['Air Programs']
['Air Quality']
12/09/2024
...
1.0 Applicability, Principle, and Summary of Procedure.
1.1 Applicability.
This procedure applies to the determination of capture efficiency of automobile and light-duty truck spray booth emissions from solvent-borne coatings using panel testing. This procedure can be used to determine capture efficiency for partially controlled spray booths (e.g., automated spray zones controlled and manual spray zones not controlled) and for fully controlled spray booths.
1.2 Principle.
1.2.1 The volatile organic compounds (VOC) associated with the coating solids deposited on a part (or panel) in a controlled spray booth zone (or group of contiguous controlled spray booth zones) partition themselves between the VOC that volatilize in the controlled spray booth zone (principally between the spray gun and the part) and the VOC that remain on the part (or panel) when the part (or panel) leaves the controlled spray booth zone. For solvent-borne coatings essentially all of the VOC associated with the coating solids deposited on a part (or panel) in a controlled spray booth zone that volatilize in the controlled spray booth zone pass through the waterwash and are exhausted from the controlled spray booth zone to the control device.
1.2.2 The VOC associated with the overspray coating solids in a controlled spray booth zone partition themselves between the VOC that volatilize in the controlled spray booth zone and the VOC that are still tied to the overspray coating solids when the overspray coating solids hit the waterwash. For solvent-borne coatings almost all of the VOC associated with the overspray coating solids that volatilize in the controlled spray booth zone pass through the waterwash and are exhausted from the controlled spray booth zone to the control device. The exact fate of the VOC still tied to the overspray coating solids when the overspray coating solids hit the waterwash is unknown. This procedure assumes that none of the VOC still tied to the overspray coating solids when the overspray coating solids hit the waterwash are captured and delivered to the control device. Much of this VOC may become entrained in the water along with the overspray coating solids. Most of the VOC that become entrained in the water along with the overspray coating solids leave the water, but the point at which this VOC leave the water is unknown. Some of the VOC still tied to the overspray coating solids when the overspray coating solids hit the waterwash may pass through the waterwash and be exhausted from the controlled spray booth zone to the control device.
1.2.3 This procedure assumes that the portion of the VOC associated with the overspray coating solids in a controlled spray booth zone that volatilizes in the controlled spray booth zone, passes through the waterwash and is exhausted from the controlled spray booth zone to the control device is equal to the portion of the VOC associated with the coating solids deposited on a part (or panel) in that controlled spray booth zone that volatilizes in the controlled spray booth zone, passes through the waterwash, and is exhausted from the controlled spray booth zone to the control device. This assumption is equivalent to treating all of the coating solids sprayed in the controlled spray booth zone as if they are deposited coating solids (i.e., assuming 100 percent transfer efficiency) for purposes of using a panel test to determine spray booth capture efficiency.
1.2.4 This is a conservative (low) assumption for the portion of the VOC associated with the overspray coating solids in a controlled spray booth zone that volatilizes in the controlled spray booth zone. Thus, this assumption results in an underestimate of conservative capture efficiency. The overspray coating solids have more travel time and distance from the spray gun to the waterwash than the deposited coating solids have between the spray gun and the part (or panel). Therefore, the portion of the VOC associated with the overspray coating solids in a controlled spray booth zone that volatilizes in the controlled spray booth zone should be greater than the portion of the VOC associated with the coating solids deposited on a part (or panel) in that controlled spray booth zone that volatilizes in that controlled spray booth zone.
1.3 Summary of Procedure
1.3.1 A panel test is performed to determine the mass of VOC that remains on the panel when the panel leaves a controlled spray booth zone. The total mass of VOC associated with the coating solids deposited on the panel is calculated.
