[]
[]
07/25/2021
...
[Editor’s Note: This section is removed and reserved effective January 1, 2022.]
(a)Annual average baseline values.For any facility of a refiner or importer of conventional gasoline, the annual average baseline values of the facility's exhaust benzene emissions, exhaust toxics emissions, NOXemissions, sulfur, olefins and T90 shall be determined using the following equation:
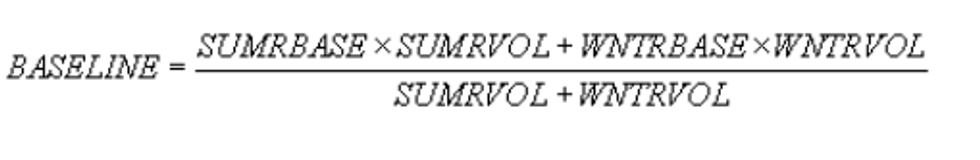
where
BASELINE = annual average baseline value of the facility,
SUMRBASE = summer baseline value of the facility,
SUMRVOL = summer baseline gasoline volume of the facility, per § 80.91,
WNTRBASE = winter baseline value of the facility,
WNTRVOL = winter baseline gasoline volume of the facility, per § 80.91.
(b)Baseline exhaust benzene emissions - simple model.(1) Simple model exhaust benzene emissions of conventional gasoline shall be determined using the following equation:
EXHBEN = (1.884 0.949 × BZ 0.113 × (AR ? BZ))
where
EXHBEN = exhaust benzene emissions,
BZ = fuel benzene value in terms of volume percent (per § 80.91), and
AR = fuel aromatics value in terms of volume percent (per § 80.91).
(2) The simple model annual average baseline exhaust benzene emissions for any facility of a refiner or importer of conventional gasoline shall be determined as follows:
(i) The simple model baseline exhaust benzene emissions shall be determined separately for summer and winter using the facility's oxygenated individual baseline fuel parameter values for summer and winter (per §80.91), respectively, in the equation specified in paragraph (b)(1) of this section.
(ii) The simple model annual average baseline exhaust benzene emissions of the facility shall be determined using the emissions values determined in paragraph (b)(2)(i) of this section in the equation specified in paragraph (a) of this section.
(c)Baseline exhaust benzene emissions - complex model.The complex model annual average baseline exhaust benzene emissions for any facility of a refiner or importer of conventional gasoline shall be determined as follows:
(1) The summer and winter complex model baseline exhaust benzene emissions shall be determined separately using the facility's oxygenated individual baseline fuel parameter values for summer and winter (per §80.91), respectively, in the appropriate complex model for exhaust benzene emissions described in§80.45.
(2) The complex model annual average baseline exhaust benzene emissions of the facility shall be determined using the emissions values determined in paragraph (c)(1) of this section in the equation specified in paragraph (a) of this section.
(d)Baseline exhaust toxics emissions.The annual average baseline exhaust toxics emissions for any facility of a refiner or importer of conventional gasoline shall be determined as follows:
(1) The summer and winter baseline exhaust emissions of benzene, formaldehyde, acetaldehyde, 1,3-butadiene, and polycyclic organic matter shall be determined using the oxygenated individual baseline fuel parameter values for summer and winter (per §80.91), respectively, in the appropriate complex model for each exhaust toxic (per §80.45).
(2) The summer and winter baseline total exhaust toxics emissions shall be determined separately by summing the summer and winter baseline exhaust emissions of each toxic (per paragraph (d)(1) of this section), respectively.
(3) The annual average baseline exhaust toxics emissions of the facility shall be determined using the emissions values determined in paragraph (d)(2) of this section in the equation specified in paragraph (a) of this section.
(e)Baseline NOXemissions.The annual average baseline NOXemissions for any facility of a refiner or importer of conventional gasoline shall be determined as follows:
(1) The summer and winter baseline NOXemissions shall be determined using the baseline individual baseline fuel parameter values for summer and winter (per §80.91), respectively, in the appropriate complex model for NOX(per §80.45).
(2) The annual average baseline NOXemissions of the facility shall be determined using the emissions values determined in paragraph (e)(1) of this section in the equation specified in paragraph (a) of this section.
(3) The requirements specified in paragraphs (e) (1) and (2) of this section shall be determined separately using the oxygenated and nonoxygenated individual baseline fuel parameters, per§80.91.
(f)Applicability of Phase I and Phase II models.The requirements of paragraphs (d) and (e) of this section shall be determined separately for the applicable Phase I and Phase II complex models specified in§80.45.
(g)Calculation accuracy.Emissions values calculated per the requirements of this section shall be determined to four (4) significant figures. Sulfur, olefin and T90 values calculated per the requirements of this section shall be determined to the same number of decimal places as the corresponding value listed in §80.91(c)(5).
[59 FR 7860, Feb. 16, 1994, as amended at 59 FR 36965, July 20, 1994; 85 FR 78467, Dec. 4, 2020]
READ MORESHOW LESS
Load More
J. J. Keller is the trusted source for DOT / Transportation, OSHA / Workplace Safety, Human Resources, Construction Safety and Hazmat / Hazardous Materials regulation compliance products and services. J. J. Keller helps you increase safety awareness, reduce risk, follow best practices, improve safety training, and stay current with changing regulations.
Copyright 2024 J. J. Keller & Associate, Inc. For re-use options please contact copyright@jjkeller.com or call 800-558-5011.
