The Hazardous Materials Regulations (HMR) require all hazmat employers to train their hazmat employees. This training ensures that every hazmat employee is familiar with the HMR, can recognize and identify hazardous materials, understands the specific HMR requirements for their tasks, and is aware of emergency response, self-protection, and accident prevention procedures. (49 CFR Subpart H, 172.700 through 172.704)
Before performing any job function covered by the HMR, hazmat employees must be trained, tested, and certified. Until they complete their training, they can only perform hazmat functions under the direct supervision of a fully trained and certified hazmat employee. Training must also be completed within 90 days.
Additionally, hazmat employees must receive recurrent training at least once every three years and be tested after each training session. Training can be provided by the hazmat employer or other public or private sources. Regardless of who provides the training, the hazmat employer is responsible for ensuring that the training is effective, appropriate, and successful in equipping employees with the necessary knowledge and skills to perform their job functions safely.
Types of training
- Hazmat employees are required to be trained in areas such as General Awareness and Familiarization, Function Specific, Safety, Security Awareness, In-depth Security, and Modal Specific.
- It is up to each hazmat employer to determine which kind of information needs to be covered in each type of training.
Hazmat employees are required to be trained in areas such as General Awareness and Familiarization, Function Specific, Safety, Security Awareness, In-depth Security, and Modal Specific. Even though the Hazardous Materials Regulations (HMR) list the areas of training required, they are not specific on everything that needs to be addressed within those areas. The HMR leaves it up to each hazmat employer to determine the appropriate information that needs to be covered within each area.
General awareness and familiarization
General awareness training provides hazmat employees with a broad understanding of the HMR and enables hazmat employees to readily recognize and identify hazardous materials. All hazmat employees are required to have general awareness and familiarization training. Training typically provides a basic understanding of:
- The identification of hazardous materials,
- The Hazard Classification System,
- How to use the Hazardous Materials Table,
- Packaging,
- Markings and labels,
- Placards,
- Shipping papers,
- Segregation,
- Training requirements,
- Incident reporting, and
- Security.
Function specific
Function specific training provides hazmat employees with a detailed study of regulation requirements applicable to the hazmat function(s) the employee is responsible for. Training needs will depend on many things, including company operations, type of hazmat, packaging, and the hazmat employee’s responsibilities. Examples include:
- Loading and unloading hazmat,
- Filling out shipping papers,
- Packaging hazmat, and
- Labeling hazmat.
Safety
Safety training includes information on the hazards related to the hazmat the employee will handle, such as safe handling practices, emergency response procedures, and accident prevention methods. Training that complies with Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) regulations may also satisfy the requirements of the HMR. Topics may include:
- Emergency response information,
- Emergency response telephone numbers,
- Accident avoidance,
- Package handling,
- Personnel protection procedures, and
- Employee emergency action plans.
Security awareness
Security awareness training provides hazmat employees with a general understanding of the security risks associated with hazardous materials transportation and the methods designed to enhance transportation security. All hazmat employees are required to have security awareness training. Examples of subjects that could be included are:
- Regulatory requirements,
- Potential threats,
- Potential targets, and
- Prevention tools.
In-depth security
In-depth security training gives a detailed overview of a company’s security plan. It covers the company’s security goals, specific procedures, employee responsibilities, actions to take during a security breach, and the overall security structure. This training is required for hazmat employees who handle or perform regulated tasks related to transporting materials covered by the security plan, as well as for those responsible for implementing the security plan. Training must include:
- Security objectives,
- Specific security procedures,
- Employee responsibilities,
- Actions to take in the event of a security breach, and
- Organizational security structure.
Modal specific
- The four basic modes of transportation are rail, aircraft, vessel, and highway.
- Focusing on the highway mode of transportation, all drivers are required to have training that covers the requirements and procedures needed for safe motor vehicle operation.
- Specialized training is needed for drivers who operate a cargo tank or a vehicle with a portable tank having a capacity of 1,000 gallons or more.
Within the transportation world, there are four basic modes of transportation: rail, aircraft, vessel, and highway. When transporting hazmat, it is required to have training on the specific mode of transportation used. This type of training provides an overview of the safe operation of each specific mode of transport while moving hazmat. This section focuses on the highway mode of transportation.
Highway (Driver)
Drivers are prohibited from transporting hazmat until they have been trained in the applicable requirements of 49 CFR Parts 390 through 397 and the procedures necessary for the safe operation of that motor vehicle. Driver training must include the following subjects:
- Pre-trip safety inspection;
- Use of vehicle controls and equipment, including operation of emergency equipment;
- Operation of vehicle, including:
- Turning,
- Backing,
- Braking,
- Parking,
- Handling, and
- Vehicle characteristics, including:
- Those that affect vehicle stability, such as effects of braking and curves;
- Effects of speed on vehicle control;
- Dangers associated with maneuvering through curves;
- Dangers associated with weather or road conditions that a driver may experience (e.g., blizzards, mountainous terrain, high winds); and
- High center of gravity.
- Procedures for maneuvering tunnels, bridges, and railroad crossings;
- Requirements pertaining to attendance of vehicles, parking, smoking, routing, and incident reporting; and
- Loading and unloading of materials, including:
- Compatibility and segregation of cargo in a mixed load,
- Package handling methods, and
- Load securement.