1.3.2 The percent of the total VOC associated with the coating solids deposited on the panel in the controlled spray booth zone that remains on the panel when the panel leaves the controlled section of the spray booth is then calculated from the ratio of the two previously determined masses. The percent of the total VOC associated with the coating solids deposited on the panel in the controlled spray booth zone that is captured and delivered to the control device equals 100 minus this percentage. (The mass of VOC associated with the coating solids deposited on the panel which is volatilized and captured in the controlled spray booth zone equals the difference between the total mass of VOC associated with the coating solids deposited on the panel and the mass of VOC remaining with the coating solids deposited on the panel when the panel leaves the controlled spray booth zone.)
1.3.3 The percent of the total VOC associated with the coating sprayed in the controlled spray booth zone that is captured and delivered to the control device is assumed to be equal to the percent of the total VOC associated with the coating solids deposited on the panel in the controlled spray booth zone that is captured and delivered to the control device. The percent of the total VOC associated with the coating sprayed in the entire spray booth that is captured and delivered to the control device can be calculated by multiplying the percent of the total VOC associated with the coating sprayed in the controlled spray booth zone that is captured and delivered to the control device by the fraction of coating sprayed in the spray booth that is sprayed in the controlled spray booth zone.
2.0 Procedure
2.1 You may conduct panel testing to determine the capture efficiency of spray booth emissions. You must follow the instructions and calculations in this appendix A, and use the panel testing procedures in ASTM D5087–02 (Reapproved 2021), “Standard Test Method for Determining Amount of Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) Released from Solventborne Automotive Coatings and Available for Removal in a VOC Control Device (Abatement)” (incorporated by reference, see §60.17), or the guidelines presented in “Protocol for Determining the Daily Volatile Organic Compound Emission Rate of Automobile and Light-Duty Truck Primer-Surfacer and Topcoat” EPA–453/R–08–002 (incorporated by reference, see §60.17). You must weigh panels at the points described in section 2.5 of this appendix A and perform calculations as described in sections 3 and 4 of this appendix A. You may conduct panel tests on the production paint line in your facility or in a laboratory simulation of the production paint line in your facility.
2.2 You may conduct panel testing on representative coatings as described in “Protocol for Determining the Daily Volatile Organic Compound Emission Rate of Automobile and Light-Duty Truck Primer-Surfacer and Topcoat” EPA–453/R–08–002 (incorporated by reference, see §60.17). If you panel test representative coatings, then you may calculate either a unique percent capture efficiency value for each coating grouped with that representative coating, or a composite percent capture efficiency value for the group of coatings. If you panel test each coating, then you must convert the panel test result for each coating to a unique percent capture efficiency value for that coating.
2.3 Identification of Controlled Spray Booth Zones.
You must identify each controlled spray booth zone or each group of contiguous controlled spray booth zones to be tested. (For example, a controlled bell zone immediately followed by a controlled robotic zone.) Separate panel tests are required for non-contiguous controlled spray booth zones. The flash zone between the last basecoat zone and the first clearcoat zone makes these zones non-contiguous.
2.4 Where to Apply Coating to the Panel.
If you are conducting a panel test for a single controlled spray booth zone, then you must apply coating to the panel only in that controlled spray booth zone. If you are conducting a panel test for a group of contiguous controlled spray booth zones, then you must apply coating to the panel only in that group of contiguous controlled spray booth zones.
2.5 How to Process and When to Weigh the Panel.
The instructions in this section pertain to panel testing of coating, i, or of the coating representing the group of coatings that includes coating, i.
2.5.1 You must weigh the blank panel. (Same as in bake oven panel test.) The mass of the blank panel is represented by W blank,i (grams).
2.5.2 Apply coating, i, or the coating representing coating, i, to the panel in the controlled spray booth zone or group of contiguous controlled spray booth zones being tested (in plant test), or in a simulation of the controlled spray booth zone or group of contiguous controlled spray booth zones being tested (laboratory test).
2.5.3 Remove and weigh the wet panel as soon as the wet panel leaves the controlled spray booth zone or group of contiguous controlled spray booth zones being tested. (Different than bake oven panel test.) This weighing must be conducted quickly to avoid further evaporation of VOC. The mass of the wet panel is represented by W wet,i (grams).
