Identify waste

- Waste must be classified at the point of generation, before any mixing or other alteration of the waste occurs.
- Before making a waste determination for a particular waste, identify all the waste streams at the facility.
When most people talk about a waste, they mean anything that is thrown away. But in regulatory terms, the definition of a waste is very specific. Anything that is still being used, or that is intended to be used or sold, is not a waste. Once a company decides to dispose of it, then it becomes a waste.
Waste must be classified at the point of generation, before any mixing or other alteration of the waste occurs. The “point of generation” is the point at which the material is first identified as a solid waste.
Waste identification is an ongoing obligation. In the case of a waste that may, at some point during its management, exhibit a hazardous waste characteristic, the generator must monitor and reassess the waste.
Before making a waste determination for a particular waste, identify all the waste streams at the facility. This is called a waste survey, and it involves identifying all the wastes — both hazardous and non-hazardous — at the facility.
Once all of the waste streams have been located, the business must identify, or characterize, each waste. To do this:
- Characterize the waste using internal expertise,
- Hire a consultant,
- Use the services of the waste disposal company, or
- Use a combination of all three options above.
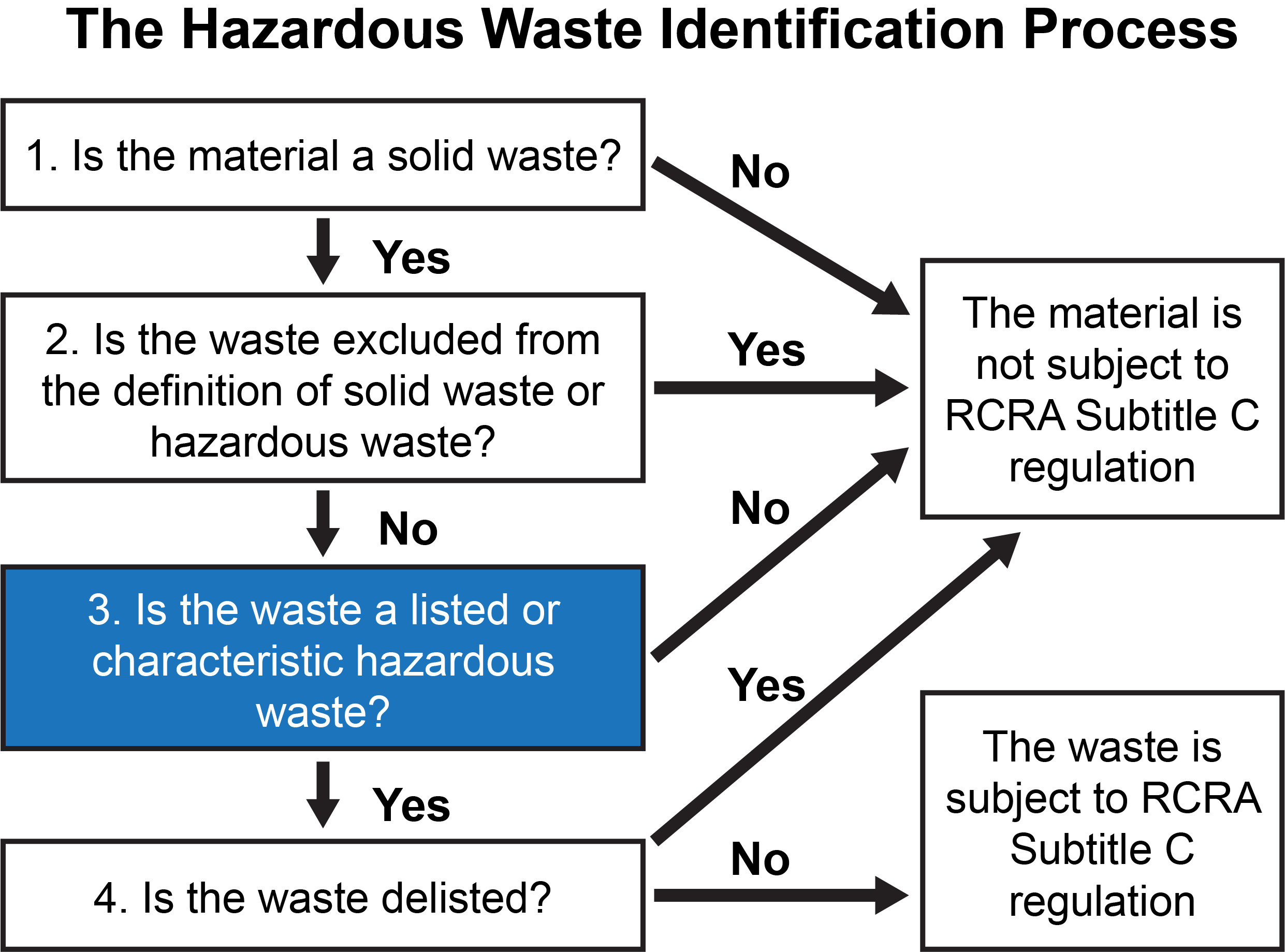
To identify a waste, ask the following questions:
- Is it a solid waste?
- Is it an excluded solid waste?
- Is it a hazardous waste?
- Is it exempted from the definition of a hazardous waste?
- Is it a listed waste?
- Is it a characteristic waste?
The flow chart below considers all these questions to help determine whether a waste is subject to Subtitle C of the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA), which outlines hazardous solid waste management requirements.