['CMV Parts and Maintenance']
['Vehicle maintenance']
04/07/2025
...
[Editor’s Note: This section is added effective December 30, 2024.][Change Notice]
S1. Scope. This standard establishes requirements to improve side and roof bus portals by way of glazing that is highly resistant to partial or complete occupant ejection in all types of crashes.
S2. Purpose. The purpose of this standard is to reduce death and injuries resulting from complete and partial ejections of bus occupants through side and roof portals during rollovers and other crashes.
S3. Application.
(a) Subject to S3(b) of this section, this standard applies to:
(1) Over-the-road buses manufactured on or after October 30, 2027, and
(2) Buses, other than over-the-road buses, that have a gross vehicle weight rating (GVWR) greater than 11,793 kilograms (kg) manufactured on or after October 30, 2027.
(b) This standard does not apply to school buses, transit buses, prison buses, and perimeter-seating buses.
S4. Definitions.
Daylight opening means, for openings on the side of the vehicle (other than a door opening), the locus of all points where a horizontal line, perpendicular to the vehicle longitudinal centerline, is tangent to the periphery of the opening. For openings on the roof of the vehicle, daylight opening means the locus of all points where a vertical line is tangent to the periphery of the opening. The periphery includes surfaces 100 millimeters (mm) inboard of the inside surface of the window glazing and 25 mm outboard of the outside surface of the window glazing. The periphery excludes the following: Any flexible gasket material or weather stripping used to create a waterproof seal between the glazing and the vehicle interior; grab handles used to facilitate occupant egress and ingress; and any part of a seat.
Over-the-road bus means a bus characterized by an elevated passenger deck located over a baggage compartment.
Perimeter-seating bus means a bus with 7 or fewer designated seating positions rearward of the driver's seating position that are forward-facing or can convert to forward-facing without the use of tools.
Portal means an opening that could, in the event of a crash involving the vehicle, permit the partial or complete ejection of an occupant from the vehicle, including a young child.
Prison bus means a bus manufactured for the purpose of transporting persons subject to involuntary restraint or confinement and has design features consistent with that purpose.
Stop-request system means a vehicle-integrated system for passenger use to signal to a vehicle operator that they are requesting a stop.
Transit bus means a bus that is equipped with a stop-request system sold for public transportation provided by, or on behalf of, a Federal, State, or local government and that is not an over-the-road bus.
S5. Requirements. When tested according to the procedures specified in S6 of this section and under the conditions specified in paragraph S7 of this section, each applicable bus shall meet the following requirements specified in this section. The requirements of this paragraph S5 n do not apply to portals other than side and roof portals, and do not apply to a side or roof portal whose minimum surface dimension measured through the center of its area is less than 279 mm.
S5.1 Edge impact.
(a) When the ejection impactor described in S8 of this section contacts the target location specified in S6.1.1 of this section of each side or roof daylight opening of a vehicle at 21.6 km/h ± 0.4 km/h, no portion of the window (excluding glazing shards) may pass the ejection reference plane defined under the procedures of S6 of this section.
(b) Each piece of window glazing and each surrounding window frame shall be retained by its surrounding structure in a manner that prevents the formation of any opening large enough to admit the complete passage of a 102 mm diameter sphere when a force of no more than 22 newtons (N) is applied with the sphere at any vector in a direction from the interior to the exterior of the vehicle.
S5.2 Center impact.
(a) When the ejection impactor described in paragraph S8 of this section contacts the target location specified in paragraph S6.1.2 of this section of each side or roof daylight opening of a vehicle at 21.6 km/h ± 0.4 km/h, no portion of the window (excluding glazing shards) may pass the ejection reference plane defined under the procedures of paragraph S6.3 of this section.
(b) Each piece of window glazing and each surrounding window frame shall be retained by its surrounding structure in a manner that prevents the formation of any opening large enough to admit the complete passage of a 102 mm diameter sphere when a force of no more than 22 N is applied with the sphere at any vector in a direction from the interior to the exterior of the vehicle.
S5.3 Center impact to pre-broken glazing.
(a) When the ejection impactor described in S8 of this section contacts the target location specified in S6.1.3 of this section of each side or roof daylight opening of a vehicle at 21.6 km/h ± 0.4 km/h, no portion of the impactor may displace more than 175 mm past where the surface of the glazing had been in an unbroken condition.
(b) Each piece of window glazing and each surrounding window frame shall be retained by its surrounding structure in a manner that prevents the formation of any opening large enough to admit the complete passage of a 102 mm diameter sphere when a force of no more than 22 N is applied with the sphere at any vector in a direction from the interior to the exterior of the vehicle.
