['Air Programs']
['Air Emissions']
03/16/2023
...
(a) Calculate your average emission level for each type of recreational vehicle or engine for each model year according to the following equation and round it to the nearest tenth of a g/km or g/kW-hr. Use consistent units throughout the calculation.
(1) For exhaust emissions:
(i) Calculate the average emission level as:
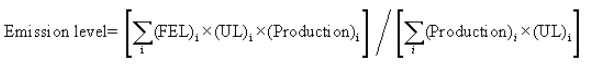
Where:
FELi = The FEL to which the engine family is certified.
ULi = The useful life of the engine family.
Productioni = The number of vehicles in the engine family.
(ii) Use U.S.-directed production projections for initial certification, and actual U.S.-directed production volumes to determine compliance at the end of the model year.
(2) For vehicles that have standards expressed as g/kW-hr and a useful life in kilometers, convert the useful life to kW-hr based on the maximum engine power and an assumed vehicle speed of 30 km/hr as follows: UL (kW-hr) = UL (km) × Maximum Engine Power (kW) ÷ 30 km/hr. (Note: It is not necessary to include a load factor, since credit exchange is not allowed between vehicles certified to g/kW-hr standards and vehicles certified to g/km standards.)
(3) For evaporative emission standards expressed as g/m 2/day, use the useful life value in years multiplied by 365.24 and calculate the average emission level as:
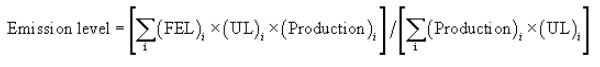
Where:
FEL i = The FEL to which the engine family is certified, as described in paragraph (a)(4) of this section.
Production i = The number of vehicles in the engine family times the average internal surface area of the vehicles' fuel tanks.
(4) Determine the FEL for calculating credits under paragraph (a)(3) of this section using any of the following values:
(i) The FEL to which the tank is certified, as long as the FEL is at or below 3.0 g/m 2/day.
(ii) 10.4 g/m 2/day. However, if you use this value to establish the FEL for any of your tanks, you must use this value to establish the FEL for every tank not covered by paragraph (a)(4)(i) of this section.
(iii) The measured permeation rate of the tank or the measured permeation rate of a thinner-walled tank of the same material. However, if you use this approach to establish the FEL for any of your tanks, you must establish an FEL based on emission measurements for every tank not covered by paragraph (a)(4)(i) of this section.
(b) If your average emission level is below the average standard, calculate credits available for banking according to the following equation and round them to the nearest tenth of a gram:

C
(c) If your average emission level is above the average standard, calculate your preliminary credit deficit according to the following equation, rounding to the nearest tenth of a gram:

[67 FR 68347, Nov. 8, 2002, as amended at 70 FR 40505, July 13, 2005; 73 FR 59256, Oct. 8, 2008]
READ MORESHOW LESS
['Air Programs']
['Air Emissions']
Load More
J. J. Keller is the trusted source for DOT / Transportation, OSHA / Workplace Safety, Human Resources, Construction Safety and Hazmat / Hazardous Materials regulation compliance products and services. J. J. Keller helps you increase safety awareness, reduce risk, follow best practices, improve safety training, and stay current with changing regulations.
Copyright 2024 J. J. Keller & Associate, Inc. For re-use options please contact copyright@jjkeller.com or call 800-558-5011.
