['Air Programs']
['Air Emissions']
06/20/2024
...
The procedures in this section describe how to determine an engine's steady-state fuel map and fuel consumption at idle for model year 2021 and later vehicles; these procedures apply as described in §1036.505. Vehicle manufacturers may need these values to demonstrate compliance with emission standards under 40 CFR part 1037.
(a) General test provisions. Perform fuel mapping using the procedure described in paragraph (b) of this section to establish measured fuel-consumption rates at a range of engine speed and load settings. Measure fuel consumption at idle using the procedure described in paragraph (c) of this section. Paragraph (d) of this section describes how to apply the steady-state mapping from paragraph (b) of this section for the special case of cycle-average mapping for highway cruise cycles as described in §1036.540. Use these measured fuel-consumption values to declare fuel-consumption rates for certification as described in paragraph (g) of this section.
(1) Map the engine's torque curve and declare engine idle speed as described in §1036.505(c)(1) and (3). Perform emission measurements as described in 40 CFR 1065.501 and 1065.530 for discrete-mode steady-state testing. This section uses engine parameters and variables that are consistent with 40 CFR part 1065.
(2) Measure NO X emissions as described in paragraph (f) of this section. Include these measured NO X values any time you report to us your fuel consumption values from testing under this section.
(3) You may use shared data across engine configurations to the extent that the fuel-consumption rates remain valid.
(4) The provisions related to carbon balance error verification in §1036.543 apply for all testing in this section. These procedures are optional, but we will perform carbon balance error verification for all testing under this section.
(5) Correct fuel mass flow rate to a mass-specific net energy content of a reference fuel as described in paragraph (e) of this section.
(b) Steady-state fuel mapping. Determine steady-state fuel-consumption rates for each engine configuration over a series of paired engine speed and torque setpoints as described in this paragraph (b). For example, if you test a high-output (parent) configuration and create a different (child) configuration that uses the same fueling strategy but limits the engine operation to be a subset of that from the high-output configuration, you may use the fuel-consumption rates for the reduced number of mapped points for the low-output configuration, as long as the narrower map includes at least 70 points. Perform fuel mapping as follows:
(1) Generate the fuel-mapping sequence of engine speed and torque setpoints as follows:
(i) Select the following required speed setpoints: warm idle speed, fnidle the highest speed above maximum power at which 70% of maximum power occurs, nhi, and eight (or more) equally spaced points between fnidle and nhi. (See 40 CFR 1065.610(c)). For engines with adjustable warm idle speed, replace fnidle with minimum warm idle speed fnidlemin.
(ii) Select the following required torque setpoints at each of the selected speed setpoints: zero (T = 0), maximum mapped torque, Tmax mapped, and eight (or more) equally spaced points between T = 0 and Tmax mapped. Select the maximum torque setpoint at each speed to conform to the torque map as follows:
(A) Calculate 5 percent of Tmax mapped. Subtract this result from the mapped torque at each speed setpoint, Tmax.
(B) Select Tmax at each speed setpoint as a single torque value to represent all the required torque setpoints above the value determined in paragraph (b)(1)(ii)(A) of this section. All the other default torque setpoints less than Tmax at a given speed setpoint are required torque setpoints.
(iii) You may select any additional speed and torque setpoints consistent with good engineering judgment. For example, you may need to select additional points if the engine's fuel consumption is nonlinear across the torque map. Avoid creating a problem with interpolation between narrowly spaced speed and torque setpoints near Tmax. For each additional speed setpoint, we recommend including a torque setpoint of Tmax; however, you may select torque setpoints that properly represent in-use operation. Increments for torque setpoints between these minimum and maximum values at an additional speed setpoint must be no more than one-ninth of Tmax,mapped. Note that if the test points were added for the child rating, they should still be reported in the parent fuel map. We will test with at least as many points as you. If you add test points to meet testing requirements for child ratings, include those same test points as reported values for the parent fuel map. For our testing, we will use the same normalized speed and torque test points you use, and we may select additional test points.