S5.4 Post-Impact Emergency Exit Release and Operability.
After the impacts described in paragraphs S5.1, S5.2, and S5.3 of this section, each emergency exit provided in accordance with Standard No. 217 (§ 571.217) shall be capable of releasing and opening according to the requirements specified in that standard.
S6. Test procedures.
S6.1 Target locations.
S6.1.1 Edge impact. Position the impactor face on the glazing adjacent to a latch or discrete attachment point such that, when viewed perpendicular to the glazing surface, the center of the impactor face plate is as close as practicable to the center of the latch attachment point or discrete attachment point with the impactor face plate either horizontal or vertical, whichever orientation provides the shortest distance between the two centers, while maintaining at least a 25 mm ± 2 mm distance between the impactor face plate edge and the window frame. “Window frame” includes latches, handles, attachments, and any solid structures other than the glazing material or flexible gaskets. If the window does not have any latches or discrete attachment points (e.g., it is fully rubber bonded or glued), position the impactor as follows:
(a) For side windows, directly above the center of the lower window edge, with the impactor face plate either horizontal or vertical, whichever orientation provides the shortest distance between the two centers, with the bottom edge of the impactor face plate 25 mm ± 2 mm above the daylight opening periphery when viewed perpendicular to the glazing surface.
(b) For roof glazing panels or roof windows, directly forward of the center of the rearmost window edge, with the impactor face plate either horizontal or vertical, whichever orientation provides the shortest distance between the two centers, with the rearmost edge of the impactor face plate 25 mm ± 2 mm forward of the daylight opening periphery when viewed perpendicular to the glazing surface.
S6.1.2 Center impact.
Position the center of the impactor face, with the long axis of the impactor face plate either vertical or horizontal, at the center of the daylight opening area of the window with the glazing intact.
S6.1.3 Center impact to pre-broken glazing.
Position the center of the impactor face, with the long axis of the impactor face plate either vertical or horizontal, at the center of the daylight opening area of the window with the glazing pre-broken following the procedure in paragraphs S6.2.1 and S6.2.2 of this section.
S6.2 Window glazing pre-breaking procedure.
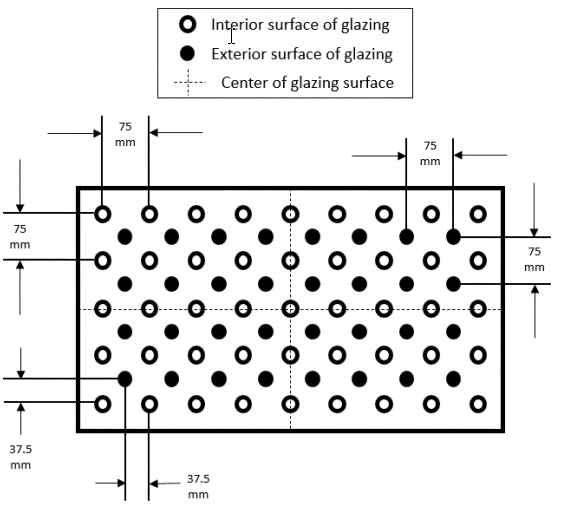
S6.2.1 Breakage pattern. Locate the geometric center of the daylight opening. Mark the surface of the window glazing in a horizontal and vertical grid of points separated by 75 mm ± 2 mm with one point coincident within ± 2 mm of the geometric center of the daylight opening (Figure 2).
(a) If the window is a single-pane unit, then both the occupant space interior and outside exterior surfaces of the glass pane are marked with the 75 mm grid pre-break pattern. The patterns are offset diagonally from one another (the points on one surface of the glass pane are offset 37.5 mm ± 2 mm horizontally and 37.5 mm ± 2 mm vertically from the points on the contralateral surface of the glass pane).
(b) If the window is an insulated unit or double-glazed window, then both the occupant space side of the interior pane and the outside of the exterior pane are marked with the 75 mm grid prebreak pattern.
(1) If one of the glass panes is constructed of tempered or toughened glass, the insulated surface of the remaining glass pane (within the air gap) is marked with the 75 mm grid pre-break pattern. The patterns are offset diagonally from the remaining glass pane's contralateral surface.
(2) If neither pane is tempered glass, then both the occupant space side of the interior pane and the outside of the exterior pane are marked with the 75 mm grid pre-break pattern. The patterns are not diagonally offset from one another. The insulated surfaces of the glass panes (within the air gap) are not marked.
S6.2.2 Breakage method.