2.5.4 Return the wet panel to the point in the coating process or simulation of the coating process where it was removed for weighing.
2.5.5 Allow the panel to travel through the rest of the coating process in the plant or laboratory simulation of the coating process. You must not apply any more coating to the panel after it leaves the controlled spray booth zone (or group of contiguous controlled spray booth zones) being tested. The rest of the coating process or simulation of the coating process consists of:
2.5.5.1 All of the spray booth zone(s) or simulation of all of the spray booth zone(s) located after the controlled spray booth zone or group of contiguous controlled spray booth zones being tested and before the bake oven where the coating applied to the panel is cured,
2.5.5.2 All of the flash-off area(s) or simulation of all of the flash-off area(s) located after the controlled spray booth zone or group of contiguous controlled spray booth zones being tested and before the bake oven where the coating applied to the panel is cured, and
2.5.5.3 The bake oven or simulation of the bake oven where the coating applied to the panel is cured.
2.5.6 After the panel exits the bake oven, you must cool and weigh the baked panel. (Same as in bake oven panel test.) The mass of the baked panel is represented by W baked,i (grams).
3.0 Panel Calculations
The instructions in this section pertain to panel testing of coating, i, or of the coating representing the group of coatings that includes coating, i.
3.1 The mass of coating solids (from coating, i, or from the coating representing coating, i, in the panel test) deposited on the panel equals the mass of the baked panel minus the mass of the blank panel as shown in Equation A–1.
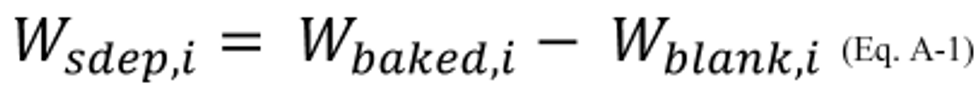
Where:
W sdep, i = Mass of coating solids (from coating, i, or from the coating representing coating, i, in the panel test) deposited on the panel, grams.
3.2 The mass of VOC (from coating, i, or from the coating representing coating, i, in the panel test) remaining on the wet panel when the wet panel leaves the controlled spray booth zone or group of contiguous controlled spray booth zones being tested equals the mass of the wet panel when the wet panel leaves the controlled spray booth zone or group of contiguous controlled spray booth zones being tested minus the mass of the baked panel as shown in Equation A–2.
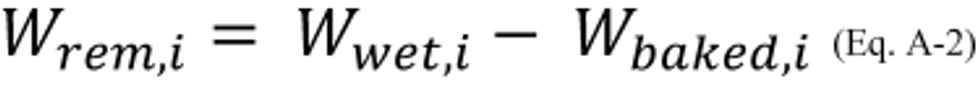
Where:
W rem, i = Mass of VOC (from coating, i, or from the coating representing coating, i, in the panel test) remaining on the wet panel when the wet panel leaves the controlled spray booth zone or group of contiguous controlled spray booth zones being tested, grams.
3.3 Calculate the mass of VOC (from coating, i, or from the coating representing coating, i, in the panel test) remaining on the wet panel when the wet panel leaves the controlled spray booth zone or group of contiguous controlled spray booth zones being tested per mass of coating solids deposited on the panel as shown in Equation A–3.
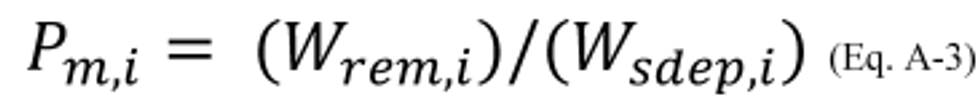
Where:
P m, i = Mass of VOC (from coating, i, or from the coating representing coating, i, in the panel test) remaining on the wet panel when the wet panel leaves the controlled spray booth zone or group of contiguous controlled spray booth zones being tested per mass of coating solids deposited on the panel, grams of VOC remaining per gram of coating solids deposited.
