...
S1. Scope. This standard establishes requirements for devices, without self-contained energy sources, that are designed to be carried in motor vehicles and used to warn approaching traffic of the presence of a stopped vehicle, except for devices designed to be permanently affixed to the vehicle.
S2. Purpose. The purpose of this standard is to reduce deaths and injuries due to rear end collisions between moving traffic and disabled vehicles.
S3. Application. This standard applies to devices, without self-contained energy sources, that are designed to be carried in buses and trucks that have a gross vehicle weight rating (GVWR) greater than 10,000 pounds. These devices are used to warn approaching traffic of the presence of a stopped vehicle, except for devices designed to be permanently affixed to the vehicle.
S4. Definitions. Entrance angle
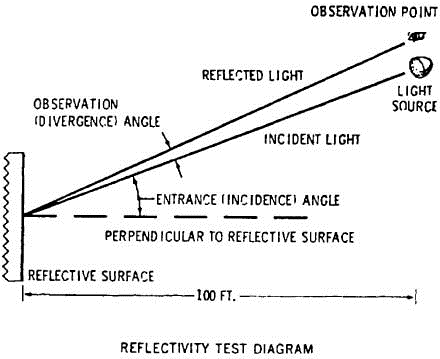
means the angle having as its sides the line through the center, and normal to the face, of the object to be tested, and the line from the center of the object to the center of the source of illumination (Figure 2).
Fluorescent
means the property of emitting visible light due to the absorption of radiation of a shorter wavelength which may be outside the visible spectrum.
Observation angle
means the angle having as its sides the line from the observation point to the center of the object to be tested and the line from the center of that object to the center of the source of illumination (Figure 2).
Reflex reflective
means reflective of light in directions close to the direction of incident light, over a wide range of variations in the direction of incident light.
S5. Requirements.
S5.1 Equipment.
S5.1.1 Reflex reflective material and fluorescent material that meet the requirements of this standard shall be affixed to both faces of the warning device. Alternatively, a dual purpose orange fluorescent and red reflective material that meets the requirements of this standard (hereafter referred to as “dual purpose material”) may be affixed to both faces in places of the reflective and fluorescent materials.
S5.1.2 Each warning device shall be protected from damage and deterioration—
(a) By enclosure in an opaque protective reusable container, except that two or three warning devices intended to be sold for use as a set with a single vehicle may be enclosed in a single container; or
(b) By secure attachment to any light-tight, enclosed, and easily accessible compartment of a new motor vehicle with which it is supplied by the vehicle manufacturer.
S5.1.3 The warning device shall be designed to be erected, and replaced in its container, without the use of tools.
S5.1.4 The warning device shall be permanently and legibly marked with:
(a) Name of manufacturer;
(b) Month and year of manufacture, which may be expressed numerically, as “6/72”; and
(c) The symbol DOT, or the statement that the warning device complies with all applicable Federal motor vehicle safety standards.
S5.1.5 Each warning device shall have instructions for its erection and display.
(a) The instructions shall be either indelibly printed on the warning device or attached in such a manner that they cannot be easily removed.
(b) Instructions for each warning device shall include a recommendation that the driver activate the vehicular hazard warning signal lamps before leaving the vehicle to erect the warning device.
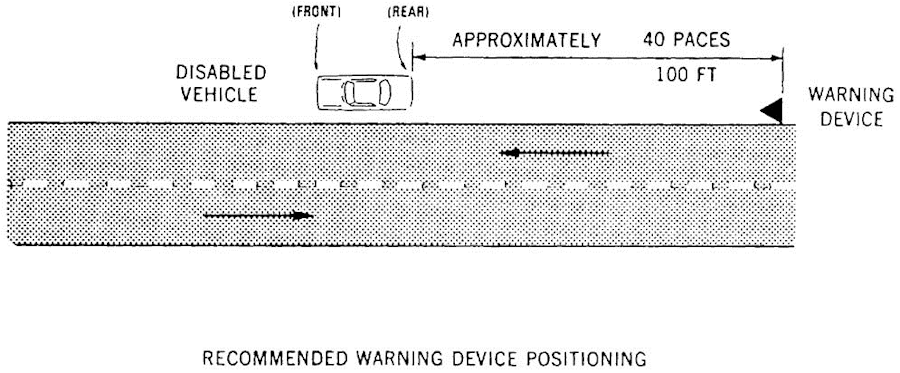
(c) Instructions shall include the illustration depicted in Figure 3 indicating recommended positioning.
S5.2 Configuration.
S5.2.1 When the warning device is erected on level ground:
(a) Part of the warning device shall form an equilateral triangle that stands in a plane not more than 10° from the vertical, with the lower edge of the base of the triangle horizontal and not less than 1 inch above the ground.