(a) Use a 100 mm ± 10 mm × 100 mm ± 10 mm piece of rigid material as a reaction surface on the opposite side of the glazing to prevent to the extent possible the window surface from deforming by more than 10 mm when pressure is being applied by the staple gun.
(b) Start with the inside surface of the window and forwardmost, lowest mark made as specified in S6.2.1 of this section. Use an electric staple gun without any staples to apply a load along a line of 12 to 14 mm onto the glazing. The applied force shall be 4,200 N ± 850 N. Apply the line load only once at each marked location, even if the glazing does not break or no perceptible mark or hole results.
(c) Continue applying the line load with the electric staple gun by moving rearward in the grid until the end of a row is reached. Then move to the forwardmost mark on the next higher row and apply the line load. Continue in this pattern until the line load has been applied to all grid points on the inside surface of the glazing.
(d) Repeat the process on the outside surface of the window.
(e) If applying the line load causes the glazing to disintegrate, halt the breakage procedure and proceed with the next step in the compliance test.
S6.3 Determination of ejection reference planes.
(a) For side windows, the “ejection reference plane” is a vertical plane parallel to the longitudinal vertical center plane of the bus passing through a point located at a lateral distance of 102 mm from the lateral most point on the glazing and surrounding frame, with the window in the closed position.
(b) For roof glazing panels/windows, the “ejection reference plane” is a horizontal plane passing through a point located at a vertical distance of 102 mm from the highest point on the glazing and surrounding frame, with the window/panel in the closed position.
S7. Test conditions.
During testing, the ambient temperature is between 18 degrees C. and 29 degrees C., at any relative humidity between 10 percent and 70 percent.
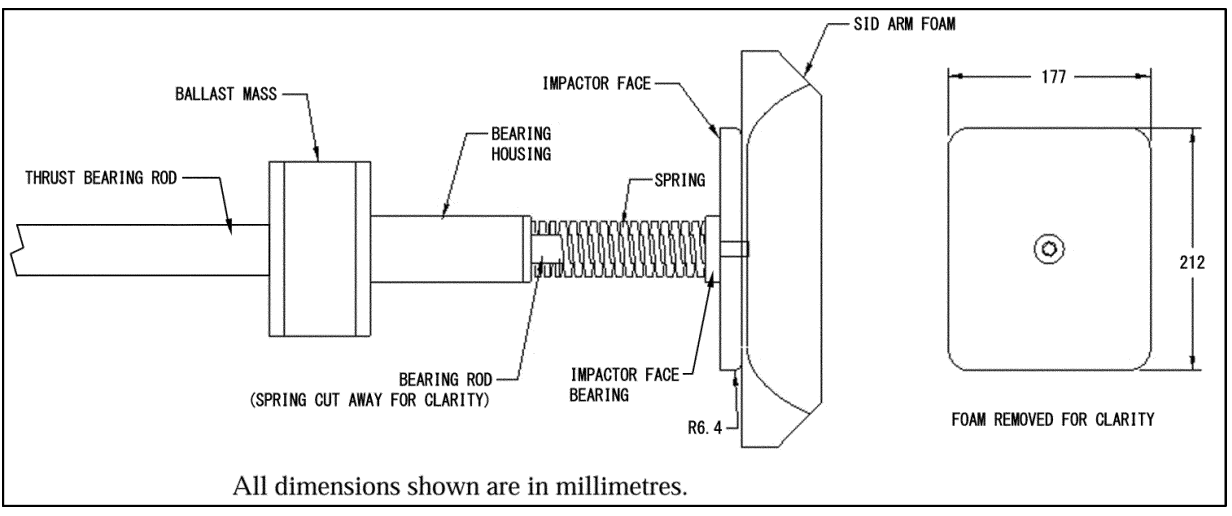
S8. Guided impactor.
The impactor test device has the dimensions shown in Figure 1 of this section. It has a total impactor mass of 26 kg ± 1.0 kg and a spring stiffness of 258 N/mm ± 39 N/mm. The impactor is propelled in the horizontal direction in impacts to the side daylight openings and is propelled vertically in impacts to the roof daylight openings.
[89 FR 86282, Oct. 30, 2024]
['CMV Parts and Maintenance']
['Vehicle maintenance']
UPGRADE TO CONTINUE READING
Load More
J. J. Keller is the trusted source for DOT / Transportation, OSHA / Workplace Safety, Human Resources, Construction Safety and Hazmat / Hazardous Materials regulation compliance products and services. J. J. Keller helps you increase safety awareness, reduce risk, follow best practices, improve safety training, and stay current with changing regulations.
Copyright 2025 J. J. Keller & Associate, Inc. For re-use options please contact copyright@jjkeller.com or call 800-558-5011.