(iv) Start fuel-map testing at the highest speed setpoint and highest torque setpoint, followed by decreasing torque setpoints at the highest speed setpoint. Continue testing at the next lowest speed setpoint and the highest torque setpoint at that speed setpoint, followed by decreasing torque setpoints at that speed setpoint. Follow this pattern through all the speed and torque points, ending with the lowest speed (fnidle or fnidlemin) and torque setpoint (T = 0). The following figure illustrates an array of test points and the corresponding run order.
Figure 1 to Paragraph (b)(1)(iv) of §1036.535—Illustration of Steady-State Fuel-Mapping Test Points and Run Order
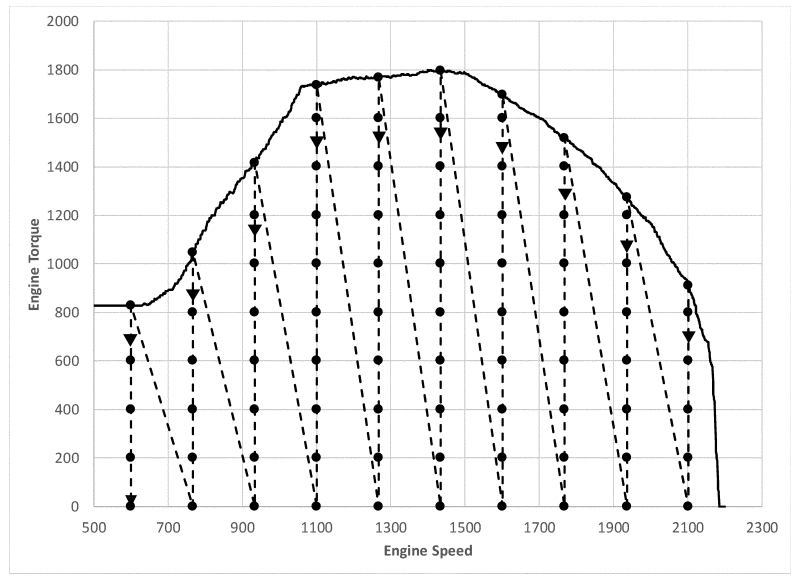
(v) The highest torque setpoint for each speed setpoint is an optional reentry point to restart fuel mapping after an incomplete test run.
(vi) The lowest torque setpoint at each speed setpoint is an optional exit point to interrupt testing. Paragraph (b)(7) of this section describes how to interrupt testing at other times.
(2) If the engine's warm idle speed is adjustable, set it to its minimum value, fnidlemin.
(3) The measurement at each unique combination of speed and torque setpoints constitutes a test interval. Unless we specify otherwise, you may program the dynamometer to control either speed or torque for a given test interval, with operator demand controlling the other parameter. Control speed and torque so that all recorded speed points are within ±1% of nhi from the target speed and all recorded engine torque points are within ±5% of Tmax mapped from the target torque during each test interval, except as follows:
(i) For steady-state engine operating points that cannot be achieved, and the operator demand stabilizes at minimum; program the dynamometer to control torque and let the engine govern speed (see 40 CFR 1065.512(b)(1)). Control torque so that all recorded engine torque points are within ±25 N·m from the target torque. The specified speed tolerance does not apply for the test interval.
(ii) For steady-state engine operating points that cannot be achieved and the operator demand stabilizes at maximum and the speed setpoint is below 90% of nhi even with maximum operator demand, program the dynamometer to control speed and let the engine govern torque (see 40 CFR 1065.512(b)(2)). The specified torque tolerance does not apply for the test interval.
(iii) For steady-state engine operating points that cannot be achieved and the operator demand stabilizes at maximum and the speed setpoint is at or above 90% of nhi even with maximum operator demand, program the dynamometer to control torque and let the engine govern speed (see 40 CFR 1065.512(b)(1)). The specified speed tolerance does not apply for the test interval.