(b) None of the required portion of the reflective material and fluorescent material shall be obscured by any other part of the warning device except for any portion of the material over which it is necessary to provide fasteners, pivoting beads or other means to allow collapsibility or support of the device. In any event, sufficient reflective and fluorescent material shall be used on the triangle to meet the requirements of S5.4 and S5.5.
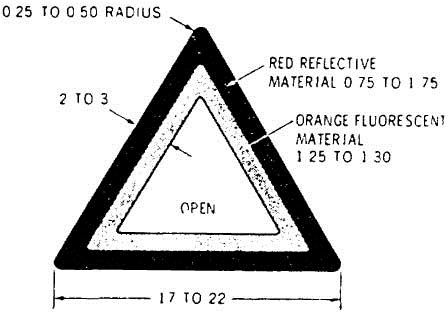
S5.2.2 Each of the three sides of the triangular portion of the warning device shall not be less than 17 and not more than 22 inches long, and not less than 2 and not more than 3 inches wide (Figure 1).
S5.2.3 Each face of the triangular portion of the warning device shall have an outer border of red reflex reflective material of uniform width and not less than 0.75 and not more than 1.75 inches wide, and an inner border of orange fluorescent material of uniform width and not less than 1.25 and not more than 1.30 inches wide (Figure 1). However, this requirement shall not apply if the dual purpose material is used.
S5.2.4 Each vertex of the triangular portion of the warning device shall have a radius of not less than 0.25 inch and not more than 0.50 inch.
S5.2.5 All edges shall be rounded or chamfered, as necessary, to reduce the possibility of cutting or harm to the user.
S5.2.6 The device shall consist entirely of the triangular portion and attachments necessary for its support and enclosure, without additional visible shapes or attachments.
S5.3 Color.
S5.3.1 The color of the red reflex reflective material on the warning device shall have the following characteristics, both before and after the warning device has been conditioned in accordance with S6.1, when the source of illumination is a lamp with a tungsten filament operating at 2856° Kelvin color temperature. Expressed in terms of the International Commission on Illumination (CIE) 1931 standard colorimetric observer system (CIE chromaticity diagram, Figure 4), the chromaticity coordinates of the red reflex reflective material shall lie within the region bounded by the spectrum locus and the lines on the diagram defined by the following equations:
| Boundary | Equations |
|---|---|
| Yellow | y = 0.33 |
| White | x + y = 0.98 |
S5.3.2 The color of the orange fluorescent material on the warning device shall have the following characteristics, both before and after the warning device has been conditioned in accordance with S6.1, when the source of illumination is a 150-watt high pressure xenon compact arc lamp. Expressed in terms of the International Commission on Illumination (CIE) 1931 standard colorimetric observer system, the chromaticity coordinates of the orange fluorescent material shall lie within the region bounded by the spectrum locus and the lines on the diagram defined by the following equations:
| Boundary | Equations |
|---|---|
| Yellow | y = 0.49x+0.17 |
| White | x + y = 0.93 |
| Red | y = 0.35 |
The 150-watt high pressure xenon compact arc lamp shall illuminate the sample using the unmodified spectrum at an angle of incidence of 45° and an angle of observation of 90°. If dual purpose material is being tested, it shall be illuminated by a 150-watt high pressure xenon compact arc lamp, whose light is diffused by an integrating sphere.
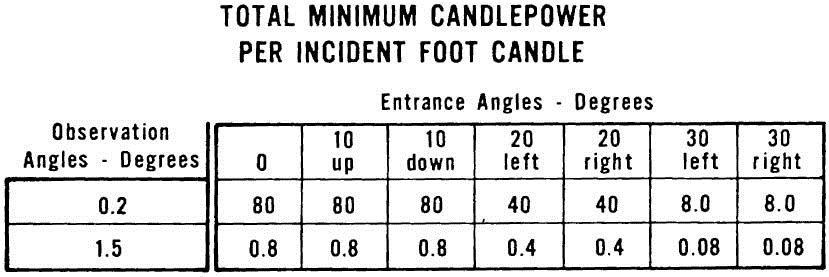
S5.4 Reflectivity. When the red reflex reflective material on the warning device is tested in accordance with S6.2, both before and after the warning device has been conditioned in accordance with S6.1, its total candlepower per incident foot candle shall be not less than the values specified in Table I for each of the listed entrance angles.
S5.5 Luminance. When the orange fluorescent material on the warning device is tested in accordance with S6.3, both before and after the warning device has been conditioned in accordance with S6.1, it shall have a minimum relative luminance of 25 percent of a flat magnesium oxide surface and a minimum product of that relative luminance and width in inches of 44.