W rem, i = Mass of VOC (from coating, i, or from the coating representing coating, i, in the panel test) remaining on the wet panel when the wet panel leaves the controlled spray booth zone or group of contiguous controlled spray booth zones being tested, grams.
W sdep, i = Mass of coating solids (from coating, i, or from the coating representing coating, i, in the panel test) deposited on the panel, grams.
4.0 Converting Panel Result to Percent Capture
The instructions in this section pertain to panel testing of for coating, i, or of the coating representing the group of coatings that includes coating, i.
4.1 If you panel test representative coatings, then you may convert the panel test result for each representative coating from section 3.3 of this appendix A either to a unique percent capture efficiency value for each coating grouped with that representative coating by using coating specific values for the mass fraction coating solids and mass fraction VOC in section 4.2 of this appendix A, or to a composite percent capture efficiency value for the group of coatings by using the average values for the group of coatings for mass fraction coating solids and mass fraction VOC in section 4.2 of this appendix A. If you panel test each coating, then you must convert the panel test result for each coating to a unique percent capture efficiency value by using coating specific values for the mass fraction coating solids and mass fraction VOC in section 4.2 of this appendix A. The mass fraction of VOC in the coating and the mass fraction of solids in the coating must be determined by Method 24 (appendix A–7 to 40 CFR part 60) or by following the guidelines for combining analytical VOC content and formulation solvent content presented in “Protocol for Determining the Daily Volatile Organic Compound Emission Rate of Automobile and Light-Duty Truck Primer-Surfacer and Topcoat” EPA–453/R–08–002 (incorporated by reference, see §60.17).'>
4.2 The percent of VOC for coating, i, or composite percent of VOC for the group of coatings including coating, i, associated with the coating solids deposited on the panel that remains on the wet panel when the wet panel leaves the controlled spray booth zone or group of contiguous controlled spray booth zones being tested is calculated using Equation A–4.
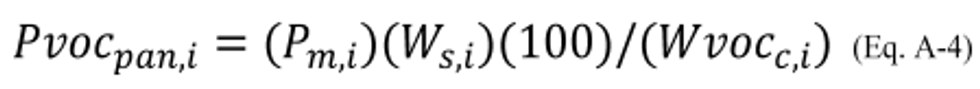
Where:
Pvoc pan, i = Percent of VOC for coating, i, or composite percent of VOC for the group of coatings including coating, i, associated with the coating solids deposited on the panel that remains on the wet panel when the wet panel leaves the controlled spray booth zone (or group of contiguous controlled spray booth zones) being tested, percent.
P m, i = Mass of VOC (from coating, i, or from the coating representing coating, i, in the panel test) remaining on the wet panel when the wet panel leaves the controlled spray booth zone or group of contiguous controlled spray booth zones being tested per mass of coating solids deposited on the panel, grams of VOC remaining per gram of coating solids deposited.
W s, i = Mass fraction of coating solids for coating, i, or average mass fraction of coating solids for the group of coatings including coating, i, grams coating solids per gram coating, determined by EPA Method 24 (appendix A–7 to 40 CFR part 60) or by following the guidelines for combining analytical VOC content and formulation solvent content presented in “Protocol for Determining the Daily Volatile Organic Compound Emission Rate of Automobile and Light-Duty Truck Primer-Surfacer and Topcoat, EPA–453/R–08–002” (incorporated by reference, see §60.17).
Wvoc c, i = Mass fraction of VOC in coating, i, or average mass fraction of VOC for the group of coatings including coating, i, grams VOC per grams coating, determined by EPA Method 24 (appendix A–7 to 40 CFR part 60) or the guidelines for combining analytical VOC content and formulation solvent content presented in “Protocol for Determining the Daily Volatile Organic Compound Emission Rate of Automobile and Light-Duty Truck Topcoat Operations,” EPA–453/R–08–002 (incorporated by reference, see §60.17).