(iv) For the steady-state engine operating points at the minimum speed setpoint and maximum torque setpoint, you may program the dynamometer to control speed and let the engine govern torque. The specified torque tolerance does not apply for this test interval if operator demand stabilizes at its maximum or minimum limit.
(4) Record measurements using direct and/or indirect measurement of fuel flow as follows:
(i) Direct fuel-flow measurement. Record speed and torque and measure fuel consumption with a fuel flow meter for (30 ± 1) seconds. Determine the corresponding mean values for the test interval. Use of redundant direct fuel-flow measurements requires our advance approval.
(ii) Indirect fuel-flow measurement. Record speed and torque and measure emissions and other inputs needed to run the chemical balance in 40 CFR 1065.655(c) for (30 ± 1) seconds. Determine the corresponding mean values for the test interval. Use of redundant indirect fuel-flow measurements requires our advance approval. Measure background concentration as described in 40 CFR 1065.140, except that you may use one of the following methods to apply a single background reading to multiple test intervals:
(A) For batch sampling, you may sample periodically into the bag over the course of multiple test intervals and read them as allowed in paragraph (b)(7)(i) of this section. You must determine a single background reading for all affected test intervals if you use the method described in this paragraph (b)(4)(ii)(A).
(B) You may measure background concentration by sampling from the dilution air during the interruptions allowed in paragraph (b)(7)(i) of this section or at other times before or after test intervals. Measure background concentration within 30 minutes before the first test interval and within 30 minutes before each reentry point. Measure the corresponding background concentration within 30 minutes after each exit point and within 30 minutes after the final test interval. You may measure background concentration more frequently. Correct measured emissions for test intervals between a pair of background readings based on the average of those two values. Once the system stabilizes, collect a background sample over an averaging period of at least 30 seconds.
(5) Warm up the engine as described in 40 CFR 1065.510(b)(2). Within 60 seconds after concluding the warm-up, linearly ramp the speed and torque setpoints over 5 seconds to the starting test point from paragraph (b)(1) of this section.
(6) Stabilize the engine by operating at the specified speed and torque setpoints for (70 ± 1) seconds and then start the test interval. Record measurements during the test interval. Measure and report NO X emissions over each test interval as described in paragraph (f) of this section.
(7) After completing a test interval, linearly ramp the speed and torque setpoints over 5 seconds to the next test point.
(i) You may interrupt the fuel-mapping sequence before a reentry point as noted in paragraphs (b)(1)(v) and (vi) of this section. If you zero and span analyzers, read and evacuate background bag samples, or sample dilution air for a background reading during the interruption, the maximum time to stabilize in paragraph (b)(6) of this section does not apply. If you shut off the engine, restart with engine warm-up as described in paragraph (b)(5) of this section.
(ii) You may interrupt the fuel-mapping sequence at a given speed setpoint before completing measurements at that speed. If this happens, you may measure background concentration and take other action as needed to validate test intervals you completed before the most recent reentry point. Void all test intervals after the last reentry point. Restart testing at the appropriate reentry point in the same way that you would start a new test. Operate the engine long enough to stabilize aftertreatment thermal conditions, even if it takes more than 70 seconds. In the case of an infrequent regenerationevent, interrupt the fuel-mapping sequence and allow the regeneration event to finish with the engine operating at a speed and load that allows effective regeneration.
(iii) If you void any one test interval, all the testing at that speed setpoint is also void. Restart testing by repeating the fuel-mapping sequence as described in this paragraph (b); include all voided speed setpoints and omit testing at speed setpoints that already have a full set of valid results.
(8) If you determine fuel-consumption rates using emission measurements from the raw or diluted exhaust, calculate the mean fuel mass flow rate, m fuel, for each point in the fuel map using the following equation:
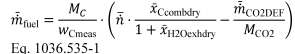
Where:
m fuel = mean fuel mass flow rate for a given fuel map setpoint, expressed to at least the nearest 0.001 g/s.