S5.6 Stability. When the warning device is erected on a horizontal brushed concrete surface both with and against the brush marks and subjected to a horizontal wind of 40 miles per hour in any direction for 3 minutes—
(a) No part of it shall slide more than 3 inches from its initial position;
(b) Its triangular portion shall not tilt to a position that is more than 10° from the vertical; and
(c) Its triangular position shall not turn through a horizontal angle of more than 10° in either direction from the initial position.
S5.7 Durability. When the warning device is conditioned in accordance with S6.1, no part of the warning device shall become warped or separated from the rest of the warning device.
S6. Test Procedures.
S6.1 Conditions.
S6.1.1 Submit the warning device to the following conditioning sequence, returning the device after each step in the sequence to ambient air at 68 °F. for at least 2 hours.
(a) Minus 40 °F. for 16 hours in a circulating air chamber using ambient air which would have not less than 30 percent and not more than 70 percent relative humidity at 70 °F.;
(b) 150 °F. for 16 hours in a circulating air oven using ambient air which would have not less than 30 percent and not more than 70 percent relative humidity at 70 °F.;
(c) 100 °F. and 90 percent relative humidity for 16 hours;
(d) Salt spray (fog) test in accordance with ASTM B117-64 (incorporated by reference, see §571.5 ), except that the test shall be for 4 hours rather than 40 hours; and
(e) Immersion for 2 hours in water at a temperature of 100 °F.
S6.2 Reflectivity Test. Test the red reflex reflective materials as follows:
(a) Unless dual purpose material is used, prevent the orange fluorescent material from affecting the photometric measurement of the reflectivity of the red reflex reflective material, either by separation or masking.
(b) Use a lamp with a tungsten filament operating at 2856° Kelvin color temperature as the source of illumination.
(c) Place the source of illumination 100 feet from the red reflex reflective material (Figure 2).
(d) Place the observation point directly above the source of illumination (Figure 2).
(e) Calculate the total candlepower per incident foot candle of the red reflex reflective material at each of the entrance and observation angles specified in Table 1.
S6.3 Luminance Test. Test the orange fluorescent material as follows:
(a) Unless dual purpose material is used, prevent the red reflex reflective material from affecting the photometric measurement of the luminance of the orange fluorescent material.
(b) Using a 150-watt high pressure xenon compact arc lamp as the light source, illuminate the test sample at an angle of incidence of 45° and an angle of observation of 90°. If dual purpose material is being tested, illuminate the sample diffusely through an integrating sphere.
(c) Measure the luminance of the material at a perpendicular viewing angle, with no ray of the viewing beam more than 5° from the perpendicular to the specimen.
(d) Repeat the procedure for a flat magnesium oxide surface, and compute the quotient (percentage) of the luminance of the material relative to that of the magnesium oxide surface.
 |
 |
| Figure 2 |
 |
| Figure 3 |
 |
| Table 1 |
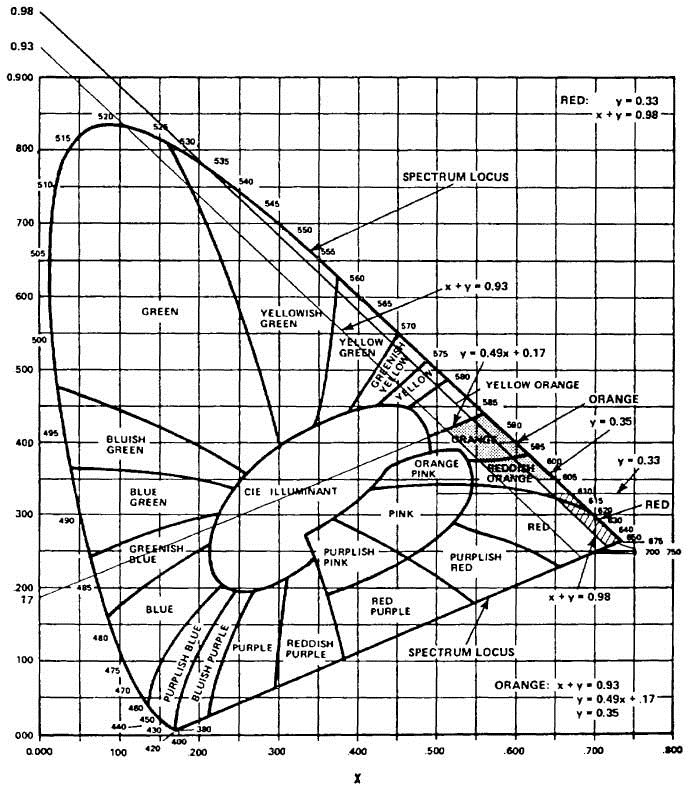 |
| Figure 4. CIE Chromaticity Diagram. |
[39 FR 28636, Aug. 9, 1974, as amended at 40 FR 4, Jan. 2, 1975; 59 FR 49591, Sept. 29, 1994; 77 FR 760, Jan. 6, 2012]
