['Air Programs']
['Air Quality']
04/23/2024
...
(a) Percent oxygen. Adjust all pollutant concentrations to 7 percent oxygen using equation 1 of this section.
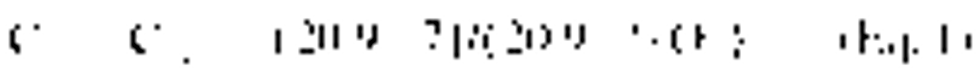
Where:
Cadj = pollutant concentration adjusted to 7 percent oxygen
Cmeas = pollutant concentration measured on a dry basis
(20.9-7) = 20.9 percent oxygen-7 percent oxygen (defined oxygen correction basis)
20.9 = oxygen concentration in air, percent
%O2 = oxygen concentration measured on a dry basis, percent
(b) Capacity of a very small municipal waste combustion unit. For very small municipal waste combustion units that can operate continuously for 24-hour periods, calculate the unit capacity based on 24 hours of operation at the maximum charge rate. To determine the maximum charge rate, use one of two methods:
(1) For very small municipal waste combustion units with a design based on heat input capacity, calculate the maximum charging rate based on the maximum heat input capacity and one of two heating values:
(i) If your very small municipal waste combustion unit combusts refuse-derived fuel, use a heating value of 12,800 kilojoules per kilogram (5,500 British thermal units per pound).
(ii) If your very small municipal waste combustion unit combusts municipal solid waste, use a heating value of 10,500 kilojoules per kilogram (4,500 British thermal units per pound).
(2) For very small municipal waste combustion units with a design not based on heat input capacity, use the maximum design charging rate.
(c) Capacity of a batch very small municipal waste combustion unit. Calculate the capacity of a batch OSWI unit as the maximum design amount of municipal solid waste it can charge per batch multiplied by the maximum number of batches it can process in 24 hours. Calculate the maximum number of batches by dividing 24 by the number of hours needed to process one batch. Retain fractional batches in the calculation. For example, if one batch requires 16 hours, the unit can combust 24/16, or 1.5 batches, in 24 hours.
(d) Carbon monoxide pollutant rate. When hourly average pollutant rates (Eh) are obtained (e.g., CEMS values), compute the rolling average carbon monoxide pollutant rate (Ea) for each 12-hour period using the following equation:
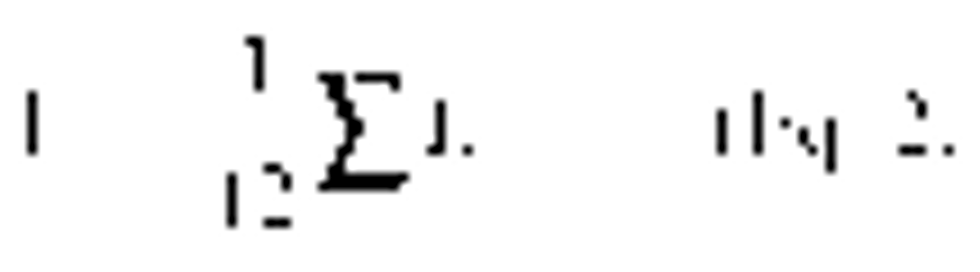
Where:
Ea = Average carbon monoxide pollutant rate for the 12-hour period, ppm corrected to 7 percent O2.
Ehj = Hourly arithmetic average pollutant rate for hour “j,” ppm corrected to 7 percent O2.
READ MORESHOW LESS
['Air Programs']
['Air Quality']
Load More
J. J. Keller is the trusted source for DOT / Transportation, OSHA / Workplace Safety, Human Resources, Construction Safety and Hazmat / Hazardous Materials regulation compliance products and services. J. J. Keller helps you increase safety awareness, reduce risk, follow best practices, improve safety training, and stay current with changing regulations.
Copyright 2024 J. J. Keller & Associate, Inc. For re-use options please contact copyright@jjkeller.com or call 800-558-5011.