WCmeas = carbon mass fraction of fuel (or mixture of test fuels) as determined in 40 CFR 1065.655(d), except that you may not use the default properties in 40 CFR 1065.655(e)(5) to determine α, β, and wC . You may not account for the contribution to α, β, γ,and δ of diesel exhaust fluid or other non-fuel fluids injected into the exhaust.
n = the mean exhaust molar flow rate from which you measured emissions according to 40 CFR 1065.655.
x Ccombdry = the mean concentration of carbon from fuel and any injected fluids in the exhaust per mole of dry exhaust as determined in 40 CFR 1065.655(c).
x H2Oexhdry = the mean concentration of H 2 O in exhaust per mole of dry exhaust as determined in 40 CFR 1065.655(c).
m CO2DEF = the mean CO 2 mass emission rate resulting from diesel exhaust fluid decomposition as determined in paragraph (b)(9) of this section. If your engine does not use diesel exhaust fluid, or if you choose not to perform this correction, set m CO2DEF equal to 0.
MCO2 = molar mass of carbon dioxide.
Example:

(9) If you determine fuel-consumption rates using emission measurements with engines that utilize diesel exhaust fluid for NO X control and you correct for the mean CO 2 mass emission rate resulting from diesel exhaust fluid decomposition as described in paragraph (b)(8) of this section, perform this correction at each fuel map setpoint using the following equation:
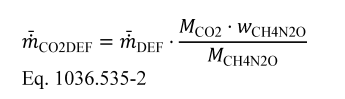
Where:
m DEF = the mean mass flow rate of injected urea solution diesel exhaust fluid for a given sampling period, determined directly from the ECM, or measured separately, consistent with good engineering judgment.
MCO2 = molar mass of carbon dioxide.
wCH4N2O = mass fraction of urea in diesel exhaust fluid aqueous solution. Note that the subscript “CH4N2O” refers to urea as a pure compound and the subscript “DEF” refers to the aqueous urea diesel exhaust fluid as a solution of urea in water. You may use a default value of 32.5% or use good engineering judgment to determine this value based on measurement.
MCH4N2O = molar mass of urea.
Example:
m DEF = 0.304 g/s
MCO2 = 44.0095 g/mol
wCH4N2O = 32.5% = 0.325
MCH4N2O = 60.05526 g/mol
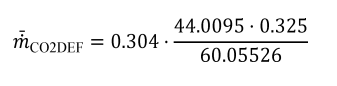
m CO2DEF = 0.0726 g/s
(10) Correct the measured or calculated mean fuel mass flow rate, at each of the operating points to account for mass-specific net energy content as described in paragraph (e) of this section.
(c) Fuel consumption at idle. Determine fuel-consumption rates at idle for each engine configuration that is certified for installation in vocational vehicles. Determine fuel-consumption rates at idle by testing engines over a series of paired engine speed and torque setpoints as described in this paragraph (c). Perform measurements as follows:
(1) The idle test sequence consists of measuring fuel consumption at four test points representing each combination of the following speed and torque setpoints in any order.
(i) Speed setpoints for engines with adjustable warm idle speed are minimum warm idle speed, fnidlemin , and maximum warm idle speed, fnidlemax . Speed setpoints for engines with no adjustable warm idle speed (with zero torque on the primary output shaft) are fnidle and 1.15 times fnidle .
(ii) Torque setpoints are 0 and 100 N·m.
(2) Control speed and torque as follows:
(i) Adjustable warm idle speed. Set the engine's warm idle speed to the next speed setpoint any time before the engine reaches the next test point. Control both speed and torque when the engine is warming up and when it is transitioning to the next test point. Start to control both speed and torque. At any time prior to reaching the next engine-idle operating point, set the engine's adjustable warm idle speed setpoint to the speed setpoint of the next engine-idle operating point in the sequence. This may be done before or during the warm-up or during the transition. Near the end of the transition period control speed and torque as described in paragraph (b)(3)(i) of this section shortly before reaching each test point. Once the engine is operating at the desired speed and torque setpoints, set the operator demand to minimum; control torque so that all recorded engine torque points are within ±25 N·m from the target torque.