4.3 The percent of VOC for coating, i, or composite percent of VOC for the group of coatings including coating, i, associated with the coating sprayed in the controlled spray booth zone (or group of contiguous controlled spray booth zones) being tested that is captured in the controlled spray booth zone or group of contiguous controlled spray booth zones being tested, CE zone,i (percent), is calculated using Equation A–5.
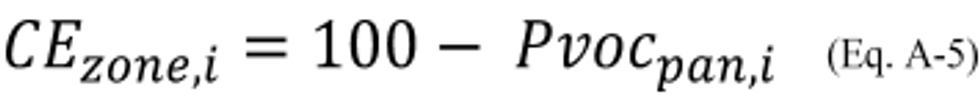
Where:
CE zone, i = Capture efficiency for coating, i, or for the group of coatings including coating, i, in the controlled spray booth zone or group of contiguous controlled spray booth zones being tested as a percentage of the VOC in the coating, i, or of the group of coatings including coating, i, sprayed in the controlled spray booth zone or group of contiguous controlled spray booth zones being tested, percent.
4.4 Calculate the percent of VOC for coating, i, or composite percent of VOC for the group of coatings including coating, i, associated with the entire volume of coating, i, or with the total volume of all of the coatings grouped with coating, i, sprayed in the entire spray booth that is captured in the controlled spray booth zone or group of contiguous controlled spray booth zones being tested, using Equation A–6. The volume of coating, i, or of the group of coatings including coating, i, sprayed in the controlled spray booth zone or group of contiguous controlled spray booth zones being tested, and the volume of coating, i, or of the group of coatings including coating, i, sprayed in the entire spray booth may be determined from gun on times and fluid flow rates or from direct measurements of coating usage.
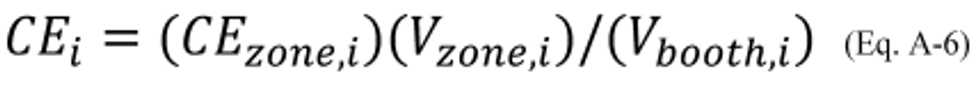
Where:
CE i = Capture efficiency for coating, i, or for the group of coatings including coating, i, in the controlled spray booth zone (or group of contiguous controlled spray booth zones) being tested as a percentage of the VOC in the coating, i, or of the group of coatings including coating, i, sprayed in the entire spray booth in which the controlled spray booth zone (or group of contiguous controlled spray booth zones) being tested, percent.
V zone, i = Volume of coating, i, or of the group of coatings including coating, i, sprayed in the controlled spray booth zone or group of contiguous controlled spray booth zones being tested, liters.
V booth, i = Volume of coating, i, or of the group of coatings including coating, i, sprayed in the entire spray booth containing the controlled spray booth zone (or group of contiguous controlled spray booth zones) being tested, liters.
4.5 If you conduct multiple panel tests for the same coating or same group of coatings in the same spray booth (either because the coating or group of coatings is controlled in non-contiguous zones of the spray booth, or because you choose to conduct separate panel tests for contiguous controlled spray booth zones), then you may add the result from section 4.4 for each such panel test to get the total capture efficiency for the coating or group of coatings over all of the controlled zones in the spray booth for the coating or group of coatings.
[88 FR 30002, May 9, 2023]
['Air Programs']
['Air Quality']
UPGRADE TO CONTINUE READING
Load More
J. J. Keller is the trusted source for DOT / Transportation, OSHA / Workplace Safety, Human Resources, Construction Safety and Hazmat / Hazardous Materials regulation compliance products and services. J. J. Keller helps you increase safety awareness, reduce risk, follow best practices, improve safety training, and stay current with changing regulations.
Copyright 2026 J. J. Keller & Associate, Inc. For re-use options please contact copyright@jjkeller.com or call 800-558-5011.
