...
(a) Flare equipment and operating requirements. Flares subject to this subpart shall meet the performance requirements of paragraphs (a)(1) through (7) of this section.
(1) Flares shall be operated at all times when emissions are vented to them.
(2) Flares shall be designed for and operated with no visible emissions as determined by the methods specified in paragraph (b)(3)(i) of this section, except for periods not to exceed a total of 5 minutes during any 2 consecutive hours.
(3) Flares shall be operated with a flare flame or at least one pilot flame present at all times, as determined by the methods specified in paragraph (c) of this section.
(4) An owner/operator has the choice of adhering to either the heat content specifications in paragraph (a)(4)(ii) of this section and the maximum tip velocity specifications in paragraph (a)(6) of this section, or adhering to the requirements in paragraph (a)(4)(i) of this section.
(i)(A) Flares shall be used that have a diameter of 3 inches or greater, are nonassisted, have a hydrogen content of 8.0 percent (by volume), or greater, and are designed for and operated with an exit velocity less than 37.2 m/sec (122 ft/sec) and less than the velocity, Vmax, as determined by Equation 147-1 of this section:
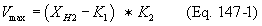
Where:
Vmax = Maximum permitted velocity, m/sec.
K1 = Constant, 6.0 volume-percent hydrogen.
K2 = Constant, 3.9 (m/sec)/volume-percent hydrogen.
XH2 = The volume-percent of hydrogen, on a wet basis, as calculated by using the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) Method D1946-77 (incorporated by reference as specified in §65.13).
(B) The actual exit velocity of a flare shall be determined by the method specified in paragraph (b)(3)(iii) of this section.
(ii) Flares shall be used only when the net heating value of the gas being combusted is 11.2 megajoules per standard cubic meter (300 British thermal units per standard cubic foot) or greater if the flare is steam-assisted or air-assisted, or when the net heating value of the gas being combusted is 7.45 megajoules per standard cubic meter (200 British thermal units per standard cubic foot) or greater if the flare is nonassisted. The net heating value of the gas being combusted shall be determined by the methods specified in paragraph (b)(3)(ii) of this section.
(5) Flares used to comply with this section shall be steam-assisted, air-assisted, or nonassisted.
(6) Steam-assisted and nonassisted flares shall be designed for and operated with an exit velocity as determined by the methods specified in paragraph (b)(3)(iii) of this section, less than 18.3 meters per second (60 feet per sec) except as provided in the following two paragraphs, as applicable:
(i) Steam-assisted and nonassisted flares shall be designed for and operated with an exit velocity as determined by the methods specified in paragraph (b)(3)(iii) of this section, equal to or less than 122 meters per second (400 feet per second) if the net heating value of the gas being combusted is greater than 37.3 megajoules per standard cubic meter (1,000 British thermal units per standard cubic foot).
(ii) Steam-assisted and nonassisted flares shall be designed for and operated with an exit velocity as determined by the methods specified in paragraph (b)(3)(iii) of this section, less than the velocity, V max, and less than 122 meters per second (400 feet per sec), where the maximum permitted velocity, Vmax, is determined by Equation 147-2 of this section:
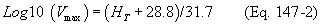
Where:
Vmax = Maximum permitted velocity, meters per second.
28.8 = Constant.
31.7 = Constant.
HT = The net heating value as determined in paragraph (b)(3)(ii) of this section.
(7) Air-assisted flares shall be designed for and operated with an exit velocity as determined by the methods specified in paragraph (b)(3)(iii) of this section, less than the velocity, Vmax, where the maximum permitted velocity, Vmax, is determined by Equation 147-3 of this section:
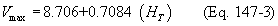
Where:
Vmax = Maximum permitted velocity, meters per second.
8.706 = Constant.
0.7084 = Constant.
HT = The net heating value as determined in paragraph (b)(3)(ii) of this section.
(b) Flare compliance determination.(1) Unless an initial flare compliance determination of the flare was previously conducted and submitted under the referencing subpart, the owner or operator shall conduct an initial flare compliance determination of any flare used to comply with the provisions of this subpart. Flare compliance determination records shall be kept as specified in §65.159(a) and (b) and a flare compliance determination report shall be submitted as specified in §65.164. An owner or operator is not required to conduct a performance test to determine percent emission reduction or outlet regulated material or TOC concentration when a flare is used.
(2) Unless already permitted by the applicable title V permit, if an owner or operator elects to use a flare to replace an existing control device at a later date, the owner or operator shall notify the Administrator, either by amendment of the regulated source's title V permit or, if title V is not applicable, by submission of the notice specified in §65.167(a). Upon implementing the change, a flare compliance determination shall be performed using the methods specified in paragraph (b)(3) of this section within 180 days. The compliance determination report shall be submitted to the Administrator within 60 days of completing the determination as provided in §65.164(b)(2). If an owner or operator elects to use a flare to replace an existing final recovery device that is used on a Group 2A process vent, the owner or operator shall comply with the applicable provisions of §§65.63(e) and 65.67(b) and submit the notification specified in §65.167(a).
(3) Flare compliance determinations shall meet the requirements specified in paragraphs (b)(3)(i) through (iv) of this section.
(i) Method 22 of appendix A of part 60 shall be used to determine the compliance of flares with the visible emission provisions of this subpart. The observation period is 2 hours, except for transfer racks as provided in either one of the following:
(A) For transfer racks, if the loading cycle is less than 2 hours, then the observation period for that run shall be for the entire loading cycle.
(B) For transfer racks, if additional loading cycles are initiated within the 2-hour period, then visible emissions observations shall be conducted for the additional cycles.
(ii) The net heating value of the gas being combusted in a flare shall be calculated using Equation 147-4 of this section:
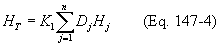
Where:
HT = Net heating value of the sample, megajoules per standard cubic meter; where the net enthalpy per mole of offgas is based on combustion at 25°C and 760 millimeters of mercury (30 inches of mercury), but the standard temperature for determining the volume corresponding to 1 mole is 20°C;
K1 = 1.740 × 10?7 (parts per million by volume)?1 (gram-mole per standard cubic meter) (megajoules per kilocalories), where the standard temperature for gram mole per standard cubic meter is 20°C;
Dj = Concentration of sample component j, in parts per million by volume on a wet basis, as measured for organics by Method 18 of appendix A of 40 CFR part 60 and measured for hydrogen and carbon monoxide by American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) D1946-77 (incorporated by reference as specified in §65.13); and
Hj = Net heat of combustion of sample component j, kilocalories per gram-mole at 25°C and 760 millimeters of mercury (30 inches of mercury). The heats of combustion of stream components may be determined using ASTM D2382-76 (incorporated by reference as specified in §65.13) if published values are not available or cannot be calculated.
(iii) The actual exit velocity of a flare shall be determined by dividing the volumetric flow rate (in units of standard temperature and pressure), as determined by Method 2, 2A, 2C, or 2D of appendix A of 40 CFR part 60 as appropriate, by the unobstructed (free) cross-sectional area of the flare tip.
(iv) Flare flame or pilot monitors, as applicable, shall be operated during any flare compliance determination.
(c) Flare monitoring requirements. Where a flare is used, a device (including but not limited to a thermocouple, ultraviolet beam sensor, or infrared sensor) capable of continuously detecting that at least one pilot flame or the flare flame is present is required. Flame monitoring and compliance records shall be kept as specified in §65.159(c) and (d).