(ii) Nonadjustable warm idle speed. For the lowest speed setpoint, control speed and torque as described in paragraph (c)(2)(i) of this section, except for adjusting the warm idle speed. For the second-lowest speed setpoint, control speed and torque so that all recorded speed points are within ±1% of nhi from the target speed and engine torque within ±5% of Tmax mapped from the target torque.
(3) Record measurements using direct and/or indirect measurement of fuel flow as follows:
(i) Direct fuel flow measurement. Record speed and torque and measure fuel consumption with a fuel flow meter for (600 ±1) seconds. Determine the corresponding mean values for the test interval. Use of redundant direct fuel-flow measurements require prior EPA approval.
(ii) Indirect fuel flow measurement. Record speed and torque and measure emissions and other inputs needed to run the chemical balance in 40 CFR 1065.655(c) for (600 ±1) seconds. Determine the corresponding mean values for the test interval. Use of redundant indirect fuel-flow measurements require prior EPA approval. Measure background concentration as described in paragraph (b)(4)(ii) of this section. We recommend setting the CVS flow rate as low as possible to minimize background, but without introducing errors related to insufficient mixing or other operational considerations. Note that for this testing 40 CFR 1065.140(e) does not apply, including the minimum dilution ratio of 2:1 in the primary dilution stage.
(4) Warm up the engine as described in 40 CFR 1065.510(b)(2). Within 60 seconds after concluding the warm-up, linearly ramp the speed and torque over 20 seconds to the first speed and torque setpoint.
(5) The measurement at each unique combination of speed and torque setpoints constitutes a test interval. Operate the engine at the selected speed and torque set points for (180 ±1) seconds, and then start the test interval. Record measurements during the test interval. Measure and report NO X emissions over each test interval as described in paragraph (f) of this section.
(6) After completing each test interval, repeat the steps in paragraphs (c)(4) and (5) of this section for all the remaining engine-idle test points.
(7) Each test point represents a stand-alone measurement. You may therefore take any appropriate steps between test intervals to process collected data and to prepare engines and equipment for further testing. Note that the allowances for combining background in paragraph (b)(4)(ii)(B) of this section do not apply. If an infrequent regeneration event occurs, allow the regeneration event to finish; void the test interval if the regeneration starts during a measurement.
(8) Correct the measured or calculated mean fuel mass flow rate, at each of the engine-idle operating points to account for mass-specific net energy content as described in paragraph (e) of this section.
(d) Steady-state fuel maps used for cycle-average fuel mapping of the highway cruise cycles. Determine steady-state fuel-consumption rates for each engine configuration over a series of paired engine speed and torque setpoints near idle as described in this paragraph (d). Perform fuel mapping as described in paragraph (b) of this section with the following exceptions:
(1) Select speed setpoints to cover a range of values to represent in-use operation at idle. Speed setpoints for engines with adjustable warm idle speed must include at least minimum warm idle speed, fnidlemin , and a speed at or above maximum warm idle speed, fnidlemax. Speed setpoints for engines with no adjustable idle speed must include at least warm idle speed (with zero torque on the primary output shaft), fnidle, and a speed at or above 1.15 · fnidle.
(2) Select the following torque setpoints at each speed setpoint to cover a range of values to represent in-use operation at idle:
(i) The minimum torque setpoint is zero.
(ii) Choose a maximum torque setpoint that is at least as large as the value determined by the following equation:
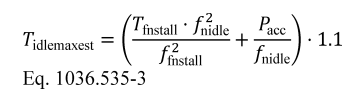
Where:
Tfnstall = the maximum engine torque at fnstall.
fnidle = for engines with an adjustable warm idle speed, use the maximum warm idle speed, fnidlemax. For engines without an adjustable warm idle speed, use warm idle speed, fnidle.
fnstall = the stall speed of the torque converter; use fntest or 2250 r/min, whichever is lower.