Specialized training
Drivers who operate a cargo tank or a vehicle with a portable tank having a capacity of 1,000 gallons or more must also receive the following specialized training:
- Operation of emergency control features of the cargo tank or portable tank;
- Special vehicle handling characteristics, including:
- High center of gravity;
- Fluid load subject to surge;
- Effects of fluid-load surge on braking;
- Characteristic differences in stability among baffled, unbaffled, and multi-compartmented tanks; and
- Effects of partial loads on vehicle stability.
- Loading and unloading procedures;
- Properties and hazards of the material transported; and
- Retest and inspection requirements for cargo tanks.
Retention and recordkeeping
- A hazmat employer must create and retain records of current training inclusive of the preceding three years for each hazmat employee.
- The HMR mandates what needs to be in the training records and for how long the records must be retained by the employer.
- The training record must include employee name, date of training completion, certification of training, and more.
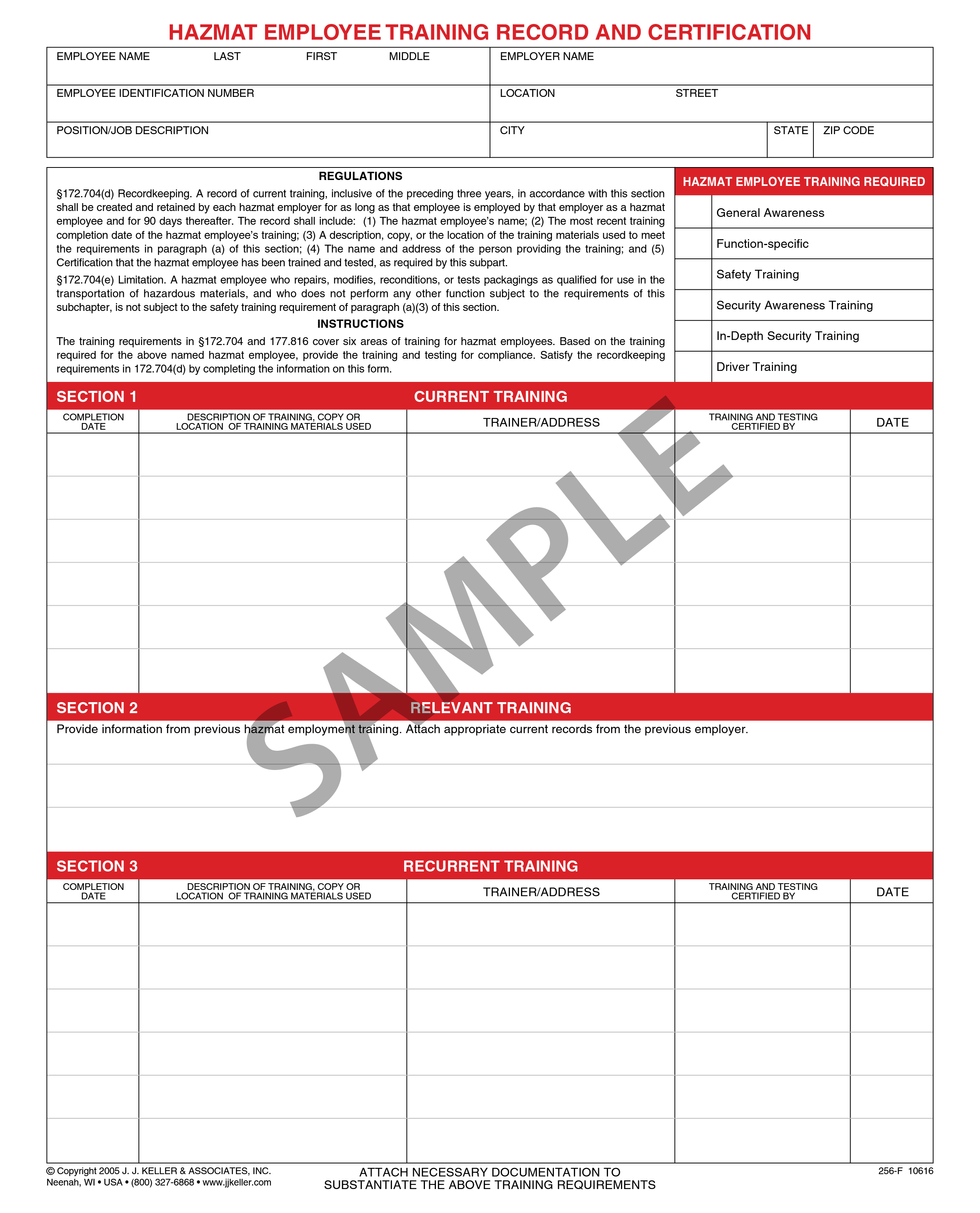
A very important part of the training process is to make sure the training, testing, and certification have been documented. In most cases, this will be the only way the employer can prove that hazmat training was conducted.
The hazmat employer must create and retain a record of current training, inclusive of the preceding three years, for each hazmat employee. Hazmat training records must be maintained for as long as that individual is employed by the employer as a hazmat employee and for 90 days thereafter.
The Hazardous Materials Regulations (HMR) mandate what needs to be in the training records and for how long employers need to retain them. However, it does not prescribe the training record format. Training records must include:
- The hazmat employee’s name;
- The most recent training completion date of the hazmat employee’s training;
- A description, copy, or the location of the training materials used;
- The name and address of the person providing the training; and
- A certification statement that the hazmat employee has been trained and tested.
The following is a sample to illustrate what a record may look like: