition | R | R | R | R | 1 | |
| 860.1650 | Submittal of analytical reference standards | R | R | R | R | PAI/ROC | 2 |
| Food-Contact Surfaces or Impregnated Materials | |||||||
| 860.1460 | Food-handling | CR | CR | CR | CR | TEP | 3 |
| None | Nature of residue on surfaces | CR | CR | CR | CR | PAIRA or TGAI | 4 |
| None | Migration studies | CR | CR | CR | CR | TEP | 5 |
| 860.1340 | Residue analytical method for data collection | CR | CR | CR | CR | ROC | 6 |
| 860.1380 | Storage stability | R | R | R | R | TEP or ROC | 7 |
| Higher tiered | |||||||
| 860.1300 | Nature of the residue in plants | CR | CR | CR | CR | PAIRA | 8 |
| 860.1300 | Nature of the residue in livestock | CR | CR | CR | CR | PAIRA | 9 |
| 860.1340 | Residue analytical methods for tolerance/tolerance exemption enforcement | CR | CR | CR | CR | ROC | 10 |
| 860.1360 | Multiresidue method testing | CR | CR | CR | CR | ROC | 11 |
| 860.1400 | Potable water | CR | CR | CR | CR | TEP | 12 |
| 860.1400 | Fish | CR | CR | CR | CR | TEP | 13 |
| 860.1400 | Irrigated crops | CR | CR | CR | CR | TEP | 14 |
| 860.1480 | Meat/milk/poultry/eggs | CR | CR | CR | CR | TGAI or ROC | 15 |
| 860.1500 | Crop field trials | CR | CR | CR | CR | TEP | 16 |
| 860.1520 | Processed food or feed | CR | CR | CR | CR | TEP | 17 |
| None | Anticipated residues | CR | CR | CR | CR | ROC | 18 |
(i) Test notes. The following test notes apply to the data requirements in the table to paragraph (h) of this section:
1. A petition proposing a numerical tolerance or a tolerance exemption is required for any food or feed use subject to section 408 of FFDCA if the use is not covered by an existing tolerance or tolerance exemption. If the use is subject to FFDCA section 409, the applicant must identify to EPA an applicable section 409 food additive regulation or clearance, or submit a copy of a petition to FDA requesting a section 409 food additive regulation or clearance for the food or feed use.
2. An analytical reference standard is required for any food or feed use requiring a numeric tolerance or exemption. Material safety data sheets as specified by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration in 29 CFR 1910.1200 must accompany analytical standards.
3. Data are required if a pesticide may be used in a food-handling establishment unless data including, but not limited to, theoretical (high-end) estimates, radiolabeled laboratory data, or the nature of the residue on surfaces study show that residues will not occur in food or feed.
4. If an antimicrobial pesticide may be applied to a food-contact surface or impregnated into a food-contact material and if theoretical (high-end) estimates of exposure exceed EPA's risk level of concern, then the nature of the residue on surfaces study is required. Protocols must be approved by the Agency prior to the initiation of the study.
5. Based on the results of the nature of the residue on surfaces study, if residues of concern are identified, then the migration study will be required. Protocols must be approved by the Agency prior to the initiation of the study.
6. If a magnitude of the residue study, as specified in §158.2290(d), is required, then a residue analytical method suitable for collecting data is also required. The method must be capable of determining all residues of concern, to permit calculation of dietary risk or to establish a tolerance or tolerance exemption.
7. If a magnitude of the residue study, as specified in §158.2290(d), is required, then storage stability data are also required, unless analytical samples are stored for 30 days or less. If, during hazard characterization, a residue has been identified as “of concern” and is known to be volatile or labile, then storage stability data are required regardless of sample storage time.
8. If crop plants or metabolically active raw agricultural commodities of food crops may be directly or indirectly exposed to an antimicrobial, plant metabolism studies are required to determine the transformation products that may enter the human diet. Such exposure could include, but is not limited to:
i. Treatment of storage or shipping containers,
ii. Postharvest fruit and vegetable treatment prior to shipping or storage,
iii. Use of antimicrobial-treated water for irrigation, and
iv. Any direct food contact use.
9. If livestock may be exposed to an antimicrobial, then hen and ruminant metabolism studies are required to determine the identities of residues of concern that may enter the human diet from consumption of livestock commodities. Livestock may be exposed via the oral, dermal, or inhalation route following treatment or contamination of sites including, but not limited to, livestock premises, feed, and drinking water. Shell eggs and other metabolically active livestock products may also be treated. If livestock may be exposed to one or more residues of concern differing from those found in animals, then one or more additional livestock metabolism studies involving dosing with these residues may be required.
10. If there is a numerical tolerance or tolerance exemption level to enforce, then a residue analytical method suitable for enforcement purposes is required. The method must be supported by an independent laboratory validation.
11. If there is a numerical tolerance or tolerance exemption level to enforce, then testing is required to determine whether the Food and Drug Administration/United States Department of Agriculture multiresidue methodology would detect and identify the antimicrobial and its residues of concern, as part of programs to monitor pesticides in the U.S. food supply.
12. Data are required if an antimicrobial may be applied directly to water or if there is the potential that the antimicrobial-treated water could be used directly for drinking water purposes by humans or animals or that contaminated water could run-off, leach, or be discharged from treated sites or materials and make its way into potable water.
13. Data are required if an antimicrobial may be applied directly to water inhabited by fish or that will be inhabited by fish or if contaminated water could run-off, leach, or be discharged from treated sites or materials and make its way into bodies of water containing fish that may be used for human consumption.
14. Data are required if an antimicrobial may be applied directly to water used for irrigation of food crops or such that contaminated water could run-off, leach, or be discharged from treated sites or materials to make its way into water used for irrigation of food crops.
15. If the antimicrobial may be applied directly to livestock, metabolically-active livestock commodities (e.g., eggs), livestock feed or drinking water, or livestock premises, or a livestock metabolism study indicates that residues of the antimicrobial may result in livestock commodities, studies are required to determine the magnitude of the residues of concern in fat, meat, meat by-products, milk, poultry, and eggs that may be consumed by humans. These studies, however, may not be required in cases where the livestock metabolism studies indicate that transfer of pesticide residues of concern to tissues, milk, and eggs is not expected to occur at the maximum expected exposure level for the animals.
16. If food crops or raw agricultural commodities of food crops may be exposed to an antimicrobial, then residue studies are required to determine the magnitude of the residues of concern that may enter the human diet. Such exposures include, but are not limited to, postharvest fruit and vegetable treatments and application of antimicrobial chemicals to field crops, mushroom houses, empty or occupied beehives, or wood used to construct beehives.
17. Data on the nature and magnitude of residues in processed food or feed are required if antimicrobial residues could potentially concentrate on processing. If so, the establishment of a separate tolerance higher than that in the raw agricultural commodity may be required.
18. Data are required when dietary exposure values at the tolerance level or screening-level (high-end) result in estimates of dietary or aggregate risk that meet or exceed the Agency's level of concern. These data may include, but are not limited to, washing, cooking, processing, or degradation studies as well as market basket surveys for a more realistic residue determination. Protocols must be approved by the Agency prior to the initiation of the study.