Pacc = accessory power for the vehicle class; use 1500 W for Vocational Light HDV, 2500 W for Vocational Medium HDV, and 3500 W for Tractors and Vocational Heavy HDV. If your engine is going to be installed in multiple vehicle classes, perform the test with the accessory power for the largest vehicle class the engine will be installed in.
Example:
Tfnstall = 1870 N·m
fntest = 1740.8 r/min = 182.30 rad/s
fnstall = 1740.8 r/min = 182.30 rad/s
fnidle = 700 r/min = 73.30 rad/s
Pacc = 1500 W

Tidlemaxest = 355.07 N·m
(iii) Select one or more equally spaced intermediate torque setpoints, as needed, such that the increment between torque setpoints is no greater than one-ninth of Tmax,mapped .
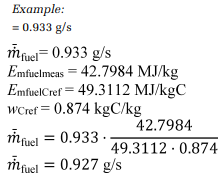
(e) Correction for net energy content. Correct the measured or calculated mean fuel mass flow rate, m fuel, for each test interval to a mass-specific net energy content of a reference fuel using the following equation:
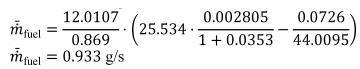
Eq. 1036.535-4
Where:
Emfuelmeas = the mass-specific net energy content of the test fuel as determined in §1036.550(b)(1). Note that dividing this value by wCref (as is done in this equation) equates to a carbon-specific net energy content having the same units as EmfuelCref.
EmfuelCref = the reference value of carbon-mass-specific net energy content for the appropriate fuel. Use the values shown in table 1 to paragraph (b)(4) of §1036.550 for the designated fuel types, or values we approve for other fuel types.
WCref = the reference value of carbon mass fraction for the test fuel as shown in table 1 to paragraph (b)(4) of §1036.550 for the designated fuels. For any fuel not identified in the table, use the reference carbon mass fraction of diesel fuel for engines subject to compression-ignition standards, and use the reference carbon mass fraction of gasoline for engines subject to spark-ignition standards.
Example:
= 0.933 g/s
(f) Measuring NO emissions. Measure NO X emissions for each sampling period in g/s. You may perform these measurements using a NO X emission-measurement system that meets the requirements of 40 CFR part 1065, subpart J. If a system malfunction prevents you from measuring NO X emissions during a test under this section but the test otherwise gives valid results, you may consider this a valid test and omit the NO X emission measurements; however, we may require you to repeat the test if we determine that you inappropriately voided the test with respect to NO X emission measurement.
(g) Measured vs. declared fuel consumption. Determine declared fuel consumption as follows:
(1) Select fuel consumption rates in g/s to characterize the engine's fuel maps. You must select a declared value for each test point that is at or above the corresponding value determined in paragraphs (b) through (d) of this section, including those from redundant measurements.
(2) Declared fuel consumption serves as emission standards under §1036.108. These are the values that vehicle manufacturers will use for certification under 40 CFR part 1037. Note that production engines are subject to GEM cycle-weighted limits as described in §1036.301.
(3) If you perform the carbon balance error verification, select declared values that are at or above the following emission measurements:
(i) If you pass the rC verification, you may use the average of the values from direct and indirect fuel measurements.
(ii) If you fail rC verification, but pass either the aC or aCrate verification, use the value from indirect fuel measurement.
(iii) If you fail all three verifications, you must either void the test interval or use the highest value from direct and indirect fuel measurements. Note that we will consider our test results to be invalid if we fail all three verifications.
[88 FR 4487, Jan. 24, 2023; 89 FR 29750, Apr. 22, 2024]
['Air Programs']
['Air Emissions']
UPGRADE TO CONTINUE READING
Load More
J. J. Keller is the trusted source for DOT / Transportation, OSHA / Workplace Safety, Human Resources, Construction Safety and Hazmat / Hazardous Materials regulation compliance products and services. J. J. Keller helps you increase safety awareness, reduce risk, follow best practices, improve safety training, and stay current with changing regulations.
Copyright 2026 J. J. Keller & Associate, Inc. For re-use options please contact copyright@jjkeller.com or call 800-558-5011.
