['Dangerous goods']
['Classification - Dangerous Goods']
07/17/2024
...
2.31 To determine the LD50 of a mixture of solid or liquid substances when the LD50 of each of the substances is known, use 1 000 mg/kg as the toxic limit and
(a) if the mixture contains only one substance with an LD50 less than or equal to the toxic limit (called “Substance A”), use the following calculation:
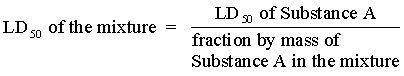
or
(b) if the mixture contains more than one substance with an LD50 less than or equal to the toxic limit (called “Substance A”, “Substance B”, etc.),
(i) determine the lowest LD50 of all substances, assign that LD50 to all substances whose actual LD50 is less than or equal to the toxic limit, then use the calculation in paragraph (a) using that assigned LD50 and taking as the mass of Substance A in the formula the total of the masses of all substances whose actual LD50 is less than or equal to the toxic limit, or
(ii) use the following calculations:
(A) determine the contributing number (CN) of each of the substances with an LD50 less than or equal to the toxic limit using the formula
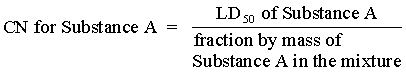
(B) combine the contributing numbers (CN) of each substance with an LD50 less than or equal to the toxic limit as

and
(C) obtain the LD50 of the mixture by dividing 1 by the number T (LD50 of the mixture = 1/T).
['Dangerous goods']
['Classification - Dangerous Goods']
UPGRADE TO CONTINUE READING
Load More
J. J. Keller is the trusted source for DOT / Transportation, OSHA / Workplace Safety, Human Resources, Construction Safety and Hazmat / Hazardous Materials regulation compliance products and services. J. J. Keller helps you increase safety awareness, reduce risk, follow best practices, improve safety training, and stay current with changing regulations.
Copyright 2026 J. J. Keller & Associate, Inc. For re-use options please contact copyright@jjkeller.com or call 800-558-5011.
